A Regularization Homotopy Strategy for the Constrained Parameter Inversion of Partial Differential Equations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inversion Model
3. Homotopy Theory
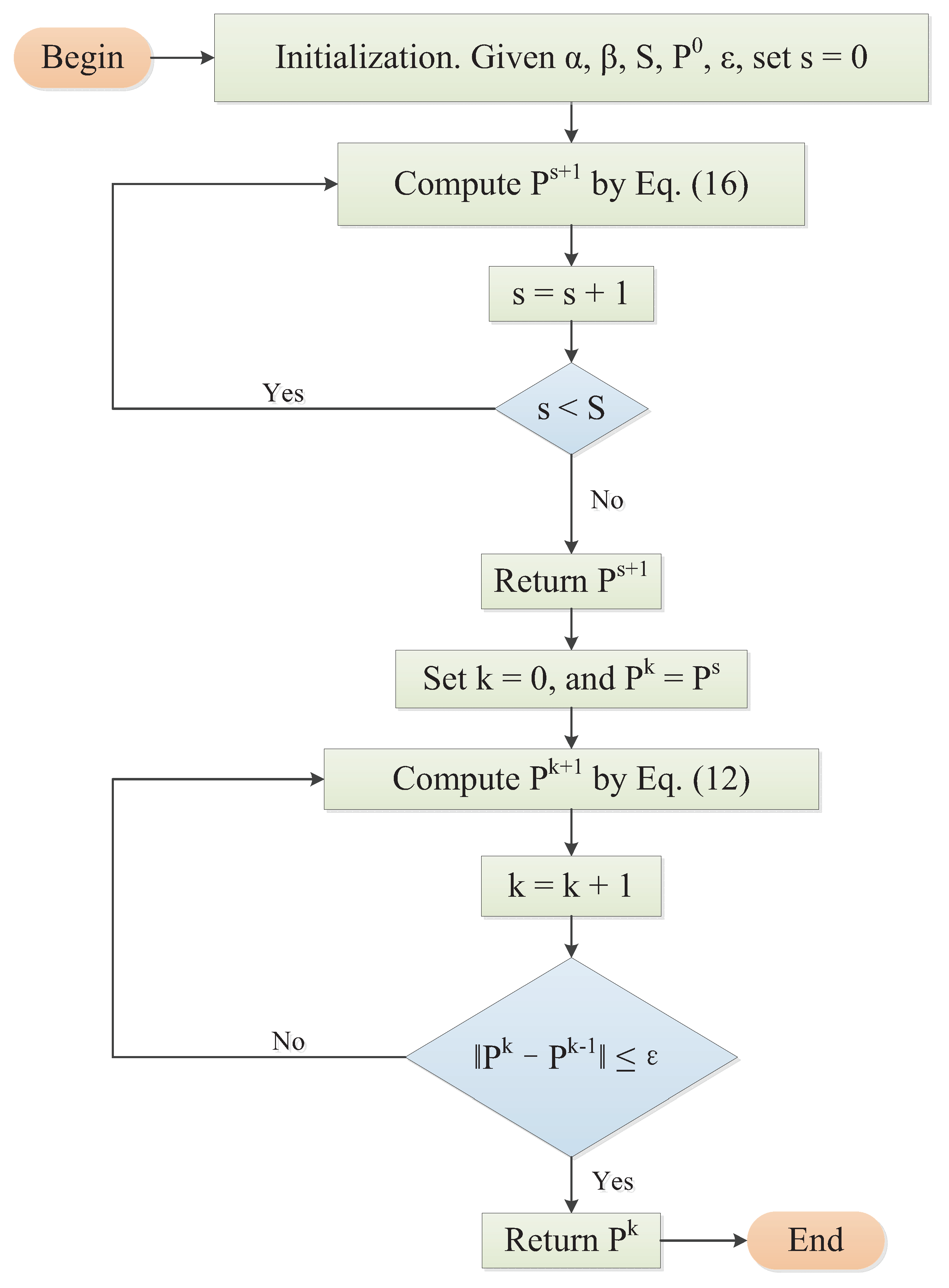
4. Homotopy Strategy
| Algorithm 1: Homotopy method with constraints. |
| 1. Initialization. Given α, β, S, , ε, . |
| 2. Compute by Equation (16). |
| 3. Let and check if then go to Step 2, else if , then return . |
| 4. set and . |
| 5. Compute by Equation (12). |
| 6. Let and check if , then go to Step 5, else if , then return . |
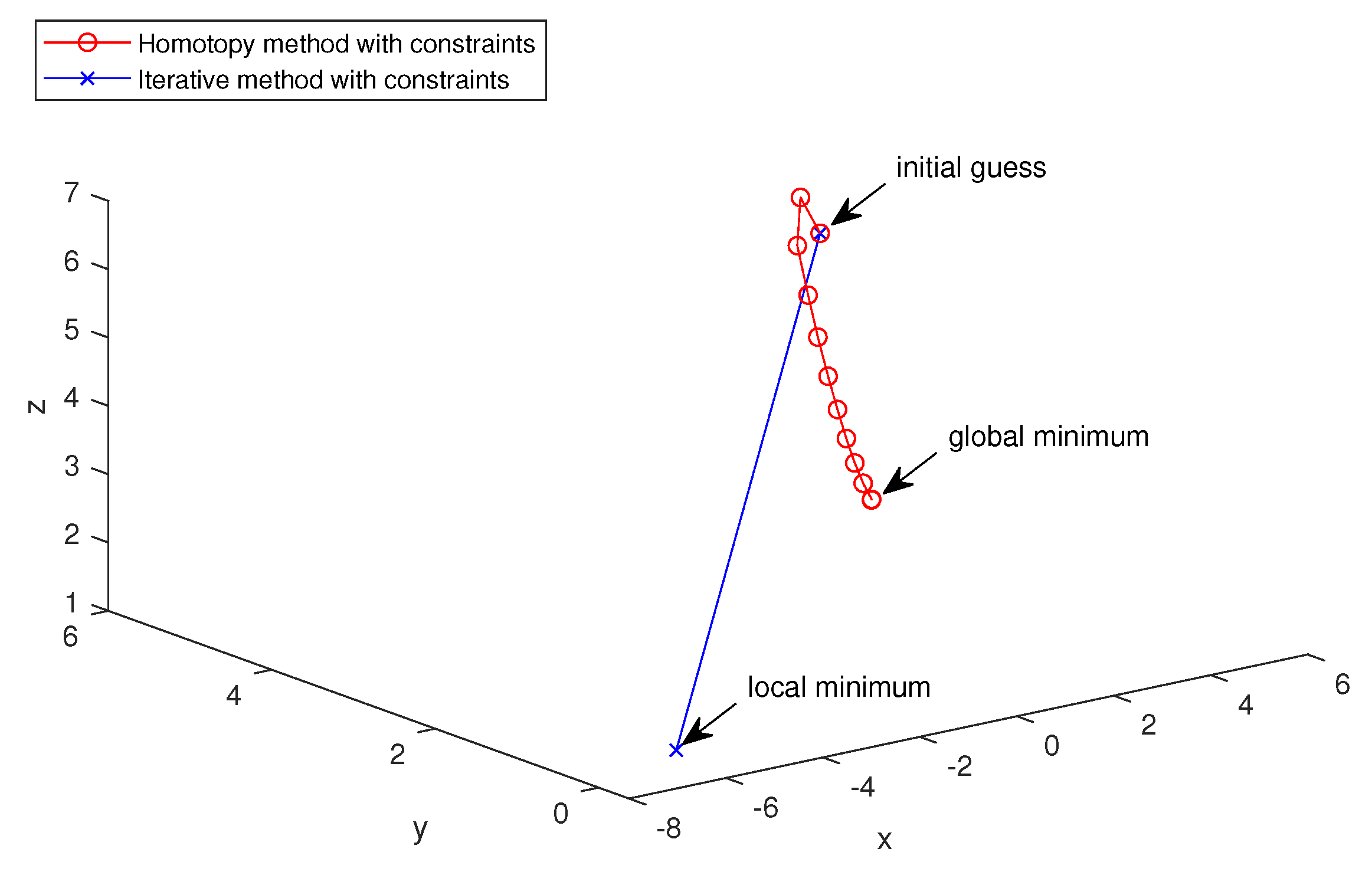
5. An Application
5.1. Mathematical Model
5.2. Numerical Simulations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hume, R.I.; Dingledine, R.; Heinemann, S.F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science 1991, 253, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantola, A. Popper, Bayes and the inverse problem. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, A.; Cox, B.T.; Arridge, S.R.; Goh, H.; Kaipio, J.P.; Tarvainen, T. Direct estimation of optical parameters from photoacoustic time series in quantitative photoacoustic tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, H.; Jin, K.H.; Nguyen, H.Q.; McCann, M.T.; Unser, M. CNN-based projected gradient descent for consistent CT image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grana, D.; Fjeldstad, T.; Omre, H. Bayesian Gaussian mixture linear inversion for geophysical inverse problems. Math. Geosci. 2017, 49, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godio, A.; Santilano, A. On the optimization of electromagnetic geophysical data: Application of the PSO algorithm. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 148, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Araya-Polo, M.; Poggio, T. Deep learning for seismic inverse problems: Toward the acceleration of geophysical analysis workflows. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2021, 38, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Zabaras, N.; Shi, X.; Wu, J. Deep autoregressive neural networks for high-dimensional inverse problems in groundwater contaminant source identification. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 3856–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Izady, A.; Abdalla, O.A.; Amerjeed, M. A surrogate-based sensitivity quantification and Bayesian inversion of a regional groundwater flow model. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.T. Globally convergent homotopy methods: A tutorial. Appl. Math. Comput. 1989, 31, 369–396. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, H.B.; Perozzi, D.J. Fast seismic ray tracing. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 1983, 43, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasco, D.W. Singularity and branching: A path-following formalism for geophysical inverse problems. Geophys. J. Int. 1994, 119, 809–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shidfar, A.; Babaei, A.; Molabahrami, A. Solving the inverse problem of identifying an unknown source term in a parabolic equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, S. An adaptive homotopy method for permeability estimation of a nonlinear diffusion equation. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2013, 21, 585–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hirasawa, K.; Kumamaru, K. A homotopy approach to improving PEM identification of ARMAX models. Automatica 2001, 37, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Han, B. Convergence analysis of the homotopy perturbation method for solving nonlinear ill-posed operator equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 61, 2058–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzberger, C.; Richter, K. Spatially constrained inversion of radiative transfer models for improved LAI mapping from future Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, A.; Bras, R.L. A physically constrained inversion for high-resolution passive microwave retrieval of soil moisture and vegetation water content in L-band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Sadeghi, M.; Ebtehaj, A. Microwave retrievals of soil moisture and vegetation optical depth with improved resolution using a combined constrained inversion algorithm: Application for SMAP satellite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebtehaj, A.; Durand, M.; Tedesco, M. Constrained Inversion of a Microwave Snowpack Emission Model Using Dictionary Matching: Applications for GPM Satellite. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Laterally constrained inversion of helicopter-borne frequency-domain electromagnetic data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 67, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulaimani, S.; Chakiri, S.; Manar, A.; Soulaimani, A.; Miftah, A.; Boujamaoui, M. Gravity and magnetic data processing further constrained inversion