Exploration of Quantum Interference in Document Relevance Judgement Discrepancy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Relevance in Information Retrieval
2.2. Quantum-Inspired IR Research
2.3. Classical and Quantum Probability Measurement
2.3.1. Classical Probability Measurement
2.3.2. Quantum Probability Theory
2.4. Quantum Cognition and Quantum Interference
3. Methodology
3.1. Verification of Quantum Interference
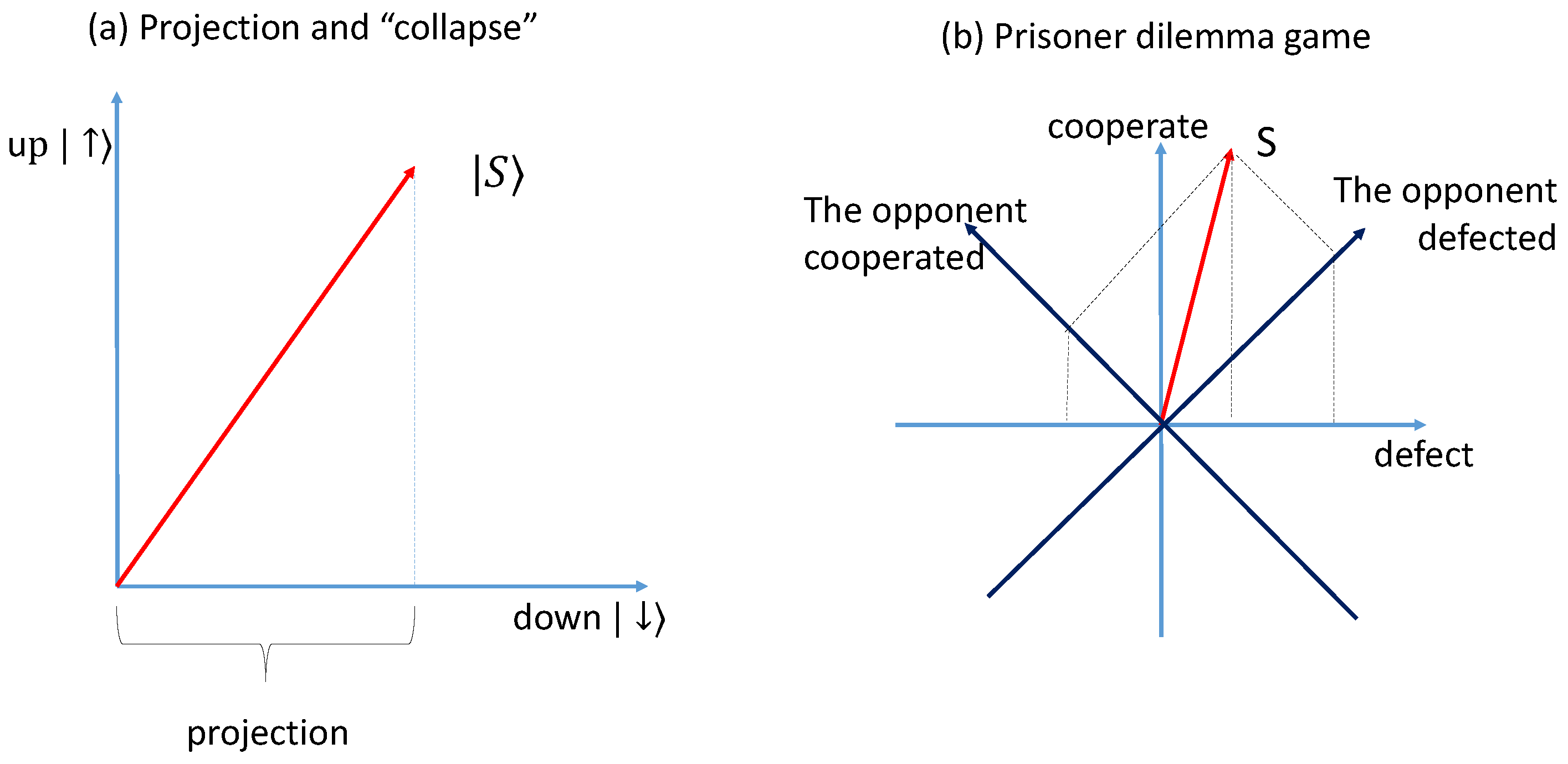
3.1.1. Test of the Law of the Total Probability
3.1.2. Test of the Order Effect and Incompatibility
3.2. Dynamic Information Need Model in Quantum Measurement
4. User Study for Quantum Interference
4.1. Experimental Procedure of the User Study
4.2. Statistics for the Judgement Discrepancy of Relevance Probability
4.3. Evaluation of Quantum Interference in Relevance Judgement
4.3.1. Violation of the Law of Total Probability
4.3.2. Test of the Order Effect and Incompatibility
5. Discussions for Quantum Interference in Relevance Judgement
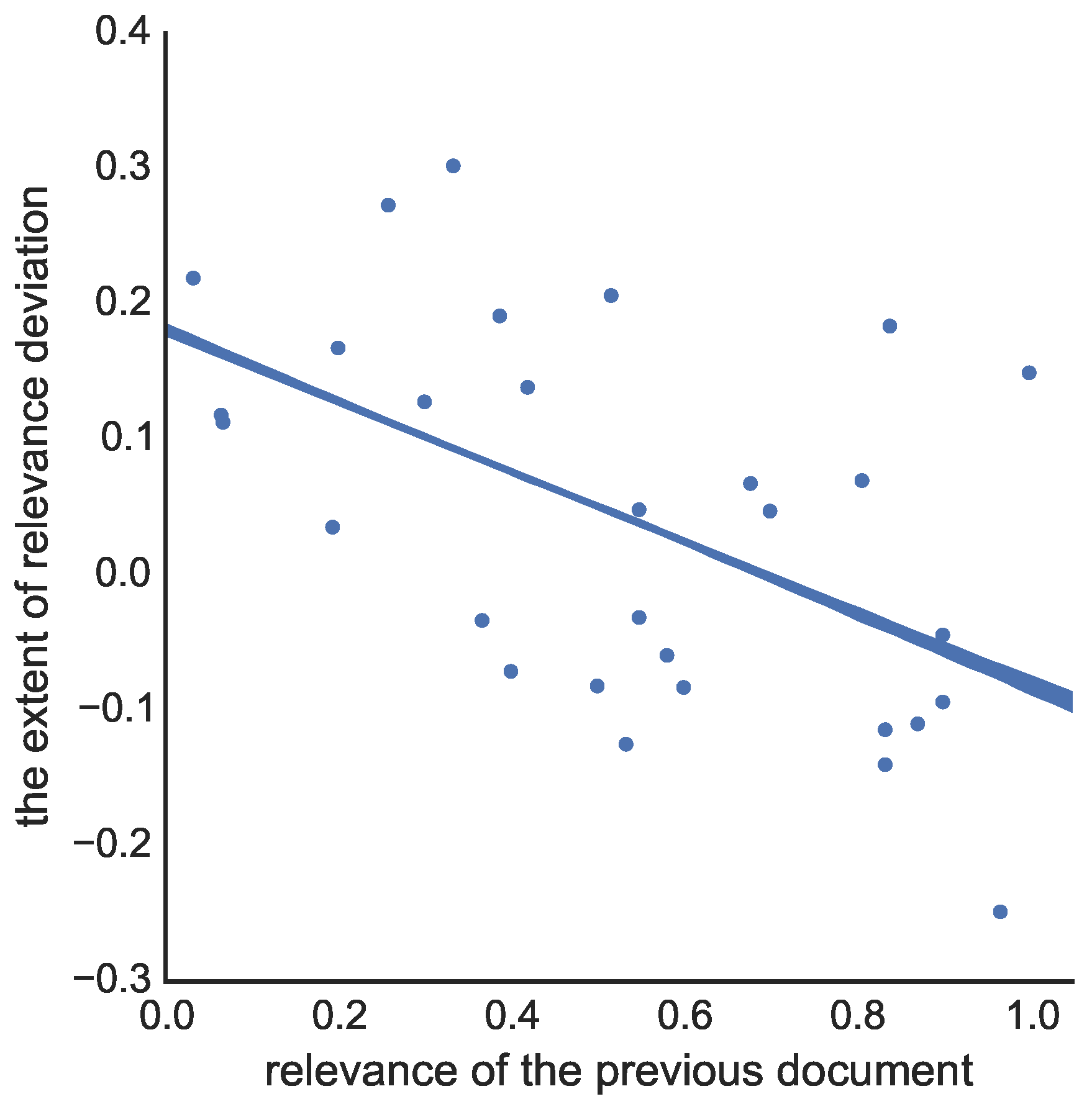
5.1. Comparison Effect
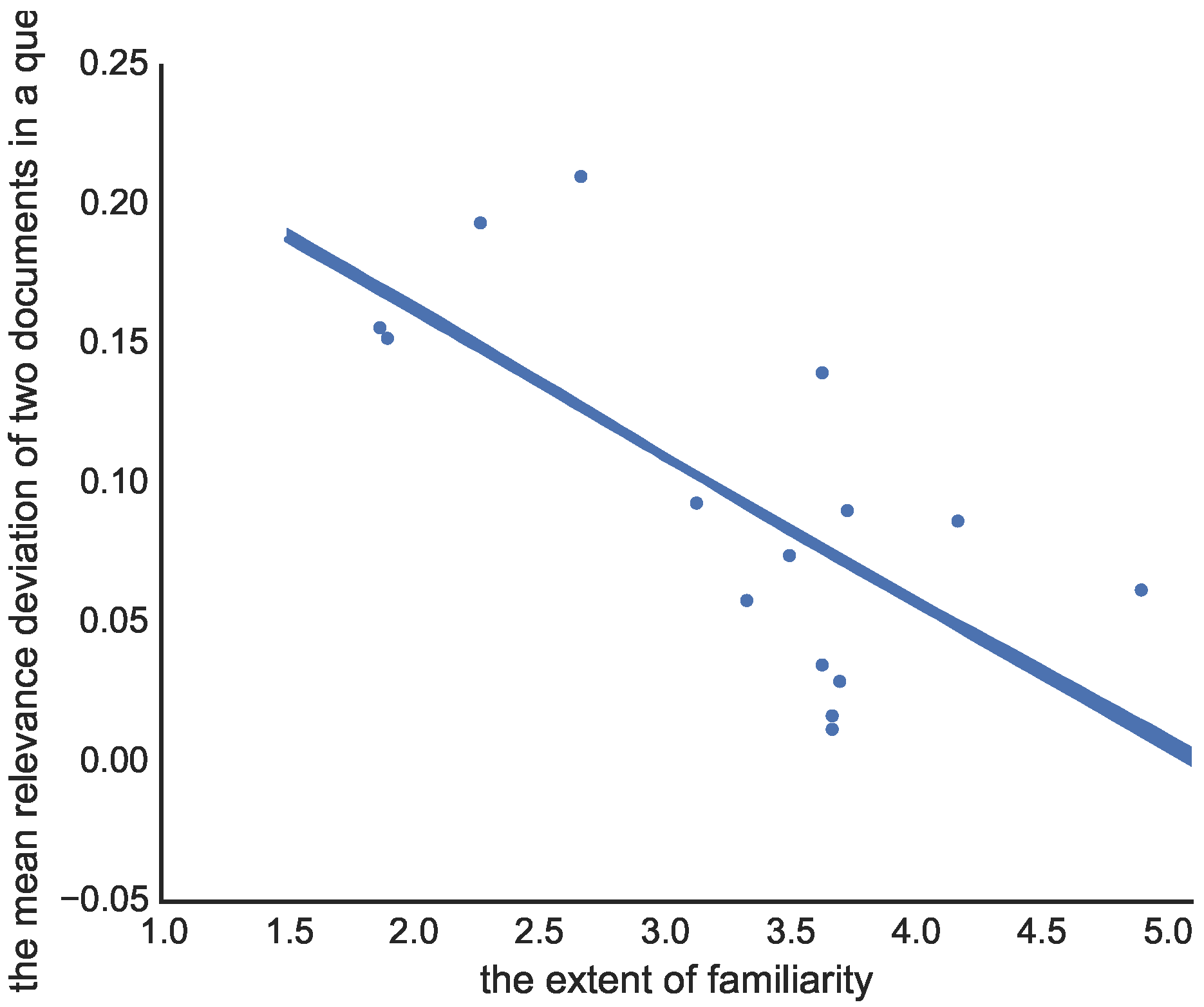
5.2. Unfamiliar Effect
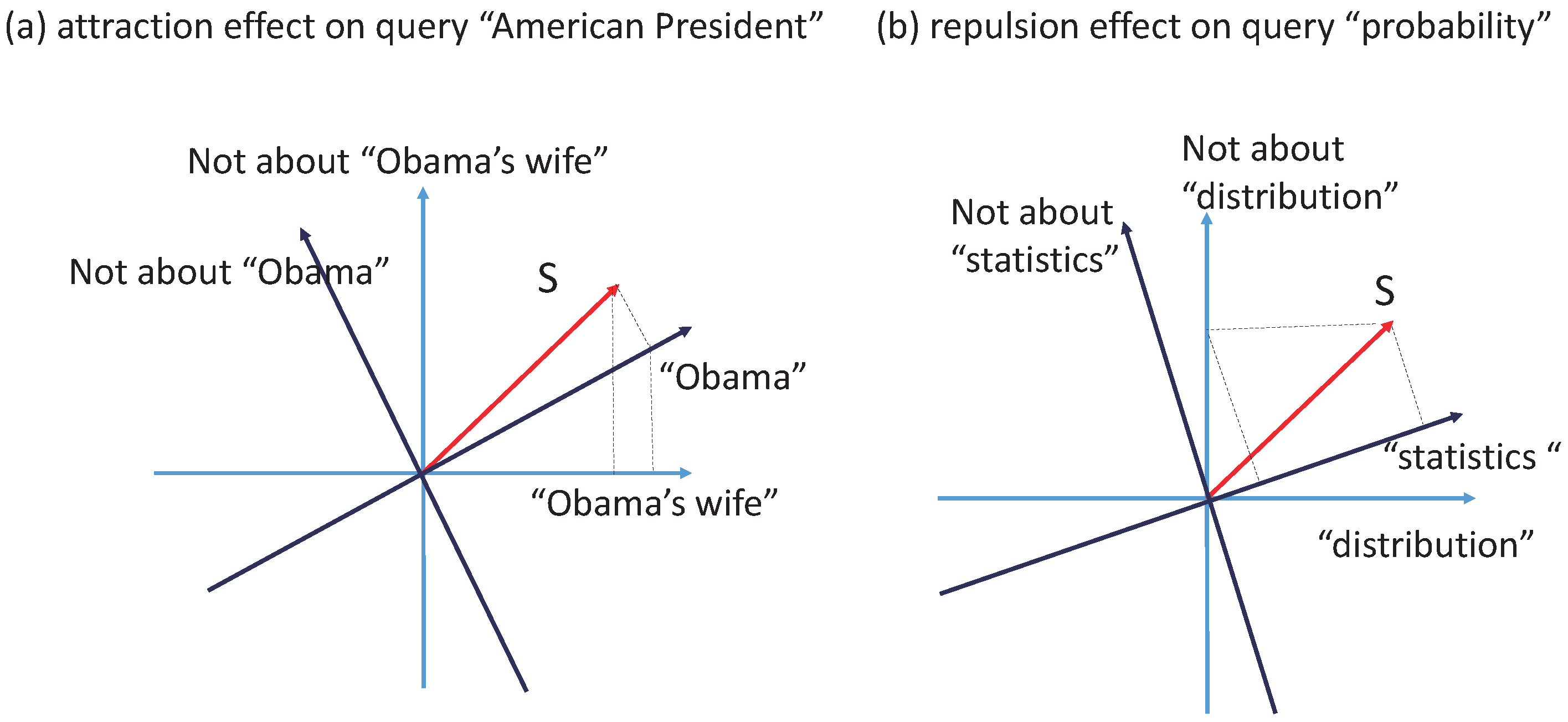
5.3. Attraction Effect and Repulsion Effect
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix: Derivation of the Interference Term in the Game of the Prisoner Dilemma
