Entropy Estimation Using a Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Model for Natural Sequences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model-Based Entropy Estimation
2.1. Coincidence Counting Approach
2.2. Linguistic Entropy Estimation
2.3. Remarks on Bias and Convergence Properties
3. Linguistic Probabilistic Models
3.1. Limitations of Zipfian Models for Language
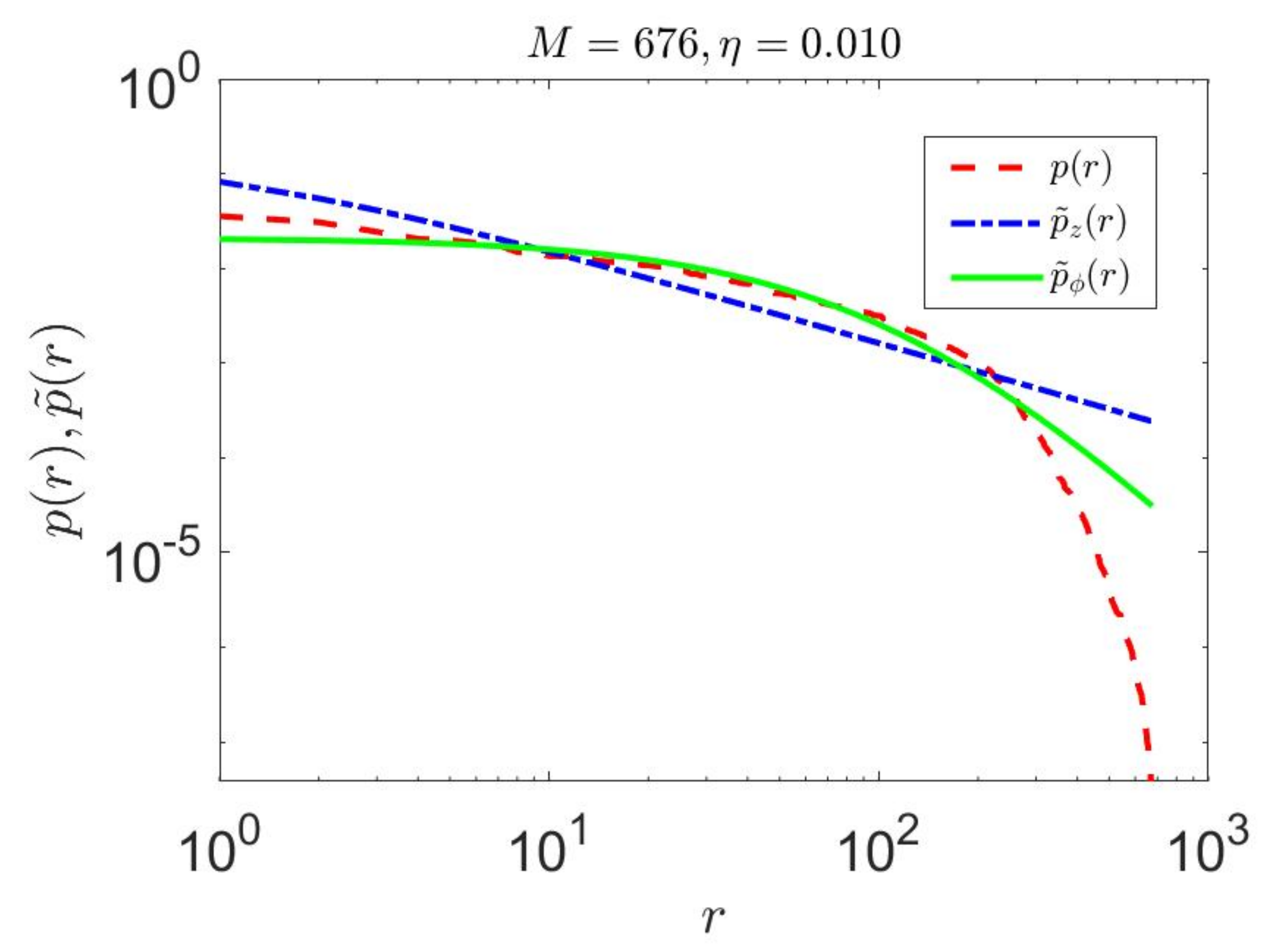
3.2. Unconstrained Rank-Ordered Probabilistic Model
3.3. Constrained Linguistic Probabilistic Model
3.4. Constrained Linguistic Probabilistic Model II
4. Performance Results
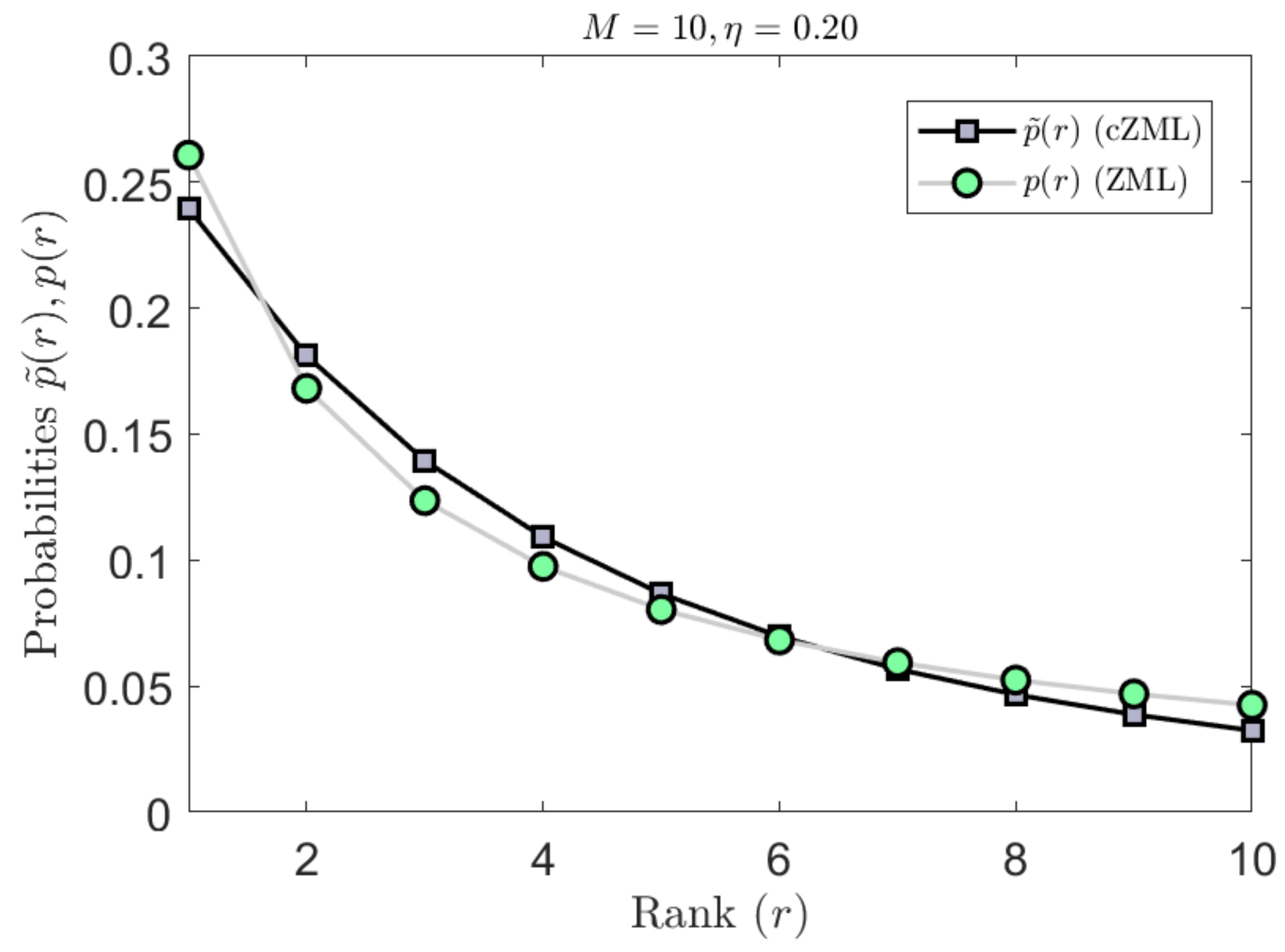
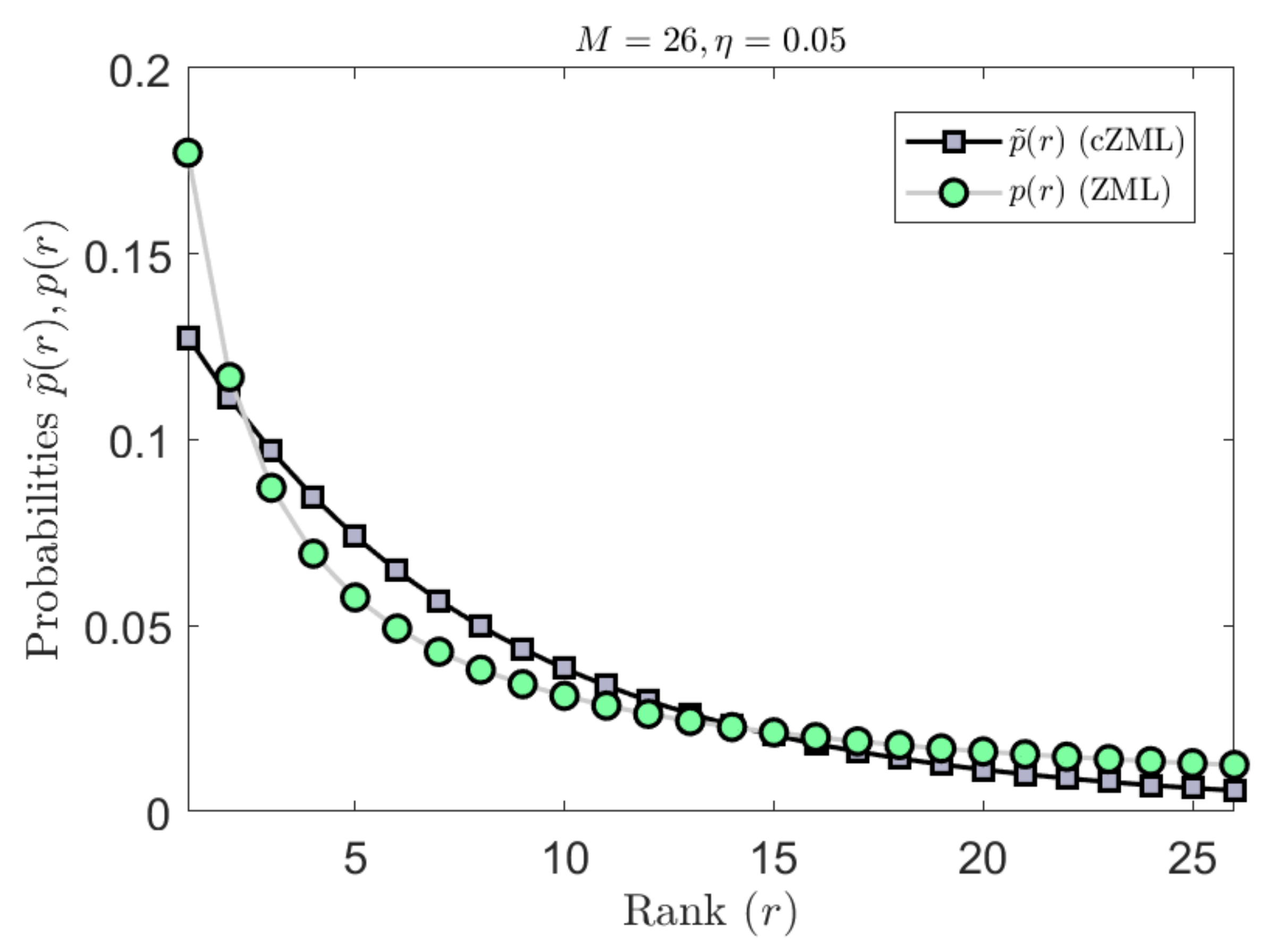
4.1. Constrained Linguistic ZML Model for Natural Language
4.2. Entropy Rate Estimation
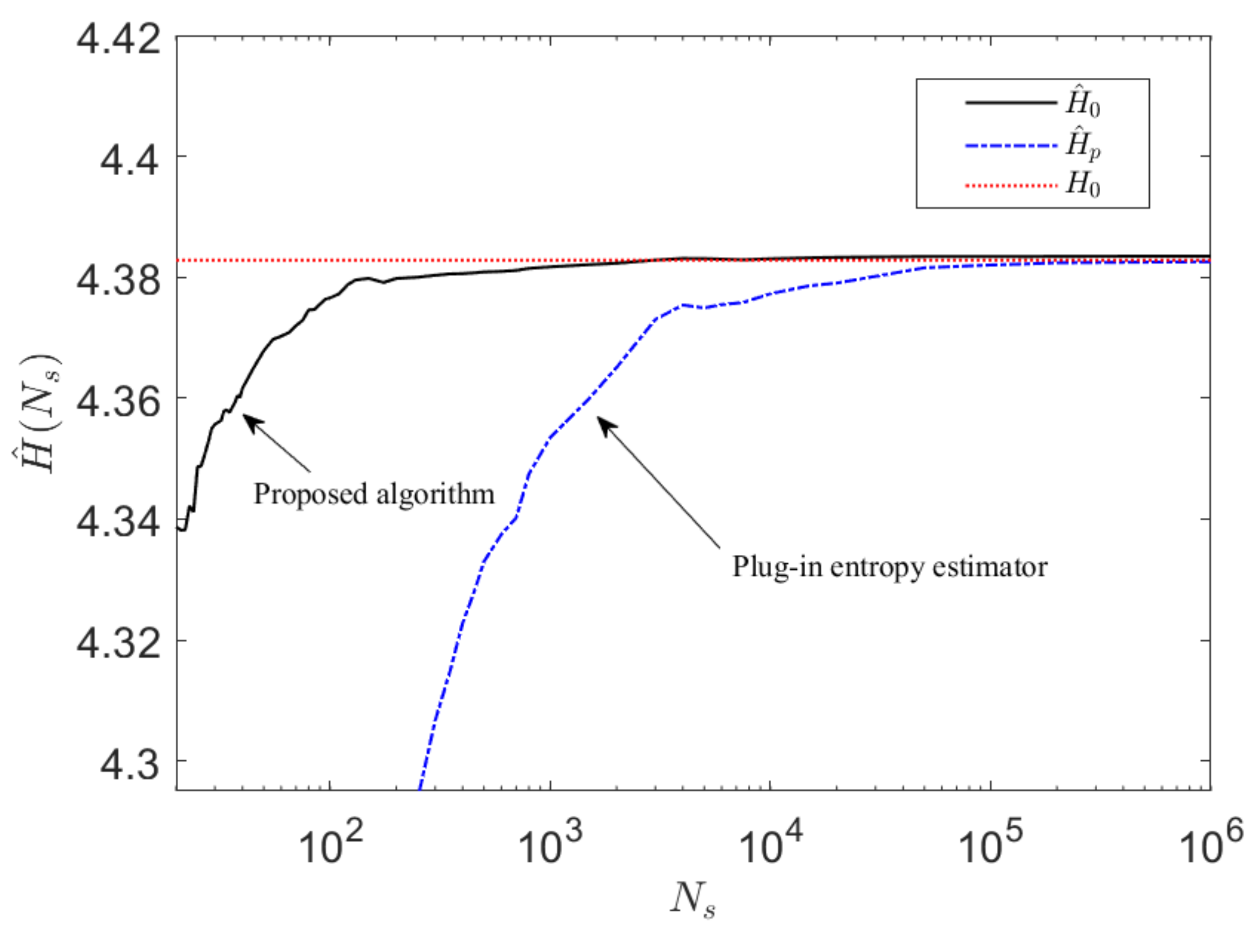
4.3. Convergence of Constrained cZML Entropy Estimation Algorithm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Constrained Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Models
Appendix A.1. cZML Model I
Appendix A.2. cZML Model II
References
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication (Parts I and II). Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, XXVII, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication (Part III). Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, XXVII, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, T.; Grassberger, P. Entropy estimation of symbol sequences. Chaos 1996, 6, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, F.; Mercer, R.L.; Bahl, L.R.; Baker, J.K. Perplexity—A measure of the difficulty of speech recognition tasks. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1977, 62, S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. Prediction and Entropy of Printed English. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1951, 30, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziv, J.; Lempel, A. Compression of individual sequences via variable-rate coding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1978, 24, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigó, J.; Szczepanski, J.; Wajnryb, E.; Sanchez-Vives, M. Estimating the Entropy Rate of Spike Trains via Lempel-Ziv Complexity. Neural Comput. 