Double-Layer Micro Porous Media Burner from Lean to Rich Fuel Mixture: Analysis of Entropy Generation and Exergy Efficiency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
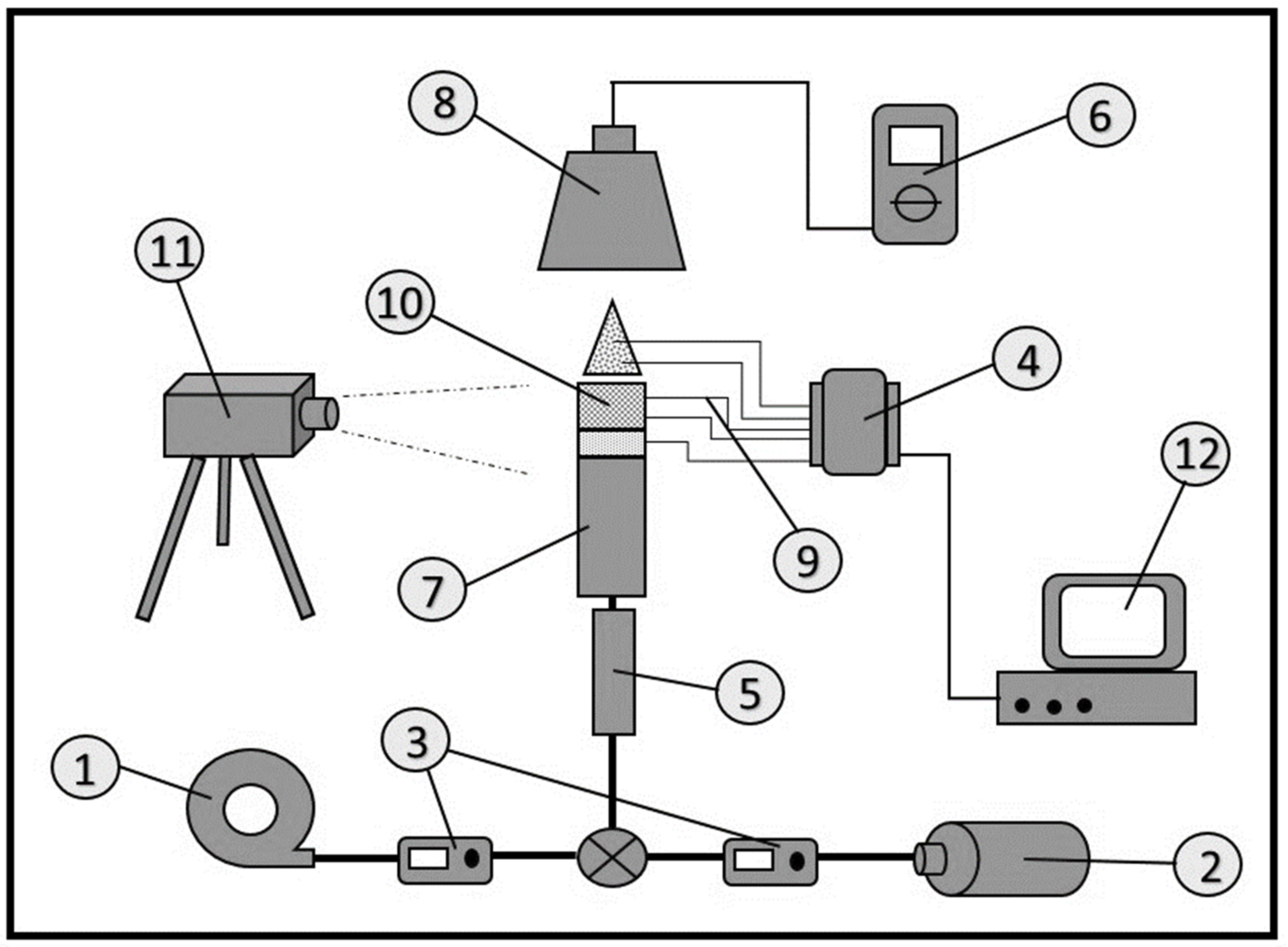
2.1. Experimental Setup and Materials
2.2. Parameter Studies
2.3. Thermal Efficiency Measurement and Second Law of Thermodynamics Data Calculation