References
- Khrennikov, A. Quantum-like model of cognitive decision making and information processing. Biosystems 2009, 95, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, E. Advances in Application of Quantum Mechanics in Neuroscience and Psychology: A Clifford Algebraic Approach; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haven, E.; Khrennikov, A. Quantum Social Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Bruza, P.D. Quantum Models of Cognition and Decision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ashtiani, M.; Azgomi, M.A. A survey of quantum-like approaches to decision making and cognition. Math. Soc. Sci. 2015, 75, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijsbergen, C.J. The Geometry of Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tversky, A.; Kahneman, D. Extensional versus intuitive reasoning: The conjunction fallacy in probability judgement. Psychol. Rev. 1983, 90, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tversky, A.; Shafir, E. The disjunction effect in choice under uncertainty. Psychol. Sci. 1992, 3, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.T.; Silva, K.M.; Spencer-Smith, J.; Wenger, M.J. Exploring the relations between categorization and decision making with regard to realistic face stimuli. Pragmat. Cognit. 2000, 8, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Khrennikov, A.; Todarello, O.; Federici, A.; Zbilut, J.P. A preliminary experimental verification on the possibility of Bell inequality violation in mental states. Neuro Quantol. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Khrennikov, A.Y.; Todarello, O.; Federici, A.; Mendolicchio, L.; Zbilut, J.P. Mental states follow quantum mechanics during perception and cognition of ambiguous figures. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 2009, 16, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A.Y.; Haven, E. Quantum mechanics and violations of the sure-thing principle: The use of probability interference and other concepts. J. Math. Psychol. 2009, 53, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Khrennikov, A.Y.; Todarello, O.; de Robertis, R.; Federici, A.; Zbilut, J.P. On the possibility that we think in a quantum mechanical manner: An experimental verification of existing quantum interference effects in cognitive anomaly of conjunction fallacy. Chaos Complex. Lett. 2011, 4, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Busemeyer, J.R.; Atmanspacher, H.; Pothos, E.M. The potential of using quantum theory to build models of cognition. Top. Cognit. Sci. 2013, 5, 672–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Lambert-Mogiliansky, A. Empirical comparison of Markov and quantum models of decision making. J. Math. Psychol. 