Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity Measure for Biomedical Signal Analysis: Interpretation and Application to Focal EEG Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
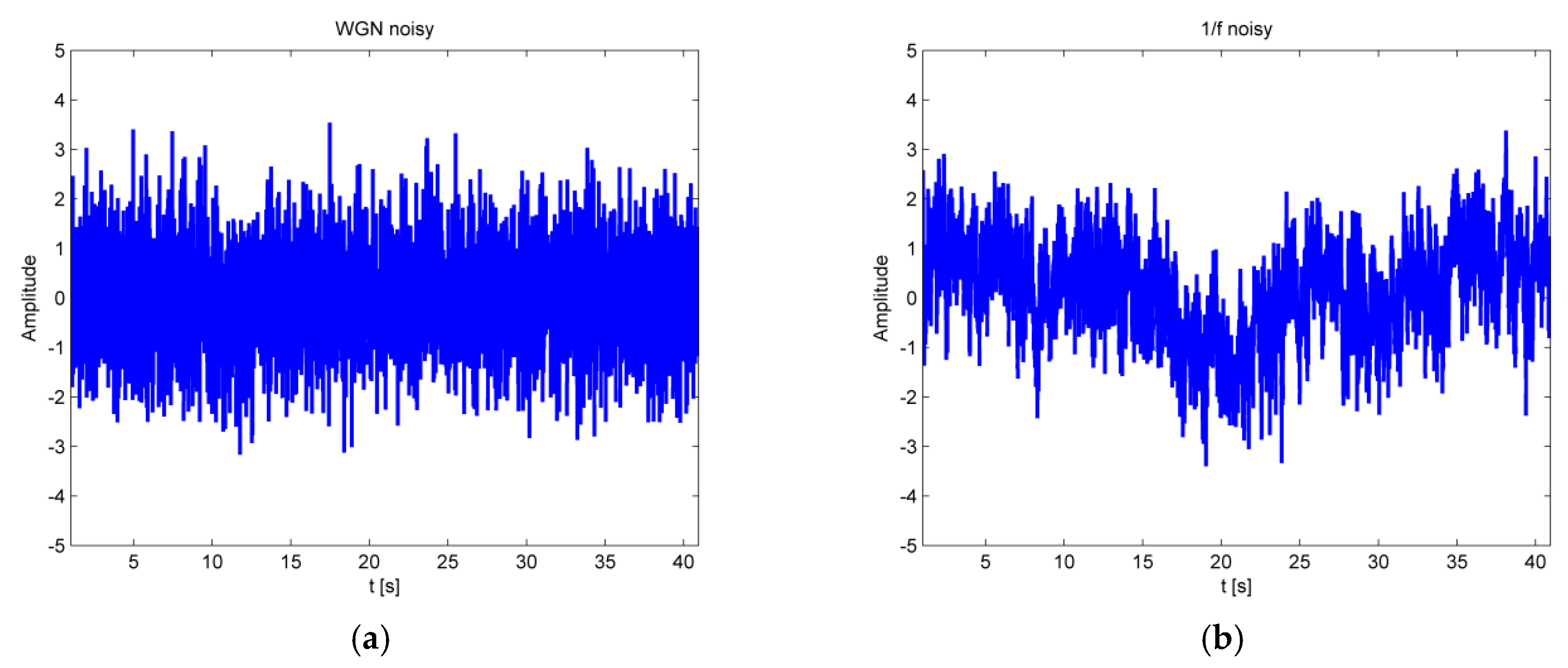
2.1. Simulated Data
- Gaussian noise
- Sinusoidal signals with variable amplitude and frequency
- Amplitude modulated quasi-periodic signal with the addition of WGN of diverse power
- Bandwidth of coloured Gaussian noise signal
- Signal with spectral colour noise content
- Periodic deterministic process
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Lempel–Ziv Complexity
2.4. Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity
2.5. Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity
2.6. Classfication
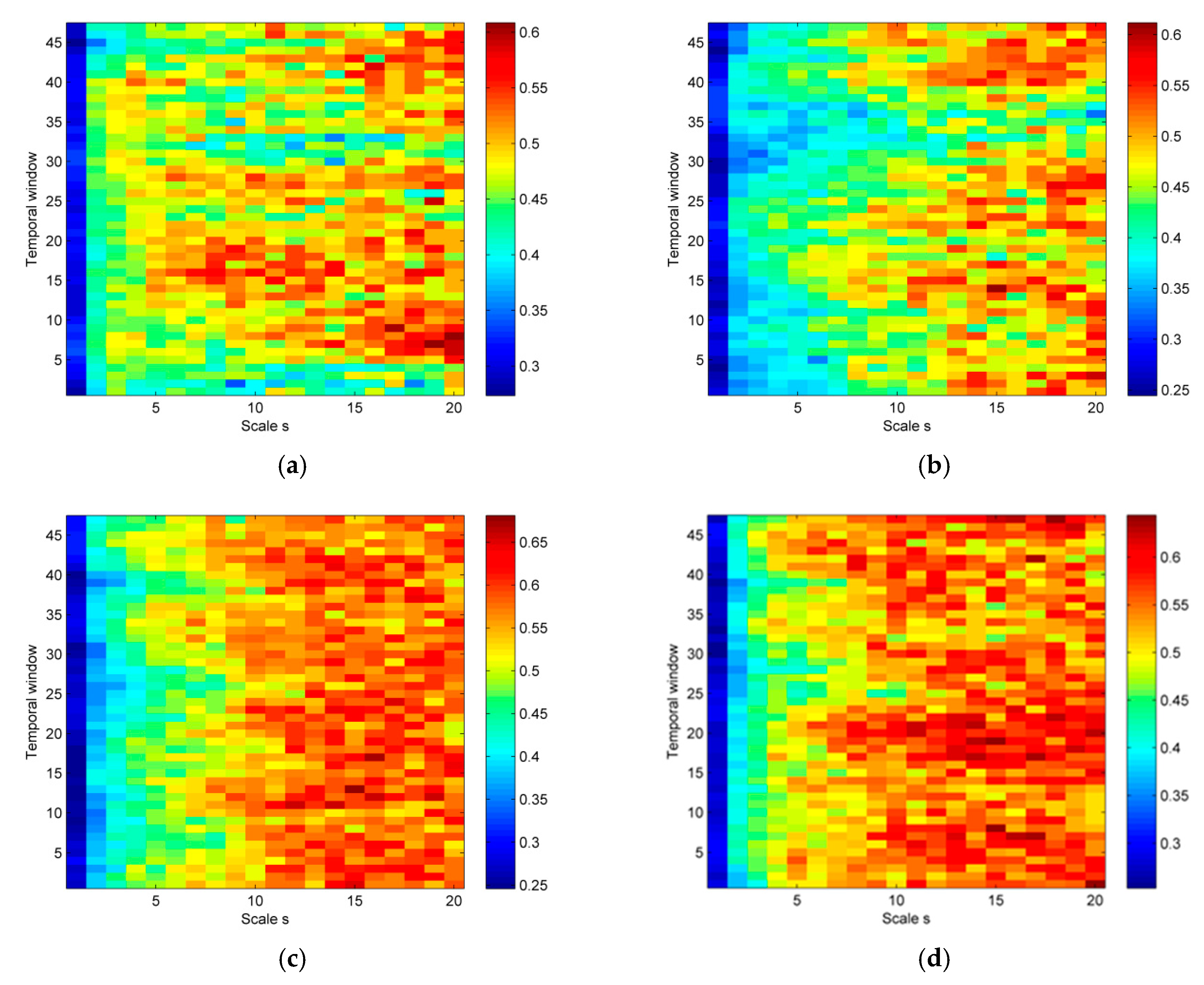
3. Results
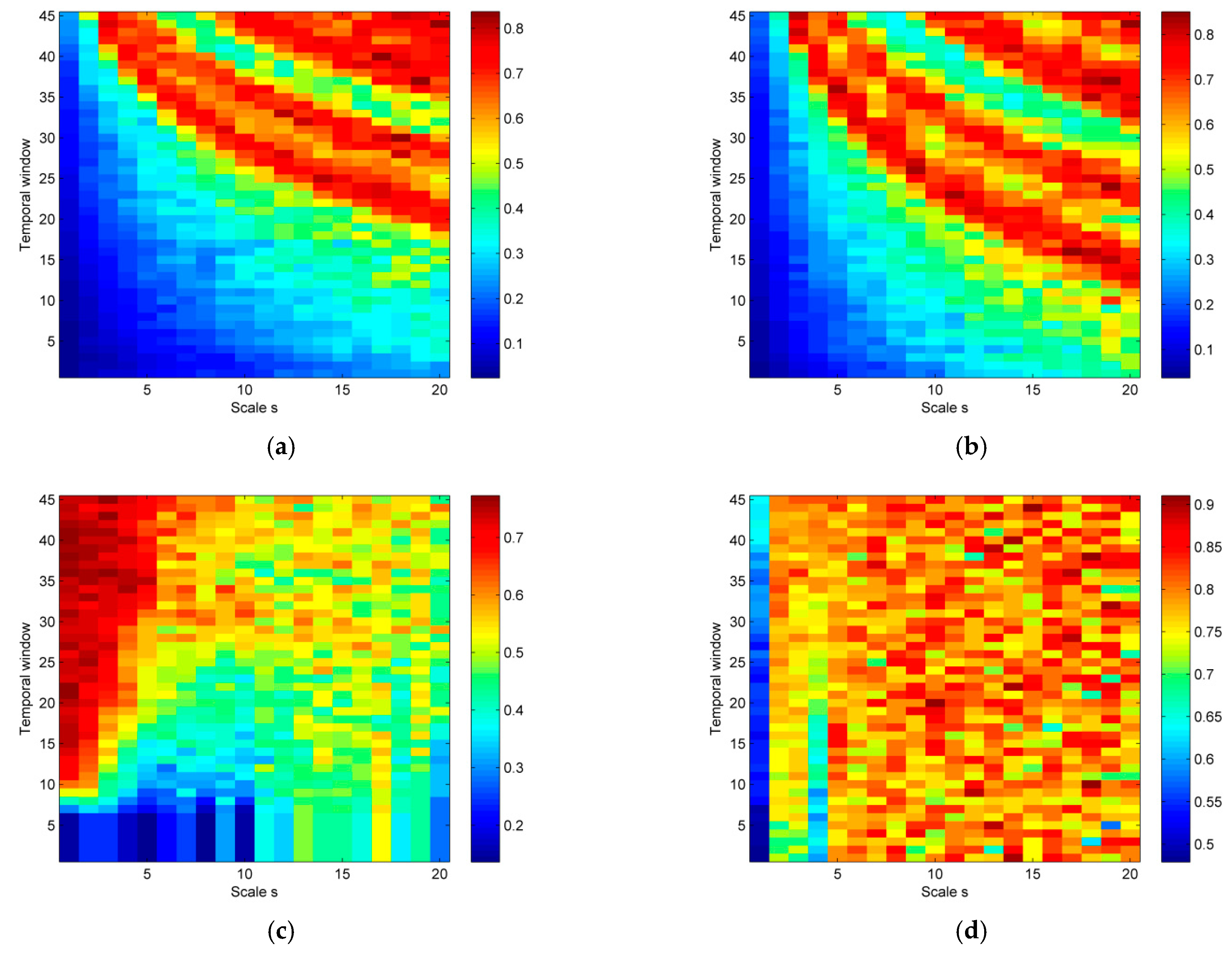
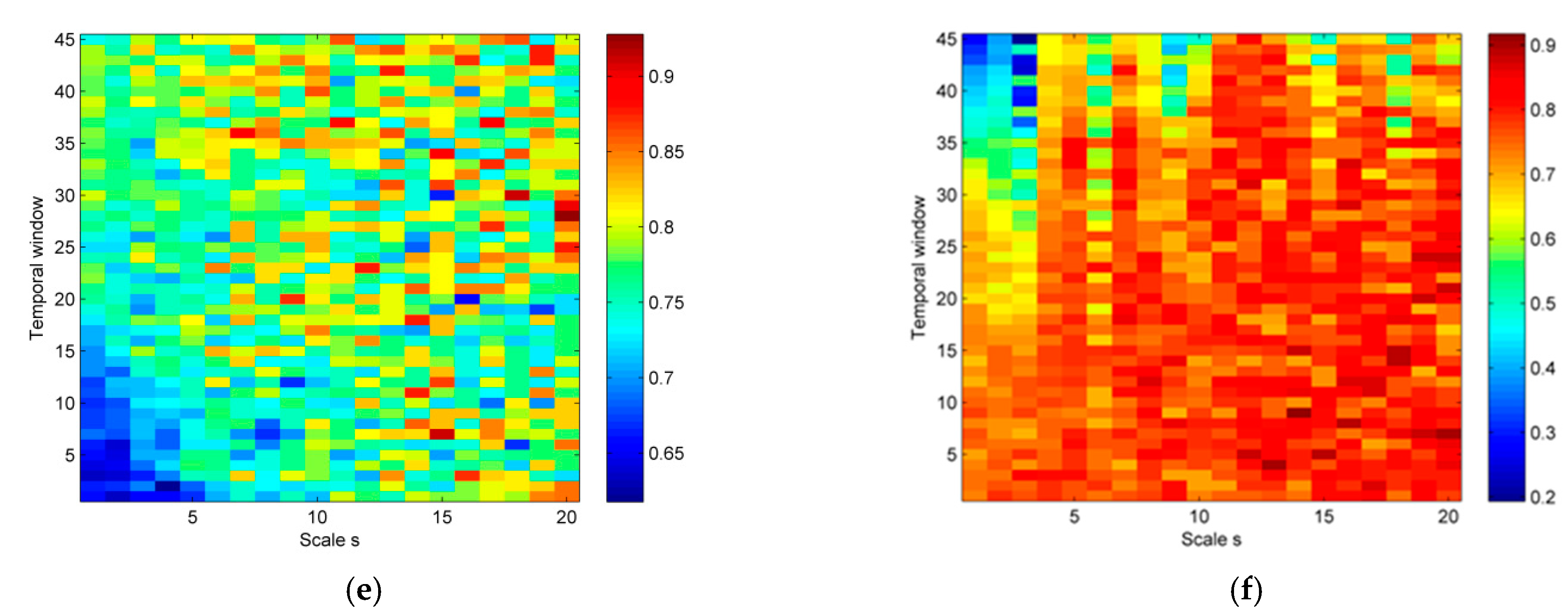
3.1. Parameter Selection
3.2. Synthetic Signals
3.3. Neurological Focal—Non-Focal Dataset
4. Discussion
- This is the first study to introduce a new methodology of complex systems analysis;
- The features obtained from MPLZC analysis allow for distinguishing two classes of EEG signals;
- We used only one measure, so it can be useful in building a real system supporting identification of a epileptogenic activity in an area of the brain.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- International League Against Epilepsy. Available online: https://www.ilae.org/guidelines/definition-and-classification (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Andrzejak, R.G.; Schindler, K.; Rummel, C. Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 046206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lempel, A.; Ziv, J. On the complexity of finite sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liang, Z.; Li, X. A permutation Lempel-Ziv complexity measure for EEG analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015, 19, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z. Measuring complexity using fuzzyen, apen, and sampen. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.-K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Mandic, D.P. Multivariate multiscale entropy: A tool for complexity analysis of multichannel data. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 061918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, G.; Dang, C.; Li, X. Complexity analysis of EEG data with multiscale permutation entropy. In Advances in Cognitive Neurodynamics (II); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 741–745. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-D.; Chen, M.; Cheng, J.-S.; Yang, Y. Multiscale fuzzy entropy and its application in rolling bearing fault diagnosis. J. Vib. Eng. 2014, 27, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Marwan, N.; Romano, M.C.; Thiel, M.; Kurths, J. Recurrence plots for the analysis of complex systems. Phys. Rep. 2007, 438, 237–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; WH Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gruszczyńska, I.; Mosdorf, R.; Sobaniec, P.; Żochowska-Sobaniec, M.; Borowska, M. Epilepsy identification based on EEG signal using RQA method. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. An integrated index for the identification of focal electroencephalogram signals using discrete wavelet transform and entropy measures. Entropy 2015, 17, 5218–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. Application of entropy measures on intrinsic mode functions for the automated identification of focal electroencephalogram signals. Entropy 2015, 17, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Dhere, A.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. An automatic detection of focal EEG signals using new class of time–frequency localized orthogonal wavelet filter banks. Knowl. Based Syst. 2017, 118, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Pratiher, S.; Bose, R. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis based novel feature extraction technique for automated detection of focal and non-focal electroencephalogram signals. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2017, 11, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diykh, M.; Abdulla, S.; Saleh, K.; Deo, R.C. Fractal dimension undirected correlation graph-based support vector machine model for identification of focal and non-focal electroencephalography signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019, 54, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artan, N.S. EEG analysis via multiscale Lempel-Ziv complexity for seizure detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 4535–4538. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, U.R.; Hagiwara, Y.; Deshpande, S.N.; Suren, S.; Koh, J.E.W.; Oh, S.L.; Arunkumar, N.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Lim, C.M. Characterization of focal EEG signals: A review. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 91, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abásolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Gómez, C.; García, M.; López, M. Analysis of EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients with Lempel–Ziv complexity and central tendency measure. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboy, M.