Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Signal Complexity Analysis
2.1.1. Reconstructed Phase Space
2.1.2. Approximate Entropy
2.1.3. Sample Entropy
2.2. Signal Self-Similarity Analysis
2.2.1. Self-Similar Processes
2.2.2. Rescaled Range Analysis for Self-Similarity Assessment
- (1)
- Divide into n equisized non-overlapping segments with the length of , where and . This process is repeated as long as has more than four data points.
- (2)
- For each segment ,
- (a)
- Center it as , where is the mean of . shows the deviation of from its mean.
- (b)
- Compute the cumulative sum of centered segment as . shows the total sum of as it proceeds in time.
- (c)
- Calculate the largest difference within the cumulative sum , namely,
- (d)
- Calculate the standard deviation of as and obtain its as .
- (3)
- Compute the average rescaled range at n as .
2.3. Complexity and Self-Similarity Analyses Combined
2.3.1. RangeEn: A Proposed Modification to ApEn and SampEn
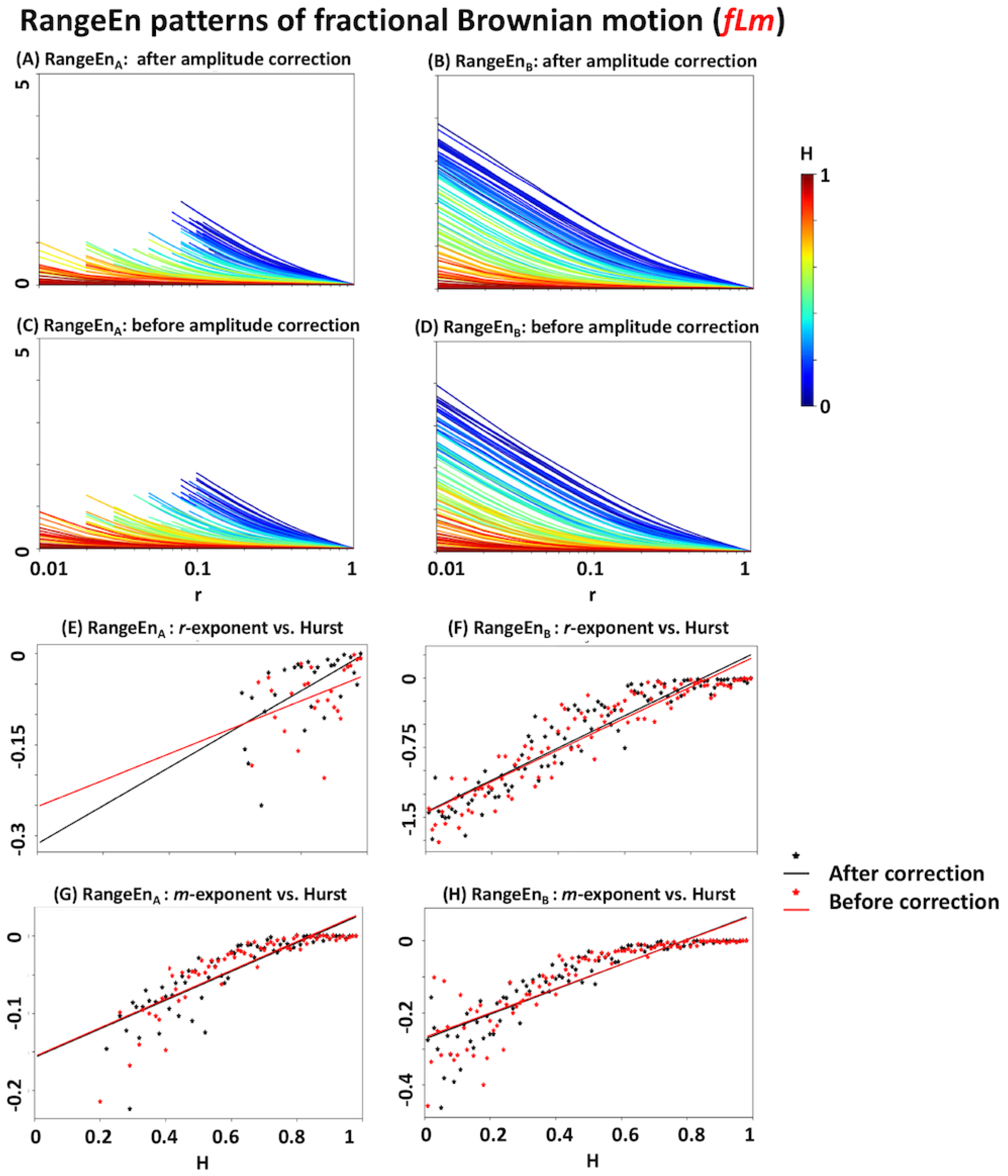
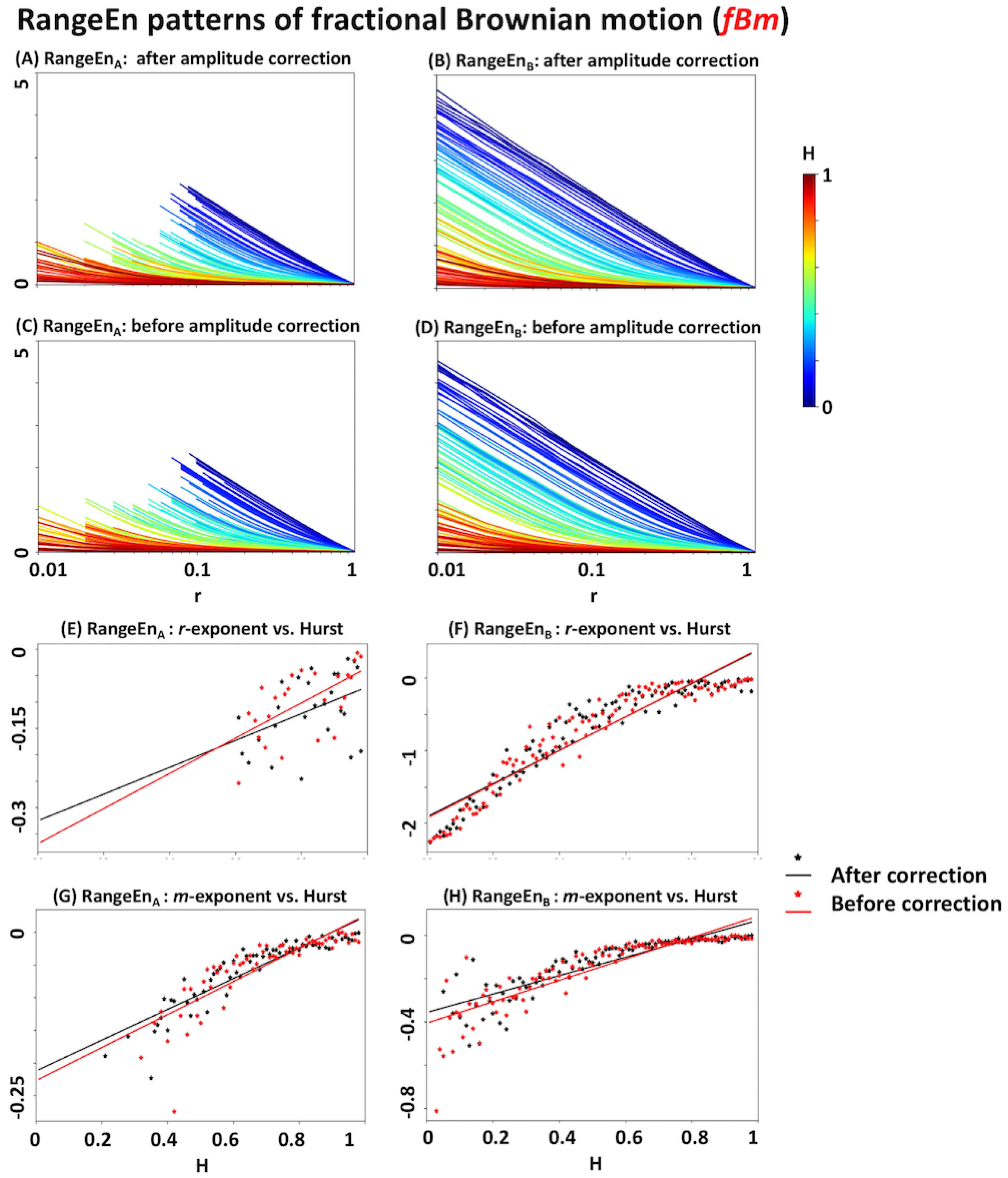
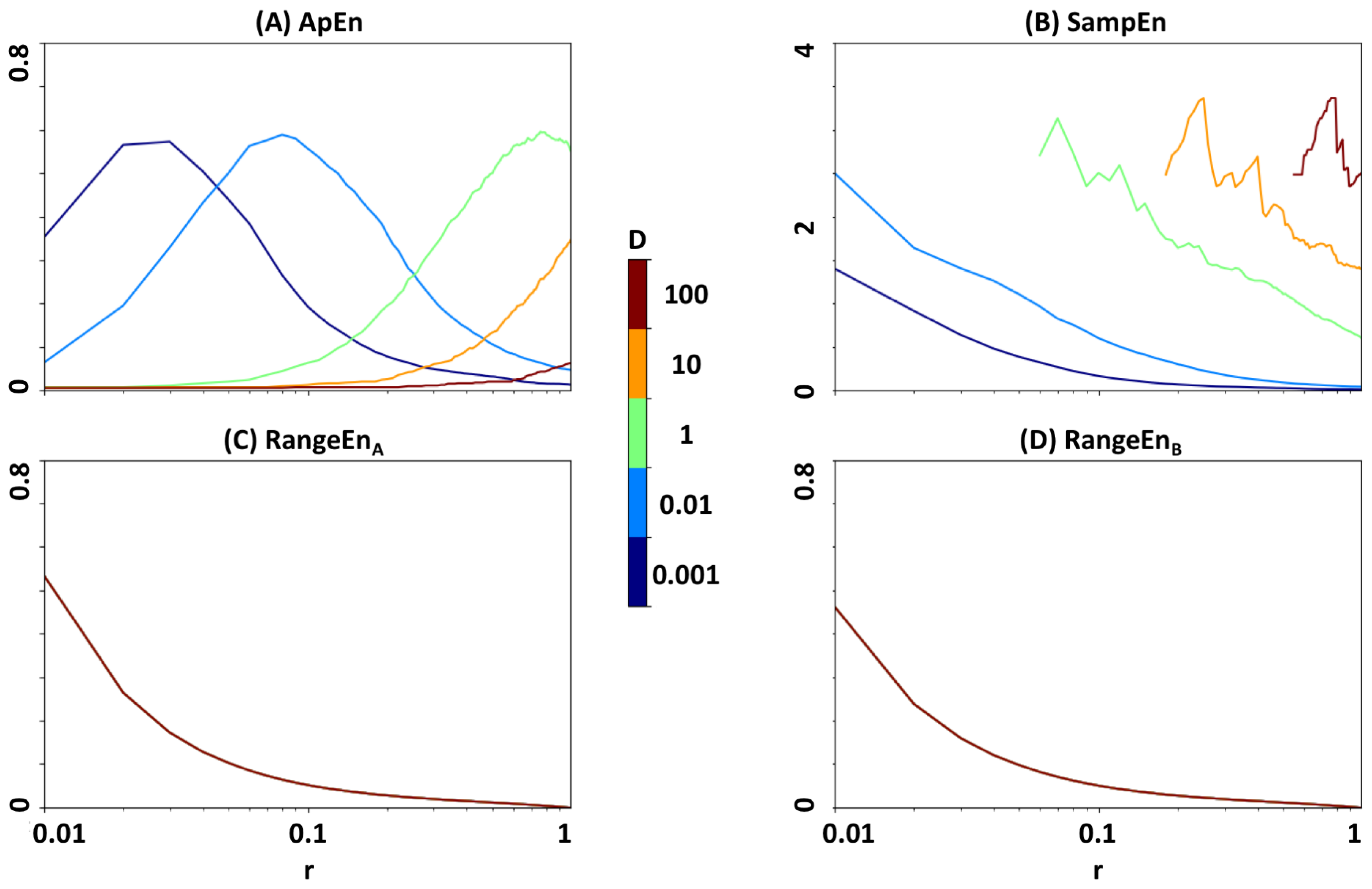
2.3.2. Properties of RangeEn
2.4. Simulations
2.4.1. Synthetic Data
2.4.2. Tolerance Parameter r of Entropy and the Hurst Exponent
2.4.3. Embedding Dimension m of Entropy and the Hurst Exponent
2.5. Epileptic EEG Datasets
