Finite Element Iterative Methods for the Stationary Double-Diffusive Natural Convection Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Existence and Uniqueness
4. Several Iterative Methods Based on the Finite Element Discretization
5. Numerical Experiments
5.1. An Analytical Solution Problem
5.2. The Cavity Problem
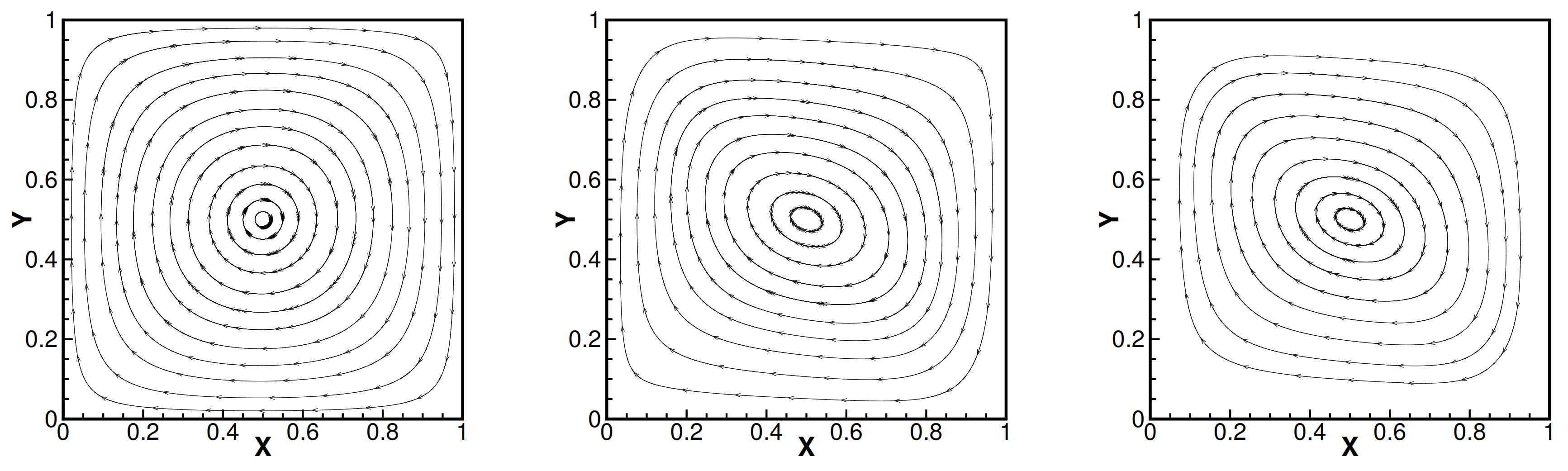
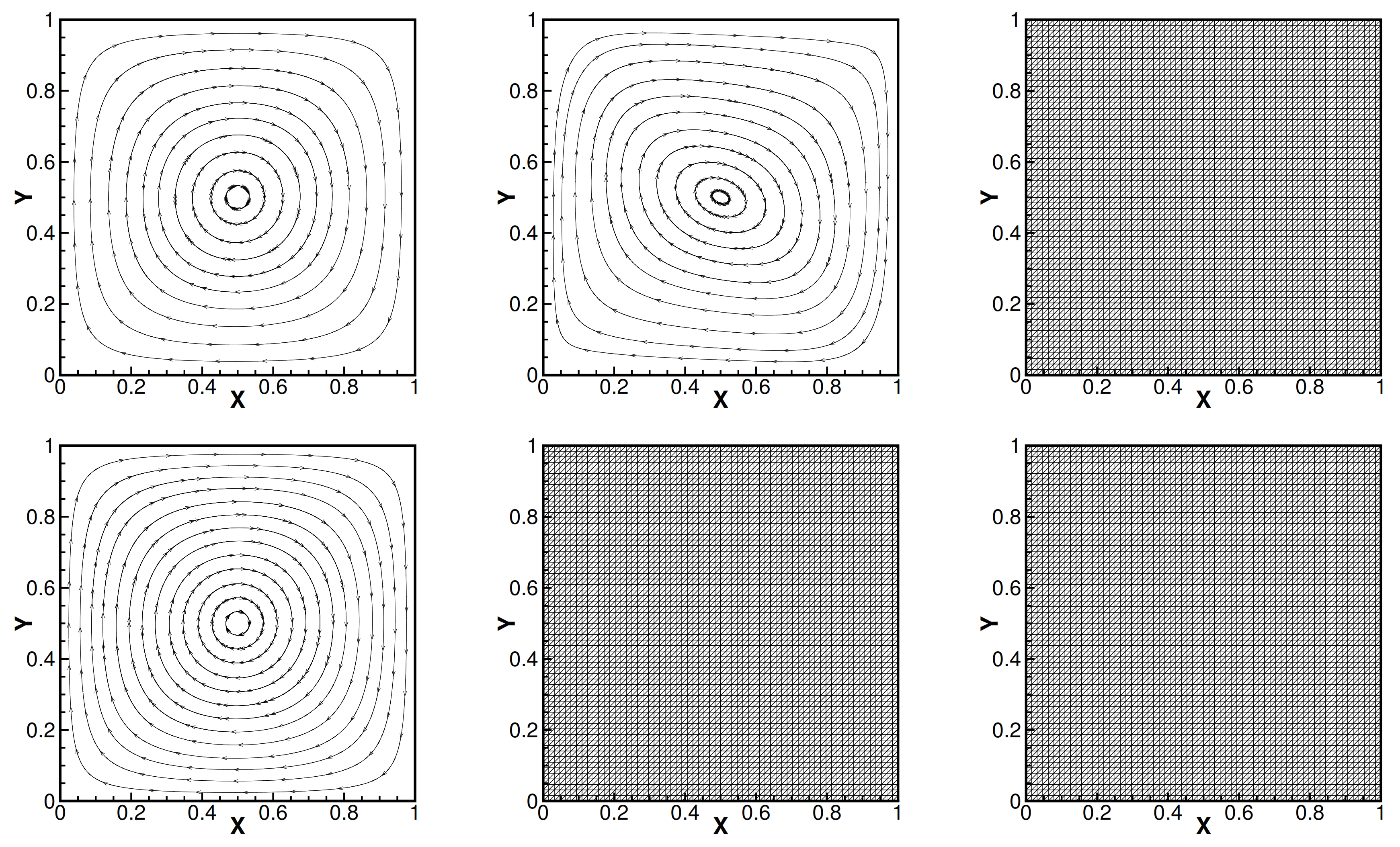

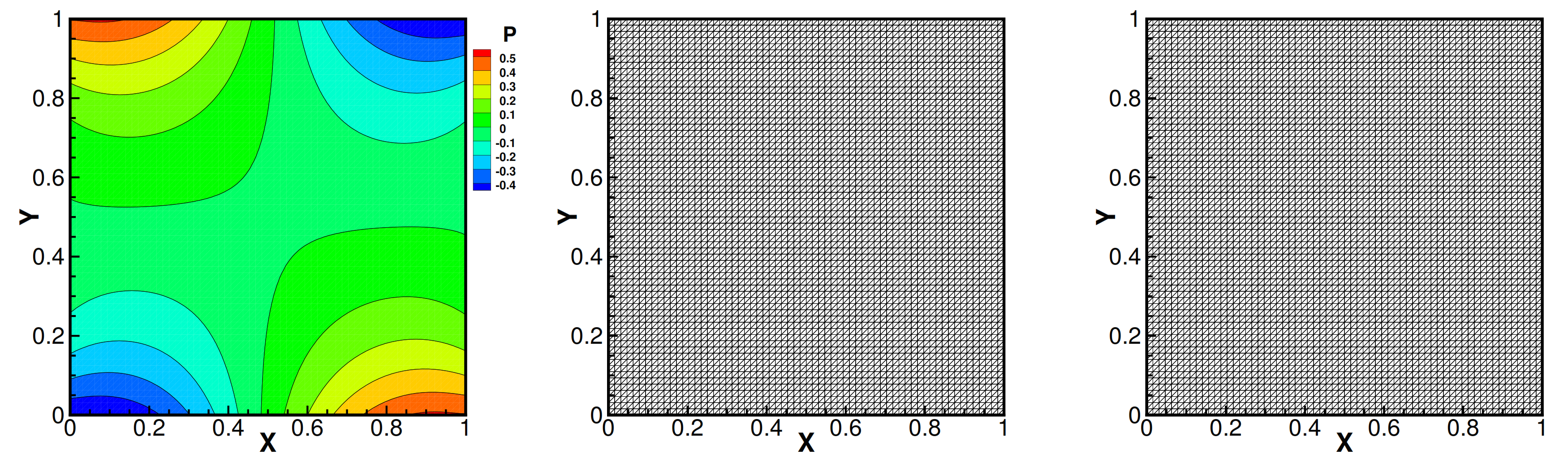
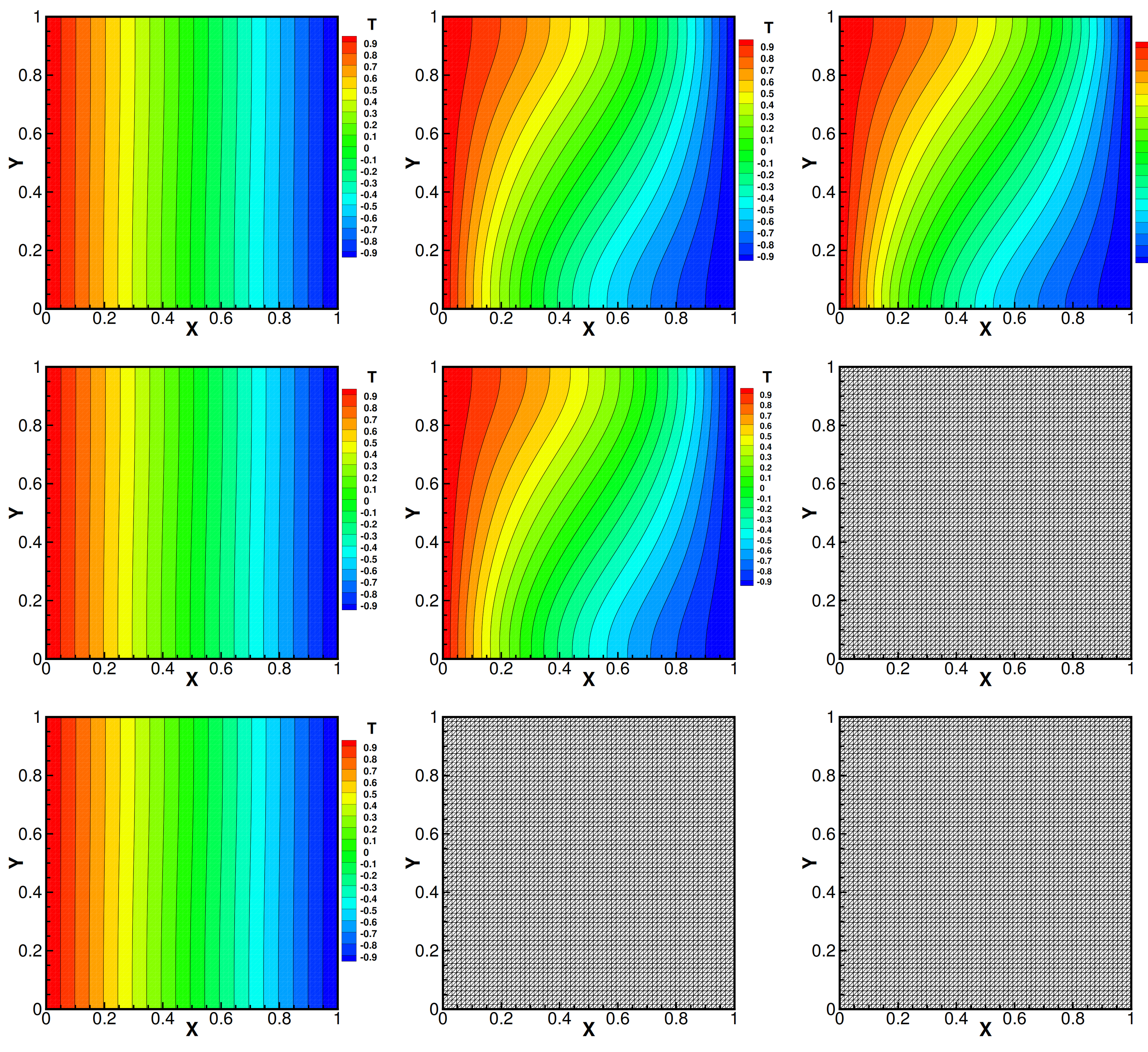
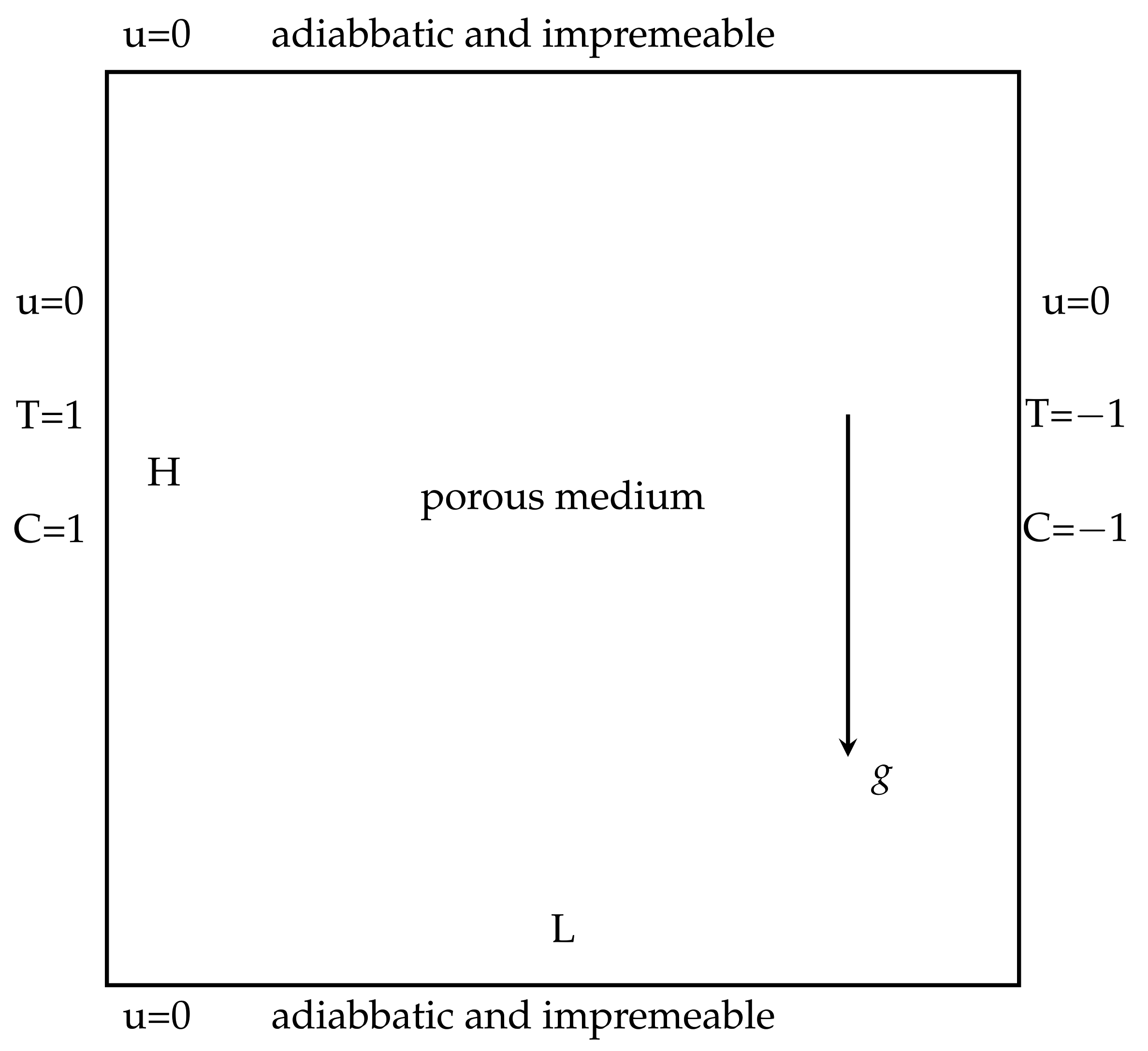
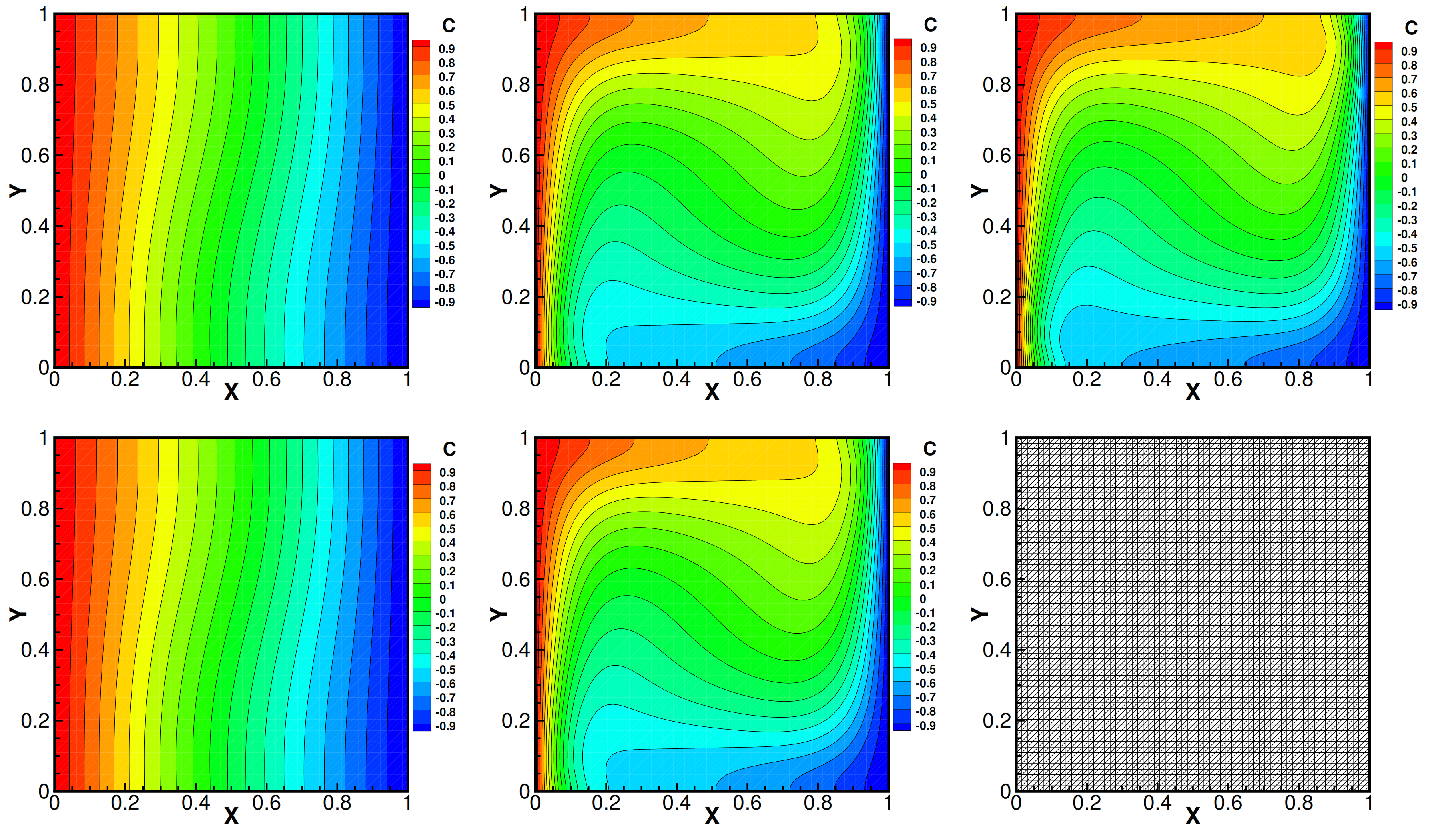
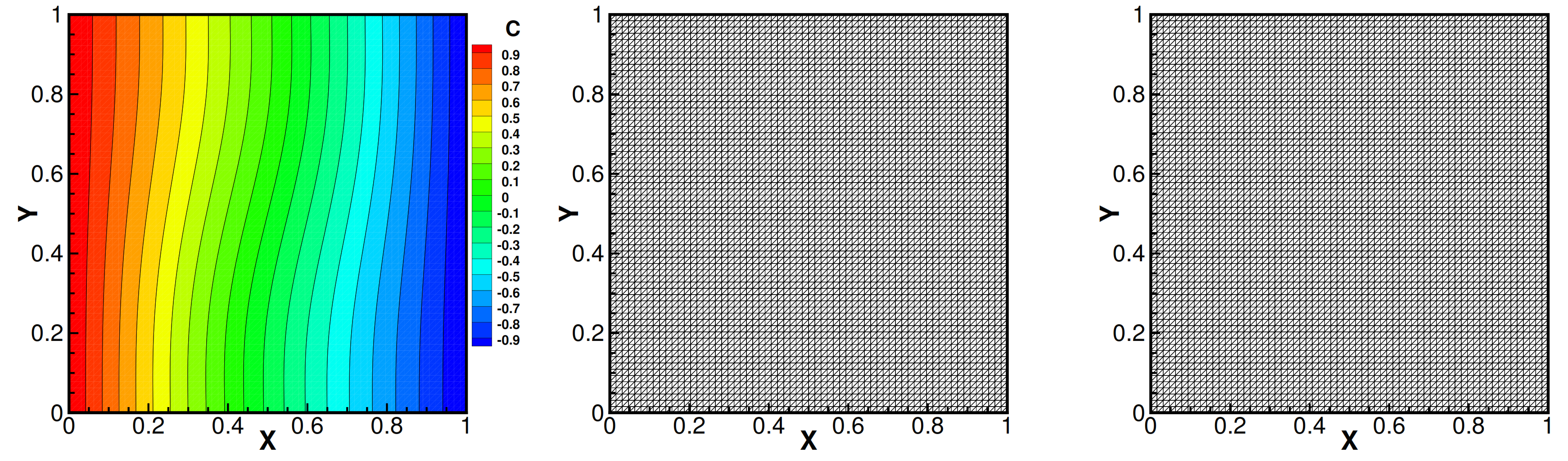

6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| a | bilinear form | w | mapping difference |
| A | a mapping | W | temperature space |
| c | trilinear form | x | dimensionless coordinate |
| C | concentration | X | velocity space |
| Darcy number | y | dimensionless coordinate | |
| mass diffusivity | |||
| e | iterative error of velocity | thermal expansion coefficient | |
| f | forcing function | solutal expansion coefficient | |
| g | gravitational acceleration vector | positive constant | |
| h | mesh size | heat diffusivity | |
| H | dual space | test function for temperature | |
| k | iterative step | uniqueness condition | |
| K | triangular region | constant[0,1] | |
| L | Lebegue space | viscosity | |
| m | Poincaré constant | ||
| M | pressure space | iterative error of pressure | |
