Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Properties of Signature Schemes
- (1)
- Unforgeability: A dishonest party should not be able to successfully send a message pretending to be someone else.
- (2)
- Non-repudiation: A signer should be unable to successfully deny that he sent a message signed with his signature.
- (3)
- Transferability: If a verifier accepts a signature, he should be confident that any other verifier (e.g., a judge) would also accept the signature.
3. “Classical” Signature Schemes
3.1. Public-Key Digital Signatures
3.2. Cryptographic and Universal Hash Functions
- (1)
- Pre-image resistance: Given , it should be difficult to find x, that is, these hash functions are one-way functions.
- (2)
- Second pre-image resistance: Given , it should be difficult to find an , such that .
- (3)
- Collision resistance: It should be difficult to find any distinct pair , such that .
3.3. Lamport–Diffie One-Time Signatures
3.4. Unconditionally Secure “Classical” Signature Schemes
- (1)
- A signing key: ;
- (2)
- A pair of verification keys: and .
4. Quantum Signature Schemes
4.1. Quantum One-Way Functions and Quantum Hash Functions
4.2. Quantum Digital Signatures
- (1)
- Alice chooses M pairs of L-bit classical strings, , . The ’s will be used if the future message is chosen to be the bit zero and the ’s will be used if the future message is chosen to be the bit one. Increasing the value of M will increase the security level of the protocol (security is exponential in M).
- (2)
- Alice assigns each of the L-bit strings to a different element in the set of fingerprinting states, or whatever the chosen set of output quantum states is, according to a mapping known to all participants. That is, all participants know the one-way function, but not the L-bit strings used as input. She then distributes the quantum states to the t participants, so that each participant has a suitable number of copies of each of the the quantum states , .
- (3)
- Unless the distribution is managed by a trusted third party, the participants should perform some sort of test to ensure that they all received the same public keys. In the three-party setting, Gottesman and Chuang suggest that Alice sends two copies of each public key to each participant. Bob and Charlie would then both perform a SWAP test on their two keys to check that they are the same. One participant, say Bob, would then pass one of his keys to Charlie, who would perform a SWAP test on this key and one of his own to determine if they are equal. Bob performs a similar test on a key received directly from Alice and one forwarded by Charlie. The keys used in these last SWAP tests would then be discarded, and Bob and Charlie are left with one copy of the public key each. If any of the SWAP tests fail, the protocol is aborted. If none of the tests fail, the participants have evidence that Alice did in fact send out the same public key states. By sending each participant more copies of the public key, the probability of discovering a cheating Alice can be made arbitrarily close to one.In the more general t-party setting, the authors suggest a distributed symmetry test performed by all participants. In this case, Alice would distribute copies of the public key to each participant. They would perform a test to check for complete symmetry of their copies. If the test is passed, they would send one copy of the public key to each of the other participants, keeping one copy to use for signature verification and the remaining copy for a further symmetry test using all of the public keys received from other participants.
- (4)
- To later send the message b, Alice would send . From this, a recipient can easily compute for each i and compare the state to the public keys they previously received from Alice (again using a SWAP test). The recipient counts the number of mismatches he gets.
- (5)
- If the mismatch rate is less than some rate , the recipient will accept the message. If the message is forwarded on from another recipient, the mismatch rate must be less than to be accepted, where .
- (6)
- All used and unused keys are discarded.
