Solutions to the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem without Equilibrium Initial Conditions
Abstract
1. The Entropy of the Universe, the Second Law, the Past Hypothesis, and the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem
2. Gravitational Entropy and Penrose’s Weyl Curvature Hypothesis
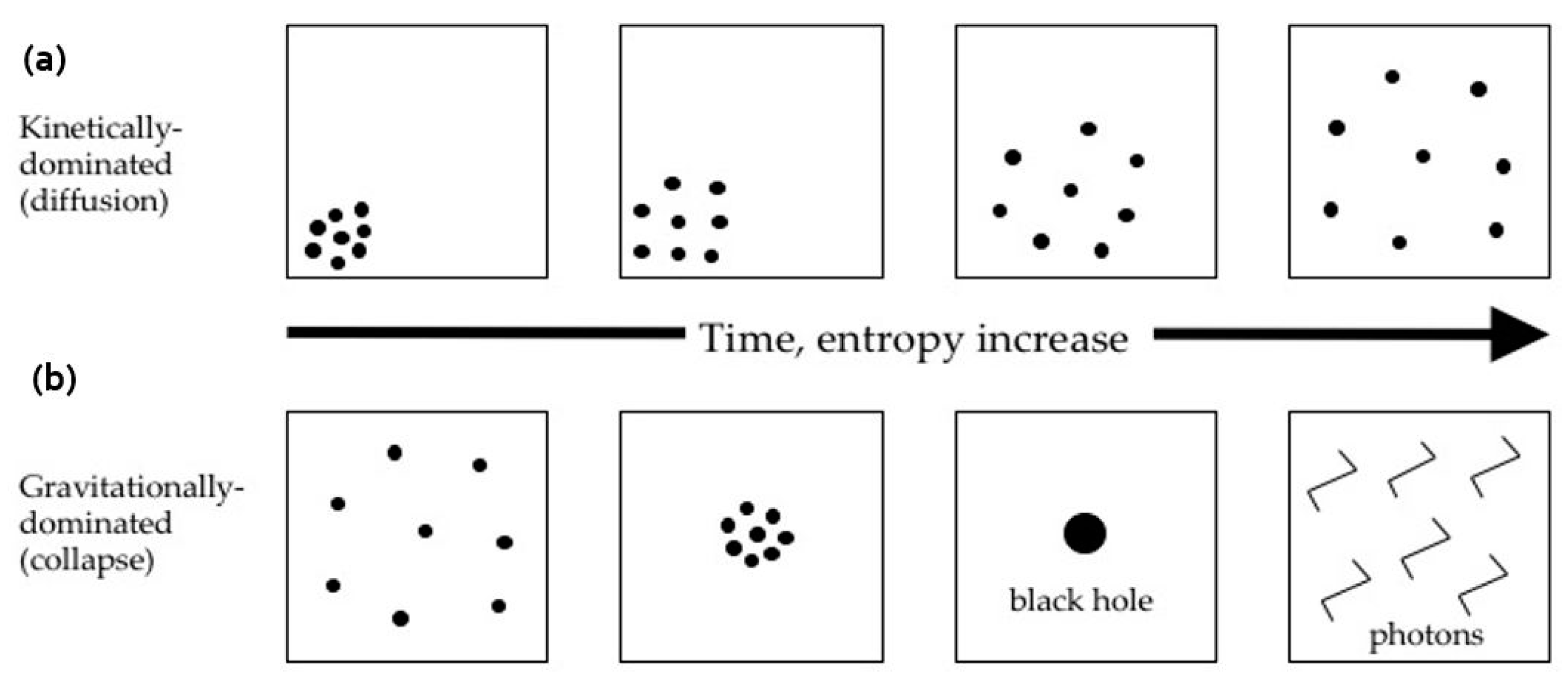
2.1. Kinetically vs. Gravitationally-Dominated Systems
2.2. Penrose’s Weyl Curvature Hypothesis
The Weyl curvature vanishes … at the initial singularity and is unconstrained, no doubt diverging wildly to infinity, at final singularities.—Penrose [6] (p. 767)
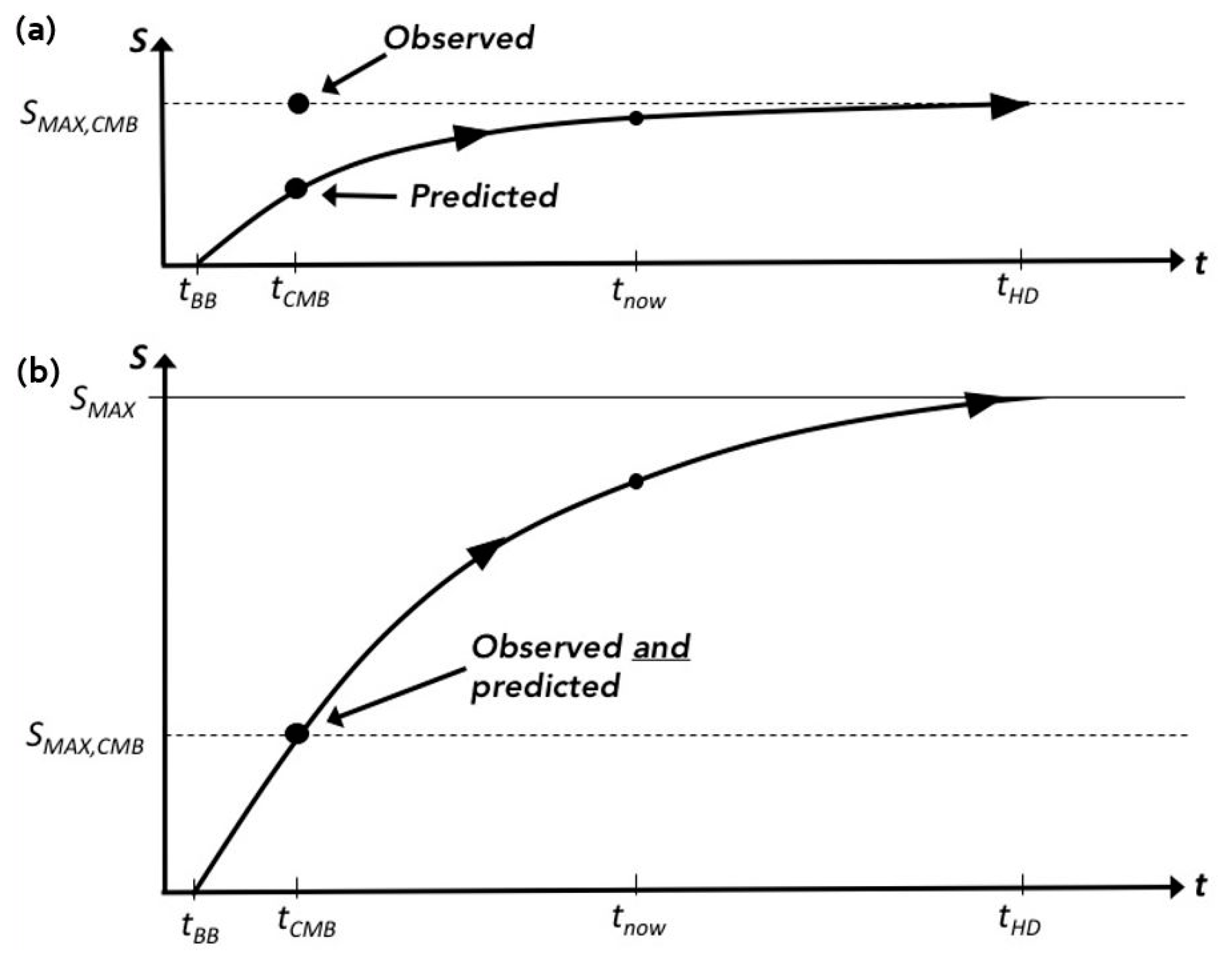
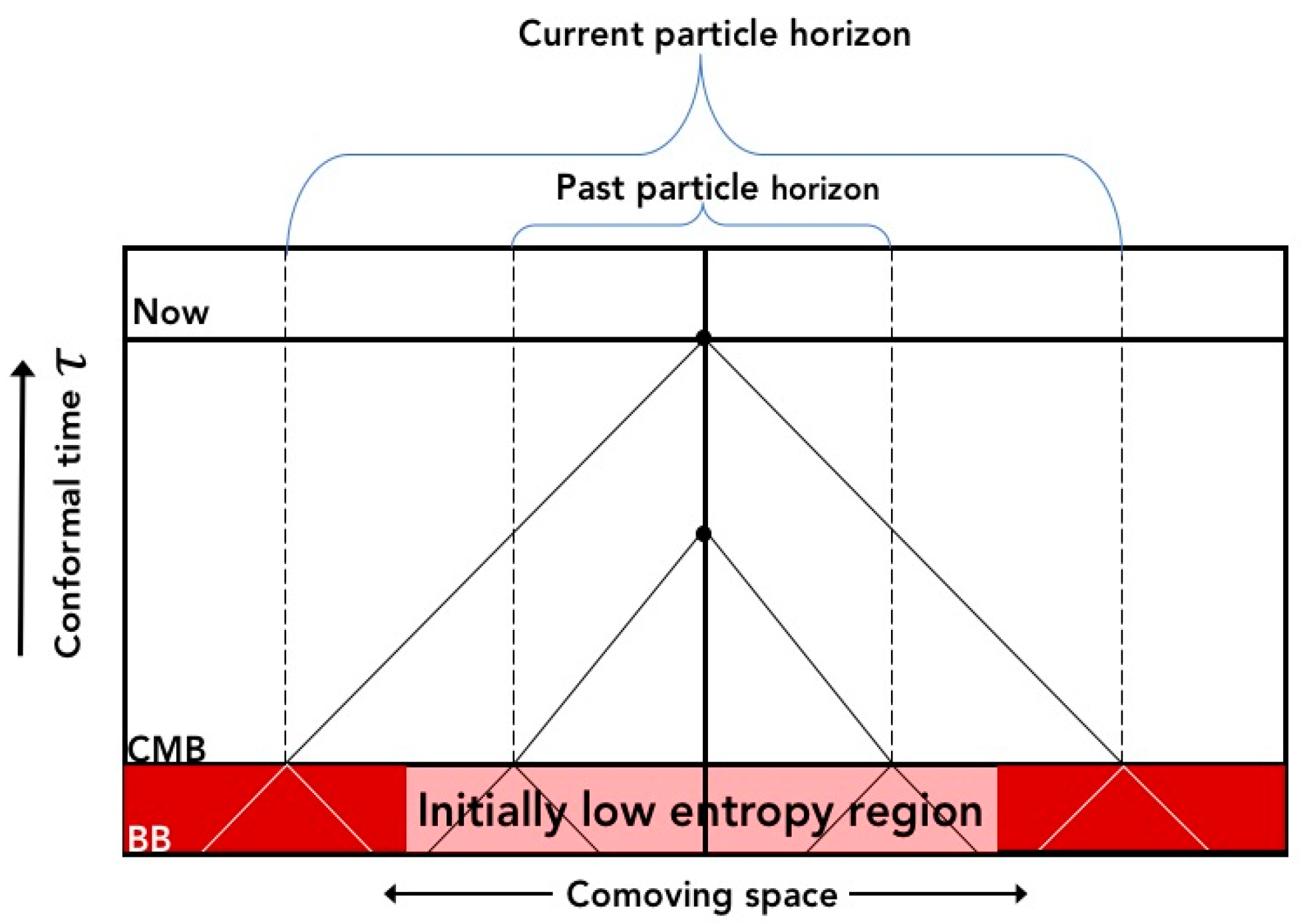
3. Inflation Produces Low Entropy Initial Conditions
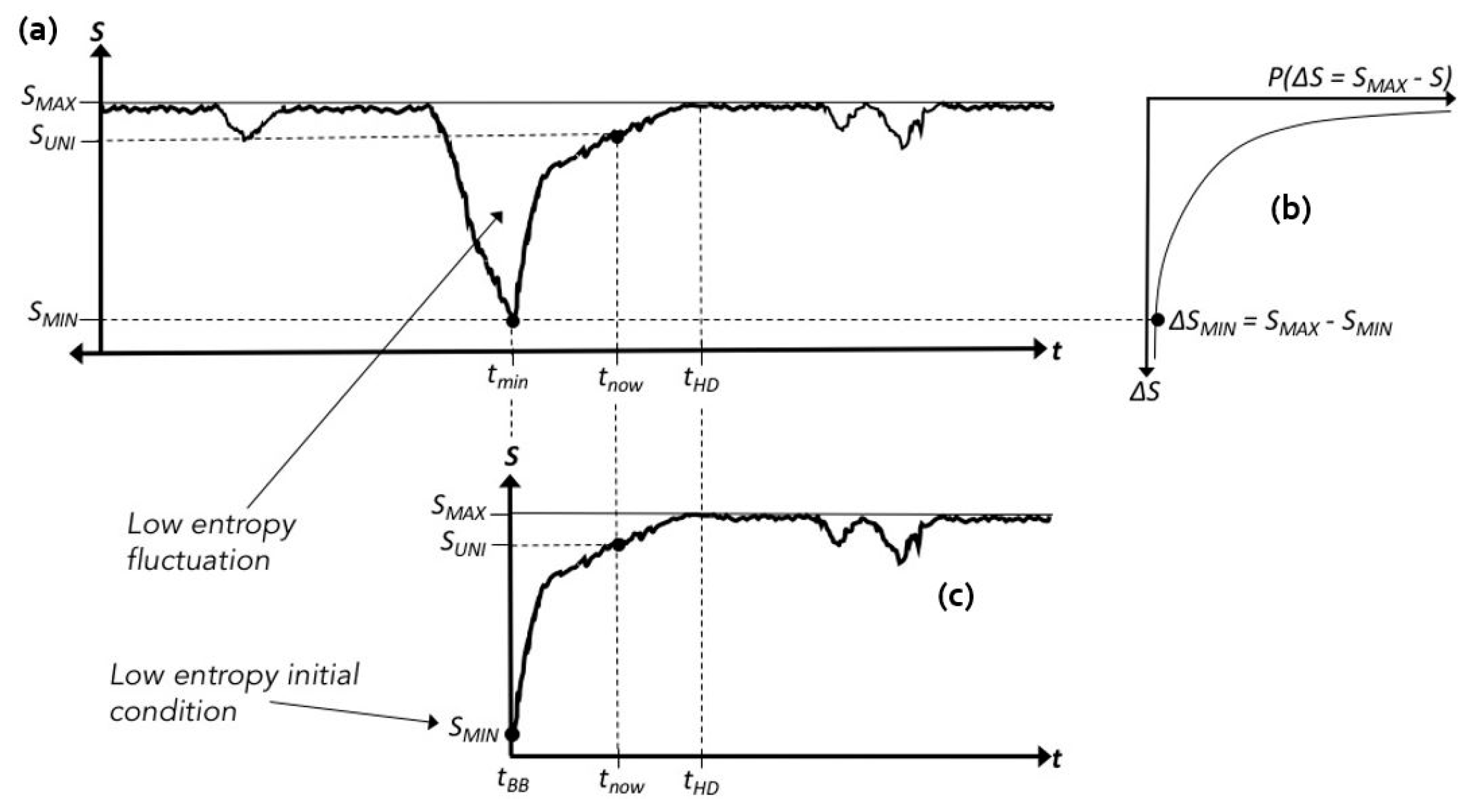
