Analytical and Numerical Treatment of Continuous Ageing in the Voter Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Voter Model with Age-Dependent Switching Rates
2.2. Modified Thinning Algorithm for Simulation
- Set . Initialise all ages and draw the states from the desired initial distribution.
- Assume that the simulation has reached time t. Set .
- Draw a uniform random number from the interval and calculate the time interval to the next event . Update time and the ages of all voters such that , and for .
- Choose the type of event to occur (all rates are evaluated at the updated time):
- (i)
- With probability , nothing happens.
- (ii)
- With probability , voter i switches opinion, ; set ; update .
- Go to item 2.
3. Results
3.1. Deterministic Approximation for the Model without Spontaneous Opinion Changes ()
3.2. Ordering Dynamics with Continuous Ageing
3.2.1. Linearisation Close to the Absorbing State
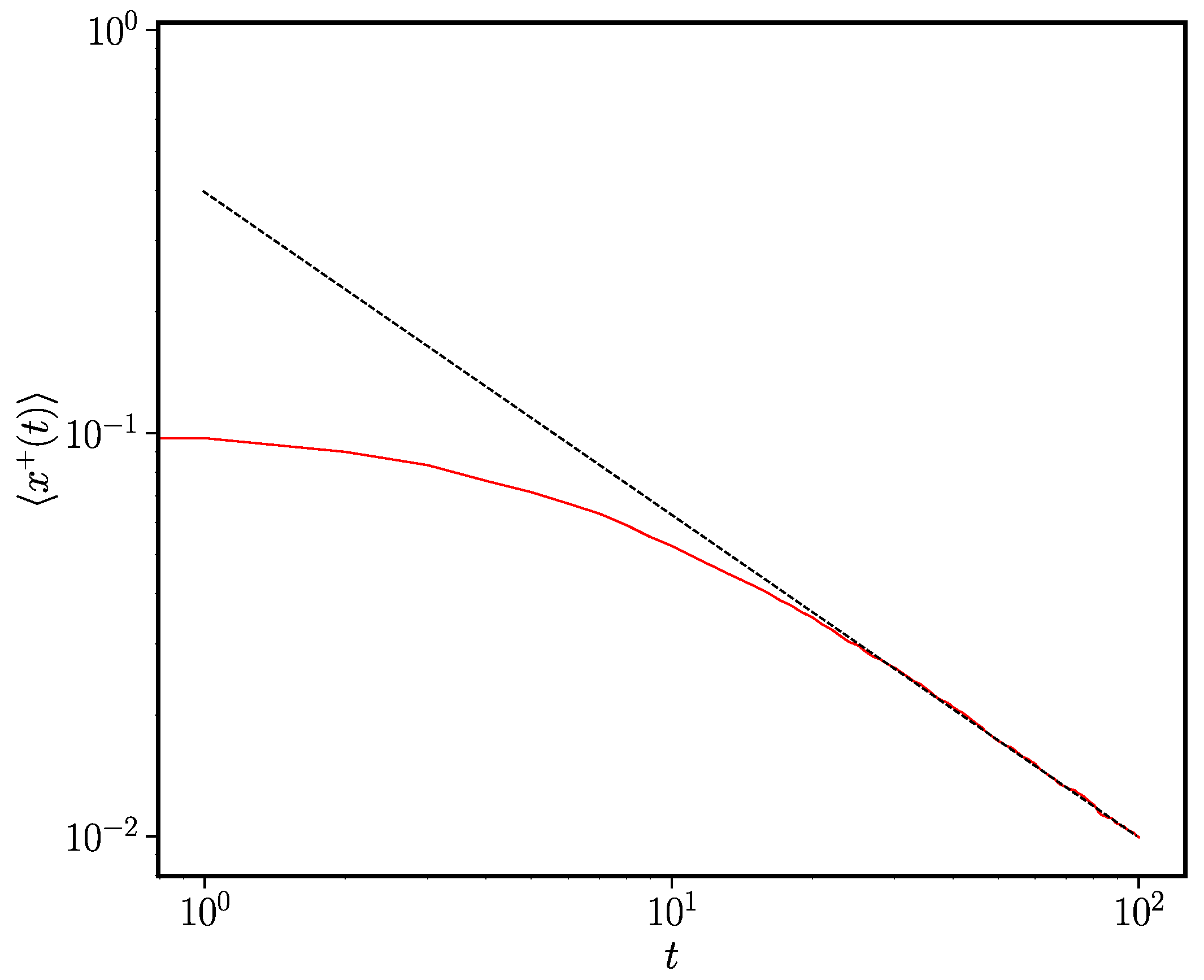
3.2.2. Power-Law Ageing and the Approach to Consensus
- -
- Fractional differential equation
- -
- Asymptotic behaviour
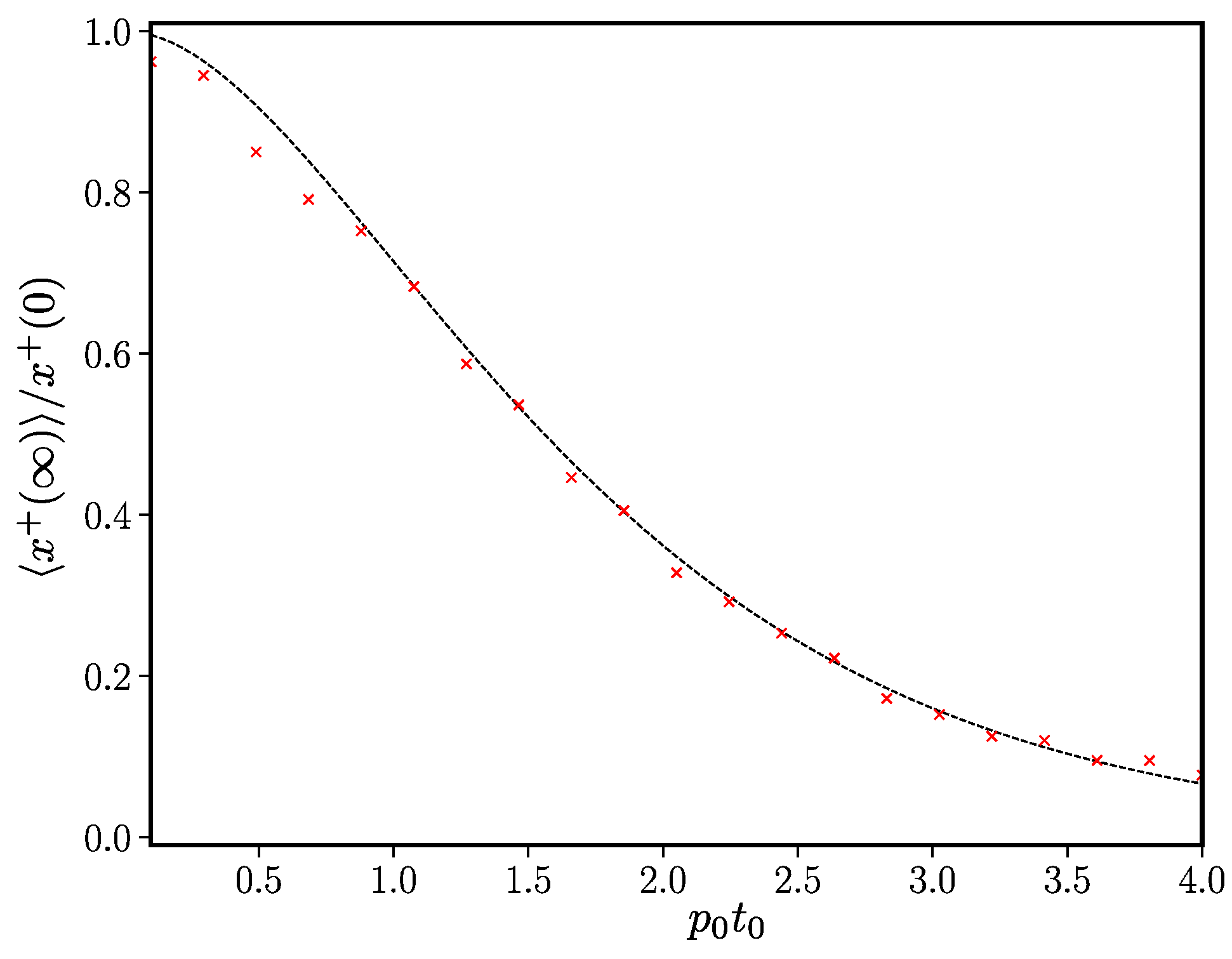
3.2.3. Ageing Profile with Non-Zero Asymptotic Value
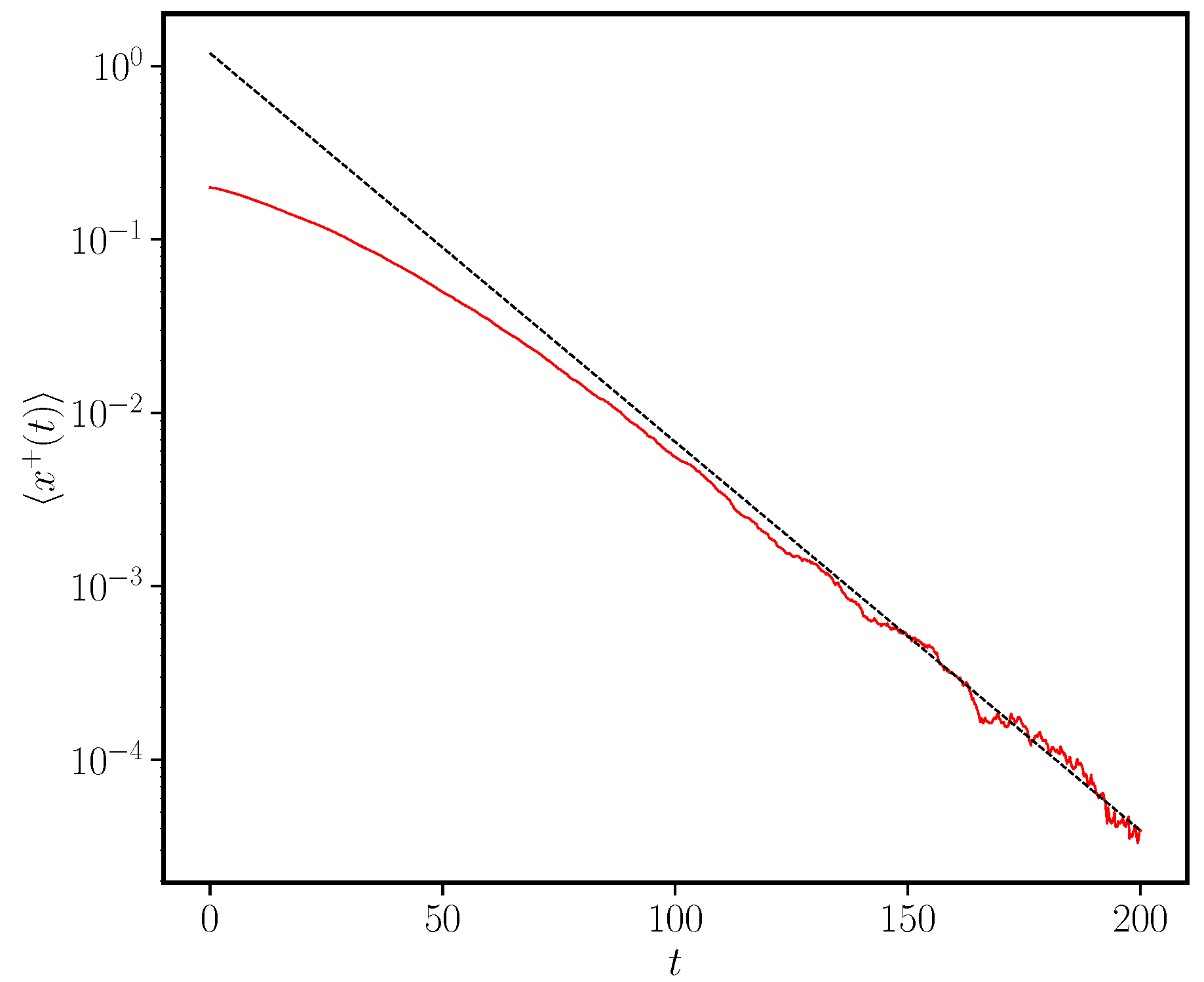
3.2.4. Exponential Ageing and the Frozen State
3.3. Model with Spontaneous Opinion Changes ()
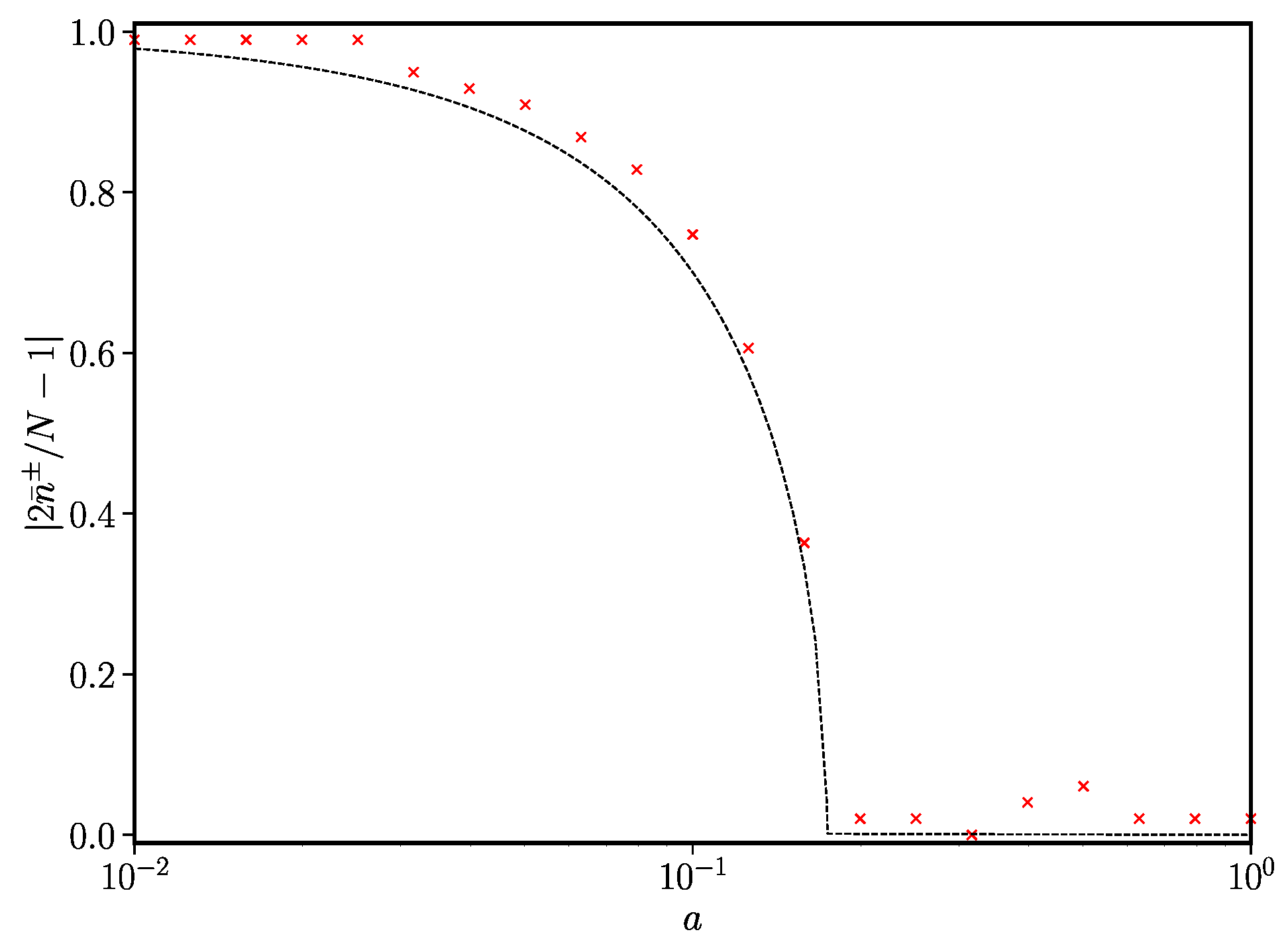
3.3.1. Continuous Phase Transition
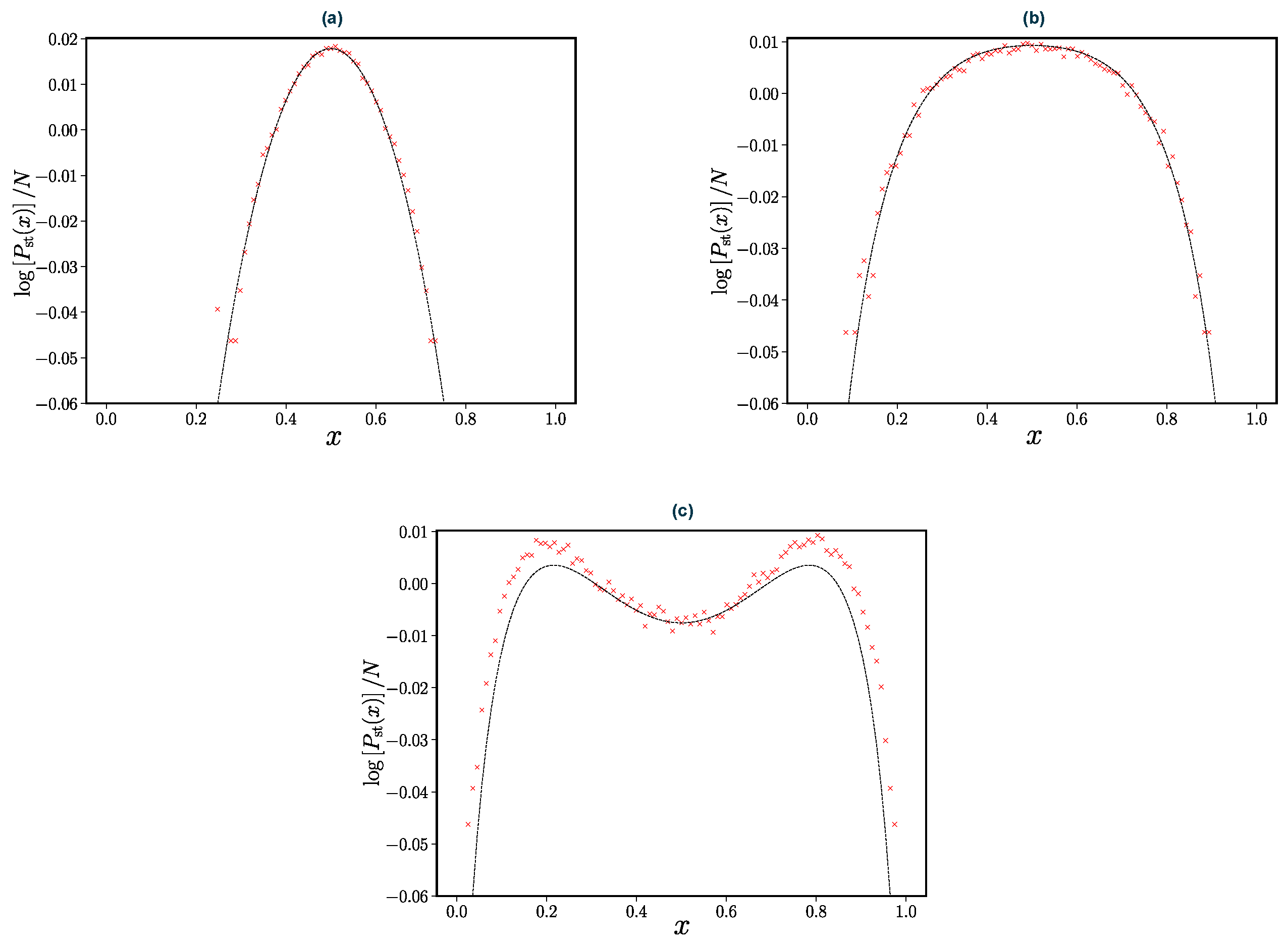
3.3.2. Fluctuations about the Steady State
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Equation (17)
Appendix B. An Alternative to the Linearised Equation (17)
References
