Rotating Minimal Thermodynamic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
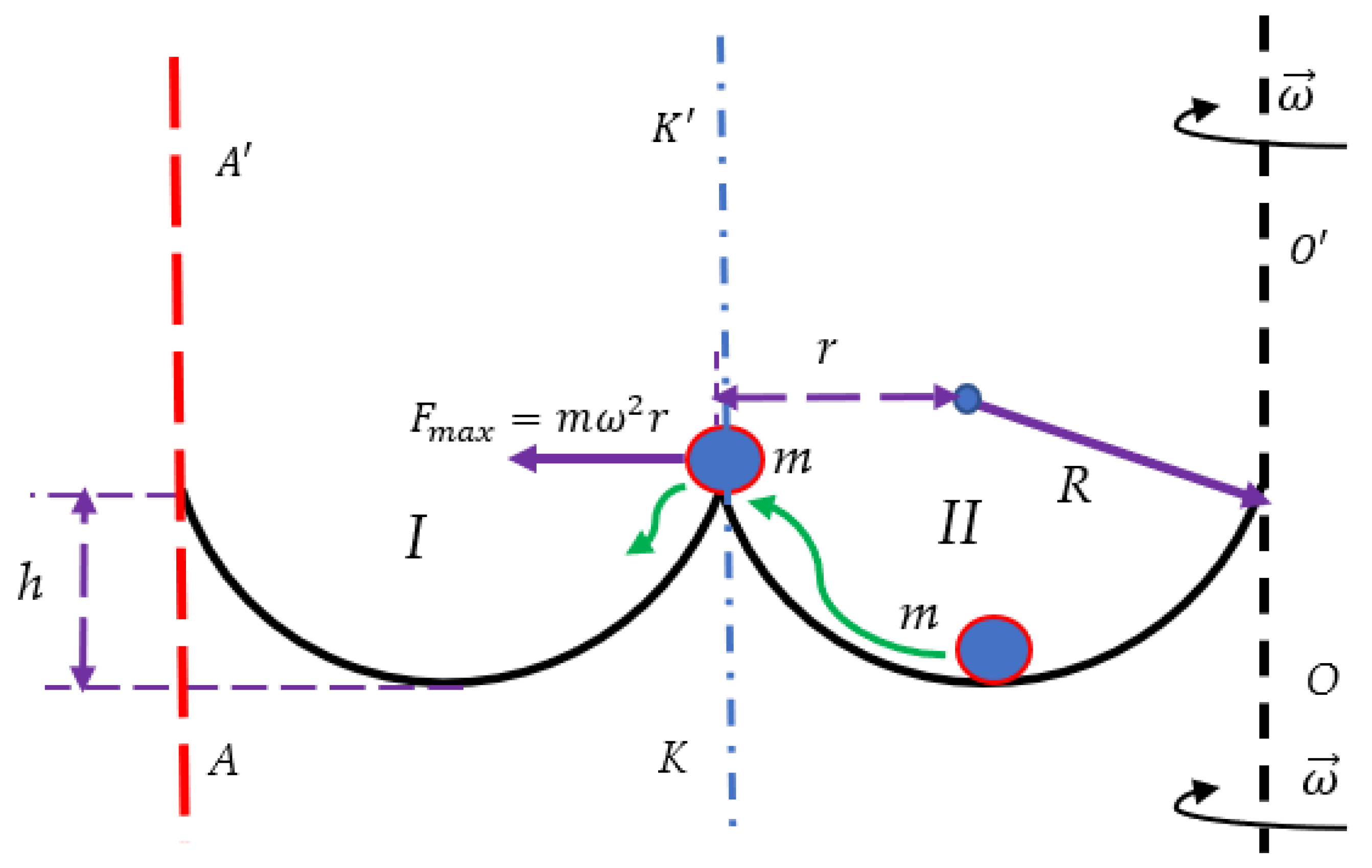
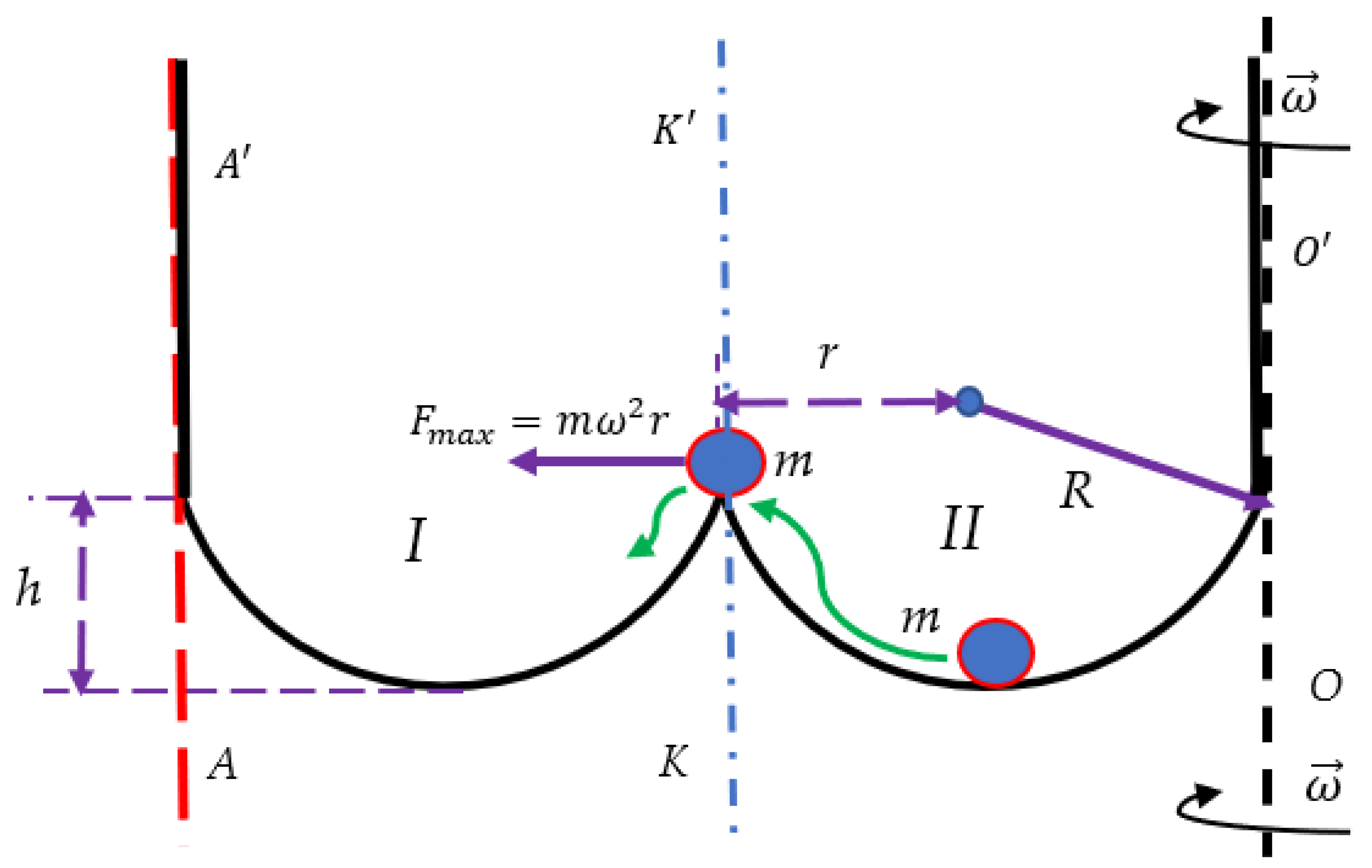
2.1. Particle Placed in a Double-Well Potential Exerted to the Centrifugal Force
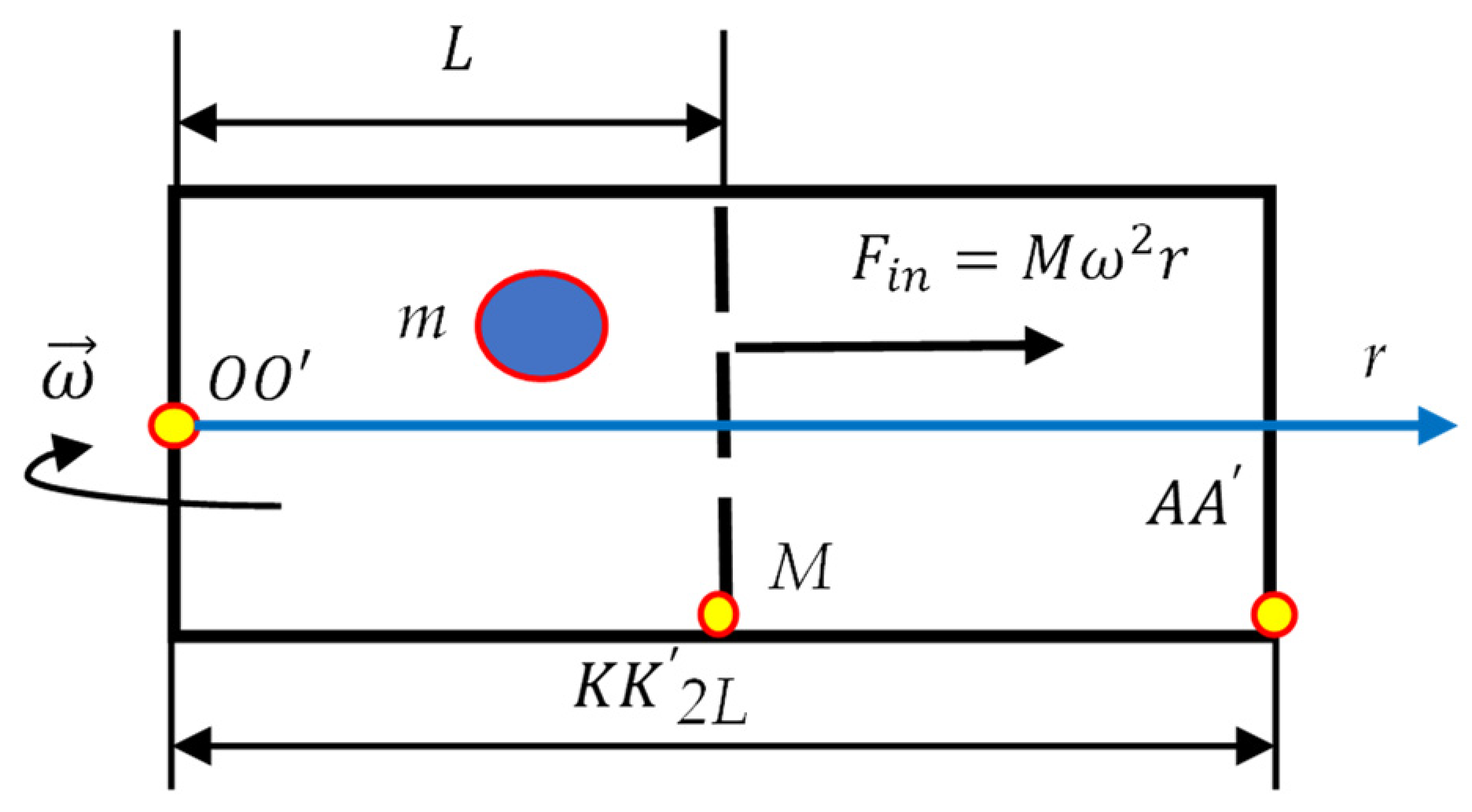
2.2. Minimal Rotating Thermal Engine
3. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hawking, S.W. Arrow of time in cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 1985, 32, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawking, S.W.; Laflamme, R.; Lyons, G.W. Origin of time asymmetry. Phys. Rev. D 1993, 47, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elitzur, A.C.; Dolev, S. Black-hole uncertainty entails an intrinsic time arrow: A note on the Hawking-Penrose controversy. Phys. Lett. A 1999, 251, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dace, T. The arrow of time, Cosmos and History. J. Nat. Soc. Philos. 2018, 14, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, T. The Arrow of Time. Am. J. Phys. 1962, 30, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, K.R. The Arrow of Time. Nature 1956, 177, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, R.; Chatterjee, A. Causality in Discrete Time Physics Derived from Maupertuis Reduced Action Principle. Entropy 2021, 23, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, R. Entropy Derived from Causality. Entropy 2020, 22, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riek, R. A Derivation of a Microscopic Entropy and Time Irreversibility from the Discreteness of Time. Entropy 2014, 16, 