Abstract
The paper presents a new approach to restoration characteristics randomized models under small amounts of input and output data. This approach proceeds from involving randomized static and dynamic models and estimating the probabilistic characteristics of their parameters. We consider static and dynamic models described by Volterra polynomials. The procedures of robust parametric and non-parametric estimation are constructed by exploiting the entropy concept based on the generalized informational Boltzmann’s and Fermi’s entropies.1. Introduction
The problem of useful information retrieval (we comprehend it as parametric and nonparametric estimation based on real data) is a major one in modern science. Different scientific disciplines suggest numerous methods of solving this problem. Each method stems from certain hypotheses regarding the properties of data accumulated during the normal functioning of their source. Among advanced scientific disciplines in this field, we mention mathematical statistics [1–4], econometrics [5–7], financial mathematics [8,9], control theory [10,11] and others.
Methods developed within their frameworks rest upon two groups of fundamental hypotheses. The first one relates to models, whereas the other concerns data. Notably, models are supposed to have well-defined parameters (we call them deterministic). Parameter values appear unknown and unmeasurable directly.
The second group of hypotheses applies to data and plays an essential role. In fact, these hypotheses are stated in terms of the statistical properties of data arrays (e.g., a sufficient number of data arrays, a property of a sample from a universal set, normal probability density). In practice, it seems impossible to check such properties and assumptions in concrete problems.
The described situation happens in a class of problems, where the sizes of real data arrays are limited and data incorporate errors [5,6,12].
Consequently, the characteristics (parameters) of a model are estimated by a small amount of incompletely reliable data. We can treat them as random objects. In this case, the estimated characteristics of a model acquire the properties of random variables.
Therefore, one naturally arrives at the idea of considering model parameters as random quantities. This idea transforms the model with deterministic parameters to the model with random parameters. In the sequel, we adopt the term of a randomized model (RM). The characteristics of an RM include the probability density functions (pdfs) of the model parameters. Thus, one should estimate the pdfs of model parameters (not the estimates of their values) based on available data. Having such estimates at one’s disposal, one can apply an RM for:
constructing = moment models (MMs), where appropriate moments of random parameters serve as the model parameters;
generating an ensemble of random vectors (ERV) of RM “output” with a pdf estimate (by the Monte Carlo method) and performing the statistical processing of the ensemble to form the desired numerical characteristics (including moment ones).
Both directions of RM usage enlarge appreciably the application domains of such models (especially, the ones with a high level of uncertainties). However, a researcher still faces a certain problem. How could the probability density functions of parameters be estimated in randomized models?
This paper proposes involving the informational entropy maximization principle on sets defined by the “input-output” measurements of an RM. The proposal originates from a couple of considerations discussed and formalized below.
The first consideration is connected with the generalized notion of likelihood, viz., with transition from likelihood functions to likelihood functionals and, subsequently, to informational entropy functionals.
The second consideration is based on methodological interpretations of the notion of informational entropy as a measure of uncertainty. Entropy maximization guarantees the best solutions under the maximal uncertainty. This line of reasoning was pioneered in [13]. Informational entropy characterizes uncertainty caused by random parameters of an RM and by measurement noises. The last property of informational entropy ensures the best estimates for maximally uncertain noises (in units of entropy). Hence, the pdf estimates resulting from informational entropy maximization can be viewed as robust. This interpretation varies from the classic conception of robustness suggested in [14].
2. Randomized Models
2.1. Static Objects
Consider a static parameterized object with a measurable “input” described by a matrix, X, of sizes (s × n) and a measurable “output” characterized by a vector, y, of length s. Here, s indicates the amount of input observations, and n stands for the number of the object’s parameters.
The relationship between the “input” and “output” (including measurement errors) is defined by the randomized static model (RSM):
We adopt the following notation: F is a given s-dimensional vector-function; adesignates a random n-dimensional vector of some parameters with independent components ai, , possessing values in the ranges , .
The linear modification of the RSM acquires the form:
Measurements incorporate errors modeled by a matrix, η, of sizes (s × n) (“input” errors) and by a vector, ξ, of length s (“output” errors). The elements and the components represent independent random variables. Their values lie within the intervals and , j ∈ [1, s], respectively.
2.2. Dynamic Objects
Consider a discrete dynamic object with a finite “memory”, m. The object’s input, x[k], is measured precisely, while the output, y[k], is measured with an additive noise, ξ[k]. Here, k ∈ = [m, m + s], and s corresponds to the number of measurements. Suppose that the process, ξ[k], is random with independent values.