- Castellano, C.; Fortunato, S.; Loreto, V. Statistical physics of social dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Miguel, M.; Toral, R. Introduction to the Chaos Focus Issue on the Dynamics of Social Systems. Chaos 2020, 30, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redner, S. Reality-inspired voter models: A mini-review. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2019, 20, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrzejewski, A.; Sznajd-Weron, K. Statistical Physics Of Opinion Formation: Is it a SPOOF? Comptes Rendus Phys. 2019, 20, 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galam, S.; Moscovici, S. Towards a theory of collective phenomena: Consensus and attitude changes in groups. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 1991, 21, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weron, T.; Sznajd-Weron, K. How to Reach Consensus? Better Disagree with Your Neighbor. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12744 LNCS, pp. 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, A.F.; Kertész, J.; Iñiguez, G. Opinion dynamics in social networks: From models to data. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.01322. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, P.; Sudbury, A. A model for spatial conflict. Biometrika 1973, 60, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, R.A.; Liggett, T.M. Ergodic theorems for weakly interacting infinite systems and the voter model. Ann. Probab. 1975, 3, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, V.; Redner, S. Voter model on heterogeneous graphs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 178701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, F.; Eguíluz, V.M. Analytical solution of the voter model on uncorrelated networks. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 063011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary Dynamics: Exploring the Equations of Life; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Traulsen, A.; Hauert, C. Stochastic evolutionary game dynamics. In Reviews of Nonlinear