3149–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, P.D. Loss of Temporal Homogeneity and Symmetry in Statistical Systems: Deterministic Versus Stochastic Dynamics. Symmetry 2010, 2, 1201–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Naim, A. Entropy and Time. Entropy 2020, 22, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.L. Thermodynamics of Small Systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 36, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.K.; Vlugt, T.J.H.; Simon, J.M.; Bedeaux, D.; Kjelstrup, S. Thermodynamics of small systems embedded in a reservoir: A detailed analysis of finite size effects. Mol. Phys. 2012, 110, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Dissipation and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1961, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Information is physical. Phys. Today 1991, 44, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Minimal energy requirements in communication. Science 1996, 272, 1914–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeb, D.; Wolf, M.N. An improved Landauer principle with finite-size corrections. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 103011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E. Informational Reinterpretation of the Mechanics Notions and Laws. Entropy 2020, 22, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H. On kinetic stability. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1908, 80, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chefranov, S.G. Centrifugal-dissipative instability of Rossby vortices and their cyclonic-anticyclonic asymmetry. JETP. Lett. 2001, 73, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefranov, S.G. Cyclone–anticyclone vortex asymmetry mechanism and linear Ekman friction. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2016, 122, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilard, L. Über die Entropieverminderung in einem thermodynamischen System bei Eingriffen intelligenter Wesen. J. Phys. 1929, 53, 840–856. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Filliger, R.; Reimann, P. Brownian Gyrator: A Minimal Heat Engine on the Nanoscale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 230602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Shkorbatov, A.; Gendeman, O. The Carnot engine based on the small thermodynamic system: Its efficiency and the ergodic hypothesis. Am. J. Phys. 2007, 75, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogedby, H.C.; Imparato, A. A minimal model of an autonomous thermal motor. EPL 2017, 119, 50007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, A.; Soni, J.; Dabelow, L.; Bo, S.; Pesce, G.; Eichhorn, R.; Volpe, G. Experimental realization of a minimal microscopic heat engine. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 052106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.L.; Xiong, T.P.; Rehan, K.; Zhou, F.; Liang, D.F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yang, W.L.; Ma, Z.H.; Feng, M. Single-Atom Demonstration of the Quantum Landauer Principle. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 210601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Statistical Physics, 3rd ed.; Course of Theoretical Physics; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Kittel, C. Thermal Physics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz, J.L.; Percus, J.K. Thermodynamic Properties of Small Systems. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, S.K.; Liu, X.; Simon, J.-M.; Bardow, A.; Bedeaux, D.; Vlugt, T.J.H.; Kjelstrup, S. Calculating Thermodynamic Properties from Fluctuations at Small Scales. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 10911–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopson, M.M. The mass-energy-information equivalence principle. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 095206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E. The Landauer Principle: Re-Formulation of the Second Thermodynamics Law or a Step to Great Unification? Entropy 2019, 21, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadomski, A.; Rubí, J.M.; Łuczka, J.; Ausloos, M. On temperature- and space-dimension dependent matter agglomerations in a mature growing stage. Chem. Phys. 2005, 310, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bormashenko, E. Rotating Minimal Thermodynamic Systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020168
Bormashenko E. Rotating Minimal Thermodynamic Systems. Entropy. 2022; 24(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020168
Chicago/Turabian StyleBormashenko, Edward. 2022. "Rotating Minimal Thermodynamic Systems" Entropy 24, no. 2: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020168
APA StyleBormashenko, E. (2022). Rotating Minimal Thermodynamic Systems. Entropy, 24(2), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020168