The connection between the observed input and output (including output measurement errors) is defined by a randomized dynamic model (RDM). This model is described by the discrete functional Volterra polynomial of degree, R [15]:
Equality Equation (3) employs the weight functions (actually, impulse responses) w(h)[n1, . . . , nh]. These functions are random with independent ordinates belonging to the intervals:
The discrete dynamic model has the nonlinear expression Equation (3). Nevertheless, it can be linearized by the lexicographic ordering of the variables {n1, . . . , nh}. Renumber the resulting sets from zero to th = (m + 1)h − 1 according to a lexicographic rule. Introduce a local index, i(h) ∈ [0, th], and a set, such that:
According to the accepted numbering, adopt the following indexing of random parameters that correspond to the values of weight functions in Equation (3):
Construct the random vector:
Components of the vector, a(h), belong to the ranges:
By virtue of Equation (4), we have:
Similarly to Equation (5), introduce the lexicographic ordering of the variables {k − n1, . . . , k − nh}, where k indicates a fixed parameter and indexes n1, . . . , nh possess values in the interval [0, m]. For each fixed k, renumber the resulting sets according to Equation (5):
Consequently, for fixed k in formula Equation (3), the lexicographically ordered products of the variables, x[k − nr], form the vector:
Therefore, equality Equation (3) can be rewritten as:
Consider the interval = [m, m + s], which corresponds to the measurements of the RDM input and output at instants m + k, k ∈ [0, s]. The observed output and noise are characterized by the vectors:
Define the input measurement matrices, whose rows are formed from vector Equation (10):
Build the block matrix, X, of sizes [(s + 1) × u], where :
Finally, construct the block random vector of model parameters (of length u):
Thus, dynamic model Equation (3) belongs to the class of randomized models with the random parameters, a, and the output noise, ξ. It can be reduced to the linear form:
Structurally, this expression is analogous to linear static data model Equation (2). However, the input matrix embraces the nonlinearity and dynamics of model Equation (14).
3. Probabilistic Characteristics of RMs
Numerical characteristics of RMs are understood as the probability density functions (alternatively, probability functions) of model parameters and noise components.
In the sequel, we believe that RMs whose random components are described by probability density functions belong to the class RM-PWQ. By analogy, RMs described by the probabilities of lying within appropriate intervals will form the class RM-pwq.
3.1. RM-PWQ
The parameters of an RDM from this class and the measurement noises represent continuous random variables. They take values in intervals, where there exist probability density functions (pdfs):
-for the random parameters of an RSM:
- for the random parameters of an RDM:
- for the “input” measurement noises:
- for the “output” measurement noises:
The above-mentioned pdfs of the random parameters and noises should be estimated using measurements of the RM “input” and “output” and a priori information on the pdfs. Formalization of such information involves the a priori pdfs of the parameters and noises, (P0(a), W0(η) and Q0(ξ)), as well as the classes of pdfs.
An RM generates an ensemble, , of the random vectors, v, Equations (2) and (14). Measurements make up the vector, y, with measured components. Therefore, the estimation of pdfs lies in the forming of the vectors of the appropriate numerical characteristics of this ensemble. We employ moments of random components of the vector v:
This paper utilizes the first moments, viz., the average values of components from the vector, v. For static model RSM-PWQ Equation (1), we obtain:
For the dynamic model RM-PQ Equation (14), we similarly have:
3.2. RM-pwq
The parameters of an RM from this class and the measurement noises turn out continuous random variables. Their belonging to an appropriate interval is characterized by some probability.
The parameters a1, . . . , an possess values within the intervals 𝒜1, . . . , 𝒜n with the probabilities p1, . . . , pn, respectively. Actually, the probabilities pi ∈ [0, 1], . By analogy, the elements, ηji, of the “input” measurement noise matrix take values from the intervals, ji, with the probabilities, wji ∈ [0, 1], respectively. Finally, the components, ξj, of the “output” measurement noises lie inside the intervals, Ξj, with the probabilities, qj ∈ [0, 1], respectively. Denote by , , the a priori values of the listed probabilities ( , ).
Just like models from the class RM-PWQ, RMs belonging to the class considered to reproduce an ensemble, , of the random vectors, v. This is done by generating the random parameters with the probabilities, p, the elements of the “input” measurement noise matrix with the probabilities, W, and the components of the “output” measurement noises with the probabilities, q.
As a numerical characteristic for the ensemble generated by an RM of this class, select the vector of the first quasi-moments (see [5]):
In the previous formula, ⊗ stands for element-wise multiplication,
The transform Equation (23) can be interpreted as a substitution of the random parameters and noises by their “quasi-average” values.
By applying Equation (23) to Equation (1), we obtain the following expression for the first quasi-moment of the random vector, v, for RSM Equation (1):
In the case of RDMs, the first quasi-moment formula of the random vector, v, Equation (10), acquires the form:
Concluding this section, we emphasize a relevant aspect. For the class RM-PWQ, it is necessary to estimate probability density functions. For the class RM-pwq, one has to estimate vectors characterizing probability distributions.
4. Principles of Entropy-Robust Estimation
We propose to introduce a likelihood functional for the estimation of probability density functions for RM-PWQ (RM-PQ). So long as the model parameters and measurement noises are independent, their joint distribution function takes the form:
Suppose that we know the a priori density functions, P0(a), W0(η), Q0(ξ).
