Improving Document-Level Sentiment Classification Using Importance of Sentences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Work
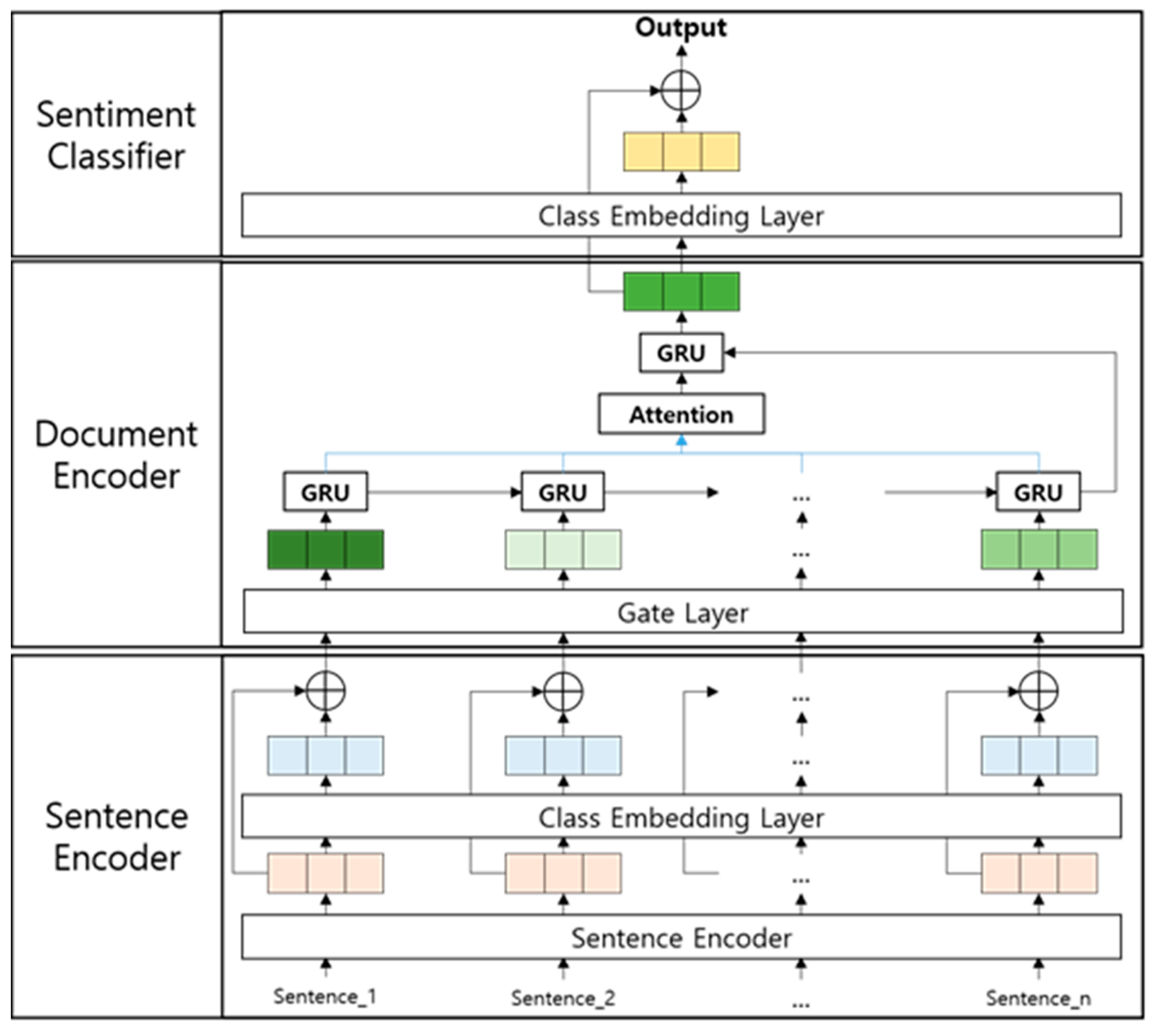
3. Document-Level Sentiment Analysis Model
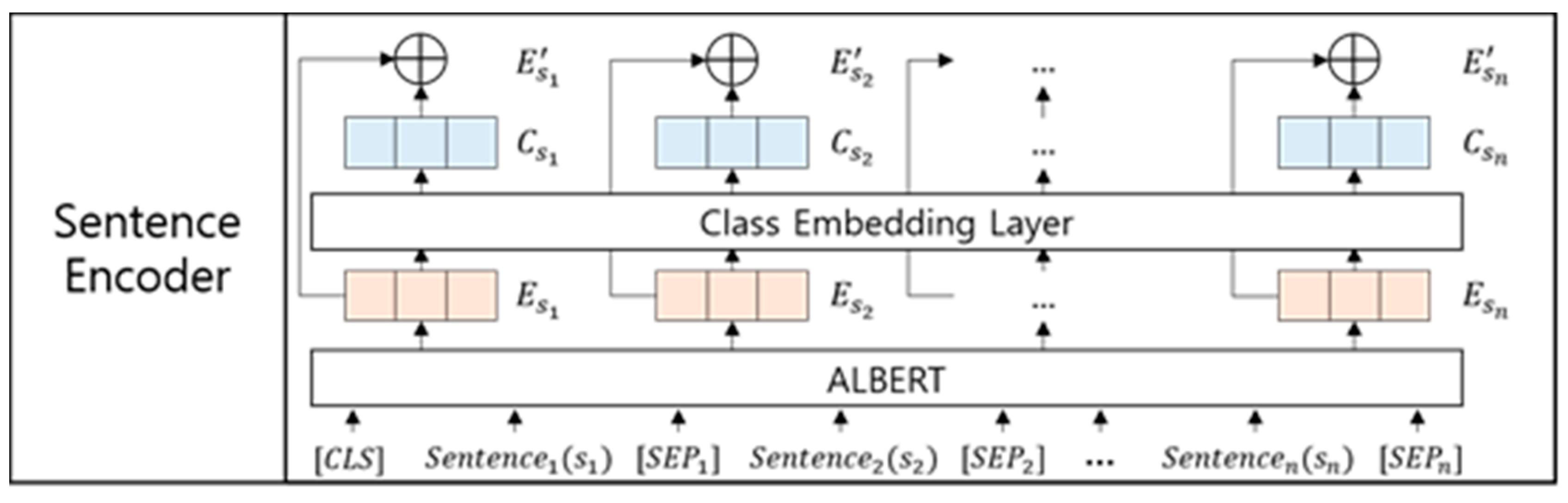
3.1. Sentence Encoder
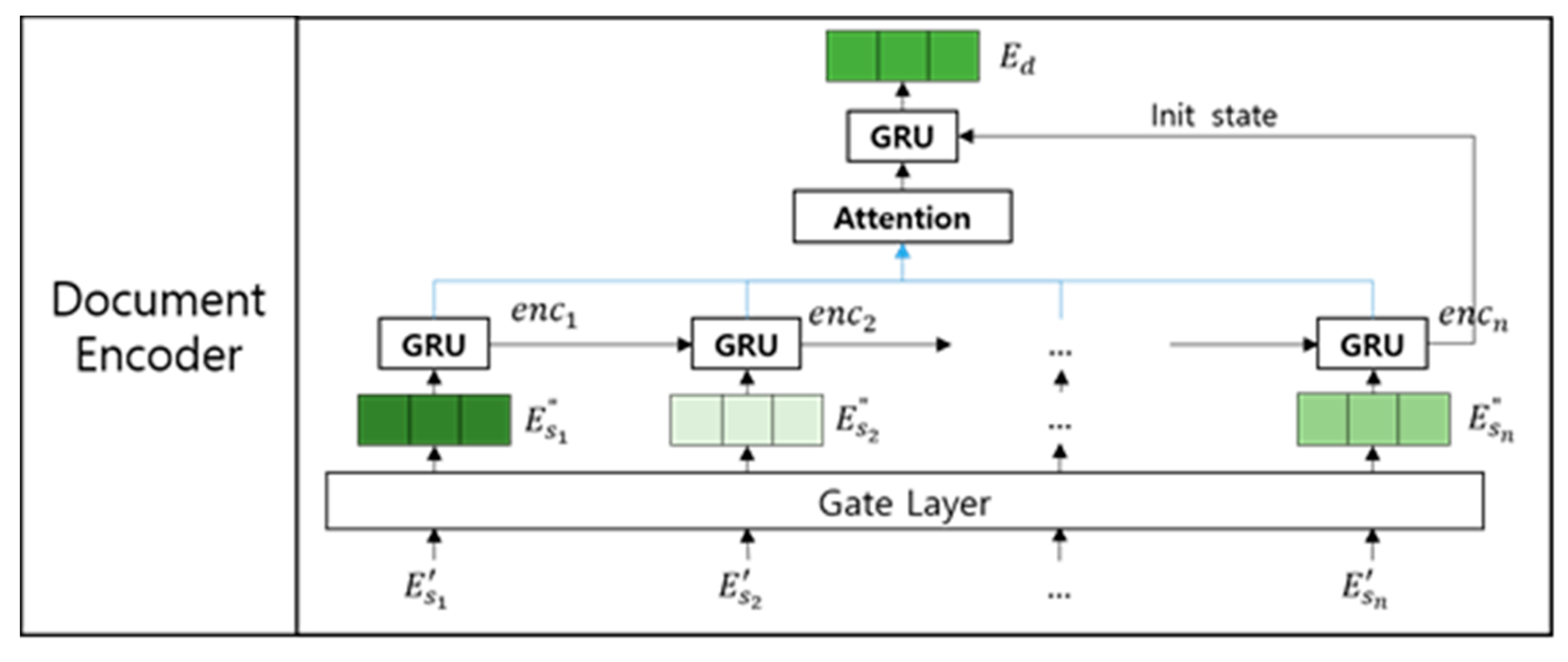
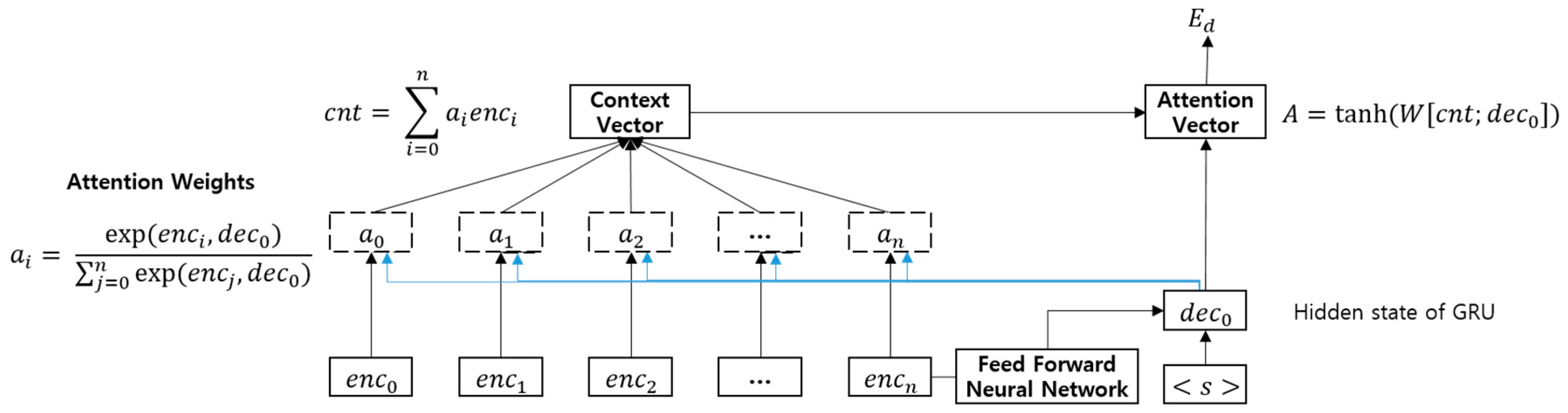
3.2. Document Encoder
3.3. Sentiment Classifier
4. Results
4.1. Datasets and Experimental Settings
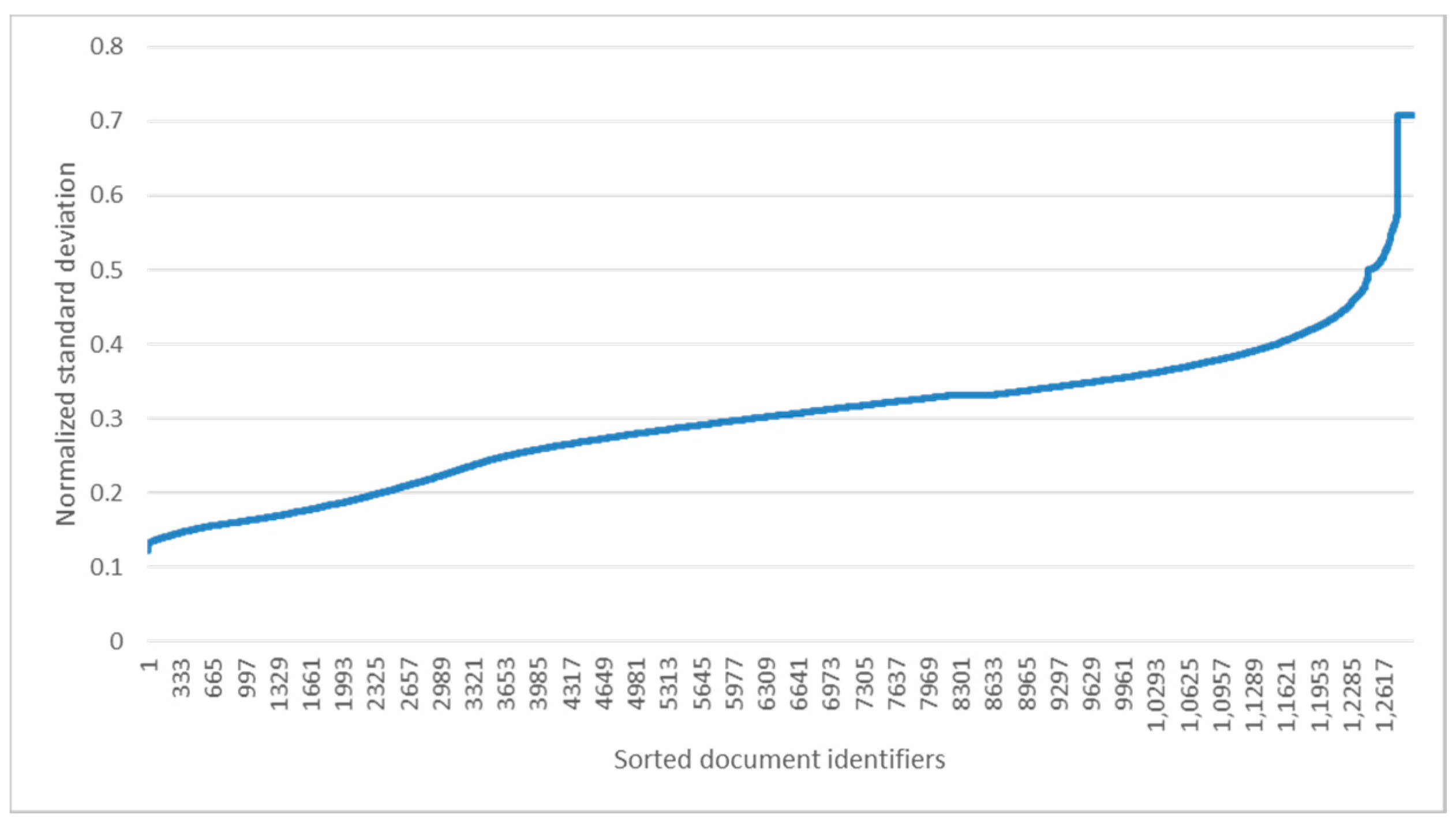
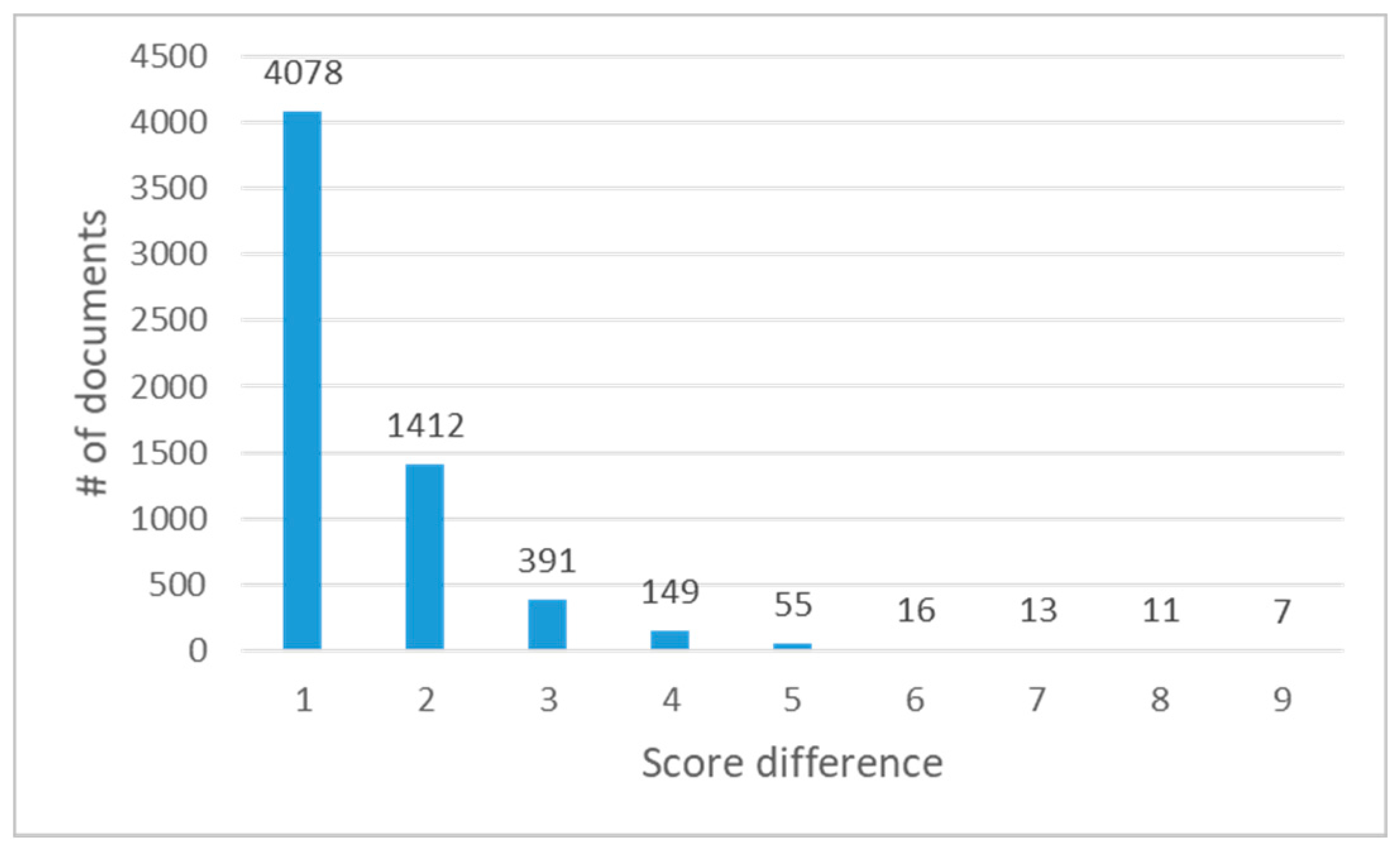
4.2. Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baccianella, S.; Esuli, A.; Sebastiani, F. Sentiwordnet 3.0: An enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis and opinion mining. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Valletta, Malta, 17–23 May 2010; Volume 10, pp. 2200–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Liu, B. Mining and summarizing customer reviews. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Seattle, DC, USA, 22–25 August 2004; pp. 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.; Wiebe, J.; Hoffmann, P. Recognizing contextual polarity in phrase-level sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Human Language Technology Conference and Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–8 October 2005; pp. 