Energy Dissipation and Information Flow in Coupled Markovian Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
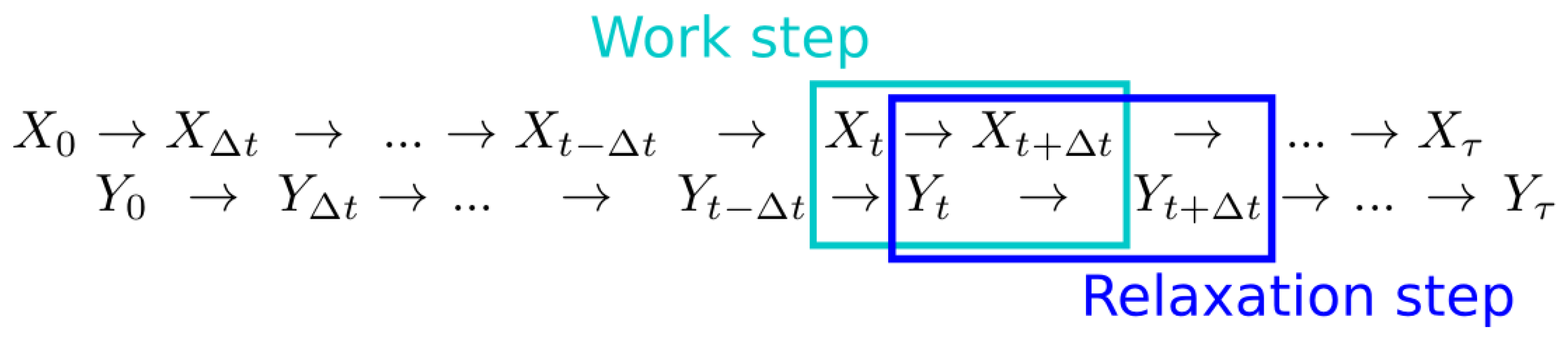
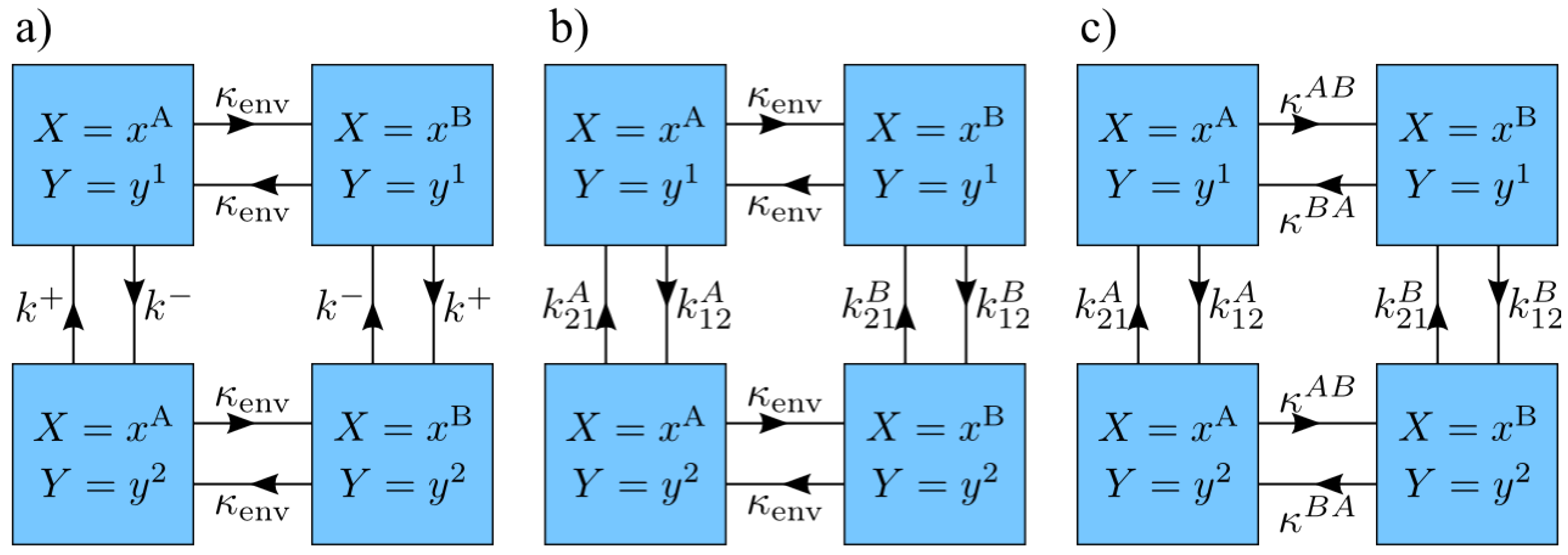
2. Theoretical Background
3. Results
3.1. Alternating Energy Levels
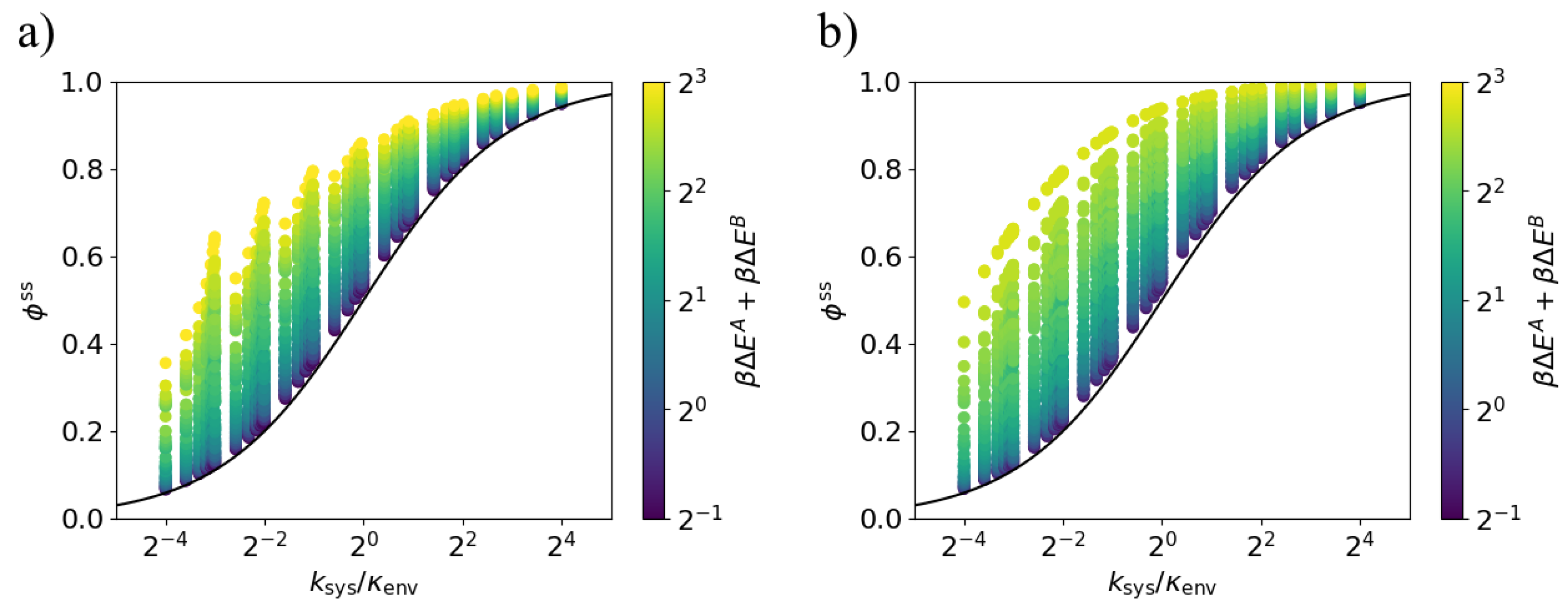
3.2. Arbitrary System Rates
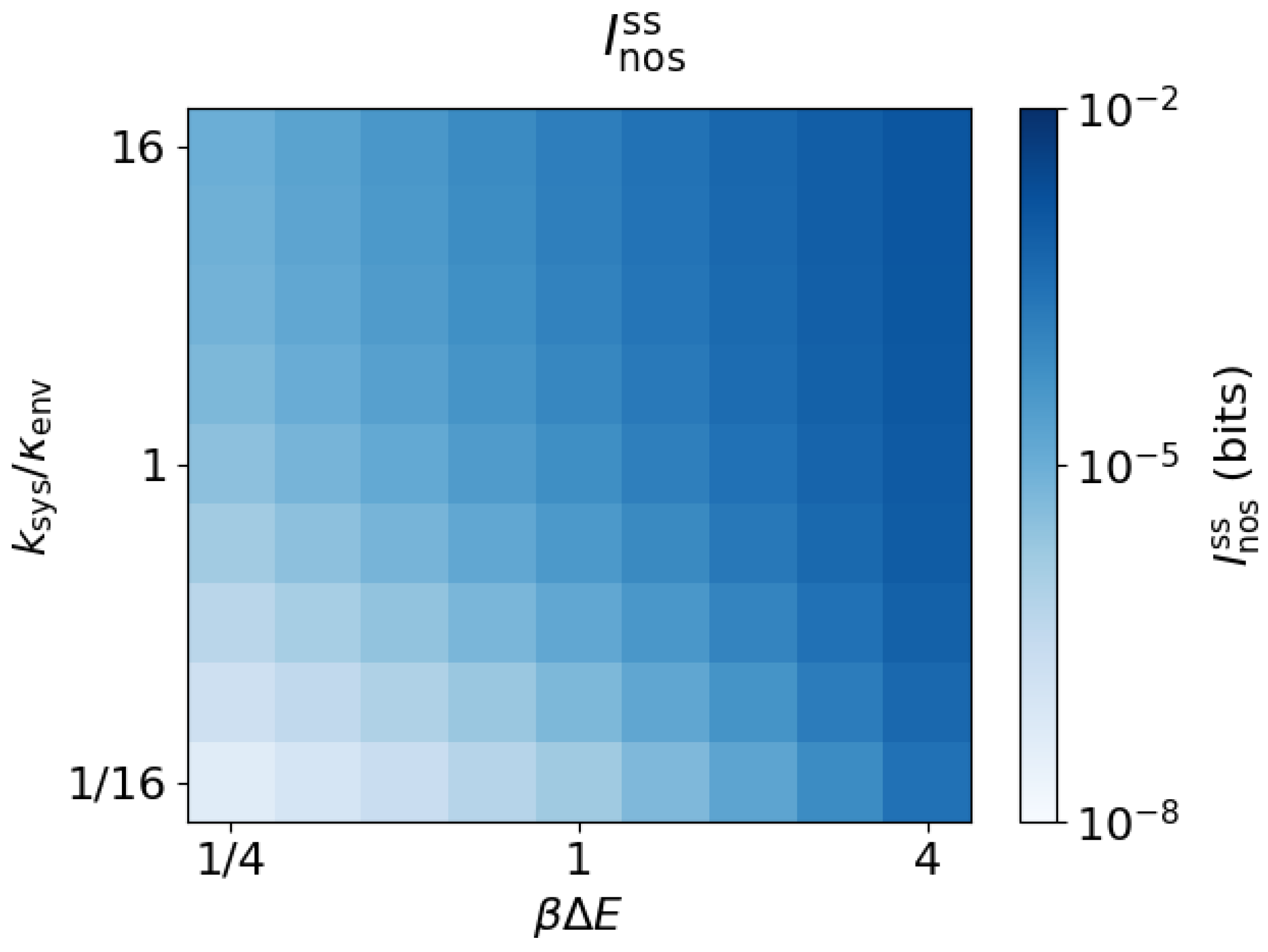
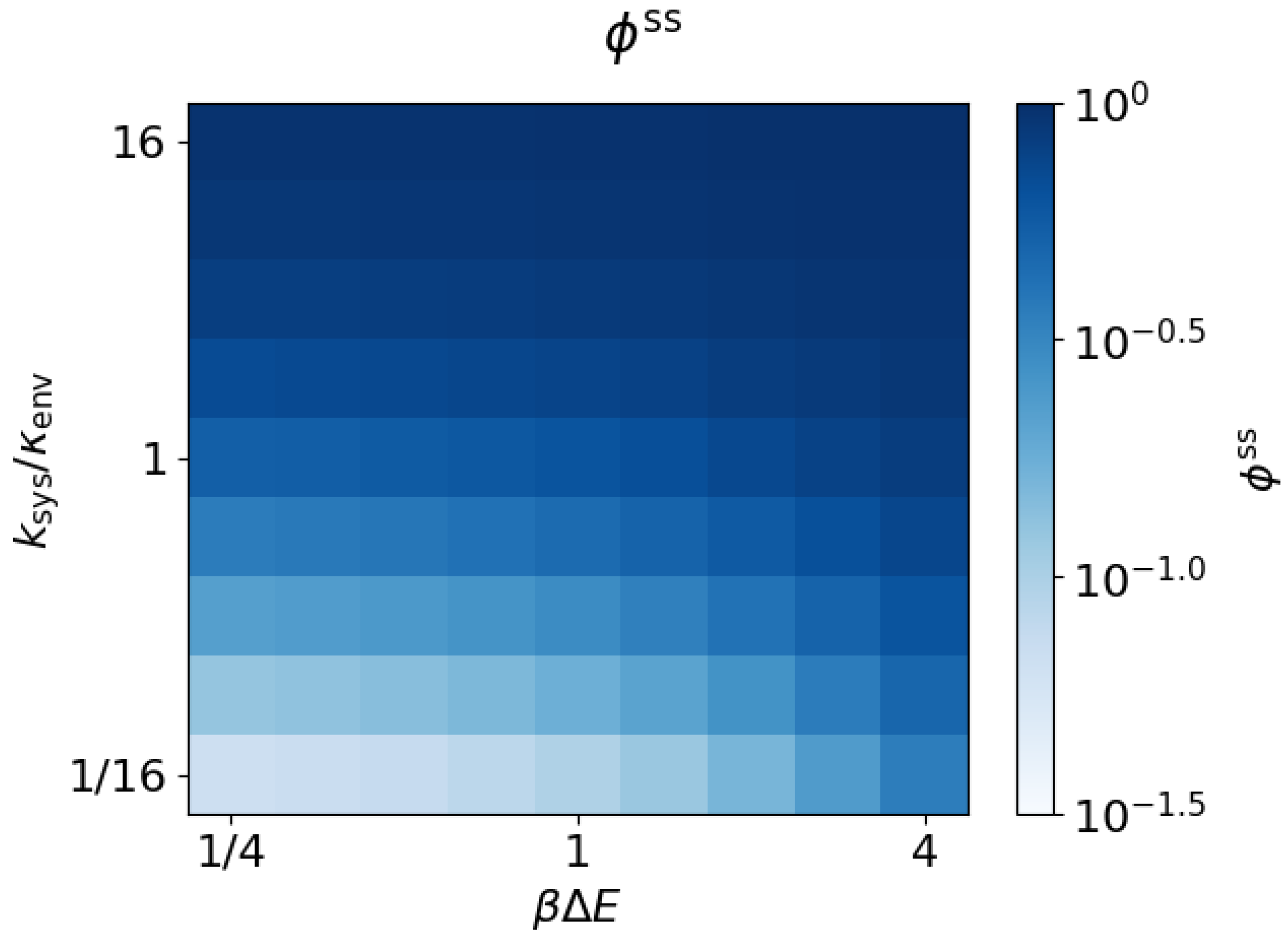
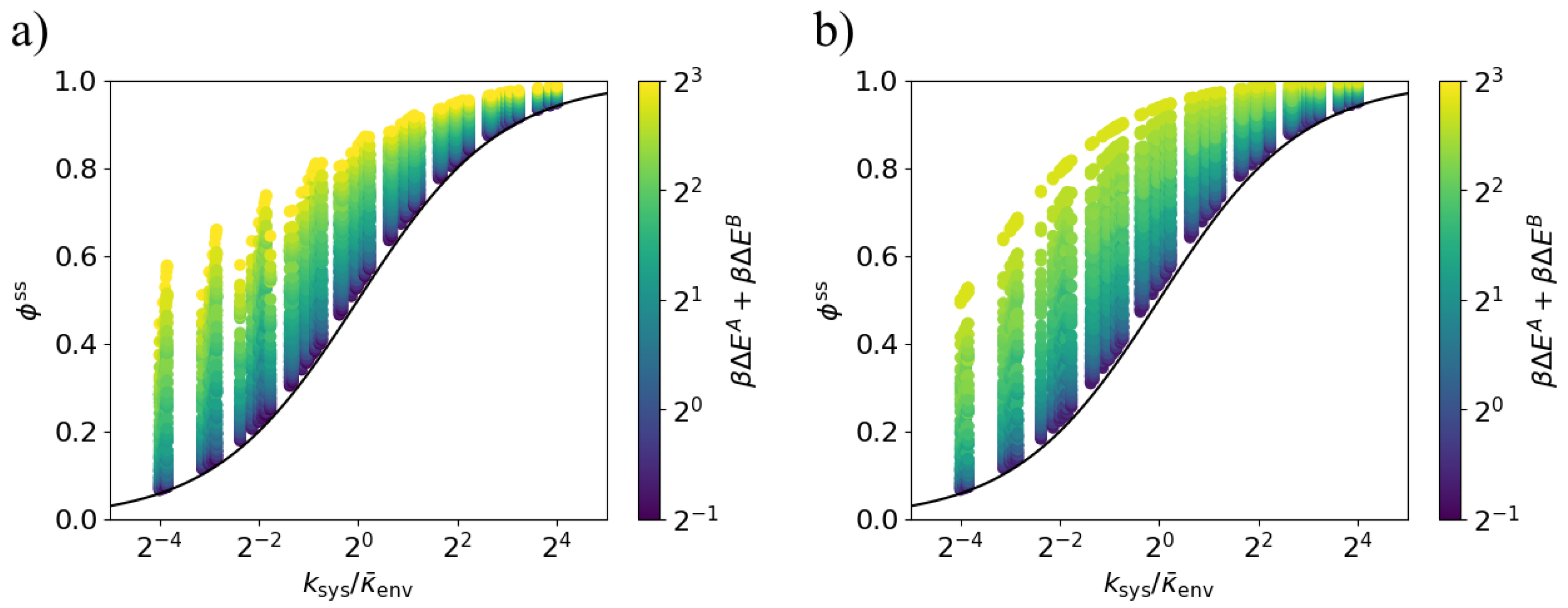
3.3. Arbitrary Environment Rates
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaynes, E.T. Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landauer, R. Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1961, 5, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérut, A.; Arakelyan, A.; Petrosyan, A.; Ciliberto, S.; Dillenschneider, R.; Lutz, E. Experimental verification of Landauer’s principle linking information and thermodynamics. Nature 2012, 483, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.; Gavrilov, M.; Bechhoefer, J. High-precision