Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
2.2. Correlation Coefficient and Normalized Correlation Coefficient
2.3. Permutation Entropy
2.4. Weighted Permutation Entropy
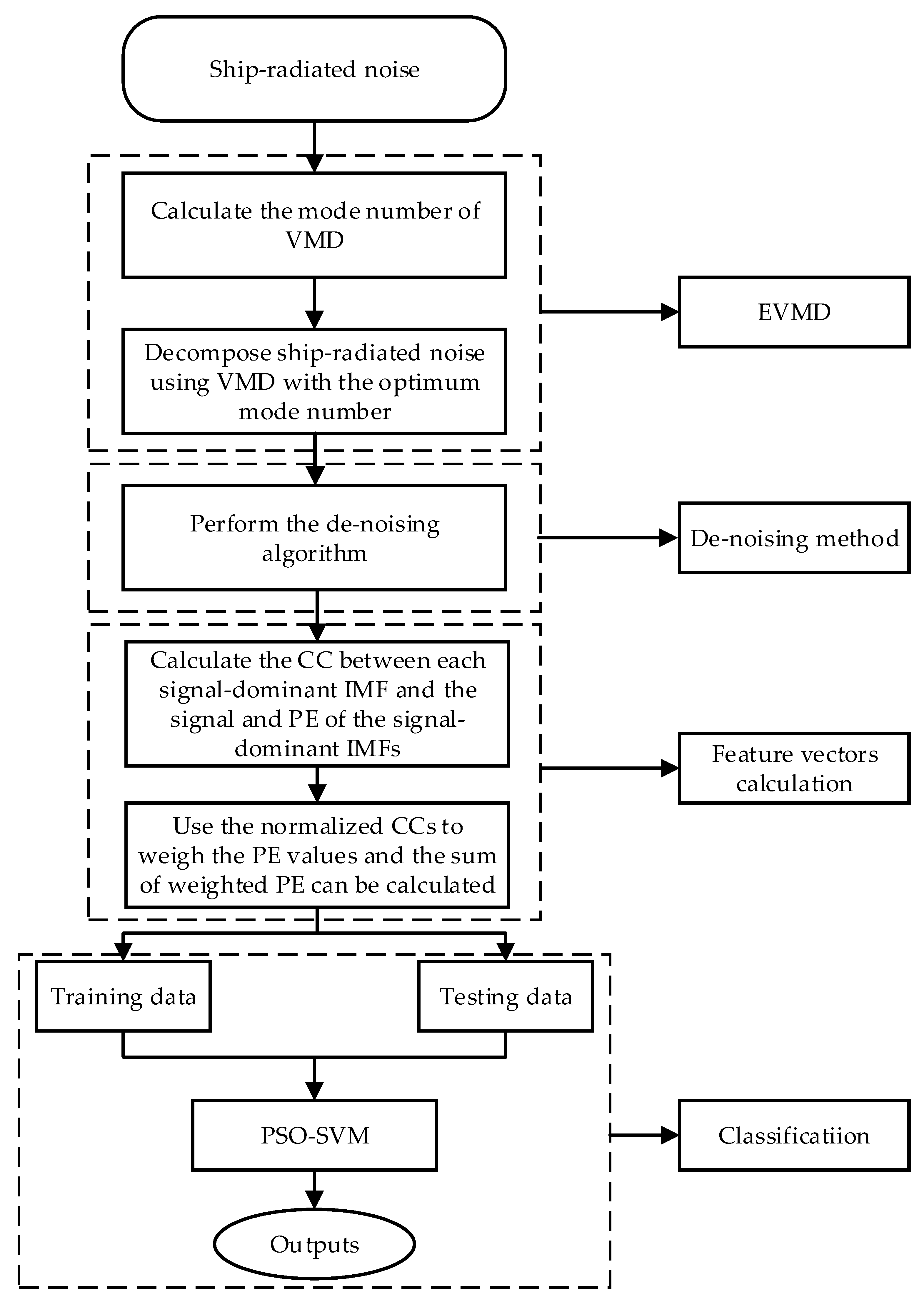
3. The Proposed Feature Extraction Method
