Abstract
The dynamics of human electroencephalography (EEG) have been proved to be related to cognitive activities. This study separately assessed the two EEG components, amplitude and rhythm, aiming to capture their individual contributions to cognitive functions. We extracted the local peaks of EEGs under rest or photic stimulation and calculated the symbolic dynamics of their voltages (amplitude) and interpeak intervals (instantaneous frequency), individually. The sample consisted of 89 geriatric outpatients in three patient groups: 38 fresh cases of vascular dementia (VD), 22 fresh cases of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and 29 controls. Both sample entropy and number of forbidden words revealed significantly less regular symbolic dynamics in the whole EEG tracings of the VD than the AD and control groups. We found consistent results between groups with the symbolic dynamics in the local-peak voltage sequence rather than the interpeak interval sequence. Photic stimulation amplified the differences between groups. These results suggest that the EEG dynamics which relates to either cognitive functions or the underlying pathologies of dementia are embedded within the dynamics of the amount of but not the interval between each synchronized firing of adjacent cerebral neurons.
1. Introduction
Although there are two aspects of electroencephalography (EEG) dynamics, the rhythm and amplitude, analyses of EEG signals have mostly focused on the rhythm. The dynamics of EEG rhythm has been proved to provide information related to cognitive functions [1]. Whether the dynamics of EEG amplitude also correlate to cognitive functions rarely discussed. The EEG amplitude of a normal subject in the awake state recorded with the scalp electrodes is 10 μV to 100 μV. Higher background amplitudes are associated with lower frequencies in normal EEGs for all age groups [2]. Symmetrical low voltage and even visually unrecognizable alpha rhythm was not regarded as pathological. We expected nonlinear approaches can reveal more hidden characteristics of the EEG amplitude. The question was how to evaluate the dynamics of amplitude and rhythm separately.
The human brain is believed to function on the base of networks of interactivity of neural assemblies, which could be approached through the transient phase couplings of EEG signals from various regions. A balanced dynamical pattern that switches between synchronization (phase coupling between two regions) and desynchronization (phase shifting) is crucial to proper brain function [3–7]. The scalp EEG mainly records large postsynaptic potentials [8]. Only large populations of active neurons can generate enough potential to be recordable using the scalp electrodes. The peaks and troughs of a physical wave indicate levels of probability for the occurrence of certain phenomenon. One peak of a single-channel EEG implies a local maximal (in time domain) amount of synchronized active neurons in a localized region. Therefore, the dynamics of the local maxima of a single-channel EEG reflects the changing degree of neuronal couplings in a localized brain area. We supposed that discrete events rather than continuous recordings can provide more concentrated information in certain dimensions of the dynamics. When extracting the peaks from a single-channel EEG, one obtains two sequences, the local-peak voltage sequence and the interpeak interval sequence. The local-peak voltage sequence depicts the amplitude change whereas the interpeak interval sequence illustrates the instantaneous frequency. This is our approach to treating the amplitude and rhythm separately.
We used wakeful resting EEGs with or without photic stimulation (PS) in a sample of geriatric outpatients with or without dementia to identify the amplitude or rhythm which correlates better with cognitive status and image findings. The wakeful resting EEG represents the stimulus-independent intrinsic activity of the brain, which accounts for a big part of the energy budget of the brain [9], and its alteration may lead to disorders ranging from Alzheimer’s to schizophrenia [10]. Photic stimulation is a procedure meant to elicit or accentuate epileptiform discharges during a routine EEG. The brain is stimulated by periodic lighting impulses during the PS procedure. Despite the widespread utilization, the complete understanding of the brain response to PS is still an open problem. A continuous visually clean EEG recording could only be acquired in a very limited period because of copious artifacts from muscles or environments. The derived sequences of the local peaks of EEG are even shorter. Therefore we adopted a symbolic approach, which can avoid noise interference and is suitable for short time series [11]. Symbolic dynamics can detect well the phase transitions in EEG signal analyses. It provides an especially good reflection of the state changes in epileptic EEGs [12–16]. It was also successfully applied with neural network models in EEG dynamics during mental tasks [17]. The phase changes in the wakeful resting EEG of dementia may not be as prominent as those during epileptic bursts or mental tasks, but the degree of change could be compared.
Symbolic dynamics is based on a way of coarse-graining or reduction of description. At first, the data is transformed into a pattern which is composed of only a few symbols; therefore the phase space is divided into a finite number of partitions. Only the dynamics of the symbol series is studied. Although a great amount of detailed information is lost, some of the invariant, robust properties of the dynamics such as periodicity, symmetry and chaotic nature of an orbit may be kept [18]. The partition process acts just like down-sampling, through which the entropy can increase since the statistical dependence of consecutive samples decreases [19,20], and can keep a stable entropy difference between different clinical situations, without a decrease in sensitivity [21]. With the symbolic series, statistical methods such as measures of entropy (Shannon entropy [22]) and entropy rate (approximate entropy [23] and sample entropy (SampEn) [24]), as well as the classification of frequent deterministic patterns are generally adopted to explore the dynamics [25–27]. Various methods of entropy measurement techniques have showed that both heart rate variability and brain signal variability convey important information about network dynamics [28]. SampEn, without counting self-matches, is less dependent on the signal length and shows more consistency on a broader range of parameters than approximate entropy [24].
The underlying origins of EEG rhythms remain a mystery. EEG contain arrhythmic components which are called the slow cortical potential (SCP, mainly <1 Hz, can extend up to 4 Hz) [29]. The SCP does not only correlate with fMRI signals, but also seems to modulate the amplitude of higher-frequency activity [30,31]. In order to approach the SCP in an intuitive way, we calculated the excursion amplitude of EEG, the difference between the respective envelopes of the peaks and troughs of a single-channel EEG. The excursion amplitude of EEG depicts the brain dynamics in the frequency range close to the SCP. We could obtain another two sequences, the voltage and interpeak interval of the peaks of the excursion amplitude of EEG. We suspect that the origin of the SCP may be related to other organs such as the heart. The human body consists of multiple organs which interact with each other. We have previously found correlations between separately recorded EEGs and 2-hour R-R interval (RRI) data [32] using multiscale entropy. Therefore, we expected to explore the relationship between simultaneous EEG and RRI data with the symbolic techniques.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
The final study population included 89 geriatric outpatients, who were free of previously diagnosed neurologic and cardiovascular diseases (except mild hypertension), and found to have varied cognitive abilities (female = 43; age = 79.3 ± 6.4 years, mean ± standard deviation (SD), range 65.3–93.7 years). Sixty (female = 30; 81.1 ± 5.7 years) newly diagnosed cases of dementia presented on the first visit with a chief complaint of memory or cognitive decline, corroborated by informants, and had a Chinese version of the mini-mental state examination, the mini-mental state examination of Taiwan, version 1 (MMSE-T1) score with illiteracy adjustment less than or equal to 26. After laboratory tests and brain-imaging referrals, the recruited demented patients included only two types: probable Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (n = 22; females = 7; age = 81.9 ± 6.6 years; MMSE-T1 = 22.2 ± 5.8) according to NINCDS-ADRDA [33] and vascular dementia (VD) (n = 38; females = 23; age = 80.6 ± 5.1 years; MMSE-T1 = 18.4 ± 7.2) of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy according to NINDS-AIREN [34]. The control group consisted of twenty-nine ambulatory geriatric patients (females = 13; age = 75.5 ± 6.2 years; MMSE-T1 = 28.4 ± 0.9) with only mild hypertension and/or mild diabetes. The original MMSE-T1 scores were adjusted for illiteracy by multiplying 30/27 (3 points for reading or writing Chinese characters). Exclusion criteria included mixed dementia, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, frequent atrial premature complex or ventricular premature complex, major systemic diseases, infection, hypothyroidism, vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency, psychosis, previous stroke, major head injury, epilepsy, normal pressure hydrocephalus, subdural effusion or hemorrhage, and exposure to sympatholytic agents (including beta blockers), acetyl cholinesterase inhibitors, tranquilizers, or antidepressants. The ethics committee on human research of Tainan Hospital approved the study. All participants or their surrogates gave written informed consent. The investigation conformed to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Data Collection
All subjects underwent routine EEG recordings with determination of arousal reaction to eye opening and references at ear electrodes. The routine multichannel EEG includes two parts: the 30-minute resting-awake recording and the 2.5-minute recording under intermittent photic stimulation. The surface EEG was collected by a digital EEG recorder (Harmonie version 3.1 digital EEG Stellate Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada) at 200 Hz from the 19 electrodes of the international standard 10/20 system. The raw data, contaminated with artifacts such as eye movements, blinks, muscle activities and others, were saved in text files for off-line analysis on a personal computer. We chose three 80-second segments from each file: one visually-censored (by an experienced neurologist) artifact-free eye-closed resting-awake recording, one photic-simulated recording at frequencies 1, 3, 6 and 9 Hz (slowPS, duration 10 s and interval 10 s) and one photic-simulated recording at frequencies 12, 15, 18 and 24 Hz (fastPS, duration 10 s and interval 10 s). The ECGs simultaneously recorded with the EEGs were also obtained. R-peak detection and the beat annotations were performed by an automated arrhythmia detection algorithm and verified by visual inspection. The series of interbeat interval between successive R-peaks, that is the RRI (Figure 1a), served as the basis for the calculations. Occasional ectopic beats were identified and replaced with linearly interpolated RRI data. Those subjects with more than 1% ectopic beats were excluded from the final analysis.