4. Boltzmann’s Anthropic Hypothesis: Low Entropy Fluctuation in a Maximum Entropy Background
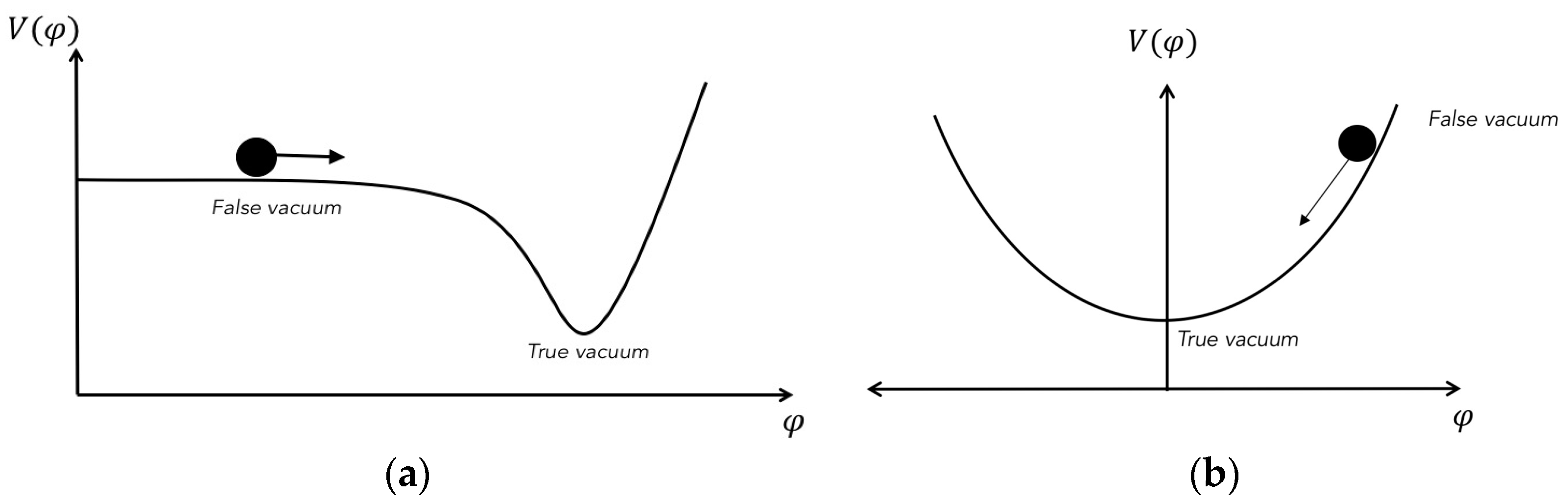
4.1. Problems with Boltzmann’s Hypothesis
…from the hypothesis that the world is a fluctuation, all of the predictions are that if we look at a part of the world we have never seen before, we will find it mixed up, and not like the piece we looked at. If our order was due to a fluctuation, we would not expect order anywhere but where we have just noticed it.—Feynman [40] (lecture 46)
The fact that we inhabit at least a Hubble volume of low entropy must be counted as strong evidence against Boltzmann’s hypothesis.—Davies [41] (p. 9)
4.2. Boltzmann Brains: How Small Can the Low Entropy Region Be and Still Produce Observers?