Dynamics and Complexity; Schuster, H.G., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume II, pp. 25–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, D.M.; Strogatz, S.H. Linguistics: Modelling the dynamics of language death. Nature 2003, 424, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelló, X.; Eguíluz, V.M.; San Miguel, M. Ordering dynamics with two non-excluding options: Bilingualism in language competition. New J. Phys. 2006, 8, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, F.; Castelló, X.; Miguel, M.S. Agent based models of language competition: Macroscopic descriptions and order-disorder transition. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp 2010, 2010, P04007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauhanen, H.; Gopal, D.; Galla, T.; Bermúdez-Otero, R. Geospatial distributions reflect temperatures of linguistic features. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, R.A. Neutral evolution: A null model for language dynamics. Adv. Complex Syst. 2012, 15, 1150015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.J. Isotropic majority-vote model on a square lattice. J. Stat. Phys. 1992, 66, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.; Mendes, J.; Santos, M. Nonequilibrium spin models with Ising universal behaviour. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1993, 26, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C. Stochastic Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kampen, N.G. Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Starnini, M.; Gleeson, J.P.; Boguñá, M. Equivalence between non-Markovian and Markovian dynamics in epidemic spreading processes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 128301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Cai, S.M.; Tang, M.; Lai, Y.C. Equivalence and its invalidation