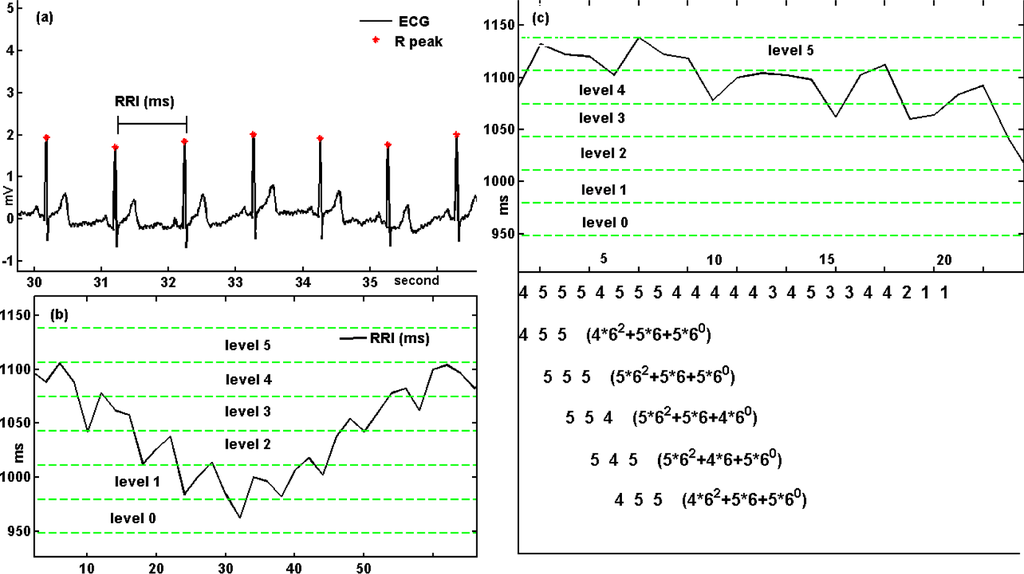
Figure 1.
(a) The R-peak detection was performed by an automated arrhythmia detection algorithm and corrected by visual inspection; (b) The normalized RRI series was uniformly spread on 6 levels (from 0 to 5) and transformed into a series of symbols from the limited alphabet of symbols {0,1, …, 5}; (c) From a symbolic sequence, patterns of three delayed samples were constructed. The overlapping triplet symbols of the constructed pattern were codified in decimal format.
2.3. Four Sequences Derived from Each Channel of the EEG
We detected the local peaks (points from which all paths are downhill) along the EEG waveform and made two sequences from them: the local-peak voltage and interpeak interval sequences (Figure 2a). We then calculated the difference between the respective envelopes of the peaks and troughs to acquire the EEG excursion amplitude (AmpEEG) [35] using a method based on the envelope fitting procedure defined in the sifting process of the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) [36]. We also detected the local peaks of the AmpEEG to make another two sequences: the local-peak voltage and interpeak interval of the AmpEEG.
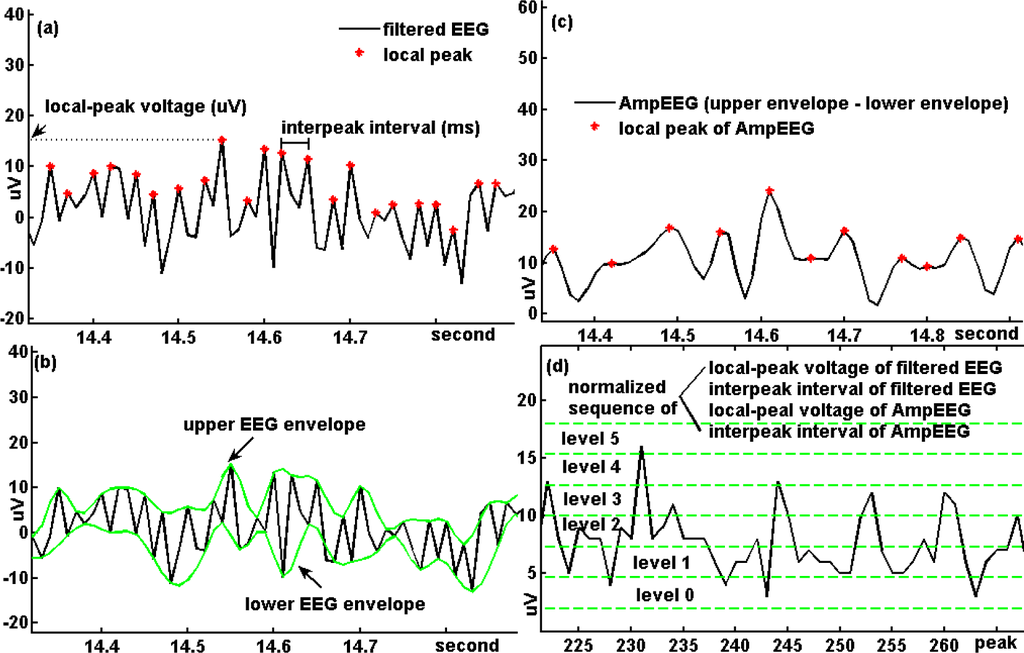
Figure 2.
