Analyses of Heart Rate, Respiration and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Patients with Schizophrenia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Recordings and Pre-Processing
- – Time series of heart rate consisting of successive beat-to-beat intervals (BBI, tachogram); and
- – Time series of respiratory frequency (RESP, respirogram) as being the time intervals between consecutive breathing cycles. Figure 1.
2.2. Methods of Heart Rate Variability and Respiratory Variability
2.2.1. Time and Frequency Domains
- – The mean value of the NN intervals (meanNN) of BBI (_BBI, [ms]) and RESP (_RESP, [s]; BR: breathing rate as the number of breaths per minute, [1/min]);In addition, inspiration time (tin, [s]) and expiration time (tex, [s]) intervals were determined for each breath (Figure 2).
- – Standard deviation (sdNN) of the NN intervals of BBI (_BBI, [ms]) and RESP (_RESP, [s]);
- – Renyi entropy (HRenyi025, [bit]) as generalization of the Shannon entropy quantifies the dispersion of the BBI time series values. The measure of variability is calculated by using the density distribution (histogram) of the NN intervals (class width of 8ms) along with the class probability pi (i = 1, …, k with k as the total number of all classes) (1). The coefficient α determines the manner in which the probabilities of NN intervals of BBI (_BBI) and RESP (_RESP) are weighted (here: α = 0.25) (2).
- – Normalized low-frequency power (0.04–0.15 Hz) [s2] of the NN intervals of BBI LFn_BBI;
- – Normalized high-frequency power (0.15–0.4 Hz) [s2] of the NN intervals of BBI HFn_BBI;
- – The ratio between the low- and high-frequency powers of the estimated spectrum LF/HF_BBI [a.u.]. The power spectra of the time series were estimated using the Fast Fourier Transform. To avoid leakage effects, a Blackman Harris window function was applied.
2.2.2. Symbolic Dynamics
2.2.3. Compression Entropy
2.2.4. Sample Entropy
2.3. Methods of Cardiorespiratory Coupling Analyses
2.3.1. High Resolution Joint Symbolic Dynamics Analyses
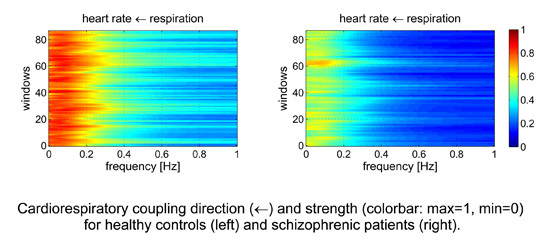
2.3.2. Normalized Short Time Partial Directed Coherence
2.3.3. Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia
2.4. Patients
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Univariate Analyses of Heart Rate Variability, Respiratory Variability and Cardiorespiratory Coupling Analyses
3.1.1. Time- and Frequency Domains
3.1.2. Nonlinear Domain
3.1.3. Cardiorespiratory Coupling Analyses
3.2. Multivariate Analyses of Heart Rate Variability, Respiratory Variability and Cardiorespiratory Coupling Analyses
3.2.1. Multivariate Discriminant Analysis—Sets of Two Indices
- – meanNN_BBI, SDRenyi025_RESP: sensitivity = 91.3%, specificity = 95.7%, AUC = 97%;
- – HRJSDRenyi025, meanNN_BBI: sensitivity = 91.3%, specificity = 95.7%, AUC = 96%;
3.2.2. Multivariate Discriminant Analysis—Sets of Three Indices
- – HRenyi025_BBI, HCE_BBI, ABBI→RESP: sensitivity = 91.3%, specificity = 95.7%, AUC = 98%;
- – tin, tex, HRJSDRenyi025: sensitivity = 95.7%, specificity = 91.3%, AUC = 97%;
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hennekens, C.H.; Hennekens, A.R.; Hollar, D.; Casey, D.E. Schizophrenia and increased risks of cardiovascular disease. Am. Heart J 2005, 150, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Laursen, T.M.; Nordentoft, M.; Mortensen, P.B. Excess early mortality in schizophrenia. Ann. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2014, 10, 425–448. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.; Saha, S.; Chant, D.; Welham, J. Schizophrenia: A concise overview of incidence, prevalence, and mortality. Epidemiol. Rev. 2008, 30, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ringen, P.A.; Engh, J.A.; Birkenaes, A.B.; Dieset, I.; Andreassen, O.A. Increased mortality in schizophrenia due to cardiovascular disease—A non-systematic review of epidemiology, possible causes, and interventions. Front. Psychiatry. 2014, 5, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Straus, S.M.; Bleumink, G.S.; Dieleman, J.P.; van der Lei, J.; ´t Jong, G.W.; Kingma, J.H.; Sturkenboom, M.C.; Stricker, B.H. Antipsychotics and the risk of sudden cardiac death. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Bär, K.J.; Boettger, M.K.; Koschke, M.; Schulz, S.; Chokka, P.; Yeragani, V.K.; Voss, A. Non-linear complexity measures of heart rate variability in acute schizophrenia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bar, K.J.; Letzsch, A.; Jochum, T.; Wagner, G.; Greiner, W.; Sauer, H. Loss of efferent vagal activity in acute schizophrenia. J. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 39, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.S.; Yoo, C.S.; Yi, S.H.; Hong, K.H.; Oh, H.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Ahn, Y.M.; Kim, Y.S. Differential pattern of heart rate variability in patients with schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2009, 33, 991–995. [Google Scholar]