2004, 16, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Furlan, R.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Entropy, entropy rate, and pattern classification as tools to typify complexity in short heart period variability series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Gao, W. Measuring visual saliency by Site Entropy Rate. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2368–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Kershenbaum, A. Entropy rate as a measure of animal vocal complexity. Bioacoustics 2014, 23, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewenstern, D.; Yianilos, P.N. Significantly Lower Entropy Estimates for Natural DNA Sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 1999, 6, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegetabile, B.G.; Stout-Oswald, S.A.; Davis, E.P.; Baram, T.Z.; Stern, H.S. Estimating the Entropy Rate of Finite Markov Chains With Application to Behavior Studies. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 2019, 44, 282–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, M.; Chen, X.; Kakade, S.; Narasimhan, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Calibration, Entropy Rates, and Memory in Language Models. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; Hal, D., III, Singh, A., Eds.; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. ML Research Press: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Volume 119, pp. 1089–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Back, A.D.; Angus, D.; Wiles, J. Determining the Number of Samples Required to Estimate Entropy in Natural Sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2019, 65, 4345–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesne, A.; Blanc, J.L.; Pezard, L. Entropy estimation of very short symbolic sequences. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 046208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausser, J.; Strimmer, K. Entropy inference and the James-Stein estimator, with application to nonlinear gene association networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Wolf, D.R. Estimating functions of probability distributions from a finite set of samples. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 52, 6841–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemenman, I.; Shafee, F.; Bialek, W. Entropy and Inference, Revisited. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 14; Dietterich, T.G., Becker, S., Ghahramani, Z., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Montalvão, J.; Silva, D.; Attux, R. Simple entropy estimator for small datasets. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonachela, J.A.; Hinrichsen, H.; Muñoz, M.A. Entropy Estimates of Small Data Sets. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2008, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavola, M. An Efficient Entropy Estimation Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach, M.; Font-Clos, F.; Altmann, E.G. Similarity of Symbol Frequency Distributions with Heavy Tails. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 021009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugiumtzis, D. Partial Transfer Entropy on Rank Vectors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paninski, L. Estimation of Entropy and Mutual Information. Neural Comput. 2003, 15, 1191–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolchinsky, A.; Tracey, B.D. Estimating Mixture Entropy with Pairwise Distances. Entropy 2017, 19, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaai, H.; Onken, A.; Harvey, C.D.; Panzeri, S. Information estimation using nonparametric copulas. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 053302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.G.; Samengo, I. Estimating the Mutual Information between Two Discrete, Asymmetric Variables with Limited Samples. Entropy 2019, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S. Calculation of Entropy from Data of Motion. J. Stat. Phys. 1981, 26, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvão, J.; Attux, R.; Silva, D. A