(a) Local peaks of a filtered EEG were detected according to the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method to make two sequences of the local-peak voltage and interpeak interval; (b) Natural cubic splines were applied to the local maximal and local minimal points respectively according to the sifting procedure of the EMD. The upper and lower EEG envelopes were formed from the maximal points and minimal points, respectively; (c) The EEG excursion amplitude (AmpEEG) was defined as the difference between the upper and lower envelopes. The local peaks of the AmpEEG were again detected to form another two sequences of the local-peak voltage and interpeak interval; (d) Any normalized sequence formed from (a) and (c) was uniformly spread on 6 levels (from 0 to 5) and transformed into a series of symbols from the limited alphabet of symbols {0, 1, …, 5}.
The details of the procedures are as follows: the EEG data were firstly processed by a notch filter at the frequency of current 60 Hz. They were further processed by the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) techniques to collect the frequency components between 0.5 and 59 Hz for artifacts removal. Then peak detection was performed for each channel of the EEG according to the EMD method:
where x(n) is the filtered EEG signal, n = {0,1,2, …, N−1} and N is the signal length. With the local peaks of the filtered EEG, we made two sequences, the local-peak voltage (x(nmax)) and interpeak interval (difference (nmax)) sequences (Figure 2a). Next, natural cubic splines were applied to the maximal (nmax, x(nmax)) and minimal (nmin, x(nmin)) points respectively according to the sifting procedure of the EMD. Thus the upper EEG envelope (EEGenvu) and the lower EEG envelop (EEGenvl) were formed from the maximal points and minimal points, respectively. The EEG excursion amplitude (AmpEEG) was defined as the difference between the upper and lower envelopes, AmpEEG (n) = EEGenvu − EEGenvl (Figure 2b). The local peaks of the AmpEEG were again detected to form another two sequences, the local-peak voltage and interpeak interval of the AmpEEG (Figure 2c).
2.4. Construction of Symbolic Sequences
We followed the method developed and validated by Porta et al. [25]. Each sample of the series X = {Xi, i = 1, …, N} (either a RRI, a filtered single-channel EEG whole tracing, or any of the four sequences derived from each single-channel EEG) is first normalized by subtracting the mean and, then, divided by the standard deviation, thus obtaining the series x = {xi, i = 1, …, N}. Next, through coarse-graining, the full range of a series x = {xi, i = 1, …, N} was uniformly spread on six levels (from 0 to 5) and transformed into a series of symbols x6 = {x6i, i = 1, …, N} from the limited alphabet of symbols {0,1, …, 5} (Figures 1b and 2d). From the symbolic series x6, patterns of three delayed samples (L = 3) were constructed as x63,i = (x6i, x6i−1, x6i−2). The overlapping triplet symbol x63,i was codified in decimal format as (x6i, x6i−1, x6i−2)decimal = x6i * 63−1 + x6i−1 * 63−2 + x6i−2 * 63−3 = wi, w = {wi, i = 1, …, N−L+1} with wi ranging from zero to
(Figure 1c).
2.5. Number of Forbidden Words and Surrogate Data
We counted the number of forbidden words (NumFW, i.e., the number of patterns which never occur) of the overlapping triplet symbols x63,i—that is the number of patterns which never occur. The number of all possible patterns of the overlapping triplet symbols x63,i equals 216 = 63 (also equals 1 + Np). A high NumFW stands for a rather regular behavior in the time series [37]. The sample length of the of the overlapping triplet symbols x63,i would be checked to ensure that all patterns (i.e., 216) could be found several times. To test the presence of deterministic structures in a sequence, we carried out a surrogate data analysis using Gaussian-scaled random-phase surrogates by iterated amplitude adjusted Fourier transform (IAAFT). [38] An IAAFT surrogate time series is random, matches the original power spectrum and preserves the exact original marginal distribution.
2.6. Steps, Sample Entropy and Others
First we applied five methods to measure the symbolic dynamics of each RRI and filtered single-channel EEG whole tracing. Sample entropy (SampEn) [24], Shannon entropy [22], alpha (1) for detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) [39] and Hurst exponent for rescaled range analysis (RS) [40] were calculated for each decimalized symbolic sequence, w, of the RRIs and filtered EEG whole tracings. Number of forbidden words (NumFW) was calculated for each sequence of the overlapping triplet symbols, x63,i, of the RRIs and EEG whole tracings. Methods that showed no significant between group differences by multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) statistics would not be applied in the analysis of the four EEG-derived sequences. The second step was aimed to explore the issue of amplitude versus instantaneous frequency. Methods chosen from the first step would be calculated for the symbolic sequences of the four EEG-derived sequences (the local-peak voltage, interpeak interval, local-peak voltage of the AmpEEG and interpeak interval of the AmpEEG). On the other hand, SampEn, Shannon entropy, alpha (1) for DFA and Hurst exponent for RS of the filtered EEG whole tracings without the symbolization procedure were also calculated for comparison.
SampEn was chosen in the first step. To describe SampEn in short, where m, r, and N refer to the pattern length, normalized threshold (tolerance), and signal length respectively, suppose Bm(r) is the probability that two sequences will match for m points, and Am(r) is the probability that two sequences will match for m + 1 points. The match is considered within tolerance and with self-matches excluded. The parameter, SampEn, is estimated by the statistic: SampEn(m, r, N) = −ln[Am(r)/Bm(r)]. We chose m = 2 and r = 0.2. For the algorithms for other calculations, please refer to the references.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using R 2.11.0 at a 0.05 alpha level. We performed analysis of variance (ANOVA) or multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) to test for significant differences between means. For the post-hoc analyses in a one-way MANOVA, we used Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) test to correct for multiple comparisons of 19 electrode sites in three conditions. The Tukey p values were further adjusted by Bonferroni corrections for five methods (by multiplication with five). SampEn and NumFW were chosen from the first step. In the second step, we also performed MANOVA to examine SampEn and NumFW in the symbolic analysis of the four EEG-derived sequences. The post-hoc comparisons using Tukey’s HSD test were also followed by Bonferroni corrections for two methods and four sequences (by multiplication with eight). We used age- and gender-adjusted Pearson’s partial correlation coefficients to evaluate correlations between any two variables. Paired-t tests with Bonferroni corrections (19 electrode sites) were used to compare the corresponding data in three EEG conditions. The comparisons among the three EEGs or the three RRIs were also calculated by paired t-tests. Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Levene tests were used to assess the normality of distribution and homoscedasticity, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Significant Group Differences Were Found Only after the Symbolization Procedure
In the symbolic analyses of the EEG whole tracing, we found that: (1) Both DFA and RS demonstrated no significant differences among groups; (2) Shannon entropy shared nearly the same statistical findings with SampEn, only with larger p-values; (3) NumFW reveled highest discriminative power. We chose SampEn and NumFW for the second step. On the other hand, we did not find any significant group differences in the analyses of the EEG whole tracing without the symbolization procedure.
3.2. The Symbolic Dynamics in the EEG Whole Tracing Were Only Found Again in the Local-Peak Voltage Sequence of the EEG
In the symbolic analyses of both the EEG whole tracing and its local-peak voltage sequence, we found consistent relative SampEn (Control = AD < VD) and NumFW (Control = AD > VD) values among groups. The symbolic analyses of the other three EEG-derived sequences (the interpeak interval sequence of the local peak of the EEG, the interpeak interval sequence of the local peak of the AmpEEG, and the local-peak voltage sequence of the AmpEEG) or any RRI sequence did not show significant group differences.