Following [4], specify the log-likelihood ratio (LLR) by:
Hence, the LLR represents a nonrandom function of random arguments.
The probabilities, p, W, q, of certain events (e.g., entering appropriate intervals by the parameters, “input” and “output” noises) being estimated, one should define the LLR by:
Now, introduce the likelihood functional (the generalized informational Boltzmann entropy functional), (see Equation (29)), in the form:
Obviously (see Equation (28)), the likelihood functional with the minus mark represents the generalized Boltzmann entropy functional. This function has numerous interpretations. In particular, it is treated as the “distance” between pdfs [16], as an uncertainty measure [12,13,17] or as a robustness measure [6] (the degree of invariance of the pdfs P(a), W(η), Q(ξ), with respect to observations). In this paper, we involve the last interpretation of the entropy functional to construct estimates of the pdfs.
Define the likelihood function (the generalized informational Boltzmann entropy function) by (see [18]):
The estimation quality for pdfs or probability vector components is characterized by the maximal value of the generalized informational Boltzmann entropy functional (or function). In the sequel, we distinguish between two types of estimates.
The -robust entropy estimate (the -robust entropy estimate) of the pdfs of the parameters and measurement noises results from solving the problem:
provided that:the probability density functions belong to the class:
where , and denote the classes of the pdfs of the parameters, “input” and “output” noises, respectively;the balance condition holds true for the degree (1/k) of the k-th moment, v, and the measured vector, y. For RSM-PWQ, this condition becomes:
For RDM-PQ, the balance condition takes the form:
The -robust entropy estimate of the probability distributions (pds) of the model parameters and measurement noise components follow from solving the problem:
provided that:the probability distributions belong to the class:
where ℙ, 𝕎 and ℚ designate the classes of the pds of the parameters, “input” and “output” noises, respectively;the balance condition holds true for the quasi-average vector, ṽ, and the measured vector, y:
5. Structural Properties of -Estimates
5.1. Power-Type RSM-PQ
Consider the subclass of power-type RSM-PQ with the following nonlinearities:
The vector of parameters, a, turns out to be random with independent components (a1, . . . , an) possessing values in the intervals , ( ) with the pdfs p1(a1), . . . , pn(an).
The “input” and “output” are observed at instants t1, . . . , ts. The measured “input” is characterized by the set of R matrices:
Additionally, the observed “output” of the RM is characterized by the random vector v = {v(t1), . . . , v(ts)}.
Therefore, using observation results, we rewrite the RSM-PQ as:
Here, , ξ = {ξ(t1), . . . , ξ(ts)} = {ξ1, . . . , ξs} denotes the “output” measurement noise vector. It has independent components belonging to the intervals , ( ) with the pdfs q1(ξ1), . . . , qs(ξs). Suppose that a priori information is absent, i.e., P0(a) = Q0(ξ) = const.
To proceed, we analyze the -robust entropy estimate of the pdfs P(a) = {p1(a1), . . . , pn(an)} and Q(ξ) = {q1(ξ1), . . . , qs(ξs)}. Moreover, we study some structural properties of the estimate.
Revert to problem Equations (32)–(34). Reexpress these as:
The structural properties of the -estimate are understood as a certain class of the robust family of probability density functions of the model parameters and noise. The procedure of -estimation consists in solving problem Equations (32)–(34) for RSM-PWQ (alternatively, problem Equations (32), (33) and (35) for RDM-PQ). Both problems belong to the class of functional entropy-linear programming problems with equality constraints. The standard approach to such variational problems (see [19]) naturally brings the following result. The entropy-optimal pdfs (in the class of continuously differentiable functions) of the parameters and noise components are defined by:
In the last formulas, the Lagrange multipliers, γi, ωj, correspond to constraint Equation (43), while the ones of θj correspond to constraint Equation (44).
Figures 1 and 4 demonstrate some examples of estimating the pdfs of the parameters. For a linear RM, the -estimate always represents an exponential function (see Figure 1). The “input” and “output” measurements do not affect the structure of the estimate (yet, they change the shape of the functions).