2009, 53, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Shiffrin, R.M. Bayesian model comparison favors quantum over standard decision theory account of dynamic inconsistency. Decision 2015, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccon, G.; Azzopardi, L. Using the Quantum Probability Ranking Principle to Rank Interdependent Documents. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 357–369. [Google Scholar]
- Di Buccio, E.; Melucci, M.; Song, D. Towards Predicting Relevance Using a Quantum-Like Framework. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 755–758. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Hou, Y. A Novel Re-Ranking Approach Inspired by Quantum Measurement. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Zhao, X.; Hou, Y. Investigating Query-Drift Problem from a Novel Perspective of Photon Polarization. In Advances in Information Retrieval Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Piwowarski, B.; Lalmas, M.; Frommholz, I.; van Rijsbergen, K. Exploring a multidimensional representation of documents and queries. In Proceedings of the Adaptivity, Personalization and Fusion of Heterogeneous Information, Paris, France, 28–30 April 2010; pp. 57–60.
- Sordoni, A.; Nie, J.Y.; Bengio, Y. Modeling Term Dependencies with Quantum Language Models for IR. In Proceedings of the 36th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR ’13), Dublin, Ireland, 28 July–1 August 2013; pp. 653–662.
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Song, D. Modeling multi-query retrieval tasks using density matrix transformation. In Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR ’15), Santiago, Chile, 9–13 August 2015; pp. 871–874.
- Xie, M.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Song, D. Modeling Quantum Entanglements in Quantum Language Models. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI ’15), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 25–31 July 2015; pp. 1362–1368.
- Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bruza, P.D. Automata modeling for cognitive interference in users’ relevance judgement. In Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium: Quantum Informatics for Cognitive, Social and Semantic Processes 2010, Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 November 2010; pp. 125–133.
- Wang, J.; Song, D.; Zhang, P.; Hou, Y.; Bruza, P. Explanation of Relevance Judgement Discrepancy with Quantum Interference. In Proceedings of the AAAI Fall Symposium: Quantum Informatics for Cognitive, Social, and Semantic Processes, Washington, DC, USA, 11–13 November 2010; pp. 117–124.