The discriminative brain regions are presented as topographic maps in Figures 3 and 4. In the analyses of the EEG whole tracings, lower NumFW (NumFW_EEGwhole) values in the VD compared with the control group are presented in Figure 3 (a1–a3) at Fp2 (corrected p-value: 0.025), F4 (0.025), F8 (4 × 10−4), C4 (5 × 10−5), T4 (0.002), P4 (5 × 10−4), T6 (2 × 10−4), O2 (0.005), Fp1 (0.030), F3 (0.010), F7 (0.040), C3 (0.015), P3 (7 × 10−4), Fz (0.001), Cz (0.005) and Pz (6 × 10−4) with the wakeful resting EEG; at C4 (0.030), T4 (0.010), T6 (0.020), F7 (0.005), C3 (0.001), T3 (0.002), P3 (2 × 10−4), T5 (0.005), O1 (0.005) and Pz (0.005) with the slowPS EEG; and at F4 (0.030), F8 (0.010), C4 (0.005), T4 (0.020), P4 (0.035), T6 (0.005), O2 (0.001), Fp1 (0.005), F3 (0.010), F7 (0.030), C3 (8 × 10−4), T3 (4 × 10−4), P3 (8 × 10−4), T5 (0.001), O1 (2 × 10−4), Fz (0.015), Cz (0.020) and Pz (0.002) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the EEG whole tracings, higher SampEn values in the VD compared with the control group are presented in Figure 3 (b1–b3) at C4 (2 × 10−4), P4 (0.015), T6 (0.010), Fz (0.010), Cz (0.012) and Pz (0.002) with the wakeful resting EEG; at F7 (0.025), P3 (0.015) and T5 (0.005) with the slowPS EEG; and at P4 (0.03), T6 (0.035), O2 (0.010), F3 (0.040), F7 (0.015), C3 (0.010), T3 (0.005), P3 (0.010), T5 (0.010), and Pz (0.005) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the EEG whole tracings, lower NumFW_EEGwhole values in the VD compared with the AD group are presented in Figure 3 (c1–c3) at F8 (0.028), C4 (0.049), T4 (0.002), P4 (8 × 10−4), T6 (2 × 10−4), O2 (7 × 10−4), T5 (0.040), Fz (0.035) and Pz (0.005) with the wakeful resting EEG; at C4 (0.005), T6 (0.030), C3 (0.020), T3 (0.035), T5 (0.005), O1 (0.015), Cz (0.030) and Pz (0.005) with the slowPS EEG; and at F4 (0.005), C4 (0.005), T4 (0.005), P4 (0.020), T6 (0.001), O2 (0.001), F3 (0.020), C3 (0.020), T3 (0.005), P3 (0.005), T5 (0.005), O1 (0.025), Fz (0.005), Cz (0.005) and Pz (0.002) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the EEG whole tracings, higher SampEn values in the VD compared with the AD group are presented in Figure 3 (d1–d3) at T6 with the wakeful resting EEG; at T6 (0.040) with the slowPS EEG; and at C4 (0.025), T4 (0.005), P4 (0.010), T6 (0.010), O2 (0.005) and Cz (0.045) with the fastPS EEG.
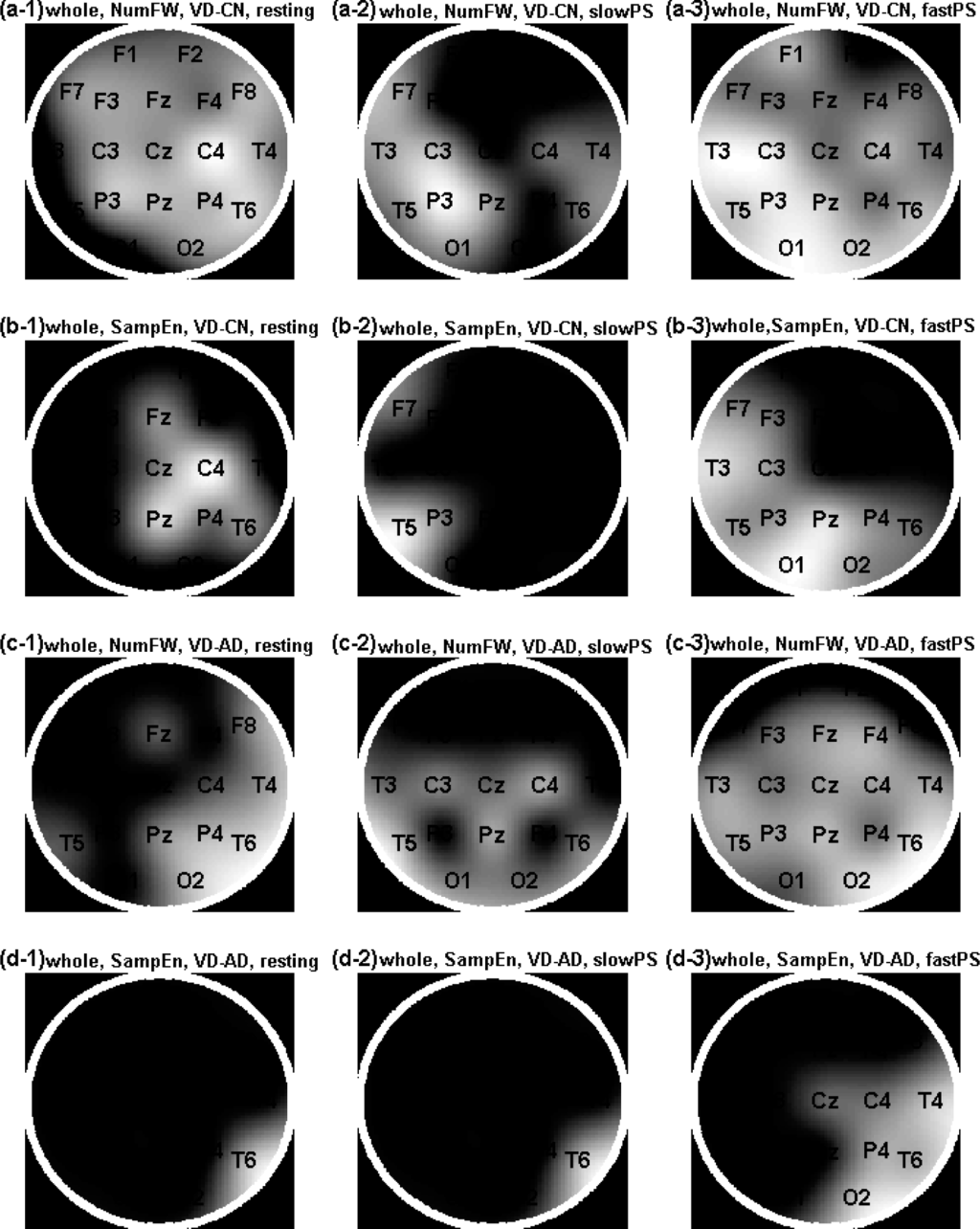
Figure 3.
Topographic maps of the significant findings from the post-hoc analyses of one-way multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) in the analyses of the filtered EEG whole tracings. The relative brightness is correlated with the p-values as the brightest the smallest p-value. (a1–3) Brain regions showing significant lower NumFW in patients with VD (n = 38) compared with the control group (n = 29) in three conditions (resting: wakeful resting (a1), slowPS: slow photic stimulation (a2), fastPS: fast photic stimulation (a3)); (b1–3) Brain regions showing significant higher sample entropy (SampEn, m = 2) in the VD compared with the control group; (c1–3) Brain regions showing significant lower NumFW in the VD compared with the AD (n = 22); (d1–3) Brain regions showing significant higher SampEn in the VD compared with the AD.