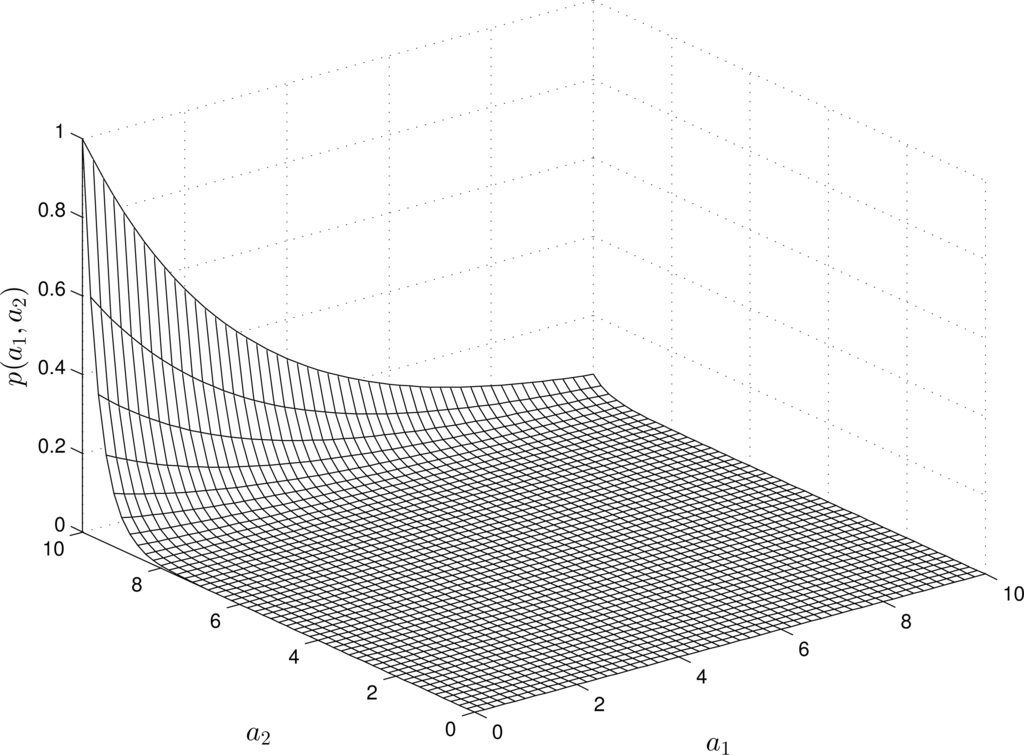
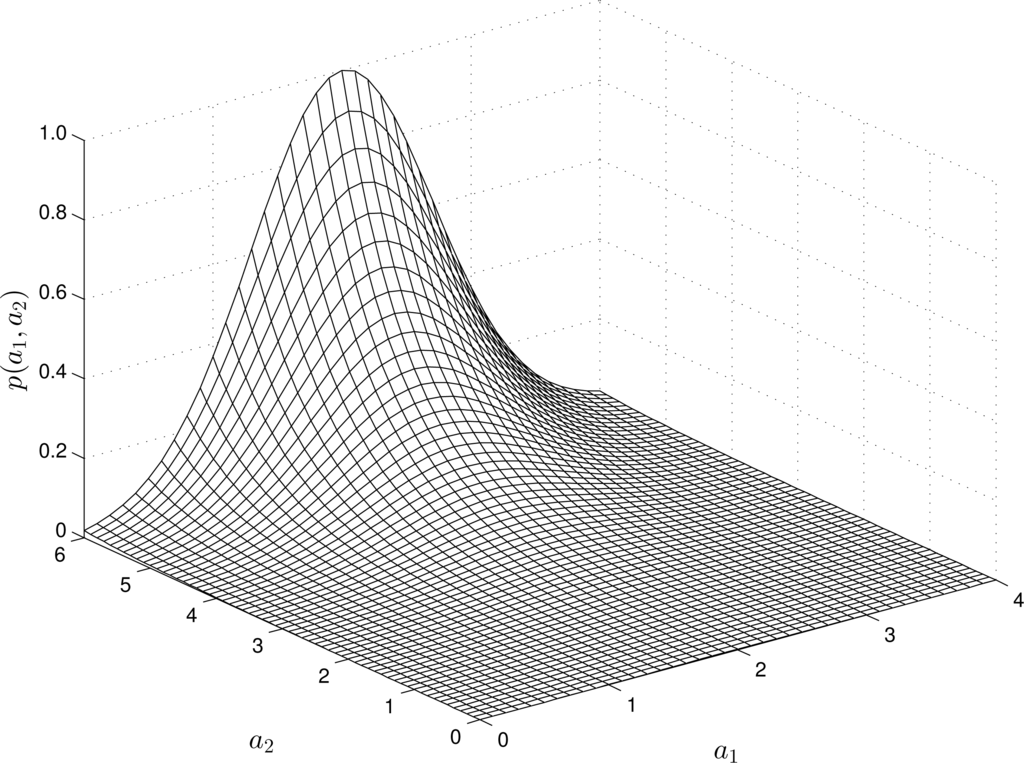
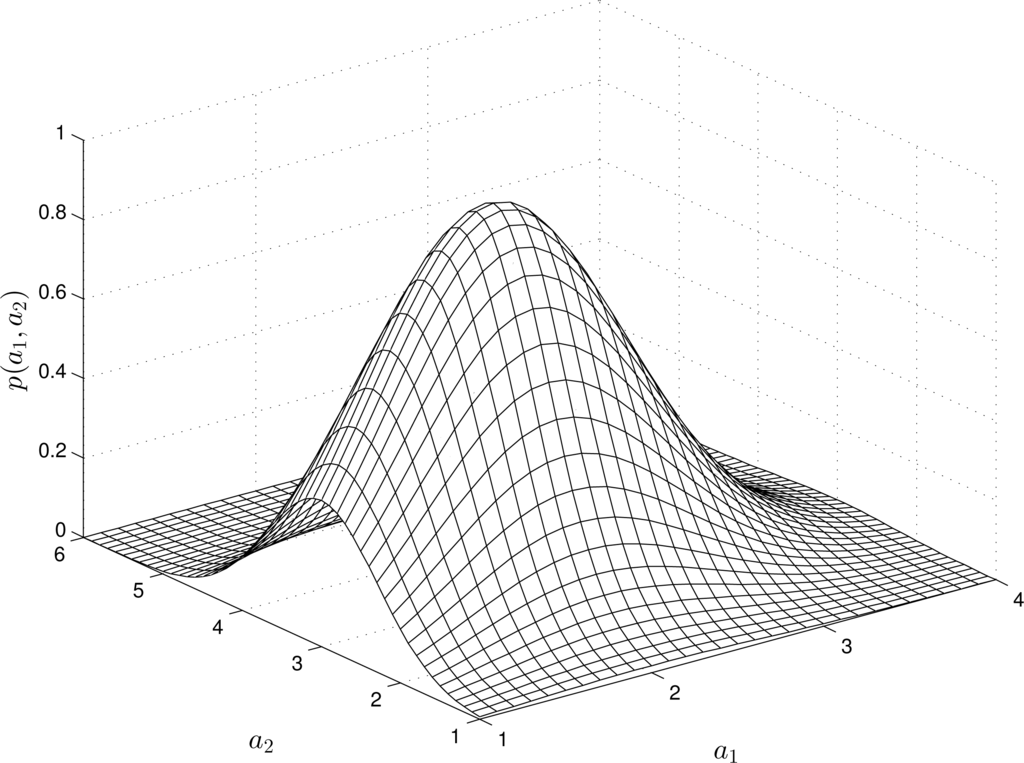
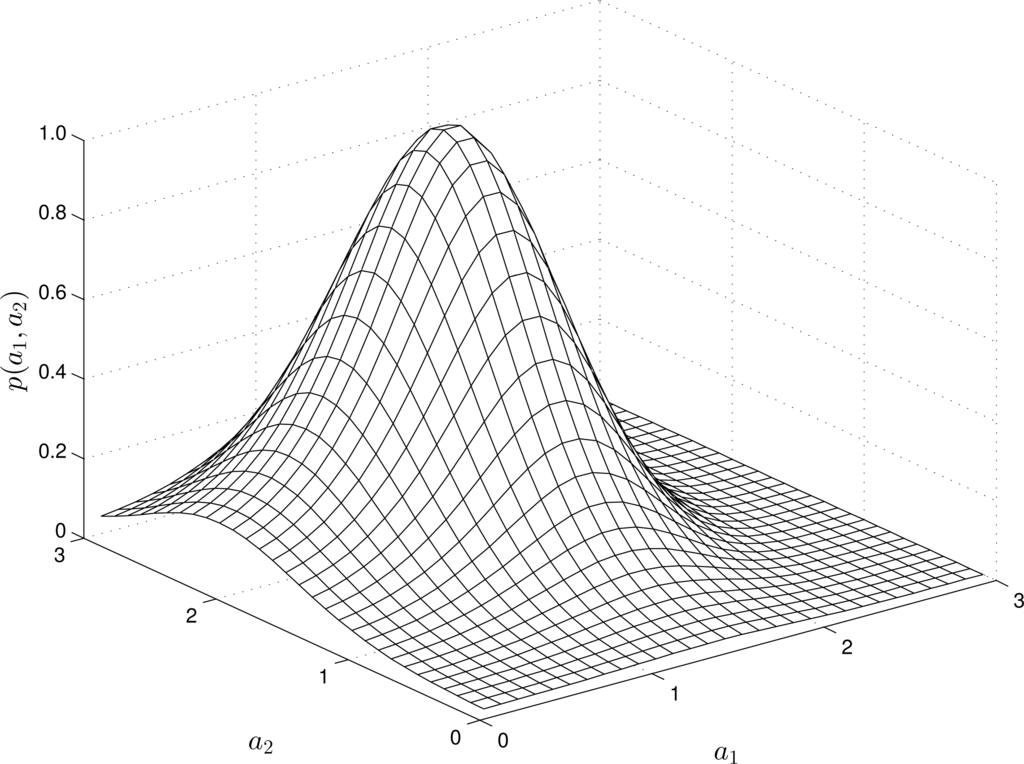
For nonlinear RMs, the structure of the -estimates varies depending on the “input” and “output” measurements. For instance, Figures 2 and 4 show the estimates of the pdfs for a quadratic, quadratic-linear and cubic RM-PQ.