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D.; Álvarez, D. Interpretation of the Lempel-Ziv complexity measure in the context of biomedical signal analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakovleva, T.V.; Kutepov, I.E.; Karas, A.Y.; Yakovlev, N.M.; Dobriyan, V.V.; Papkova, I.V.; Zhigalov, M.V.; Saltykova, O.A.; Krysko, A.V.; Yaroshenko, T.Y. EEG Analysis in Structural Focal Epilepsy Using the Methods of Nonlinear Dynamics (Lyapunov Exponents, Lempel–Ziv Complexity, and Multiscale Entropy). Sci. World J. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Shi, W. Generalized multiscale Lempel–Ziv complexity of cyclic alternating pattern during sleep. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 93, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregowska, A.; Proniewska, K.; van Dam, P.; Szczepanski, J. Using Lempel-Ziv complexity as effective classification tool of the sleep-related breathing disorders. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 182, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeti, M.; Katebi, S.; Boostani, R. Entropy and complexity measures for EEG signal classification of schizophrenic and control participants. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 47, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abásolo, D.; James, C.J.; Hornero, R. Non-linear analysis of intracranial electroencephalogram recordings with approximate entropy and Lempel-Ziv complexity for epileptic seizure detection. In Proceedings of the 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 1953–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez-Molina, A.J.; Iglesias-Parro, S.; Soriano, M.F.; Aznarte, J.I. Multiscale Lempel–Ziv complexity for EEG measures. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, J.; Hornero, R.; Abásolo, D. Interpretation of the auto-mutual information rate of decrease in the context of biomedical signal analysis. Application to electroencephalogram recordings. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami, H.; Escudero, J. Improved multiscale permutation entropy for biomedical signal analysis: Interpretation and application to electroencephalogram recordings. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2016, 23, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sejdić, E.; Lipsitz, L.A. Necessity of noise in physiology and medicine. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2013, 111, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, A.T.; El-Said, S.A. Performance analysis of support vector machines classifiers in breast cancer mammography recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Cai, C.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Wen, Y. Diagnosis of breast tumours and evaluation of prognostic risk by using machine learning approaches. Adv. Intell. Comput. Theor. Appl. Asp. Contemp. Intell. Comput. Tech. 2007, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.B.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. Discrimination and classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals using entropy-based features in the EMD-DWT domain. Biomed. signal Process. Control. 2016, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Pachori, R.B.; Acharya, U.R. Tunable-Q wavelet transform based multivariate sub-band fuzzy entropy with application to focal EEG signal analysis. Entropy 2017, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, V.; Pachori, R.B. A new method for classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals. In Machine Intelligence and Signal Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 235–246. [Google Scholar]




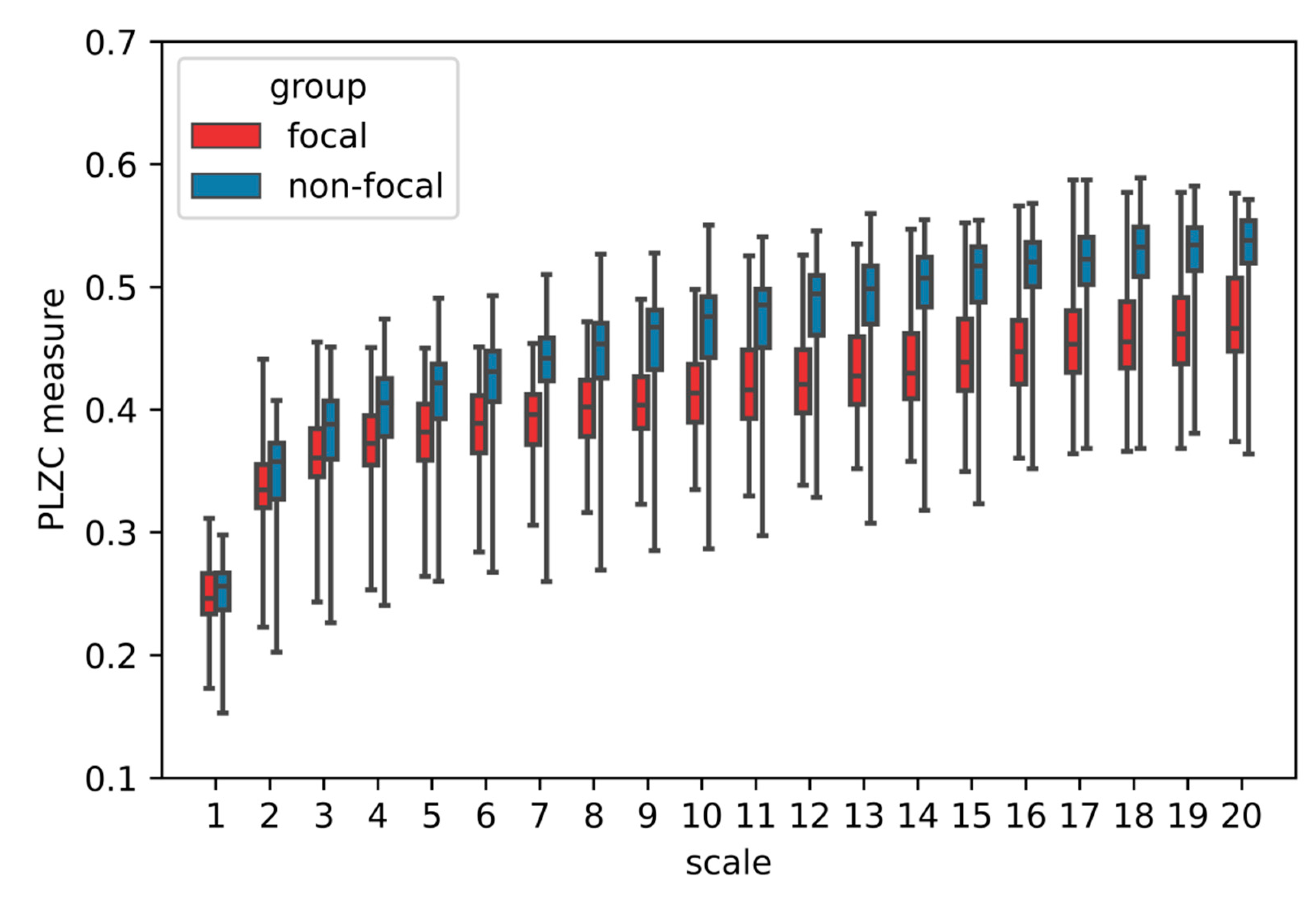
| Measure | m | Focal Group (Mean ± std) N = 100 | Non-Focal Group (Mean ± std) N = 100 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLZC_01 | 3 | 0.390 ± 0.039 | 0.387 ± 0.042 | 2.23E-01 |
