Dynamic Effects Arise Due to Consumers’ Preferences Depending on Past Choices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Model
3. Analysis of Map 5
3.1. Analysis of 1D-Map
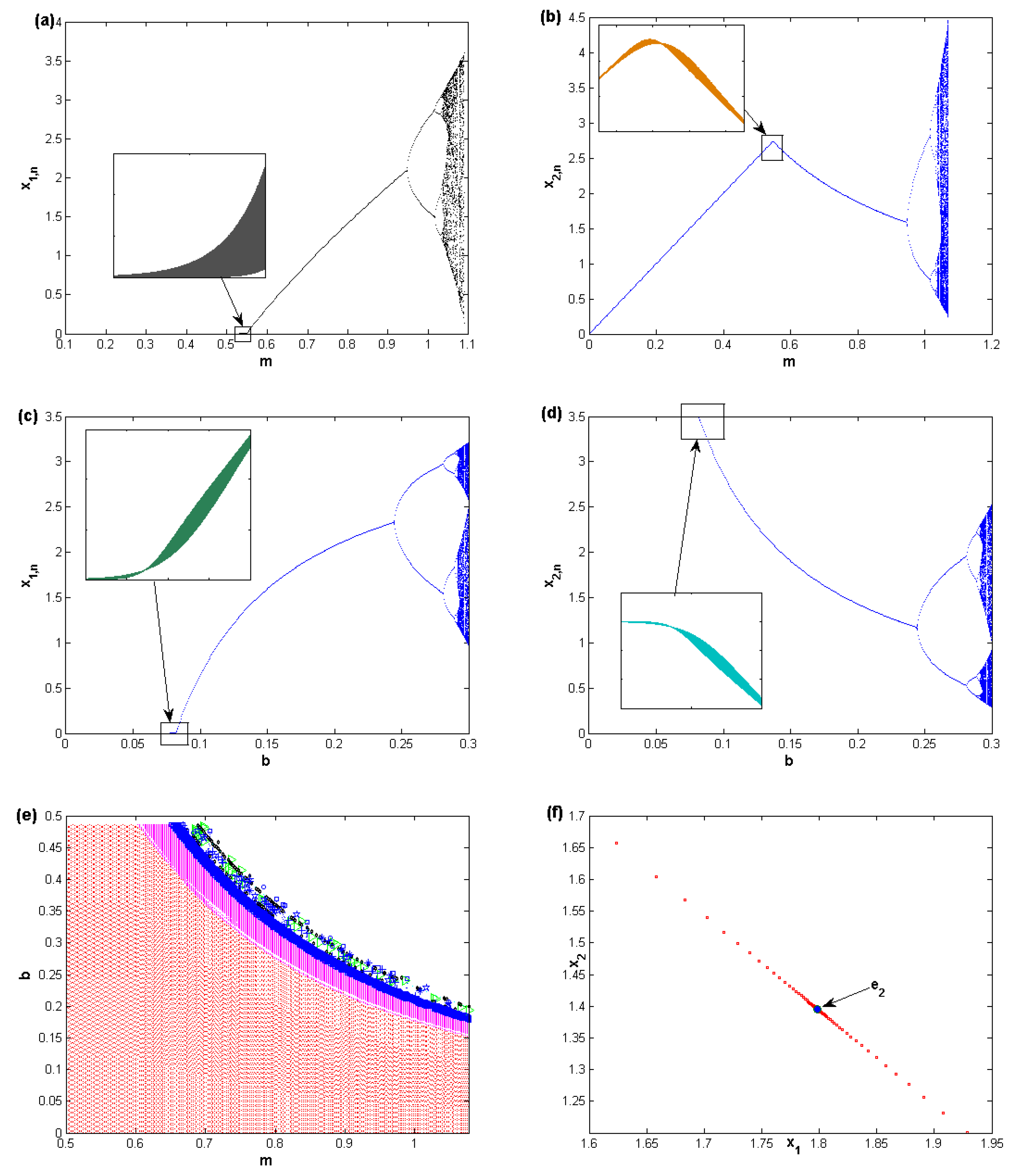
Numerical Simulation (1D-Map)
3.2. Analysis of the 2D-Map
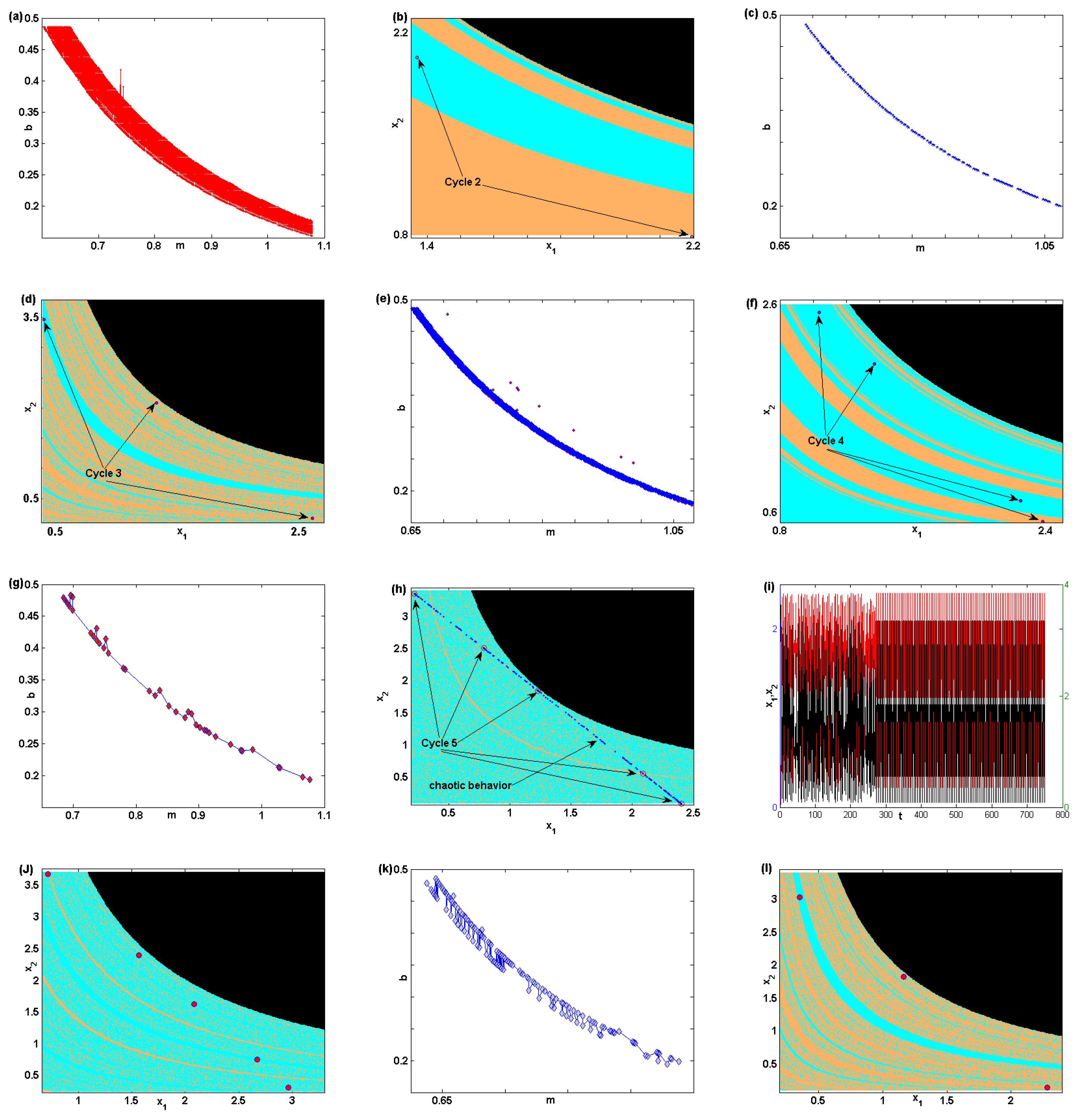
3.2.1. Numerical Simulation (2D-map)
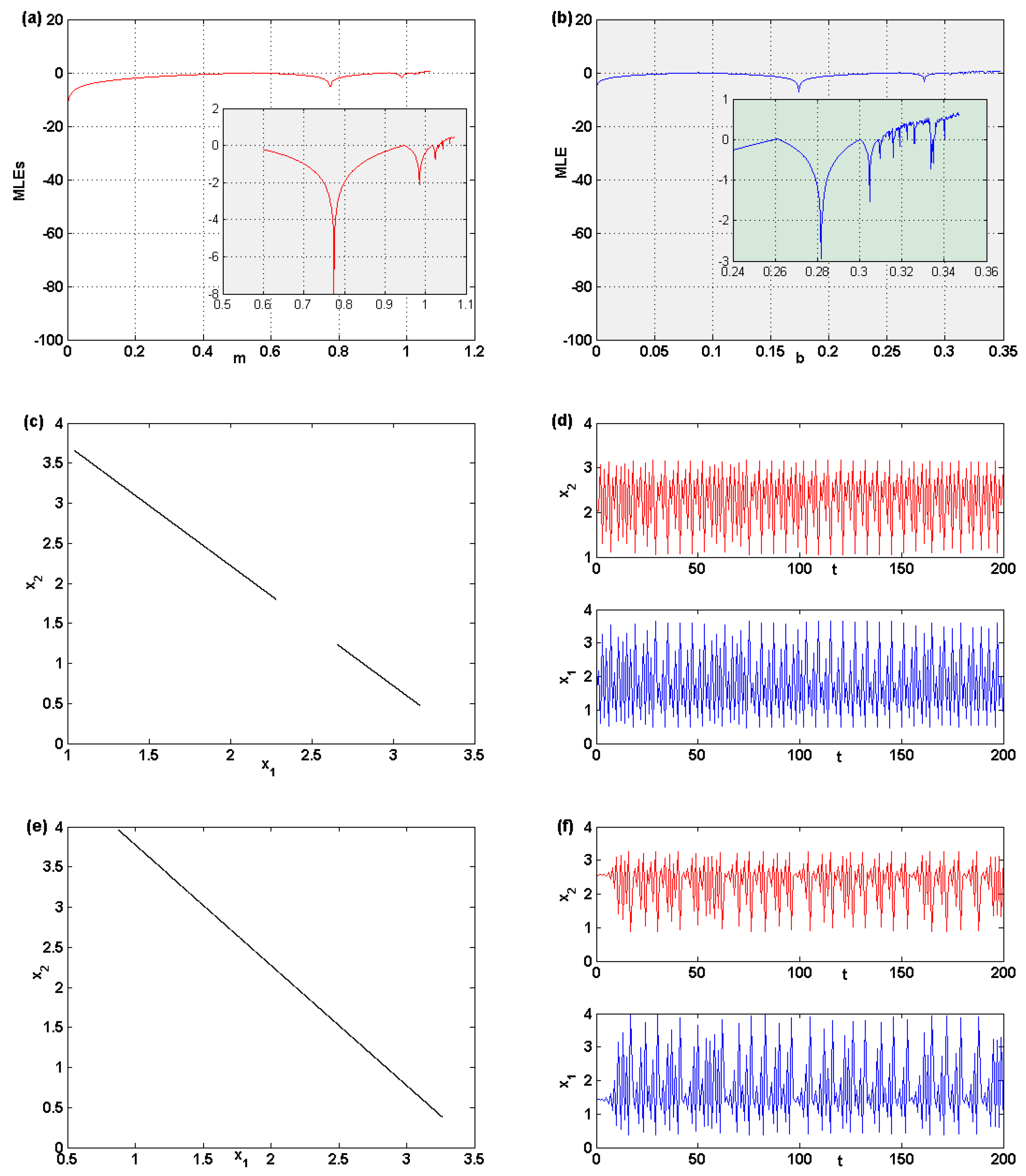
3.2.2. Chaotic Attractor
3.2.3. Entropy Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puu, T. A new approach to modeling Bertrand duopoly. Rev. Behav. Econ. 2017, 4, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar, S.S.; Alnowibet, K. Nonlinear oligopolistic game with isoelastic demand function: Rationality and local monopolistic approximation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 84, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, A.A.; Naimzada, A.; Sodini, M. Bifurcations and Chaotic Attractors in an Overlapping Generations Model with Negative Environmental Externalities. In Nonlinear Dynamics in Economics, Finance and Social Sciences; Bischi, G., Chiarella, C., Gardini, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberger, Germany, 2010; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tramontana, F. Heterogeneous duopoly with isoelastic demand function. Econ. Model. 2010, 27, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, E. Complex dynamics analysis on fish stock harvested by two players with heterogeneous rationality. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2009, 42, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchuk, A.; Puu, T. Oligopoly model with recurrent renewal of capital revisited. Math. Comput. Simul. 2015, 108, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Chen, Y. Duopoly competitions with capacity constrained input. Econ. Model. 2012, 29, 1715–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Naimzada, A. A Cournot duopoly game with heterogeneous players: Nonlinear dynamics of the gradient rule versus local monopolistic approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 249, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puu, T.; Norin, A. Cournot duopoly when the competitors operate under capacity constraints. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2003, 18, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsadany, A.A. Dynamics of a Cournot duopoly game with bounded rationality based on relative profit maximization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 294, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, N.; Dieci, R.; NArdini, F. Bifurcation analysis of a dynamic duopoly model with heterogeneous costs and behavioural rules. Math. Comput. Simul. 2009, 79, 3179–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Naimzada, A.; Tramontana, F. Nonlinear dynamics and global analysis of a heterogeneous Cournot duopoly with local monopolistic approach versus a gradient rule with endogenous reactivity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 23, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisi, M.; Gabriel, S.; Fahimnia, B. Supply chain competition on shelf space and pricing for soft drinks: A bilevel optimization approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 211, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar, S.S.; Al-Khedhairi, A. Analysis of a Four-Firm Competition Based on a Generalized Bounded Rationality and Different Mechanisms. Complexity 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiza, H.N.; Elsadany, A.A. Nonlinear dynamics in the Cournot duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Phys. A 2003, 320, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Si, F. Complex Dynamics of a Continuous Bertrand Duopoly Game Model with Two-Stage Delay. Entropy 2016, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacha, O.I.; Volos, C.K.; Kyprianidis, I.M.; Stouboulos, I.N.; Vaidyanathan, S. Analysis, adaptive control and circuit simulation of a novel nonlinear finance system. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 276, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacha, O.I.; Munoz-Pacheco, J.M.; Zambrano-Serrano, E.; Stouboulos, I.N.; Pham, V.T. Determining the chaotic behavior in a fractional-order finance system with negative parameters. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 94, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepomuceno, E.G.; Martins, S.A.M.; Silva, B.C.; Amaral, G.F.V.; Perc, M. Detecting unreliable computer simulations of recursive functions with interval extensions. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 329, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diks, C.; Hommes, C.; Panchenko, V.; Van der Weide, R. E and F Chaos: A User Friendly Software Package for Nonlinear Economic Dynamics. Comput. Econ. 2008, 32, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouannas, A.; Wang, X.; Khennaoui, A.; Bendoukha, S.; Pham, V.; Alsaadi, F. Fractional form of a chaotic map without fixed points: Chaos, entropy and control. Entropy 2018, 20, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canovas, J.; Medina, D. Topological entropy of Cournot-Puu duopoly. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Askar, S.S.; Al-khedhairi, A. Dynamic Effects Arise Due to Consumers’ Preferences Depending on Past Choices. Entropy 2020, 22, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020173
Askar SS, Al-khedhairi A. Dynamic Effects Arise Due to Consumers’ Preferences Depending on Past Choices. Entropy. 2020; 22(2):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020173
Chicago/Turabian StyleAskar, Sameh S., and A. Al-khedhairi. 2020. "Dynamic Effects Arise Due to Consumers’ Preferences Depending on Past Choices" Entropy 22, no. 2: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020173
APA StyleAskar, S. S., & Al-khedhairi, A. (2020). Dynamic Effects Arise Due to Consumers’ Preferences Depending on Past Choices. Entropy, 22(2), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020173





