Comparison between Highly Complex Location Models and GAMLSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location Models
2.2. GAMLSS Framework
2.3. Estimation and Model Selection
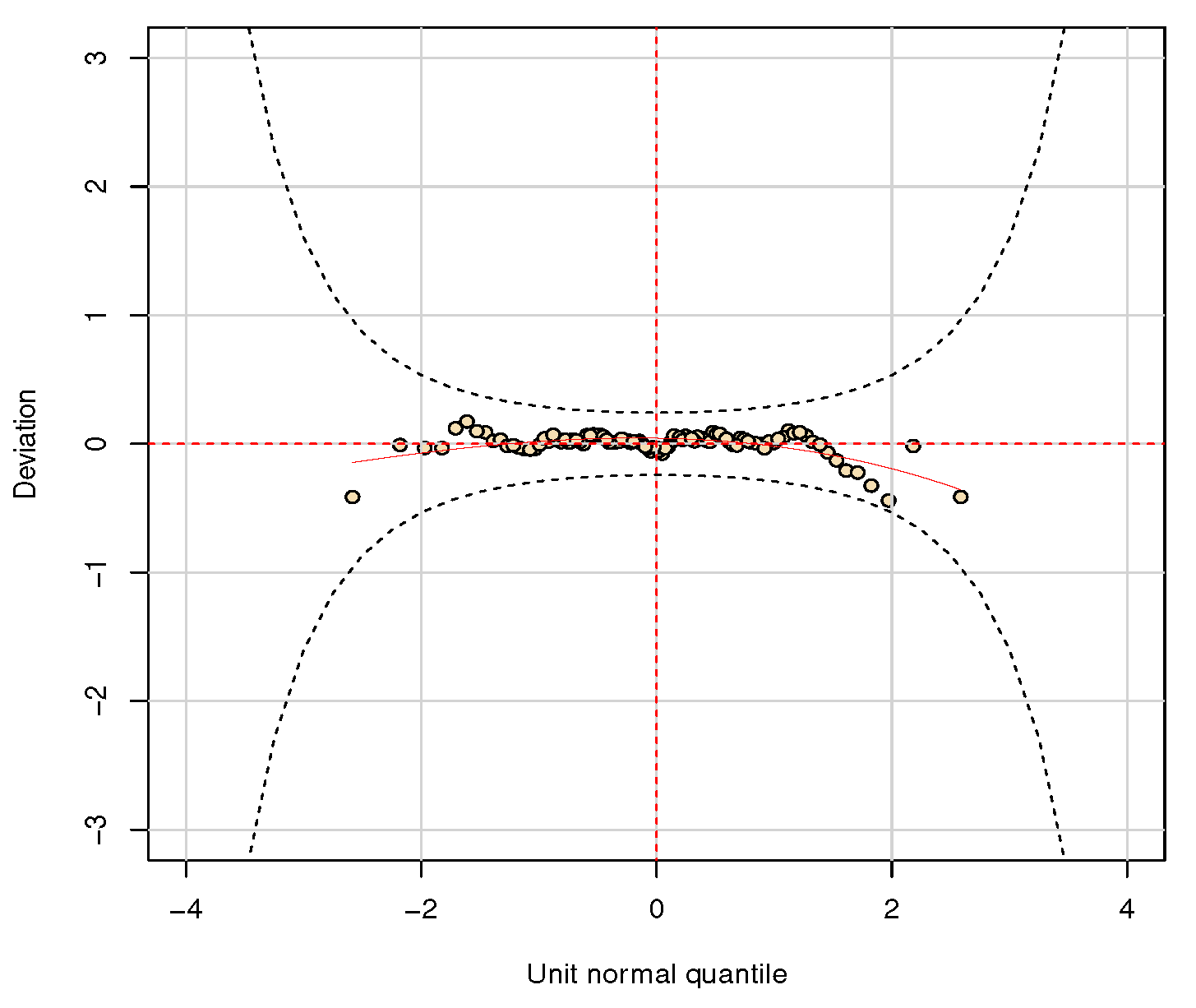
3. Results
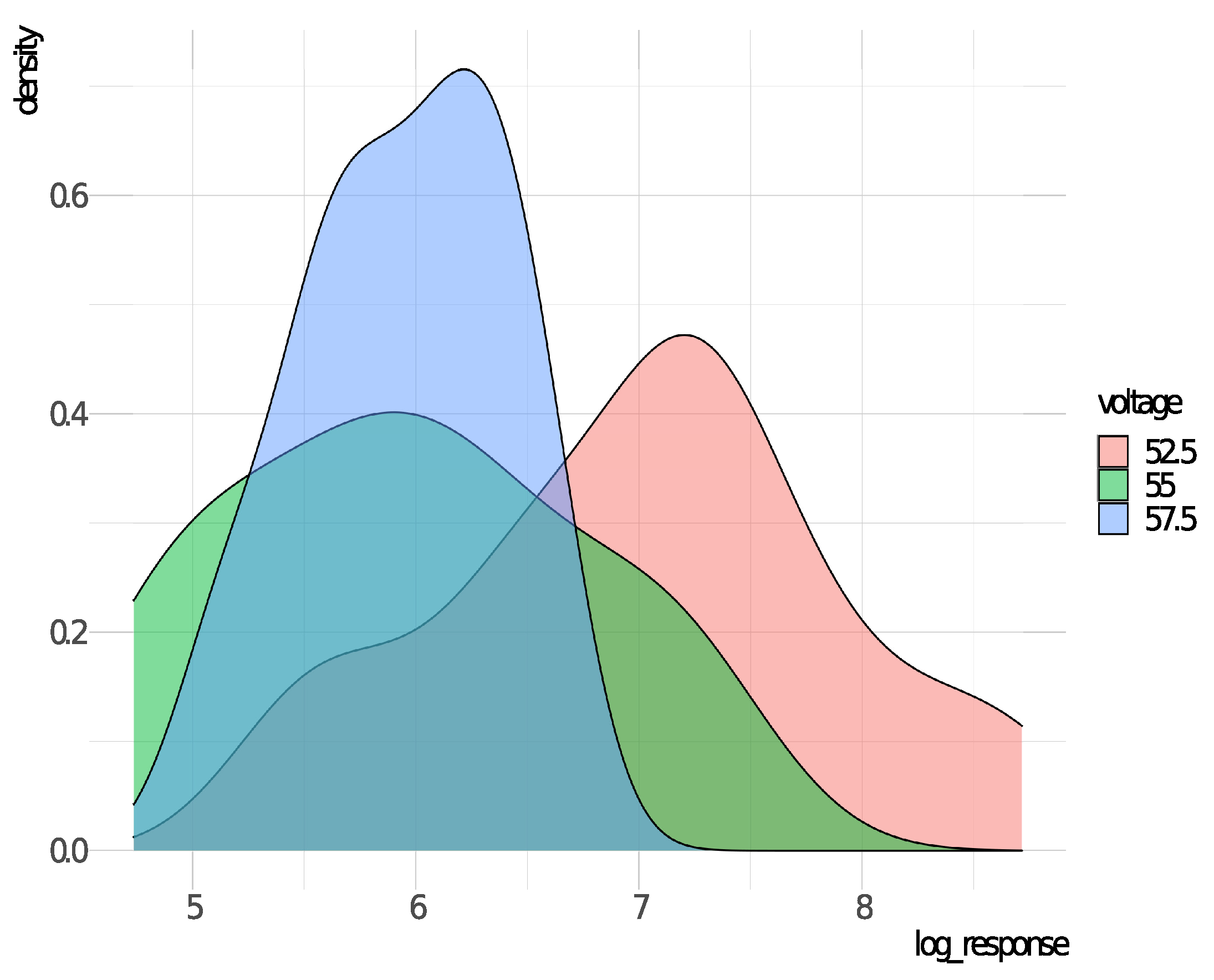
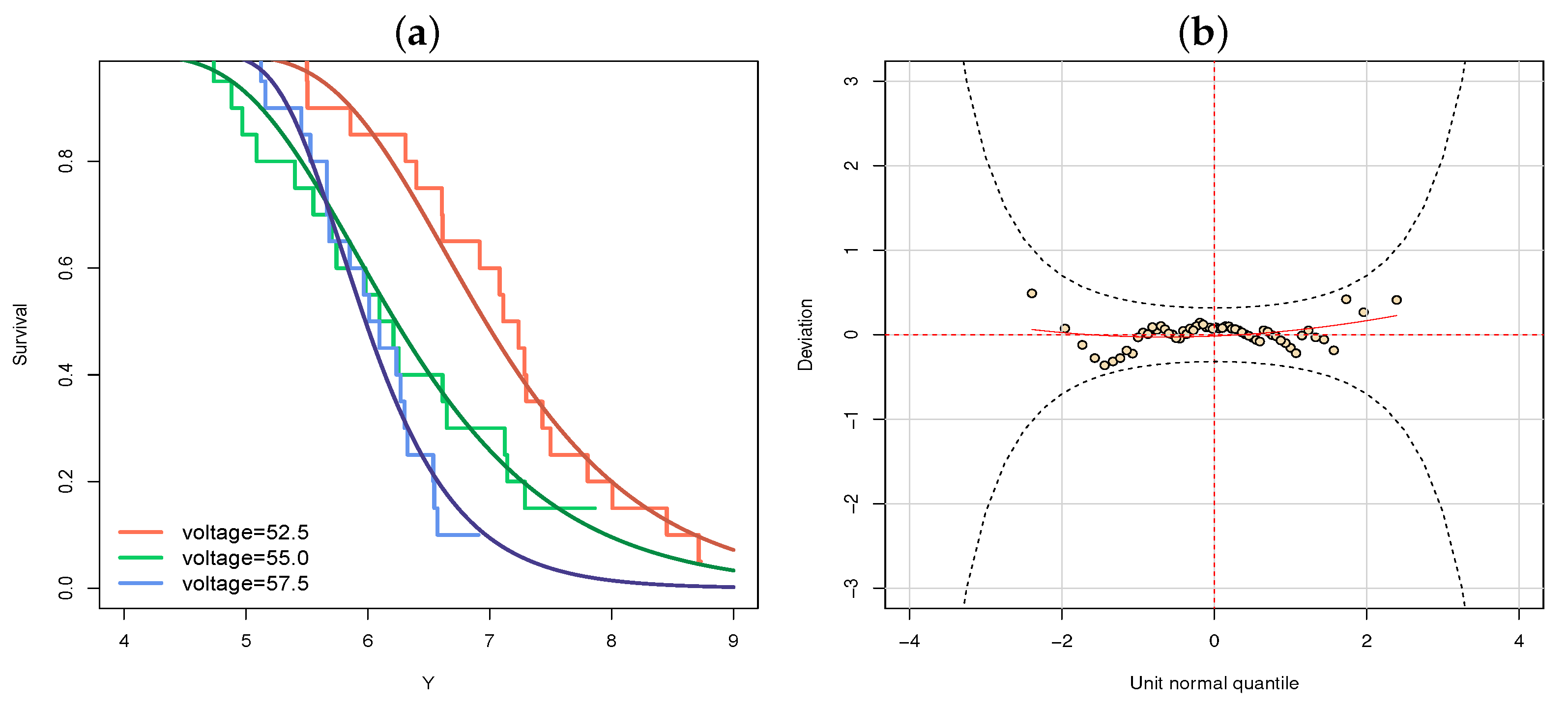
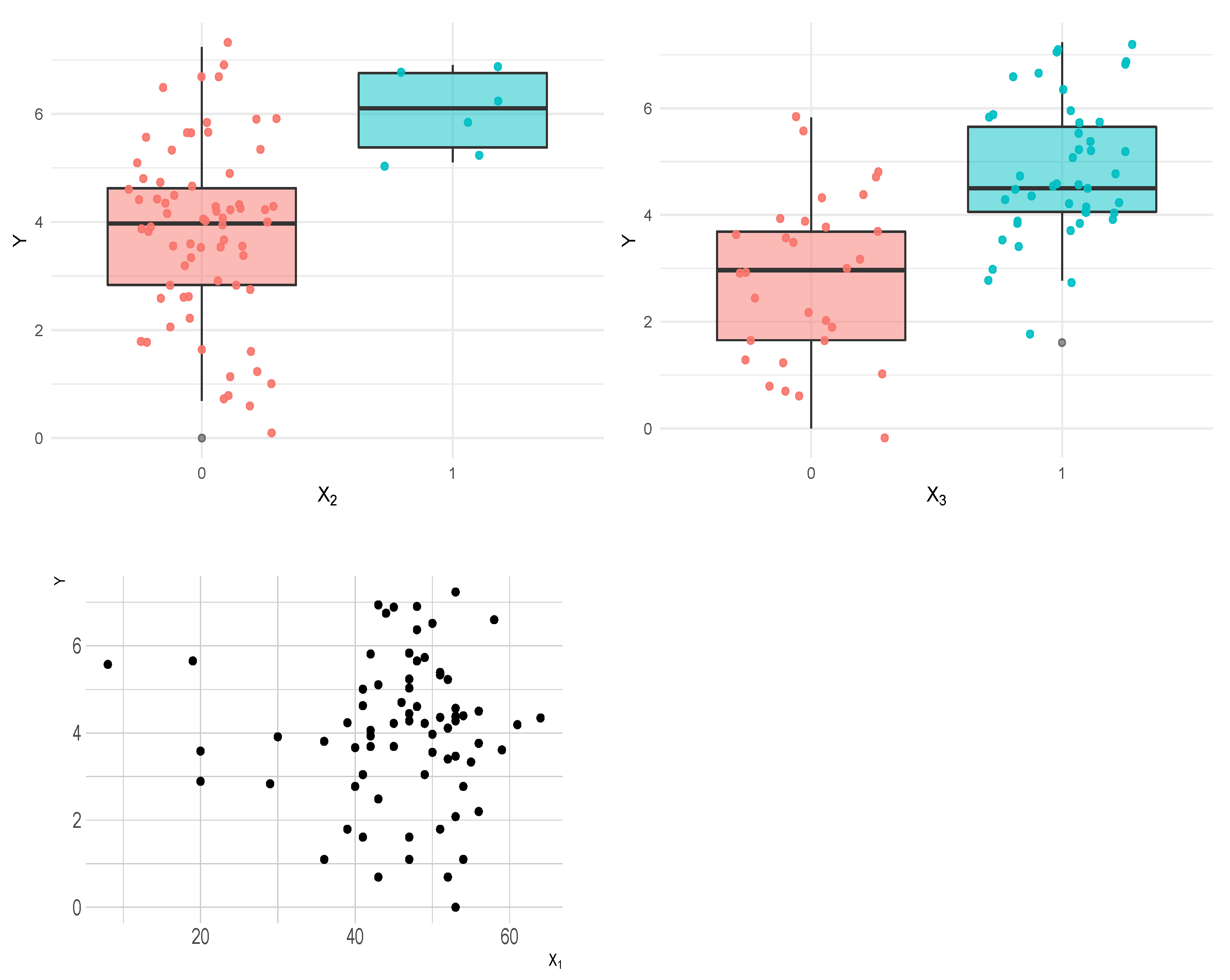
3.1. Application 1: Voltage Data