5.2. Power-Type RM-PQ
Address the linear form of RM-PQ Equation (26). In this case, the problem of -estimation of the pdfs for parameter Equation (16) and noise Equation (18) acquires the form:
The vector, Φ̄[P(a), Q(ξ)], has the length of (s + 1) (the number of measurements).
Problem Equations (47)–(49) represent a modification of functional entropy-linear programming problem Equations (42)–(44), which involves the linear data model. To obtain the solution, again, adopt the standard technique for such variational problems [19]. This yields the following entropy-optimal pdfs of the parameters and noises:
Here, γ, ω designate the Lagrange multipliers associated with constraint Equation (48). In addition, the vector, θ (whose length equals (s + 1)), comprises the Lagrange multipliers for constraint Equation (49).
Formula (50) indicates that the entropy-optimal pdfs of the parameters and noises belong to the exponential class, with the parameters representing the Lagrange multipliers. The latter quantities meet a system of equations generated by constraint Equations (48),(49).
6. Normalized and Interval -Estimates for Linear RSM-pq
Consider the subclass of linear RSM-pq with accurate “input” measurements:
Denote by p0 and q0 the a priori probabilities of the parameters and noises, respectively.
Let us study the -estimates for some classes of the vectors, p, q.
Problem 1. Normalized probabilities: the-estimate results from solving the problem:
This problem belongs to the class of entropy-linear programming problems [20]. Its solution employs the necessary conditions of optimality in terms of the Lagrange function:
Consequently, we derive a system of equations determining the entropy-optimal probabilities, p*, q*:
Problem 2. The interval probabilities: the-estimate satisfies the following maximization problem for the generalized informational Fermi–Dirac entropy. The application of the generalized informational Fermi–Dirac entropy provides estimates lying in appropriate intervals [18]:
Lagrange’s method of multipliers gives the following system of equations for the estimates of the probabilities, p, q:
So long as the estimates of p and q are expressed analytically through the Lagrange multipliers, θ, one should only solve the system of Equation (64). For this, it is possible to use the following multiplicative algorithm [20] for the exponential Lagrange multipliers zj = exp(−θj), j ∈ [1, s]:
Under certain conditions, the estimates generated by Problems 1–2 differ in the values of some entropy (e.g., generalized Boltzmann entropy Equation (53)). Let us introduce the following notation:
the entropy:
the estimate, , obtained for normalized probabilities (Problem 1), and the estimate, , obtained for interval probabilities (Problem 2);
the absolute maximum of the entropy ĝ = arg max H(g);
the set:
Theorem Assume that.
Then:
Proof. Entropy Equation (53) represents a strictly concave function with a unique absolute maximum at the point, ĝ. The value of the entropy at an arbitrary point, g, depends on the distance to the absolute maximum point. Denote by and the distances between the absolute maximum point, ĝ, and the points corresponding to the optimal estimates in Problems (53)–(55) and (59)–(62), respectively. By virtue of the premise above, expression Equation (67) and strict concavity, we have:
These distances coincide only if .
7. Examples
7.1. Entropy Estimation of the Parameters of Linear RSM-pq under a Small Amount of Data
Consider a linear RM with five random parameter Equations (51) belonging to the same intervals 𝒜 = [0, 10] and with the noise vector ξ = {ξ1, ξ2}, whose components lie within the intervals Ξ1 = [−3, 3] and Ξ2 = [−6, 6]. There are two “output” measurements, y = {y1, y2}.
The reference model has fixed parameters a0 = {1, 2, 2, 4, 1}. The deviation from these values is described by the relative square error:
The “input” measurement matrix makes up:
The “output” measurement vector (distorted by noises from appropriate intervals) takes the form:
The first quasi-moments for the parameters and noise are defined by:
Substituting the last equalities into Equation (51) yields the following RM-pq:
As a priori information, we have selected three scenarios for the a priori probabilities (see Tables 1 and 2).


Scenario AE corresponds to uniform a priori distributions of the parameters and noise. Next, Scenario BD reflects nonuniform a priori distributions of the parameters and noise. Finally, CE is the combined scenario (the parameters possess nonidentical a priori distributions, whereas the noise has uniform a priori distributions).
We study the -estimates corresponding to Problems 1–2.
Problem 1. Normalized probabilities.
Problem 2. Interval probabilities.
The entropy, H, attains the absolute maximum at the point ; ; i ∈ [1, 5], j ∈ [1, 2]. Tables 3 and 4 present the coordinates of the absolute maximum point for the above scenarios of the a priori probabilities (see Tables 1 and 2).


Solutions to Problem 1 can be found in Tables 5 and 6.


Solutions to Problem 2 are shown by Tables 7 and 8.


