Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing with Paying Dividend Yield under Non-Extensive Statistical Mechanics for Time-Varying Model †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In our model, we allow the coefficients of the drift term and diffusion term to be time-varying functions. In some sense, we extend the model of Zhao et al. [30].
- In this paper, we propose the geometric average Asian option pricing with paying dividend yield. So, our results are more widely applicable than that of Zhao et al. [30].
- When we derive the price formula of geometric average Asian option, the most important part is calculating the integral which is defined by Equation (13). Zhao et al. [30] got their results by using Lemma 1 in their paper. We use the Feynman–Kac formula and ansatz to deal with the integral. A simulation study shows that our method can better fit the simulation data than that of Zhao et al. [30].
2. Model Setting
3. Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing Formula
4. Simulation Study
- (1)
- Monte-Carlo simulation;
- (2)
- in Zhao et al. [30];
- (3)
- Feynman–Kac formula and ansatz method in our paper.
- Step 1:
- We assume the value of , etc.
- Step 2:
- We generate 1000 random numbers of the Tsallis distribution.
- Step 3:
- According to step 2, we can calculate the price of a risky asset by Equation (8).
- Step 4:
- We derive the geometric average Asian call option price by Equation (21) and generate the resulting figures.
5. Analysis of Real Data
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Black, F.; Scholes, M. The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. J. Polit. Econ. 1973, 81, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L. Study on Black–Scholes stock option pricing model based on dynamic investment strategy. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2007, 3, 1755–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Glazyrina, A.; Melnikov, A. Bernstein’s inequalities and their extensions for getting the Black–Scholes option pricing formula. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2016, 111, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyah, S.M.; Lin, X.C.; Miao, D.W. Pricing short-dated foreign equity options with a bivariate jump-diffusion model with correlated fat-tailed jumps. Financ. Res. Lett. 2017, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L. The stable paretian hypothesis and the frequency of large returns: An examination of major German stocks. Appl. Financ. Econ. 1996, 6, 463–475. [Google Scholar]
- Kittiakarasakun, J.; Tse, Y. Modeling the fat tails in asian stock markets. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2011, 20, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, M. Modeling fat tails in stock returns: A multivariate stable-garch approach. Comput. Stat. 2012, 27, 499–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J.C. Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Merton, R.C. Option pricing when underlying returns are discontinuous. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, F.; Keller-Ressel, M.; Sgarra, C. Geometric asian option pricing in general affine stochastic volatility models with jumps. Quantit. Financ. 2017, 17, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necula, C. Option Pricing in a Fractional Brownian Motion Environment. 2002. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1286833 (accessed on 26 October 2018).
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.L. Pricing currency options in a fractional Brownian motion with jumps. Econ. Model. 2010, 27, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y. Time-changed geometric fractional Brownian motion and option pricing with transaction costs. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2012, 391, 3971–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsallis, C. Possible Generalization of Boltzmann-Gibbs statistics. J. Stat. Phys. 1988, 52, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.D.; Geanakoplosy, J. Power Laws in Economics and Elsewhere; Santa Fe Institute: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Borland, L. A theory of non-Gaussian option pricing. Quant. Financ. 2002, 2, 415–431. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, D.; Paterlini, S. Efficient and Robust Estimation for Financial Returns: An Approach Based on Q-Entropy. 2010. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1906819 (accessed on 26 October 2018).
