Entropy Generation During the Interaction of Thermal Radiation with a Surface
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Radiation Entropy
2.1. Equilibrium Situation
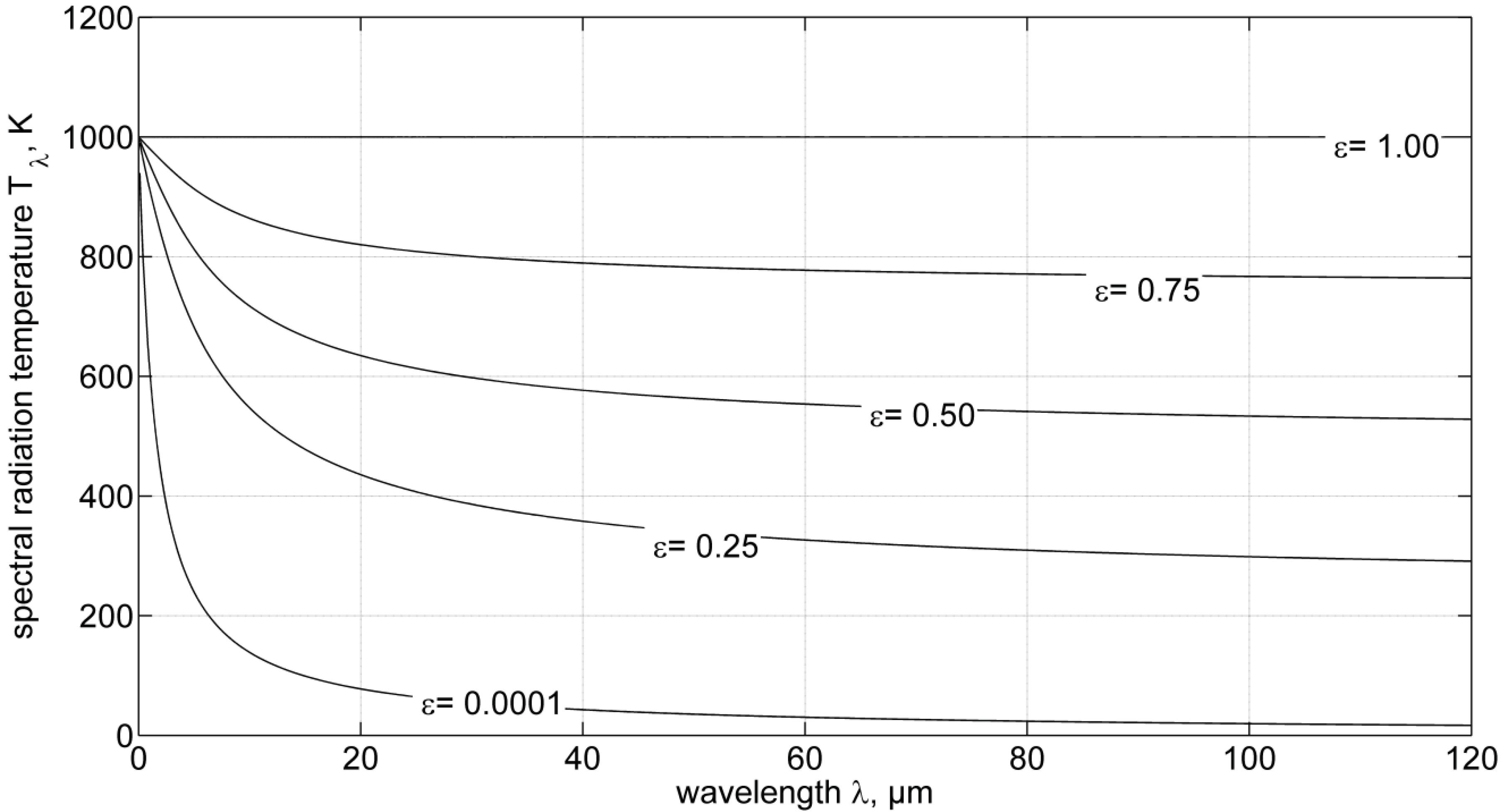
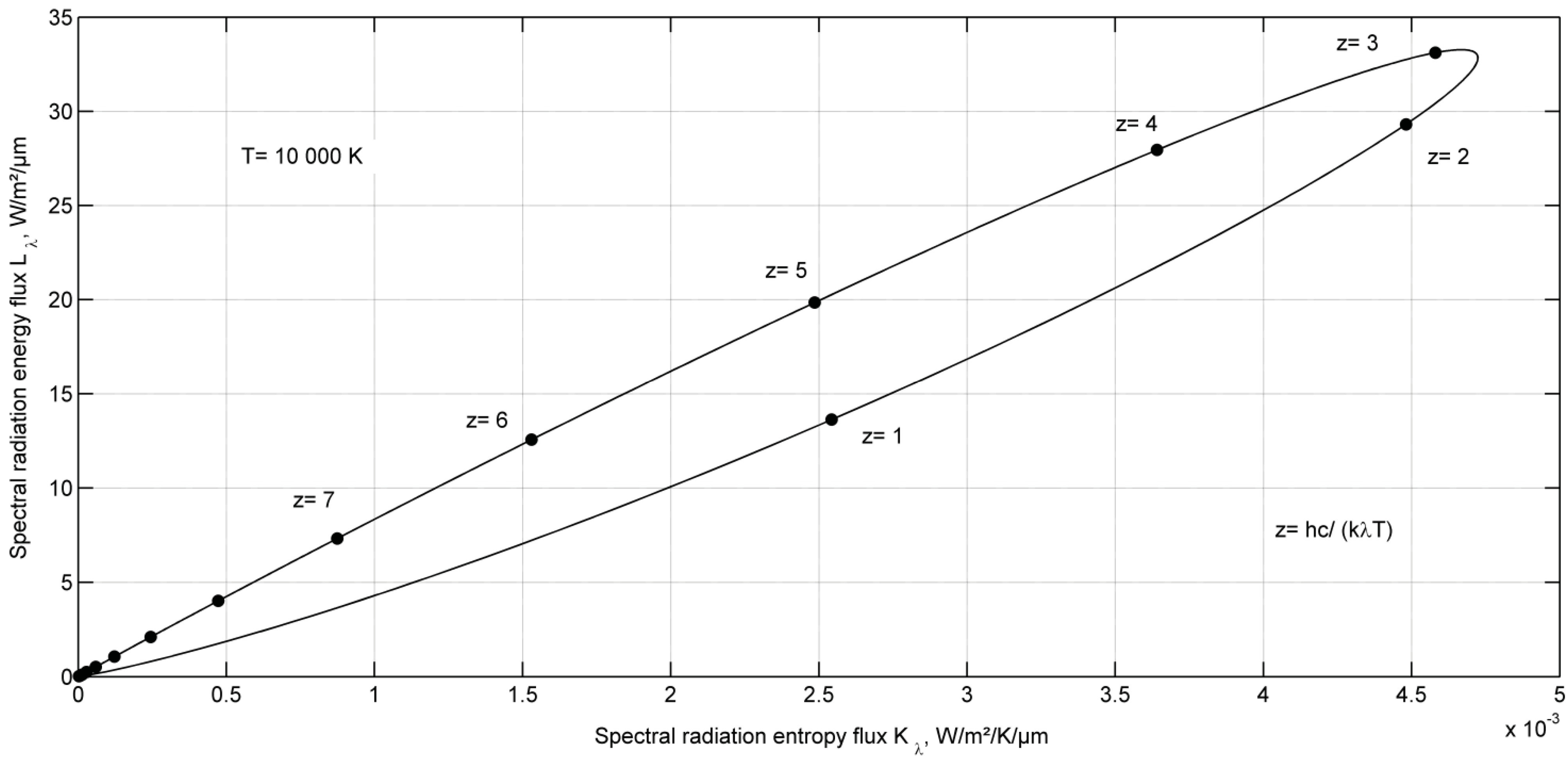
2.2. Fluxes
3. Entropy Production upon Absorption and Emission of Radiation

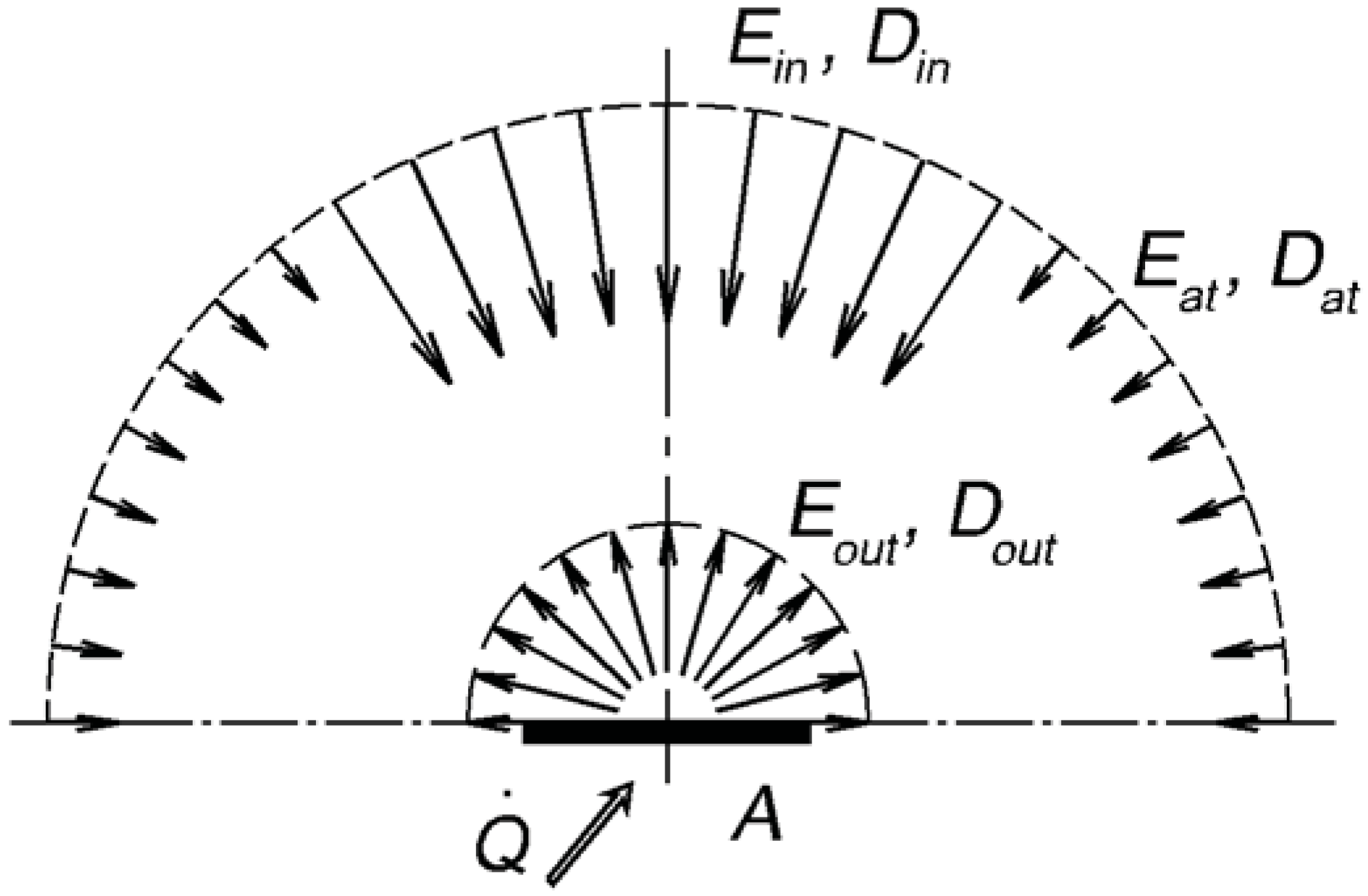
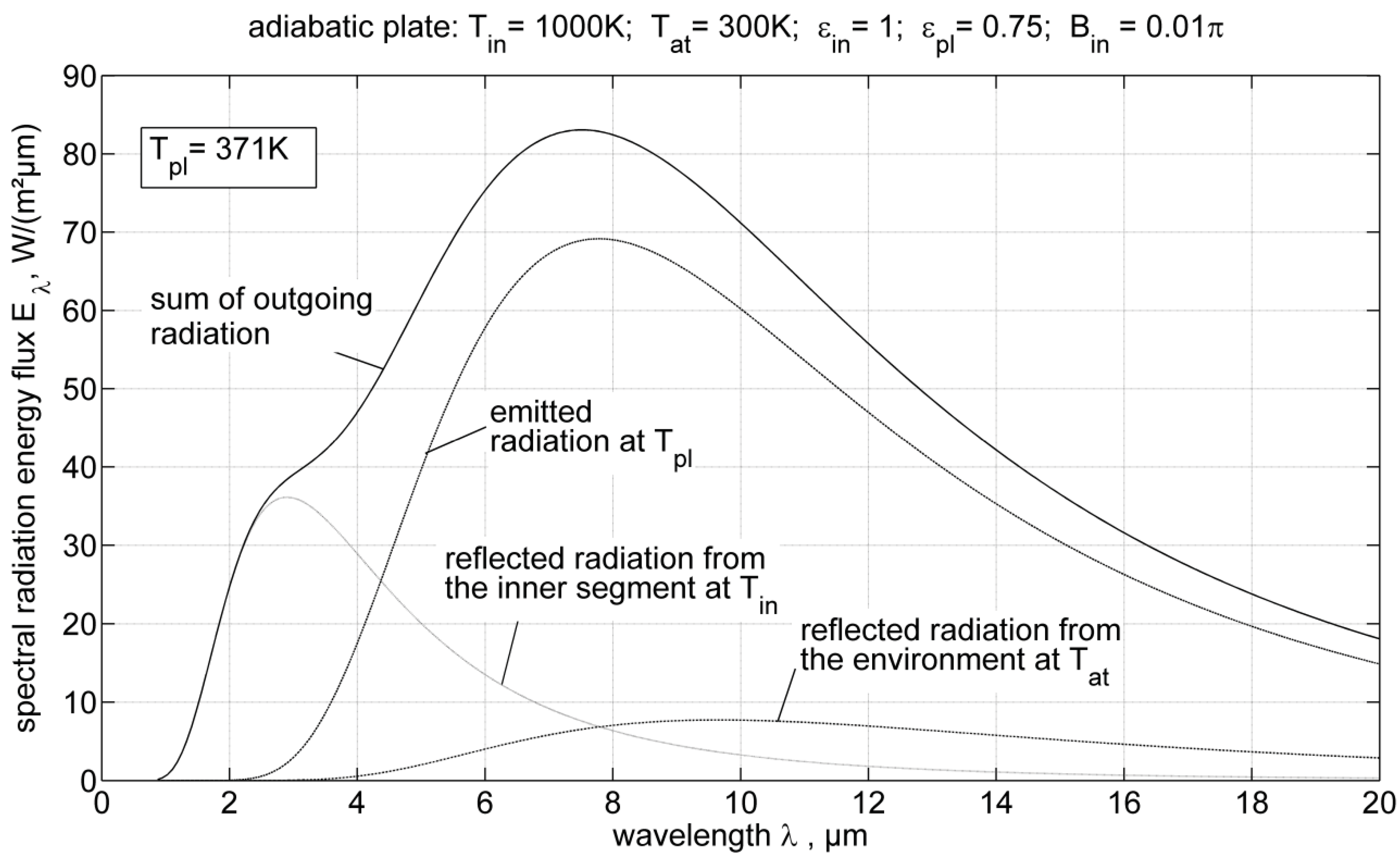
Adiabatic Plate
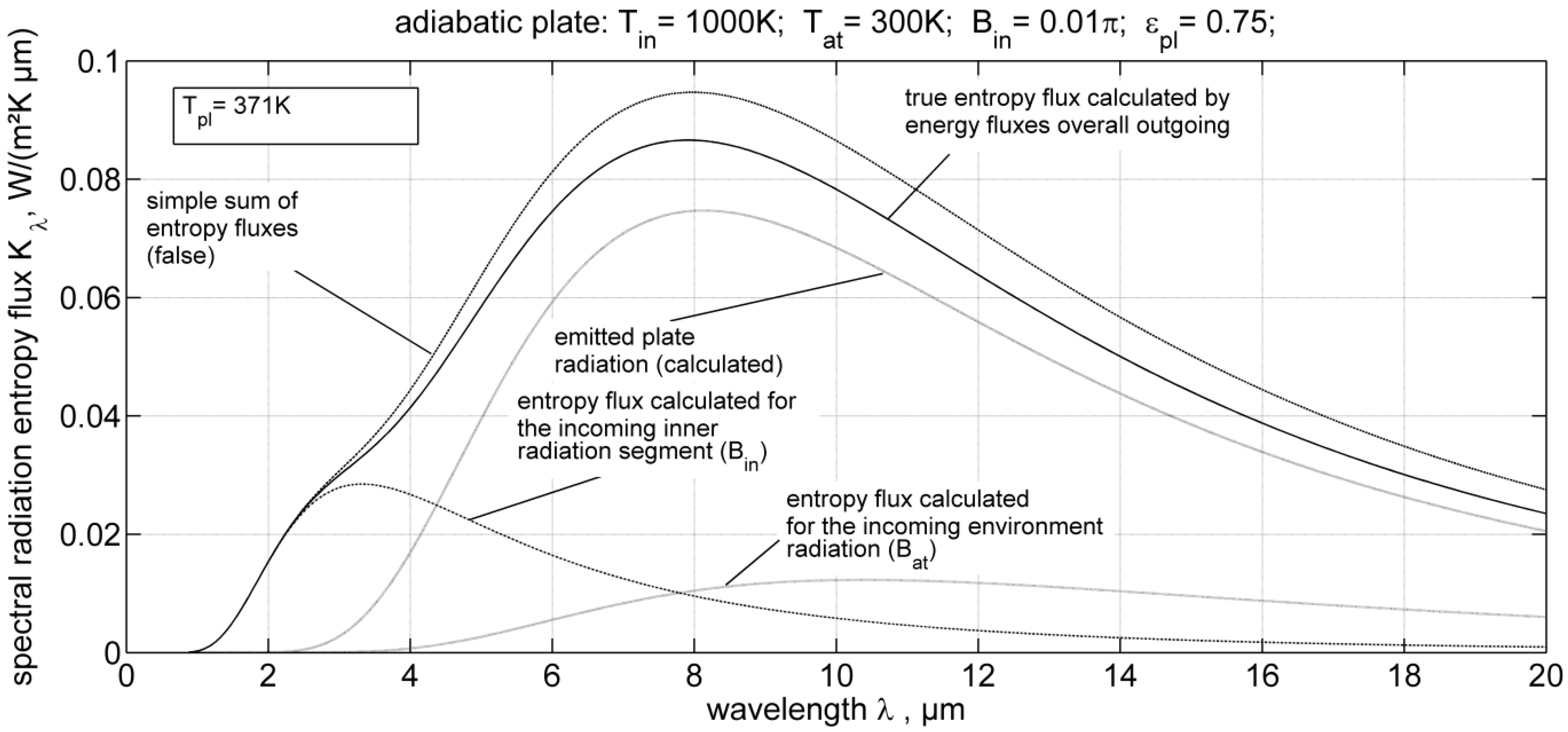
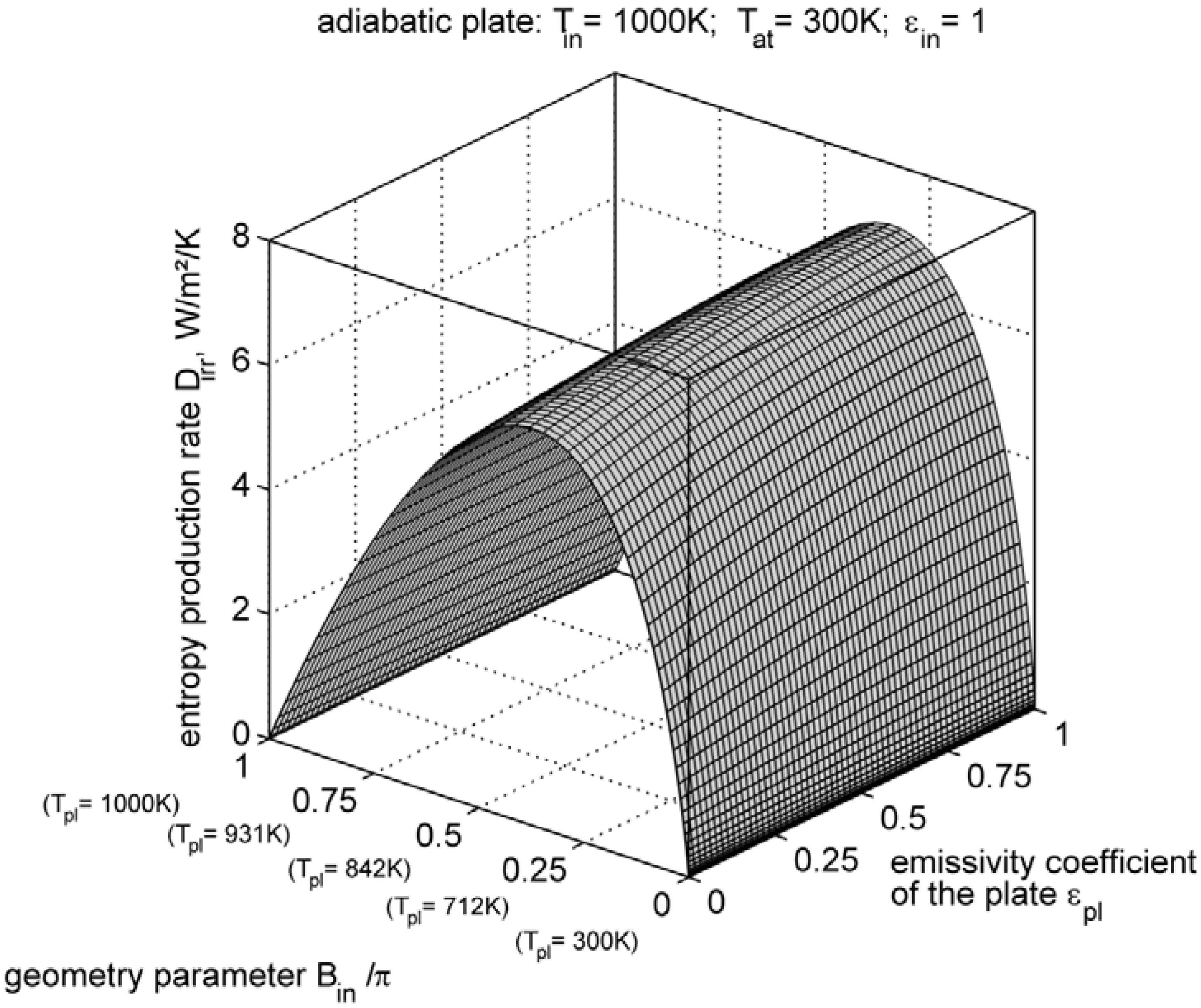
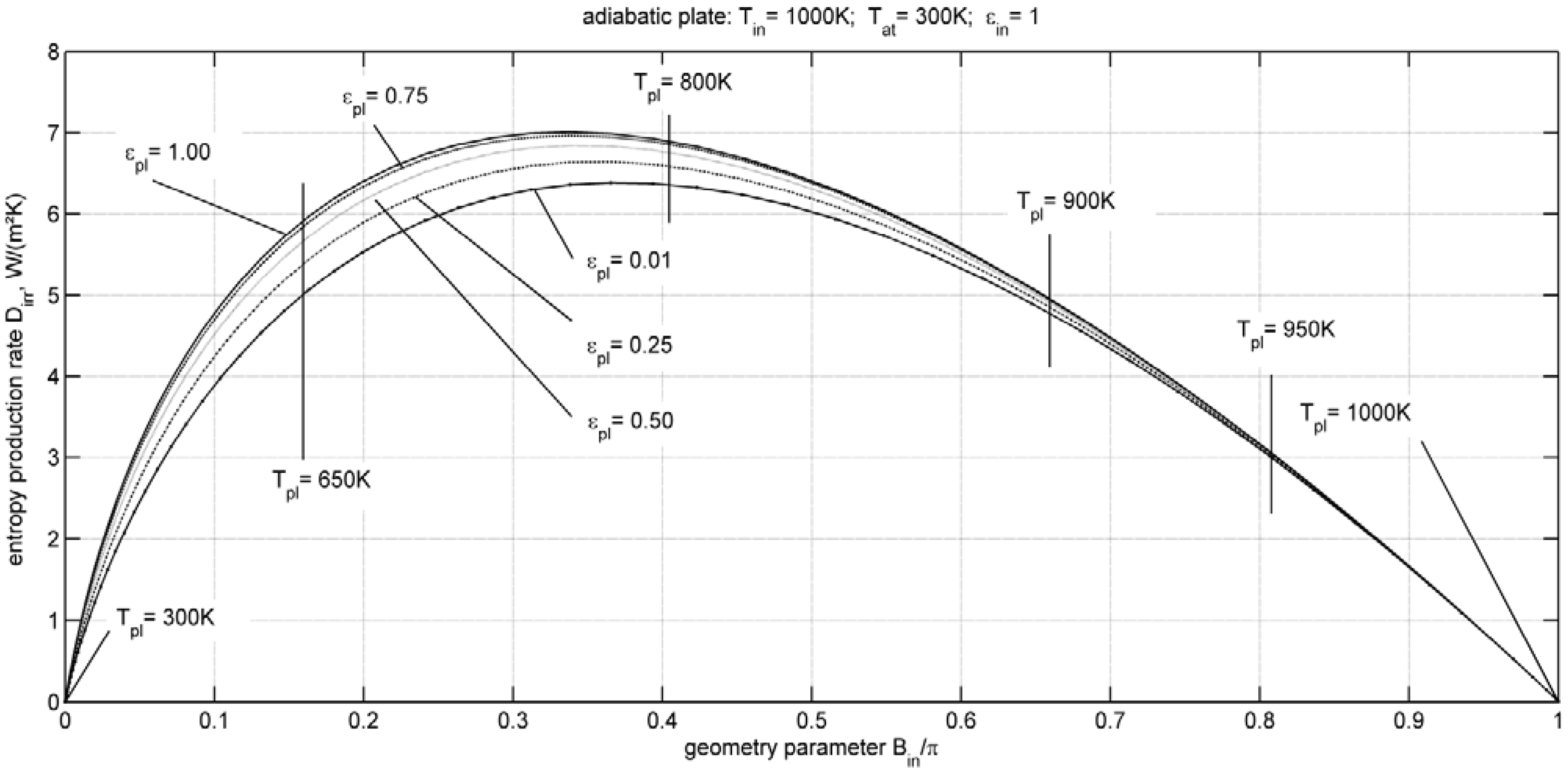
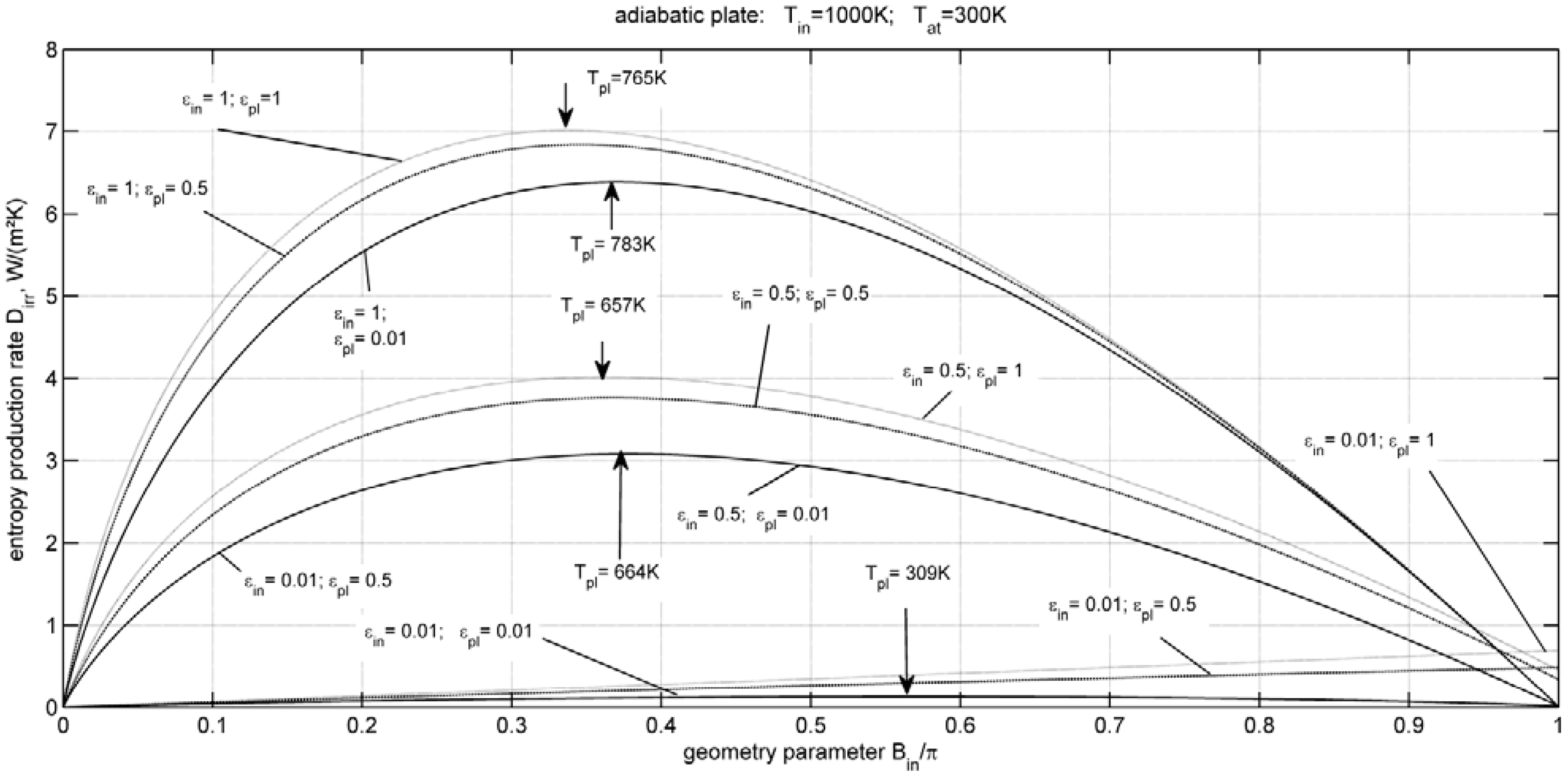
4. Entropy Production Minimization

5. Conclusions
6. Summary
Nomenclature
| A | area, m2 |
| B | geometry parameter related to solid angle [see Equation (17)]; sr |
| Bin | geometry parameter of the inner radiation source; sr |
| Bat | geometry parameter of the (atmospheric) environment |
| c | speed of light in vacuum, c = 299,792,458 m/s |