pragmatic entropy and differential entropy estimator for small datasets. J. Commun. Inf. Syst. 2014, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Random texts exhibit Zipf’s-law-like word frequency distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1992, 38, 1842–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpert, E.; Stahel, W.A.; Abbt, M. Log-normal Distributions across the Sciences: Keys and Clues. BioScience 2001, 51, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesbrecht, F.; Kempthorne, O. Maximum Likelihood Estimation in the Three-Parameter Lognormal Distribution. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1976, 38, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gui, W. Corrected Maximum Likelihood Estimations of the Lognormal Distribution Parameters. Symmetry 2020, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li1, B.; Yashchin, E.; Christiansen, C.; Gill, J.; Filippi, R.; Sullivan, T. Application of Three-Parameter Lognormal Distribution in EM Data Analysis. In Mathematics IBM Research Report RC23680 (W0507-213); IBM Systems and Technology Group: Essex Junction, VT, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky, A.; Kiefer, J.; Wolfowitz, J. Asymptotic minimax character of the sample distribution function and of the classical multinomial estimator. Ann. Math. Statist. 1956, 27, 642–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, G. The Psycho-Biology of Language: An Introduction to Dynamic Philology; Houghton Mifflin: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Piantadosi, S.T. Zipf’s word frequency law in natural language: A critical review and future directions. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2014, 21, 1112–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, C.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. Zipf’s law of abbreviation as a language universal. In Proceedings of the Leiden Workshop on Capturing Phylogenetic Algorithms for Linguistics, Lorentz Center, Leiden, 26–30 October 2015; Bentz, C., Jäger, G., Yanovich, I., Eds.; University of Tübingen: Tübingen, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mantegna, R.N.