for 3D modelling and tonnage calculation. Appl. Earth Sci. 2020, 129, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolon, L.; Mohaghegh, S.D.; Ameri, S.; Gaskari, R.; McDaniel, B. Using artificial neural networks to generate synthetic well logs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2009, 1, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Y. Multidomain petrophysically constrained inversion and geology differentiation using guided fuzzy c-means clustering. Geophysics 2015, 80, ID1–ID18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, M.; Lamiraux, F.; Laumond, J.P. A gradient-based path optimization method for motion planning. Adv. Robot. 2016, 30, 1126–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, T.D.; Rezaei, A.; Linthout, T.; Mollaert, M.; Hemelrijck, D.V.; Paepegem, W.V. A computational compensation method for fabric panels of tensioned membrane structures using a shape optimization method based on gradientless algorithms. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 112, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, D.J. A bidirectional evolutionary structural optimization algorithm for mass minimization with multiple structural constraints. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2019, 118, 93–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakushinskii, A.B. The problem of the convergence of the iteratively regularized Gauss-Newton method. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1992, 32, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Fu, H.S.; Li, Z. A homotopy method for the inversion of a two-dimensional acoustic wave equation. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2005, 13, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

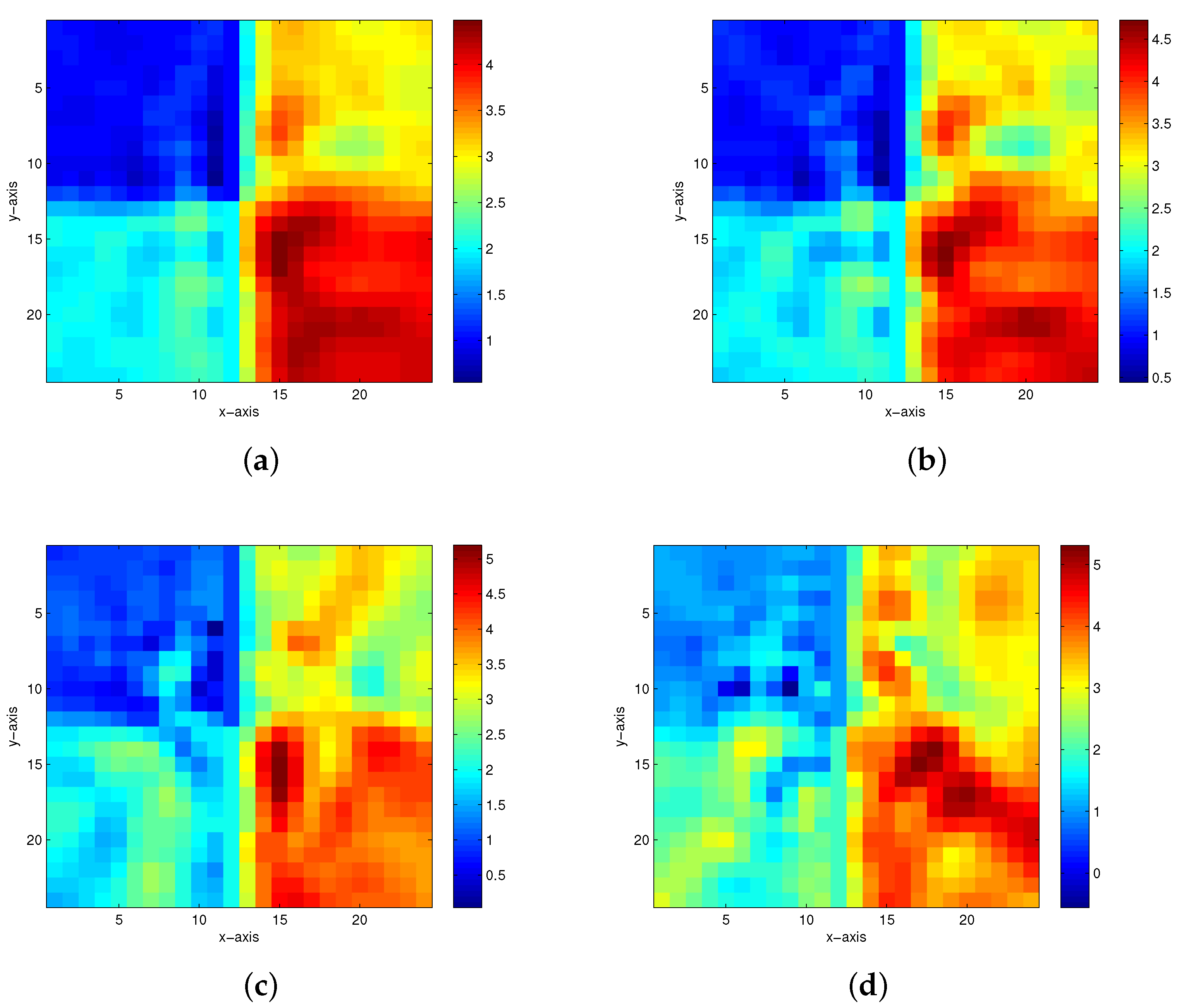
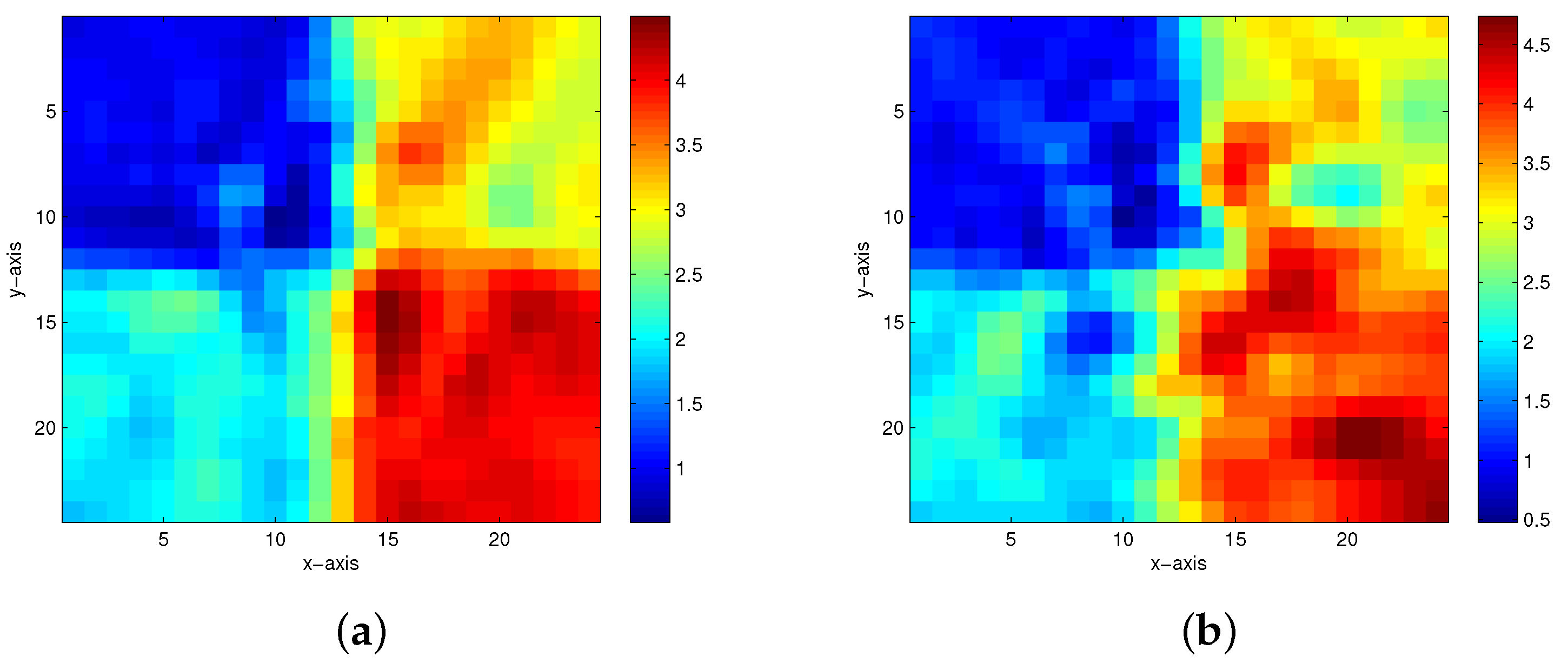

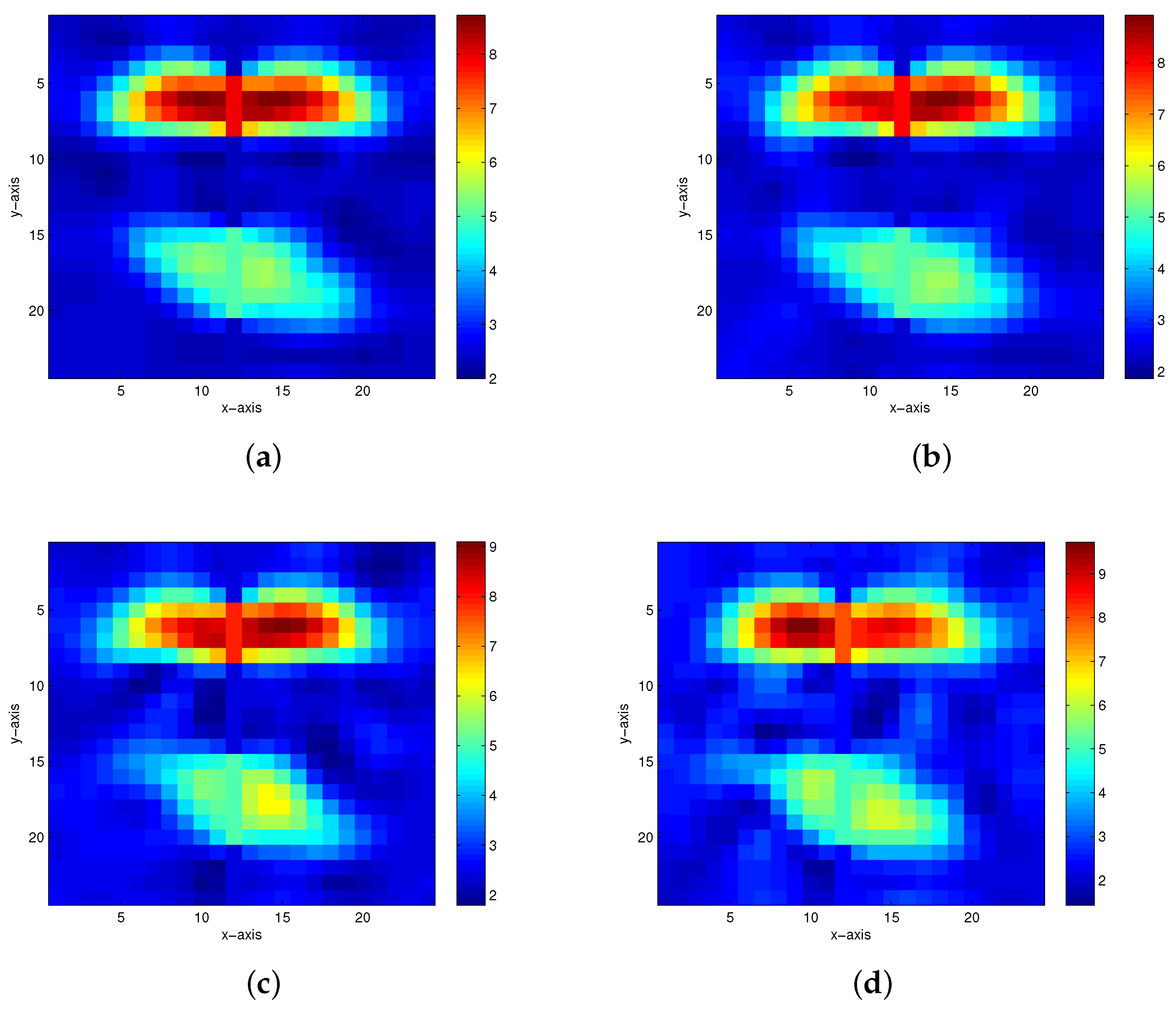


| Model Number | Method | 5% Noise Level | 10% Noise Level | 15% Noise Level | 20% Noise Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Homotopy method with constraints | 8.33% | 8.62% | 9.24% | 9.26% |
| Homotopy method without constraints | 8.65% | 9.06% | × | × | |
| Iterative method with constraints | × | × | × | × | |
| 2 | Homotopy method with constraints | 17.23% | 18.38% | 18.72% | 18.76% |
| Homotopy method without constraints | 18.90% | 18.93% | × | × | |
| Iterative method with constraints | × | × | × | × |
| Method | Relative Error | CPU Run Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Homotopy method with constraints | 8.33% | 1335.556 |
| Wavelet multiscale method | × | × |
| Nonlinear multigrid method | × | × |
| Adaptive multigrid conjugate gradient method | × | × |
| Homotopy perturbation method | 10.26% | 1666.718 |
| Method | Relative Error | CPU Run Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Homotopy method with constraints | 8.35% | 1328.798 |
| Wavelet multiscale method | 9.39% | 952.2021 |
| Nonlinear multigrid method | 9.43% | 894.9691 |
| Adaptive multigrid conjugate gradient method | 9.76% | 1072.533 |
| Homotopy perturbation method | 10.54% | 1674.663 |
| Compared Method | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Homotopy method without constraints | better anti-noise ability | × |
| Iterative method with constraints | larger convergence region | × |
