A Damping-Tunable Snap System: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Proposed Snap System
2.1. The General Form of a Snap System
2.2. A New Damping-Tunable Snap System
2.3. Snap-Based Dissipative Hyperchaos
2.4. Snap-Based Conservative Chaos
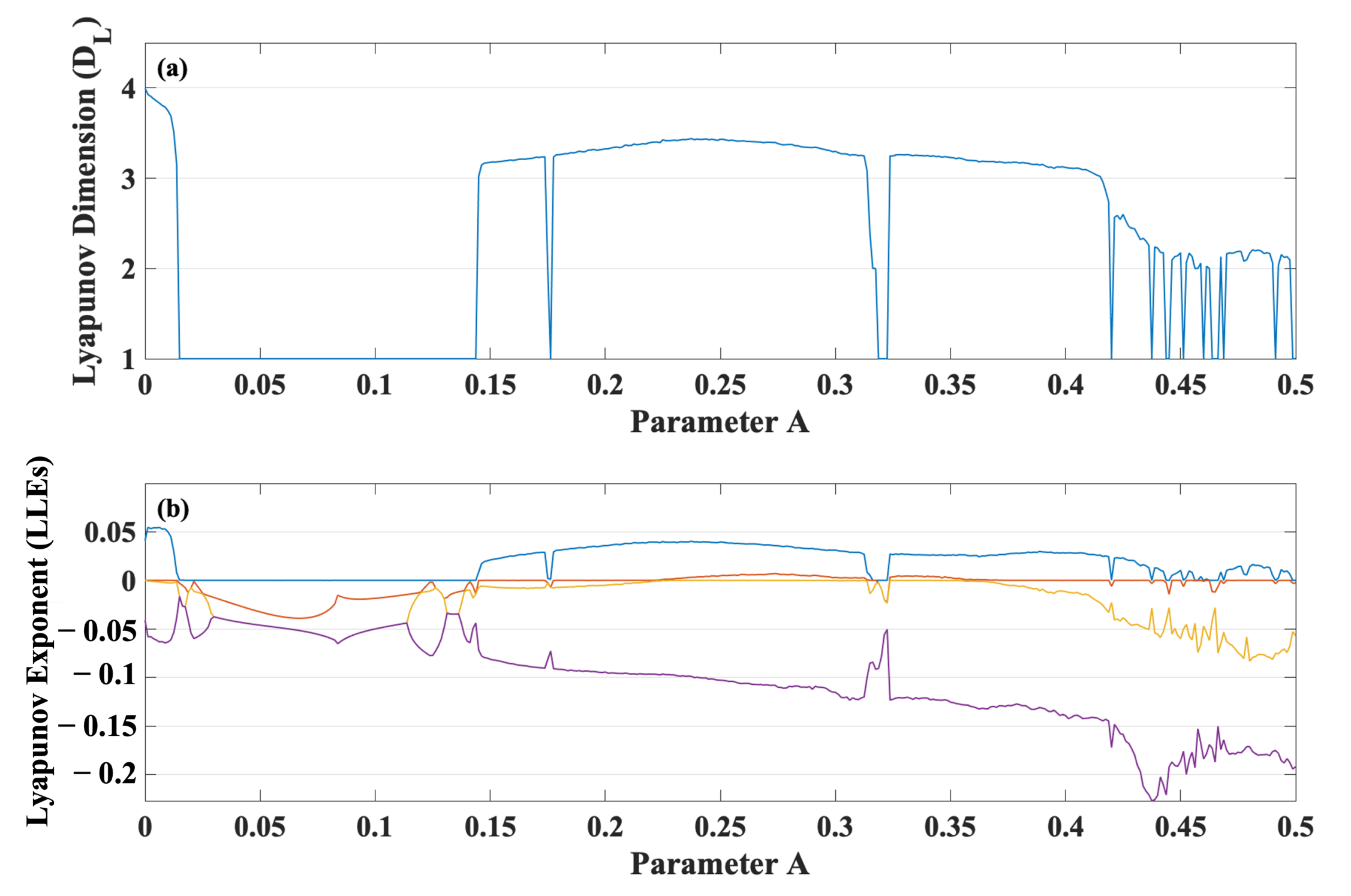
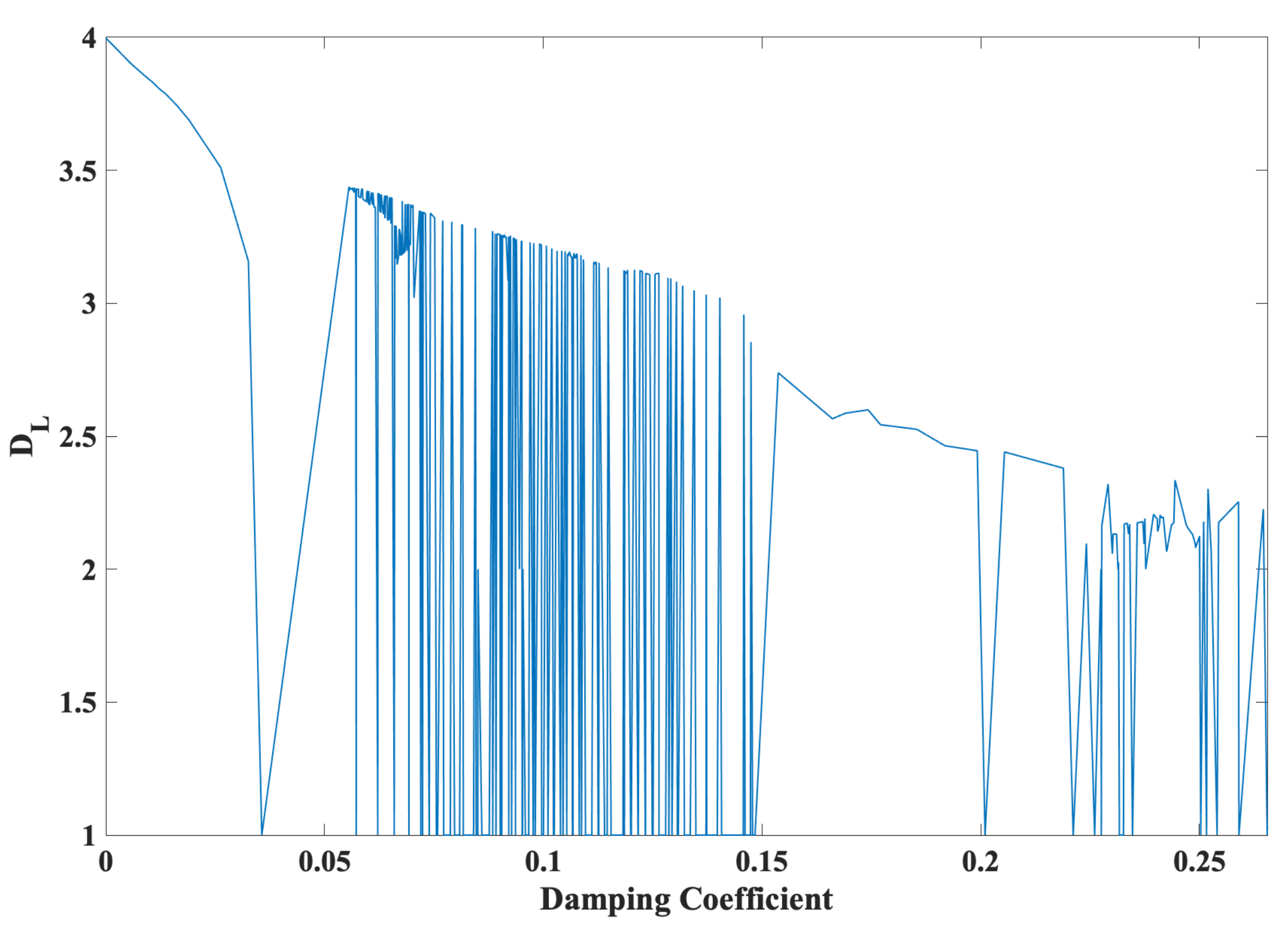
2.5. Tunable Damping: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos
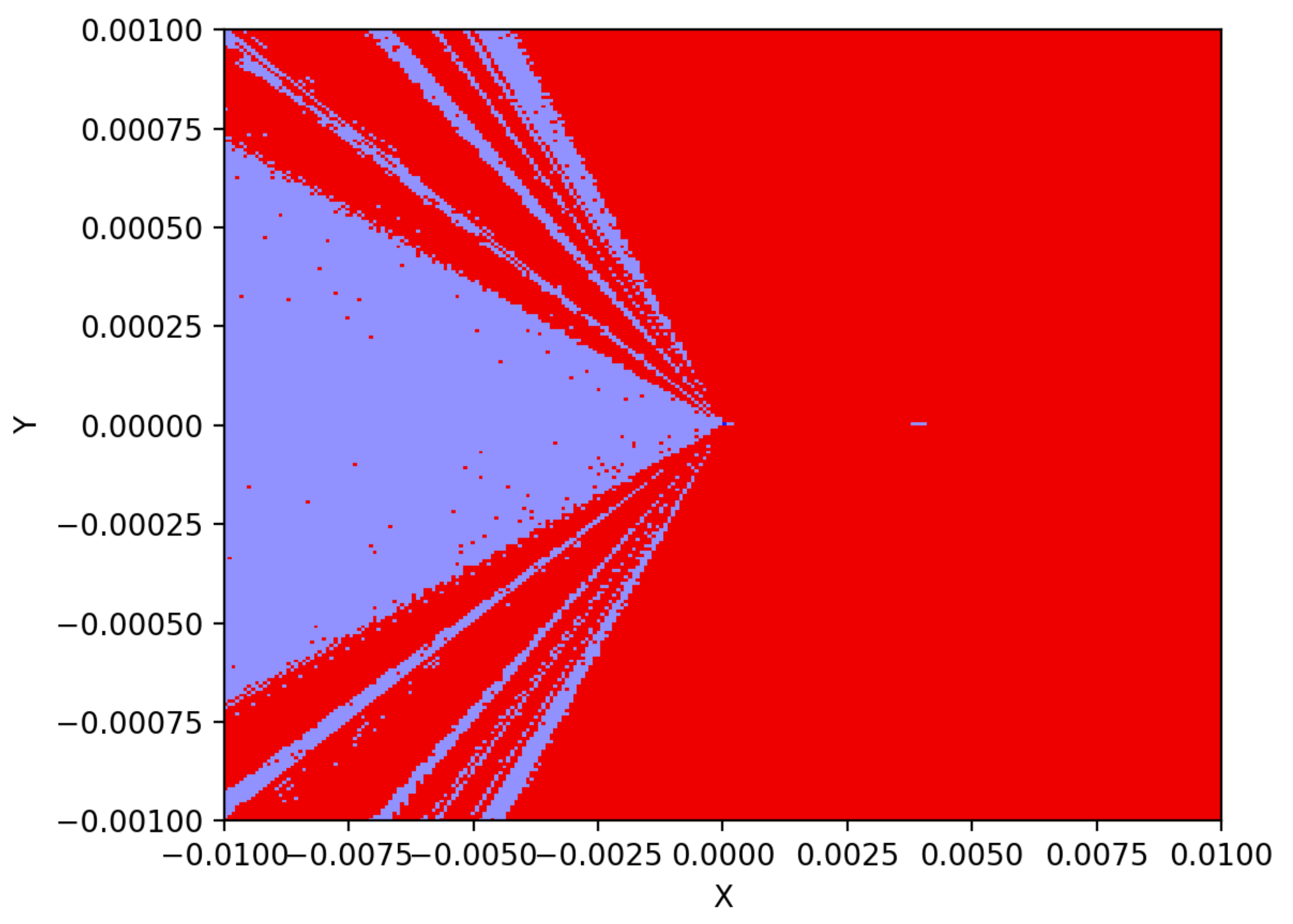
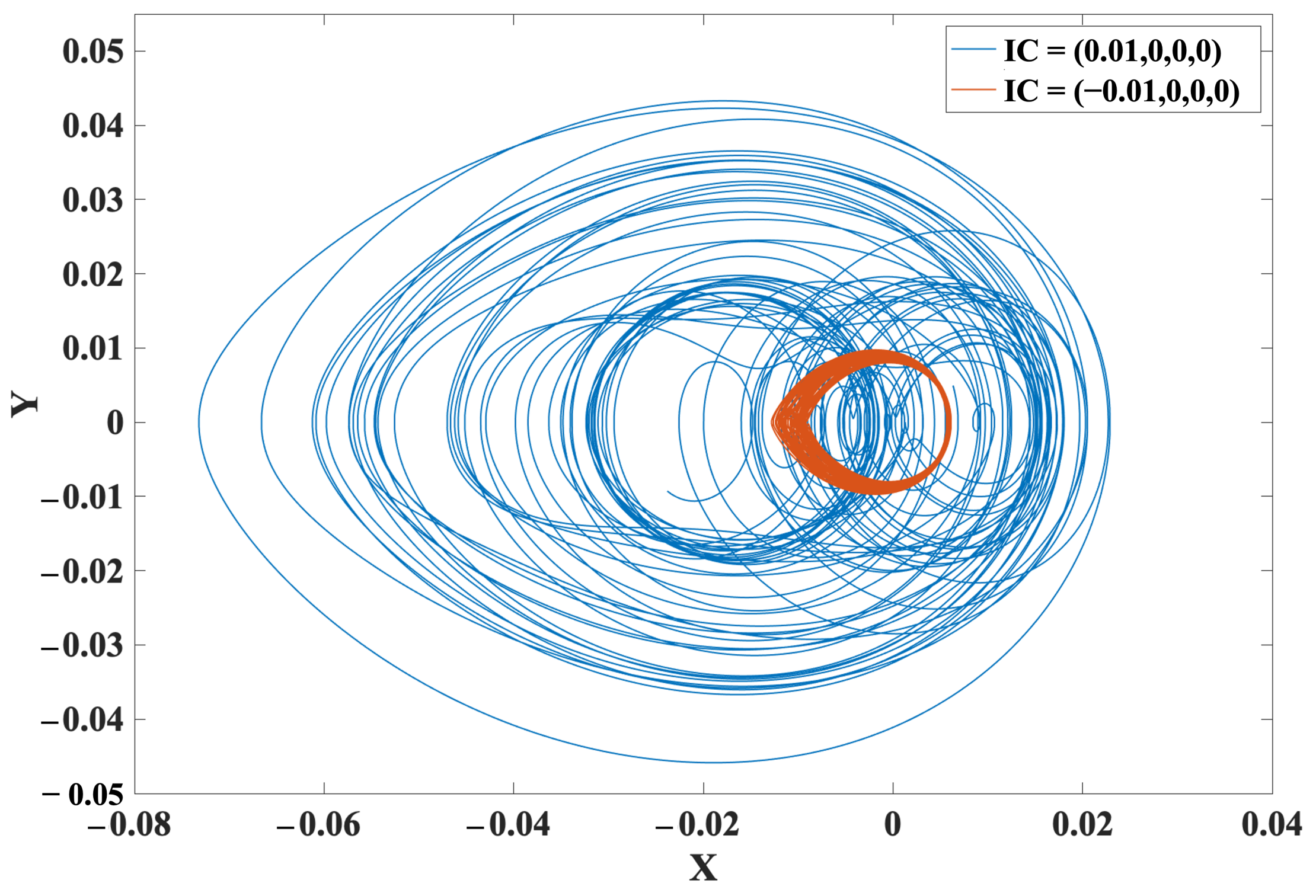
2.6. Multistability and Coexisting Attractor
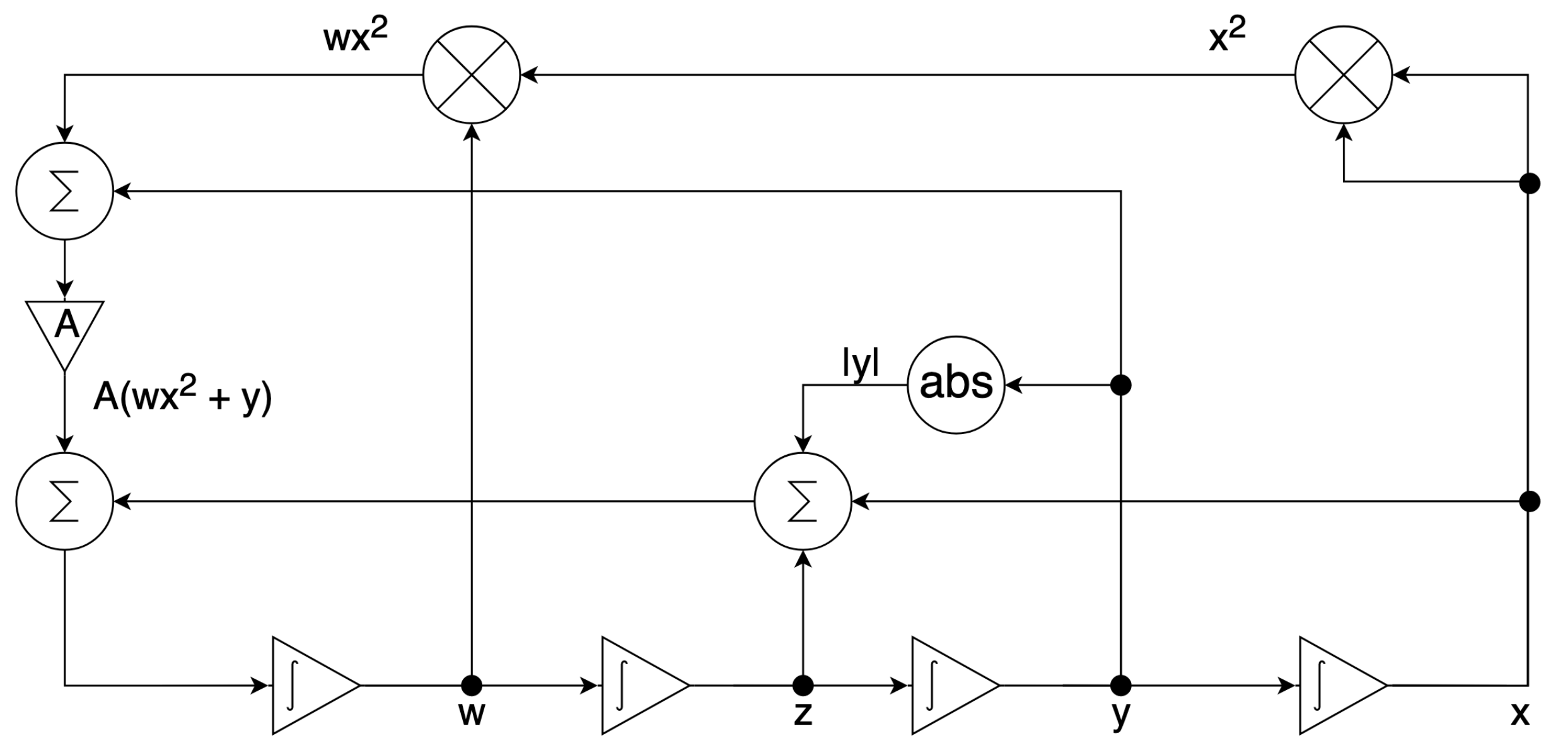
3. FPAA-Based Circuit Implementation
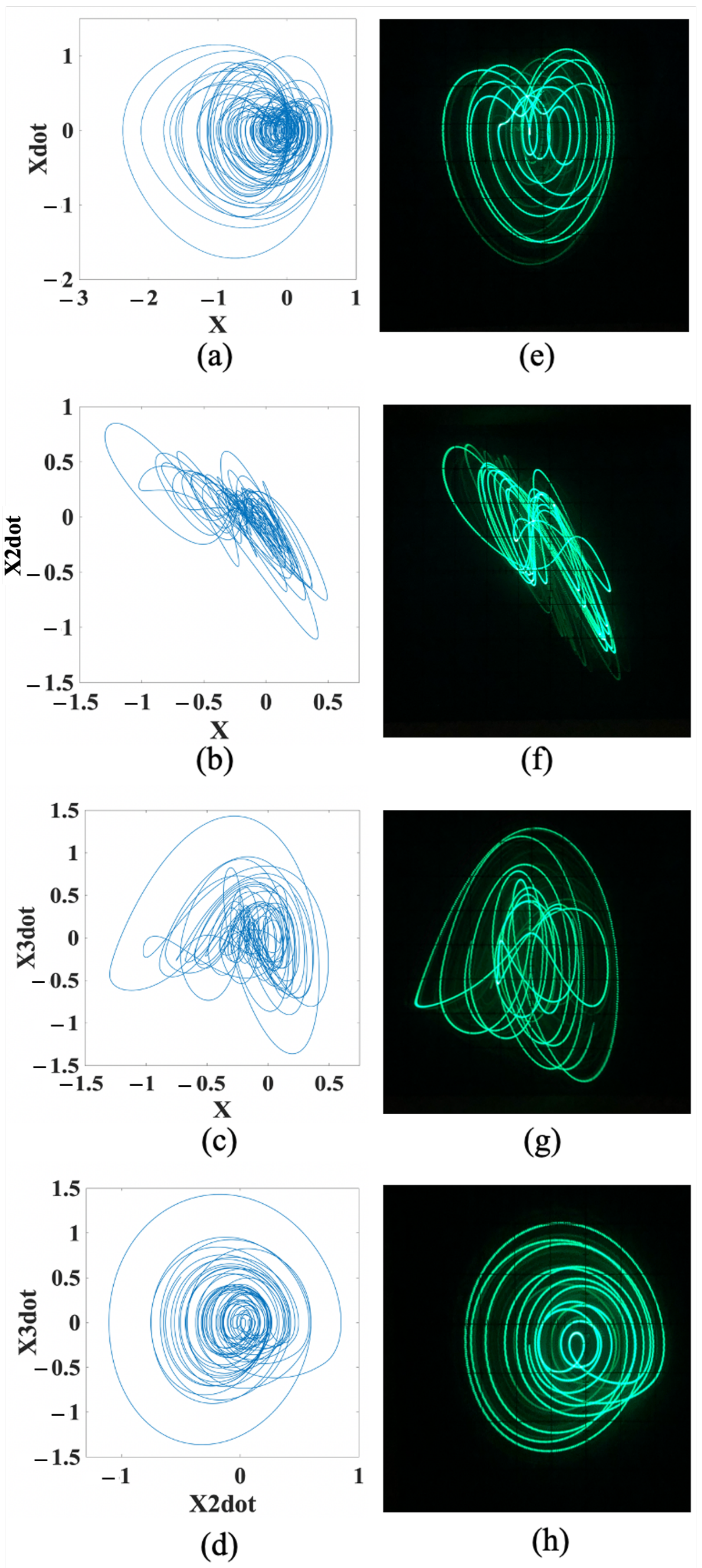
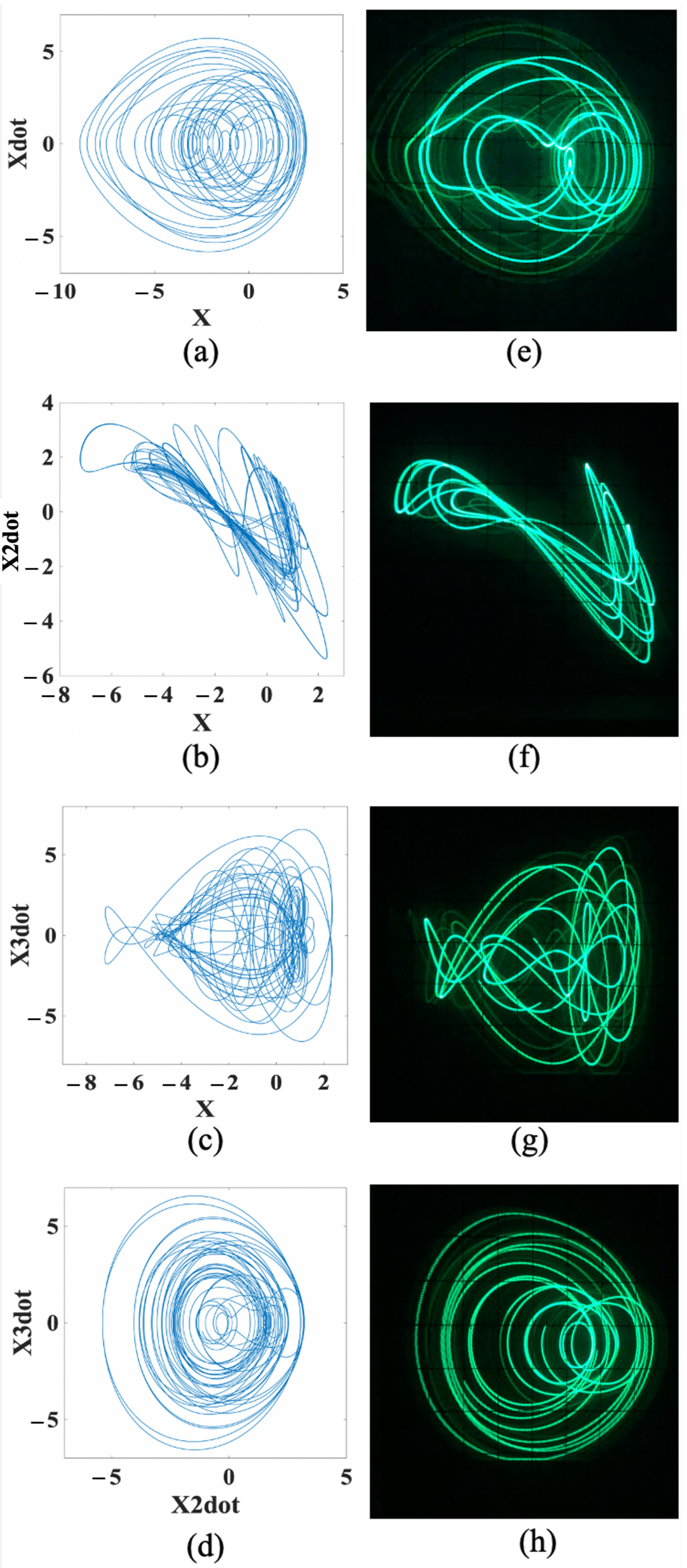
4. Numerical and Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coumo, K.M.; Oppenheim, A.V. Circuit implementation of synchronized chaos with application to communications. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 71, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Miyano, T. Chaotic Cryptography Using Augmented Lorenz Equations Aided by Quantum Key Distribution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 62, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, G.; Rovatti, R.; Mazzini, G. Synchronization mechanism and optimization of spreading sequence in chaos-based DS-CDMA systems. IEICE Trans. Fundam. 1999, 82, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Schot, S.H. Jerk: The time rate of change of acceleration. Am. J. Phys. 1978, 46, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Elegant Chaos: Algebraically Simple Chaotic Flows; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Civita, A.; Fiori, S.; Romani, G. A Mobile Acquisition System and a Method for Hips Sway Fluency Assessment. Information 2018, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chlouverakis, E.; Sprott, J.C. Chaotic hyperjerk systems. Chaos Solut. Fractals 2006, 28, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munmuangsaen, B.; Srisuchinwong, B. Elementary chaotic snap flows. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2011, 44, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Maximally complex simple attractor. Chaos 2007, 17, 033124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruy, B. Dynamics of a hyperchaotic Lorenz system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2007, 17, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar]
- Sprott, J.C. Chaos and Time-Series Analysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Srisuchinwong, B.; Munmuangsaen, B.; Ahmad, I.; Suibkitwanchai, K. On a simple single-transistor-based chaotic snap circuit: A maximized attractor dimension at minimized damping and a stable equilibrium. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116643–116660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, S.; Wu, A.; Zhang, R. Conservative chaos in a class of nonconservative system: Theoretical analysis and numerical demonstrations. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2018, 28, 1850087-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munmuangsaen, B.; Sprott, J.C.; Thio, W.J.; Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L. A Simple Chaotic Flow with a Continuously Adjustable Attractor Dimension. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2015, 25, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AnadigmDesigner2. Available online: https://www.anadigm.com/anadigmdesigner2.asp (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Kilic, R.; Dalkiran, F.Y. Reconfigurable implementations of Chua’s circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2009, 19, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, R.; Dalkiran, F.Y. Programmable design and implementation of a chaotic system utilizing multiple nonlinear functions. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2010, 18, 647–656. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Joo-Chen Thio, W.; Sprott, J.C.; Iu, H.H.; Xu, Y. Constructing Infinitely Many Attractors in a Programmable Chaotic Circuit. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29003–29012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, S. Analysis, adaptive control and synchronization of a novel 4-D hyperchaotic hyperjerk system via backstepping control method. Arch. Control Sci. 2016, 26, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Volos, C.; Pham, V.T. Analysis, adaptive control and synchronization of a novel 4-D hyperchaotic hyperjerk system and its SPICE implementation. Arch. Control Sci. 2015, 25, 135–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltzis, P.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Pham, V.T.; Volos, C.; Nistazakis, E.; Tombras, G. Hyperchaotic attractor in a novel hyperjerk system with two nonlinearities. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 37, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltzis, P.; Volos, C.; Nistazakis, E.; Tsigopoulos, A.D.; Tombras, G. Analysis, Synchronization and Circuit Design of a 4D Hyperchaotic Hyperjerk System. Computation 2018, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Sambas, A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mamat, M.; Mada Sanjaya, W.S. A New Hyperchaotic Hyperjerk System with Three Nonlinear Terms, its Synchronization and Circuit Simulation. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mujiarto; Vaidyanathan, S.; Zhang, S.; Sambas, A.; Sukono; Praiwi, A.S.; Subiyanto, A. A hyperchaotic hyperjerk system with four nonlinearities, its dynamical analysis and circuit realization. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 567, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Volos, C.; Pham, V.T.; Kapitaniak, T. Dynamics, circuit realization, control and synchronization of a hyperchaotic hyperjerk system with coexisting attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Singh, J.P.; Karthikeyan, A.; Roy, B.K. Existence of Metastable, Hyperchaos, Line of Equilibria and Self-Excited Attractors in a New Hyperjerk Oscillator. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 2030037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G.; Sprott, J.C.; Hoover, C.G. Adaptive Runge–Kutta integration for stiff systems: Comparing Nose and Nose-Hoover dynamics for the harmonic oscillator. Am. J. Phys. 2016, 6, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiori, S. Nonlinear damped oscillators on Riemannian manifolds: Numerical simulation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2017, 47, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, F.; Haghiri, S.; Imani, M.A. FPGA realization of Hodgkin-Huxley Neuronal Model. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ketthong, P.; Srisuchinwong, B. A Damping-Tunable Snap System: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos. Entropy 2022, 24, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010121
Ketthong P, Srisuchinwong B. A Damping-Tunable Snap System: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos. Entropy. 2022; 24(1):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010121
Chicago/Turabian StyleKetthong, Patinya, and Banlue Srisuchinwong. 2022. "A Damping-Tunable Snap System: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos" Entropy 24, no. 1: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010121
APA StyleKetthong, P., & Srisuchinwong, B. (2022). A Damping-Tunable Snap System: From Dissipative Hyperchaos to Conservative Chaos. Entropy, 24(1), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24010121