2.4. Analysis of Uncertainty
3. Results and Discussions
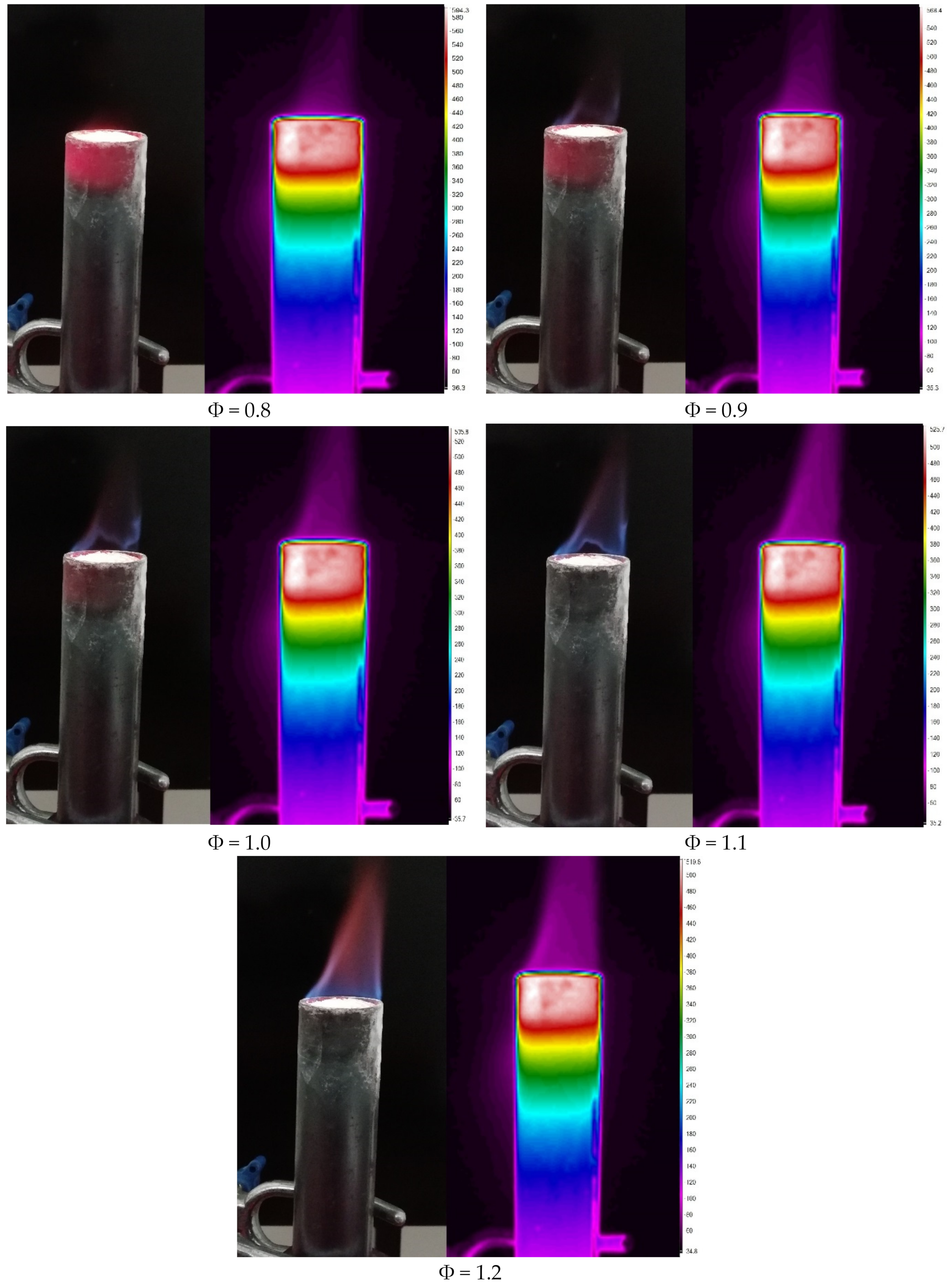
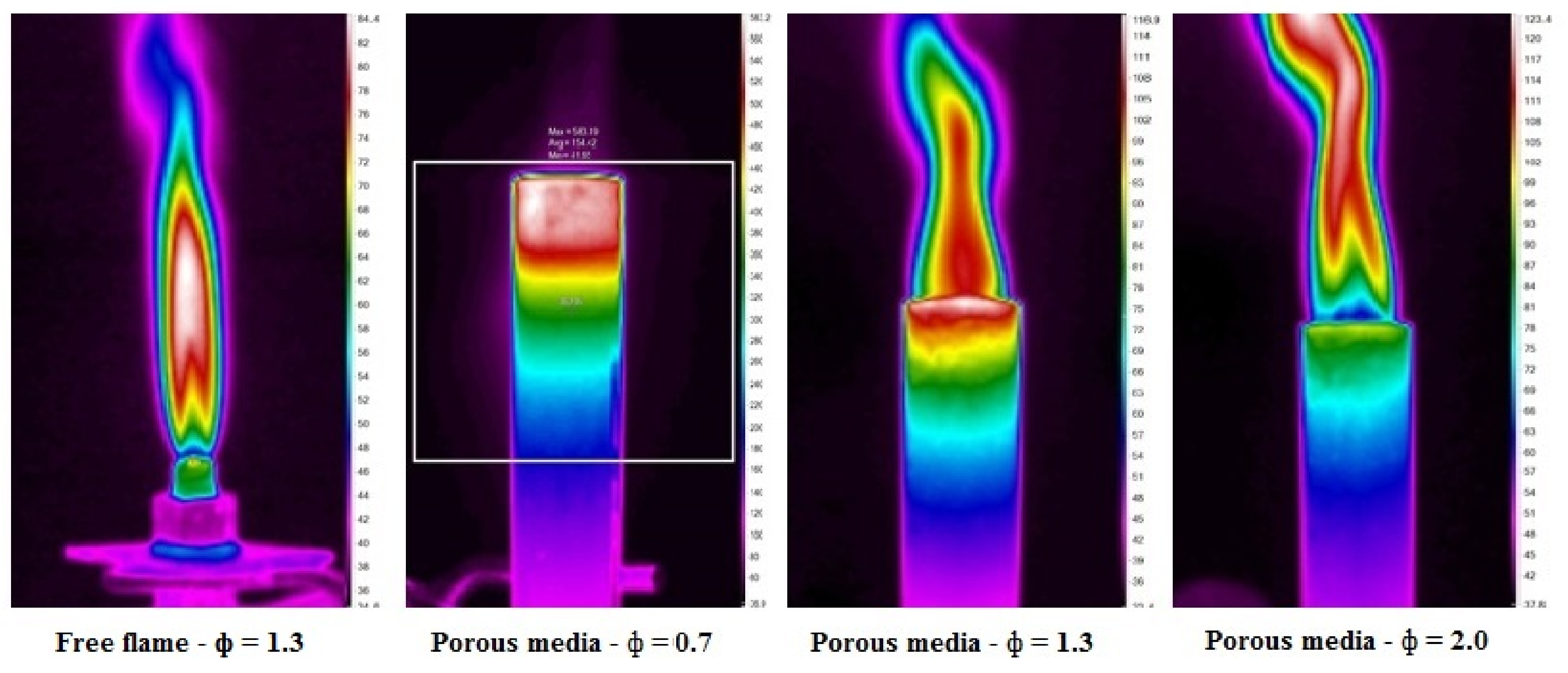
3.1. Flame Stabilization and Thermal Imager
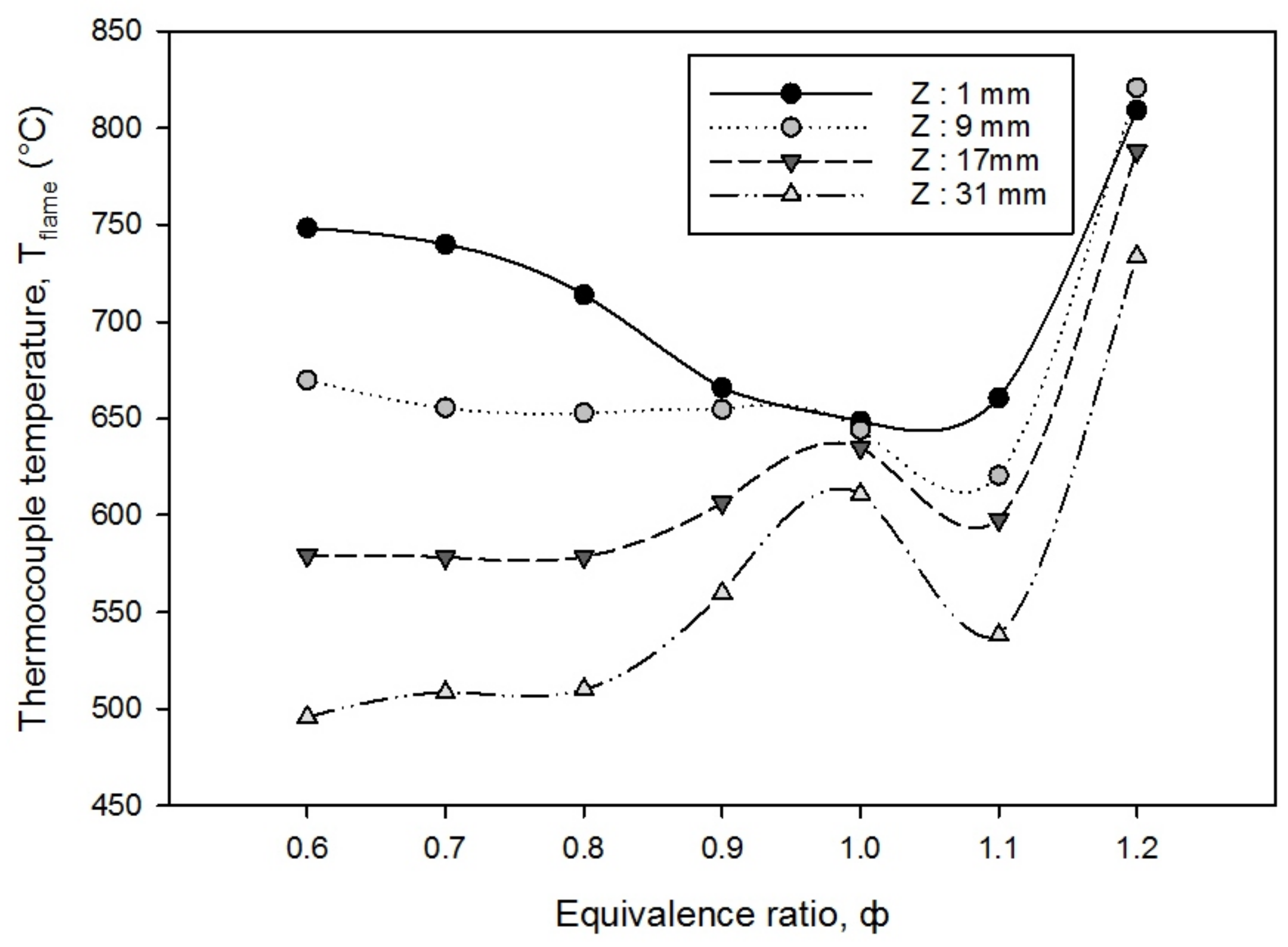
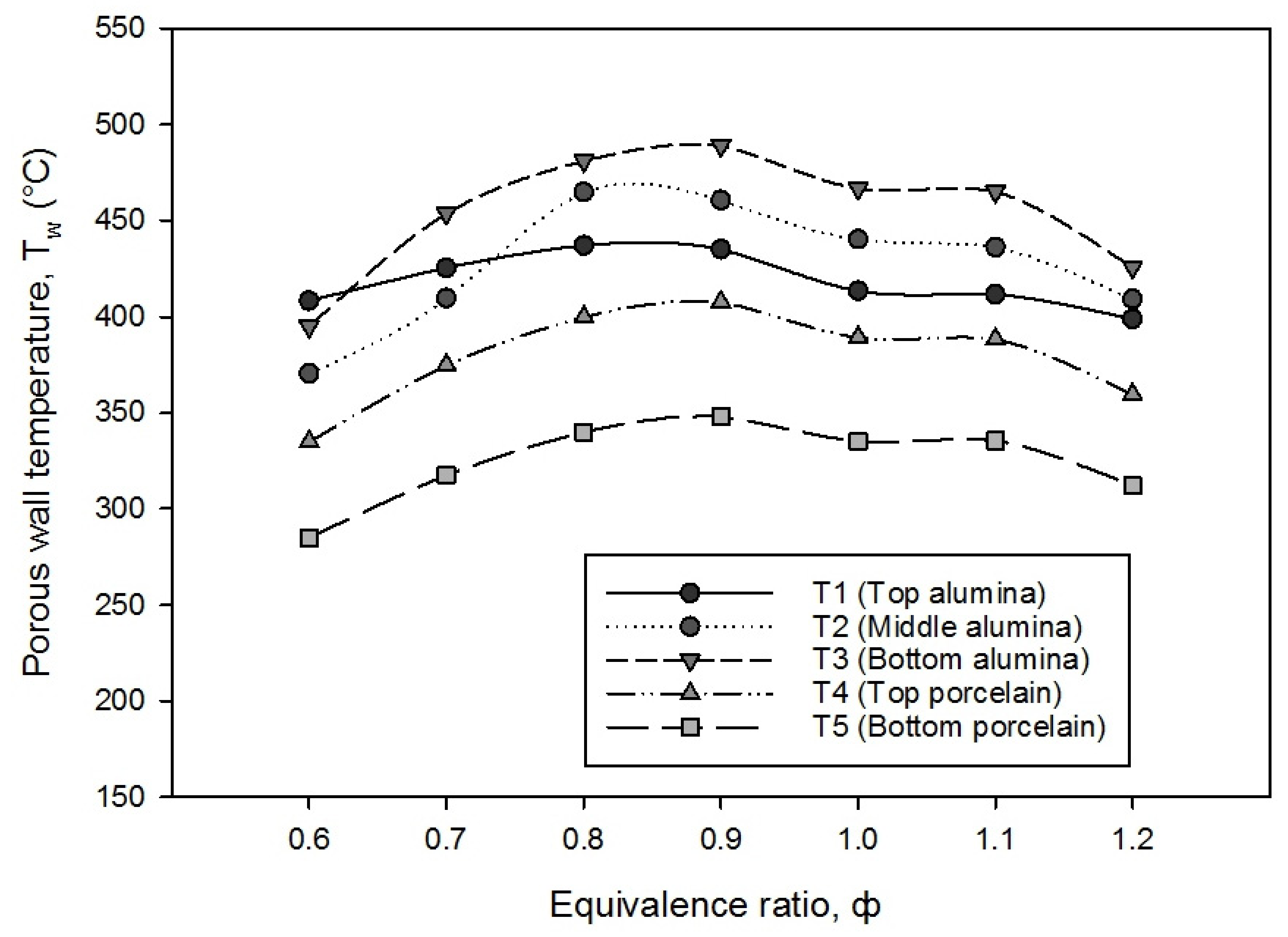