- (1)
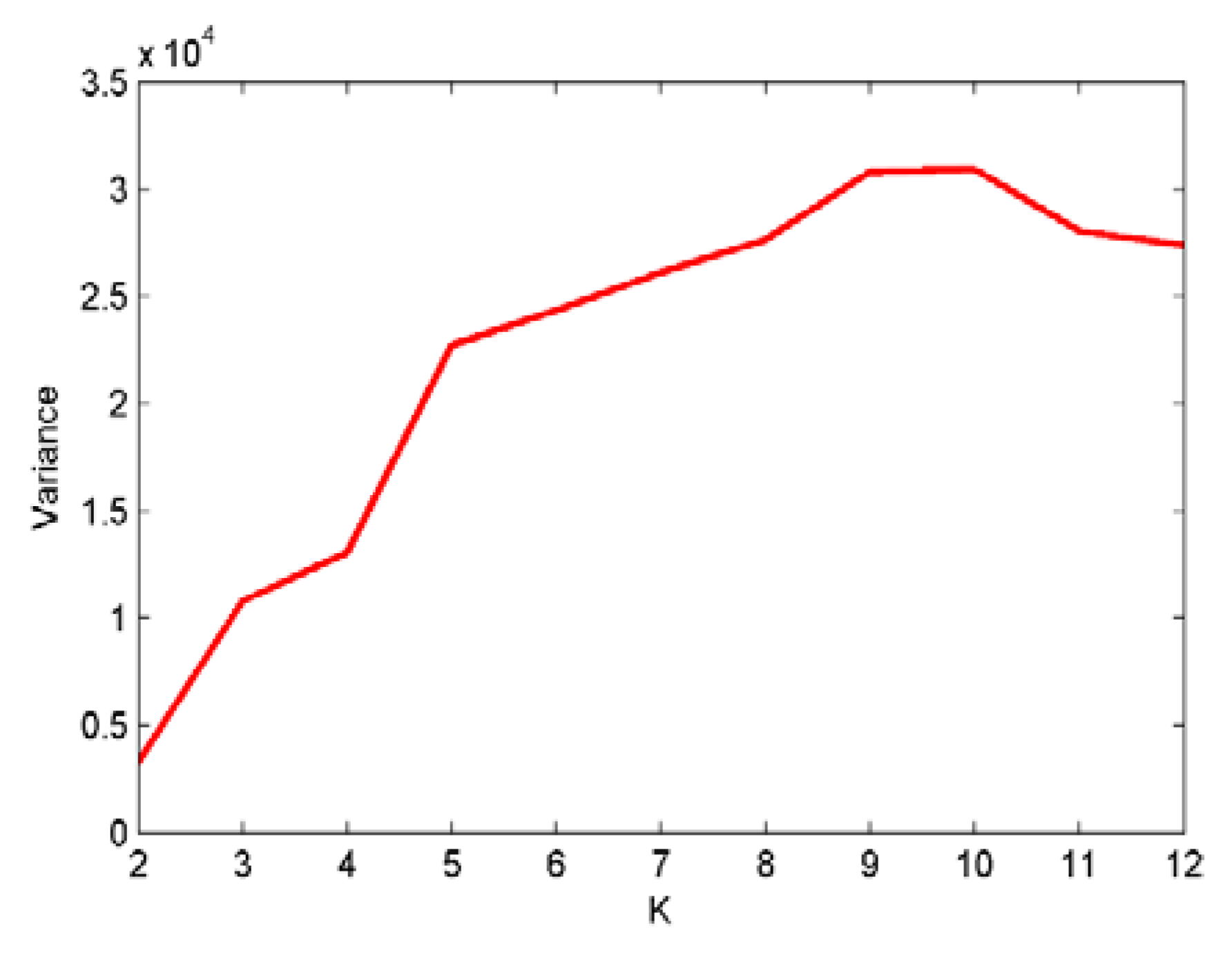
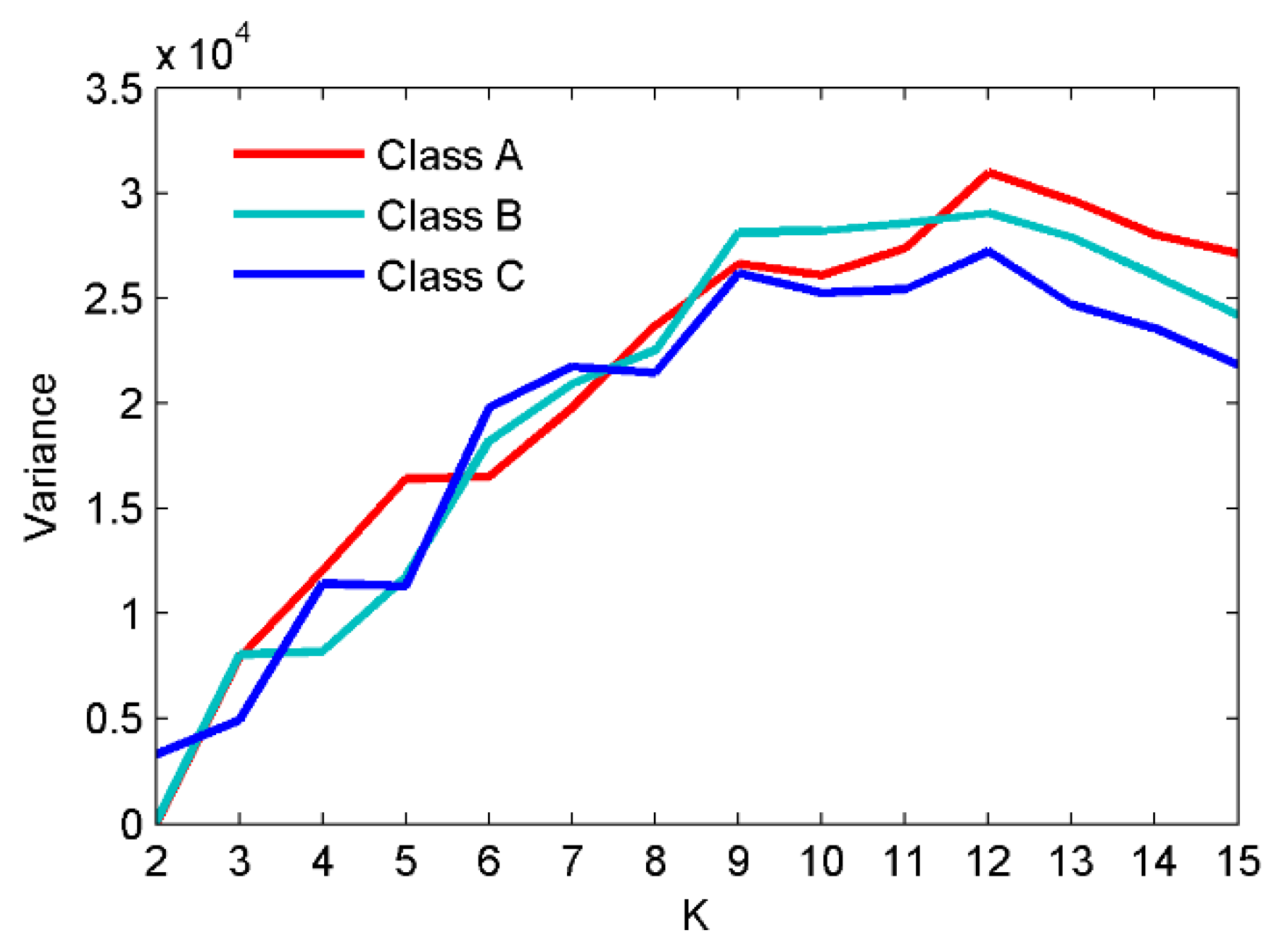
- The mode number K of VMD is first calculated using the variance of the IMF center frequency to improve the decomposition performance of VMD.