- Five-parameter log-Topp Leone generated Burr XII (LTLGBXII) [2] distribution;
- Four-parameter log-Weibull Marshall-Olkin Weibull (LWMOW) [23] distribution;
- Four-parameter log-Zografos-Balakrishnan odd log-logistic generalized half-normal (LZBOLL-GHN) [24] distribution;
- Four-parameter log-odd log-logistic Fréchet (LOLLFr) [25] distribution;
- Four-parameter heteroscedastic log-extended generalized odd half-Cauchy Weibull (HLEGOHC-W) distribution; four-parameter log-extended generalized odd half-Cauchy Weibull (LEGOHC-W) distribution; two-parameter heteroscedastic log-Weibull (HLW) [26] distribution;
- Three-parameter log-odd log-logistic generalized half-normal (LOLLGHN) distribution; two-parameter log-generalized half-normal (LGHN) distribution; four-parameter log-beta generalized half-normal (LBGHN) [27] distribution;
- Four-parameter log-gamma extended Weibull (LGE-W) [28] distribution
- Four-parameter log-Kumaraswamy generalized Rayleigh (LKwGR); distribution three-parameter log-exponentiated generalized Rayleigh(LEGR) distribution; two-parameter log-generalized Rayleigh (LGR) [29] distribution;
- Four-parameter exponentiated logistic geometric type I(ELGI) distribution; four-parameter exponentiated logistic geometric type II (ElGII) distribution [30].