- Valkonen-Korhonen, M.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Ranta-Aho, P.; Karjalainen, P.A.; Partanen, J.; Karhu, J.; Lehtonen, J. Heart rate variability in acute psychosis. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 716–726. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, S.; Tupaika, N.; Berger, S.; Haueisen, J.; Bär, K.J.; Voss, A. Cardiovascular coupling analysis with high-resolution joint symbolic dynamics in patients suffering from acute schizophrenia. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, 883–901. [Google Scholar]
- Bär, K.J.; Rachow, T.; Schulz, S.; Bassarab, K.; Haufe, S.; Berger, S.; Koch, K.; Voss, A. The phrenic component of acute schizophrenia—A name and its physiological reality. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33459. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, S.; Bär, K.J.; Voss, A. Cardiovascular and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Unmedicated Schizophrenic Patients in Comparison to Healthy Subjects, Proceedings of 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 3664–3667.
- Schulz, S.; Haueisen, J.; Bär, K.J.; Voss, A. Quantification of Cardiorespiratory Coupling in acute Schizophrenia Applying High Resolution Joint Symbolic Dynamics, Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), Zaragoza, Spain, 22–25 September 2013; pp. 101–104.
- Schulz, S.; Bär, K.J.; Voss, A. Respiratory variability and cardiorespiratory coupling analyses in patients suffering from schizophrenia and their healthy first-degree relatives. Biomed. Tech. (Berl.) 2012, 57(Suppl. 1), 1044. [Google Scholar]
- Peupelmann, J.; Boettger, M.K.; Ruhland, C.; Berger, S.; Ramachandraiah, C.T.; Yeragani, V.K.; Bar, K.J. Cardio-respiratory coupling indicates suppression of vagal activity in acute schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2009, 112, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, S.; Haueisen, J.; Bär, K.J.; Voss, A. Changed cardiorespiratory phase-coupling pattern in patients suffering from schizophrenia. Biomed. Tech. (Berl.) 2014, 59, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Eckberg, D.L. The human respiratory gate. J. Physiol. 2003, 548, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Eckberg, D.L. Point: Counterpoint: Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is due to a central mechanism vs. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is due to the baroreflex mechanism. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1740–1742, discussion 1744. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey, M.P.; Jordan, D.; Richter, D.W.; Spyer, K.M. Synaptic mechanisms involved in the inspiratory modulation of vagal cardio-inhibitory neurones in the cat. J. Physiol. 1984, 356, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- Triedman, J.K.; Saul, J.P. Blood pressure modulation by central venous pressure and respiration. Buffering effects of the heart rate reflexes. Circulation 1994, 89, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, V.; Novak, P.; de Champlain, J.; le Blanc, A.R.; Martin, R.; Nadeau, R. Influence of respiration on heart rate and blood pressure fluctuations. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 74, 617–626. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Guzzetti, S.; Montano, N.; Furlan, R.; Pagani, M.; Malliani, A.; Cerutti, S. Entropy, entropy rate, and pattern classification as tools to typify complexity in short heart period variability series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, N.; Voss, A.; Malberg, H.; Ziehmann, C.; Voss, H.; Schirdewan, A.; Meyerfeldt, U.; Kurths, J. Nonlinear analysis of complex phenomena in cardiological data. Z. Herzschr. Elektrophys. 2000, 11, 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, A.; Kurths, J.; Kleiner, H.J.; Witt, A.; Wessel, N.; Saparin, P.; Osterziel, K.J.; Schurath, R.; Dietz, R. The application of methods of non-linear dynamics for the improved and predictive recognition of patients threatened by sudden cardiac death. Cardiovasc. Res. 1996, 31, 419–433. [Google Scholar]