- Bruza, P.; Chang, V. Perceptions of document relevance. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Solloway, T.; Shiffrin, R.M.; Busemeyer, J.R. Context effects produced by question orders reveal quantum nature of human judgements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9431–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Busemeyer, J.R. A quantum question order model supported by empirical tests of an a priori and precise prediction. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2013, 5, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schamber, L.; Eisenberg, M.B.; Nilan, M.S. A re-examination of relevance: Toward a dynamic, situational definition. Inf. Process. Manag. 1990, 26, 755–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlund, P. The concept of relevance in IR. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2003, 54, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D.R. Subjective versus objective relevance in bibliographic retrieval systems. Libr. Q. 1986, 56, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Song, D. Characterizing Pure High-Order Entanglements in Lexical Semantic Spaces via Information Geometry. In Quantum Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Mizzaro, S. Relevance: The Whole History. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1997, 48, 810–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Order effect in relevance judgement. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2008, 59, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, M.; Barry, C. Order effects: A study of the possible influence of presentation order on user judgements of document relevance. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1988, 39, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccon, G.; Azzopardi, L.A.; Rijsbergen, K.V. The Quantum Probability Ranking Principle for Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson, S. Quantum Computing since Democritus; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kondacs, A.; Watrous, J. On the power of quantum finite state automata. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 20–22 October 1997; pp. 66–75.
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Foundations of the theory of probability. Math. Gaz. 1951, 2, 280–283. [Google Scholar]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Wang, Z. Quantum Information Processing Explanation for Interactions between Inferences and Decisions. Available online: http://www.cogsci.msu.edu/DSS/2008-2009/Busemeyer/Inf_Dec_2.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2016).
- Moreira, C.; Wichert, A. Quantum-Like Bayesian Networks for Modeling Decision Making. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafir, E.; Tversky, A. Thinking through uncertainty: Nonconsequential reasoning and choice. Cognit. Psychol. 1992, 24, 449–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1932. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, V. Penguin Dictionary of Physics; Penguin Books: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E. A reformulation of von Neumann’s postulates on quantum measurement by using two theorems in Clifford algebra. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2010, 49, 587–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. A proof of von Neumann’s postulate in quantum mechanics. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1232, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E.; Todarello, O.; Federici, A.; Vitiello, F.; Lopane, M.; Khrennikov, A. A Preliminary Evidence of Quantum Like Behavior in Measurements of Mental States. In Quantum Theory: Reconsideration of Foundations 2; Växjö University Press: Växjö, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E.; Todarello, O.; Federici, A.; Vitiello, F.; Lopane, M.; Khrennikov, A.; Zbilut, J.P. Some remarks on an experiment suggesting quantum-like behaviour of cognitive entities and formulation of an abstract quantum mechanical formalism to describe cognitive entity and its dynamics. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2007, 31, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A. Quantum-like brain: “Interference of minds”. BioSystems 2006, 84, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khrennivov, A. Classical and quantum mechanics on information spaces with applications to cognitive, psychological, social, and anomalous phenomena. Found. Phys. 1999, 29, 1065–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A. On quantum-like probabilistic structure of mental information. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 2004, 11, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearsall, J.; Hanks, P. Definition of Cognition. In New Oxford Dictionary of English; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Aristotle, H.; Lulofs, D. Aristotelis De Generatione Animalium; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, D. It from Qubit. In Science and Ultimate Reality: Quantum Theory, Cosmology, and Complexity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 90–102. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, E. A Clifford algebraic analysis gives mathematical explanation of quantization of quantum theory and delineates a model of quantum reality in which information, primitive cognition entities and a principle of existence are intrinsically represented ab initio. World J. Neurosci. 