| Wavelet multiscale method | better anti-noise ability and larger convergence region | more computation |
| Nonlinear multigrid method | better anti-noise ability and larger convergence region | more computation |
| Adaptive multigrid conjugate gradient method | better anti-noise ability and larger convergence region | more computation |
| Homotopy perturbation method | better anti-noise ability | × |
| with , | 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative error | × | 10.05% | 9.26% | 9.24% |
| with , | ||||
| Relative error | 14.27% | 12.13% | 9.24% | × |
| with , | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 |
| Relative error | 9.25% | 9.23% | 9.24% | 9.25% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Xue, R.; Liu, C.; Qi, Y. A Regularization Homotopy Strategy for the Constrained Parameter Inversion of Partial Differential Equations. Entropy 2021, 23, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111480
Liu T, Xue R, Liu C, Qi Y. A Regularization Homotopy Strategy for the Constrained Parameter Inversion of Partial Differential Equations. Entropy. 2021; 23(11):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tao, Runqi Xue, Chao Liu, and Yunfei Qi. 2021. "A Regularization Homotopy Strategy for the Constrained Parameter Inversion of Partial Differential Equations" Entropy 23, no. 11: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111480
APA StyleLiu, T., Xue, R., Liu, C., & Qi, Y. (2021). A Regularization Homotopy Strategy for the Constrained Parameter Inversion of Partial Differential Equations. Entropy, 23(11), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23111480