- Ziv, J.; Lempel, A. Universal algorithm for sequential data compression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 1977, 23, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Baumert, M.; Baier, V.; Haueisen, J.; Wessel, N.; Meyerfeldt, U.; Schirdewan, A.; Voss, A. Forecasting of life threatening arrhythmias using the compression entropy of heart rate. Methods Inf. Med. 2004, 43, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Pincus, S.M. Approximate entropy as a measure of system complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991, 88, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, S.; Adochiei, F.C.; Edu, I.R.; Schroeder, R.; Costin, H.; Bar, K.J.; Voss, A. Cardiovascular and cardiorespiratory coupling analyses: A review. Philos. Trans. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120191. [Google Scholar]
- Baccala, L.A.; Sameshima, K. Partial directed coherence: A new concept in neural structure determination. Biol. Cybern. 2001, 84, 463–474. [Google Scholar]
- Milde, T.; Schwab, K.; Walther, M.; Eiselt, M.; Schelenz, C.; Voss, A.; Witte, H. Time-variant partial directed coherence in analysis of the cardiovascular system. A methodological study. Physiol. Meas. 2011, 32, 1787–1805. [Google Scholar]
- Adochiei, F.; Schulz, S.; Edu, I.; Costin, H.; Voss, A. A new normalised short time pdc for dynamic coupling analyses. Biomed. Tech. (Berl.) 2013, 58(Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossman, P.; Stemmler, G.; Meinhardt, E. Paced respiratory sinus arrhythmia as an index of cardiac parasympathetic tone during varying behavioral tasks. Psychophysiology 1990, 27, 404–416. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, P.; van Beek, J.; Wientjes, C. A comparison of three quantification methods for estimation of respiratory sinus arrhythmia. Psychophysiology 1990, 27, 702–714. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, T.L.; Dugan, E.L.; Humphries, B.; Newton, R.U. Discriminating between elderly and young using a fractal dimension analysis of centre of pressure. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2004, 1, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The positive and negative syndrome scale (panss) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, J.; Ducharme, M.B.; Thompson, M. Study on the correlation of the autonomic nervous system responses to a stressor of high discomfort with personality traits. Physiol. Behav. 2004, 82, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Mujica-Parodi, L.R.; Yeragani, V.; Malaspina, D. Nonlinear complexity and spectral analyses of heart rate variability in medicated and unmedicated patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 2005, 51, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Gnecchi-Ruscone, T.; Tobaldini, E.; Guzzetti, S.; Furlan, R.; Montano, N. Progressive decrease of heart period variability entropy-based complexity during graded head-up tilt. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, A.; Schulz, S.; Schroeder, R.; Baumert, M.; Caminal, P. Methods derived from nonlinear dynamics for analysing heart rate variability. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- Homma, I.; Masaoka, Y. Breathing rhythms and emotions. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Boiten, F.A.; Frijda, N.H.; Wientjes, C.J. Emotions and respiratory patterns: Review and critical analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1994, 17, 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Goldberger, A.L.; Peng, C.K. Multiscale entropy analysis of complex physiologic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 068102. [Google Scholar]
- Weiden, P.J.; Weiden, M. Schizophrenia and respiratory symptoms: A serious, but overlooked, comorbidity. CNS Spectr 2010, 15, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, R.; Lyons, J.S.; McNally, R.J. Panic attacks in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 58, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, P.F.; Miller, B.J.; Lehrer, D.S.; Castle, D.J. Psychiatric comorbidities and schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 383–402. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Bassani, T.; Bari, V.; Tobaldini, E.; Takahashi, A.C.; Catai, A.M.; Montano, N. Model-based assessment of baroreflex and cardiopulmonary couplings during graded head-up tilt. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Porta, A. Information domain approach to the investigation of cardio-vascular, cardio-pulmonary, and vasculo-pulmonary causal couplings. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, T.E.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Dhingra, R.R.; Baekey, D.M.; Galan, R.F.; Wehrwein, E.; Morris, K.F. Cardiorespiratory coupling: Common rhythms in cardiac, sympathetic, and respiratory activities. Prog. Brain Res 2014, 209, 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Riedl, M.; Muller, A.; Kraemer, J.F.; Penzel, T.; Kurths, J.; Wessel, N. Cardio-respiratory coordination increases during sleep apnea. PLoS One 2014, 9, e93866. [Google Scholar]



| Data | Healthy subjects (CO) | Schizophrenic patients (SZ) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 23 | 23 |
| Gender (male/female) | 13/10 | 12/11 |
| Age (mean ± std in years) | 30.3 ± 9.5 | 30.4 ± 10.3 |
| PANSS, mean (min-max) | n.a. | 85.7 (43–124) |
| SANS, mean (min-max) | n.a. | 49.6 (14–81) |
| SAPS, mean (min-max) | n.a. | 60.9 (6–108) |
| Index | p | CO | SZ | SENS | SPEC | AUC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | ± | std | mean | ± | std | ||||||
| TD_BBI | meanNN_BBI [ms] | *** | 954.5 | ± | 128.0 | 741.2 | ± | 112.5 | 91.3 | 73.9 | 0.89 |
| sdNN_BBI [ms] | ** | 61.3 | ± | 19.9 | 43.0 | ± | 16.1 | 65.2 | 91.3 | 0.78 | |
| HRenyi025_BBI [bit] | *** | 5.26 | ± | 0.56 | 4.80 | ± | 0.53 | 56.5 | 95.7 | 0.78 | |
| FD_BBI | LFn_BBI [s2] | * | 0.54 | ± | 0.20 | 0.69 | ± | 0.12 | 69.6 | 73.9 | 0.72 |
| HFn_BBI [s2] | * | 0.46 | ± | 0.20 | 0.31 | ± | 0.12 | 52.2 | 91.3 | 0.72 | |
| LF/HF_BBI [a.u.] | * | 1.74 | ± | 1.57 | 2.94 | ± | 2.28 | 52.2 | 91.3 | 0.72 | |
| TD_RESP | meanNN_RESP [s] | *** | 4.53 | ± | 1.54 | 3.20 | ± | 0.80 | 69.6 | 91.3 | 0.83 |
| sdNN_RESP [s] | n.s. | 0.92 | ± | 0.50 | 0.87 | ± | 0.64 | 43.5 | 82.6 | 0.58 | |
| tin [s] | *** | 1.87 | ± | 0.47 | 1.35 | ± | 0.23 | 78.3 | 91.3 | 0.89 | |
| tex [s] | *** | 2.50 | ± | 1.00 | 1.65 | ± | 0.49 | 65.2 | 100.0 | 0.83 | |
| Index | p | CO | SZ | SENS | SPEC | AUC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | ± | std | mean | ± | std | ||||||
| SD | SDRenyi025_BBI [a.u.] | ** | 3.74 | ± | 0.37 | 3.47 | ± | 0.37 | 56.5 | 87.0 | 0.73 |
| SDRenyi025_RESP [a.u.] | *** | 3.23 | ± | 0.15 | 3.47 | ± | 0.19 | 78.3 | 78.3 | 0.84 | |
| HCE | HCE_BBI [a.u.] | *** | 0.82 | ± | 0.10 | 0.69 | ± | 0.10 | 69.6 | 95.7 | 0.84 |
| HCE_RESP [a.u.] | n.s. | 0.59 | ± | 0.08 | 0.59 | ± | 0.12 | 56.5 | 43.5 | 0.45 | |
| SampEn | SampEn_BBI [bit] | ** | 2.29 | ± | 0.30 | 1.96 | ± | 0.47 | 69.6 | 73.9 | 0.75 |
| SampEn_RESP [bit] | n.s. | 1.32 | ± | 0.37 | 1.49 | ± | 0.50 | 56.5 | 78.3 | 0.62 | |
| Index | p | CO | SZ | SENS | SPEC | AUC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | ± | std | mean | ± | std | ||||||
| HRJSDRenyi025 [bit] | *** | 4.06 | ± | 0.11 | 4.37 | ± | 0.15 | 91.3 | 91.3 | 0.95 | |
| NSTPDC | NF [a.u.] | *** | −1.85 | ± | 0.17 | −1.03 | ± | 0.80 | 87.0 | 87.0 | 0.91 |
| ABBI→RESP [a.u.] | *** | 0.05 | ± | 0.02 | 0.09 | ± | 0.04 | 91.3 | 65.2 | 0.83 | |
| ARESP→BBI [a.u.] | *** | 0.47 | ± | 0.09 | 0.29 | ± | 0.12 | 91.3 | 65.2 | 0.88 | |
| RSA | RSAP2V [ms] | *** | 125.9 | ± | 74.2 | 36.5 | ± | 25.4 | 82.6 | 78.3 | 0.87 |
| ShannonRSA [bit] | *** | 2.41 | ± | 0.05 | 2.36 | ± | 0.04 | 87.0 | 65.2 | 0.82 | |
| HFDRSA [a.u.] | ** | 1.14 | ± | 0.03 | 1.19 | ± | 0.05 | 60.9 | 82.6 | 0.75 | |
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schulz, S.; Bär, K.-J.; Voss, A. Analyses of Heart Rate, Respiration and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy 2015, 17, 483-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17020483
Schulz S, Bär K-J, Voss A. Analyses of Heart Rate, Respiration and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy. 2015; 17(2):483-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17020483
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchulz, Steffen, Karl-Jürgen Bär, and Andreas Voss. 2015. "Analyses of Heart Rate, Respiration and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Patients with Schizophrenia" Entropy 17, no. 2: 483-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17020483
APA StyleSchulz, S., Bär, K.-J., & Voss, A. (2015). Analyses of Heart Rate, Respiration and Cardiorespiratory Coupling in Patients with Schizophrenia. Entropy, 17(2), 483-501. https://doi.org/10.3390/e17020483