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Goldberger, A.L.; Havlin, S.; Peng, C.K.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E. Linguistic Features of Noncoding DNA Sequences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipf, G.; Thiele, L. Human Behavior and the Principle of Least Effort; Addison Wesley: Oxford, UK, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.A. Some effects of intermittent silence. Am. J. Psychol. 1957, 70, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, D. Zipf’s Law and Miller’s Random-Monkey Model. Am. J. Psychol. 1968, 81, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Conrad, B.; Mitzenmacher, M. Power laws for monkeys typing randomly: The case of unequal probabilities. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2004, 50, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perline, R.; Perline, R. Two Universality Properties Associated with the Monkey Model of Zipf’s Law. Entropy 2016, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantadosi, S.T.; Tily, H.; Gibson, E. Word lengths are optimized for efficient communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, R.; Solé, R.V. Least effort and the origins of scaling in human language. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, E.; Futrell, R.; Piantadosi, S.P.; Dautriche, I.; Mahowald, K.; Bergen, L.; Levy, R. How Efficiency Shapes Human Language. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinert-Threlkeld, S.; Szymanik, J. Ease of learning explains semantic universals. Cognition 2020, 195, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Zipf’s Law Everywhere. Glottometrics 2002, 5, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Corral, Á.; Boleda, G.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. Zipf’s Law for Word Frequencies: Word Forms versus Lemmas in Long Texts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, R.; Elvevåg, B. Random Texts Do Not Exhibit the Real Zipf’s Law-Like Rank Distribution. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Lessard, P.R.; Desu, S.; Clark, E.; Bagrow, J.P.; Danforth, C.; Dodds, P. Zipf’s law holds for phrases, not words. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, Á.; Serra, I. The Brevity Law as a Scaling Law, and a Possible Origin of Zipf’s Law for Word Frequencies. Entropy 2020, 22, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, R.; Solé, R.V. The Small-World of Human Language. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2001, 268, 2261–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Leimkuhler, F. A relationship between Lotka’s Law, Bradford’s Law, and Zipf’s Law. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1986, 37, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Leimkuhler, F. Booth’s law of word frequency. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1990, 41, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, A.D.; Angus, D.; Wiles, J. Transitive Entropy—A Rank Ordered Approach for Natural Sequences. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2020, 14, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.D. A Law of occurrences for words of low frequency. Inf. Control 1967, 10, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, M.A. Beyond the Zipf-Mandelbrot law in quantitative linguistics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2001, 300, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Taft, M.; Krebs-Lazendic, L. The role of orthographic syllable structure in assigning letters to their position in visual word recognition. J. Mem. Lang. 2013, 68, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallows, D. Experimental evidence for English syllabification and syllable structure. J. Linguist. 1981, 17, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetail, F.; Drabs, V.; Content, A. The role of consonant/vowel organization in perceptual discrimination. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2014, 40 4, 938–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, R.; Dalby, J. Consonant/vowel ratio as a cue for voicing in English. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 1982, 32, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Bowers, J. Contrasting five different theories of letter position coding: Evidence from orthographic similarity effects. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2006, 323, 535–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.; Ziegler, J.C.; Zorzi, M. A Computational and Empirical Investigation of Graphemes in Reading. Cogn. Sci. 2013, 37, 800–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Wiley-Interscience: John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, New Jersey, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-i-Cancho, R.; Bentz, C.; Seguin, C. Optimal Coding and the Origins of Zipfian Laws. J. Quant. Linguist. 2020, 0, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Goodman, J. An empirical study of smoothing techniques for language modeling. Comput. Speech Lang. 1999, 13, 359–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norvig, P. Natural Language Corpus Data. In Beautiful Data; Segaran, T., Hammerbacher, J., Eds.; O’Reilly: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- Norvig, P. English Letter Frequency Counts: Mayzner Revisited or ETAOIN SRHLDCU. 2020. Available online: https://norvig.com/mayzner.html (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Tanaka-Ishii, K.; Aihara, S. Computational Constancy Measures of Texts—Yule’s K and Rényi’s Entropy. Comput. Linguist. 2015, 41, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.; King, R.C. A convergent gambling estimate of the entropy of English. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1978, 24, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.F.; Pietra, V.J.D.; Mercer, R.L.; Pietra, S.A.D.; Lai, J.C. An Estimate of an Upper Bound for the Entropy of English. Comput. Linguist. 