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Xie, B.; Vovsha, I.; Rambow, O.; Passonneau, R. Sentiment analysis of twitter data. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Language in Social Media, Portland, OR, USA, 23 June 2011; pp. 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Alqasemi, F.; Abdelwahab, A.; Abdelkader, H. Constructing automatic domain-specific sentiment lexicon using KNN search via terms discrimination vectors. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 41, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Park, H.; Shin, K.-S. Attention-based long short-term memory network using sentiment lexicon embedding for aspect-level sentiment analysis in Korean. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtipour, K.; Poria, S.; Hussain, A.; Cambria, E.; Hawalah, A.Y.A.; Gelbukh, A.F.; Zhou, Q. Multilingual Sentiment Analysis: State of the Art and Independent Comparison of Techniques. Cogn. Comput. 2016, 8, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. In Proceedings of the the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1746–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Chair-Lapata, M.P.; Chair-Ng, H.T.P. Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–27 October 2008; pp. 1631–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Sobhani, P.; Guo, H. Long Short-Term Memory over Tree Structures. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 1604–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Taboada, M.; Brooke, J.; Tofiloski, M.; Voll, K.; Stede, M. Lexicon-Based Methods for Sentiment Analysis. Comput. Linguist. 2011, 37, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ji, D. Context-sensitive twitter sentiment classification using neural network. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Vo, D.T.; Zhang, Y. Context-Sensitive Lexicon Features for Neural Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–5 November 2016; pp. 1629–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Qiu, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, X. Multi-Timescale Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network for Modelling Sentences and Documents. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 2326–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Vo, D.T. Gated neural networks for targeted sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 3087–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, pp. 3087–3093. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, M.; Bihorac, O.A.; Rouces, J. Aspect-based sentiment analysis using BERT. In Proceedings of the 22nd Nordic Conference on Computational Linguistics, Turku, Finland, 30 September–2 October 2019; pp. 