Thermodynamic Analysis and Crystallographic Properties of MFe2O4, MCr2O4 and MAl2O4 (M = Fe, Ni, Zn) Formed on Structural Materials in Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Circuit under Zinc and Zinc-aluminum Water Chemistry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Thermodynamic
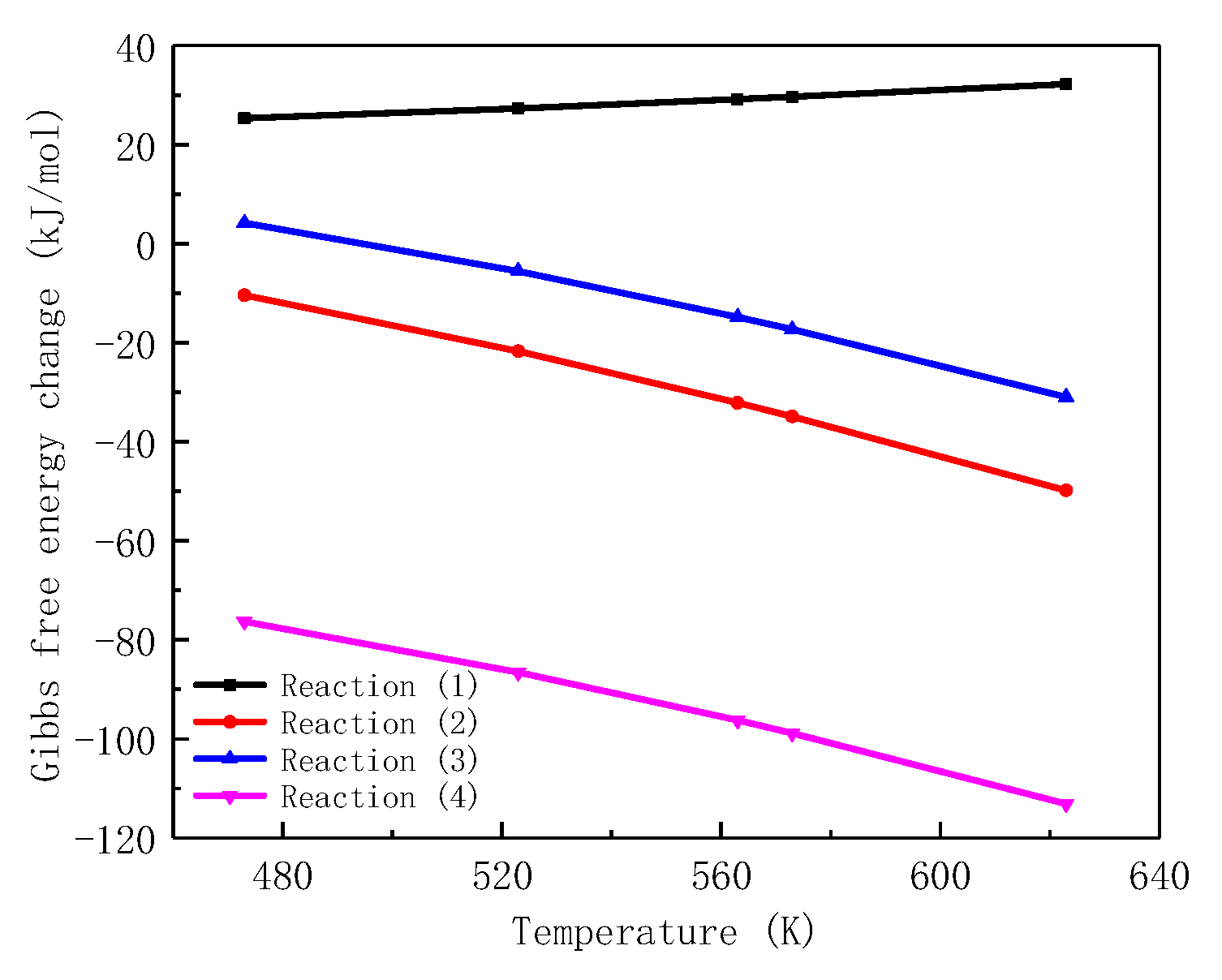
2.1. Zinc Injection
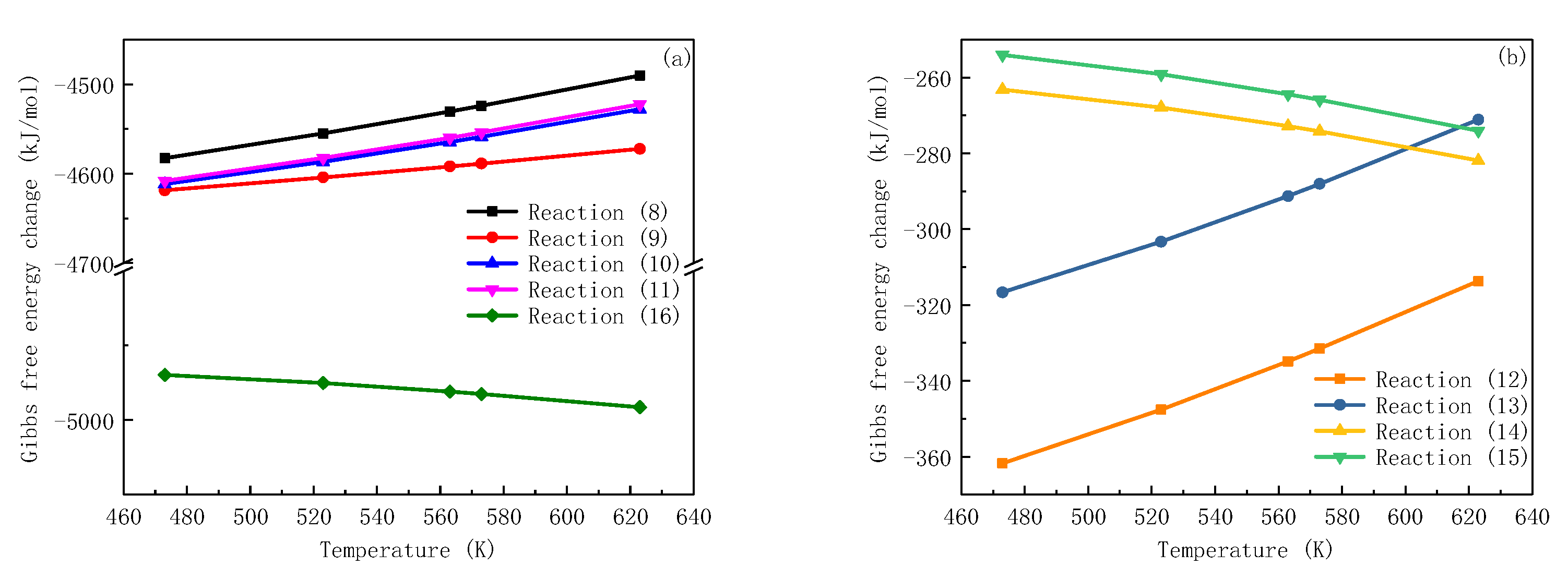
2.2. Zinc-Aluminum Simultaneous Injection
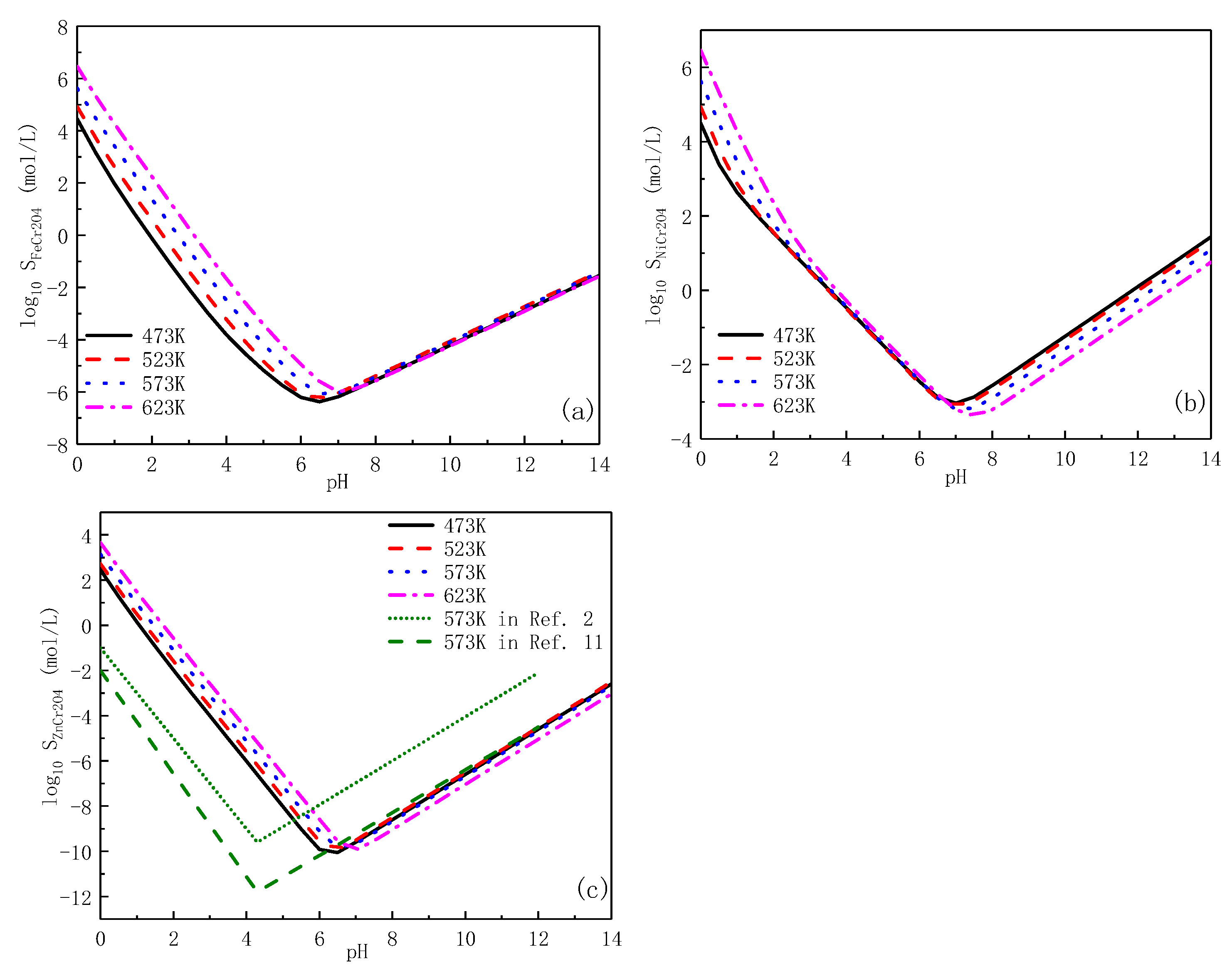
3. Solubility
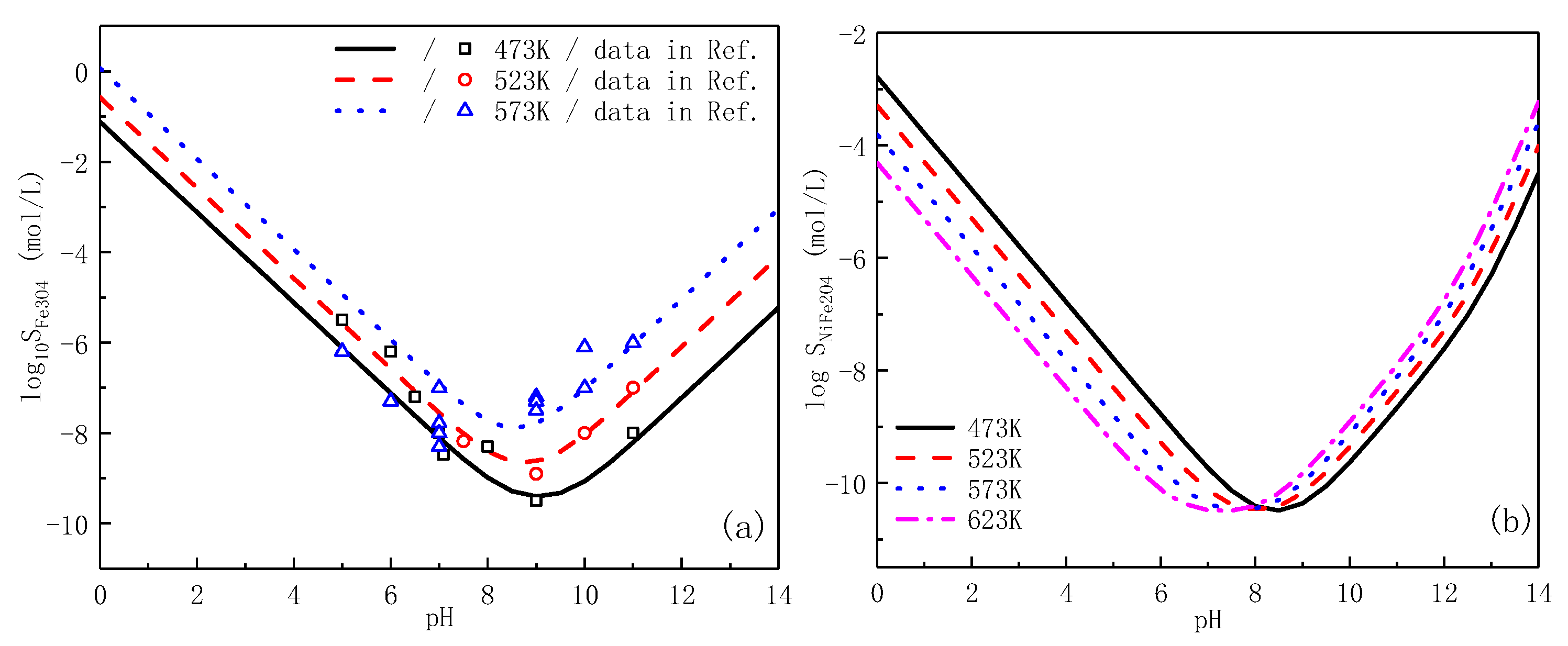
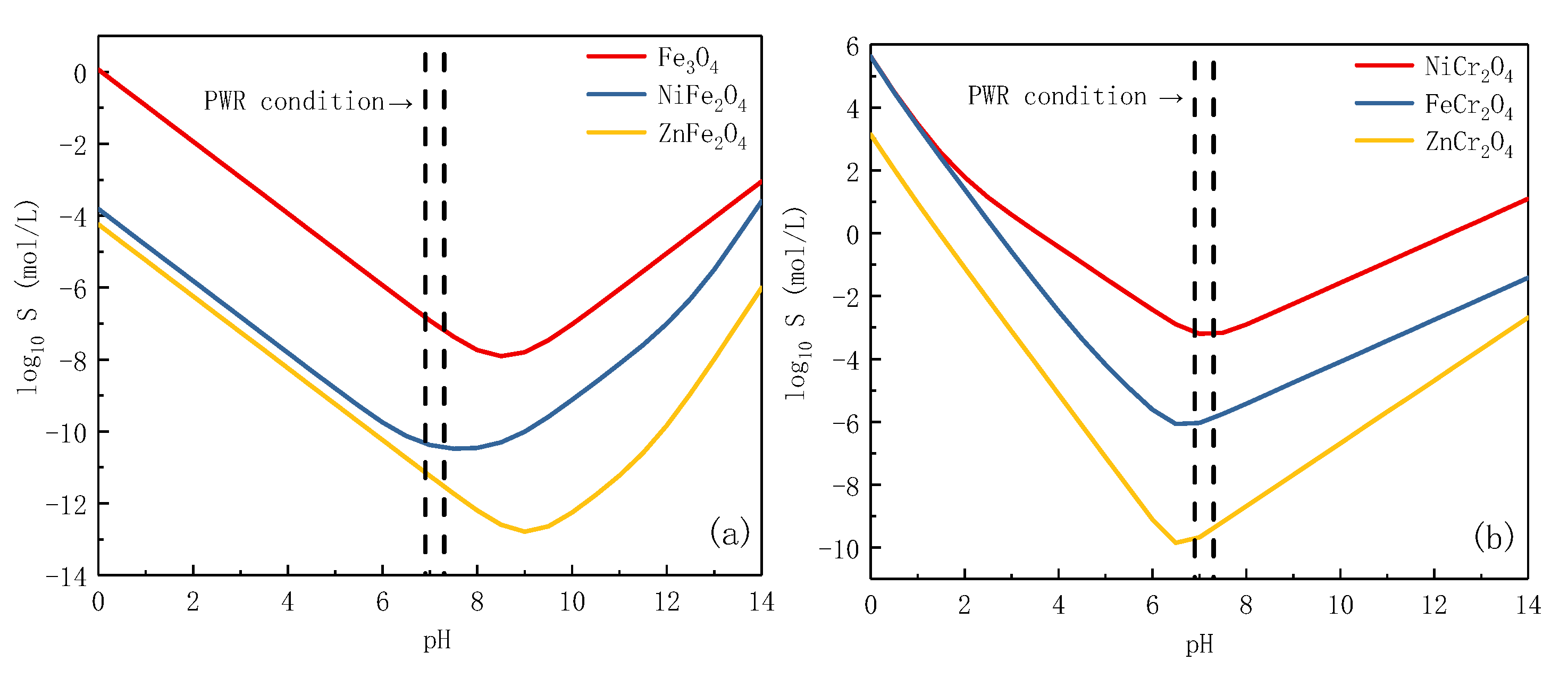
3.1. Cr-Rich Inner Laryer Oxide
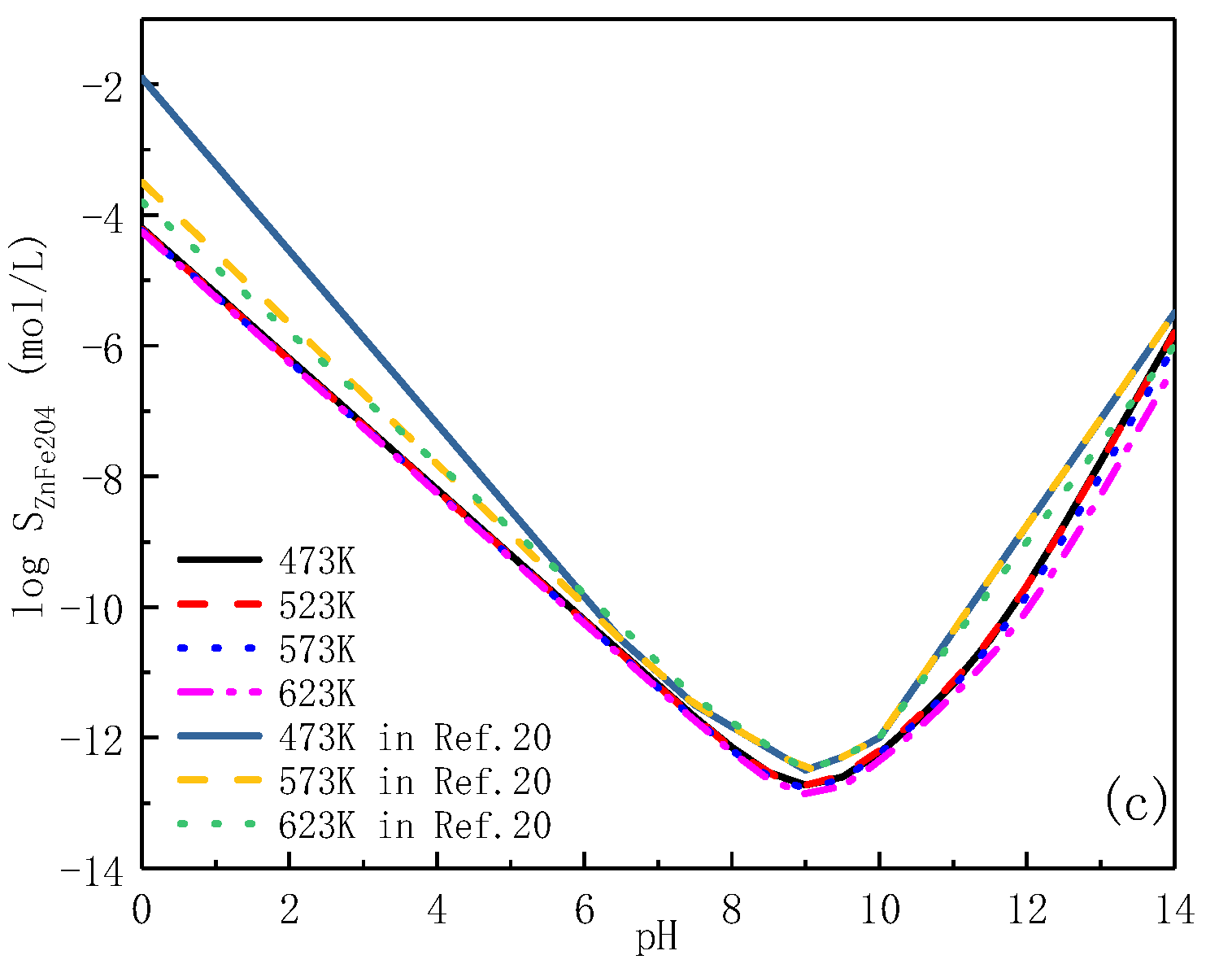
3.2. Fe-Rich Outer Layer Oxide
3.3. Al-Rich Oxide
4. Mechanism Discussion
4.1. Thermodynamic Property
4.2. Crystallographic Property
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvar, M.L.; Curieres, I.D. Corrosion issues in pressurized water reactor (PWR) systems. Nucl. Corros. Sci. Eng. 2012, 473–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, K.; Hirano, H. Thermodynamic consideration on the effect of zinc injection into PWR primary coolant for the reduction of radiation buildup and corrosion control. In Proceedings of the CORROSION 2001, Houston, TX, USA, 11–16 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, P.M.; Combrade, P. General corrosion and stress corrosion cracking of Alloy 600 in light water reactor primary. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 524, 340–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hwang, W.; Park, J.; Van, D.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Han, S.; Lee, B. Toward the multiscale nature of stress corrosion cracking. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2018, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terachi, T.; Fujii, K.; Arioka, K. Microstructural characterization of SCC crack tip and oxide film for SUS 316 stainless steel in simulated PWR primary water at 320 °C. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2005, 42, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemniak, S.E.; Hanson, M. Corrosion behavior of 304 stainless steel in high temperature hydrogenated water. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 2209–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staehle, R.W. QMN approach to SCC mechanism prediction-starting third meeting. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 7–11 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiahe, L.; Xinqiang, W.; Enhou, H. Status and progress on study of corrosion behavior of structural materials in Zn-injected water for LWRs. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. 2011, 23, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth, S.; Scenini, F.; Burke, M.G.; Bertali, G.; Ito, T.; Wada, Y.; Hosokawa, H.; Ota, N.; Nagase, M. The effect of high-temperature water chemistry and dissolved zinc on the cobalt incorporation on type 316 stainless steel oxide. Corros. Sci. 2018, 140, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Han, E.-H.; Wu, X. Influence of Zn on oxide films on Alloy 690 in borated and lithiated high temperature water. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiahe, L.; Xinqiang, W.; Enhou, H. Influence of Zn injection on characteristics of oxide film on 304 stainless steel in borated and lithiated high temperature water. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shi, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M. Corrosion behavior of oxide films on AISI 316L SS formed in high temperature water with simultaneous injection of zinc and aluminum. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 731, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenhao, S. Effect of Zinc and Aluminum Simultaneous Injection on Corrosion Behavior of Structure Materials in PWR. Ph.D. Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-J. Analysis of Oxide Film Formed on Type 304 Stainless Steel in 288 °C Water Containing Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Hydrogen Peroxide. Corrosion 1999, 55, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J. Characterization of the Oxide Film Formed on Type 316 Stainless Steel in 288 °C Water in Cyclic Normal and Hydrogen Water Chemistries. Corrosion 2012, 51, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, L. Influence of Water Chemistry on Corrosion Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel in High Temperature High Pressure Solution. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cissé, S.; Laffont, L.; Tanguy, B.; Lafont, M.-C.; Andrieu, E. Effect of surface preparation on the corrosion of austenitic stainless steel 304 L in high temperature steam and simulated PWR primary water. Corros. Sci. 2012, 56, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, D.-S.; Jeon, S.-H.; Bae, B.J.; Choi, J.; Song, K.M.; Hur, D.H. Effect of zinc addition scenarios on general corrosion of Alloy 690 in borated and lithiated water at 330 °C. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaofang, S. Influence of Aluminum Ion on Corrosion Behavior of Stainless Steel in High Temperature Water of Nuclear Power Plant. Ph.D. Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rongxue, S. Electrochemical Research on Mechanism of Corrosion Resistance of Oxide Films on Fe-Base Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shenghan, Z.; Chenhao, S.; Yu, T. Influence of zinc and aluminum simultaneous injection on corrosion behavior and semiconducting properties of oxide film on 304 L. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 9874–9887. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.A. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 15th ed.; McGraw-Hil: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Barin, I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1996; pp. 1–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.M.; Aral, K.; Theus, G.J. Computer-Calculated