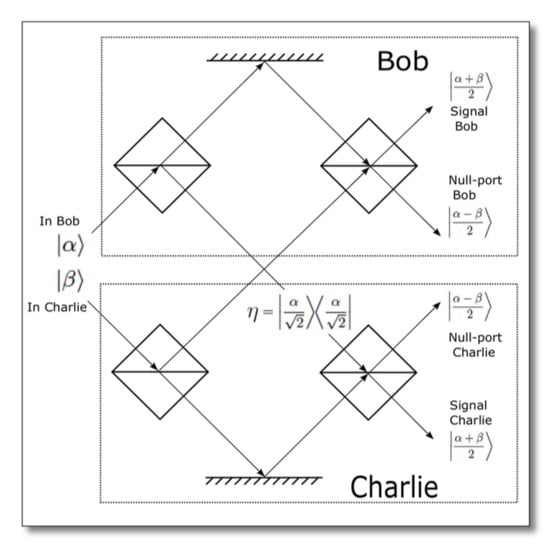
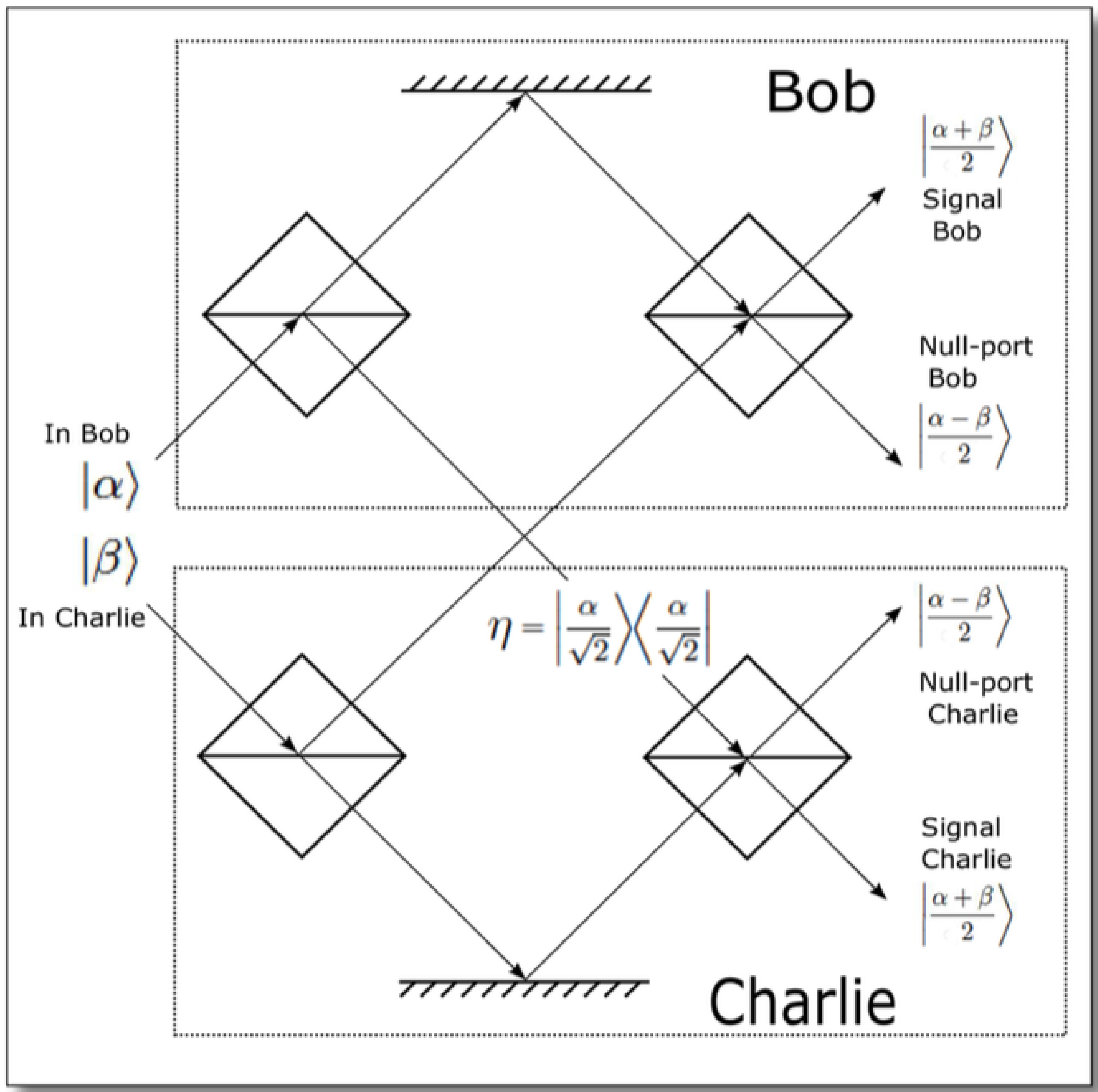
4.3. Quantum Signatures Using a Multi-Port without Quantum Memory
4.4. Quantum Signatures with Quantum Key Distribution Components
4.5. Security against Tampering with the Quantum Channels
4.6. Coherent State Mappings
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G.; Breidbart, S.; Wiesner, S. Quantum Cryptography, or Unforgeable Subway Tokens. In Advances in Cryptology, Proceedings of the Crypto’82; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Brassard, G. Brief History of Quantum Cryptography: A Personal Perspective. In Proceedings of the IEEE Information Theory Workshop on Theory and Practice in Information-Theoretic Security, Awaji Island, Japan, 19 October 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, 10–19 December 1984; pp. 175–179.