3.2. Application 2: Class-H
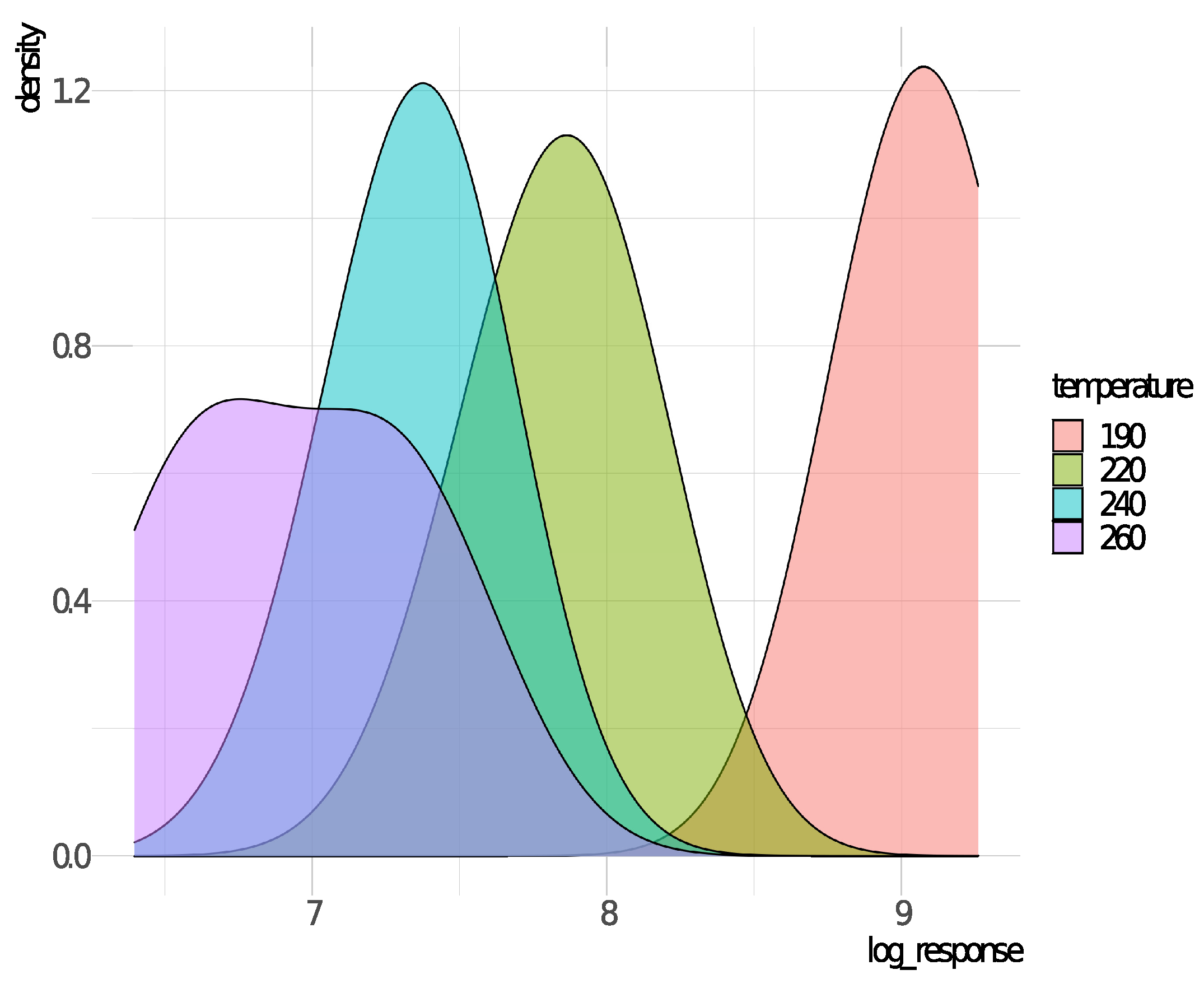
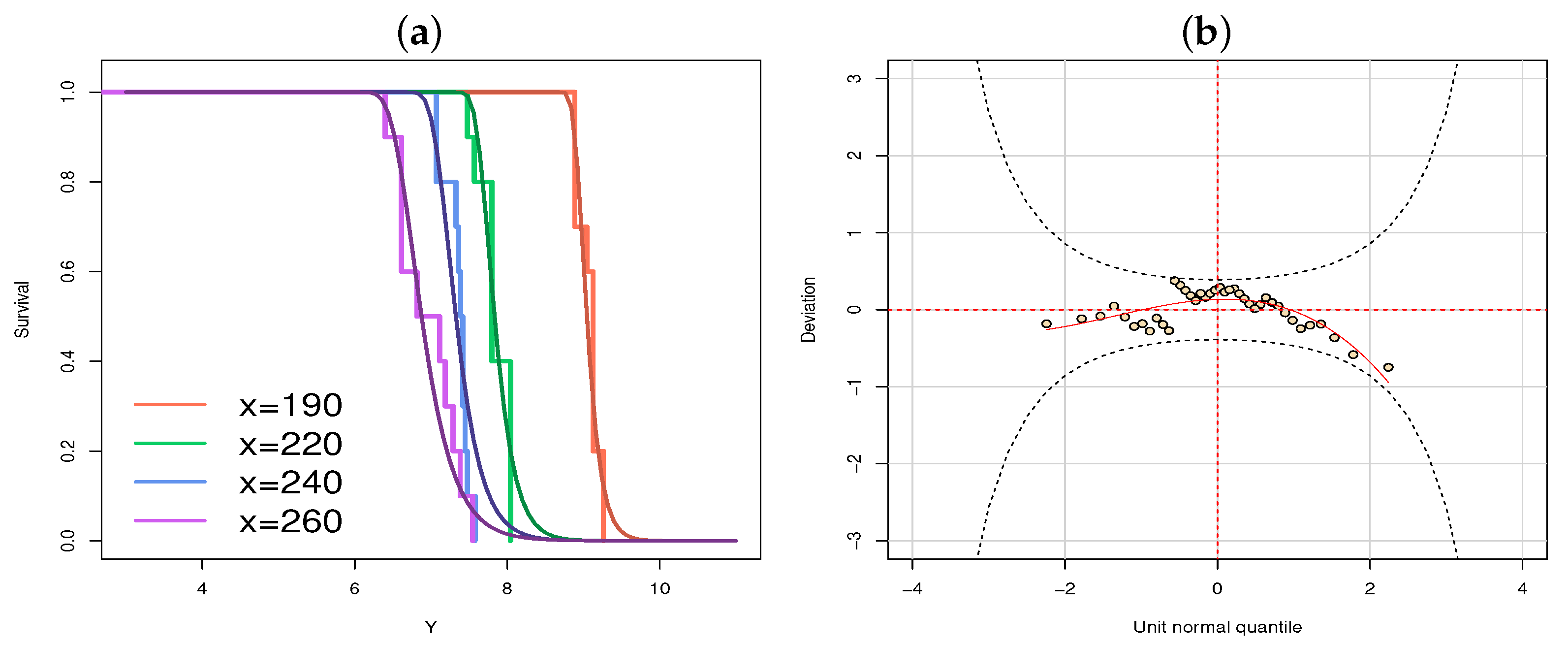
3.3. Application 3: Heart
- Four-parameter log-odd power Lindley Weibull (LOPLW) distribution [37];
- Four-parameter log-extended odd Fréchet generalized half-normal (LEOF-GHN) distribution [38];
- Four-parameter log-extended-exponentioned Weibull (LEE-W) distribution [39];
- Four-parameter log-Burr XII-Weibull (LBXII-W) distribution [40];
- Four-parameter log-log-gamma generated-Weibull (LLGG-W) distribution [41];
- Four-parameter log-Topp-Leone odd log-logistic-Weibull (LTLOLL-W) distribution [42];
- Three-parameter log-odd log-logistic Weibull (LOLLW) distribution [43].