Potential PH Diagrams to 300 °C; EPRI: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Shock, E.L.; Sassani, D.C.; Willis, M.; Sverjensky, D.A. Inorganic species in geologic fluids: Correlations among standard molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous ions and hydroxide complexes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 907–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenghan, Z.; Chenhao, S.; Yu, T. Corrosion behavior of high-strength low-alloy steel in high-temperature water with zinc and aluminum simultaneous injection. Corrosion 2020, 76, 919–929. [Google Scholar]
- Beverskog, B.; Puigdomenech, I. Revised pourbaix diagrams for iron at 25–300 °C. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénézeth, P.; Palmer, D.A.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Xiao, C. New measurements of the solubility of zinc oxide from 150 to 350 °C. J. Solut. Chem. 2002, 31, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaine, P.R.; LeBlanc, J.C. The solubility of magnetite and the hydrolysis and oxidation of Fe2+ in water to 300 °C. J. Solut. Chem. 1980, 9, 415–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeton, F.H.; Baes, C.F., Jr. The solubility of magnetite and hydrolysis of ferrous ion in aqueous solutions at elevated temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 1970, 2, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. The Mechanism of High Temperature Aqueous Corrosion of Stainless Steels. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 443–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.H. The Structure of Magnetite and the Spinels. Nature 1915, 95, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S. Structure of Some Crystals of Spinel Group. Proc. Tokyo Math.-Phys. Soc. 1916, 8, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, T.F.W.; Posnjak, E. Spinel structures: With and without variate atom equipoints. Z. Kristallogr. 