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.-C.; Wang, J.; Lai, R.K.; Zhang, X. Refining Word Embeddings for Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 September 2017; pp. 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Tree Communication Models for Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 3518–3527. [Google Scholar]
- Thongtan, T.; Phienthrakul, T. Sentiment Classification Using Document Embeddings Trained with Cosine Similarity. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Student Research Workshop, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi, A.; Shamsuddin, S.M.; Hasan, S.; Piran, J. Deep learning-based sentiment classification of evaluative text based on Multi-feature fusion. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Cohan, A.; Beltagy, I.; King, D.; Dalvi, B.; Weld, D. Pretrained Language Models for Sequential Sentence Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.04054. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, H. Reliable Classification of FAQs with Spelling Errors Using an Encoder-Decoder Neural Network in Korean. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merrienboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the Properties of Neural Machine Translation: Encoder–Decoder Approaches. In Proceedings of the SSST@EMNLP 2014, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, Doha, Qatar, 25 October 2014; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 1412–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, A.; Ram, A.; Tang, R.; Lin, J. Rethinking Complex Neural Network Architectures for Document Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4046–4051. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Paul, M.J. Neural Temporality Adaptation for Document Classification: Diachronic Word Embeddings and Domain Adaptation Models. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL): Stroudsburg, PA, USA; pp. 4113–4123. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, E.; Bird, S. NLTK: The Natural Language Toolkit. arXiv 2002, arXiv:cs/0205028, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS): San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Dyer, C.; He, X.; Smola, A.; Hovy, E. Hierarchical Attention Networks for Document Classification. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 1480–1489. [Google Scholar]
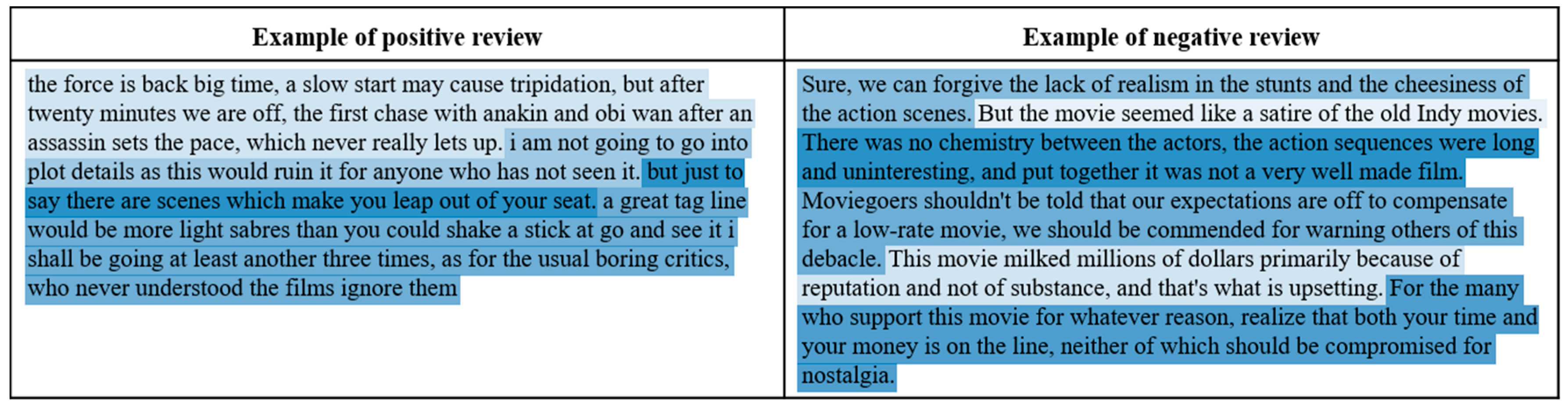
| Sentence | Polarity of a Sentence | Polarity of a Document |
|---|---|---|
| “From my opinion, No Country for Old Men isn’t the best weak Coen brothers film.” | Weak negative | Strong positive |