| 4 | 0.299 ± 0.028 | 0.296 ± 0.031 | 3.22E-01 | |
| 5 | 0.251 ± 0.026 | 0.248 ± 0.028 | 2.65E-01 | |
| PLZC_02 | 3 | 0.501 ± 0.046 | 0.503 ± 0.061 | 3.09E-02 * |
| 4 | 0.385 ± 0.0364 | 0.388 ± 0.046 | 1.92E-02 * | |
| 5 | 0.340 ± 0.036 | 0.344 ± 0.044 | 1.54E-02 * | |
| PLZC_03 | 3 | 0.526 ± 0.046 | 0.533 ± 0.064 | 6.96E-03 * |
| 4 | 0.404 ± 0.035 | 0.415 ± 0.049 | 3.62E-04 * | |
| 5 | 0.364 ± 0.036 | 0.375 ± 0.048 | 3.11E-04 * | |
| PLZC_04 | 3 | 0.533 ± 0.046 | 0.551 ± 0.063 | 4.80E-05 * |
| 4 | 0.413 ± 0.033 | 0.429 ± 0.048 | 2.42E-06 * | |
| 5 | 0.373 ± 0.034 | 0.393 ± 0.049 | 1.22E-06 * | |
| PLZC_05 | 3 | 0.537 ± 0.044 | 0.559 ± 0.059 | 1.69E-06 * |
| 4 | 0.418 ± 0.033 | 0.441 ± 0.045 | 5.91E-09 * | |
| 5 | 0.379 ± 0.034 | 0.406 ± 0.048 | 9.22E-10 * | |
| PLZC_06 | 3 | 0.541 ± 0.041 | 0.569 ± 0.057 | 1.90E-08 * |
| 4 | 0.424 ± 0.032 | 0.451 ± 0.044 | 1.24E-10 * | |
| 5 | 0.386 ± 0.033 | 0.418 ± 0.046 | 1.45E-11 * | |
| PLZC_07 | 3 | 0.547 ± 0.039 | 0.577 ± 0.055 | 4.26E-10 * |
| 4 | 0.429 ± 0.031 | 0.461 ± 0.044 | 2.43E-12 * | |
| 5 | 0.393 ± 0.033 | 0.431 ± 0.047 | 2.52E-13 * | |
| PLZC_08 | 3 | 0.552 ± 0.041 | 0.588 ± 0.052 | 5.36E-11 * |
| 4 | 0.434 ± 0.031 | 0.470 ± 0.041 | 2.07E-13 * | |
| 5 | 0.400 ± 0.033 | 0.441 ± 0.046 | 8.31E-14 * | |
| PLZC_09 | 3 | 0.555 ± 0.039 | 0.596 ± 0.052 | 9.69E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.441 ± 0.031 | 0.478 ± 0.040 | 7.13E-14 * | |
| 5 | 0.406 ± 0.033 | 0.453 ± 0.045 | 1.79E-15 * | |
| PLZC_10 | 3 | 0.559 ± 0.042 | 0.601 ± 0.050 | 5.07E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.447 ± 0.032 | 0.486 ± 0.039 | 1.62E-14 * | |
| 5 | 0.413 ± 0.035 | 0.463 ± 0.045 | 5.78E-16 * | |