The comparative analysis of these computations draws the following conclusions:
the estimates of the parameters derived for interval probabilities have a larger constrained maximum of the entropy than the ones derived for normalized probabilities (see Theorem 2);
the reference parameters and a priori probabilities appear interconnected: their “successful” choice (Scenario BD) leads to “better” approximation of the reference parameters in terms of the relative squared error than in the case of an “unsuccessful” choice (Scenario CD).
7.2. The Entropy Estimation of the pdfof Second-Order RDM-PQ Characteristics
Consider the following RDM-PQ:
Therefore, the dynamic RM-PQ in question incorporates nine parameters:
The values of constants in Equation (8) are combined in Table 9.

Table 10 demonstrates interval Equation (6) covering the components of the vector, a.

We have two measurements of the “input” and “output.” Construct the blocks X(1), X(2) Equation (11):
The matrix X = [X(1), X(2)] has the form:
The noise components become ξ[0] = ξ0 ∈ Ξ0 = [−3, 3]; ξ[1] = ξ1 ∈ Ξ1 = [−6, 6]. Additionally, the measured values of the “output” are given by y[2] = y0 = 18.51, y[3] = y1 = 43.36.
The -estimate of the pdf of the parameters, , j ∈ [0, 8], and the pdfs of the noise, , , is defined by:
The Lagrange multipliers, αj, βi and θl, meet the following equations:
To solve these equations, we have used MATLAB for symbolic transformations and the numerical solution of nonlinear equations, known as the “trust-region dogleg” technique. The computed Lagrange multipliers form Tables 11 and 13.



Figure 5 shows the curves of the probability density functions of the parameters, pj(a(1)j), j ∈ [0, 2] (curves 0,1,2) and pj(a(2)j), j ∈ [3, 8] (curves 3–8). Finally, Figure 6 presents the curves of the probability density functions of the noise, q0(ξ0), q1(ξ1).
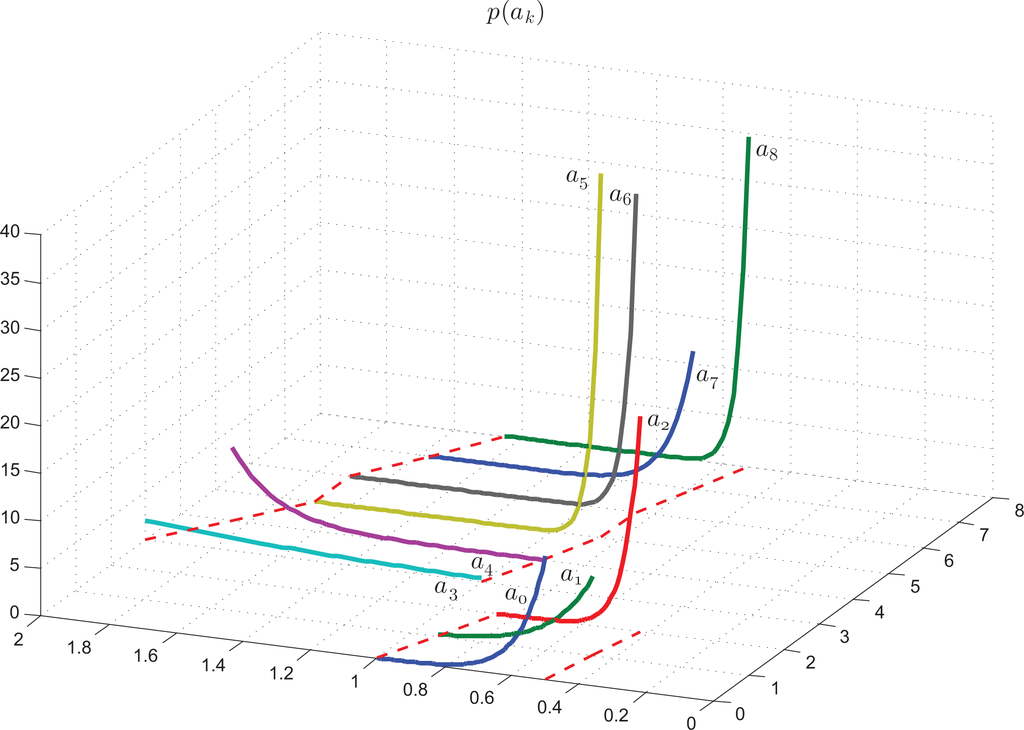
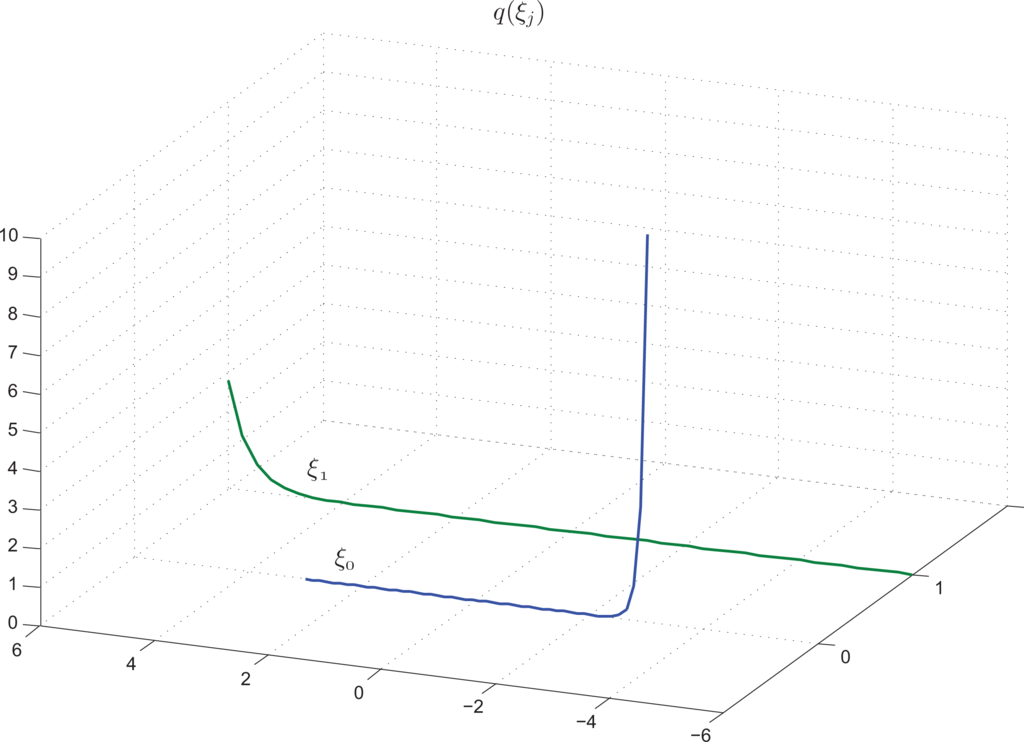
8. Conclusions
New methods of parametric (probabilities) and non-parametric (probability density functions) estimation of the randomized model characteristics are proposed. These methods are based on entropy functions or entropy functionals maximized under certain constraints. We can interpret the obtained estimate as a robust one, as the entropy function was used for its calculation. These methods are focused on the problems where data is limited and distorted by noises. It is shown that the entropy-robust estimation of the probabilities and probability density functions belong to the exponential class.