3. Results
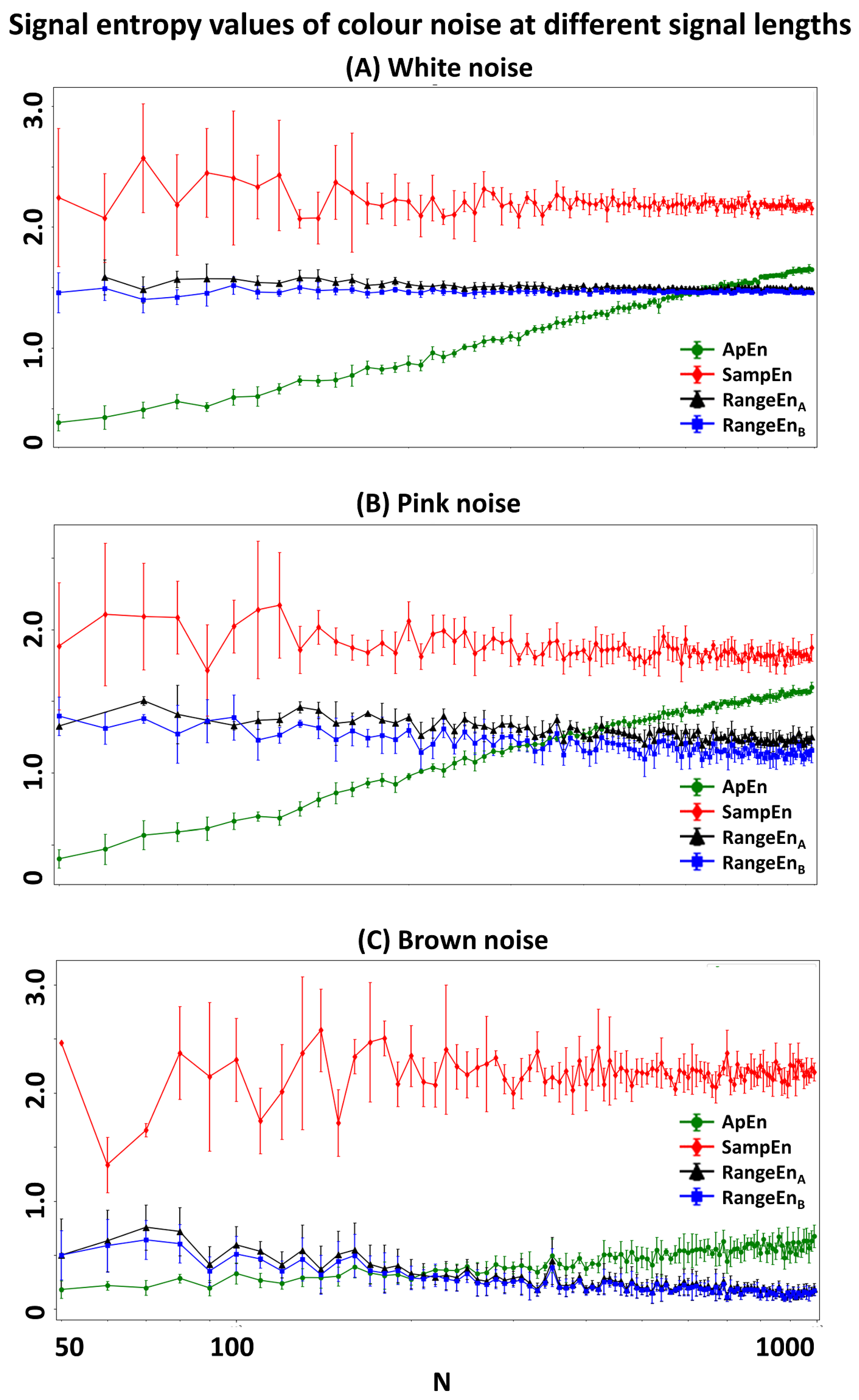
3.1. Sensitivity to Signal Length
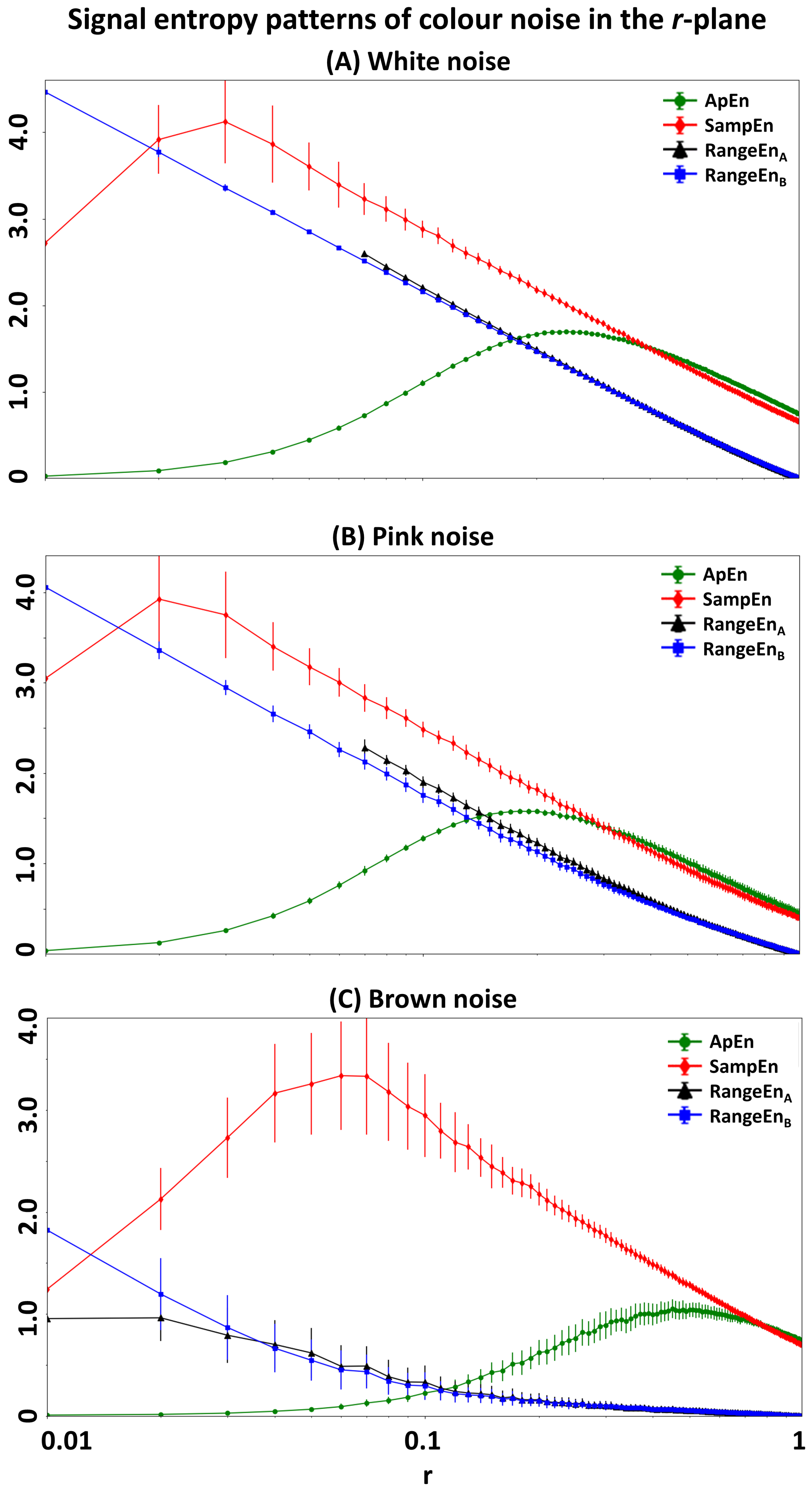
3.2. The Role of Tolerance r
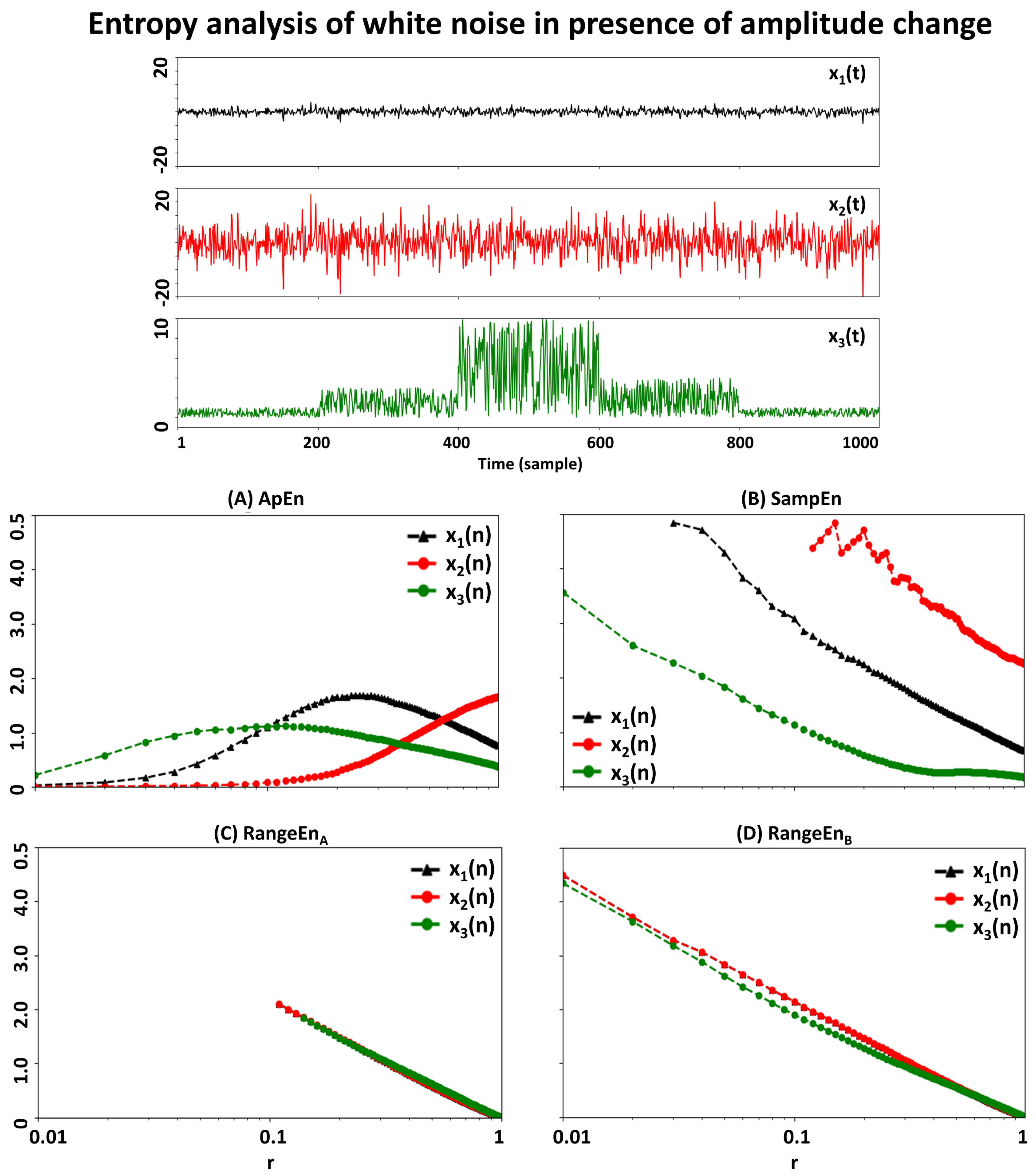
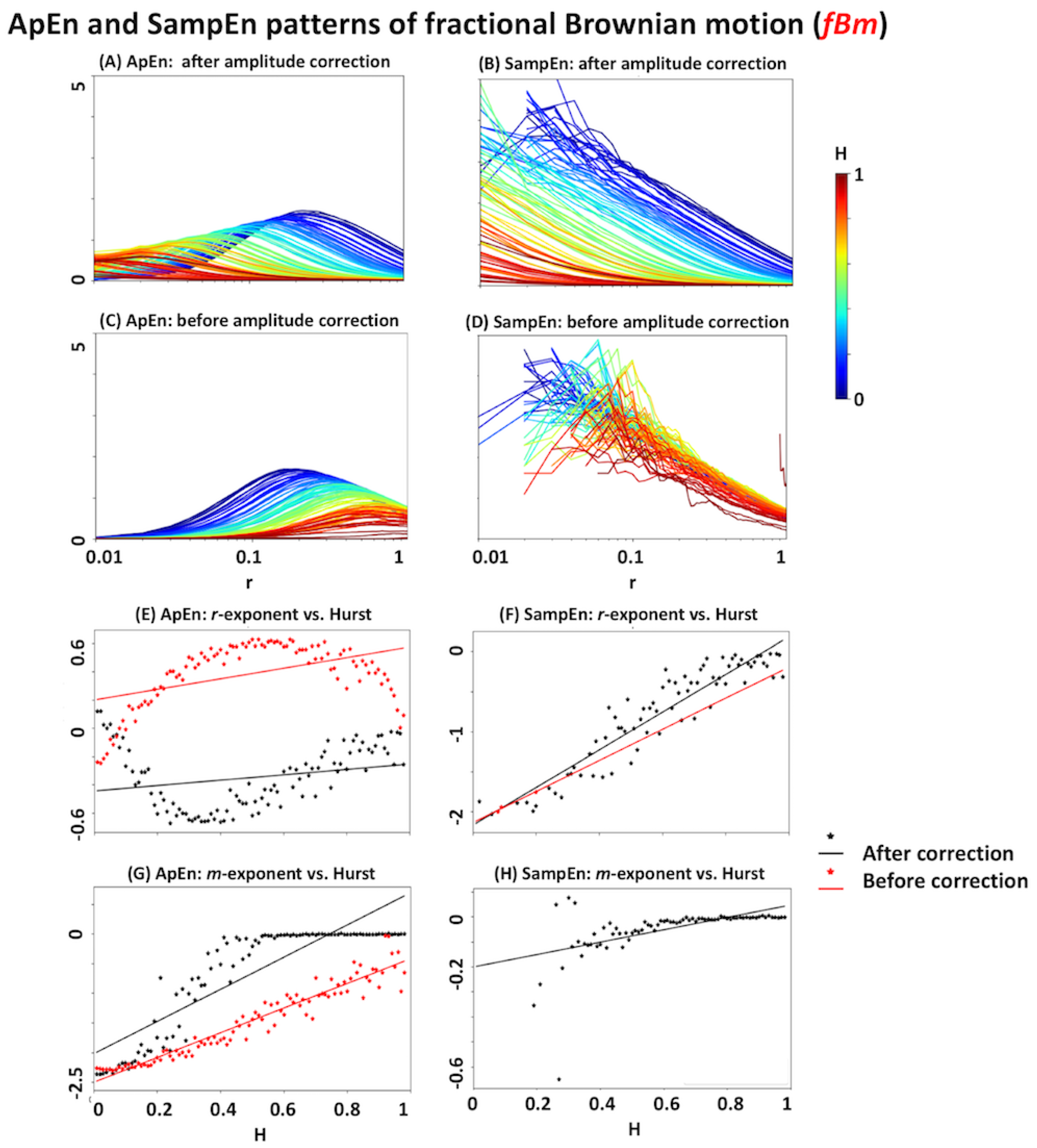
3.3. Dependency to Signal Amplitude
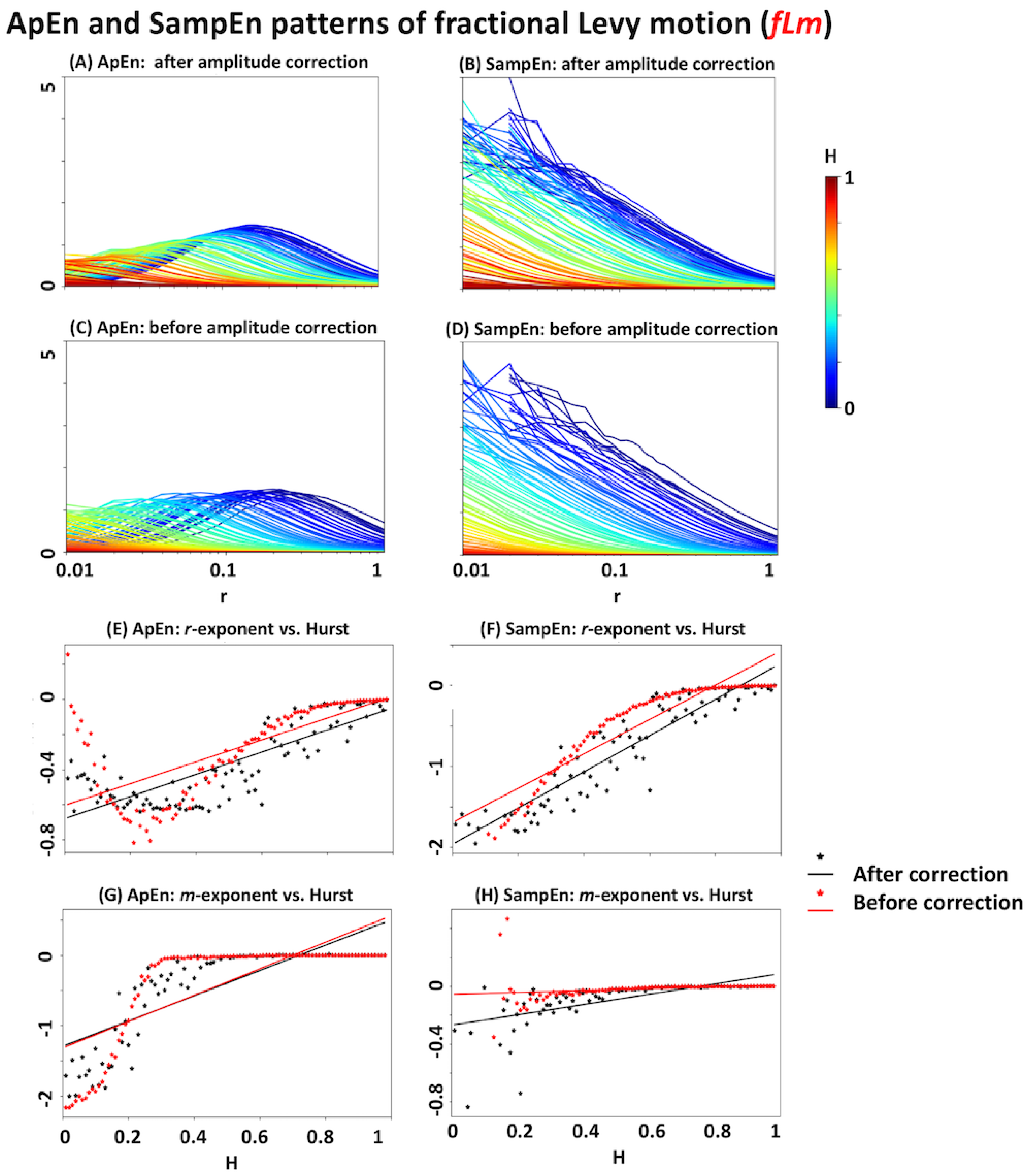
3.4. Relationship with the Hurst Exponent
3.5. Linear Scaling of the Covariance Matrix in fBm
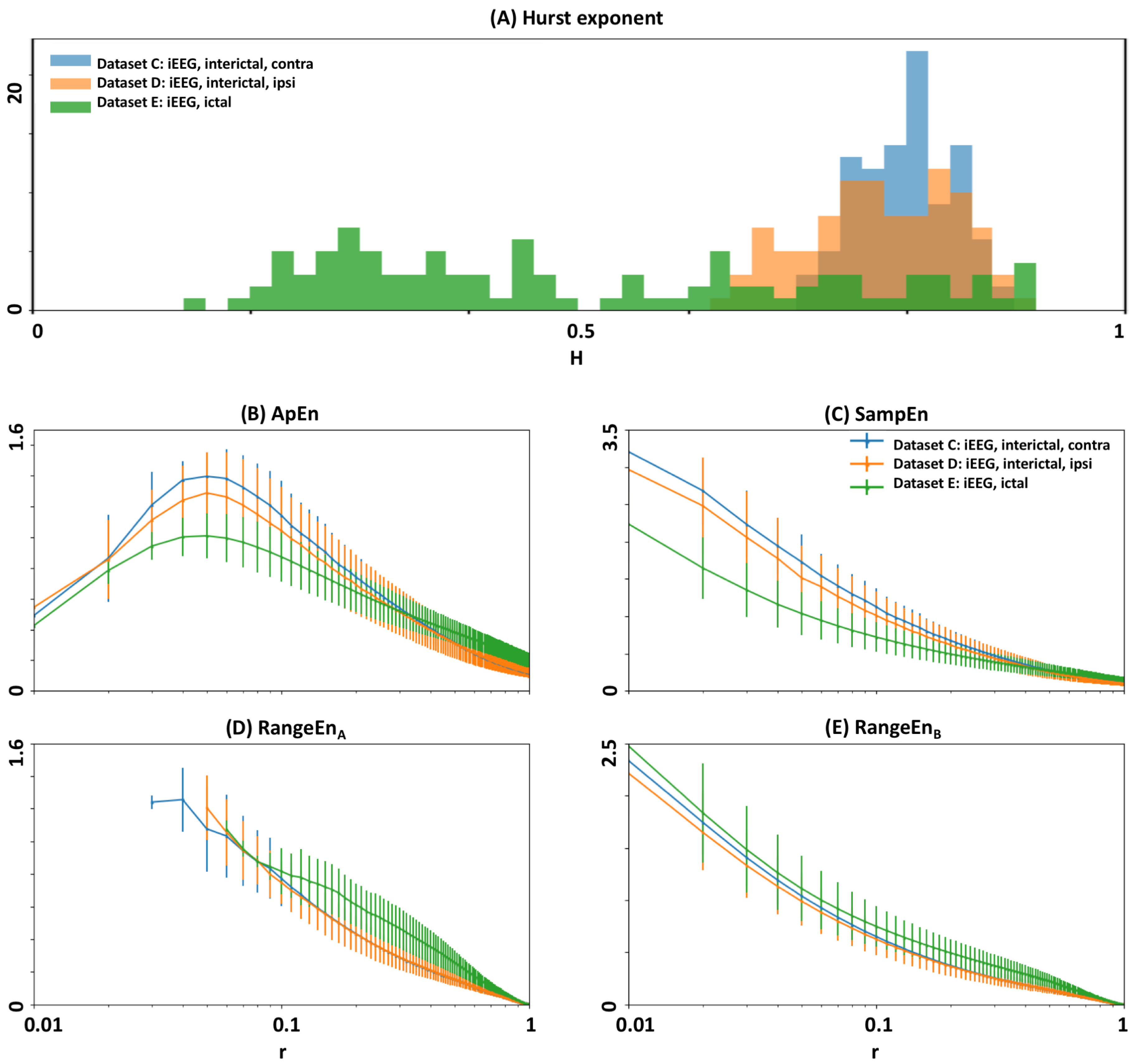
3.6. Analysis of Epileptic EEG
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, P.F.; Tsao, J.; Lo, M.T.; Lin, C.; Chang, Y.C. Symbolic Entropy of the Amplitude rather than the Instantaneous Frequency of EEG Varies in Dementia. Entropy 2015, 17, 560–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sotelo, J.L.; Osorio-Forero, A.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, A.; Cuesta-Frau, D.; Cirugeda-Roldán, E.; Peluffo, D. Automatic Sleep Stages Classification Using EEG Entropy Features and Unsupervised Pattern Analysis Techniques. Entropy 2014, 16, 6573–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.Y.; Su, M.C.; Wu, H.T.; Lin, M.C.; Tsai, I.T.; Sun, C.K. Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Heart Rate Variability for Assessing the Severity of Sleep Disordered Breathing. Entropy 2015, 17, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, L.; Fan, S.; Abbod, M.; Shieh, J. Sample entropy analysis for the estimating depth of anaesthesia through human EEG signal at different levels of unconsciousness during surgeries. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jin, Y.; Lo, I.; Zhao, H.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X. Complexity Change in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, D.; Richman, J.; Griffin, M.; Moorman, J. Sample entropy analysis of neonatal heart rate variability. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 283, R789–R797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.; Omidvarnia, A.; Walz, J.; Zalesky, A.; Jackson, G. Spontaneous brain network activity: Analysis of its temporal complexity. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, A.; Vakorin, V.; Kovacevic, N.; Wang, H.; Diaconescu, A.; Protzner, A. Spatiotemporal dependency of age-related changes in brain signal variability. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxe, G.; Calderone, D.; Morales, L. Brain entropy and human intelligence: A resting-state fMRI study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villecco, F.; Pellegrino, A. Evaluation of Uncertainties in the Design Process of Complex Mechanical Systems. Entropy 2017, 19, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villecco, F.; Pellegrino, A. Entropic Measure of Epistemic Uncertainties in Multibody System Models by Axiomatic Design. Entropy 2017, 19, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.G. Contrasting the complexity of the climate of the past 122,000 years and recent 2000 years. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, C.C.; Konstantinou, K.I. Reduction of randomness in seismic noise as a short-term precursor to a volcanic eruption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.; Guang, M.; Sarkar, N. Complexity Analysis of 2010 Baja California Earthquake Based on Entropy Measurements. In Vulnerability, Uncertainty, and Risk; American Society of Civil Engineers: Liverpool, UK, 2014; pp. 1815–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Shang, P.; Wang, J. Measuring information interactions on the ordinal pattern of stock time series. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 87, 022805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, L. (Ed.) Wavelet Transforms and Time-Frequency Signal Analysis; Birkhäuser Boston: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renyi, A. On Measures of Entropy and Information. In Proceedings of the Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Volume 