2013, 3, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, E. What Path Monitor: A Brief Note on Quantum Cognition and Quantum Interference, the Role of the Knowledge Factor. Psychology 2015, 6, 54234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beauregard, O.C. Time symmetry and interpretation of quantum mechanics. Found. Phys. 1976, 6, 539–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. A predictive model of ψ collapse-retrocollapse of quantum mechanics. Lettere al Nuovo Cimento (1971–1985) 1981, 32, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. On ψ retrocollapse in quantum mechanics. Lett. Al Nuovo Cimento (1971–1985) 1981, 31, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, Y.F. The logical origins of quantum mechanics. Ann. Phys. 1994, 234, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. On the Logical Origins of Quantum Mechanics Demonstrated by Using Clifford Algebra: A Proof that Quantum Interference Arises in a Clifford Algebraic Formulation of Quantum Mechanics. EJTP 2011, 8, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, E. On the logical origins of quantum mechanics demonstrated by using Clifford algebra. NeuroQuantology 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, E. A brief note on time evolution of quantum wave function and of quantum probabilities during perception and cognition of human subjects. NeuroQuantology 2009, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, E. On the possibility that we think in a quantum probabilistic manner. NeuroQuantology 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. Answer to Giancarlo Ghirardi: Quantum Superpositions and Definite Perceptions: Envisaging New Feasible Experimental Tests. A Novel Proposal for Quantum Mechanics, Perception and Cognitive Science? Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2015, 54, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. Additional Comments Added to Our Recent Answer to G. Ghirardi. J. Mod. Phys. 2015, 6, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conte, E. What is the Reason to Use Clifford Algebra in Quantum Cognition? Part I: ”It from Qubit” On the Possibility that the Amino Acids Can Discern Between Two Quantum Spin States. NeuroQuantology 2012, 10, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pothos, E.M.; Busemeyer, J.R. Can quantum probability provide a new direction for cognitive modeling? Behav. Brain Sci. 2013, 36, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruza, P.D.; Wang, Z.; Busemeyer, J.R. Quantum cognition: A new theoretical approach to psychology. Trends Cogni. Sci. 2015, 19, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, E.; Khrennikov, A.; Todarello, O.; Federici, A.; Zbilut, J.P. On the existence of quantum wave function and quantum interference effects in mental states: An experimental confirmation during perception and cognition in humans. 2008; arXiv:0807.4547. [Google Scholar]
- Busemeyer, J.R.; Wang, Z.; Townsend, J.T. Quantum dynamics of human decision-making. J. Math. Psychol. 2006, 50, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrennikov, A.Y. Ubiquitous Quantum Structure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hogarth, R.M.; Einhorn, H.J. Order effects in belief updating: The belief-adjustment model. Cognit. Psychol. 1992, 24, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueblood, J.S.; Busemeyer, J.R. A quantum probability account of order effects in inference. Cognit. Sci. 2011, 35, 1518–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.W. Measuring new types of question-order effects: Additive and subtractive. Public Opin. Q. 2002, 66, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E. On Some Explanations and Analysis of the Basic Foundations of Quantum Cognition: Comments on a Paper by Pothos, Busemeyer and Trueblood. NeuroQuantology 2015, 13, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordoni, A.; Bengio, Y.; Nie, J.Y. Learning Concept Embeddings for Query Expansion by Quantum Entropy Minimization. In Proceedings of the 28th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014.
- Conte, E. A Brief Comment on Some Recent Evaluations by Basieva and Khrennikov, Wang et al., Boyer-Kassem et al., on Order Effects in Quantum Cognition. NeuroQuantology 2015, 13, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tversky, A.; Kahneman, D. Judgment under uncertainty: Heuristics and biases. Science 1974, 185, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkan, R.; Busemeyer, J.R. Modeling dynamic inconsistency with a changing reference point. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2003, 16, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsalou, L.W. Context-independent and context-dependent information in concepts. Memory Cognit. 1982, 10, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Query Terms | Title of | Title of |
|---|---|---|
| Probability | Statistics | Distribution |
| Parkinsonism | Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Albert Einstein | Isaac Newton | Theory of relativity |
| The Spring Festival | Jiaozi | Grabbing tickets for the Spring Festival |
| Innovation driven | Sharing economy | New open economic system |
| Machine learning | Artificial intelligence | Pattern recognition |
| American president | Barack Obama | Obama’s wife |
| Semantic Web | Theology | Ontology |
| Computer | Boolean algebra | Turing machine |
| Religion | Politics | Culture |
| Kung Fu Panda | The Giant panda | Chinese martial arts |
| Air pollution | Haze | Spiritual therapy for smog |
| Transgene | Hybrid | Garden roses |
| Chinese literature | Classical prose | Chinese cuisine |
| Mo Yan | Nobel Prize | Red Sorghum (novel) |
| Query | Relevance Probability of | Relevance Probability of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB Order | BA Order | BA Order | AB Order | |||
| Probability | 0.58 | 0.47 | −0.11 | 0.83 | 0.77 | −0.06 |
| Parkinsonism | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 0.18 |
| Albert Einstein | 0.19 | 0.10 | −0.09 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.04 |
| The Spring Festival | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.60 | 0.81 | 0.21 | |
| Innovation driven | 0.06 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.12 |