1932, 82, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, R.; Jiao, S.; Chen, Y.; Feng, S. Physical properties of MgAl2O4, CoAl2O4, NiAl2O4, CuAl2O4, and ZnAl2O4 spinels synthesized by a solution combustion method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 215, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoliang, J. Studies on the Fabrication and Application of Oriented Mixed Metal Oxide Films Derived from Layered Doubled Hydroxides. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J. Research and Application of Zinc Injection in PWRs; Progress Report on China Nuclear Science & Technology: Guiyang, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]

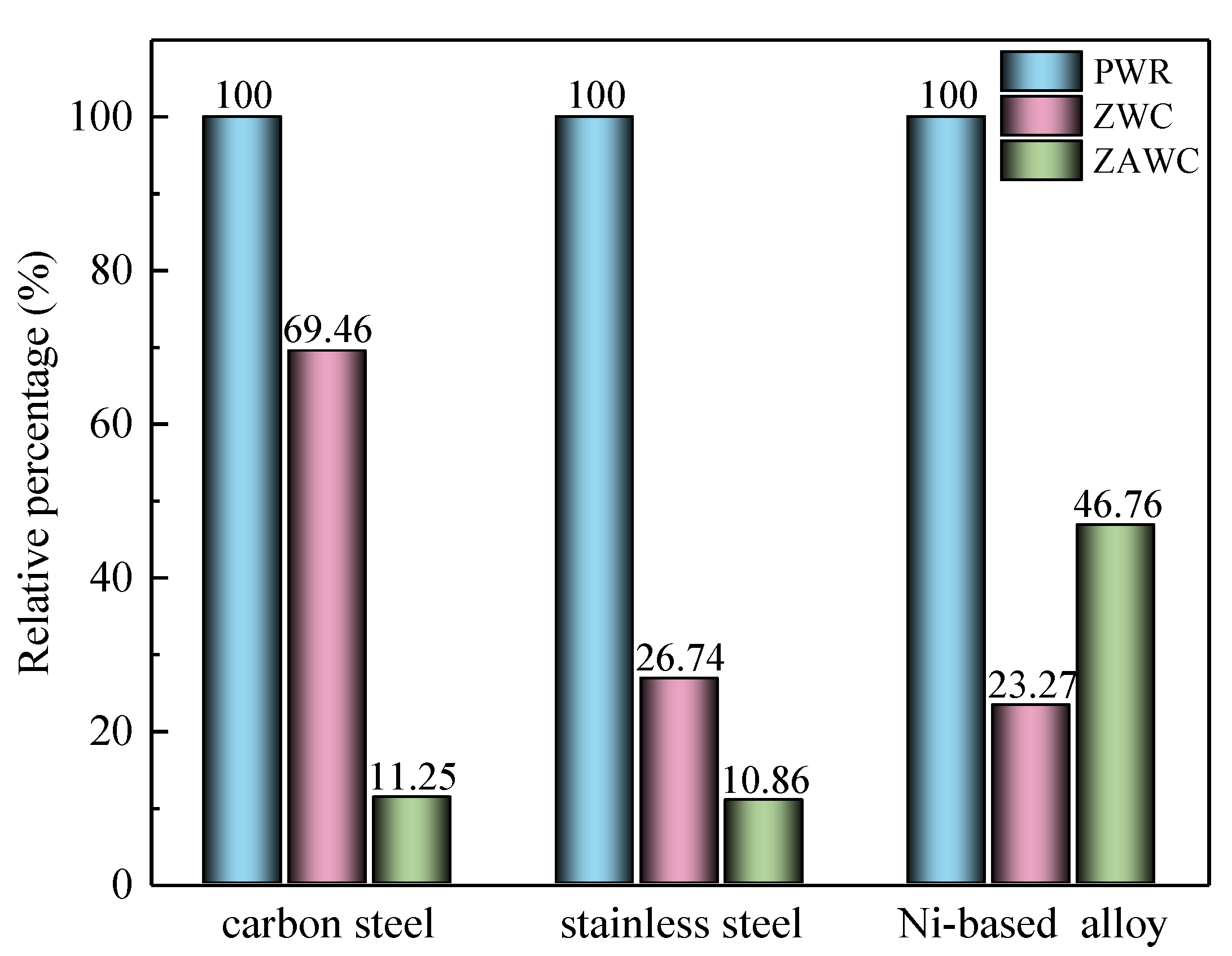


| Composition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Ni | Fe | Mn | |
| A106B CS | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | Bal. | 0.29–1.06 |
| A508-3 CS | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.5–0.80 | Bal. | 1.15–1.6 |
| 304L SS | 0.03 | 18–20 | 8–12 | Bal. | 2.0 |
| 316L SS | 0.03 | 16–18 | 10–14 | Bal. | 2.0 |
| Incoloy 800 | 0.1 | 19–23 | 30–35 | 37–47 | 1.5 |
| Inconel 600 | 0.15 | 14–17 | 72 | 6–10 | 1.0 |
| Inconel 690 | 0.023 | 30.39 | 60 | 8.88 | 0.23 |
| Species | (kJ·mol−1) | (J·mol−1·K−1) | A | B (×10−3) | C (×105) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | −1015.45 | 146.4 | 91.5 | 201 | - |
| NiFe2O4 | −974.6 | 125.9 | 77.4 | 235 | 1.42 |
| FeCr2O4 | −1347.02 | 147 | 163.2 | 22.36 | −31.95 |
| NiCr2O4 | −1269.14 | 129.7 | 167.2 | 17.87 | −21.05 |
| ZnFe2O4 | −1063.5 | 151.67 | 161.5 | 28.93 | −26.53 |
| ZnCr2O4 | −1434.0 | 116.3 | 167.4 | 14.23 | −25.1 |
| Zn2+ | −147.1 | −156.5 | −164 | - | - |
| Fe2+ | −78.9 | −182.1 | −188 | - | - |
| Ni2+ | −48.2 | −170.7 | 269.6 | - | - |
| Species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 | −1048.13 | −1059.81 | −1069.83 | −1072.43 | −1085.95 |
| NiFe2O4 | −1003.65 | −1014.31 | −1023.53 | −1025.92 | −1038.47 |
| FeCr2O4 | −1379.03 | −1390.21 | −1399.72 | −1402.18 | −1414.87 |