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum Cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H.; Cerf, N.J.; Dušek, M.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Peev, M. The Security of Practical Quantum Key Distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paar, C.; Pelzl, J. Understanding Cryptography: A Textbook for Students and Practitioners; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Diffie, W.; Hellman, M.E. New Directions in Cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, H.; Crépeau, C.; Gottesman, D.; Smith, A.; Tapp, A. Authentication of Quantum Messages. In Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–19 November 2002; pp. 449–458.
- Lu, X.; Feng, D. Quantum Digital Signature Based on Quantum One-way Functions. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, Phoenix Park, Korea, 21–23 February 2005; pp. 514–517.
- Chaum, D. Blind Signatures for Untraceable Payments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983; pp. 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wegman, M.N.; Carter, J.L. New Hash Functions and Their Use in Authentication and Set Equality. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1981, 22, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaum, D.; Roijakkers, S. Unconditionally-Secure Digital Signatures. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO’90: Proceedings; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991; Volume 537, pp. 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hanaoka, G.; Shikata, J.; Zheng, Y.; Imai, H. Unconditionally Secure Digital Signature Schemes Admitting Transferability. In Advances in Cryptology, Proceedings of the ASIACRYPT 2000; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2000; Volume 1976, pp. 130–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wallden, P.; Dunjko, V.; Kent, A.; Andersson, E. Quantum Digital Signatures with Quantum-Key-Distribution Components. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 042304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hong, C.; Kim, H.; Lim, J.; Yang, H.J. Arbitrated Quantum Signature Scheme with Message Recovery. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 321, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottesman, D.; Chuang, I. Quantum Digital Signatures. 2001; arXiv: quant-ph/0105032. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, C.M.; Stinson, D.R. Unconditionally Secure Signature Schemes Revisited. In Information Theoretic Security, Proceedings of the ICITS 2011, LNCS, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 21–24 May 2011; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 6673, pp. 100–116. [Google Scholar]
- Arrazola, J.M.; Wallden, P.; Andersson, E. Mulitparty Quantum Signature Schemes. 2015; arXiv:1505.07509. [Google Scholar]
- ElGamal, T. A Public Key Cryptosystem and a Signature Scheme Based on Discrete Logarithms. In Advances in Cryptology, Proceedings of CRYPTO’84; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1985; Volume 196, pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.; Menezes, A.; Vanstone, S. The Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA). Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2001, 1, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-Time Algorithms for Prime Factorization and Discrete Logarithms on a Quantum Computer. SIAM J. Comput. 1997, 26, 1484–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.J.; Buchmann, J.; Dahmen, E. (Eds.) Post-Quantum Cryptography; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009.
- Shannon, C. Communication Theory of Secrecy Systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1949, 28, 656–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, R.; König, R. Universally Composable Privacy Amplification Against Quantum Adversaries. In Proceedings of the TCC 2005, LNCS, Cambridge, MA, USA, 10–12 February 2005; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; Volume 3378, pp. 407–425. [Google Scholar]
- Lamport, L. Constructing Digital Signatures from a One-Way Function. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.228.2958&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 28 July 2015).