5. Which Initial Condition Is More ‘Natural’, Inflation or Equilibrium?
The goal I am pursuing is to find cosmological scenarios in which the Past Hypothesis is predicted by the dynamics, not merely assumed.—Carroll [13]
What Is Wrong with Equilibrium as an Initial Condition?
6. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lineweaver, C.H.; Egan, C. Life, Gravity and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Phys. Life Rev. 2008, 5, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemansky, M.W.; Dittman, R.H. Heat and Thermodynamics, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Frautschi, S. Entropy in an expanding universe. Science 1982, 217, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineweaver, C.H. The Entropy of the Universe and the Maximum Entropy Production Principle. In Beyond the Second Law, 1st ed.; Dewar, R.C., Lineweaver, C.H., Niven, R.K., Regenauer-Lieb, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, A. Cosmic inflation and the arrow of time. In Science and Ultimate Reality: Quantum Theory, Cosmology and Complexity, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 363–401. [Google Scholar]
- Penrose, R. The big bang and its thermodynamic legacy. In Road to Reality: A Complete Guide to the Laws of the Universe, 1st ed.; Jonathan Cape: London, UK, 2004; pp. 686–734. [Google Scholar]
- Egan, C.A.; Lineweaver, C.H. A larger estimate of the entropy of the universe. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layzer, D. The arrow of time. Sci. Am. 1975, 233, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, H. Time’s Arrow and Archimedes’ Point: New Directions for the Physics of Time; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, D.Z. The reversibility objects and the past-hypothesis. In Time and Chance, 1st ed.; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Earman, J. The ‘past hypothesis’: Not even false. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. Part B Stud. Hist. Philos. Mod. Phys. 2006, 37, 399–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D. The Logic of the Past Hypothesis. Available online: http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/8894/ (accessed on 8 August 2017).
- Carroll, S.M. Cosmology and the Past Hypothesis. Available online: http://www.preposterousuniverse.com/blog/2013/07/09/cosmology-and-the-past-hypothesis/ (accessed on 30 June 2017).