between non-Markovian and Markovian spreading dynamics on complex networks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, S.; Anderson, R. Distributed incubation and infectious periods in models of the transmission dynamics of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Math. Med. Biol. A J. IMA 1988, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, T.; Galla, T. Stochastic processes with distributed delays: Chemical Langevin equation and linear-noise approximation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 250601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brett, T.; Galla, T. Gaussian approximations for stochastic systems with delay: Chemical Langevin equation and application to a Brusselator system. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 124112. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.W.; Galla, T. Intrinsic noise, Delta-Notch signalling and delayed reactions promote sustained, coherent, synchronized oscillations in the presomitic mesoderm. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190436. [Google Scholar]
- Galla, T. Intrinsic fluctuations in stochastic delay systems: Theoretical description and application to a simple model of gene regulation. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 021909. [Google Scholar]
- Barrio, M.; Burrage, K.; Leier, A.; Tian, T. Oscillatory regulation of Hes1: Discrete stochastic delay modelling and simulation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e117. [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht, R.; Winkler, G. A delay stochastic process with applications in molecular biology. J. Math. Biol. 2008, 57, 613–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.E.; Schnell, S.; Burrage, K. Stochastic approaches for modelling in vivo reactions. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2004, 28, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, J.W.; Galla, T. Stochastic fluctuations and quasipattern formation in reaction-diffusion systems with anomalous transport. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 052124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klages, R.; Radons, G.; Sokolov, I.M. Anomalous Transport: Foundations and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations: An Introduction to Fractional Derivatives, Fractional Differential Equations, to Methods of Their Solution and Some of Their Applications; Elsevier: London, UK, 1998; Volume 198. [Google Scholar]
- De Marzo, G.; Zaccaria, A.; Castellano, C. Emergence of polarization in a voter model with personalized information. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 043117. [Google Scholar]
- Iannelli, G.; De Marzo, G.; Castellano, C. Filter bubble effect in the multistate voter model. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2022, 32, 043103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, A.F.; Khalil, N.; Toral, R. Ordering dynamics in the voter model with aging. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 552, 122475. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, A.F.; Khalil, N.; Toral, R. Reduction from non-Markovian to Markovian dynamics: The case of aging in the noisy-voter model. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2020, 2020, 024004. [Google Scholar]
- Artime, O.; Peralta, A.F.; Toral, R.; Ramasco, J.J.; San Miguel, M. Aging-induced continuous phase transition. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 032104. [Google Scholar]