test of Landauer’s principle in a feedback trap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 190601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, R.; Rhee, A.; Wang, C.J.; Nemenman, I.; Levchenko, A. Information transduction capacity of noisy biochemical signaling networks. Science 2011, 334, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; Schwab, D.J. Energetic costs of cellular computation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17978–17982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Still, S.; Sivak, D.A.; Bell, A.J.; Crooks, G.E. Thermodynamics of prediction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 120604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, H. Engineering applications of biomolecular motors. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 13, 429–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.I.; Sivak, D.A. Toward the design principles of molecular machines. Phys. Can. 2017, 73, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tagkopoulos, I.; Liu, Y.C.; Tavazoie, S. Predictive Behavior within Microbial Genetic Networks. Science 2008, 320, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughlin, S. A simple coding procedure enhances a neuron’s information capacity. Z. Naturforsch. C 1981, 36, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, S.; Vasas, V.; Husbands, P.; Fernando, C. Evolution of Associative Learning in Chemical Networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, D. Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schnakenberg, J. Network theory of microscopic and macroscopic behavior of master equation systems. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1976, 48, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, R.A.; Jones, N.S.; Ouldridge, T.E. What we learn from the learning rate. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2017, 2017, 063502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barato, A.C.; Hartich, D.; Seifert, U. Efficiency of cellular information processing. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartich, D.; Barato, A.C.; Seifert, U. Sensory capacity: An information theoretical measure of the performance of a sensor. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 022116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govern, C.C.; ten Wolde, P.R. Energy Dissipation and Noise Correlations in Biochemical Sensing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 258102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C.; Purcell, E.M. Physics of chemoreception. Biophys. J. 1977, 20, 193–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, L. Information Processing and Energy Dissipation in Neurons. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
| Driving Strength | Weak | Strong | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving Speed | () | () | |
| Quasi-static | () | ||
| Intermediate | () | ||
| Fast | () |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quenneville, M.E.; Sivak, D.A. Energy Dissipation and Information Flow in Coupled Markovian Systems. Entropy 2018, 20, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20090707
Quenneville ME, Sivak DA. Energy Dissipation and Information Flow in Coupled Markovian Systems. Entropy. 2018; 20(9):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20090707
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuenneville, Matthew E., and David A. Sivak. 2018. "Energy Dissipation and Information Flow in Coupled Markovian Systems" Entropy 20, no. 9: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20090707
APA StyleQuenneville, M. E., & Sivak, D. A. (2018). Energy Dissipation and Information Flow in Coupled Markovian Systems. Entropy, 20(9), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20090707