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Altun, E.; Korkmaz, M.Ç.; Pescim, R.R.; Afify, A.Z.; Yousof, H.M. The xgamma Family: Censored Regression Modelling and Applications. Revstat. Stat. J. 2020, 18, 593–612. [Google Scholar]
- Yousof, H.M.; Altun, E.; Rasekhi, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Hamedani, G.G.; Ali, M.M. A new lifetime model with regression models, characterizations and applications. Commun. Stat. Simul. C 2019, 48, 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.C.; Altun, E.; Alizadeh, M.; Yousof, H.M. A new flexible lifetime model with log-location regression modeling, properties and applications. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 2019, 22, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.Z.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Bourguignon, M.; Ortega, E.M.M. Properties of the transmuted Burr XII distribution, regression and its applications. J. Data Sci. 2018, 16, 485–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, M.Ç.; Altun, E.; Yousof, H.M.; Hamedani, G.G. The Hjorth’s IDB generator of distributions: Properties, characterizations, regression modeling and applications. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 2020, 19, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2005, 54, 507–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Heller, G.Z.; De Bastiani, F. Distributions for Modeling Location, Scale and Shape: Using GAMLSS in R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kneib, T. Beyond mean regression. Stat. Model. 2013, 13, 275–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Wedderburn, R.W.M. Generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A (Gen.) 1972, 135, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.J.; Tibshirani, R.J. Generalized Additive Models; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Rigby, R.A.; Heller, G.Z.; Voudouris, V.; De Bastiani, F. Flexible Regression and Smoothing: Using GAMLSS in R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eilers, P.H.; Marx, B.D. Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties. Stat. Sci. 1996, 11, 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, P.H.C.; Marx, B.D.; Durbán, M. Twenty years of P-splines. SORT 2015, 39, 149–186. [Google Scholar]
- Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Rigby, R.A. Generalized additive models for location scale and shape (GAMLSS) in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 23, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Stasinopoulos, M.; Rigby, B.; Mortan, N. gamlss.cens: Fitting an Interval Response Variable Using ‘gamlss.family’ Distributions, R Package Version 5.0-1; 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gamlss.cens (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Ramires, T.G.; Nakamura, L.R.; Righetto, A.J.; Pescim, R.R.; Mazucheli, J.; Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. Validation of stepwise-based procedure in GAMLSS. J. Data Sci. 2021, 19, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buuren, S.; Fredriks, M. Worm plot: A simple diagnostic device for modelling growth reference curves. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 1259–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, P.K.; Smyth, G.K. Randomized quantile residuals. J. Comput. Graph Stat. 1996, 5, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, J.F. Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, M.Ç.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Yousof, H.M.; Pescim, R.R.; Afify, A.Z.; Nadarajah, S. The Weibull Marshall-Olkin family: Regression model and application to censored data. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2019, 48, 4171–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, E.; Yousof, H.M.; Hamedani, G.G. A new generalization of generalized half-normal distribution: Properties and regression models. J. Stat. Dist. Appl. 2018, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousof, H.M.; Altun, E.; Hamedani, G.G. A new extension of Fréchet distribution with regression models, residual analysis and characterizations. J. Data Sci. 2018, 16, 743–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Ramires, T.G.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Alizadeh, M. The new family of distributions and applications in heteroscedastic regression analysis. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 2017, 16, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescim, R.R.; Ortega, E.M.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Alizadeh, M. A new log-location regression model: Estimation, influence diagnostics and residual analysis. J. Appl. Stat. 2017, 44, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Nadarajah, S.; Ortega, E.M.; Ramires, T.G. An alternative two-parameter gamma generated family of distributions: Properties and applications. Hacet. J. Math. Stat. 2016, 47, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.E.; da-Silva, C.Q.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Ortega, E.M.M. A new lifetime model: The Kumaraswamy generalized Rayleigh distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2014, 84, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, N.V.R.