- (2)
- The VMD algorithm will be applied on the measured SRN data using the optimum mode number K obtained in the first step.
- (3)
- Calculate the WPE of each IMF obtained by EVMD and the variance of , thus totally K variance values can be obtained. Allowing the IMF index to correspond to the maximum variance k (), the IMF1~IMFk can be regarded as the signal-dominant IMFs retained and the remaining ones will be removed.
- (4)
- Calculate the CC between each signal-dominant IMF and the raw signal and PE values of the signal-dominant IMFs.
- (5)
- Use the norCCs to weigh the PE values and the sum of the weighted PE can be calculated. Namely, .
- (6)
- The obtained feature vectors are randomly divided into two groups, first one is the training data for training the SVM classifier and the second one is testing data for classification.
- (7)
- Finally, the testing data are fed into the PSO-SVM multi-class classifier for underwater acoustic target recognition and classification.
4. Simulated Signals Analysis
4.1. Analysis of Simulated Signals Using EVMD
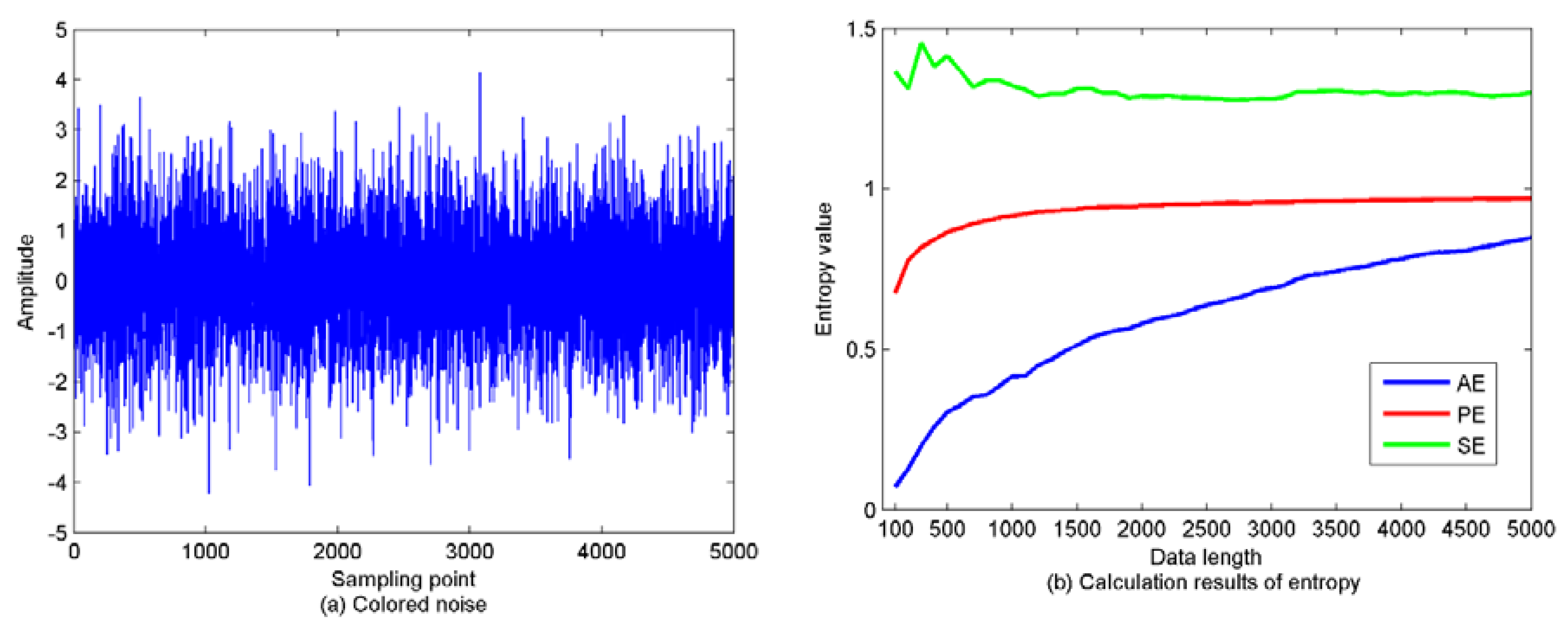
4.2. PE Properties Analysis
5. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on EVMD-norCC-PE
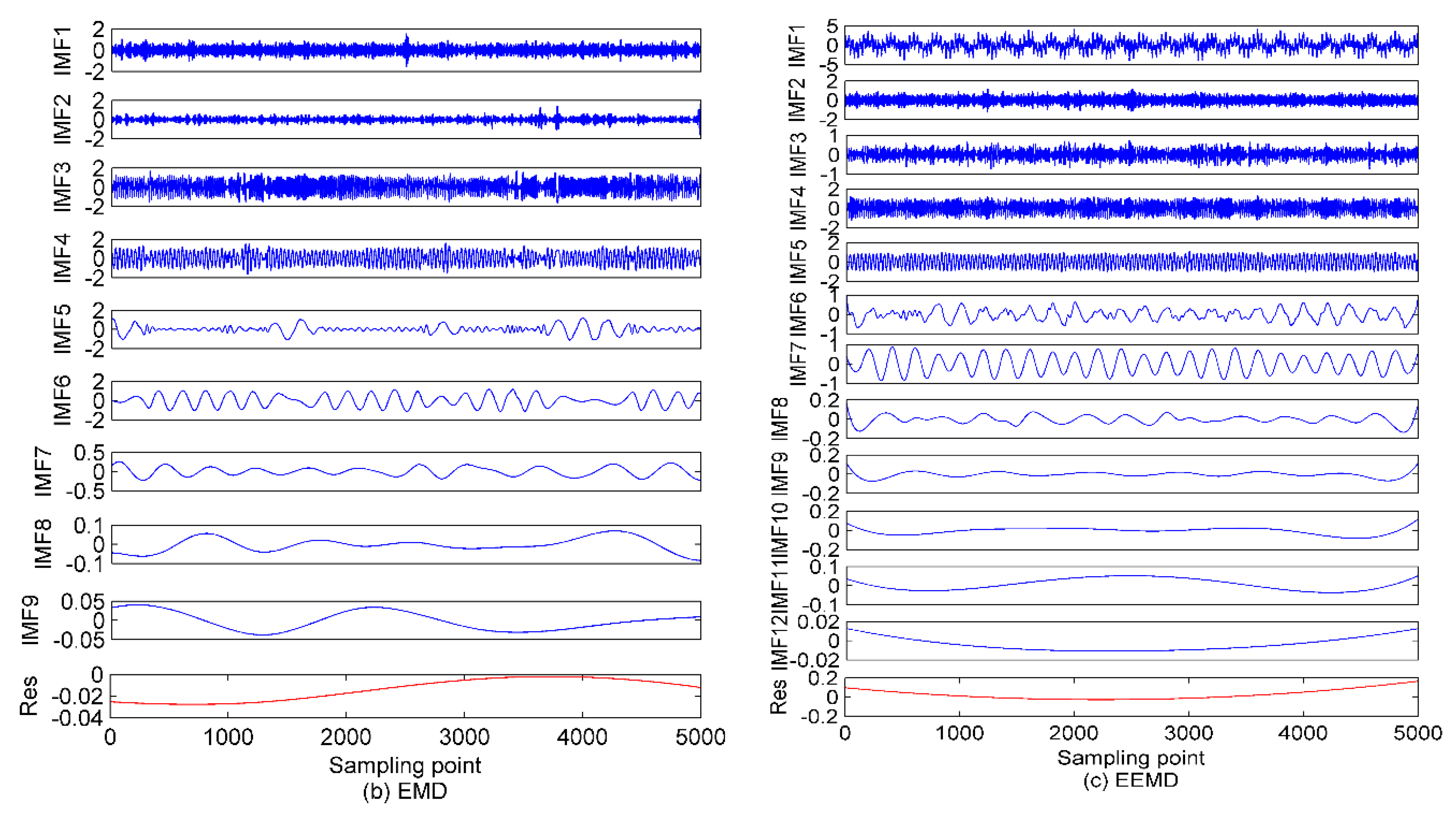
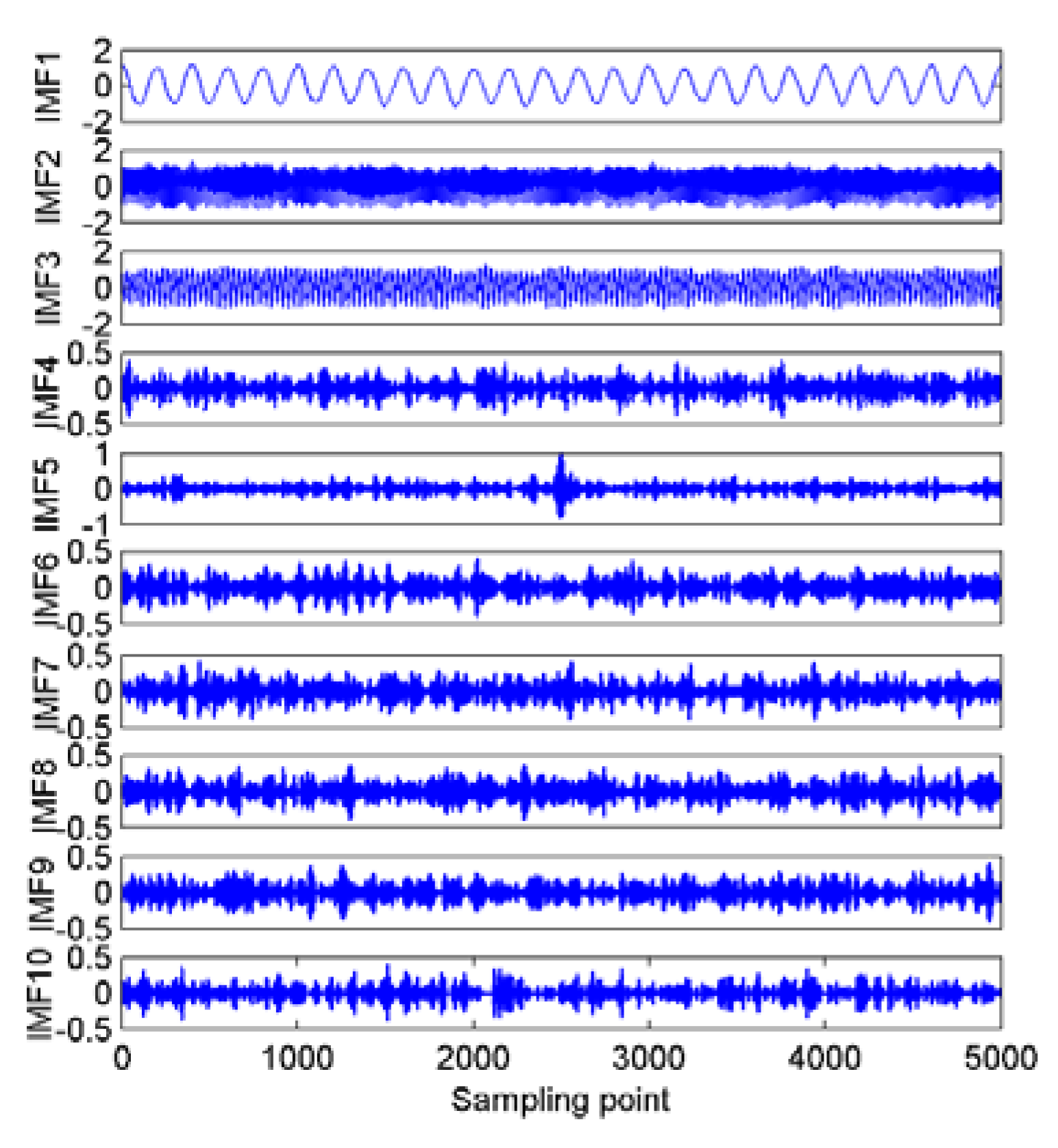
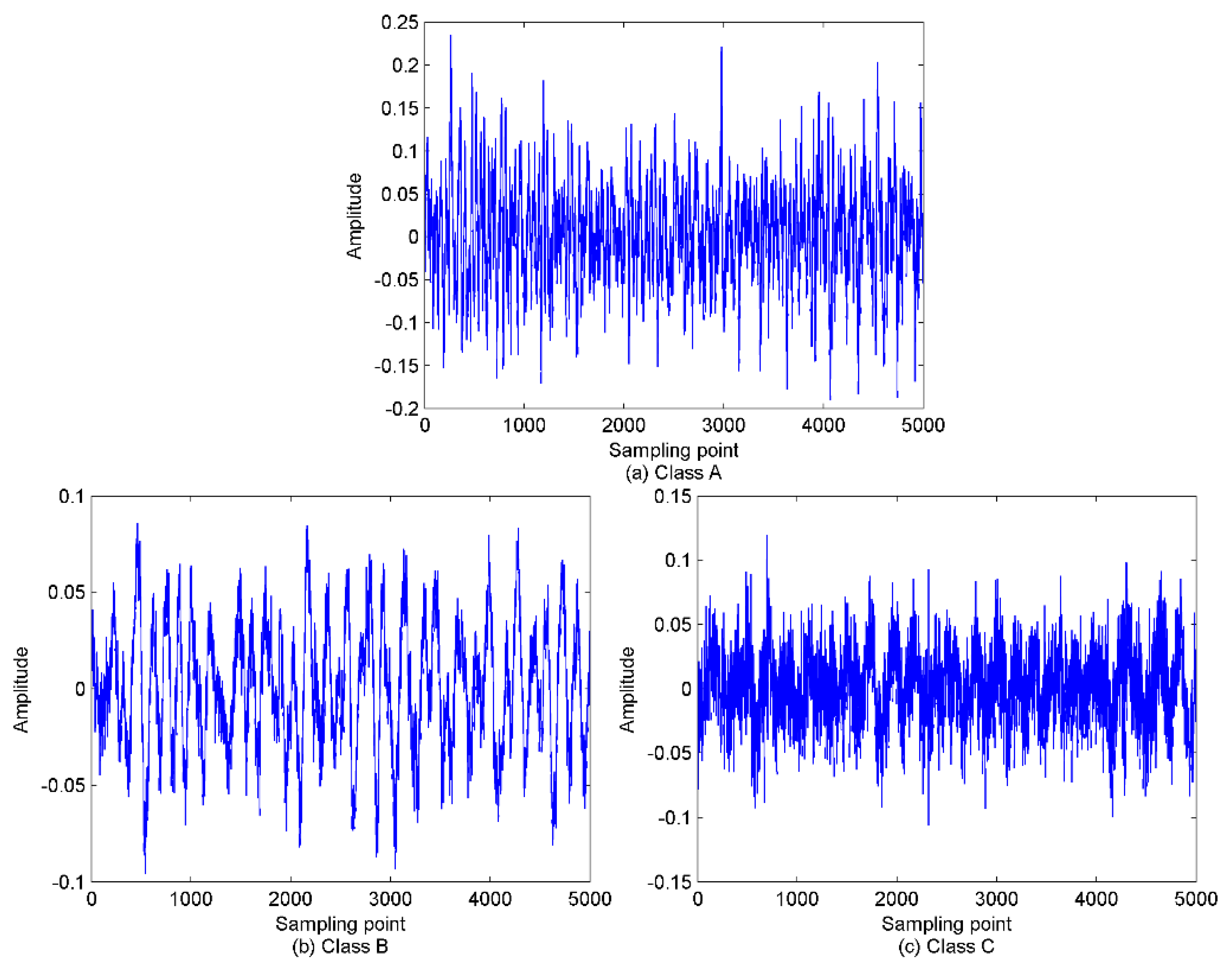
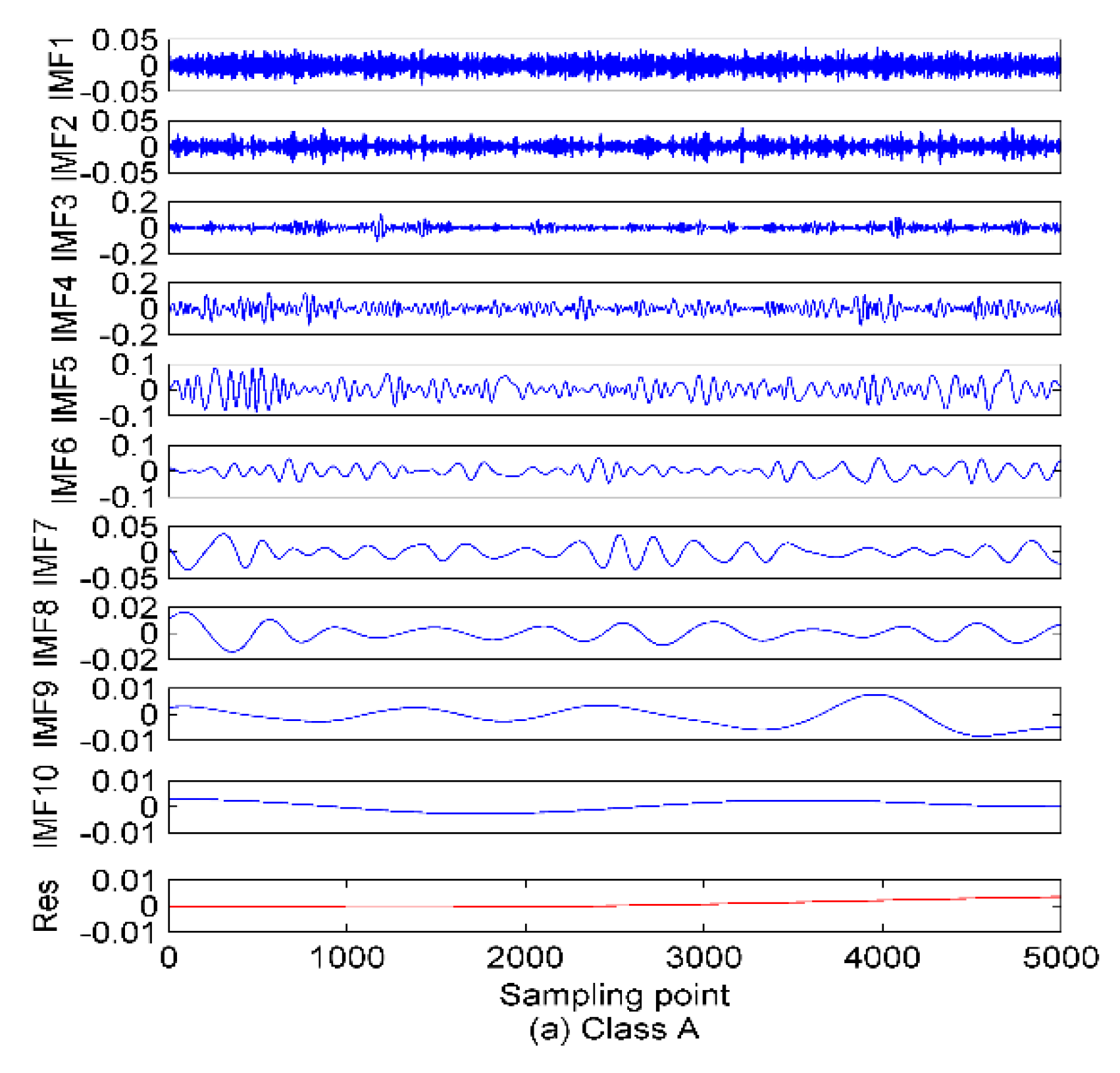
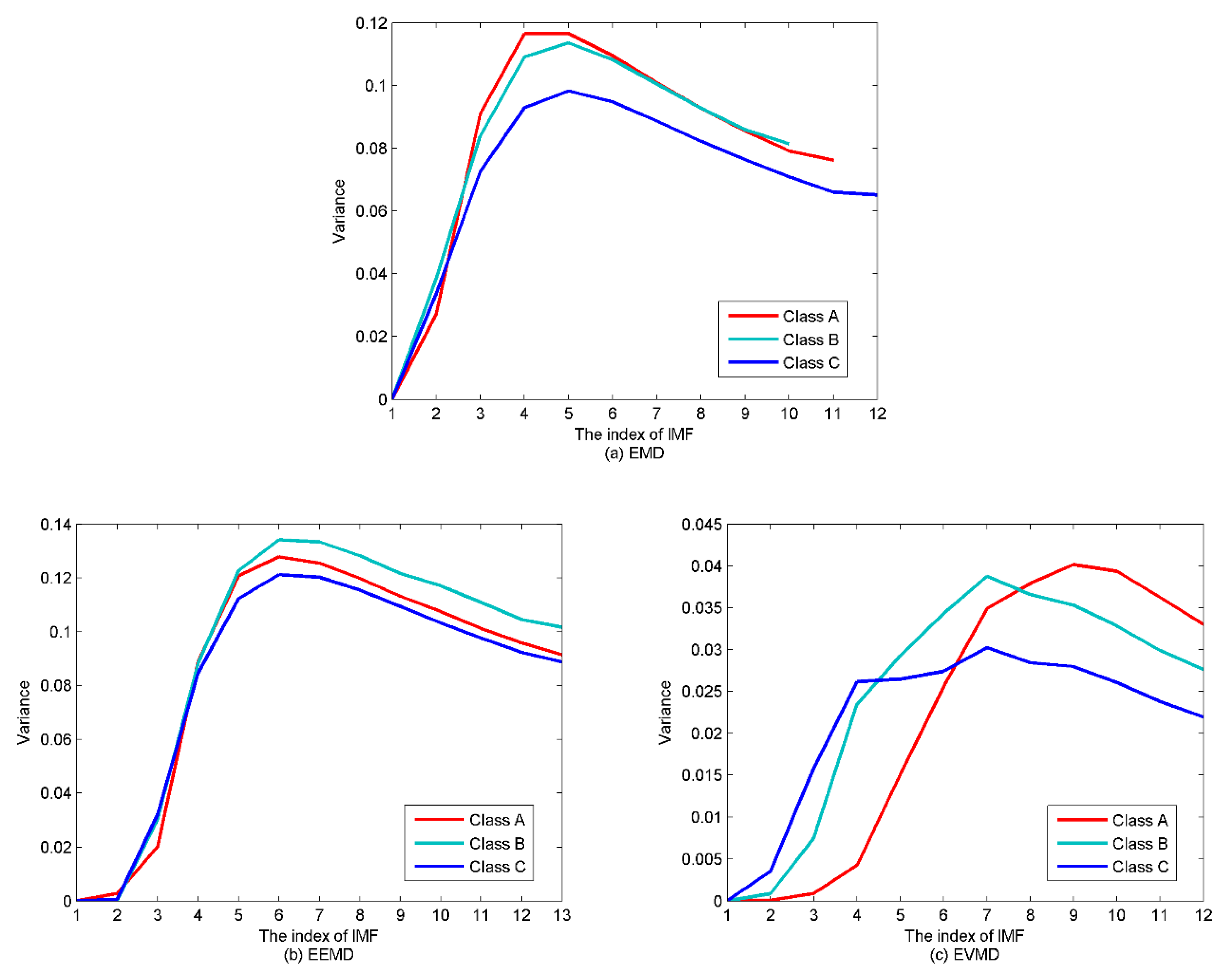
5.1. The EVMD Decomposition of Ship-Radiated Noise
5.2. The De-Noising Processing
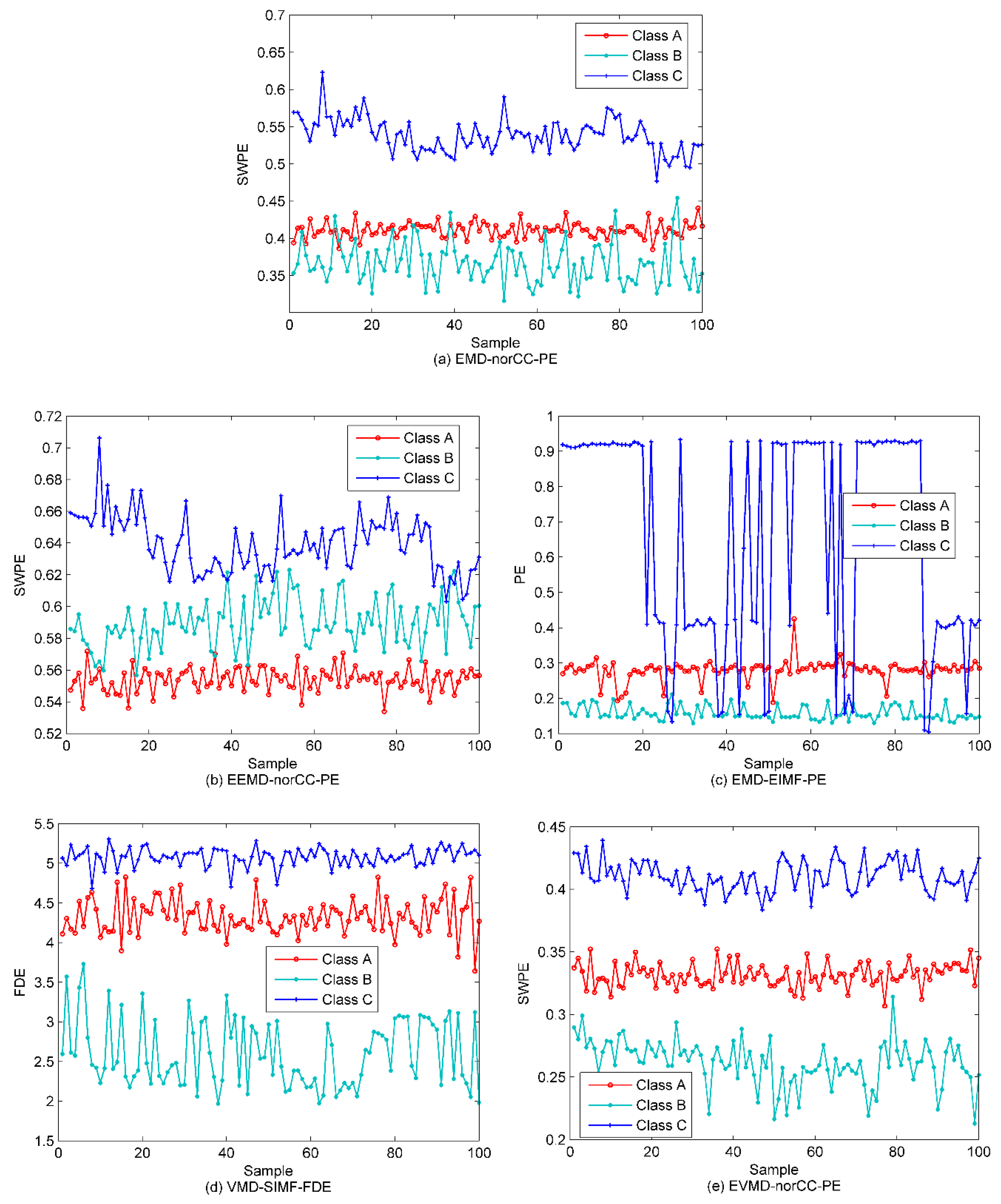
5.3. Classification of Ship-Radiated Noise