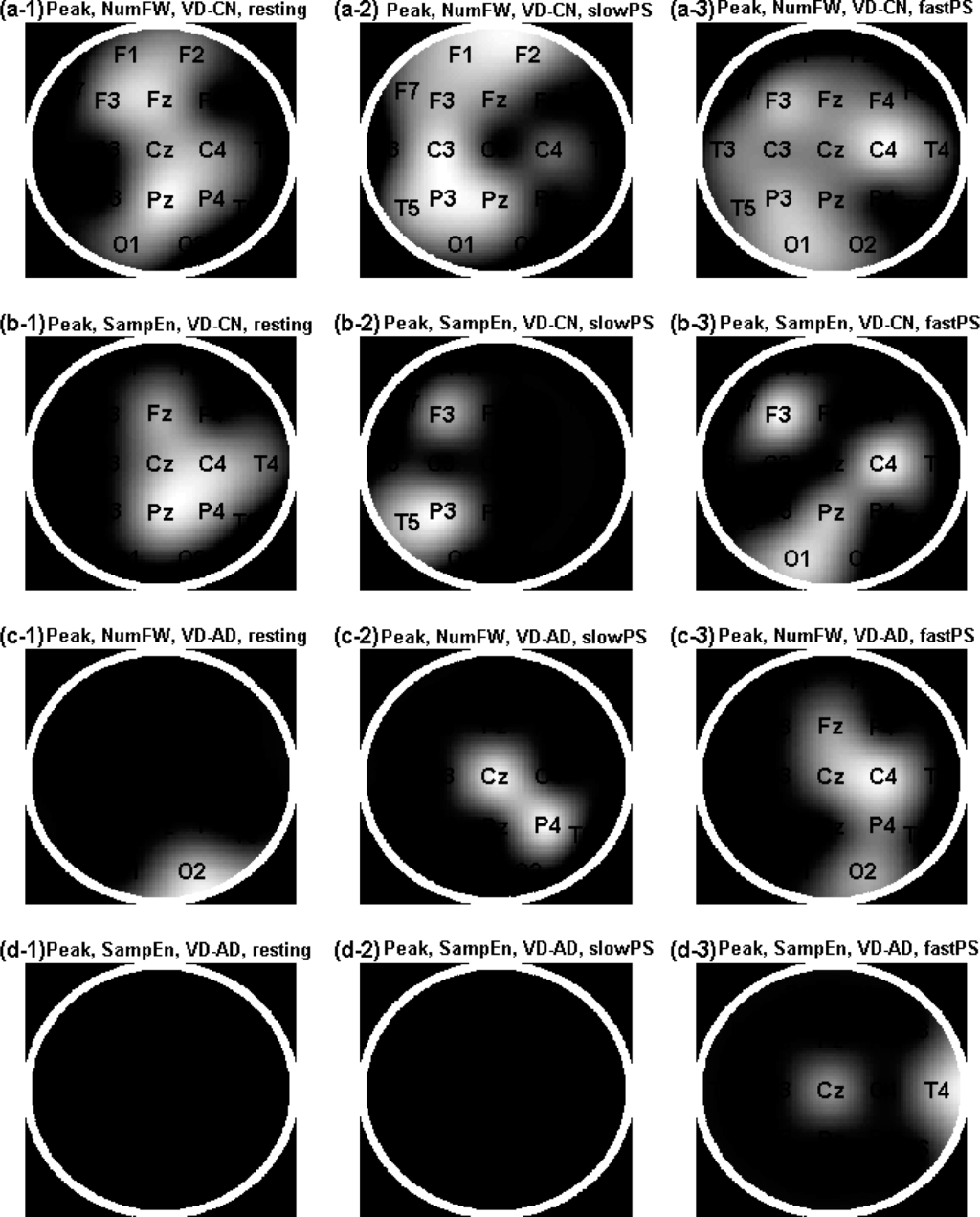
Figure 4.
Topographic maps of the significant findings from the post-hoc analyses of one-way multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) for the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequences of the filtered EEGs. The relative brightness is correlated with the p-values as the brightest the smallest p-value. (a1–3) Brain regions showing significant lower NumFW in patients with VD (n = 38) compared with the control group (n = 29) in three conditions (resting: wakeful resting (a1), slowPS: slow photic stimulation (a2), fastPS: fast photic stimulation (a3)); (b1–3) Brain regions showing significant higher sample entropy (SampEn, m = 2) in the VD compared with the control group; (c1–3) Brain regions showing significant lower NumFW in the VD compared with the AD (n = 22); (d1–3) Brain regions showing significant higher SampEn in the VD compared with the AD.
In the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequence of EEG, lower NumFW (NumFW_EEGpeak) values in the VD compared with the control group are presented in Figure 4 (a1–a3) at Fp2 (0.048), C4 (0.032), P4 (0.048), Fp1 (0.048), F3 (0.016), O1 (0.048), Fz (0.003), Cz (0.016) and Pz (10−4) with the wakeful resting EEG; at Fp2 (0.008), C4 (0.048), Fp1 (0.008), F3 (0.002), F7 (0.016), C3 (7 × 10−4), P3 (6 × 10−4), T5 (0.002), O1 (0.032), Fz (0.016) and Pz (0.008) with the slowPS EEG; and at F4 (0.032), C4 (8 × 10−4), T4 (0.048), O2 (0.048), F3 (0.008), C3 (0.016), T3 (0.040), P3 (0.008), T5 (0.032), O1 (0.003), Fz (0.016), Cz (0.016) and Pz (0.024) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequence of EEG, higher SampEn values in the VD compared with the control group are presented in Figure 4 (b1–b3) at C4 (0.003), T4 (0.032), P4 (0.008), Fz (0.008), Cz (0.008) and Pz (2 × 10−4) with the wakeful resting EEG; at F3 (0.040), P3 (0.016) and T5 (0.032) with the slowPS EEG; and at C4 (0.16), F3 (0.016), O1 (0.024) and Pz (0.040) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequence of EEG, lower NumFW_EEGpeak values in the VD compared with the AD group are presented in Figure 4 (c1–c3) at O2 (0.048) with the wakeful resting EEG; at P4 (0.040) with the slowPS EEG; and at C4 (0.008), P4 (0.040), O2 (0.016), Fz (0.032) and Cz (0.016) and Pz (0.002) with the fastPS EEG. In the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequence of EEG, higher SampEn values in the VD compared with the AD group are presented in Figure 4 (d1–d3) at T4 (0.024) with the fastPS EEG.
Tables S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Material show the means and standard deviations of all the symbolic SampEn and NumFW values. Table S1 shows the results for the EEG whole tracing and Table S2 shows the results for the local-peak voltage sequence. Significant discriminative brain regions revealed by the post-hoc study of MANOVA were denoted by the star signs as “*” for corrected p value < 0.05 and “**” for corrected p value < 0.01.
3.3. Correlations between the EEG Whole Tracing and the Local Peak Voltage Sequence
The linear correlations between the NumFWwhole and NumFW_EEGpeak in all three conditions were very high (the age- and gender-adjusted partial correlation coefficients r = 0.52 to 0.85, p = 10−7 to 10−25). We did not find any correlations between the NumFWwhole and the NumFW of any of the other three EEG-derived sequences (the interpeak interval sequence of the local peaks of the EEG, the local-peak voltage sequence of the AmpEEG and the interpeak interval sequence of the local peaks of the AmpEEG.).