| PLZC_11 | 3 | 0.567 ± 0.042 | 0.609 ± 0.049 | 3.83E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.452 ± 0.033 | 0.493 ± 0.039 | 2.50E-15 * | |
| 5 | 0.420 ± 0.039 | 0.472 ± 0.042 | 1.73E-16 * | |
| PLZC_12 | 3 | 0.569 ± 0.040 | 0.616 ± 0.048 | 1.05E-14 * |
| 4 | 0.456 ± 0.033 | 0.500 ± 0.036 | 1.06E-16 * | |
| 5 | 0.424 ± 0.038 | 0.482 ± 0.040 | 8.91E-19 * | |
| PLZC_13 | 3 | 0.576 ± 0.042 | 0.621 ± 0.049 | 1.90E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.464 ± 0.035 | 0.507 ± 0.037 | 5.55E-15 * | |
| 5 | 0.432 ± 0.040 | 0.488 ± 0.043 | 1.04E-17 * | |
| PLZC_14 | 3 | 0.579 ± 0.041 | 0.629 ± 0.050 | 3.84E-15 * |
| 4 | 0.470 ± 0.034 | 0.514 ± 0.036 | 2.92E-16 * | |
| 5 | 0.438 ± 0.040 | 0.498 ± 0.041 | 2.23E-18 * | |
| PLZC_15 | 3 | 0.585 ± 0.042 | 0.631 ± 0.047 | 6.95E-14 * |
| 4 | 0.473 ± 0.035 | 0.518 ± 0.035 | 9.75E-16 * | |
| 5 | 0.445 ± 0.042 | 0.506 ± 0.041 | 1.05E-18 * | |
| PLZC_16 | 3 | 0.591 ± 0.042 | 0.634 ± 0.047 | 3.78E-13 * |
| 4 | 0.479 ± 0.036 | 0.523 ± 0.036 | 1.12E-15 * | |
| 5 | 0.451 ± 0.041 | 0.512 ± 0.039 | 4.04E-19 * | |
| PLZC_17 | 3 | 0.596 ± 0.040 | 0.641 ± 0.045 | 1.31E-13 * |
| 4 | 0.485 ± 0.037 | 0.528 ± 0.034 | 3.60E-14 * | |
| 5 | 0.457 ± 0.041 | 0.515 ± 0.040 | 6.80E-18 * | |
| PLZC_18 | 3 | 0.600 ± 0.043 | 0.645 ± 0.046 | 4.02E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.490 ± 0.035 | 0.533 ± 0.035 | 7.88E-15 * | |
| 5 | 0.463 ± 0.042 | 0.522 ± 0.040 | 1.36E-17 * | |
| PLZC_19 | 3 | 0.607 ± 0.041 | 0.651 ± 0.043 | 1.47E-13 * |
| 4 | 0.493 ± 0.034 | 0.537 ± 0.032 | 3.95E-17 * | |
| 5 | 0.467 ± 0.041 | 0.526 ± 0.038 | 8.48E-19 * | |
| PLZC_20 | 3 | 0.610 ± 0.043 | 0.651 ± 0.043 | 8.29E-12 * |
| 4 | 0.497 ± 0.035 | 0.540 ± 0.034 | 2.67E-16 * | |
| 5 | 0.472 ± 0.041 | 0.528 ± 0.038 | 3.74E-18 * |
| m | ACC (±Confidence Intervals) | SEN | SPF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPLZC | 3 | 0.82 (8%) | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| 4 | 0.85 (4%) | 0.85 | 0.84 | |