| D | overall hemispheric radiation entropy fluxes, W/m2/K |
| Dat | incoming radiation entropy flux from the atmosphere, W/m2/K |
| Db | blackbody radiation entropy flux, W/m2/K |
| Din | incoming radiation entropy flux from the inner source, W/m2/K |
| Dpl,overall | entropy flux of overall outgoing radiation, W/m2/K |
| Dirr,cond. | entropy production rate by heat conduction |
| E | overall hemispheric radiation energy flux, W/m2 |
| Eat | incoming radiation energy flux from the atmosphere, W/m2 |
| Eb | blackbody radiation energy flux, W/m2 |
| Ein | incoming radiation energy flux from the inner radiation source, W/m2 |
| Epl | radiation energy flux, emitted from the plate, W/m2 |
| Erefl,at | reflected radiation energy flux from the atmosphere, W/m2 |
| Erefl,in | reflected radiation energy flux from the inner source, W/m2 |
| h | Planck’s constant, h = 6.6261 × 10−34 J·s |
| Kb | overall radiation entropy intensity of blackbody radiation, W/K/m2/sr |
| Kλ | spectral radiation entropy intensity, W/K/m2/µm/sr |
spectral entropy flux of blackbody radiation, W/K/m2/µm | |
| k | Boltzmann’s constant, k = 1.3806 × 10−23 J/K |
| Lb | overall energy intensity of blackbody radiation, W/m2/sr |
| Lλ | spectral radiation intensity, W/m2/µm/sr |
spectral intensity of blackbody radiation, W/m2/µm/sr | |
| Nλ | density of number of photons, 1/m3 |
density of number of photons (equilibrium), 1/m3 | |
normal vector of a surface | |
| p | pressure, N/m2 |
heat conduction flow to or from the plate, W/m2 | |
| S | entropy, J/K |
| Seq | volume specific radiation entropy in equilibrium, J/m3/K |
entropy production rate, W/K | |
| s | volume specific entropy, J/m3/K |
| sλ | volume specific spectral radiation entropy, J/m3/K |
| T | absolute temperature, K |
| Tat | temperature of (atmospheric) environment, K |