3.4. Effects of Photic Stimulation
The NumFW_EEGpeak values in the EEGs of all three conditions were highly correlated with one another (all the p-values for Pearson’s correlation coefficients < 0.001). Using paired-t tests with Bonferroni corrections, we found significant lower NumFW_EEG_whole values in the slowPS compared with the wakeful resting state at F1 (p = 6 × 10−6), Fz (p = 6 × 10−5), F2 (p = 4 × 10−4), F3 (p = 0.003), F4 (p = 0.009), Cz (p = 0.030) and F8 (0.040); significant lower NumFW_EEGpeak values in the slowPS compared with the wakeful resting state at Fz (p = 10−5), Fp2 (p = 10−4), Fp1 (p = 7 × 10−4), F8 (p = 0.007), Cz (p = 0.008), F3 (p = 0.003) and F4 (p = 0.02); significant lower NumFW_EEGwhole values in the fastPS compared with the wakeful resting state at Fz (p = 10−4), Fp1 (p = 2 × 10−4), Fp2 (p = 0.004), F3 (p = 0.007) and F8 (p = 0.01); significant lower NumFW_EEGpeak values in the fastPS compared with the wakeful resting state at F4 (p = 6 × 10−6), F1, F8, F3 and Fp2 (all p-values = 0.01). Neither NumFW_EEGwhole nor NumFW_EEGpeak were significantly different in the two PS conditions (slowPS and fastPS). The NumFW values of the RRIs in all three conditions (wakeful resting, slowPS, and fastPS) were highly correlated to each other (Pearson’s correlation, p-values < 0.0001) but not different in their means (paired-t tests). High correlations were also found with the SampEn values in three conditions.
3.5. The Number N of Words Used for Estimation of the Number of Forbidden Words
The sample length of the EEG whole tracing signal was originally 16,000 (80 s, 200 Hz). After the symbolic pattern construction of three delayed samples, the number N of words used for estimation of the number of forbidden words (N) became 15,998. The N of the local-peak derived sequences was around 1300–3000, and of the AmpEEG-derived sequence was around 400–1000. They were also large enough to allow patterns (i.e., 216) to be found several times. We also used IAAFT surrogate time series for comparison. We found that in all three conditions, the NumFW values of the whole EEG tracings or their derived sequences (around 30 to 200) were also significantly much higher than those of their surrogate data (close to 0). Non-randomness and non-linearity in our data were justified.
3.6. No Correlations Were Found Between Heartbeats and Brainwaves
We failed to find any correlation between the parameters from the symbolic analysis of the simultaneous RRIs and EEGs. No parameter derived from the RRI series revealed any group differences either.
3.7. Cognitive Tests
The MMSE-T1 score decreased linearly with age (gender-adjusted Pearson’s partial correlation coefficient r = −0.337, p = 0.001). Using ANOVA test, the MMSE-T1 score was significantly lower in the VD compared with in the control (p = 3 × 10−10) and AD (p = 0.04) groups.
4. Discussion
Using symbolic analysis, the differences between the VD and control groups in the dynamics of the EEG whole tracing could only be found again in the local-peak voltage but not the interpeak interval sequence. This implied that the dynamics of the amount of neurons (amplitude) but not the interval (instantaneous frequency) between each synchronous firing of adjacent cerebral neurons are relevant to the clinical conditions. The EEG whole tracing revealed slightly more discriminative brain regions compared with the local-peak voltage sequence. This was due to that the Bonferroni corrections were more rigorous in the analyses of the local-peak voltage sequences according the study design. SampEn of the EEG whole tracing could differ patient groups but only after the symbolization techniques. This clearly showed the merit of the symbolization techniques. Both lower NumFW and higher SampEn values of either the whole EEG tracing or the local-peak voltage sequence in the VD group implied a loss of regularity. Topographically, the regions showing significant loss of regularity in the VD group spread more widely over the whole head compared with the AD group. The NumFW, also known as missing patterns, outperformed SampEn in group differentiation. True missing patterns are robust against noise and they have the potential ability for distinguishing deterministic behavior from randomness in finite time series contaminated with observational white noise [41,42].
The symbolic entropy of EEG was consistently higher in dementia. Previous EEG studies using approximate entropy [43] and SampEn [44] showed lower entropy in AD. This discrepancy may be caused by the multifractal characteristic of EEG signals [45,46] and the limitations of the analytic methods. Various analytic methods may have explored different scales or dimensions. For example, multiscale entropy analysis revealed different results across fine- or coarse-time scales in AD, higher or less regularity, respectively [47,48]. Vaillancourt and Newell made a point that no one direction fits all results [49]. Both neuronal loss and white matter lesions are well recognized in neurodegeneration and dementia, including VD and AD. Those brain lesions are scattered irregularly over the brain, and thus induce irregularity in certain dimensions of the EEG dynamics. The increased symbolic entropy in the EEG of the VD group was in accordance with the severity of the cognitive dysfunction (significant lower MMSE-T1 score). Image studies have shown that the subcortical lesions of the VD group existed in the bilateral fronto-temporal but not the occipital regions. Nevertheless, the increased symbolic entropy in the VD group was present all over the whole head with both the EEG whole tracing and the local-peak voltage sequence. We also found increased symbolic entropy in the EEGs of the AD group compared with the control group, but they were not statistically significant. The MMSE-T1 scores were also significantly lower in the VD than in the other two groups. This was due to selection bias because we only recruited fresh demented cases in this study, and the number of the fresh VD patients surpassed that of the fresh AD patients. The patients of this public regional hospital mostly come from low-income backgrounds, and we also found significantly lower household incomes in the VD than in the control group (p = 0.034).
Photic stimulation (PS) of either slow or fast frequencies significantly interrupted the symbolic dynamics in both the EEG whole tracing and the local-peak voltage sequence. Compared with the EEG dynamics in resting condition, the dynamics under PS was significantly less regular (lower NumFW) only in the frontal but not the occipital regions. Intuitively, any changes in cortical activity that occur during the PS procedure are attributed to the visual stress, which logically should mainly affect the occipital regions. However, the occipital regions are relatively intact in all our brain images. Therefore we can attribute the change of the symbolic dynamics of the EEG under PS in the frontal regions to the vulnerability of the frontal regions. The PS procedure has amplified the group differences, especially in fast frequencies. Under PS of fast frequencies, we found more discriminative brain regions including the occipital ones. The PS procedure should have exerted a strong influence on the brain and consequently provoked varied effects on the defective brain regions. The routine PS protocol of our laboratory uses a combination of short segments of different frequencies. Whether the symbolic dynamics can also be changed by PS at any particular frequency needs further research.
In the calculation of NumFW, the number of detected patterns should be larger than the number of possible patterns in order to allow patterns to be found several times [25]. Thus, the pattern length and the number of quantization levels should maintain low. We checked the number of quantization levels varied from three to six and found out that from four to six levels, both NumFW and SampEn values changed in proportion. Therefore the statistical results were similar. We decided to use six levels to preserve more information in the data. We used a linear filter to remove power line and used a nonlinear and non-stationary filter, EMD, to remove nonlinear trending or mixed non-stationarities from artifacts such as eye and muscle movements. Compared with independent component analysis [50,51], EMD works better for eliminating muscle-artifact in EEG [52,53]. Changes in the EEG dynamics of dementia were reported in varied frequency ranges such as alpha1 (8–10.5 Hz) [54,55], theta [55,56], delta [57], all frequencies [58] and all bands except delta [59]. Therefore, we supposed that different methods may just explore different aspects or dimensions of the system. We chose wide-band EEGs without a priori assumptions of the contribution of any frequency band. This wide-band approach was supported by previous studies of approximate entropy [43], SampEn [44] and multiscale entropy [44,47,48]. We also repeated the analysis in separated conventional bands, but the discriminative power with any of the conventional bands was not as strong as with the wide band. The amplitude fluctuation, which is crucial in our study design, should be reduced by the operation of extracting certain frequency band. Although the holistic approach of the brain dynamics such as neural network models [17] or the bivariate or multivariate synchronization models [60] have showed discriminative power successfully. We took single-channel approach because the scalp EEG signals of one single-channel already contain information shifting between synchronization and desynchronization of a certain network at a microscopic aspect.