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nedelec, S.L.; Radford, A.N.; Pearl, L.; Nedelec, B.; McCormick, M.I.; Meekan, M.; Simpson, S. Motorboat noise impacts parental behaviour and offspring survival in a reef fish. In Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2017; Volume 284, p. 20170143. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, E.; Licitra, G.; Iacoponi, A.; Taburni, D. Assessing the underwater ship noise levels in the North Tyrrhenian Sea. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 943–949. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, N.D.; Pirotta, E.; Barton, T.R.; Thompson, P.M. Monitoring ship noise to assess the impact of coastal developments on marine mammals. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredianelli, L.; Nastasi, M.; Bernardini, M.; Fidecaro, F.; Licitra, G. Pass-by Characterization of Noise Emitted by Different Categories of Seagoing Ships in Ports. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Ship recognition via its radiated sound: The fractal based approaches. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Study on feature extraction of ship radiated noise based on higher order spectrum and cepstrum. Comput. Simulated 2011, 28, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hinich, J.M.; Marandino, D.; Sullivan, E.J. Bispectrum of ship-radiated noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.X.; Wang, B.H.; Xiang, J.L. Time-frequency analysis of ship-radiated noise and line spectrum extraction based on STFT. Audio Eng. 2005, 11, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- David, P.M.; Chapron, B. Underwater acoustic signal analysis with wavelet process. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 2118–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, X. Robust underwater noise targets classification using auditory inspired time–frequency analysis. Appl. Acoust. 