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cox, D.R.; Donnelly, C.A. Principles of Applied Statistics; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics: Inference and Relationship; Griffin & Co: London, UK, 1961; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.F., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Application to Linear Models, Logistic Regrassion, and Survival Analysis; Springer Series; Springer-Verlag Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, H. Mathematical Methods of Statistics (PMS-9); Vol. 9; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Golan, A.; Judge, G.; Miller, D. Maximum Entropy Econometrics: Robust Estimation with Limited Data; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Golan, A. Information and entropy econometrics—A review and synthesis. Found. Trends Econometr 2006, 2, 1–145. [Google Scholar]
- Racine, J.; Maasoumi, E. A versatile and robust metric entropy test of time-reversibility, and other hypotheses. J. Econometr 2007, 138, 547–567. [Google Scholar]
- Shiryaev, A.N. Essentials of Stochastic Finance: Facts, Models, Theory; World Scientific Publishing Co Pte. Ltd: River Edge, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Del Ruiz, M.C. A new approach to measure volatility in energy markets. Entropy 2012, 14, 74–91. [Google Scholar]
- Polyak, B.T. Robustness Analysis Multilinear Perturbations. In Robustness of Dynamic Systems with Parameter Uncertainties; Mansur, M., Balemi, S., Trueol, W., Eds.; Birkhauser: Basel, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lebiedz, D. Entropy-related extremum principles for model reduction of dissipative dynamical systems. Entropy 2010, 12, 706–719. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.; Srivastava, S. Parametricbayesian estimation of differential entropy and relative entropy. Entropy 2010, 12, 818–843. [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes, E.T. Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.J. Robust Statistics; John Willey & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Tsypkin, Y.Z.; Popkov, Y.S. Theory of Nonlinear Discrete Systems; (in Russian); “Nauka” Publisher: Moscow, Russia, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. On information and sufficiency. Ann. Math. Stat 1951, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C. Communication theory of secrecy systems. Bell Syst. Tech. J 1949, 28, 656–715. [Google Scholar]
- Popkov, Y.S. Macrosystems Theory and its Applications: Equilibrium Models, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences; Springer: London, UK, 1995; Volume 203. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand, I.M.; Fomin, S.V. Calculus of Variations; Courier Dover Publications, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Popkov, Y.S. New class of multiplicative algorithms for solving of entropy-linear programms. Eur. J. Oper. Res 2006, 174, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).