1: Contributions to the Theory of Statistics; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1961; pp. 547–561. [Google Scholar]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. New Metric Invariant of Transitive Dynamical Systems and Endomorphisms of Lebesgue Space. Dokl. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1958, 119, 861–864. [Google Scholar]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Estimation of the Kolmogorov entropy from a chaotic signal. Phys. Rev. A 1983, 28, 2591–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Baranger, M. Kolmogorov-Sinai Entropy Rate versus Physical Entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckmann, J.; Ruelle, D. Ergodic theory of chaos and strange attractors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 617–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincus, S. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.; Moorman, J. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.; Peng, C. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, R.G.; Ellison, C.J.; Crutchfield, J.P. Anatomy of a Bit: Information in a Time Series Observation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2011, 21, 037109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Hu, J.; Tung, W. Entropy measures for biological signal analyses. Nonlinear Dyns. 2012, 68, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokunbi, M.; Gradin, V.; Waiter, G.; Cameron, G.; Ahearn, T.; Murray, A.; Steele, D.; Staff, R. Nonlinear Complexity Analysis of Brain fMRI Signals in Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0095146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takens, F. Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In Dynamical Systems and Turbulence, Warwick 1980; Rand, D., Young, L.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 366–381. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.; Goldberger, A.; Goldberger, A. Irregularity and asynchrony in biologic network signals. Meth. Enzymol. 2000, 321, 149–182. [Google Scholar]
- Burnecki, K.; Weron, A. Fractional Lévy stable motion can model subdiffusive dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 021130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.H.; Bodvarsson, G.S.; Lu, S.; Molz, F.J. A Corrected and Generalized Successive Random Additions Algorithm for Simulating Fractional Levy Motions. Math. Geol. 2004, 36, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.; Wallis, J. Noah, Joseph, and Operational Hydrology. Water Resour. Res. 1968, 4, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takens, F. Invariants