- Bekenstein, J.D. Black holes and entropy. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 7, 2333–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, C.H. A Simple Treatment of Complexity: Cosmological Entropic Boundary Conditions on Increasing Complexity; Lineweaver, C.H., Davies, P.C.W., Ruse, M., Eds.; Chapter 3 of Complexity and the Arrow of Time; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 42–67. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, S.M.; Chen, J. Spontaneous inflation and the origin of the arrow of time. arXiv 2004, arXiv:hep-th/0410270. [Google Scholar]
- Smoot, G.F.; Bennett, C.L.; Kogut, A.; Wright, E.L.; Aymon, J.; Boggess, N.W.; Cheng, E.S.; de Amici, G.; Gulkis, S.; Hauser, M.G.; et al. Structure in the COBE differential microwave radiometer first-year maps. Astrophys. J. 1992, 396, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fixsen, D.J.; Cheng, E.S.; Cottingham, D.A.; Eplee, R.E., Jr.; Isaacman, R.B.; Mather, J.C.; Meyer, S.S.; Noerdlinger, P.D.; Shafer, R.A.; Weiss, R.; et al. Cosmic microwave background dipole spectrum measured by the COBE FIRAS instrument. Astrophys. J. 1994, 420, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, E.W.; Turner, M.S. The Early Universe; Avalon Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hawking, S.W.; Page, D.N. Thermodynamics of black holes in anti-De Sitter space. Commun. Math. Phys. 1983, 87, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Entropy evaporated by a black hole. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.N. Comment on “Entropy Evaporated by a Black Hole”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.N. Hawking radiation and black hole thermodynamics. New J. Phys. 2005, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Singularities and time asymmetry. In General Relativity: An Einstein Centenary Volume; Hawking, S.W., Israel, W., Eds.; University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1979; pp. 581–638. [Google Scholar]
- Binney, J.; Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, D. Gravity, entropy, and cosmology: In search of clarity. Br. J. Philos. Sci. 2010, 61, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, A.H. Inflationary universe: A possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A. A new inflationary universe scenario: A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy and primordial monopole problems. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 108, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Steinhardt, P. Cosmology for Grand Unified Theories with Radiatively Induced Symmetry Breaking. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.C.W. Inflation and time asymmetry of the universe. Nature 1983, 301, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A. de Sitter equilibrium as a fundamental framework for cosmology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 174, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, L.; Linde, A.; Starbinksy, A.A. Reheating after inflation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 3195–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtanov, Y.; Traschen, J.; Bradenberger, R. Universe reheating after inflation. Phys. Rev. D 1995, 51, 5438–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltzmann, L. On Certain Questions of the Theory of Gases. Nature 1895, 1322, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltzmann, L. Über die mechanische Erklärung irreversibler Vorgänge (Zu Hrn. Zermelo’s Abhandlung). Annalen der Physik 1897, 296, 392–398. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poincaré, H. Sur le problème des trois corps et les équations de la dynamique. Acta Math. 1890, 13, 1–270. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.J.; Searles, D.J. Equilibrium microstates which generate second law violating steady states. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 50, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. Large Number Coincidences and the Anthropic Principle in Cosmology. In Proceedings of the Confrontation of Cosmological Theories with Observational Data, Krakow, Poland, 10–12 September 1973; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, J.D.; Tipler, F.J. The Anthropic Cosmological Principle, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Feynman, R.P.; Leighton, R.B.; Sands, M. The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Desktop Edition Volume 1; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, P.C.W. Multiverse cosmological models. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 19, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, R.K.; Wolfe, A.M. Perturbations of a Cosmological Model and Angular Variations of the Microwave Background. Astrophys. J. 1967, 147, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, D.J. Dark energy and cosmic sound. New Astron. Rev. 2005, 49, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Sorbo, L. Can the universe afford inflation? Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 065328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.N. Can inflation explain the second law of thermodynamics? Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1984, 23, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A. Inflationary cosmology after Planck 2013. arXiv, 2014; arXiv:1402.0526. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, A.H.; Kaiser, D.I.; Nomura, Y. Inflationary paradigm after Planck 2013. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 733, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijjas, A.; Steinhardt, P.J.; Loeb, A. Cosmic inflation theory faces challenges. Sci. Am. 2017, 316, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, A.H.; David, I.; Kaiser, D.I.; Linde, A.D.; Nomura, Y.; Bennett, C.L.; Bond, J.R.; Bouchet, F.; Carroll, S.; Efstathiou, G.; et al. A Cosmic Controversy. Available online: https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/observations/a-cosmic-controversy/ (accessed on 30 June 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, V.M.; Lineweaver, C.H. Solutions to the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem without Equilibrium Initial Conditions. Entropy 2017, 19, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19080411
Patel VM, Lineweaver CH. Solutions to the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem without Equilibrium Initial Conditions. Entropy. 2017; 19(8):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19080411
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Vihan M., and Charles H. Lineweaver. 2017. "Solutions to the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem without Equilibrium Initial Conditions" Entropy 19, no. 8: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19080411
APA StylePatel, V. M., & Lineweaver, C. H. (2017). Solutions to the Cosmic Initial Entropy Problem without Equilibrium Initial Conditions. Entropy, 19(8), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19080411




