Transfer Entropy Analysis of Interactions between Bats Using Position and Echolocation Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Data Collection
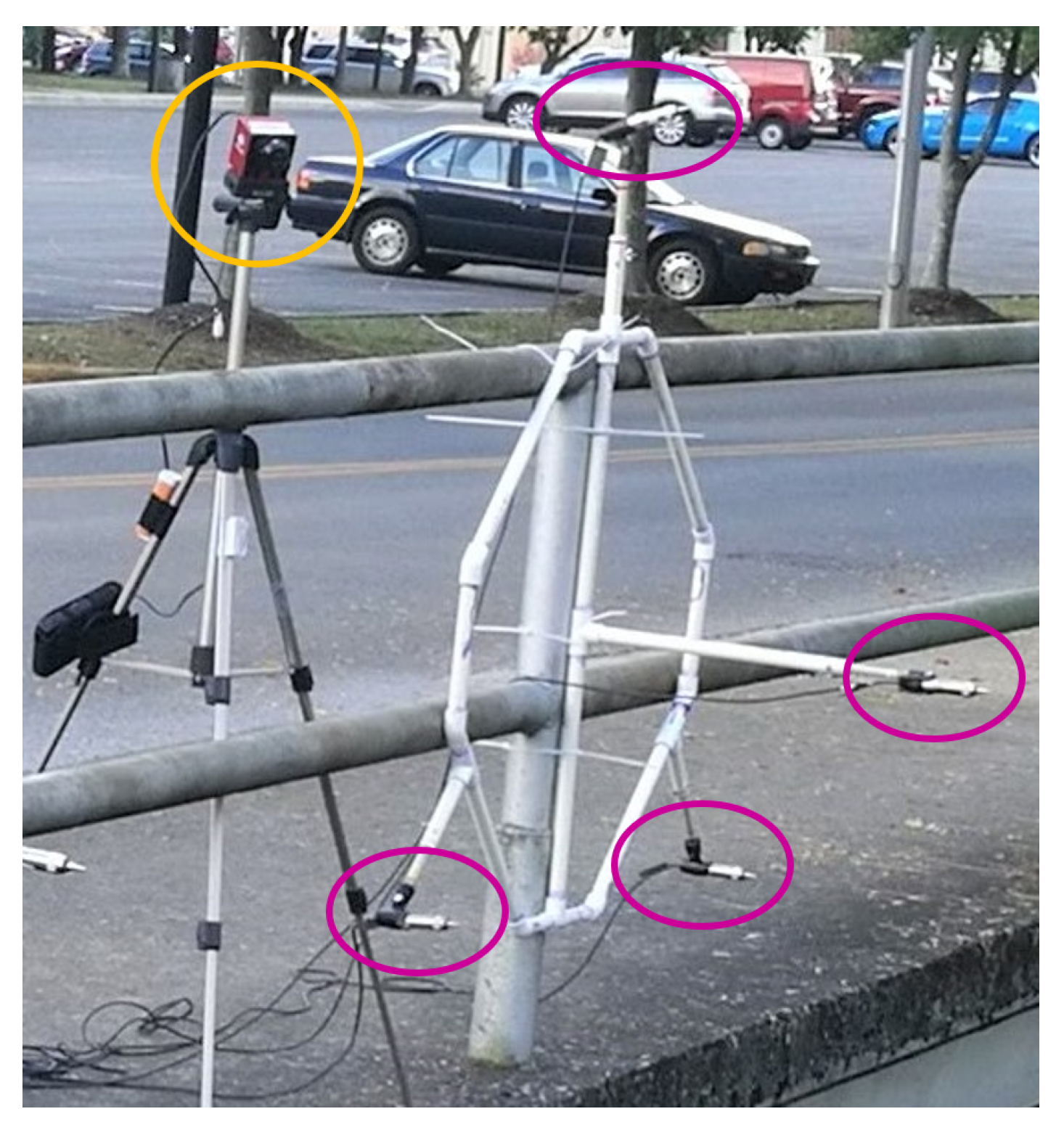
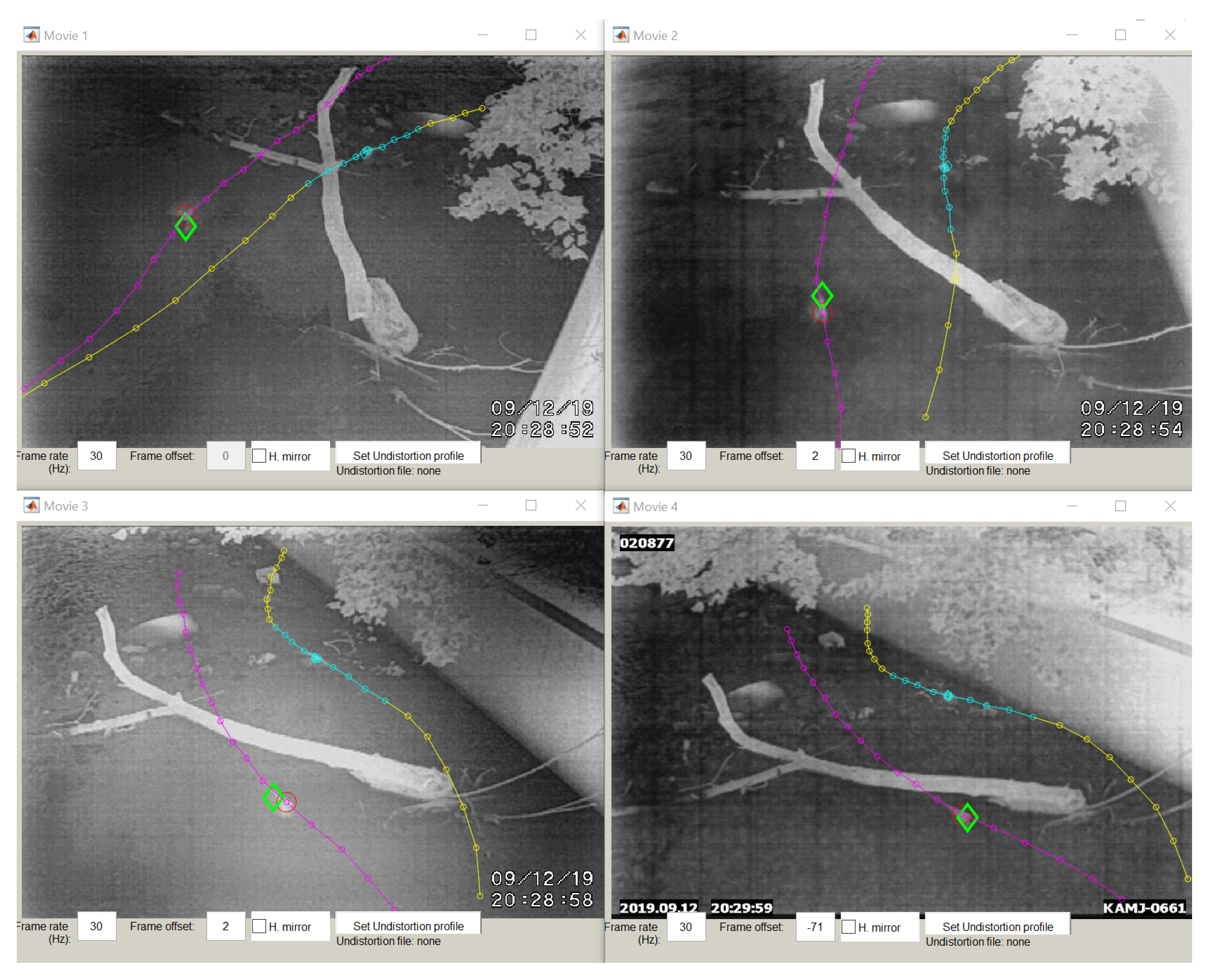
2.1.1. Cameras
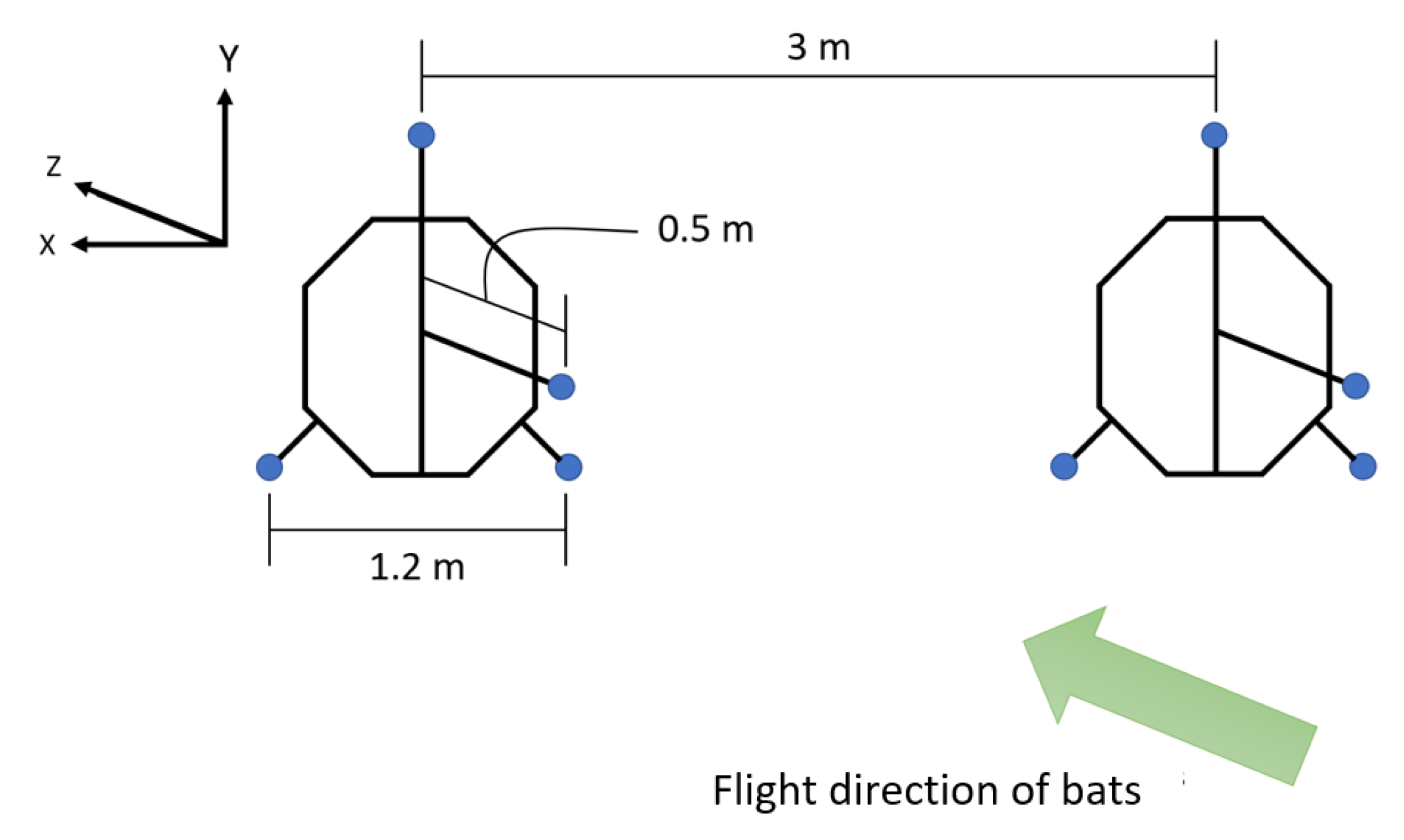
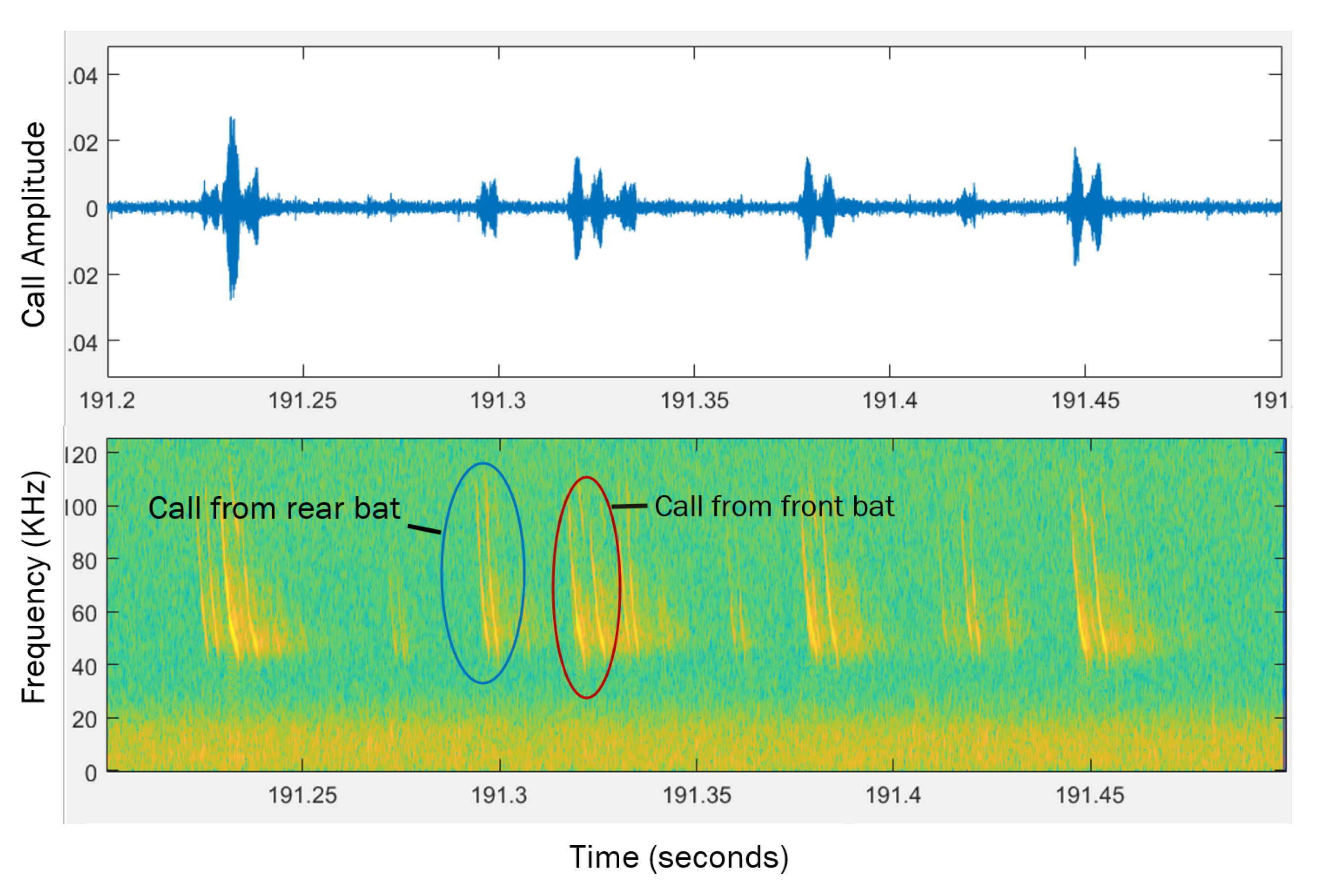
2.1.2. Microphone Array
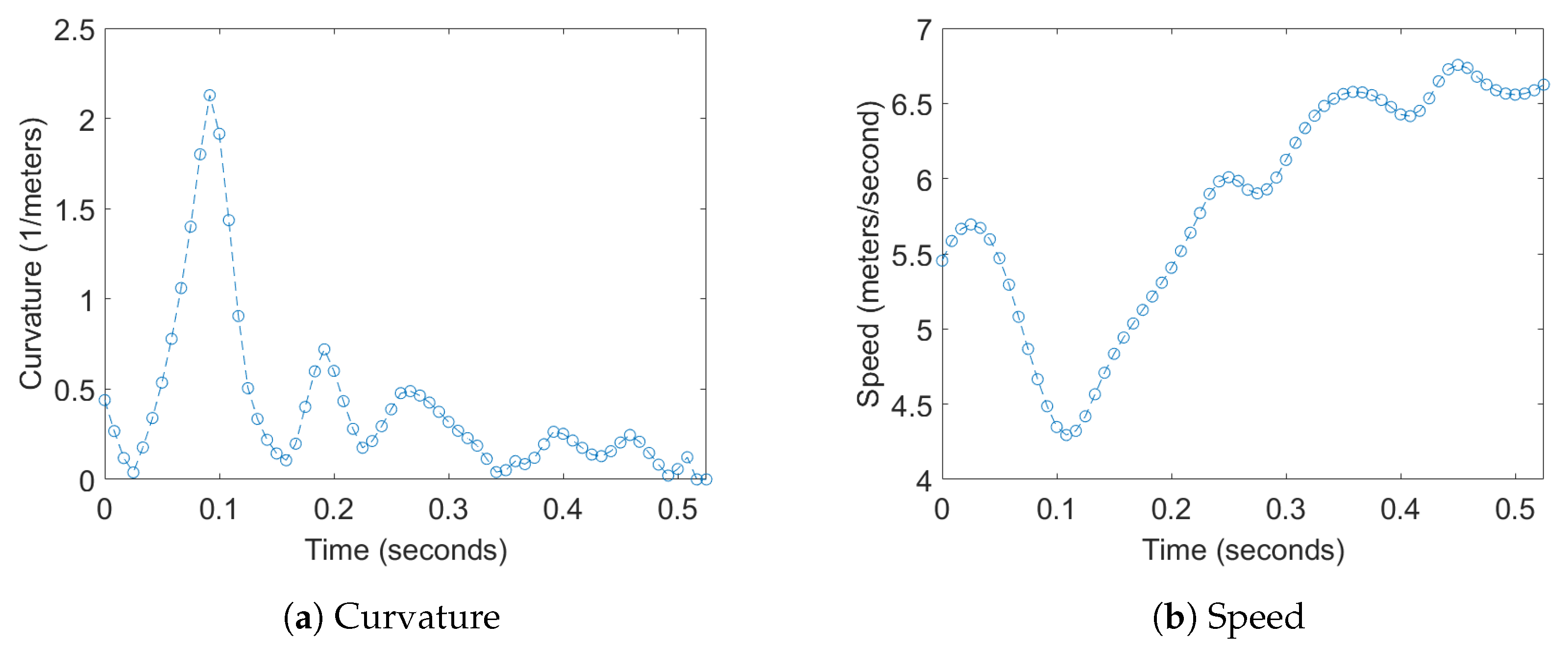
2.2. Data Analysis
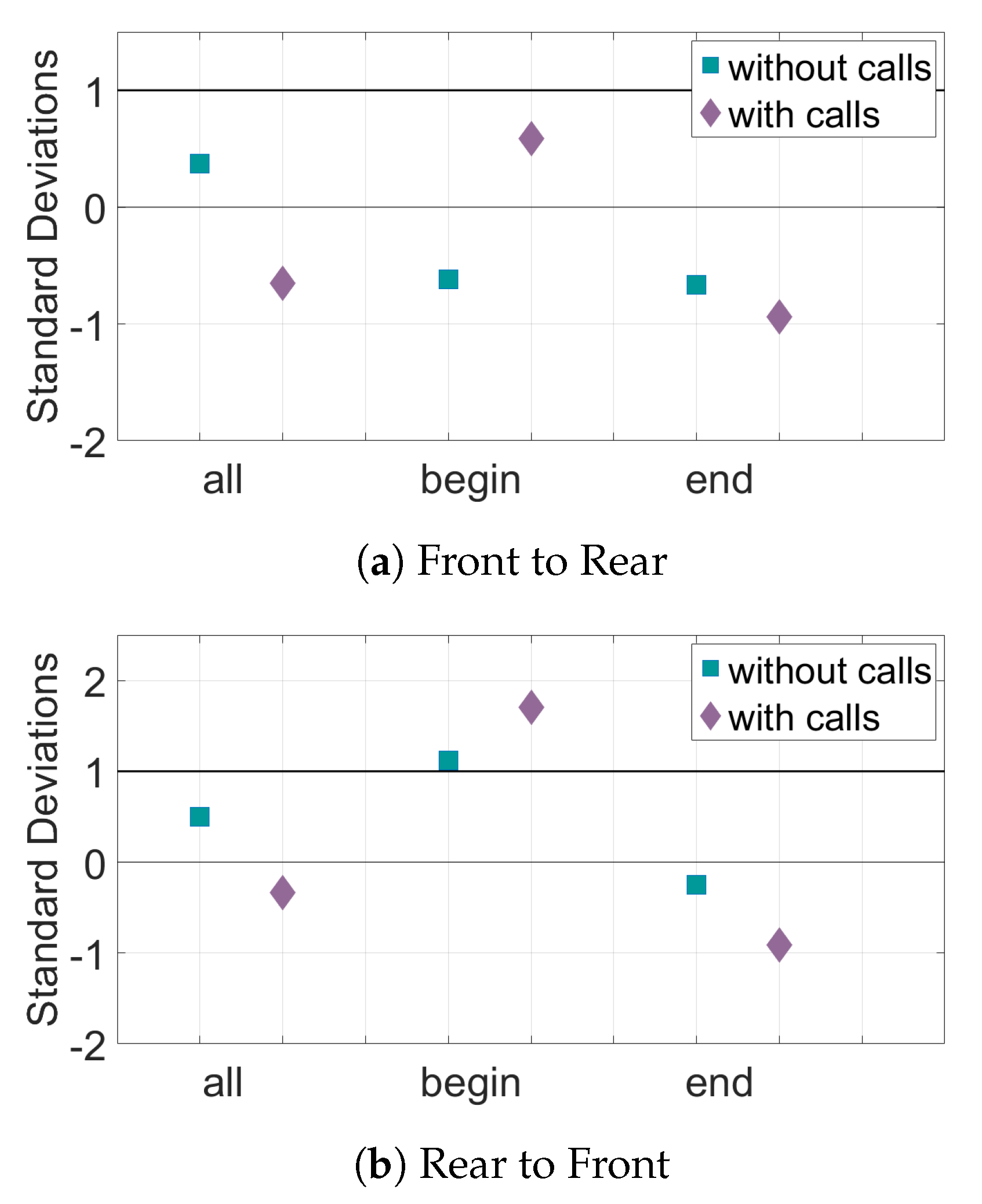
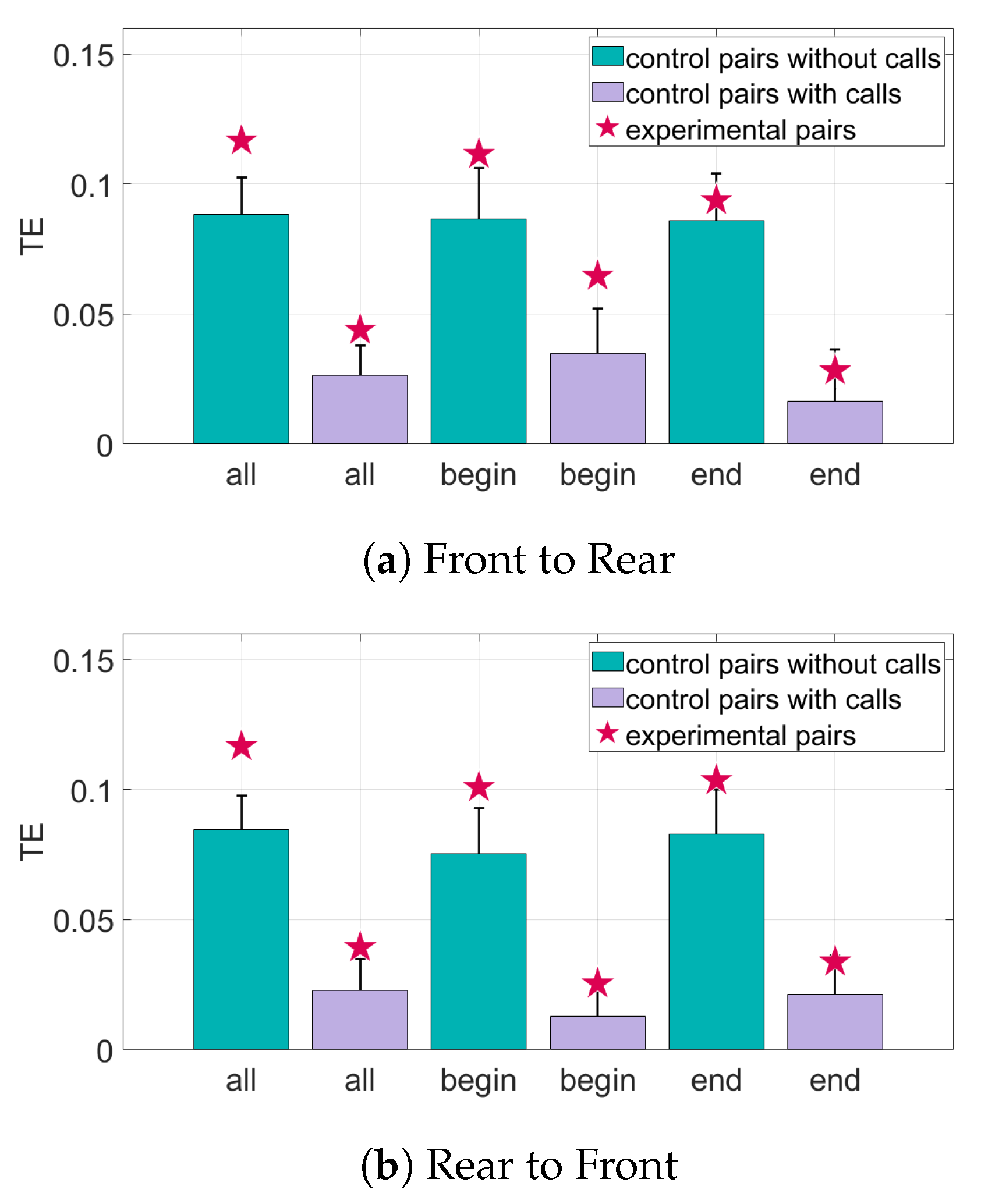
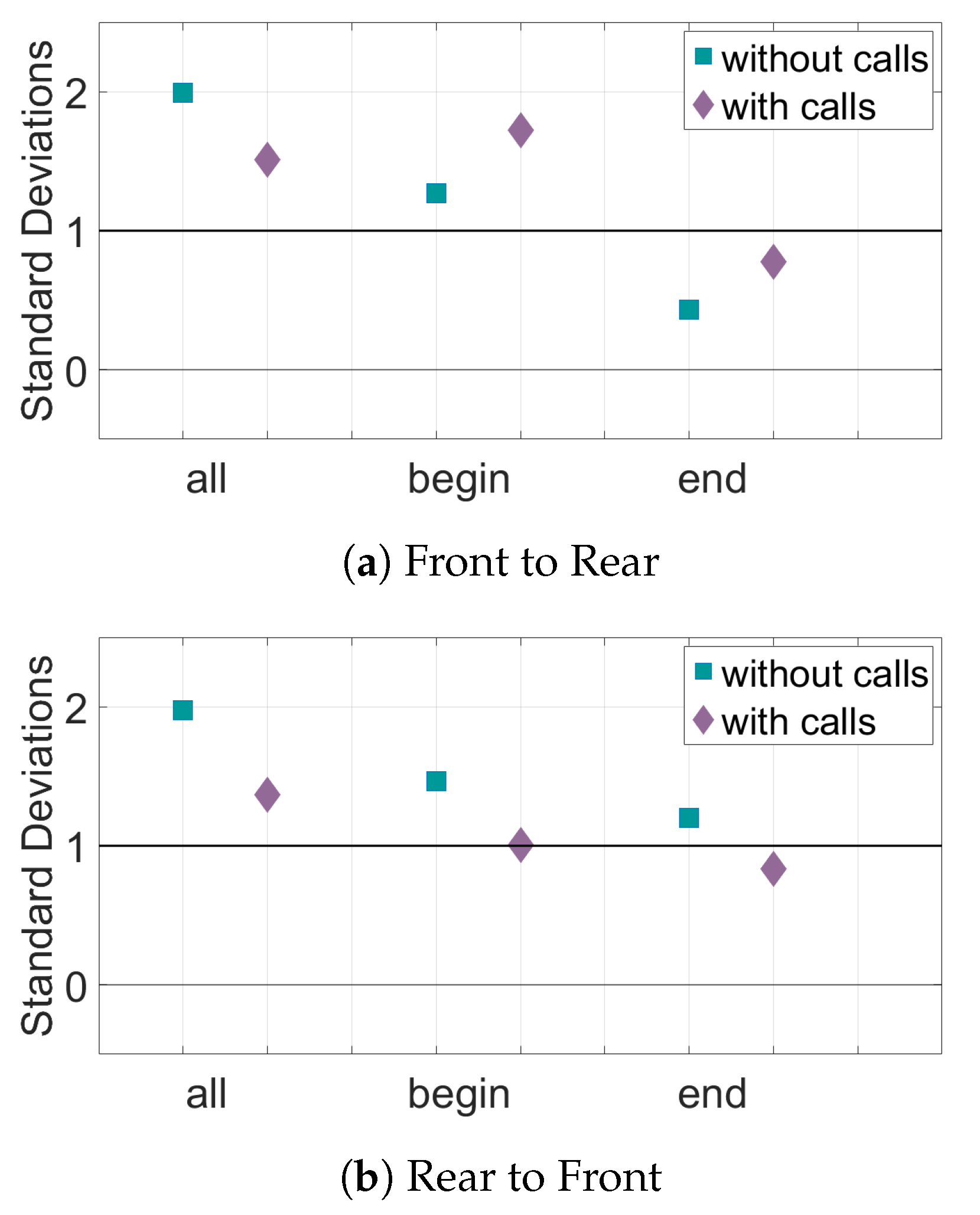
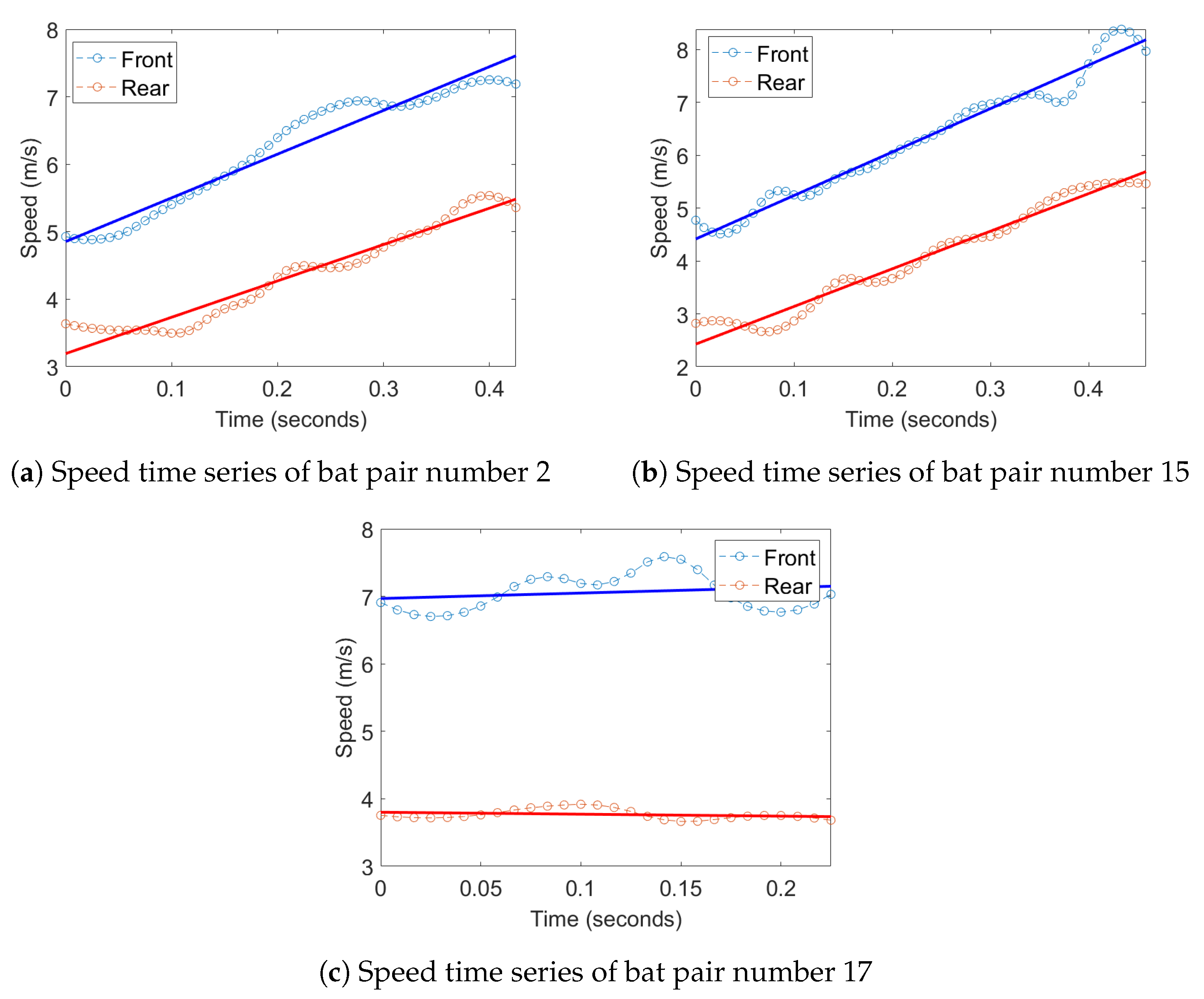
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parrish, J.K.; Hamner, W.M. Animal Groups in Three Dimensions: How Species Aggregate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Ruxton, G.D. Living in Groups; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkiewicz, K.; Lemasson, B.; Rowland, M.; Hein, A.; Sun, J.; Berdahl, A.; Mayo, M.; Moehlis, J.; Porfiri, M.; Fernández-Juricic, E.; et al. Decoding collective communications using information theory tools. J. R. Soc. Interface 2020, 17, 20190563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemasson, B.H.; Anderson, J.J.; Goodwin, R.A. Collective motion in animal groups from a neurobiological perspective: The adaptive benefits of dynamic sensory loads and selective attention. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 261, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strömbom, D. Collective motion from local attraction. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 283, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramaglia, S.; Wu, G.R.; Pellicoro, M.; Marinazzo, D. Expanding the transfer entropy to identify information circuits in complex systems. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 066211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizier, J.T.; Heinzle, J.; Horstmann, A.; Haynes, J.D.; Prokopenko, M. Multivariate information-theoretic measures reveal directed information structure and task relevant changes in fMRI connectivity. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2011, 30, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, R.; Wibral, M.; Lindner, M.; Pipa, G. Transfer entropy—a model-free measure of effective connectivity for the neurosciences. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2011, 30, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopenko, M.; Boschetti, F.; Ryan, A.J. An information-theoretic primer on complexity, self-organization, and emergence. Complexity 2009, 15, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinoli, A.; Easton, K.; Agassounon, W. Modeling swarm robotic systems: A case study in collaborative distributed manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2004, 23, 415–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Jenkin, M.R.; Milios, E.; Wilkes, D. A taxonomy for multi-agent robotics. Auton. Robot. 1996, 3, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, J.; Heitzig, J.; Petoukhov, V.; Kurths, J. Escaping the curse of dimensionality in estimating multivariate transfer entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 258701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ver Steeg, G.; Galstyan, A. Information-theoretic measures of influence based on content dynamics. In Proceedings of the Sixth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Rome, Italy, 4–8 February 2013; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, T.L.; Colbaugh, R.; Glass, K.; Schnizlein, D. Use of transfer entropy to infer relationships from behavior. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Cyber Security and Information Intelligence Research Workshop, Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 8–10 January 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Butail, S.; Mwaffo, V.; Porfiri, M. Model-free information-theoretic approach to infer leadership in pairs of zebrafish. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 042411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, T.O.; Perony, N.; Tessone, C.J.; Bousquet, C.A.; Manser, M.B.; Schweitzer, F. Dynamical coupling during collective animal motion. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1311.1417. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, W.M.; Sun, J.; Ouellette, N.T.; Bollt, E.M. Inference of causal information flow in collective animal behavior. IEEE Trans. Mol. Biol. Multi-Scale Commun. 2016, 2, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Howes, K.; Müller, R.; Butail, S.; Abaid, N. Extracting Interactions between Flying Bat Pairs Using Model-Free Methods. Entropy 2019, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, N.; Abaid, N. A transfer entropy analysis of leader-follower interactions in flying bats. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2015, 224, 3279–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butail, S.; Ladu, F.; Spinello, D.; Porfiri, M. Information flow in animal-robot interactions. Entropy 2014, 16, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; MacIver, M.A. Sensory acquisition in active sensing systems. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2006, 192, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.A.; Moss, C.F.; Vater, M. Echolocation in Bats and Dolphins; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky, N.; Fenton, M.B.; Tsoar, A.; Korine, C. Dynamics of jamming avoidance in echolocating bats. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betke, M.; Hirsh, D.E.; Makris, N.C.; McCracken, G.F.; Procopio, M.; Hristov, N.I.; Tang, S.; Bagchi, A.; Reichard, J.D.; Horn, J.W.; et al. Thermal imaging reveals significantly smaller Brazilian free-tailed bat colonies than previously estimated. J. Mammal. 2008, 89, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, D.A.; Keeler, R.C.; Mizutani, H. Ammonia volatilization in a Mexican bat cave ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 1995, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, M.E.; Stamper, S.A.; Simmons, J.A. Jamming avoidance response of big brown bats in target detection. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Kobayasi, K.I.; Hiryu, S. Rapid frequency control of sonar sounds by the FM bat, Miniopterus fuliginosus, in response to spectral overlap. Behav. Process. 2016, 128, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiryu, S.; Bates, M.E.; Simmons, J.A.; Riquimaroux, H. FM echolocating bats shift frequencies to avoid broadcast–echo ambiguity in clutter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7048–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, J.; Jackson, W.; Smotherman, M. Groups of bats improve sonar efficiency through mutual suppression of pulse emissions. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.M.; Patricio, A.; Manohar, R.; Smotherman, M. Influence of signal direction on sonar interference. Anim. Behav. 2019, 155, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Abaid, N.; Müller, R. Bats adjust their pulse emission rates with swarm size in the field. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 4318–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.; Xian, W.; Moss, C.F. Flying in silence: Echolocating bats cease vocalizing to avoid sonar jamming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13116–13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koay, G.; Kearns, D.; Heffner, H.E.; Heffner, R.S. Passive sound-localization ability of the big brown bat (Eptesicus Fuscus). Hear. Res. 1998, 119, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.J.; Weller, T.J. Inconspicuous echolocation in hoary bats (Lasiurus Cinereus). Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristau, R. Analysis Finds 37 of Nearly 500 Bridges in Region Structurally Deficient. 2017. Available online: https://www.heraldcourier.com/news/analysis-finds-of-nearly-bridges-in-region-structurally-deficient/article_fa077501-077d-5e91-8f8e-9be20b967ecf.html (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Zhang, Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. Help Center: What Is Camera Calibration. 2020. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/vision/ug/camera-calibration.html (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Hedrick, T.L. Software techniques for two-and three-dimensional kinematic measurements of biological and biomimetic systems. Bioinspir. Biomimetics 2008, 3, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriault, D.H.; Fuller, N.W.; Jackson, B.E.; Bluhm, E.; Evangelista, D.; Wu, Z.; Betke, M.; Hedrick, T.L. A protocol and calibration method for accurate multi-camera field videography. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourakis, M.I.; Argyros, A.A. SBA: A software package for generic sparse bundle adjustment. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 2009, 36, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. Help Center: Smooth. 2020. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/curvefit/smooth.html (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Yovel, Y. Batalef—Audio Analysis Software for Animal Research. 2020. Available online: www.yossiyovel.com (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Schreiber, T. Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizier, J.T. JIDT: An information-theoretic toolkit for studying the dynamics of complex systems. Front. Robot. AI 2014, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraskov, A.; Stögbauer, H.; Grassberger, P. Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Herrero, G.; Wu, W.; Rutanen, K.; Soriano, M.C.; Pipa, G.; Vicente, R. Assessing coupling dynamics from an ensemble of time series. Entropy 2015, 17, 1958–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.; Reddy, P.V.; Xian, W.; Krishnaprasad, P.S.; Moss, C.F. Effects of competitive prey capture on flight behavior and sonar beam pattern in paired big brown bats, Eptesicus fuscus. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaffer, I.; Abaid, N. Transfer Entropy Analysis of Interactions between Bats Using Position and Echolocation Data. Entropy 2020, 22, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101176
Shaffer I, Abaid N. Transfer Entropy Analysis of Interactions between Bats Using Position and Echolocation Data. Entropy. 2020; 22(10):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101176
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaffer, Irena, and Nicole Abaid. 2020. "Transfer Entropy Analysis of Interactions between Bats Using Position and Echolocation Data" Entropy 22, no. 10: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101176
APA StyleShaffer, I., & Abaid, N. (2020). Transfer Entropy Analysis of Interactions between Bats Using Position and Echolocation Data. Entropy, 22(10), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101176