Related to Dimension and Entropy. Atas do 13 Colognio Brasiliero de Mathematica 1983, 13, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Deza, M.; Deza, E. Encyclopedia of Distances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejak, R.; Lehnertz, K.; Mormann, F.; Rieke, C.; David, P.; Elger, C. Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: Dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonliner Soft Matter Phys. 2001, 64, 061907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieker, T. Simulation of Fractional Brownian Motion. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, H. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar]
- Grassberger, P.; Procaccia, I. Measuring the strangeness of strange attractors. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1983, 9, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.; Sree, S.; Swapna, G.; Martis, R.; Suri, J. Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: A review. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2013, 45, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.; Molinari, F.; Sree, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ng, K.; Suri, J. Automated diagnosis of epileptic EEG using entropies. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2012, 7, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannathal, N.; Choo, M.; Acharya, U.; Sadasivan, P. Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2005, 80, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, S.; Garcia, H.; Quiroga, R.Q.; Romanelli, L.; Rosso, O.A. Stationarity of the EEG series. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1995, 14, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omidvarnia, A.; Mesbah, M.; Pedersen, M.; Jackson, G. Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity. Entropy 2018, 20, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120962
Omidvarnia A, Mesbah M, Pedersen M, Jackson G. Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity. Entropy. 2018; 20(12):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120962
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmidvarnia, Amir, Mostefa Mesbah, Mangor Pedersen, and Graeme Jackson. 2018. "Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity" Entropy 20, no. 12: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120962
APA StyleOmidvarnia, A., Mesbah, M., Pedersen, M., & Jackson, G. (2018). Range Entropy: A Bridge between Signal Complexity and Self-Similarity. Entropy, 20(12), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20120962