| Tpl | temperature of the plate, K |
| Teq | equilibrium temperature, K |
| Tin | temperature of inner radiation source, K |
| Ts | formal radiation flux temperature, K |
| Tλ | spectral radiation temperature, K |
| t | time, s |
| U | internal energy, J |
spectral energy of cavity radiation in equilibrium, J/µm | |
| u | volume specific internal energy, J/m3 |
| ueq | volume specific overall energy of cavity radiation in equilibrium, J/m3 |
volume specific spectral energy of cavity radiation in equilibrium, J/m3/µm | |
| uλ | volume specific spectral energy of cavity radiation, J/m3/µm |
| V | Volume, m3 |
| x | average occupation number of the photon state in equilibrium |
| X(ε) | grey body entropy function |
| Ω | solid angle, sr |
| ε | emissivity coefficient |
| εin | emissivity coefficient of inner radiation source |
| εat | emissivity coefficient of outer (atmosphere) radiation source |
| εpl | emissivity coefficient of the plate |
| εre | real part of complex dielectrical constant |
| ελ | energy of a photon with wavelength λ |
| θ | polar angle measured from normal of surface, ° |
| θat | polar angle of radiation from environment, ° |
| θin | upper limit of polar angle of inner radiation source, ° |
| φ | azimuth angle, ° |
| λ | wavelength in vacuum, µm |
| σ | Stefan–Boltzmann constant, σ = 5.67 × 10−8 W/m2/K4 |
References
- Howell, J.; Siegel, R.; Mengüc, P. Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Paltridge, G.; Farquhar, G.; Cunz, M. Maximum entropy production cloud feedback and climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feistel, R.; Ebeling, W. Physics of Self—Organisation and Evolution; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kleidon, A. Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics and the Production of Entropy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pelkowski, J. Entropieerzeugung eines strahlenden Planeten: Studien zu ihrer Rolle in der Klimatheorie; Verlag Harry Deutsch: Thun, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, P.T. Thermodynamics. In Monographs in Statistical Physics and Thermodynamics; von Prigogine, I., Ed.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, J.E.; Mayer, M. Statistical Mechanics; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Callen, H.B. Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatics, 2nd ed.; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Planck, M. Theorie der Wärmestrahlung: Vorlesungen; Barth Verlag: Leipzig, Germany, 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Feistel, R. Entropy flux and entropy production of stationary black-body radiation. J. Non-Equil. Thermody. 2011, 36, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabelac, S. Thermodynamik der Strahlung; Vieweg & Sohn: Braunschweig/Wiesbaden, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Joulain, K.; Mulet, J.Ph.; Marquier, F.; Carminati, R.; Greffet, J.J. Surface electromagnetic waves thermally exited: Radiative heat transfer, coherence properties and Casimir forces revisited in the near field. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2005, 57, 59–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffet, J.J.; Carminati, R.; Joulain, K.; Mulet, J.Ph.; Mainguy, S.; Chen, Y. Coherent emission of light by thermal sources. Nature 2002, 416, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabelac, S. Thermodynamics of solar radiation. In Proceedings of the 5th European Thermal-Sciences Conference, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 18–22 May 2008.
- Landsberg, P.T.; Tonge, G. Thermodynamic of the conversion of diluted radiation. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 1979, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabelac, S.; Conrad, R. Entropy Generation During the Interaction of Thermal Radiation with a Surface. Entropy 2012, 14, 717-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040717
Kabelac S, Conrad R. Entropy Generation During the Interaction of Thermal Radiation with a Surface. Entropy. 2012; 14(4):717-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040717
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabelac, Stephan, and Rainer Conrad. 2012. "Entropy Generation During the Interaction of Thermal Radiation with a Surface" Entropy 14, no. 4: 717-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040717
APA StyleKabelac, S., & Conrad, R. (2012). Entropy Generation During the Interaction of Thermal Radiation with a Surface. Entropy, 14(4), 717-735. https://doi.org/10.3390/e14040717