- Artime, O.; Carro, A.; Peralta, A.F.; Ramasco, J.J.; San Miguel, M.; Toral, R. Herding and idiosyncratic choices: Nonlinearity and aging-induced transitions in the noisy voter model. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2019, 20, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Zhang, H.; Bianconi, G. Non-Markovian majority-vote model. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 062311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stark, H.U.; Tessone, C.J.; Schweitzer, F. Decelerating Microdynamics Can Accelerate Macrodynamics in the Voter Model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 018701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Gracia, J.; Eguíluz, V.M.; San Miguel, M. Update rules and interevent time distributions: Slow ordering versus no ordering in the voter model. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 015103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, T.; Klemm, K.; Eguíluz, V.M. Competition in the presence of aging: Dominance, coexistence, and alternation between states. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21128. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, D.T. A general method for numerically simulating the stochastic time evolution of coupled chemical reactions. J. Comput. Phys. 1976, 22, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.F. A modified next reaction method for simulating chemical systems with time dependent propensities and delays. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 214107. [Google Scholar]
- Boguná, M.; Lafuerza, L.F.; Toral, R.; Serrano, M.Á. Simulating non-Markovian stochastic processes. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 042108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.W.; Shedler, G.S. Simulation of nonhomogeneous Poisson processes by thinning. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 1979, 26, 403–413. [Google Scholar]