| NiCr2O4 | −1298.62 | −1309.19 | −1318.24 | −1320.57 | −1332.70 |
| ZnFe2O4 | −1096.55 | −1108.08 | −1117.89 | −1120.42 | −1133.50 |
| ZnCr2O4 | −1460.99 | −1470.79 | −1479.21 | −1481.39 | −1492.71 |
| Zn2+ | −112.57 | −100.54 | −90.35 | −87.72 | −74.19 |
| Fe2+ | −38.85 | −24.92 | −13.13 | −10.09 | 5.56 |
| Ni2+ | −30.10 | −28.49 | −28.13 | −28.16 | −29.01 |
| Species | (kJ·mol−1) | (J·mol−1·K−1) | A | B (×10−3) | C (×105) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnAl2O4 | −6671 | 87.03 | 166.52 | 15.48 | −46.02 |
| FeAl2O4 | −1879.67 | 106.299 | 123.544 | - | - |
| NiAl2O4 | −1791.12 | 98.324 | 131.567 | - | - |
| Fe3+ | −15.4 | −382.5 | −204 | - | - |
| Al3+ | −485.3 | −325 | 113.115 | −0.506 | - |
| Cr3+ | −215.48 | −370.3 | 488.7 | - | - |
| Fe2O3 | −740.99 | 89.96 | 98.28 | 77.82 | −14.85 |
| ZnO | −321.9 | 43.16 | 47.58 | 3.93 | −7.504 |
| Species | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnAl2O4 | −6692.04 | −6699.99 | −6706.89 | −6708.69 | −6718.10 |
| FeAl2O4 | −1903.65 | −1912.13 | −1919.35 | −1921.21 | −1930.82 |
| NiAl2O4 | −1814.05 | −1822.34 | −1829.43 | −1831.27 | −1840.76 |
| Fe3+ | 60.42 | 84.78 | 104.97 | 110.11 | 136.34 |
| Al3+ | −433.34 | −419.99 | −409.70 | −407.17 | −394.85 |
| Cr3+ | −171.95 | −165.97 | −162.88 | −162.33 | −160.83 |
| Fe2O3 | −761.66 | −769.19 | −775.67 | −777.36 | −786.13 |
| ZnO | −331.31 | −334.59 | −337.38 | −338.10 | −341.81 |
| Oxidation Product | Dissolution Equilibrium Reactions |
|---|---|
| FeCr2O4 | |
| NiCr2O4 | |
| ZnCr2O4 |
| Species | (kJ·mol−1) | (J·mol−1·K−1) | A | B (×10−3) | C (×105) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H+ | 0 | −22.2 | −71 | - | - |
| H2 | 0 | 130.6 | 27.28 | 3.264 | 0.502 |
| H2O | −237.19 | 70.08 | 75.44 | - | - |
| Fe | 0 | 27.15 | 14.1 | 29.7 | 1.799 |
| FeO | −246.35 | 79.5 | 48.79 | 8.37 | −2.803 |
| HFeO2− | −379.18 | 41.92 | −508.1 | - | - |
| Cr2O3 | −1046.84 | 81.17 | 119.3 | 9.096 | −15.64 |
| Cr2+ | −176.15 | −120.9 | 314.5 | - | - |