- Li, S.; He, J.; Song, K. Network entropies of the chinese financial market. Entropy 2016, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wei, J. Pricing of Power European Options Based on Tsallis Entropy and O-U Process under Stochastic Interest Rate. J. Zhengzhou Univ. 2017, 49, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S. Financial market dynamics: Superdiffusive or not? J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2017, 2017, 083207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, L. Exploring the dynamics of financial markets: From stock prices to strategy returns. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2016, 88, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Correa, W.O.; Ramos, A.M.T.; Vasconcelos, G.L. Investigation of non-Gaussian effects in the Brazilian option market. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2018, 496, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemna, A.G.Z.; Vorst, A.C.F. A pricing method for options based on average asset values. J. Bank. Financ. 2014, 14, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.C.G.; Shi, Z. The value of an Asian option. J. Appl. Probab. 1995, 32, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamou, E.; Duguet, A. Small dimension pde for discrete asian options. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 2010, 27, 2095–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusai, G.; Meucci, A. Pricing discretely monitored Asian options under lvy processes. J. Bank. Financ. 2008, 32, 2076–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, J.L. Efficient option pricing by frame duality with the fast Fourier transform. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2014, 6, 713–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, N.; Kou, S. Pricing Asian Options Under a Hyper-Exponential Jump Diffusion Model. Oper. Res. 2012, 60, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Kirkby, J.L.; Nguyen, D. A general valuation framework for SABR and stochastic local volatility models. SIAM J. Financ. Math. 2018, 9, 520–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J. Non-Gaussian closed form solutions for geometric average Asian options in the framework of non-extensive statistical mechanics. Entropy 2018, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borland, L.; Bouchaud, J. A non-Gaussian option pricing model with skew. Quant. Financ. 2004, 4, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreesea, J.P.A.; Lemmensa, D.; Temperea, J. Path integral approach to Asian options in the Black–Scholes model. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2011, 389, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, F.; Johnson, M.D. Financial market dynamics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2003, 320, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