| “Josh Brolin is hunting in the desert.” | Neutral | |
| “But, that is not to say that it’s a bad film.” | Positive | |
| “It really is a solid piece of cinema.” | Strong positive |
| Dataset | Train | Development | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| IMDB | 108,535 | 13,567 | 13,567 |
| Yelp-hotel | 20,975 | 6993 | 6993 |
| Yelp-rest | 106,943 | 35,648 | 35,648 |
| Amazon | 59,399 | 11,880 | 11,880 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimension of token embedding | 128 |
| Dimension of a hidden node in the class embedding | 300 |
| Dimension of q hidden nodes in the sentence encoder | 768 |
| Max sentence length | 512 |
| Max number of sentences | 50 |
| Batch size | 64 |
| Learning rate | 0.00002 |
| Model | IMDB | Yelp-Hotel | Yelp-Rest | Amazon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valid | Test | Valid | Test | Valid | Test | Valid | Test | |
| Kim-CNN [8] | 0.429 | 0.427 | 0.794 | 0.775 | 0.805 | 0.806 | 0.853 | 0.817 |
| Adhikari-support vector machine [28] | 0.425 | 0.424 | - | - | - | |||
| Adhikari-logistic regression [28] | 0.431 | 0.434 | - | - | - | |||
| HAN [32] | 0.518 | 0.512 | 0.833 | 0.810 | 0.841 | 0.839 | 0.867 | 0.848 |
| ALBERT-Base | 0.520 | 0.519 | 0.827 | 0.827 | 0.871 | 0.874 | 0.870 | 0.858 |
| LSTM-Reg [28] | 0.534 | 0.528 | 0.813 | 0.796 | 0.837 | 0.840 | 0.863 | 0.837 |
| Knowledge distillation-LSTM [28] | 0.545 | 0.537 | - | - | - | |||
| Proposed model | 0.546 | 0.548 | 0.843 | 0.833 | 0.878 | 0.882 | 0.885 | 0.876 |
| Model | Accuracy (Accuracy in the Valid. Dataset) |
|---|---|
| The whole model | 0.548 (0.546) |
| - Class similarity embedding for a sentence | 0.545 (0.545) |
| - Gated sentence embedding | 0.543 (0.543) |
| - Class similarity embedding for a document | 0.545 (0.548) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, G.; Oh, S.; Kim, H. Improving Document-Level Sentiment Classification Using Importance of Sentences. Entropy 2020, 22, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121336
Choi G, Oh S, Kim H. Improving Document-Level Sentiment Classification Using Importance of Sentences. Entropy. 2020; 22(12):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121336
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Gihyeon, Shinhyeok Oh, and Harksoo Kim. 2020. "Improving Document-Level Sentiment Classification Using Importance of Sentences" Entropy 22, no. 12: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121336
APA StyleChoi, G., Oh, S., & Kim, H. (2020). Improving Document-Level Sentiment Classification Using Importance of Sentences. Entropy, 22(12), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22121336