Although SampEn was placed on the data length constrain of 10m–20m [61], it is largely independent of data length and displays relative consistency over a broad range of possible parameters [24,62]. High discriminative power was shown in a recent study of SampEn in fMRI using short data length from 85 to 128 [63]. The length of the RRI data was around 80 to 150. It may be too short for NumFW, but still acceptable for SampEn. We did not find any correlation in the symbolic dynamics between the simultaneous RRIs and any one of the four EEG-derived sequences in this study. It may be due to that the length of the RRI data in this study, even under the symbolization procedure, was too short to be characteristic of an individual. To achieve constant heart rate variability, it is generally recommended to obtain a minimum 5-min ECG recording [64]. Both DFA and RS are applied to evaluate the presence of long range correlations in time. Successful studies in dementia and depression using DFA were reported [65]. However, we found no discriminative abilities with DFA or RS. The electromagnetic activity of the brain works at an extremely fast speed, and the quasi-stationary epochs of EEG are, in general, short lasting, in the order of tens of seconds [66]. This causes limitations in EEG studies because many regularity studies warrant long data for stable results. Nevertheless, compared with the prevailing method in cognitive neuroscience, functional MRI (fMRI), EEG possesses a remarkable advantage with its excellent time resolution which gives us a unique window on the dynamics of brain functions. When neuronal activity is measured by fMRI, a direct anatomical link does not necessarily coexist with robust functional connectivity [67] and the within-subject test-retest reliability of functional connectivity as measured was surprisingly low [68]. The study of EEG dynamics remains worthwhile until the questions between the brain and consciousness are fully answered. There were numerous other limitations in this study. Many recruited subjects were excluded due to varied reasons such as poor cooperation during the EEG procedure, poor EEG qualities, and too many ectopic heartbeats.
5. Conclusions
The symbolic dynamics of the whole EEG tracing that is correlated with cognitive functions comes mainly from the dynamics of the local-peak voltage (amplitude) but not the interpeak interval (instantaneous frequency). Further studies with subjects of different age groups and physical conditions may be helpful to further clarify these results.
Author Contributions
Pei-Feng Lin, Jenho Tsao, and Men-Tzung Lo conceived and designed the experiments. Pei-Feng Lin performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Pei-Feng Lin and Jenho Tsao wrote and revised the paper. Men-Tzung Lo participated in the discussion and checked the calculation results. Men-Tzung Lo, Chen Lin and Yi-Chung Chang participated in writing the computer codes. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vecchio, F.; Babiloni, C.; Lizio, R.; Fallani Fde, V.; Blinowska, K.; Verrienti, G.; Frisoni, G.; Rossini, P.M. Resting state cortical EEG rhythms in Alzheimer’s disease: Toward EEG markers for clinical applications: A review. Suppl. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 62, 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Aurlien, H.; Gjerde, I.O.; Aarseth, J.H.; Eldøen, G.; Karlsen, B.; Skeidsvoll, H.; Gilhus, N.E. EEG background activity described by a large computerized database. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Lackner, C.L.; Marshall, W.J.; Santesso, D.L.; Dywan, J.; Wade, T.; Segalowitz, S.J. Adolescent anxiety and aggression can be differentially predicted by electrocortical phase reset variables. Brain Cognit 2013, 89, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia Dominguez, L.; Wennberg, R.A.; Gaetz, W.; Cheyne, D.; Snead, O.C., III; Perez Velazquez, J.L. Enhanced synchrony in epileptiform activity? Local versus distant phase synchronization in generalized seizures. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8077–8084. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.E.; Summerfelt, A.; McMahon, R.; Adami, H.; Francis, G.; Elliott, A.; Buchanan, R.W.; Thaker, G.K. Evoked gamma band synchronization and the liability for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2004, 70, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pijnenburg, Y.A.l.; van der Made, Y.; van Cappellen van Walsum, A.M.; Knol, D.L.; Scheltens, Ph.; Stam, C.J. EEG synchronization likelihood in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease during a working memory task. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Stam, C.J.; van der Made, Y.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Scheltens, P. EEG synchronization in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Nunez, P. Electric Fields of the Brain: The Neurophysics of EEG; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Raichle, M.E. The brain’s dark energy. Science 2006, 314, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Raichle, M.E. Disease and the brain’s dark energy. Nat Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Z.; Tracy, E.R.; Boozer, A.D.; deBrauw, A.; Brown, R. Symbol sequence statistics in noisy chaotic signal reconstruction. Phys. Rev. E. 1995, 51, 3871–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Paternoster, L.; Vallverdu, M.; Melia, U.; Claria, F.; Voss, A.; Caminal, P. Analysis of epileptic EEG signals in children by symbolic dynamics, Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 4362–4365.
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, W. Symbolic dynamics analysis of epileptic EEG signals of the rat. J. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 29, 760–763. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, K.; Gast, H.; Goodfellow, M.; Rummel, C. On seeing the trees and the forest: Single-signal and multisignal analysis of periictal intracranial EEG. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar]
- Staniek, M.; Lehnertz, K. Symbolic transfer entropy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniek, M.; Lehnertz, K. Symbolic transfer entropy: Inferring directionality in biosignals. Biomedizinische Technik 2009, 54, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis, S.I.; Laskaris, N.A.; Tsirka, V.; Erimaki, S.; Vourkas, M.; Micheloyannis, S.; Fotopoulos, S. A novel symbolization scheme for multichannel recordings with emphasis on phase information and its application to differentiate EEG activity from different mental tasks. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2012, 6, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bai-lin, H. Symbolic dynamics and characterization of complexity. Physica D 1991, 51, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kaffashi, F.; Foglyano, R.; Wilson, C.; Loparo, K. The effect of time delay on approximate & sample entropy calculations. Physica D 2008, 237, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Solomon, I.; Chon, K. Comparison of the use of approximate entropy and sample entropy: Applications to neural respiratory signal, Proceedings of 27th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 17–18 January 2005; pp. 4212–4215.
