Towards an Evolutionary Model of Animal-Associated Microbiomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Evolutionary Pressures within a Microbiome: A Background
2.1. Intraspecific Competition—The Primary Evolutionary Pressures
2.2. Ecological Interactions—The Secondary Evolutionary Pressures

2.3. Host Influences–The Tertiary Evolutionary Pressures
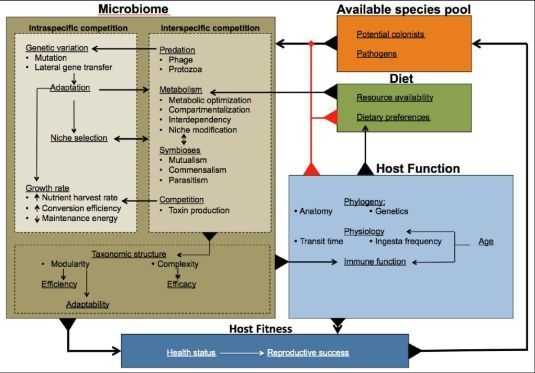
3. Towards an Understanding of Microbiome Evolution
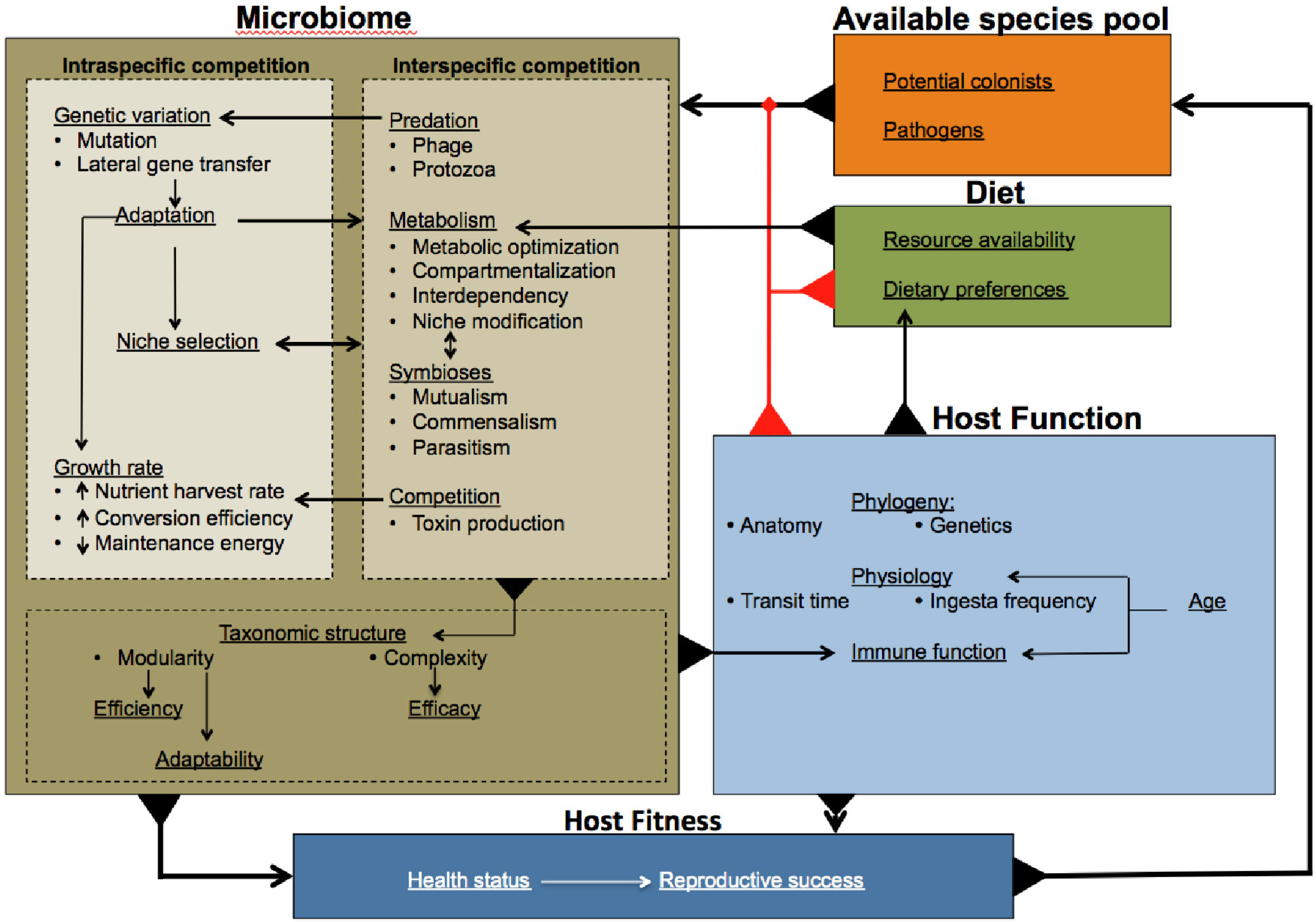
4. Multi-Level Selection
4.1. Complexity
4.2. Modularity
5. Cooperation, Altruism and Cheating
6. Perspective
Acknowledgements
References
- Corliss, J.B.; Barnes, J.A.; Hoffman, S.E. An hypothesis concerning the relationship between submarine hotsprings and the origin of life on Earth. Oceanol. Acta 1981, 4, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bada, J.L.; Lazcano, A. Origin of life: Some like it hot, but not the first biomolecules. Science 2002, 296, 1982–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wächtershäuser, G. Evolution of the first metabolic cycles. Evolution 1990, 87, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretó, J. Controversies on the origin of life. Int. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pace, N.R. Time for change. Nature 2006, 441, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allwood, A.C.; Walter, M.R.; Kamber, B.S.; Marshall, C.P.; Burch, I.W. Stromatolite reef from the early archaean era of Australia. Nature 2006, 441, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitman, W.B.; Coleman, D.C.; Wiebe, W.J. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6578–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbonne, G.M. The Ediacara biota: Neoproterozoic origin of animals and their ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2005, 33, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seilacher, A.; Grazhdankin, D.; Legouta, A. Ediacaran biota: The dawn of animal life in the shadow of giant protists. Paleontol. Res. 2003, 71, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, P.L.; Benson, A.K.; Peterson, D.A.; Patil, P.B.; Moriyama, E.N.; Roos, S.; Walter, J. Diversification of the gut symbiont Lactobacillus reuteri as a result of host-driven evolution. ISME 2010, 4, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akman, L.; Yamashita, A.; Watanabe, H.; Oshima, K.; Shiba, T.; Hattori, M.; Aksoy, S. Genome sequence of the endocellular obligate symbiont of tsetse flies, Wigglesworthia glossinidia. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, C.; Moran, N.A. Molecular interactions between bacterial symbionts and their hosts. Cell 2006, 126, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degnan, P.H.; Lazarus, A.B.; Wernegreen, J.J. Genome sequence of Blochmannia pennsylvanicus indicates parallel evolutionary trends among bacterial mutualists of insects. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, G.D.; Werren, J.H. The role of selfish genetic elements in eukaryotic evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinbauer, M.G.; Rassoulzadegan, F. Are viruses driving microbial diversification and diversity? Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.T.; Gibson, G.R. Carbohydrate fermentation, energy transduction and gas metabolism in the human large intestine. In Gastrointestinal Microbiology; Mackie, R.I., White, B.A., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 269–317. [Google Scholar]