- Lafuerza, L.F.; Toral, R. Role of delay in the stochastic creation process. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2011, 84, 021128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuerza, L.F.; Toral, R. Exact solution of a stochastic protein dynamics model with delayed degradation. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2011, 84, 051121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.W.; Galla, T. Effective diffusion coefficients in reaction-diffusion systems with anomalous transport. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 012212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y. On Lewis’ simulation method for point processes. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1981, 27, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Granovsky, B.L.; Madras, N. The noisy voter model. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 1995, 55, 23–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kirman, A. Ants, Rationality, and Recruitment. Q. J. Econ. 1993, 108, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Vlad, M.O.; Ross, J. Systematic derivation of reaction-diffusion equations with distributed delays and relations to fractional reaction-diffusion equations and hyperbolic transport equations: Application to the theory of Neolithic transition. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 061908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, S.; Falconer, S. Subdiffusive master equation with space-dependent anomalous exponent and structural instability. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 031132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste, S.B.; Abad, E.; Lindenberg, K. Reaction-subdiffusion model of morphogen gradient formation. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 061123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, W. An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications; Wiley: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Metzler, R.; Klafter, J. The random walk’s guide to anomalous diffusion: A fractional dynamics approach. Phys. Rep. 2000, 339, 1–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, J.L. The Laplace Transform: Theory and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Carro, A.; Toral, R.; San Miguel, M. The noisy voter model on complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykman, M.I.; Mori, E.; Ross, J.; Hunt, P. Large fluctuations and optimal paths in chemical kinetics. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5735–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, A.F.; Toral, R. Binary-state dynamics on complex networks: Stochastic pair approximation and beyond. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 043370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
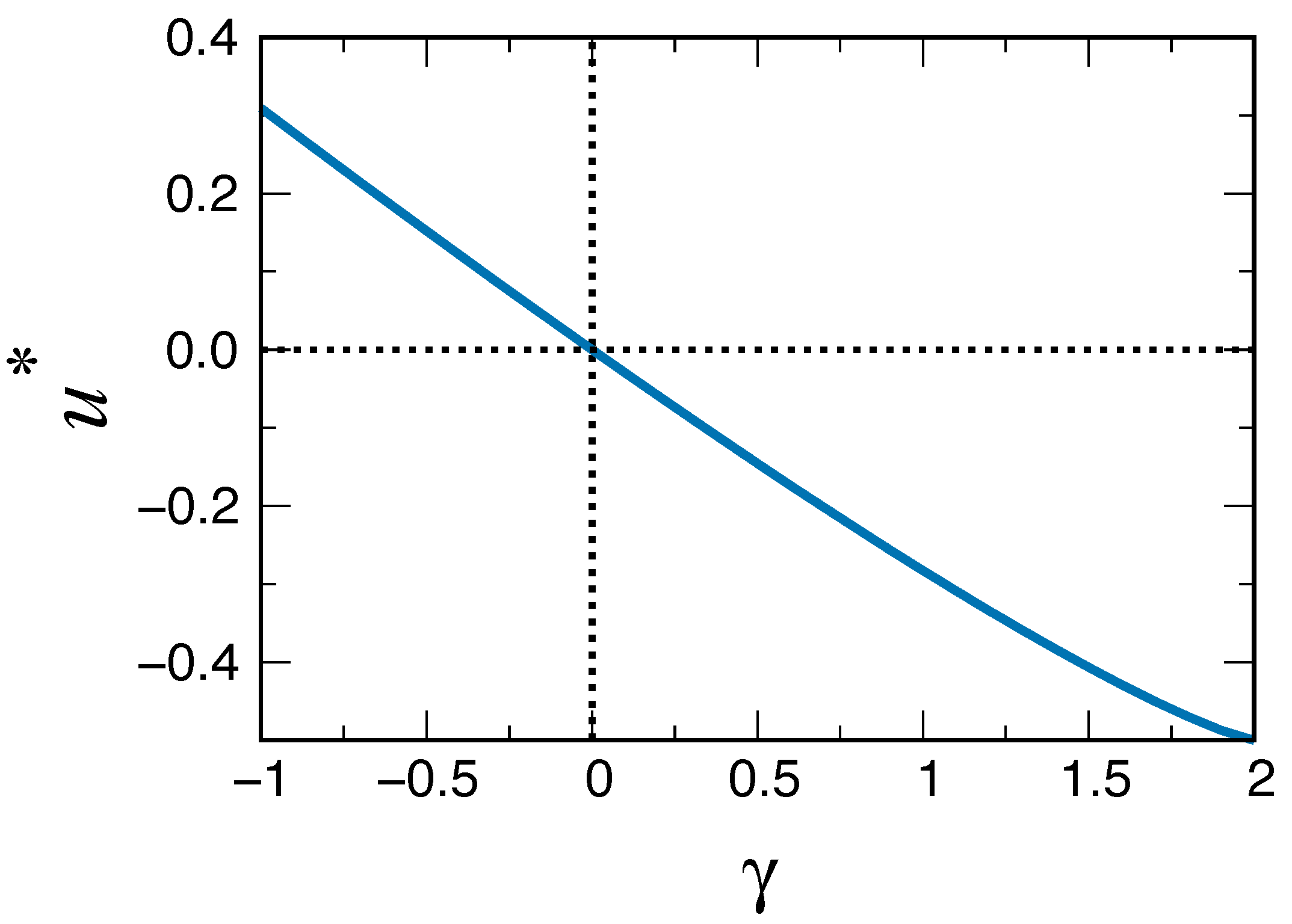
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baron, J.W.; Peralta, A.F.; Galla, T.; Toral, R. Analytical and Numerical Treatment of Continuous Ageing in the Voter Model. Entropy 2022, 24, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101331
Baron JW, Peralta AF, Galla T, Toral R. Analytical and Numerical Treatment of Continuous Ageing in the Voter Model. Entropy. 2022; 24(10):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101331
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaron, Joseph W., Antonio F. Peralta, Tobias Galla, and Raúl Toral. 2022. "Analytical and Numerical Treatment of Continuous Ageing in the Voter Model" Entropy 24, no. 10: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101331
APA StyleBaron, J. W., Peralta, A. F., Galla, T., & Toral, R. (2022). Analytical and Numerical Treatment of Continuous Ageing in the Voter Model. Entropy, 24(10), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24101331