- Boskovic, A.; Loncar-Turukalo, T.; Sarenac, O.; Japundzic-Zigon, N.; Bajic, D. Unbiased entropy estimates in stress: A parameter study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 667–679. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M.; Gladstone, I.M.; Ehrenkranz, R.A. A regularity statistic for medical data analysis. J Clin. Monit. 1991, 7, 335–345. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Furlan, R.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Entropy, entropy rate, and pattern classification as tools to typify complexity in short heart period variability series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetti, S.; Borroni, E.; Garbelli, P.E.; Ceriani, E.; Della Bella, P.; Montano, N.; Cogliati, C.; Somers, V.K.; Malliani, A.; Porta, A. Symbolic dynamics of heart rate variability: A probe to investigate cardiac autonomic modulation. Circulation 2005, 112, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Cysarz, D.; Lange, S.; Matthiessen, P.F.; Leeuwen, P. Regular heartbeat dynamics are associated with cardiac health. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R368–R372. [Google Scholar]
- Deco, G.; Jirsa, V.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Emerging concepts for the dynamical organization of resting-state activity in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Steriade, M.; Nunez, A.; Amzica, F. A novel slow (<1 hz) oscillation of neocortical neurons in vivo: Depolarizing and hyperpolarizing components. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3252–3265. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.J.; Raichle, M.E. The fmri signal, slow cortical potential and consciousness. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009, 13, 302–309. [Google Scholar]
- Monto, S.; Palva, S.; Voipio, J.; Palva, J.M. Very slow EEG fluctuations predict the dynamics of stimulus detection and oscillation amplitudes in humans. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 8268–8272. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.F.; Lo, M.T.; Tsao, J.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, C.; Ho, Y.L. Correlations between the signal complexity of cerebral and cardiac electrical activity: A multiscale entropy analysis. PloS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the nincds-adrda work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1984, 34, 939–944. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, G.C.; Tatemichi, T.K.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Cummings, J.L.; Masdeu, J.C.; Garcia, J.H.; Amaducci, L.; Orgogozo, J.M.; Brun, A.; Hofman, A.; et al. Vascular dementia: Diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN international workshop. Neurology 1993, 43, 250–260. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Korotchikova, I.; Boylan, G.B. An estimate of newborn EEG amplitude with limited frequency content, Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Information Sciences Signal Processing and their Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 10–13 May 2010; pp. 288–291.
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. A. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, N.; Ziehmann, C.; Kurths, J.; Meyerfeldt, U.; Schirdewan, A.; Voss, A. Short-term forecasting of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias based on symbolic dynamics and finite-time growth rates. Phys. Rev. E. 2000, 61, 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, T.; Schmitz, A. Improved surrogate data for nonlinearity tests. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E. 1994, 49, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, H.E. Long term storage capacity of reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar]
- Amigó, J.M.; Zambrano, S.; Sanjuán, M.A.F. True and false forbidden patterns in deterministic and random dynamics. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, L.C.; Saco, P.M.; Rosso, O.A. Missing ordinal patterns in correlated noises. Physica A 2010, 389, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar]
- Abasolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Escudero, J.; Gomez, C. Electroencephalogram background activity characterization with approximate entropy and auto mutual information in Alzheimer’s disease patients, Proceedins of 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 6192–6195.
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.H.; Cichocki, A.; Kim, K. Multiscale entropy analysis of EEG from patients under different pathological conditions. Fractals 2007, 15, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Poupard, L.; Sartène, R.; Wallet, J.-C. Scaling behavior in β-wave amplitude modulation and its relationship to alertness. Biol. Cybern. 2001, 85, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Popivanov, D.; Jivkova, S.; Stomonyakov, V.; Nicolova, G. Effect of independent component analysis on multifractality of eeg during visual-motor task. Signal Process 2005, 85, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.C.; Wang, S.J.; Lai, K.L.; Tsai, C.F.; Yang, C.H.; Hwang, J.P.; Lo, M.T.; Huang, N.E.; Peng, C.K.; Fuh, J.L. Cognitive and neuropsychiatric correlates of EEG dynamic complexity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuro-psychopharmacol. Biolog. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, J.; Abasolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Lopez, M. Analysis of electroencephalograms in Alzheimer’s disease patients with multiscale entropy. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Thaler, D.S. Design for an aging brain. Neurobiol. Aging. 2002, 23, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Process 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar]
- Plochl, M.; Ossandon, J.P.; Konig, P. Combining EEG and eye tracking: Identification, characterization, and correction of eye movement artifacts in electroencephalographic data. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.H.; Lin, C.; Tsao, J.; Lin, P.F.; Wang, P.C.; Huang, N.E.; Lo, M.T. Empirical mode decomposition based detrended sample entropy in electroencephalography for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2012, 210, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Safieddine, D.; Kachenoura, A.; Albera, L.; Birot, G.; Karfoul, A.; Pasnicu, A.; Biraben, A.; Wendling, F.; Senhadji, L.; Merlet, I. Removal of muscle artifact from EEG data: Comparison between stochastic (ICA and CCA) and deterministic (EMD and wavelet-based) approaches. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Frisoni, G.B.; Vecchio, F.; Pievani, M.; Geroldi, C.; De Carli, C.; Ferri, R.; Vernieri, F.; Lizio, R.; Rossini, P.M. Global functional coupling of resting EEG rhythms is related to white-matter lesions along the cholinergic tracts in subjects with amnesic mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis 2010, 19, 859–871. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, G.; Brassen, S.; Jajcevic, A. EEG coherence in Alzheimer’s dementia. J. Neural. Transm. 2003, 110, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Garn, H.; Waser, M.; Deistler, M.; Benke, T.; Dal-Bianco, P.; Ransmayr, G.; Schmidt, H.; Sanin, G.; Santer, P.; Caravias, G.; et al. Quantitative EEG markers relate to Alzheimer’s disease severity in the prospective dementia registry austria (PRODEM). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskaris, N.A.; Tarnanas, I.; Tsolaki, M.N.; Vlaikidis, N.; Karlovasitou, A.K. Improved detection of amnestic MCI by means of discriminative vector quantization of single-trial cognitive ERP responses. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2013, 212, 344–354. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, T.; Prichep, L.; Dierks, T.; Hubl, D.; Wahlund, L.O.; John, E.R.; Jelic, V. Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging. 2005, 26, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Van Straaten, E.C.; den Haan, J.; de Waal, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Barkhof, F.; Prins, N.D.; Stam, C.J. Disturbed phase relations in white matter hyperintensity based vascular dementia: An EEG directed connectivity study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M.; Barzegharan, E.; Knyazeva, M. Synchronization of EEG: Bivariate and multivariate measures. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 22, 212–221. [Google Scholar]
- Abasolo, D.; Hornero, R.; Espino, P.; Alvarez, D.; Poza, J. Entropy analysis of the EEG background activity in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yentes, J.M.; Hunt, N.; Schmid, K.K.; Kaipust, J.P.; McGrath, D.; Stergiou, N. The appropriate use of approximate entropy and sample entropy with short data sets. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 349–365. [Google Scholar]
- Sokunbi, M.O. Sample entropy reveals high discriminative power between young and elderly adults in short fmri data sets. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnreich, R.; Kark, J.; Friedlander, Y.; Sapoznikov, D.; Luria, M. Five minute recordings of heart rate variability for population studies: Repeatability and age-sex characteristics. Heart 1998, 80, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Imai, R.; Uchiike, T.; Mizuno, R.; Okamoto, Y. An attempt to classify patients with dementia by detrended fluctuation analysis of electroencephalographic data—a preliminary study. Rinsho Byori 2013, 61, 15–18, In Japanese. [Google Scholar]
- Fingelkurts, A.A.; Short-term, EEG. spectral pattern as a single event in eeg phenomenology. Open Neuroimag. J. 2010, 4, 130–156. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, M.A.; Norris, D.G.; Hund-Georgiadis, M. An investigation of functional and anatomical connectivity using magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Honey, C.J.; Sporns, O.; Cammoun, L.; Gigandet, X.; Thiran, J.P.; Meuli, R.; Hagmann, P. Predicting human resting-state functional connectivity from structural connectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009, 106, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).