3.2. Temperature Distributions of PMB
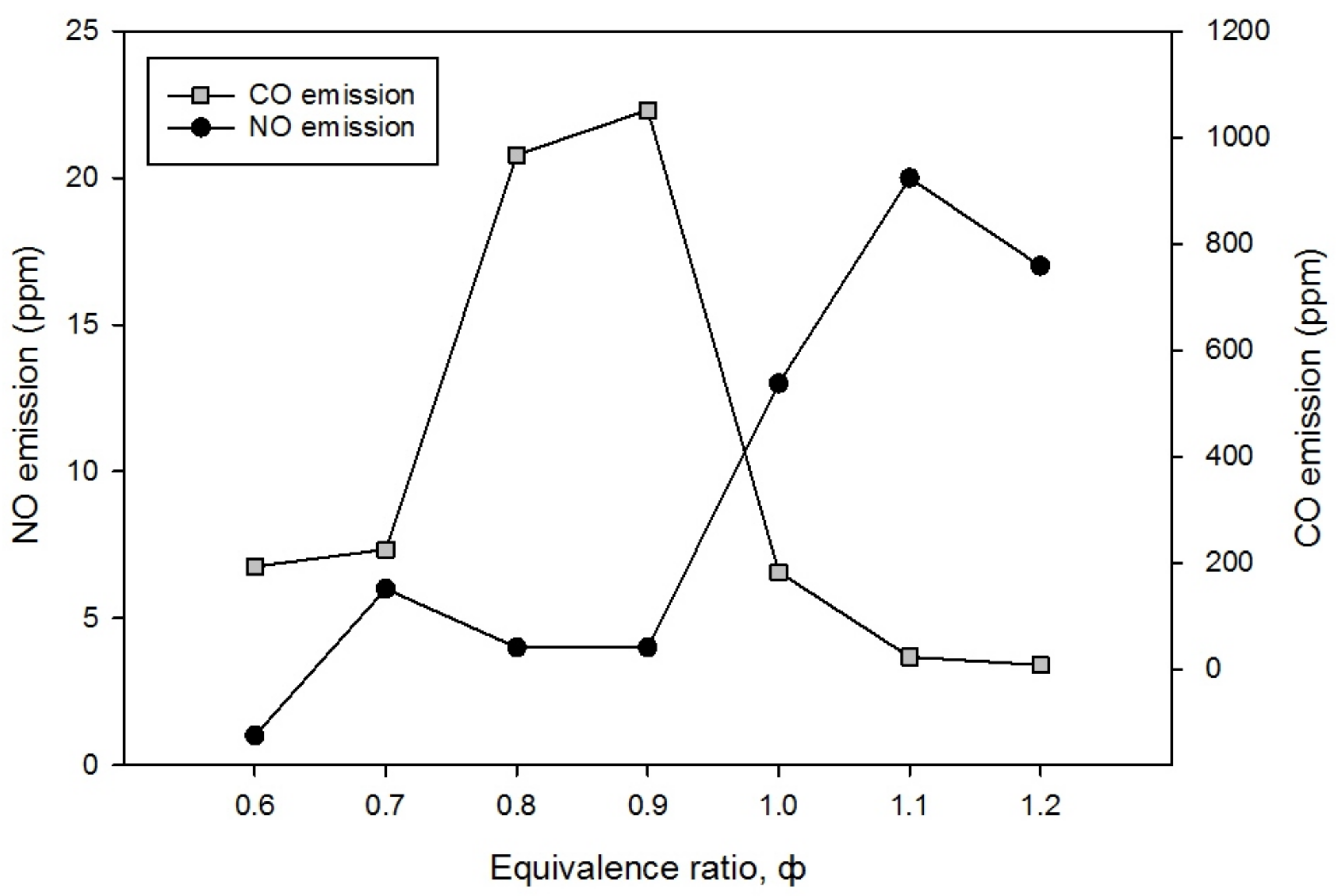
3.3. The Characteristics of CO and NO Emissions
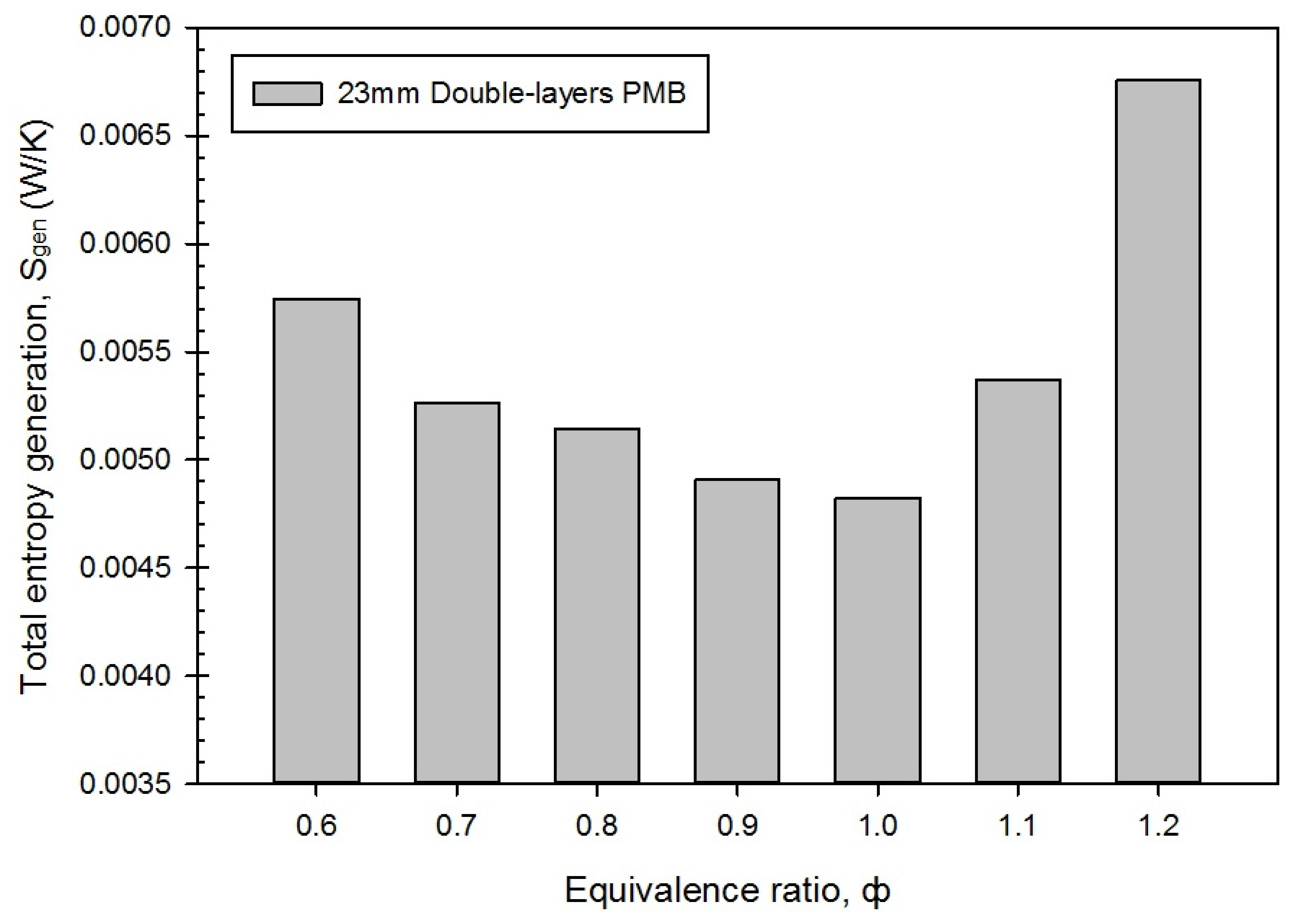
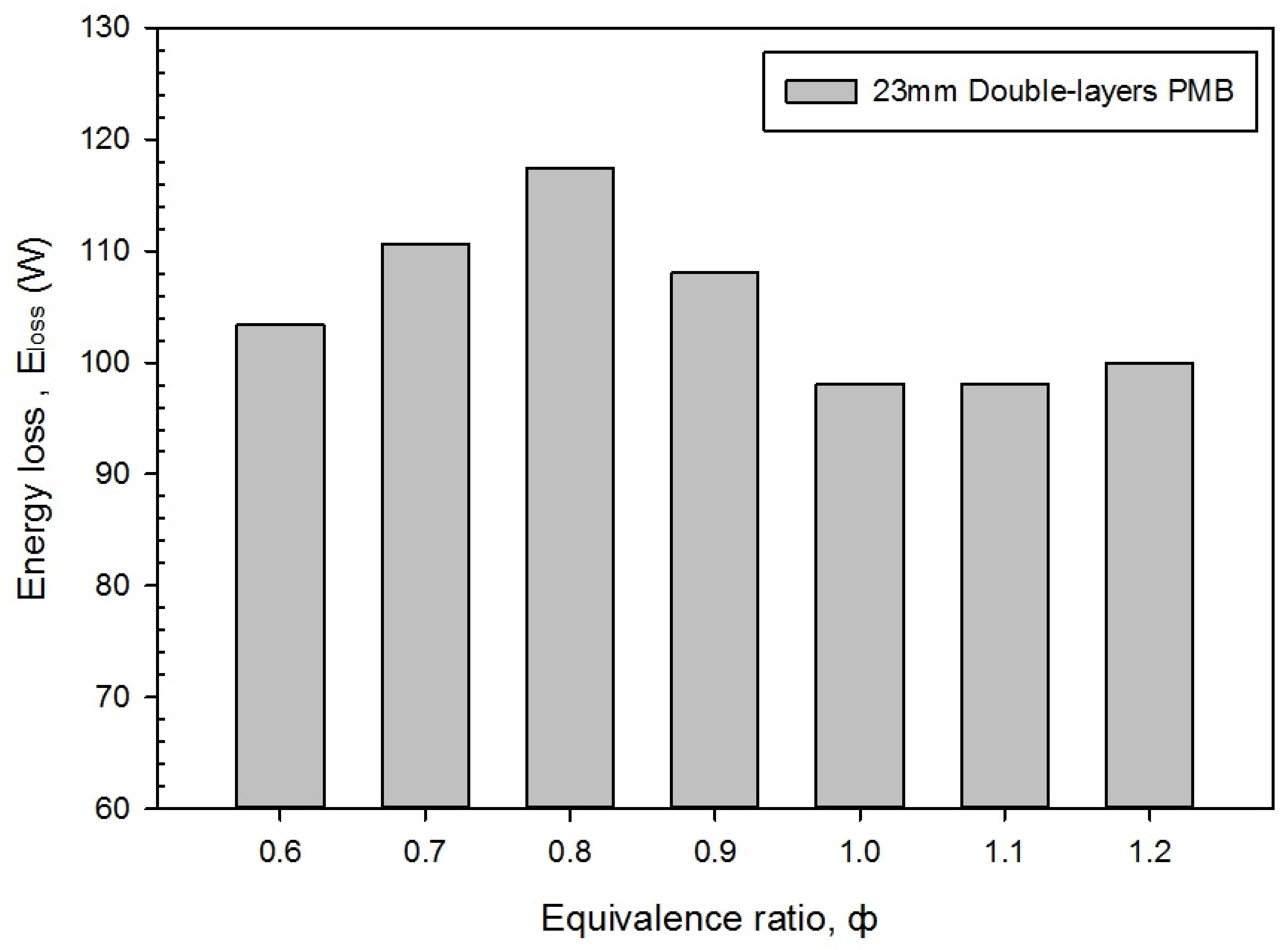
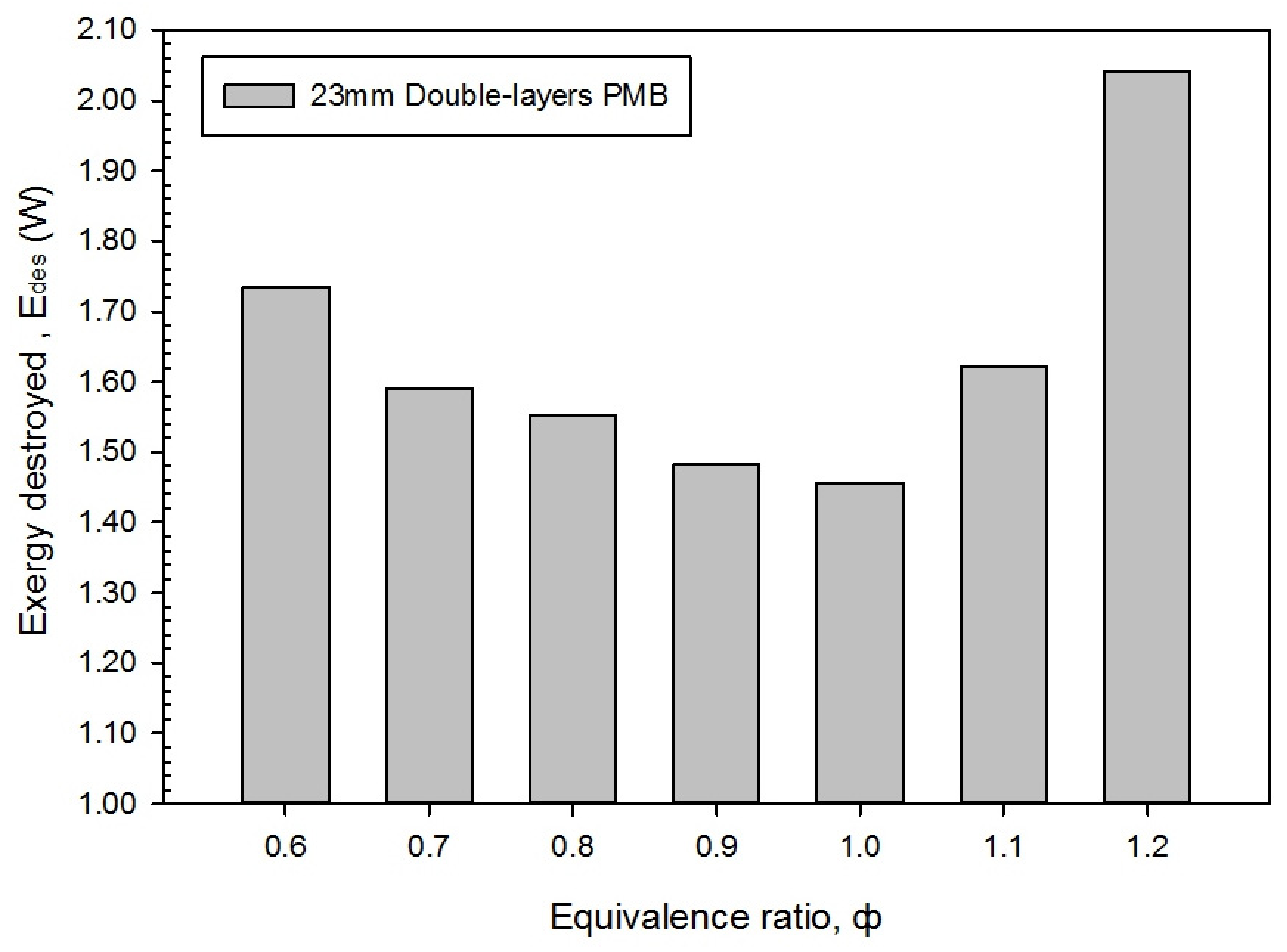
3.4. Entropy Generation Rate, Energy Loss and Exergy Destroyed in Different Equivalence Ratio