| CrO2− | −535.93 | 117.3 | −386.7 | - | - |
| CrO42− | −736.8 | 80.33 | −474 | - | - |
| Ni | 0 | 30.12 | 16.99 | 29.46 | - |
| NiO | −215.94 | 37.99 | −20.88 | 157.2 | 16.28 |
| HNiO2− | −349.22 | 62.84 | −409.7 | - | - |
| Zn | 0 | 41.63 | 22.38 | 10.04 | - |
| HZnO2− | −464 | 62.84 | −409.6 | - | - |
| ZnOH+ | −329.28 | −50.21 | 265.2 | - | - |
| Oxidation Product | Dissolution Equilibrium Reacuions |
|---|---|
| Species | (kJ·mol−1) | (J·mol−1·K−1) | A | B (×10−3) | C (×105) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(OH)+ | −270.8 | −120 | 450 | - | - |
| Fe(OH)2 | −447.43 | −80 | 435 | - | - |
| Fe(OH)3− | −612.65 | −70 | 560 | - | - |
| Ni(OH)+ | −227.2 | −49.7 | −200 | - | - |
| Ni(OH)2 | −406 | −71 | 100 | - | - |
| Ni(OH)3− | −586.5 | −133 | 300 | - | - |
| Ni(OH)42− | −743.7 | −252 | 460 | - | - |
| Fe(OH)3 | −705.29 | 106.7 | 127.61 | 41.639 | −42.17 |
| Zn(OH)+ | −339.7 | 62.76 | 41.84 | - | - |
| Zn(OH)20 | −519.27 | 61.55 | 33.47 | - | - |
| Zn(OH)3− | −700.44 | 2.98 | 159.83 | - | - |
| Zn(OH)42− | −864.69 | −27.51 | 89.54 | - | - |
| Oxidation Product | Dissolution Equilibrium Reactions |
|---|---|
| MAl2O4 (M: Zn, Fe, Ni) |
| M2+ | Mg | Ni | Co | Zn | Fe | Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radius | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.80 |
| M3+ | Al | Ni | Co | Fe | Mn | Cr |
| Radius | 0.50 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.69 |
| Cation Ion | Lattice Energy of Octahedral Sites (kcal/mol) | Preferred Lattice |
|---|---|---|
| Cr3+ | 16.6 | Octahedral (strongest) |
| Ni2+ | 9.0 | Tetrahedral |
| Fe2+ | −9.9 | Tetrahedral |
| Fe3+ | −13.3 | Tetrahedral |
| Zn2+ | −31.6 | Tetrahedral (strongest) |
| Spinel | Type | Cation Distribution (tet, oct, oct) | Total Structure Energy (TSE) | Anion Preference Energy | Cation Preference Energy | Structure Preference Energy (SPE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeAl2O4 | N | Fe2+Al3+Al3+ | −590.965 | 4.11 | −0.82 | 2.06 |