| n | iterative step | iterative error of concentration | |
| N | constant | iterative error of temperature | |
| p | fluid pressure | ||
| P | polynomial | i | 1,2 |
| q | test function for pressure | h | finite element discretization |
| Q | concentration space | ||
| s | test function for concentration | ||
| T | temperature | ||
| u | velocity field | ||
| v | test function for velocity | ||
| V | subspace of the velocity space |
References
- Ghorayeb, K.; Mojtabi, A. Double-diffusive convection in a vertical rectangular cavity. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirouh, G.M.; Garaud, P.; Stellmach, S.; Traxler, A.L.; Wood, T.S. A new model for mixing by double-diffusive convection (semi-convection). I. The conditions for layer formation. Astrophys. J. 2012, 750, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, F.; Wang, X.M.; Wirosoetisno, D. Long-time dynamics of 2d double-diffusive convection: Analysis and/of numerics. Numer. Math. 2015, 130, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehryan, S.A.M.; Izadpanahi, E.; Ghalambaz, M.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection flow caused by an oscillating cylinder in a square cavity filled with Cu–Al 2O3/water hybrid nanofluid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehryan, S.A.M.; Ghalambaz, M.; Gargari, L.S.; Hajjar, A.; Sheremet, M. Natural convection flow of a suspension containing nano-encapsulated phase change particles in an eccentric annulus. J. Energy Storage 2020, 28, 101–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiji, M.E.; Mahdi, J.M.; Mohammed, H.I.; Majdi, H.S.; Ebrahimi, A.; Mahani, R.B.; Yaïci, W. Natural convection effect on solidification enhancement in a multi-tube latent heat storage system: Effect of tubes’ arrangement. Energies 2021, 14, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.X.; Huang, P.Z.; Wang, K. Newton iterative method based on finite element discretization for the stationary Darcy-Brinkman equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2020, 80, 3098–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çıbık, A.; Kaya, S. A projection-based stabilized finite element method for steady-state natural convection problem. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2011, 381, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çıbık, A.; Kaya, S. Finite element analysis of a projection-based stabilization method for the Darcy-Brinkman equations in double-diffusive convection. Appl. Numer. Math. 2013, 64, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, P.Z.; Feng, X.L.; Liu, D. An efficient two-step algorithm for steady-state natural convection problem. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 101, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Doostanidezfuli, A.; Izadpanahi, E.; Ghalambaz, M.J.A.P.T. Phase-change heat transfer of single/hybrid nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials over a heated horizontal cylinder confined in a square cavity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 282, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çıbık, A.; Demir, M.; Kaya, S. A family of second order time stepping methods for the Darcy-Brinkman equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2019, 472, 148–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Huang, P.Z. The modified characteristics finite element method for time-dependent Darcy-Brinkman problem. Eng. Comput. 2019, 36, 356–376. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabi, M.M.; Fahs, M.; Panjehfouladgaran, A.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Belfort, B. Uncertainty quantification and global sensitivity analysis of double-diffusive natural convection in a porous enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 162, 120–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaneifar, M.; Raisi, A.; Ali, H.M.; Talebizadehsardari, P. Mixed convection heat transfer of AL2O3 nanofluid in a horizontal channel subjected with two heat sources. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 143, 2761–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibik, A.; Eroglu, F.G.; Kaya, S. On the performance of curvature stabilization time stepping methods for double-diffusive natural convection flows in the presence of magnetic field. Numer. Algorithms 2021, 88, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codina, R. An iterative penalty method for the finite element solution of the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1993, 110, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.Q.; Xu, H. Two-level Newton iterative method for the 2D/3D steady Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Methods Partial. Differ. Equ. 2012, 28, 1620–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; He, Y.N. Some iterative finite element methods for steady Navier–Stokes equations with different viscosities. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 232, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.Q. A three-step Oseen correction method for the steady Navier–Stokes equations. J. Eng. Math. 2018, 111, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, H.J.; Reiman, A.H.; Monticello, D.A. Solving the 3D MHD equilibrium equations in toroidal geometry by Newton’s method. J. Comput. Phys. 2006, 211, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.N. Euler implicit/explicit iterative scheme for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 2013, 123, 67–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.Z. Iterative