2014, 78, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. An improved Wavelet Transform using Singular Spectrum Analysis for wind speed forecasting based on Elman Neural Network. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoji, Z.; Xin, Z.; Jincai, S. Improving feature extraction of ship-radiated target signals with empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and Hilbert spectrum. J. Northwest. Polytech. Univ. 2006, 24, 456. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.M.; Machado, J.A.T. Entropy Analysis of Soccer Dynamics. Entropy 2019, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafarja, M.; Mirjalili, S. Hybrid binary ant lion optimizer with rough set and approximate entropy reducts for feature selection. Soft Comput. 2018, 23, 6249–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.F.A.; Jale, J.D.S.; Stosic, T.; Dos Santos, C.A.C.; Singh, V.P. An application of sample entropy to precipitation in Paraíba State, Brazil. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2018, 136, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo, F.H.A.; Bejan, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Stosic, T. Permutation entropy and statistical complexity analysis of Brazilian agricultural commodities. Entropy 2019, 21, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandt, C.; Pompe, B. Permutation entropy: A natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 174102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Self-adaptive bearing fault diagnosis based on permutation entropy and manifold-based dynamic time warping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 114, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Judge, G. Permutation entropy and information recovery in nonlinear dynamic economic time series. Econometrics 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, B.; Chen, B.; Keil, A.; Principe, J. Weighted-permutation entropy: A complexity measure for time series incorporating amplitude information. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 022911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Permutation Entropy of the Intrinsic Mode Function with the Highest Energy. Entropy 2016, 18, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. A New Underwater Acoustic Signal Denoising Technique Based on CEEMDAN, Mutual Information, Permutation Entropy, and Wavelet Threshold Denoising. Entropy 2018, 20, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, X. A Fusion Frequency Feature Extraction Method for Underwater Acoustic Signal Based on Variational Mode Decomposition, Duffing Chaotic Oscillator and a Kind of Permutation Entropy. Electronics 2019, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Heincke, B.; Jegen, M.; Moorkamp, M. Using empirical mode decomposition to process marine magnetotelluric data. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 190, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, Z.; Eckermann, S.D.; Bittner, M.; Hirota, I.; Yee, J.-H. Gravity wave characteristics in the middle atmosphere derived from the Empirical Mode Decomposition method. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 16545–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; He, Z.; Zuo, M.J.; Zuo, M.J. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. A novel feature extraction method for ship-radiated noise based on variational mode decomposition and multi-scale permutation entropy. Entropy 2017, 19, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, K.; Li, G. A new ship-radiated noise feature extraction technique based on variational mode decomposition and fluctuation-based dispersion entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, R.; Ali, W.; Yu, J.; Liang, H. A New Feature Extraction Method for Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Improved CEEMDAN, Normalized Mutual Information and Multiscale Improved Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2019, 21, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Pan, H.; Yang, S.; Cheng, J. Generalized composite multiscale permutation entropy and Laplacian score based rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 99, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Domínguez, D.; Torres-Guijarro, S.; Cardenal-López, A.; Pena-Gimenez, A. ShipsEar: An underwater vessel noise database. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 113, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| K | Center Frequency/Hz | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 30.00 | 199.06 | ||||||||||
| 3 | 7.73 | 52.69 | 361.73 | |||||||||
| 4 | 7.69 | 52.70 | 203.13 | 363.84 | ||||||||
| 5 | 7.68 | 52.72 | 200.82 | 320.38 | 436.90 | |||||||
| 6 | 7.53 | 52.72 | 116.38 | 208.54 | 356.33 | 445.45 | ||||||
| 7 | 7.50 | 52.73 | 113.67 | 200.28 | 277.92 | 362.95 | 448.28 | |||||
| 8 | 7.48 | 52.74 | 112.02 | 196.09 | 257.40 | 316.82 | 373.65 | 452.45 | ||||
| 9 | 5.04 | 55.11 | 30.00 | 126.71 | 202.06 | 275.88 | 353.44 | 408.78 | 467.51 | |||
| 10 | 5.04 | 55.10 | 30.01 | 124.02 | 197.93 | 256.75 | 312.74 | 365.13 | 424.43 | 474.04 | ||
| 11 | 5.04 | 55.08 | 30.00 | 112.05 | 158.93 | 206.26 | 263.24 | 316.16 | 366.31 | 452.29 | 474.42 | |
| 12 | 5.04 | 55.08 | 30.00 | 111.49 | 157.37 | 204.59 | 259.33 | 310.70 | 358.79 | 400.70 | 440.86 | 481.01 |
| EMD | EEMD | EVMD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | IMF6: 0.9294 | IMF7: 0.9575 | IMF1: 0.9936 |