| NiAl2O4 | I | Al3+Ni2+Al3+ | −619.534 | 4.23 | −3.3 | −1.43 |
| ZnAl2O4 | N | Zn2+Al3+Al3+ | −682.214 | −0.04 | 2.45 | 1.76 |
| FeCr2O4 | N | Fe2+Cr3+Cr3+ | −638.243 | 1.67 | −1.99 | 3.7 |
| NiCr2O4 | N | Ni2+Cr3+Cr3+ | −665.768 | 2.18 | −4.5 | 0.61 |
| ZnCr2O4 | N | Zn2+Cr3+Cr3+ | −730.68 | −2.04 | 1.29 | 3.84 |
| Fe3O4 | I | Fe3+Fe2+Fe3+ | −683.899 | 0 | −0.14 | −0.86 |
| NiFe2O4 | I | Fe3+Ni2+Fe3+ | −714.186 | 0.24 | −2.67 | −4.23 |
| ZnFe2O4 | N | Zn2+Fe3+Fe3+ | −775.186 | −2.23 | −3.14 | 0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tan, Y. Thermodynamic Analysis and Crystallographic Properties of MFe2O4, MCr2O4 and MAl2O4 (M = Fe, Ni, Zn) Formed on Structural Materials in Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Circuit under Zinc and Zinc-aluminum Water Chemistry. Entropy 2022, 24, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020245
Jiao Y, Zhang S, Tan Y. Thermodynamic Analysis and Crystallographic Properties of MFe2O4, MCr2O4 and MAl2O4 (M = Fe, Ni, Zn) Formed on Structural Materials in Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Circuit under Zinc and Zinc-aluminum Water Chemistry. Entropy. 2022; 24(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020245
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Yang, Shenghan Zhang, and Yu Tan. 2022. "Thermodynamic Analysis and Crystallographic Properties of MFe2O4, MCr2O4 and MAl2O4 (M = Fe, Ni, Zn) Formed on Structural Materials in Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Circuit under Zinc and Zinc-aluminum Water Chemistry" Entropy 24, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020245
APA StyleJiao, Y., Zhang, S., & Tan, Y. (2022). Thermodynamic Analysis and Crystallographic Properties of MFe2O4, MCr2O4 and MAl2O4 (M = Fe, Ni, Zn) Formed on Structural Materials in Pressurized Water Reactor Primary Circuit under Zinc and Zinc-aluminum Water Chemistry. Entropy, 24(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020245