methods in penalty finite element discretizations for the steady Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Methods Partial. Differ. Equ. 2014, 30, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.N.; Dong, X.J.; Feng, X.L. Uniform Stability and Convergence with Respect to (ν, μ, s, 1 − σ) of the Three Iterative Finite Element Solutions for the 3D Steady MHD Equations. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 90, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girault, V.; Raviart, P.A. Finite Element Method for Navier—Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Boland, J.; Layton, W. Error analysis for finite element methods for steady natural convection problems. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 1990, 11, 449–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Y.; Shang, Y.Q.; Zhang, T. New one- and two-level Newton iterative mixed finite element methods for stationary conduction-convection problems. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2011, 47, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, F. FreeFem++ Version 4.2.1. 2019. Available online: http://www.freefem.org/ff++ (accessed on 3 January 2022).
| Scheme | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 50.696 (4) | 174.857 (14) | 424.661 (41) |
| II | 49.432 (4) | 112.317 (6) | — |
| III | 78.703 (7) | — | — |
| Scheme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.000717912 | 0.000206301 | 0.000359132 | 0.00094964 |
| II | 0.000717912 | 0.000206303 | 0.000359132 | 0.00094964 |
| III | 0.000717912 | 0.000206251 | 0.000359145 | 0.000949645 |
| Scheme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.000738137 | 0.000200965 | 0.000359132 | 0.00094964 |
| II | 0.000738136 | 0.00020096 | 0.000359132 | 0.00094964 |
| III | — | — | — | — |
| Scheme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.00759437 | 0.000203286 | 0.000359133 | 0.000949641 |
| II | — | — | — | — |
| III | — | — | — | — |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Huang, P. Finite Element Iterative Methods for the Stationary Double-Diffusive Natural Convection Model. Entropy 2022, 24, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020236
Wei Y, Huang P. Finite Element Iterative Methods for the Stationary Double-Diffusive Natural Convection Model. Entropy. 2022; 24(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yaxin, and Pengzhan Huang. 2022. "Finite Element Iterative Methods for the Stationary Double-Diffusive Natural Convection Model" Entropy 24, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020236
APA StyleWei, Y., & Huang, P. (2022). Finite Element Iterative Methods for the Stationary Double-Diffusive Natural Convection Model. Entropy, 24(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020236