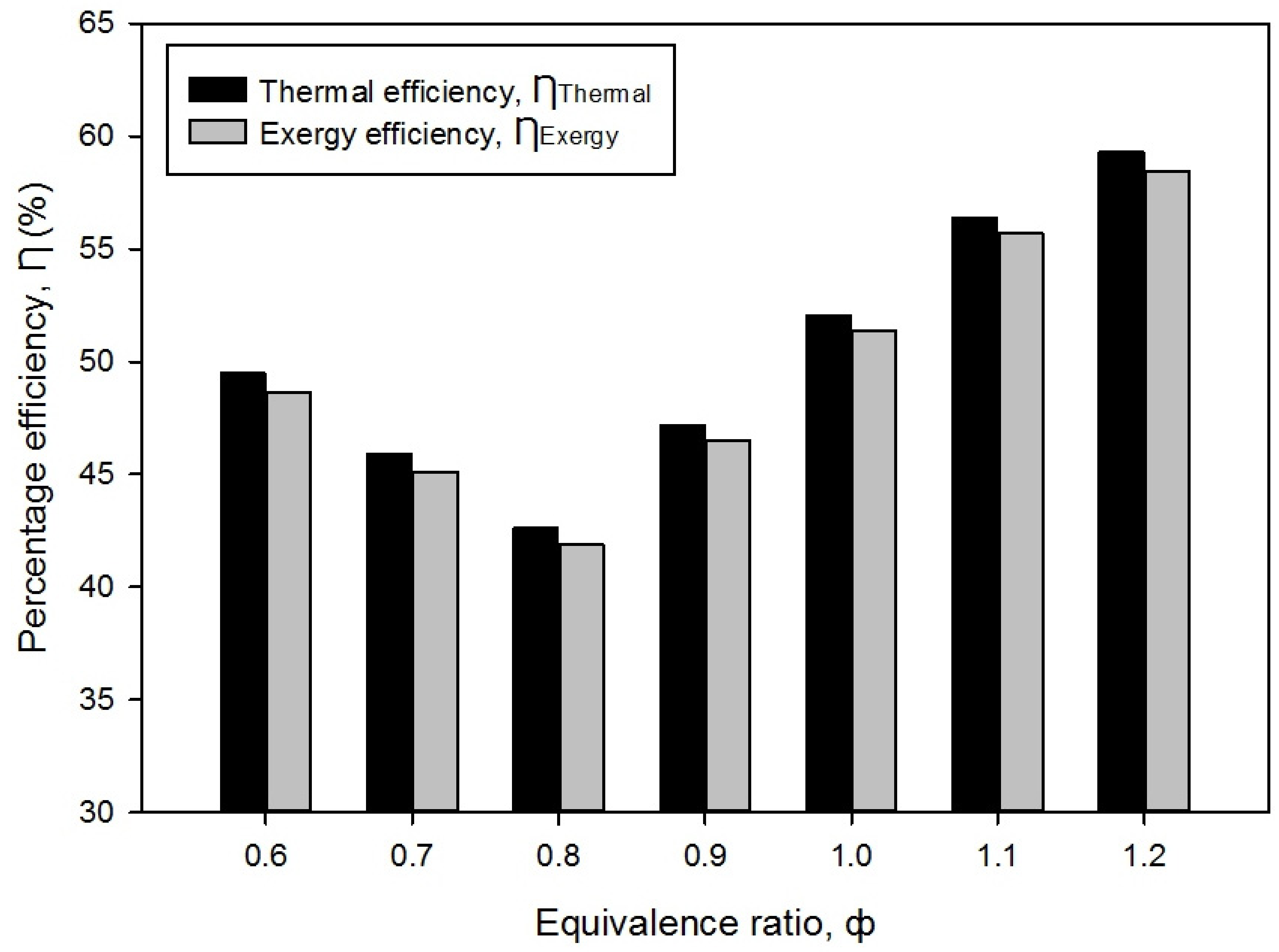
3.5. Thermal Efficiency and Exergy Efficiency
4. Conclusions
- The effects of the equivalence ratio and double-layer porous media from lean to rich mixtures has significant impact on the thermal and exergy efficiency, and therefore the flame stability and temperature change as equivalence ratio increases.
- The results demonstrated that the submerged flame occurred in a lean mixture inside a double-layer PMB with a reaction zone, resulting in a red heat wall burner.
- The maximum flame temperature ranged between 495.69 °C and 820.95 °C with the variations in the equivalence ratio, while porous wall temperature was found to be almost constant between 287.08 °C and 436.16 °C.
- The maximum overall thermal and exergy efficiencies are 59.30% and 58.47% at rich combustion. Moreover, the PMB operates at the optimal combustion at ϕ = 1.0, and produces the lowest entropy generation rate, energy loss, and exergy destroyed.