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Cordeiro, G.M. The exponentiated-log-logistic geometric distribution: Dual activation. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2016, 45, 3838–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W.B. Accelerated Testing: Statistical Models, Test Plans, and Data Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Popović, B.V.; Pescim, R.R. The Lomax generator of distributions: Properties, minification process and regression model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 247, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Tiensuwan, M. The beta transmuted Weibull distribution. Austrian J. Stat. 2014, 43, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Gomes, A.E.; da-Silva, C.Q.; Ortega, E.M.M. The beta exponentiated Weibull distribution. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2013, 83, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Famoye, F.; Olumolade, O. Beta-Weibull distribution: Some properties and applications to censored data. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2007, 6, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Prentice, R.L. The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, M.C.; Altun, E.; Yousof, H.M.; Hamedani, G.G. The odd power Lindley generator of probability distributions: Properties, characterizations and regression modeling. Int. J. Stat. Probab. 2019, 8, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousof, H.M.; Rasekhi, M.; Altun, E.; Alizadeh, M. The extended odd Fréchet family of distributions: Properties, applications and regression modeling. Int. J. Math. Comput. 2019, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Afshari, M.; Hosseini, B.; Ramires, T.G. Extended exp-G family of distributions: Properties, applications and simulation. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2018, 49, 1730–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Yousof, H.M.; Ramires, T.G.; Ortega, E.M.M. The Burr XII system of densities: Properties, regression model and applications. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2018, 88, 432–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, G.M.; Bourguignon, M.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Ramires, T.G. General mathematical properties, regression and applications of the log-gamma-generated family. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 2018, 47, 1050–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, E.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Yousof, H.M.; Alizadeh, M.; Silva, G.O. The Topp-Leone odd log-logistic family of distributions. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2017, 87, 3040–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.N.D.; Ortega, E.M.M.; Cordeiro, G.M. The log-odd log-logistic Weibull regression model: Modelling, estimation, influence diagnostics and residual analysis. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2016, 86, 1516–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | df | Model | df | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG (GAMLSS) | 5.5 | 157.6 | 168.6 | LGE-W | 5 | 168.6 | 179.1 |
| HLEGOHC-W | 6 | 161.3 | 173.9 | HLW | 4 | 171.4 | 179.8 |
| RG (pGAMLSS) | 4 | 162.1 | 170.5 | log-Weibull | 3 | 173.4 | 179.7 |
| LOLLFr | 4 | 164.3 | 172.7 | LWMOW | 5 | 173.5 | 184.0 |
| LEGOHC-W | 5 | 165.6 | 176.1 | LKwGR | 5 | 177.4 | 187.8 |
| LZBOLL-GHN | 5 | 166.2 | 176.7 | LGHN | 3 | 178.8 | 185.1 |
| LOLLGHN | 4 | 166.4 | 174.8 | LGR | 3 | 179.5 | 185.7 |
| ELGI | 5 | 166.7 | 177.2 | LEGR | 4 | 180.5 | 188.8 |
| LBGHN | 5 | 167.1 | 177.5 | ELGII | 5 | 187.3 | 197.8 |
| LTLGBXII | 6 | 168.4 | 180.9 |
| Model | df | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RG (GAMLSS) | 5.3 | 4.29 | 11.0 |
| LLW | 5 | 13.8 | 22.2 |
| RG (pGAMLSS) | 4 | 16.6 | 23.3 |
| LBEW | 6 | 16.9 | 27.0 |
| LBTW | 6 | 18.5 | 28.6 |
| LBW | 5 | 18.7 | 27.2 |
| log-Weibull | 3 | 22.4 | 27.5 |
| Model | df | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LEOF-GHN | 8 | 334.3 | 355.3 |
| RG (pGAMLSS) | 7 | 335.8 | 354.2 |
| LOPLW | 8 | 338.4 | 359.5 |
| LEE-W | 7 | 343.3 | 361.8 |
| LBXII-W | 7 | 343.3 | 361.8 |
| LTLOLL-W | 8 | 345.3 | 366.4 |
| LLGG-W | 7 | 345.7 | 364.1 |
| LOLLW | 6 | 347.5 | 363.4 |
| log-Weibull | 5 | 353.4 | 366.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramires, T.G.; Nakamura, L.R.; Righetto, A.J.; Carvalho, R.J.; Vieira, L.A.; Pereira, C.A.B. Comparison between Highly Complex Location Models and GAMLSS. Entropy 2021, 23, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23040469
Ramires TG, Nakamura LR, Righetto AJ, Carvalho RJ, Vieira LA, Pereira CAB. Comparison between Highly Complex Location Models and GAMLSS. Entropy. 2021; 23(4):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23040469
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamires, Thiago G., Luiz R. Nakamura, Ana J. Righetto, Renan J. Carvalho, Lucas A. Vieira, and Carlos A. B. Pereira. 2021. "Comparison between Highly Complex Location Models and GAMLSS" Entropy 23, no. 4: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23040469
APA StyleRamires, T. G., Nakamura, L. R., Righetto, A. J., Carvalho, R. J., Vieira, L. A., & Pereira, C. A. B. (2021). Comparison between Highly Complex Location Models and GAMLSS. Entropy, 23(4), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23040469