| Machine learning | 0.68 | 0.63 | −0.04 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.07 |
| American president | 1.00 | 0.97 | −0.03 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.15 |
| Semantic Web | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.42 | 0.22 |
| Computer | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 0.84 | 0.14 |
| Religion | 0.26 | 0.13 | −0.12 | 0.53 | 0.81 | 0.27 |
| Kung Fu Panda | 0.55 | 0.47 | −0.08 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.05 |
| Air pollution | 0.81 | 0.67 | −0.14 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.07 |
| Transgene | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.26 | 0.19 |
| Chinese literature | 0.87 | 0.80 | −0.07 | 0.40 | 0.29 | −0.11 |
| Mo Yan | 0.55 | 0.30 | −0.25 | 0.97 | 0.94 | −0.03 |
| mean() | 0.1194 | 0.1268 | ||||
| Query | p() | p() | p() | p() | (d) | p() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability | 0.89 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.42 | 0.77 | 0.83 |
| Probability | 0.52 | 0.83 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.58 |
| Parkinsonism | 0.46 | 0.84 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.30 |
| Parkinsonism | 1.00 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.97 | 0.84 |
| Albert Einstein | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.90 |
| Albert Einstein | 0.11 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.19 |
| The Spring Festival | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.80 | 0.48 | 0.81 | 0.60 |
| The Spring Festival | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.52 |
| Innovation driven | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.94 | 0.45 | 0.33 |
| Innovation driven | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.37 | 0.06 |
| Machine learning | 0.95 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
| Machine learning | 0.63 | 0.90 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.63 | 0.68 |
| American president | 0.52 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.37 |
| American president | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.95 | 0.63 | 0.97 | 1.00 |
| Semantic Web | 1.00 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.97 | 0.42 | 0.20 |
| Semantic Web | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.80 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
| Computer | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.72 | 0.58 | 0.84 | 0.70 |
| Computer | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 0.42 |
| Religion | 0.88 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.53 |
| Religion | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 0.26 |
| Kung Fu Panda | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.50 |
| Kung Fu Panda | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.55 |
| Air pollution | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.19 | 0.90 | 0.83 |
| Air pollution | 0.68 | 0.83 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 0.67 | 0.81 |
| Transgene | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.61 | 0.26 | 0.07 |
| Transgene | 1.00 | 0.07 | 0.46 | 0.93 | 0.50 | 0.39 |
| Chinese literature | 0.26 | 0.87 | 0.50 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.40 |
| Chinese literature | 0.75 | 0.40 | 0.83 | 0.60 | 0.80 | 0.87 |
| Mo Yan | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.93 | 0.45 | 0.94 | 0.97 |
| Mo Yan | 0.31 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 0.55 |
| Query | q-test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probability | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.43 | −0.11 |
| Parkinsonism | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.67 | −0.12 |
| Albert Einstein | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.00 | 0.74 | 0.80 | −0.06 |
| The Spring Festival | 0.39 | 0.10 | 0.37 | 0.20 | 0.48 | 0.57 | −0.08 |
| Innovation driven | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.08 |
| Machine learning | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.40 | −0.05 |
| American president | 0.00 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 0.60 | −0.12 |
| Semantic Web | 0.39 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.05 |
| Computer | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.42 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| Religion | 0.58 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| Kung Fu Panda | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.02 |
| Air pollution | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.37 | −0.14 |
| Transgene | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.43 | −0.18 |
| Chinese literature | 0.06 | 0.65 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.60 | 0.11 |
| Mo Yan | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.67 | −0.22 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Song, D.; Hou, Y.; Shang, Z. Exploration of Quantum Interference in Document Relevance Judgement Discrepancy. Entropy 2016, 18, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18040144
Wang B, Zhang P, Li J, Song D, Hou Y, Shang Z. Exploration of Quantum Interference in Document Relevance Judgement Discrepancy. Entropy. 2016; 18(4):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18040144
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Benyou, Peng Zhang, Jingfei Li, Dawei Song, Yuexian Hou, and Zhenguo Shang. 2016. "Exploration of Quantum Interference in Document Relevance Judgement Discrepancy" Entropy 18, no. 4: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18040144
APA StyleWang, B., Zhang, P., Li, J., Song, D., Hou, Y., & Shang, Z. (2016). Exploration of Quantum Interference in Document Relevance Judgement Discrepancy. Entropy, 18(4), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/e18040144