| 5 | 0.86 (5%) | 0.88 | 0.83 |
| Authors (Years) | Number of Signals | Techniques Proposed | K-Fold | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sharma et al. (2015) [19] | 50 | EMD, entropy, LS-SVM | Yes | 87 |
| Sharma et al. (2015) [18] | 50 | DWT, entropy, Student t-test, LS-SVM | Yes | 84 |
| Sharma et al. (2017) [20] | 3750 | WFB, entropy, Student t-test, LS-SVM | Yes | 94.25 |
| Bhattacharyya et al. (2017) [40] | 3750 | TQWT, entropy, LS-SVM | Yes | 84.67 |
| Acharya et al. (2019) [24] | 3750 | 23 features, p-value, LS-SVM | Yes | 87.93 |
| Gupta et al. (2019) [41] | 3750 | EMD, KNN entropy features, LS-SVM | Yes | 83.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borowska, M. Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity Measure for Biomedical Signal Analysis: Interpretation and Application to Focal EEG Signals. Entropy 2021, 23, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23070832
Borowska M. Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity Measure for Biomedical Signal Analysis: Interpretation and Application to Focal EEG Signals. Entropy. 2021; 23(7):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23070832
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorowska, Marta. 2021. "Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity Measure for Biomedical Signal Analysis: Interpretation and Application to Focal EEG Signals" Entropy 23, no. 7: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23070832
APA StyleBorowska, M. (2021). Multiscale Permutation Lempel–Ziv Complexity Measure for Biomedical Signal Analysis: Interpretation and Application to Focal EEG Signals. Entropy, 23(7), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23070832