- Merkle, R.C. A Certified Digital Signature. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO’89: Proceedings; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; Volume 435, pp. 218–238. [Google Scholar]
- Song, F. A Note on Quantum Security for Post-quantum Cryptography. In Post-Quantum Cryptography, Proceedings of 6th International Workshop on PQCrypto 2014, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 1–3 October 2014; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 8772, pp. 246–265. [Google Scholar]
- Chaum, D. The Dining Cryptographers Problem: Unconditional Sender and Recipient Untraceability. J. Cryptol. 1988, 1, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, L.; Shostak, R.; Pease, M. The Byzantine Generals Problem. ACM Trans. Program. Lang. Syst. 1982, 4, 382–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holevo, A.S. Bounds for the Quantity of Information Transmitted by a Quantum Communication Channel. Probl. Inf. Trans. 1973, 9, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Kashefi, E.; Kerenidis, I. Statistical Zero-Knowledge and Quantum One-way Functions. J. Theory Comput. Sci. 2007, 378, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhrman, H.; Cleve, R.; Watrous, J.; De Wolf, R. Quantum Fingerprinting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 167902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavinsky, D.; Ito, T. Quantum Fingerprints that Keep Secrets. J. Quantum Inf. Comput. 2013, 13, 583–606. [Google Scholar]
- Ablayev, F.M.; Vasiliev, A.V. Cryptographic Quantum Hashing. Laser Phys. Lett. 2014, 11, 025202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M.; Chefles, A.; Jex, I. Comparison of Two Unknown Pure Quantum States. Phys. Lett. A 2003, 307, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jex, I.; Andersson, E.; Chefles, A. Comparing the States of Many Quantum Systems. J. Mod. Opt. 2004, 51, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, E.; Curty, M.; Jex, I. Experimentally Realizable Quantum Comparison of Coherent States and Its Applications. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 74, 022304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.J.; Collins, R.J.; Dunjko, V.; Andersson, E.; Jeffers, J.; Buller, G.S. Experimental Demonstration of Quantum Digital Signatures Using Phase-Encoded Coherent States of Light. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunjko, V.; Wallden, P.; Andersson, E. Quantum Digital Signatures without Quantum Memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.J.; Donaldson, R.J.; Dunjko, V.; Wallden, P.; Clarke, P.J.; Andersson, E.; Jeffers, J.; Buller, G.S. Realization of Quantum Digital Signatures without the Requirement of Quantum Memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, S.M. Quantum Information; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jain, R.; Oppenheim, J.; Perry, C. Conclusive Exclusion of Quantum States. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 022336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croke, S.; Kent, A. Security Details for Bit Commitment by Transmitting Measurement Outcomes. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, R.J.; Collins, R.J.; Kleckowska, K.; Amiri, R.; Wallden, P.; Dunjko, V.; Andersson, E.; Jeffers, J.; Buller, G.S. An In-fiber Experimental Approach to Photonic Quantum Digital Signatures Operating over Kilometer Ranges. In Proceedings of SPIE 9254, Emerging Technologies in Security and Defence II; and Quantum-Physics-Based Information Security III, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22 September 2014. [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Petros, W.; Kent, A.; Andersson, E. Secure Quantum Signatures Using Insecure Quantum Channels. 2015; arXiv:1507.02975. [Google Scholar]
- Arrazola, J.M.; Lütkenhaus, N. Quantum Communication with Coherent States and Linear Optics. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 042335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazola, J.M.; Lütkenhaus, N. Quantum Fingerprinting with Coherent States and a Constant Mean Number of Photons. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 062305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amiri, R.; Andersson, E. Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures. Entropy 2015, 17, 5635-5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17085635
Amiri R, Andersson E. Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures. Entropy. 2015; 17(8):5635-5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17085635
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmiri, Ryan, and Erika Andersson. 2015. "Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures" Entropy 17, no. 8: 5635-5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17085635
APA StyleAmiri, R., & Andersson, E. (2015). Unconditionally Secure Quantum Signatures. Entropy, 17(8), 5635-5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17085635