Characterization of a Driven Two-Level Quantum System by Supervised Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
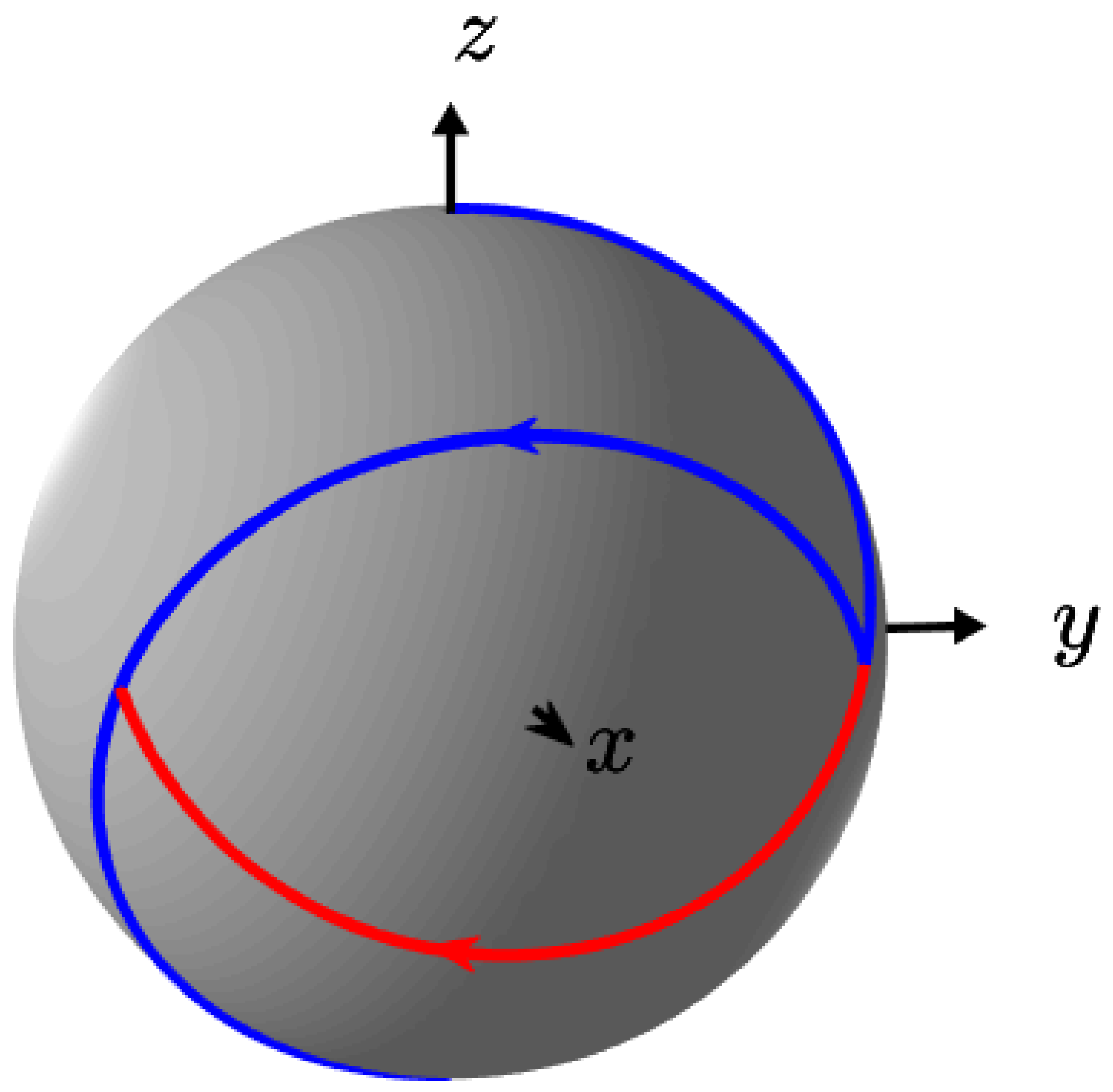
2. The Model System
3. Methodology
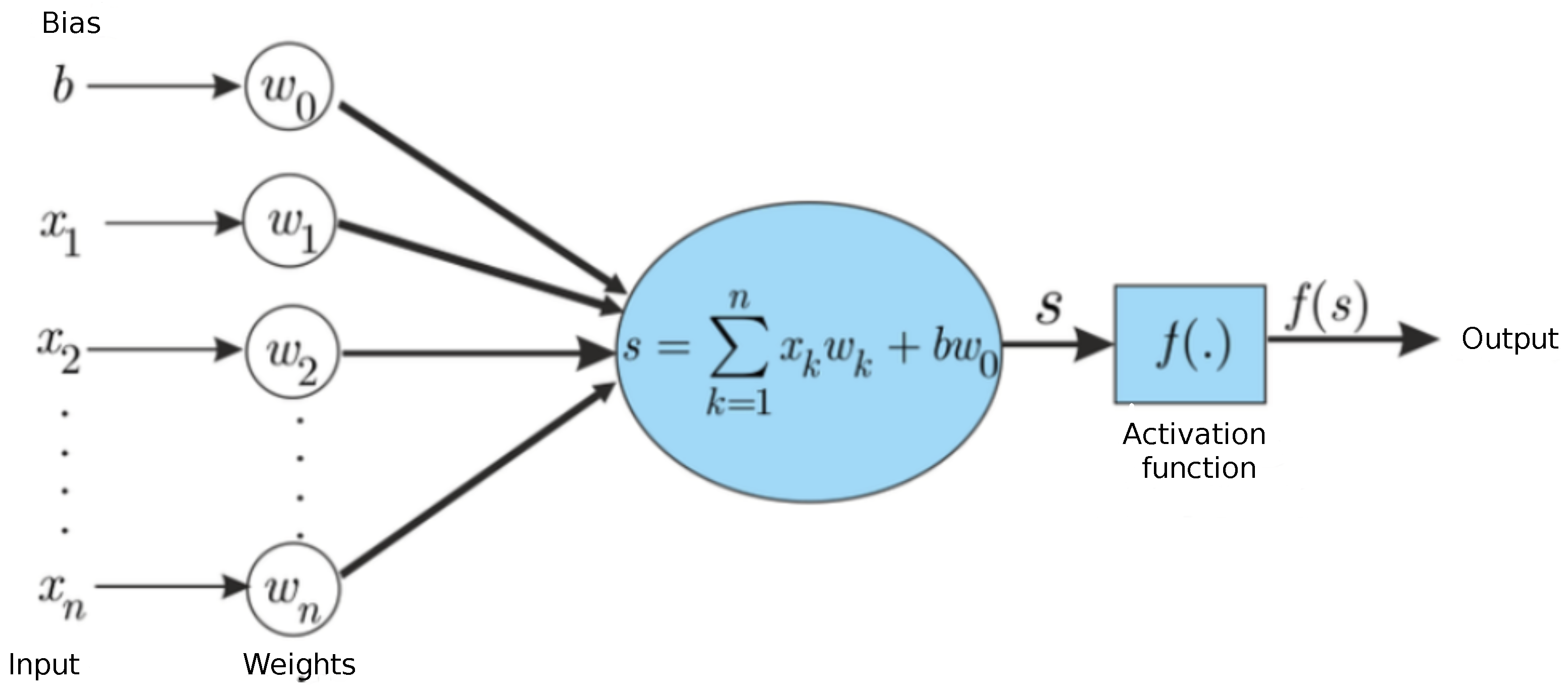
3.1. Principles of Machine Learning Techniques
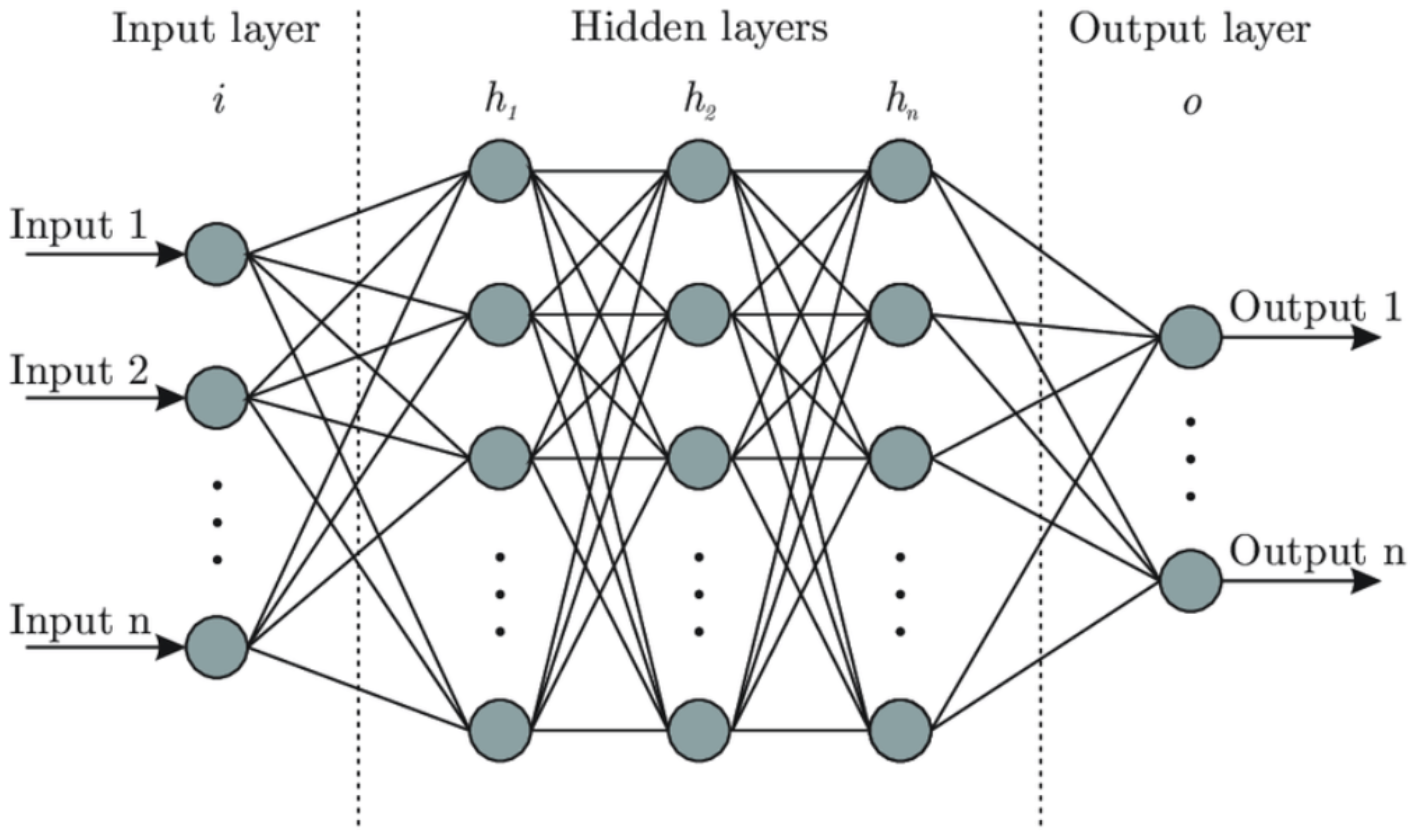
3.2. Construction of an Artificial Neural Network
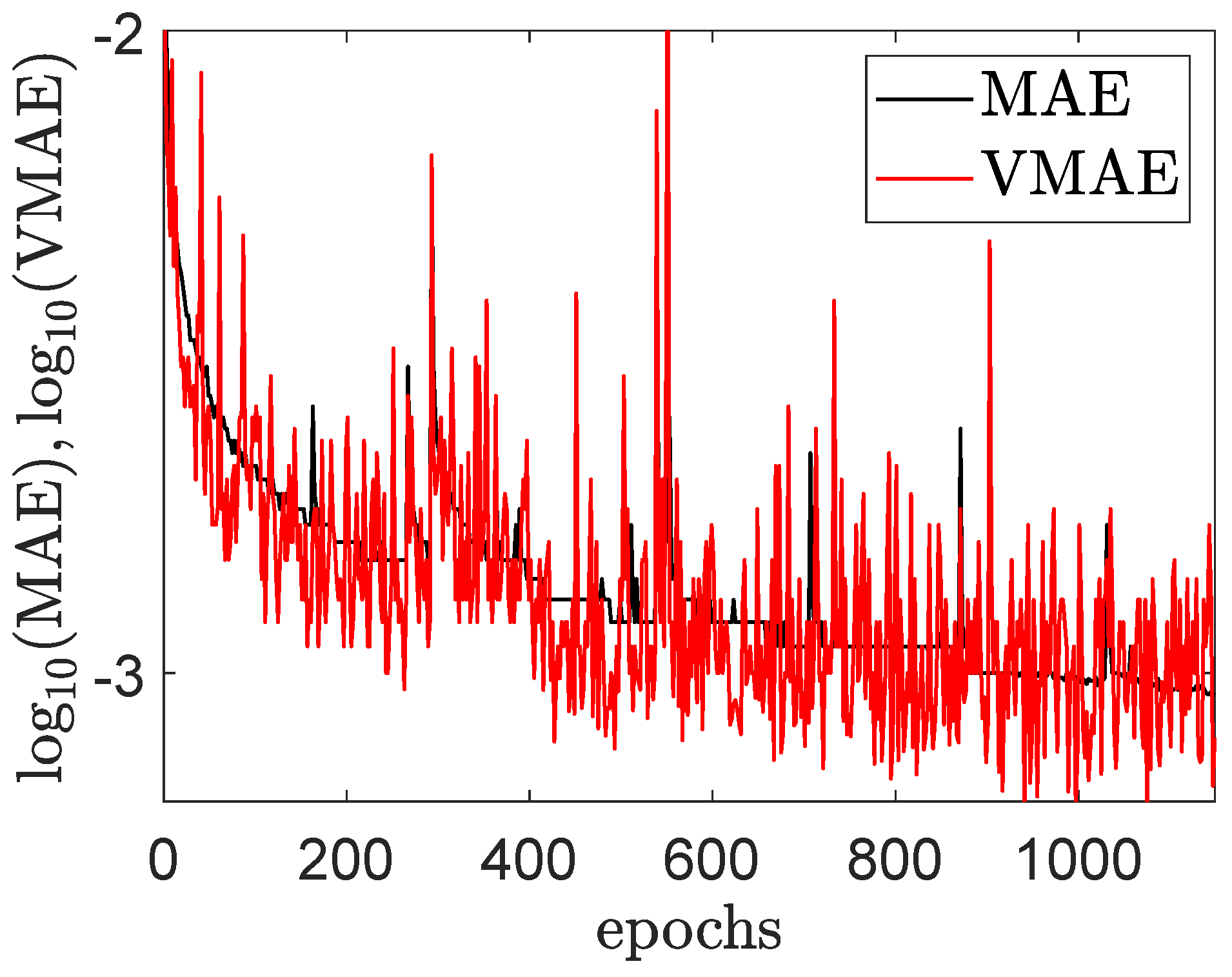
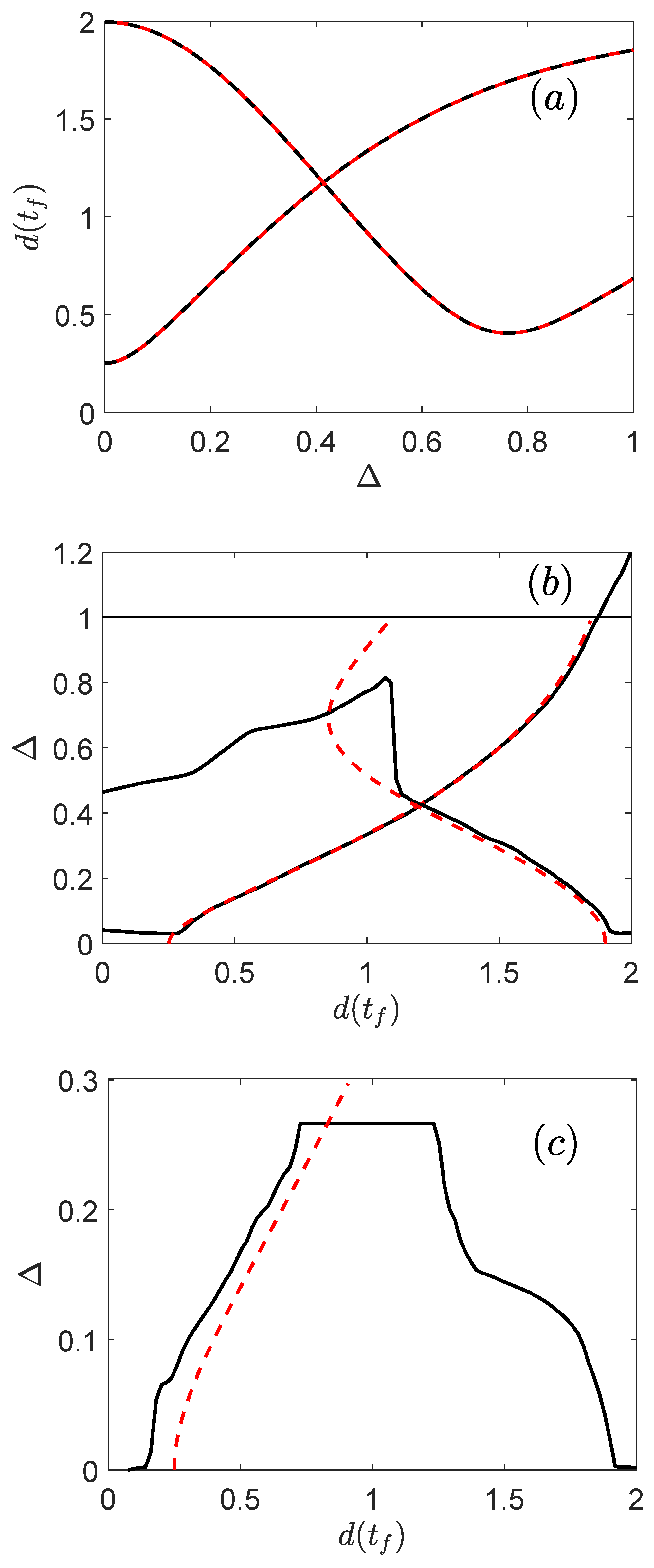
4. Numerical Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OCT | Optimal Control Theory |
| QC | Quantum Control |
| NN | Neural Networks |
Appendix A. Code for the Different NN Architectures
References
- Carleo, G.; Cirac, I.; Cranmer, K.; Daudet, L.; Schuld, M.; Tishby, N.; Vogt-Maranto, L.; Zdeborová, L. Machine learning and the physical sciences. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Bukov, M.; Wang, C.H.; Day, A.G.; Richardson, C.; Fisher, C.K.; Schwab, D.J. A high-bias, low-variance introduction to Machine Learning for physicists. Phys. Rep. 2019, 810, 1–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, R.S.; Rabitz, H. Teaching lasers to control molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hush, M.R. Machine learning for quantum physics. Science 2017, 355, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunjko, V.; Wittek, P. A non-review of Quantum Machine Learning: Trends and explorations. Quantum Views 2020, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, M.; Landgraf, J.; Foesel, T.; Marquardt, F. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for quantum technologies. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 107, 010101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleo, G.; Troyer, M. Solving the quantum many-body problem with artificial neural networks. Science 2017, 355, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquilla, J.; Melko, R.G. Machine learning phases of matter. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunjko, V.; Taylor, J.M.; Briegel, H.J. Quantum-Enhanced Machine Learning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Martín-Guerrero, J.D.; Sanz, M.; Magdalena-Benedicto, R.; Chen, X.; Solano, E. Retrieving Quantum Information with Active Learning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 140504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Flam-Shepherd, D.; Kyaw, T.H.; Aspuru-Guzik, A. Learning quantum dynamics with latent neural ordinary differential equations. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 042403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-Y.; Ren, F.-H.; He, R.-H.; Ablimit, A.; Wang, Z.-M. Stochastic learning control of adiabatic speedup in a non-Markovian open qutrit system. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 062612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convy, I.; Liao, H.; Zang, S.; Patel, S.; Livingston, W.P.; Nguyen, H.N.; Siddigi, I.; Whaley, B. Machine learning for continuous quantum error correction on superconducting qubits. New J. Phys. 2022, 24, 063019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, S.J.; Boscain, U.; Calarco, T.; Koch, C.P.; Köckenberger, W.; Kosloff, R.; Kuprov, I.; Luy, B.; Schirmer, S.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, T.; et al. Training Schrödinger’s cat: Quantum optimal control. Strategic report on current status, visions and goals for research in Europe. Eur. Phys. J. D 2015, 69, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, D. Introduction to Quantum Control and Dynamics; Applied Mathematics and Nonlinear Science Series; Chapman, Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brif, C.; Chakrabarti, R.; Rabitz, H. Control of quantum phenomena: Past, present and future. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 075008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrontegui, E.; Ibáñez, S.; Martínez-Garaot, S.; Modugno, M.; del Campo, A.; Guéry-Odelin, D.; Ruschhaupt, A.; Chen, X.; Muga, J.G. Chapter 2—Shortcuts to Adiabaticity. In Advances in Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics; Arimondo, E., Berman, P.R., Lin, C.