| f2 | IMF4: 0.8845 | IMF5: 0.9822 | IMF3: 0.9925 |
| f3 | IMF3: 0.8665 | IMF4: 0.9525 | IMF2: 0.9896 |
| f4 | IMF2: 0.1100 | IMF2: 0.1337 | IMF5: 0.4123 |
| Class | EMD | EEMD | EVMD |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | IMF1~IMF5 | IMF1~IMF6 | IMF1~IMF9 |
| B | IMF1~IMF5 | IMF1~IMF6 | IMF1~IMF7 |
| C | IMF1~IMF5 | IMF1~IMF6 | IMF1~IMF7 |
| Method | Number of Misclassified Samples | Accuracy Rate (%) | Computing Time (Second) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Class B | Class C | |||
| PE | 19 | 9 | 8 | 70 | 1205.346847 |
| EMD-norCC-PE | 2 | 9 | 0 | 90.8333 | 2044.39669 |
| EEMD-norCC-PE | 2 | 3 | 3 | 93.3333 | 17,778.779946 |
| EMD-EIMF-PE | 5 | 0 | 8 | 89.1667 | 1342.94618 |
| VMD-SIMF-FDE | 2 | 0 | 0 | 98.3333 | 8344.834518 |
| EVMD-norCC-PE | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 16,472.39683 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, D.; Esmaiel, H.; Sun, H.; Qi, J.; Qasem, Z.A.H. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy. Entropy 2020, 22, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040468
Xie D, Esmaiel H, Sun H, Qi J, Qasem ZAH. Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy. Entropy. 2020; 22(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Dongri, Hamada Esmaiel, Haixin Sun, Jie Qi, and Zeyad A. H. Qasem. 2020. "Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy" Entropy 22, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040468
APA StyleXie, D., Esmaiel, H., Sun, H., Qi, J., & Qasem, Z. A. H. (2020). Feature Extraction of Ship-Radiated Noise Based on Enhanced Variational Mode Decomposition, Normalized Correlation Coefficient and Permutation Entropy. Entropy, 22(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22040468