- Carbon monoxide, CO emission at ϕ = 0.8 and 0.9 rise significantly which indicated an incomplete combustion which cannot be regarded as an acceptable limit for human health because it could be seriously hazardous.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghorashi, S.A.; Hashemi, S.A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Mollamahdi, M. Experimental study on pollutant emissions in the novel combined porous-free flame burner. Energy 2018, 162, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mishra, S.C.; Mahanta, P. Effect of burner configuration and operating parameters on the performance of the kerosene pressure stove with submerged porous media combustion. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, L.V.; Muthukumar, P. Performance assessment of a porous radiant cook stove fueled with blend of waste vegetable oil (WVO) and kerosene. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.K.; Muthukumar, P. Development and testing of energy efficient and environment friendly porous radiant burner operating on liquefied petroleum gas. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 129, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujeebu, M.A.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Abu Bakar, M.Z.; Mohamad, A.A.; Abdullah, M.K. Applications of porous media combustion technology—A review. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, R.W., Jr.; Costa, M.; Catapan, R.C.; Oliveira, A.A.M. Combustion of hydrogen rich gaseous fuels with low calorific value in a porous burner placed in a confined heated environment. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2013, 45, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, J.X.; Shi, J.R.; Liu, X.L. Experimental study on standing wave regimes of premixed H2-air combustion in planar micro-combustor partially filled with porous media. Fuel 2016, 167, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Chidambaram, R.K.; Geo, V.E. An experimental study to analyze influence of porous media combustor on performance and emission characteristics of a DI diesel engine. Fuel 2020, 280, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Feng, M.; Zhao, D.; Shi, B.; Wang, N. Flame stability and combustion characteristics of liquid fuel in a meso-scale burner with porous media. Fuel 2019, 251, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbone, D.E.; Turan, A. Chapter 15—Combustion and Flames. In Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, 2nd ed.; Knovel: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 323–344. [Google Scholar]
- Dagaut, P. Chapter 8—Experiments for kinetic mechanism assessment. Comput. Aided Chem. Eng. 2019, 45, 445–471. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet, N.; Chauveau, C.; Gökalp, I.; Lee, S.-Y.; Santoro, R.J. Characterization of syngas laminar flames using the Bunsen burner configuration. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, Q. Effect of the elevated initial temperature on the laminar flame speed of oxy-methane mixtures. Energy 2018, 147, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Costa, M. laminar burning velocities of CH4/O2/N2 and oxygen-enriched CH4/O2/CO2 flames at elevated pressures measured using the heat flux method. Fuel 2020, 259, 116152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.F.; Yu, R.; Fan, X.Q.; Christensen, M.; Konnov, A.A.; Bai, X.S. Onset of cellular flame instability in adiabatic CH4/O2/CO2 and CH4/air laminar premixed flames stabilized on a flat-flame burner. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurcan, V.; Movileanu, C.; Musuc, A.M.; Mitu, M. Laminar burning velocity of biogas-containing mixtures. A literature review. Processes 2021, 9, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Kum, S.M.; Lee, C.E.; Lee, S. Combustion characteristics and thermal efficiency for premixed porous-media types of burners. Energy 2013, 53, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, C.; Zhao, P.; Ye, T. Experimental study on temperature variation in a porous inert media burner for premixed methane air combustion. Energy 2014, 72, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.S.; Lai, W.H.; Hwang, S.J. Experimental study of the heat recovery rate in a porous medium combustor under different hydrogen combustion modes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 15043–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, H.; Karaca, G.; Tuncer, O.; Karabeyoglu, A. Porous medium based for efficient and clean combustion of ammonia-hydrogen-air systems. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 14775–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Jiaqiang, E.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigation on the effects of wall thickness and porous media on the thermal performance of a non-premixed hydrogen fueled cylindrical micro combustor. Energy Convers. Manage. 2018, 155, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, A.; Yao, H.; Liu, W. A numerical investigation on the effect of the wall thermal conductivity on flame stability and combustion efficiency in a mesoscale channel filled with fibrous porous medium. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 101, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.F.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, H.F.; Tang, A.K.; Xue, H. Hydrogen/oxygen premixed combustion characteristics in micro porous media combustor. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansir, I.B.; Nemitallah, M.A.; Habib, M.A.; Khalifa, A.E. Experimental and numerical investigation of flow field and oxy-methane combustion characteristics in a low-power porous-plate reactor. Energy 2018, 160, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, J. Heat recirculation and heat losses in porous micro-combustor: Effects of wall and porous media properties and combustor dimensions. Energy 2021, 220, 119772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Xie, F.; Huang, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhu, X. Effects of bluff-body on the thermal performance of micro thermophotovoltaic system based on porous media combustion. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 174, 115281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Gao, H.; Feng, X.; Tao, W. Premixed combustion in a porous burner with different fuels. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2014, 187, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqiang, E.; Zou, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, H. Effect of inlet pressure on wall temperature and exergy efficiency of the micro-cylindrical combustor with a step. J. Appl. Energy 2016, 175, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Yang, W.; Chua, K.J. Entropy generation analysis of H2/air premixed flame in micro-combustors with heat recuperation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 98, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Yang, W.; Teng, J. Entropy generation analysis of fuel lean premixed CO/H2/air flames. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 5210–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurkar, S.Y.; Mishra, D.P. Effects of the wall thermal conductivity on entropy generation and exergy losses in a H2-air premixed flame microcombustor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 15851–15859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurkar, S.Y.; Mishra, D.P. Numerical analysis of entropy generation in an annular microcombustor using multistep kinetics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 52, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acampora, L.; Marra, F.S. Second law thermodynamic analysis of syngas premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 12185–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Entropy generation analysis of fuel premixed CH4/H2/air flames using multistep kinetics. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 20744–20752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.; Jiaqiang, E. Numerical and entropy studies of hydrogen-fuelled micro-combustors with different geometric shaped ribs. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 7692–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, I.; Ajam, H. A theoretical study of entropy generation of the combustion phenomenon in the porous media burner. Energy 2019, 188, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Mahanta, P.; Mishra, S.C. Usability of the burner in kerosene pressure stove: An experimental investigation aided by energy and exergy analyses. Energy 2016, 103, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, U.; Chakraborty, S.; Som, S.K. Prediction of flame speed and exergy analysis of premixed flame in a heat recirculating cylindrical micro combustor. Energy 2017, 126, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, E.; Jafarmadar, S. The numerical study of the energy and exergy efficiencies of the micro-combustor by the internal micro-fin for thermophotovoltaic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; He, Z. Effects of rectangular rib on exergy efficiency of a hydrogen-fueled micro combustor. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 10155–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Tang, A.; Cai, T.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, C. Entropy generation analysis of combustion process adopting blended propane/hydrogen fuels in micro-combustor. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process. Intensif. 2019, 143, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Zhao, D.; Karimi, N. Optimizing thermal performance and exergy efficiency in hydrogen-fueled meso-combustor by applying a bluff-body. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janvekar, A.A.; Miskam, M.A.; Abas, A.; Zainal, Z.A.; Juntakan, T.; Abdullah, M.Z. Effects of the preheat layer thickness on surface/submerged flame during porous media combustion of micro burner. Energy 2017, 122, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goa, H.B.; Qu, Z.G.; He, Y.L.; Tao, W.Q. Experimental study of combustion in a double-layer burner packed with alumina pellets of different diameters. J. Appl. Energy 2012, 100, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamamre, Z.; Diezinger, S.; Talukdar, P.; Von Issendorff, F.; Trimis, D. Combustion of low calorific gases from landfills and waste pyrolysis using porous medium burner technology. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2006, 84, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimis, D.; Durst, F. Combustion in a porous medium—Advances and applications. Comb. Sci. Technol. 1996, 121, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.C.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Mazlan, N.M.; Mustafa, K.F. Entropy generation and exergy analysis of premixed fuel-air combustion in micro porous media burner. Entropy 2020, 22, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Jiaqiang, E.; Yang, W.M.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, T.; Qiu, R. Effect analysis on combustion and thermal performance enhancement of a nozzle-inlet micro tube fueled by the premixed hydrogen/air. Energy 2018, 160, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Authors | Equivalence Ratio | Fuel/Oxidizer | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peng et al. [21] | 0.9 < ϕ < 1.1 | H2/Air | Inserting porous media or increasing the outer wall thickness can improve heat transfer in a micro-combustor and affecting flame stability. |
| Liu et al. [22] | 0.5 < ϕ < 0.9 | CH4/Air | An increase in wall thermal conductivity, both the upper and lower limits for the standing wave regime rise. |
| Pan et al. [23] | ϕ = 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 | H2/O2 | Effects of equivalence ratio, mixture flow rate, and porosity can increase the combustion efficiency. |
| Mansir et al. [24] | 0.4 < ϕ < 1.0 | CH4-CO2/O2 | The development of an enhanced mixing zone adjacent to the porous plate improved flame anchoring and stability. |
| Li et al. [25] | ϕ = 1.0 | H2/Air | Heat recirculation through the combustor wall decreases as combustor dimension decreases. |
| Qian et al. [26] | ϕ = 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2 | H2/Air | The porous media combustor with the bluff-body performs better in terms of system efficiency and blowout limit. |
| Qu et al. [27] | 0.25 < ϕ < 0.35 0.55 < ϕ < 0.70 | CH4/Air C3H8/Air H2/Air | The flame stability limits of methane, propane, and hydrogen increase as the equivalence ratio arise. |
| Equivalence Ratio, ϕ | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butane fuel (liters/min) | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.12 | ||||
| Air (liters/min) | 5.16 | 4.42 | 3.88 | 3.44 | 3.10 | ||
| Flame velocity, SL (m/s) | 0.2086 | 0.1805 | 0.1564 | 0.1404 | 0.1284 | 0.1288 | 0.1292 |
| Reynolds number, Re | 684 | 592 | 513 | 461 | 421 | 423 | 424 |
| Peclet Number, Pe | |||||||
| Alumina foam | 78.93 | 68.30 | 59.18 | 53.12 | 48.58 | 48.74 | 48.89 |
| Porcelain foam | 23.99 | 20.76 | 17.99 | 16.15 | 14.77 | 14.82 | 14.86 |
| Variables | Mean, (°C) | Standard Deviation, | Standard Error, | Uncertainty, Un (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermocouple height, Z | Flame temperature, Tflame | |||
| 1 mm | 809.29 | 1.153 | 0.665 | 0.142 |
| 9 mm | 644.12 | 3.747 | 2.163 | 0.582 |
| 17 mm | 634.87 | 3.312 | 2.771 | 0.756 |
| 31 mm | 610.82 | 22.154 | 12.790 | 3.627 |
| Porous wall Temperature, Tw | ||||
| Alumina foam | 370.53 | 8.391 | 4.845 | 2.265 |
| Porcelain foam | 334.93 | 5.444 | 4.086 | 2.113 |
| Parametric Studies | Free Flame [47] | PMB − ϕ = 0.7 | PMB − ϕ = 1.3 [47] | PMB − ϕ = 2.0 [47] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combustion mode | Rich | Lean | Rich | Rich |
| Flame type | Diffusion flame | Submerged flame | Surface flame | Surface flame |
| Flame color | Light blue | Glowing red heat | Blue | Orange |
| Energy produce, Qactual (W) | 152.57 | 93.95 | 191.12 | 344.95 |
| Thermal efficiency (%) | 57.40 | 45.91 | 71.80 | 84.30 |
| Exergy efficiency (%) | 56.48 | 45.13 | 70.95 | 83.47 |
| Max. flame temperature (°C) | 891.38 | 740.05 | 924.82 | 825.54 |
| CO emission (ppm) | 9 | 225 | 11 | 16 |
| NO emission (ppm) | 7 | 6 | 5 | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, N.C.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Mustafa, K.F.; Mazlan, N.M.; Gunnasegaran, P.; Irawan, A.P. Double-Layer Micro Porous Media Burner from Lean to Rich Fuel Mixture: Analysis of Entropy Generation and Exergy Efficiency. Entropy 2021, 23, 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121663
Ismail NC, Abdullah MZ, Mustafa KF, Mazlan NM, Gunnasegaran P, Irawan AP. Double-Layer Micro Porous Media Burner from Lean to Rich Fuel Mixture: Analysis of Entropy Generation and Exergy Efficiency. Entropy. 2021; 23(12):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121663
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Nazmi Che, Mohd Zulkifly Abdullah, Khairil Faizi Mustafa, Nurul Musfirah Mazlan, Prem Gunnasegaran, and Agustinus Purna Irawan. 2021. "Double-Layer Micro Porous Media Burner from Lean to Rich Fuel Mixture: Analysis of Entropy Generation and Exergy Efficiency" Entropy 23, no. 12: 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121663
APA StyleIsmail, N. C., Abdullah, M. Z., Mustafa, K. F., Mazlan, N. M., Gunnasegaran, P., & Irawan, A. P. (2021). Double-Layer Micro Porous Media Burner from Lean to Rich Fuel Mixture: Analysis of Entropy Generation and Exergy Efficiency. Entropy, 23(12), 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23121663