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 62, pp. 117–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéry-Odelin, D.; Ruschhaupt, A.; Kiely, A.; Torrontegui, E.; Martínez-Garaot, S.; Muga, J.G. Shortcuts to adiabaticity: Concepts, methods, and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.P.; Lemeshko, M.; Sugny, D. Quantum control of molecular rotation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2019, 91, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acín, A.; Bloch, I.; Buhrman, H.; Calarco, T.; Eichler, C.; Eisert, J.; Esteve, D.; Gisin, N.; Glaser, S.J.; Jelezko, F.; et al. The quantum technologies roadmap: A European community view. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 080201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.P.; Boscain, U.; Calarco, T.; Dirr, G.; Filipp, S.; Glaser, S.J.; Kosloff, R.; Montangero, S.; Schulte-Herbrüggen, T.; Sugny, D.; et al. Quantum optimal control in quantum technologies. Strategic report on current status, visions and goals for research in Europe. EPJ Quantum Technol. 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, L.; Sgroi, P.; Brown, J.; Paraoanu, G.S.; Paternostro, M.; Paladino, E.; Falci, G. A tutorial on optimal control and reinforcement learning methods for quantum technologies. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 434, 128054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Guerrero, J.D.; Lamata, L. Reinforcement Learning and Physics. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukov, M.; Day, A.G.R.; Sels, D.; Weinberg, P.; Polkovnikov, A.; Mehta, P. Reinforcement Learning in Different Phases of Quantum Control. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.G.R.; Bukov, M.; Weinberg, P.; Mehta, P.; Sels, D. Glassy Phase of Optimal Quantum Control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 020601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Cui, Z.W.; Wang, X.; Yung, M.H. Automatic spin-chain learning to explore the quantum speed limit. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 052333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; An, Z.; Hou, S.Y.; Zhou, D.L.; Zeng, B. Quantum imaginary time evolution steered by reinforcement learning. Comm. Phys. 2022, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Zhou, D.L. Deep reinforcement learning for quantum gate control. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 2019, 126, 60002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porotti, R.; Tamascelli, D.; Restelli, M.; Prati, E. Coherent transport of quantum states by deep reinforcement learning. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.Y.; Boixo, S.; Smelyanskiy, V.N.; Neven, H. Universal quantum control through deep reinforcement learning. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Ashida, Y.; Ueda, M. Deep Reinforcement Learning Control of Quantum Cartpoles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 100401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ban, Y.; Martín-Guerrero, J.D.; Solano, E.; Casanova, J.; Chen, X. Breaking adiabatic quantum control with deep learning. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, L040401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, S.; Sarma, B.; Kewming, M.; Milburn, G.J.; Twamley, J. Measurement-Based Feedback Quantum Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning for a Double-Well Nonlinear Potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 190403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Lin, L.; Bukov, M. Reinforcement Learning for Many-Body Ground-State Preparation Inspired by Counterdiabatic Driving. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 031070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Pan, Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Gao, Q.; Dong, D. Robust optimization for quantum reinforcement learning control using partial observations. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 062443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgroi, P.; Palma, G.M.; Paternostro, M. Reinforcement Learning Approach to Nonequilibrium Quantum Thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 020601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Sgroi, P.; Giannelli, L.; Paraoanu, G.S.; Paladino, E.; Falci, G.; Paternostro, M.; Ferraro, A. Reinforcement learning-enhanced protocols for coherent population-transfer in three-level quantum systems. New J. Phys. 2021, 23, 093035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, P.A.; Noé, F. Identifying optimal cycles in quantum thermal machines with reinforcement-learning. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.B.; Ding, H.; Dong, D.; Wang, X. Learning robust and high-precision quantum controls. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 042327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Yung, M.H.; Wang, X. Neural-network-designed pulse sequences for robust control of singlet-triplet qubits. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 042324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngördü, U.; Kestner, J.P. Robust quantum gates using smooth pulses and physics-informed neural networks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, 023155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huand, T.; Ban, Y.; Sherman, E.Y.; Chen, X. Machine-Learning-Assisted Quantum Control in a Random Environment. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 17, 024040. [Google Scholar]
- Wittler, N.; Roy, F.; Pack, K.; Werninghaus, M.; Roy, A.S.; Egger, D.J.; Filipp, S.; Wilhelm, F.K.; Machnes, S. Integrated Tool Set for Control, Calibration, and Characterization of Quantum Devices Applied to Superconducting Qubits. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, 034080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bris, C.; Mirrahimi, M.; Rabitz, H.; Turinici, G. Hamiltonian identification for quantum systems: Well-posedness and numerical approaches. ESAIM COCV 2007, 13, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, J.M.; Rabitz, H. Optimal Hamiltonian identification: The synthesis of quantum optimal control and quantum inversion. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 5369–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, N.; Geremia, J.M.; Rabitz, H. Nonlinear Kinetic Parameter Identification through Map Inversion. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndong, M.; Salomon, J.; Sugny, D. Newton algorithm for Hamiltonian characterization in quantum control. J. Phys. Math. Theor. 2014, 47, 265302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, S.G.; Langbein, F.C. Ubiquitous problem of learning system parameters for dissipative two-level quantum systems: Fourier analysis versus Bayesian estimation. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 022125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sarovar, M. Quantum Hamiltonian Identification from Measurement Time Traces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 080401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, A.; Cappellaro, P. Hamiltonian identifiability assisted by a single-probe measurement. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 95, 022335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgarth, D.; Ajoy, A. Evolution-Free Hamiltonian Parameter Estimation through Zeeman Markers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 030402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Wu, R.; Ma, S.; Li, D.; Jiang, M. Gradient algorithm for Hamiltonian identification of open quantum systems. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 022604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, S.; Ciaramella, G.; Salomon, J.; Sugny, D. Greedy reconstruction algorithm for the identification of spin distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 063112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Fung, C.H.F. Optimal Feedback Scheme and Universal Time Scaling for Hamiltonian Parameter Estimation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 110401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, H. Quantum parameter estimation with optimal control. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 012117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ma, Y.; Sels, D. Optimal control for quantum metrology via Pontryagin’s principle. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 052607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Ma, Y.; Sels, D. Application of Pontryagin’s maximum principle to quantum metrology in dissipative systems. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 042621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pang, S.; Chen, Z.; Jordan, A.N.; del Campo, A. Variational Principle for Optimal Quantum Controls in Quantum Metrology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 160505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N.; Liu, K.; Sunshine, J.L.; Duerk, J.L.; Griswold, M.A. Magnetic resonance fingerprinting. Nature 2013, 495, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansel, Q.; Tesch, M.; Glaser, S.J.; Sugny, D. Optimizing fingerprinting experiments for parameter identification: Application to spin systems. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 053419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumino, A.; Polino, E.; Rab, A.S.; Milani, G.; Spagnolo, N.; Wiebe, N.; Sciarrino, F. Experimental Phase Estimation Enhanced by Machine Learning. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2018, 10, 044033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Fan, J.; Zeng, G. Parameter estimation in quantum sensing based on deep reinforcement learning. NPJ Quantum Inf. 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Artificial neural networks. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 1988, 4, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Papič, M.; de Vega, I. Neural-network-based qubit-environment characterization. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 022605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, D.F.; Morton, J.J.; Dhomkar, S. Using Deep Learning to Understand and Mitigate the Qubit Noise Environment. PRX Quantum 2021, 2, 010316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanchini, F.F.; Karpat, G.b.u.; Rossatto, D.Z.; Norambuena, A.; Coto, R. Estimating the degree of non-Markovianity using machine learning. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 022425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, J.M.; Rabitz, H. Optimal Identification of Hamiltonian Information by Closed-Loop Laser Control of Quantum Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 263902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscain, U.; Mason, P. Time minimal trajectories for a spin 1/2 particle in a magnetic field. J. Math. Phys. 2006, 47, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assémat, E.; Lapert, M.; Zhang, Y.; Braun, M.; Glaser, S.J.; Sugny, D. Simultaneous time-optimal control of the inversion of two spin- particles. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 013415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscain, U.; Sigalotti, M.; Sugny, D. Introduction to the Pontryagin Maximum Principle for Quantum Optimal Control. PRX Quantum 2021, 2, 030203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fraction | VMAE |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 1/2 | |
| 1/4 | |
| 1/8 |
| Algorithm | VMAE (1) | VMAE (2) |
|---|---|---|
| MLP | ||
| CNN | ||
| LSTM |
| Algorithm | VMAE (3) | VMAE (4) |
|---|---|---|
| MLP | ||
| CNN | ||
| LSTM |
| Algorithm | CPU | GPU T2000 | GPU A100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | |||
| CNN | |||
| LSTM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Couturier, R.; Dionis, E.; Guérin, S.; Guyeux, C.; Sugny, D. Characterization of a Driven Two-Level Quantum System by Supervised Learning. Entropy 2023, 25, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25030446
Couturier R, Dionis E, Guérin S, Guyeux C, Sugny D. Characterization of a Driven Two-Level Quantum System by Supervised Learning. Entropy. 2023; 25(3):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25030446
Chicago/Turabian StyleCouturier, Raphaël, Etienne Dionis, Stéphane Guérin, Christophe Guyeux, and Dominique Sugny. 2023. "Characterization of a Driven Two-Level Quantum System by Supervised Learning" Entropy 25, no. 3: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25030446
APA StyleCouturier, R., Dionis, E., Guérin, S., Guyeux, C., & Sugny, D. (2023). Characterization of a Driven Two-Level Quantum System by Supervised Learning. Entropy, 25(3), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/e25030446