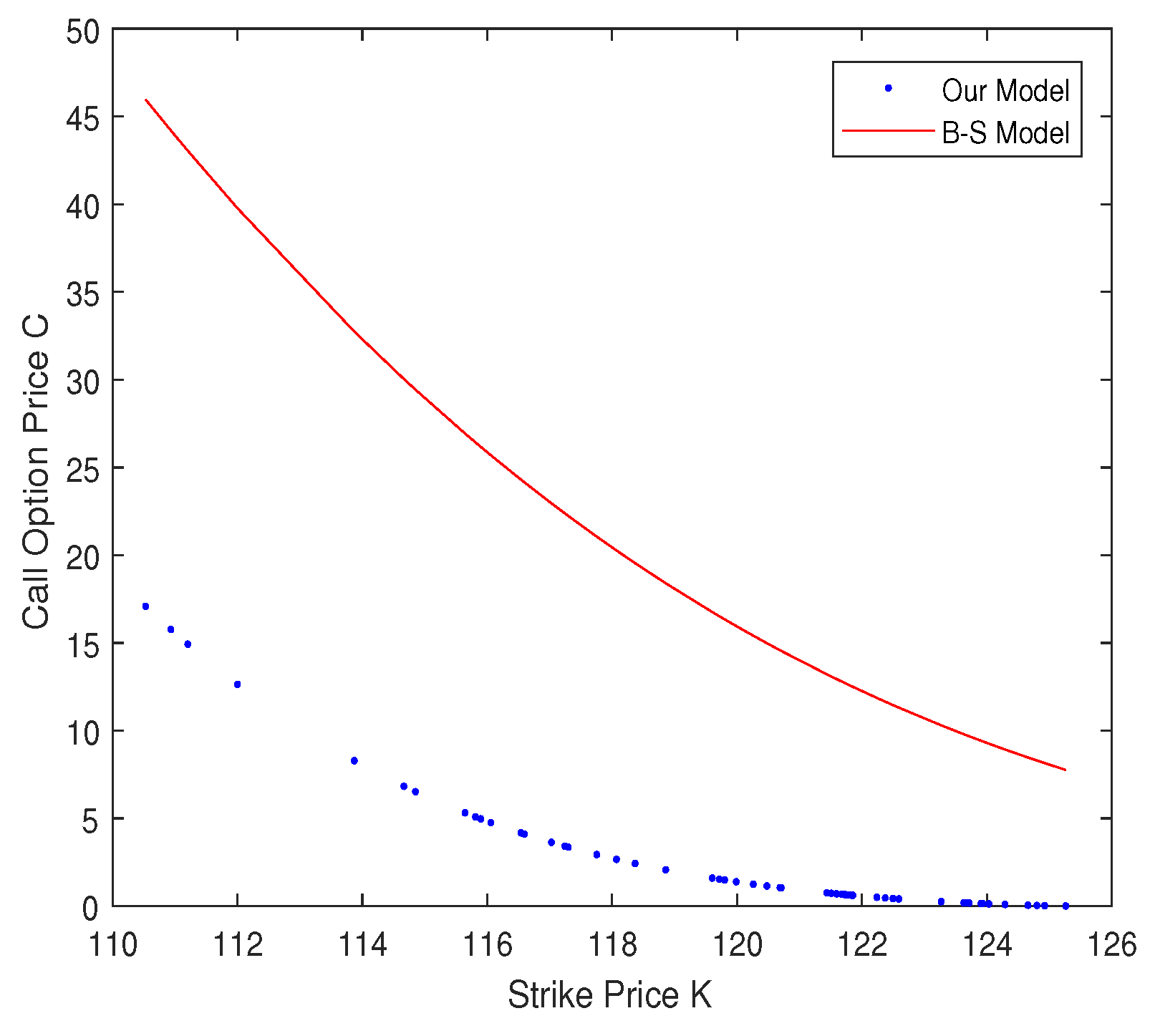
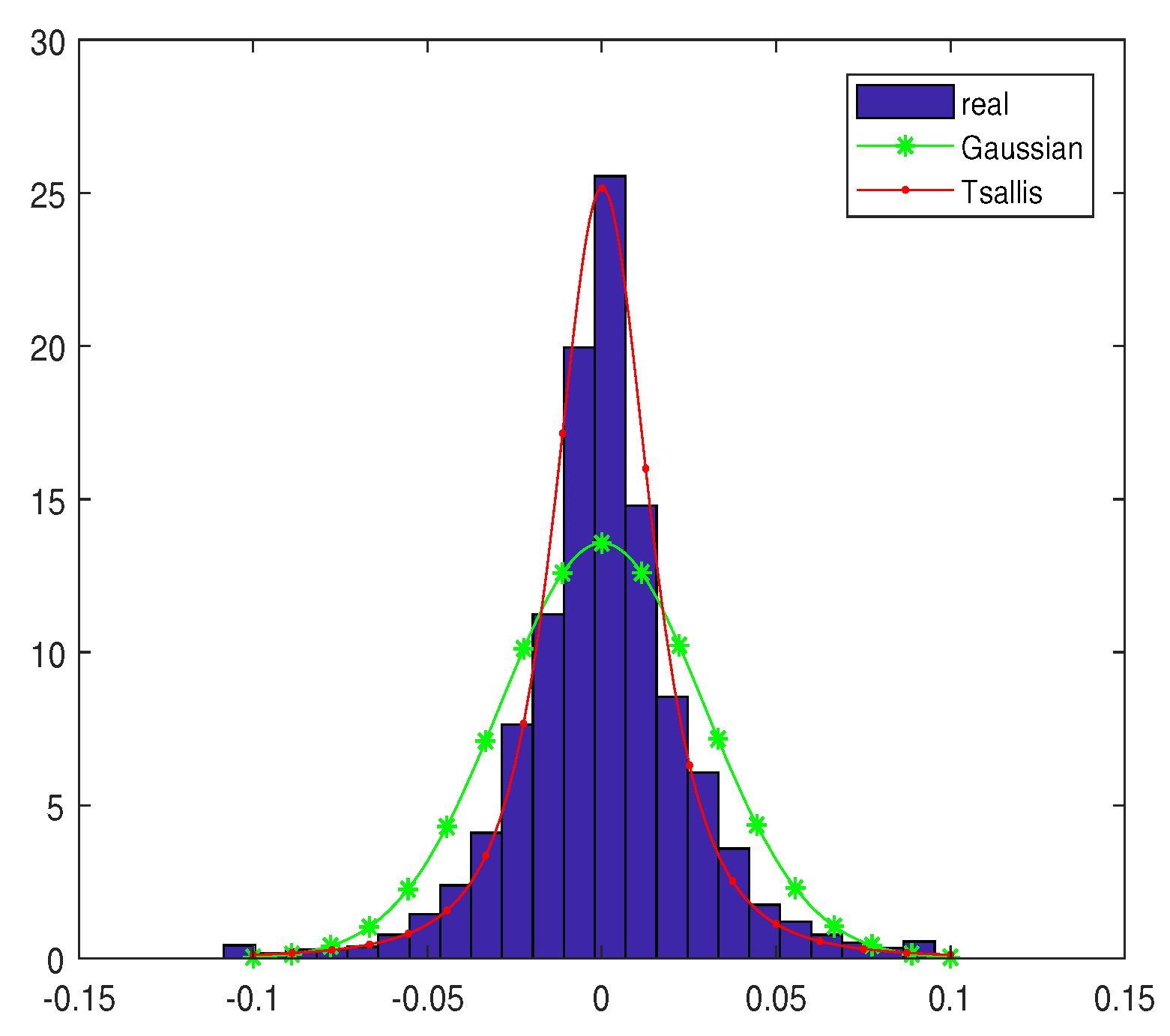
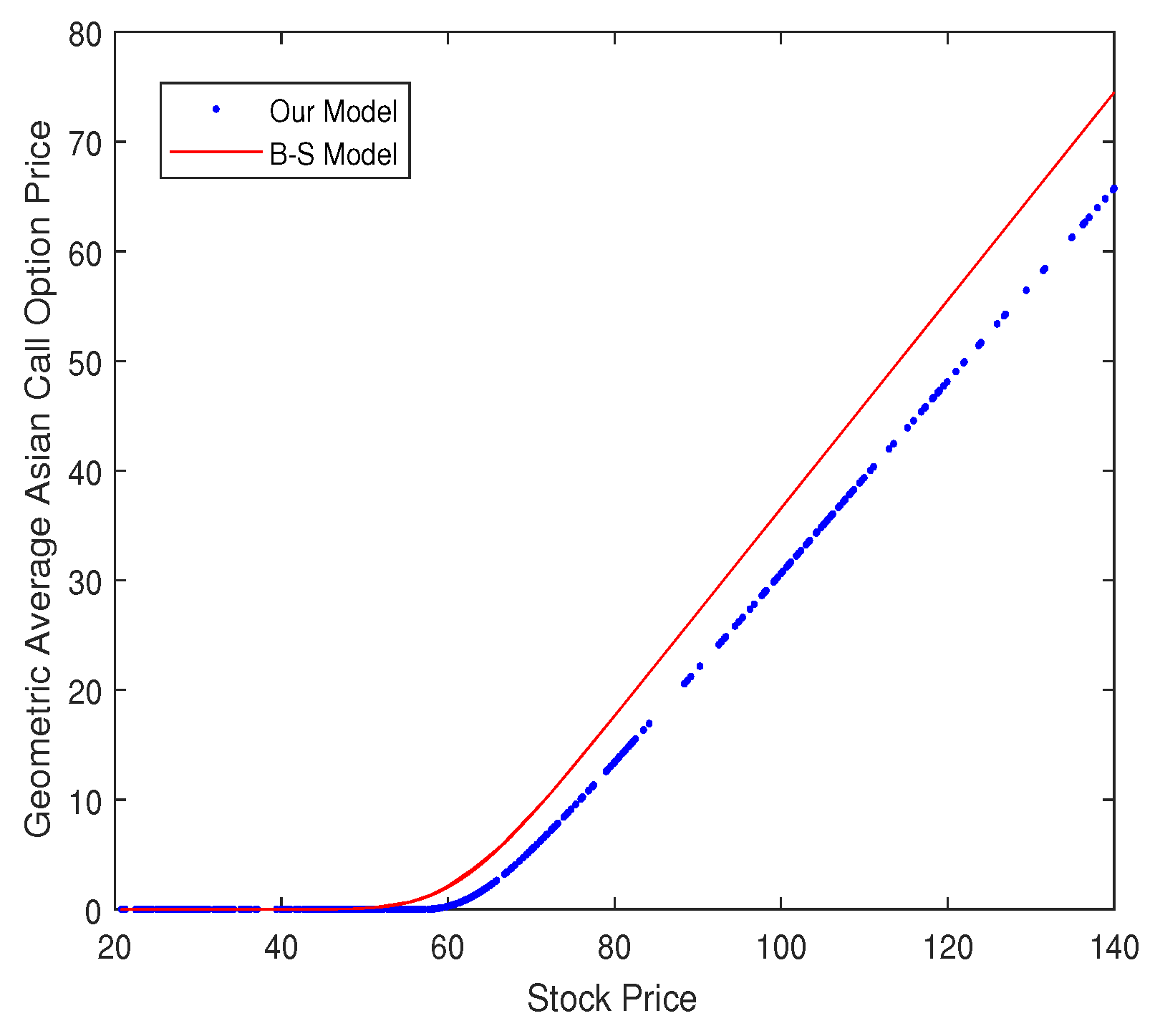
| Sample Size | Mean | Std | Kurtosis | J–B | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2612 | 1.4838 × 10 | 8.7055 × 10 | 200.9483 | 4.2867 × 10 | 0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing with Paying Dividend Yield under Non-Extensive Statistical Mechanics for Time-Varying Model. Entropy 2018, 20, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110828
Wang J, Zhang Y. Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing with Paying Dividend Yield under Non-Extensive Statistical Mechanics for Time-Varying Model. Entropy. 2018; 20(11):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110828
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jixia, and Yameng Zhang. 2018. "Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing with Paying Dividend Yield under Non-Extensive Statistical Mechanics for Time-Varying Model" Entropy 20, no. 11: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110828
APA StyleWang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Geometric Average Asian Option Pricing with Paying Dividend Yield under Non-Extensive Statistical Mechanics for Time-Varying Model. Entropy, 20(11), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20110828