1992, 18, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bentz, C.; Alikaniotis, D.; Cysouw, M.; Ferrer-i-Cancho, R. The Entropy of Words—Learnability and Expressivity across More than 1000 Languages. Entropy 2017, 19, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debowski, L. Information Theory Meets Power Laws: Stochastic Processes and Language Models; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kontoyiannis, I.; Algoet, P.; Suhov, Y.; Wyner, A. Nonparametric entropy estimation for stationary processes and random fields, with applications to English text. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1998, 44, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Kontoyiannis, I.; Bienenstock, E. Estimating the Entropy of Binary Time Series: Methodology, Some Theory and a Simulation Study. Entropy 2008, 10, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahira, R.; Tanaka-Ishii, K.; Debowski, L. Entropy Rate Estimates for Natural Language—A New Extrapolation of Compressed Large-Scale Corpora. Entropy 2016, 18, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, H.; Francis, W.N. Computational Analysis of Present-Day American English; Brown University Press: Providence, RI, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
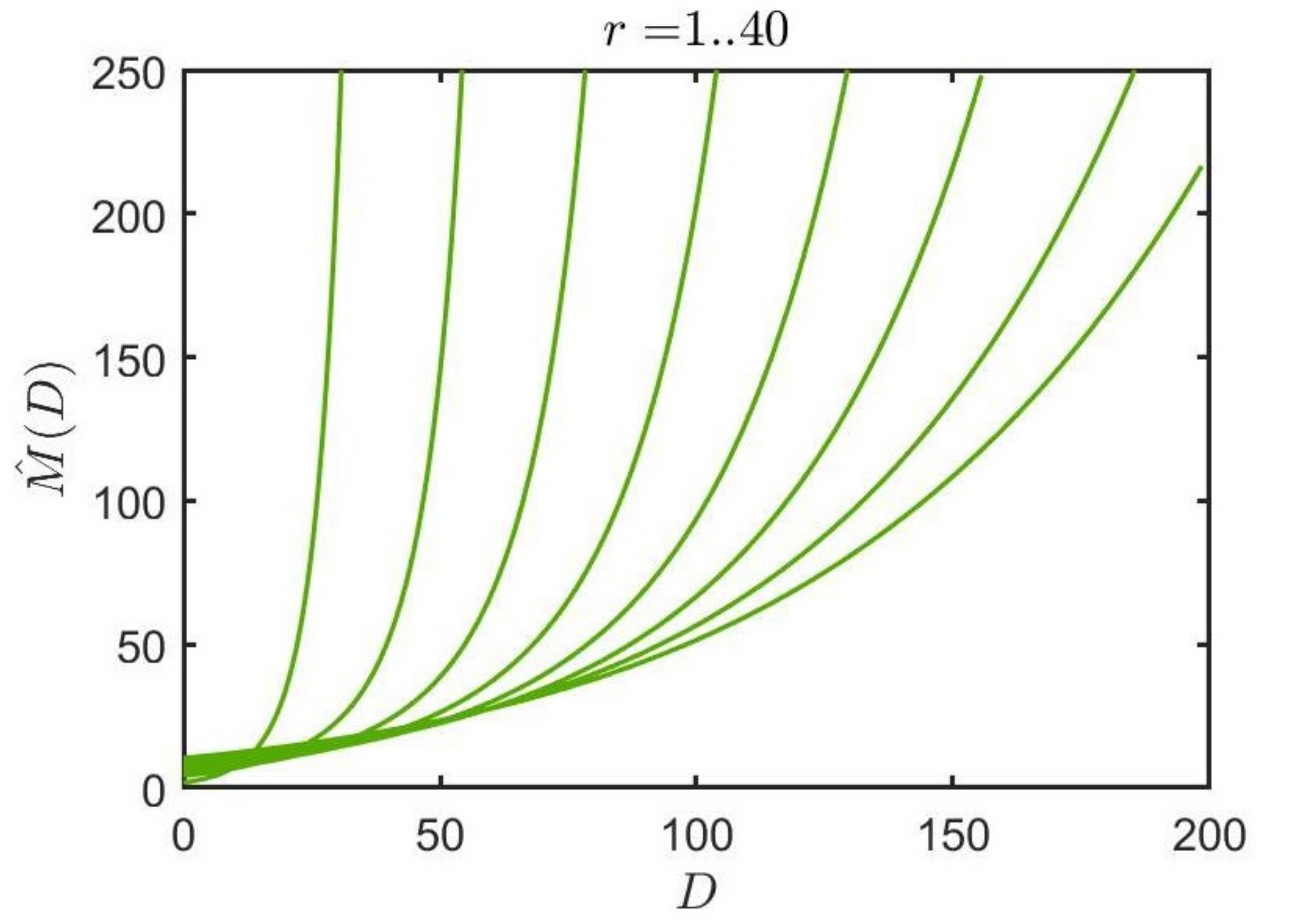
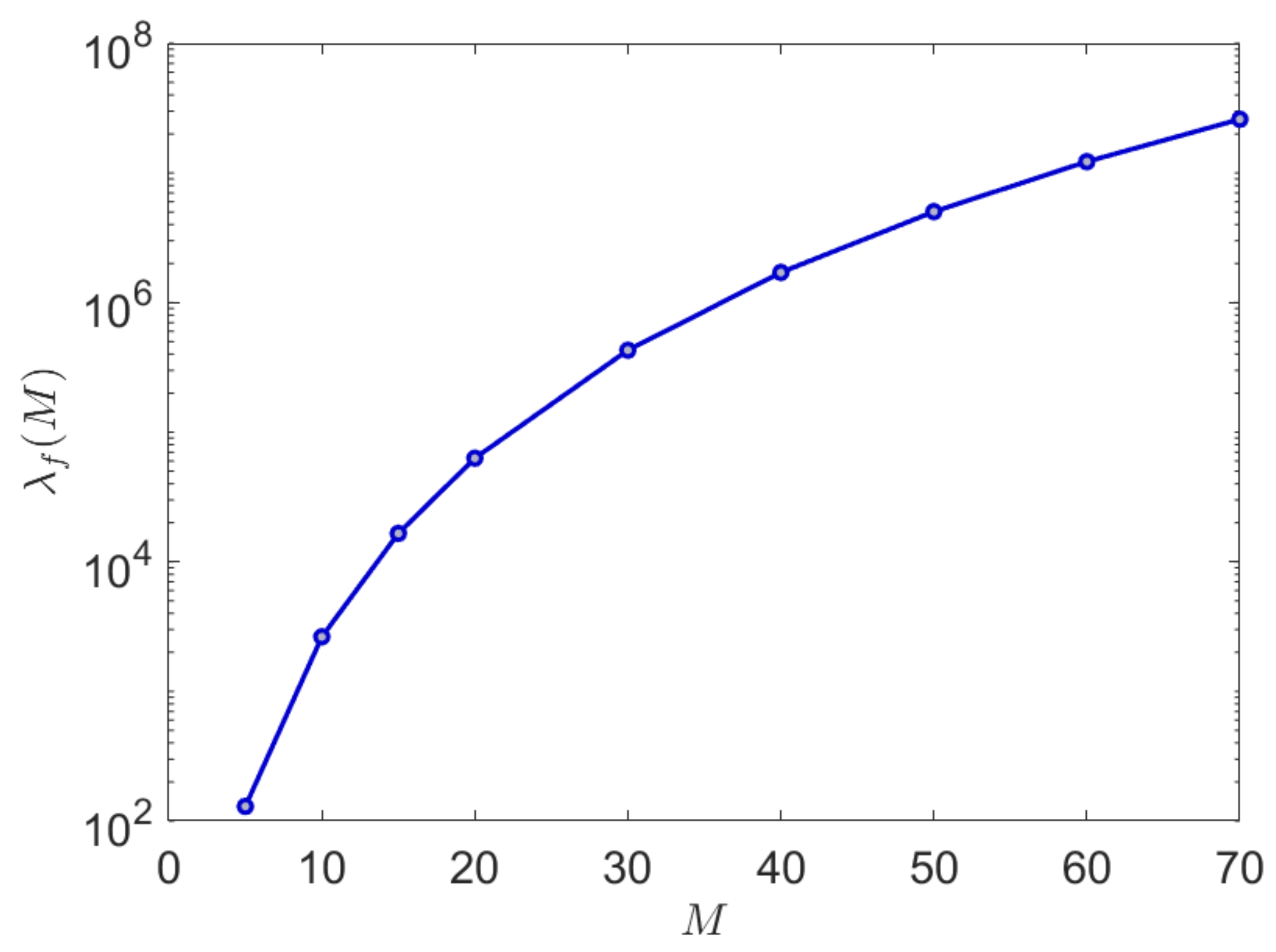
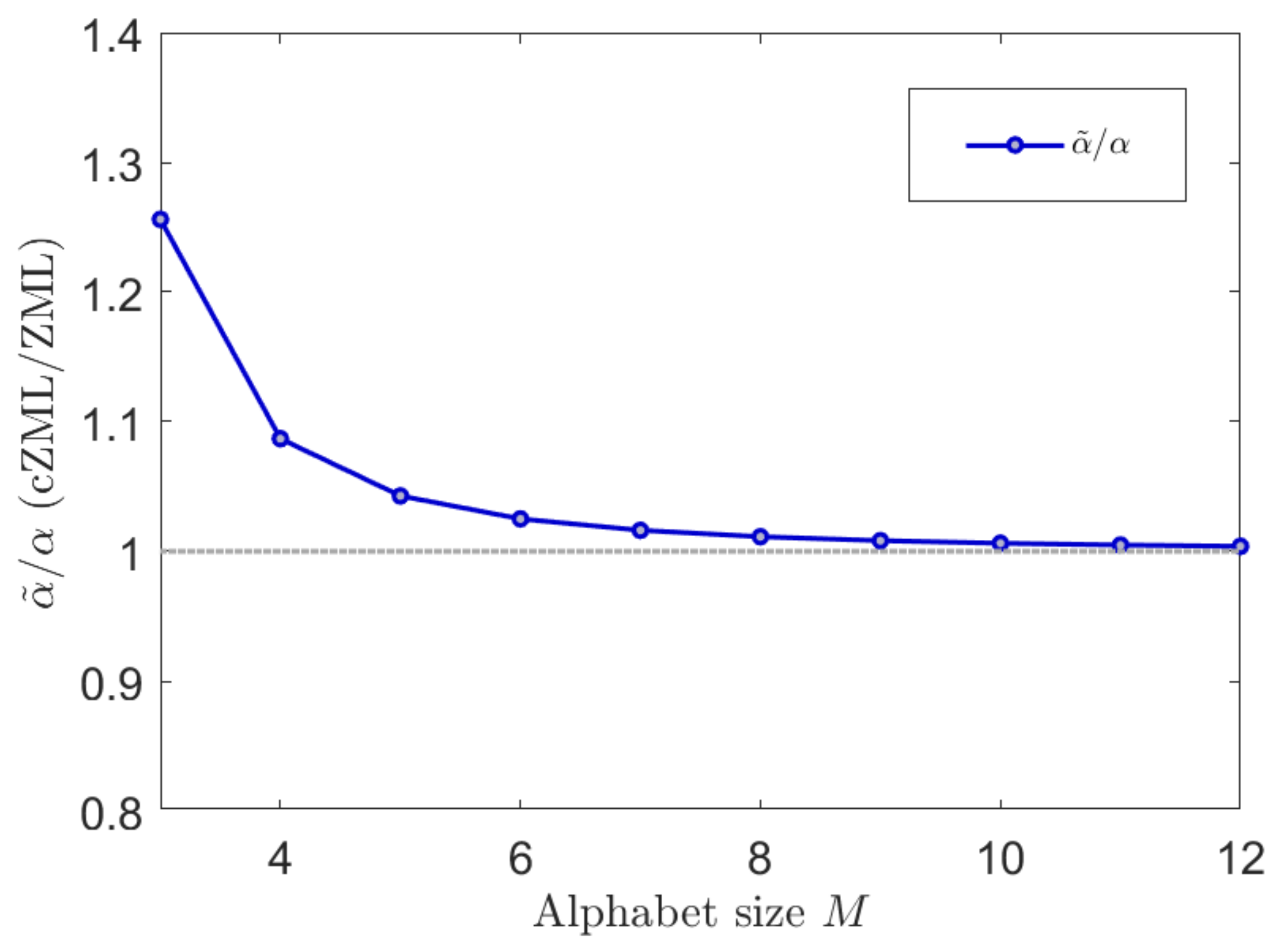
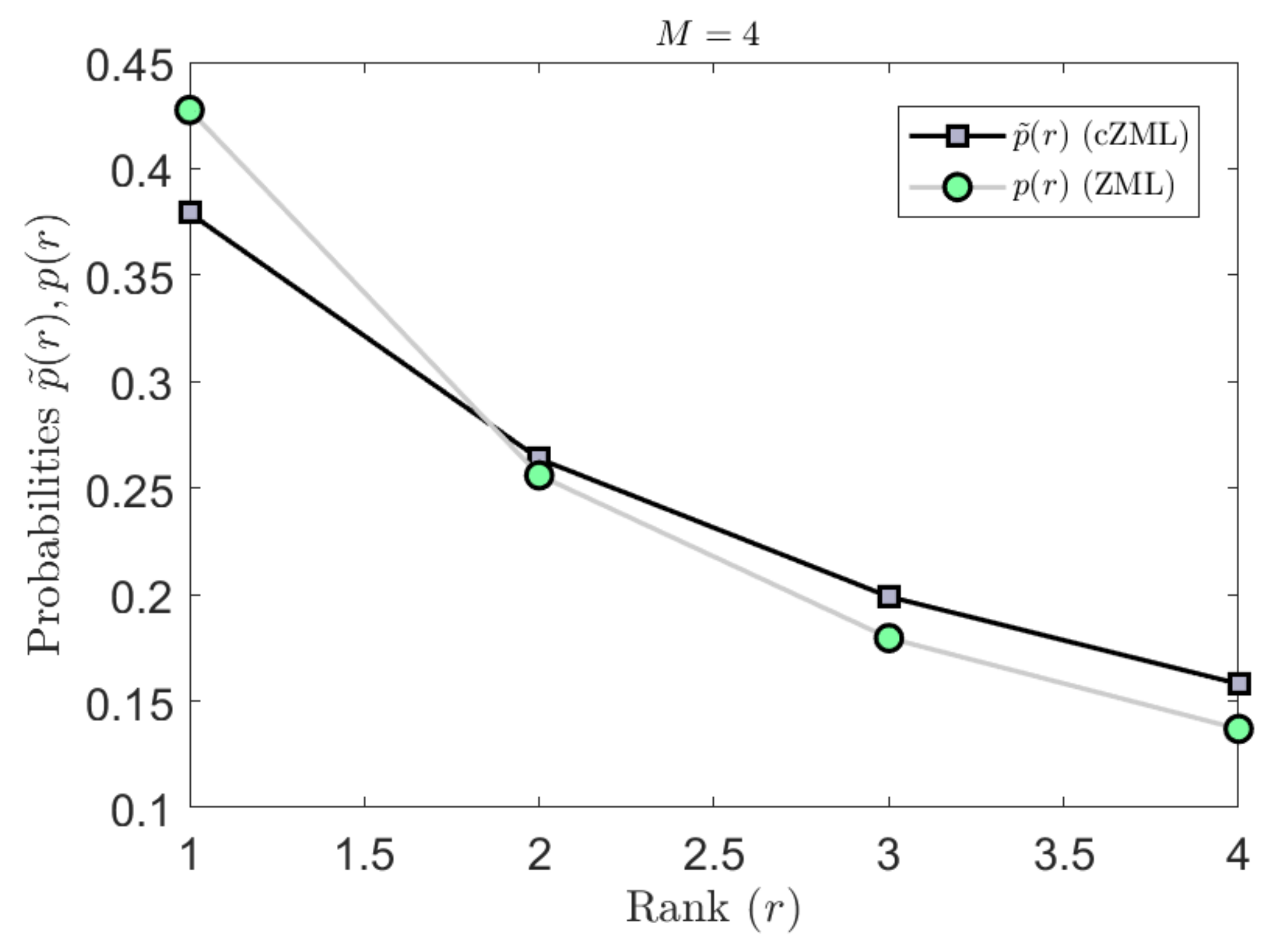
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Back, A.D.; Wiles, J. Entropy Estimation Using a Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Model for Natural Sequences. Entropy 2021, 23, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23091100
Back AD, Wiles J. Entropy Estimation Using a Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Model for Natural Sequences. Entropy. 2021; 23(9):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23091100
Chicago/Turabian StyleBack, Andrew D., and Janet Wiles. 2021. "Entropy Estimation Using a Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Model for Natural Sequences" Entropy 23, no. 9: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23091100
APA StyleBack, A. D., & Wiles, J. (2021). Entropy Estimation Using a Linguistic Zipf–Mandelbrot–Li Model for Natural Sequences. Entropy, 23(9), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23091100