- Hungate, R.E. Introduction: The ruminant and the rumen. In The Rumen Microbial Ecosystem; Hobson, P.N., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A. Plant cell wall breakdown by anaerobic microorganisms from the mammalian digestive tract. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1125, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schäfer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiome and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.J. Intestinal flora and endogenous vitamin synthesis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 1997, 6 (Suppl. 1), S43–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleim, H.A.; Scheline, R.R. Metabolism of xenobiotics by strains of intestinal bacteria. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1972, 31, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkholm, B.; Bok, C.M; Lundin, A.; Rafter, J.; Hibberd, M.L.; Pettersson, S. Intestinal microbiota regulate xenobiotic metabolism in the liver. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.; Campbell, J.I.; King, T.P.; Grant, G.; Jansson, E.A.; Coutts, A.G.P.; Pettersson, S.; Conway, S. Commensal anaerobic gut bacteria attenuate inflammation by regulating nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of PPAR-γ and RelA. Nat. Immun. 2003, 5, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, E.; Williams, B.A.; Smidt, H.; Verstegen, M.W.; Mosenthin, R. Influence of the gastrointestinal microbiota on development of the immune system in young animals. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2006, 7, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heijtz, R.D.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareau, M.G.; Wine, E.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Cho, J.H.; Whary, M.T.; Philpott, D.J.; MacQueen, G.; Sherman, P.M. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut 2011, 60, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, P.; Sudo, N.; Dinan, T.; Taylor, V.H.; Bienenstock, J. Mood and gut feelings. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, J.P.; Mazouni, C.; Salem-Cherif, I.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D.; Boubli, D.; Gamerre, M.; Bretelle, F. High vaginal concentrations of Atopobium vaginae and Gardnerella vaginalis in women undergoing preterm labor. Obstet. Gynocol. 2010, 115, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mania-Pramanik, J.; Kerkar, S.C.; Salvi, V.S. Bacterial vaginosis: a cause of infertility? Int. J. STD AIDS 2009, 20, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, G.; Markowitz, L.; Joesoef, R.; Koumans, E. Bacterial vaginosis and HIV infection. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2000, 76, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.G.; van Vliet, A.H.; Kuipers, E.J. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 449–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mobley, H.L. Vaccines for Proteus mirabilis in urinary tract infection. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2002, 19, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D.; Matz, J.; Weidinger, E.; Wagner, J.; Wildenauer, A.; Obermeier, M.; Riedel, M.; Müller, N. Association between intracellular agents and Tourette’s syndrome. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 260, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, N.E.; Deiratany, S.; Webb, D.W.; McMenamin, J.B. PANDAS (Paediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorder associated with Streptococcal infection). Ire. Med. J. 2006, 99, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, H.; Amano, A. Roles of oral bacteria in cardiovascular diseases—from molecular mechanisms to clinical cases: Implication of periodontal diseases in development of systemic diseases. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 113, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.A.; Thomas, S.M.; Ho, M. The human vaginal microbiome. In Metagenomics of The Human Body; Nelson, K.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The human microbiome project. Nature 2007, 449, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Thomas, S.M.; Ho, M.; Sharma, S.; Reich, C.I.; Frank, J.A.; Yeater, K.M.; Biggs, D.R.; Nakamura, N.; Stumpf, R.; et al. Heterogeneity of vaginal microbial communities within individuals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, L.B.; Liu, C.M.; Johnson, K.E.; Aziz, M.; Lau, M.K.; Bowers, J.; Ravel, J.; Keim, P.S.; Serwadda, D.; Wawer, M.J.; Gray, R.H. The effects of circumcision on the penis microbiome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildrim, S.; Yeoman, C.J.; Sipos, M.; Torralba, M.; Wilson, B.A; Goldberg, T.; Stumpf, R.; Leigh, S.; Nelson, K.; White, B.A. Characterization of fecal microbiome from non-human primates reveals species specific microbial communities. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A.J.; Frank, J.A.; Stumpf, R.; Salyers, A.A.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J.; Leigh, S. Differences between normal vaginal bacterial community of baboons and that of humans. Am. J. Primatol. 2010, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, P.B.; Denman, S.E.; Jones, M.; Tringe, S.G.; Barry, K.; Malfatti, S.A.; McHardy, A.C.; Cheng, J.F.; Hugenholtz, P.; McSweeny, C.S.; Morrison, M. Adaptation to herbivory by the Tammar wallaby includes bacterial and glycoside hydrolase profiles different from other herbivores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14793–14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulc, J.M.; Antonopoulos, D.A.; Miller, M.E.; Wilson, M.K.; Yannarell, A.C.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.E.; Frank, E.D.; Emerson, J.B.; Wacklin, P.; et al. Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelbos, I.S.; Vester Boler, B.M.; Qu, A.; White, B.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. Phylogenetic characterization of fecal microbial communities of dogs fed diets with or without supplemental dietary fiber using 454 pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K.; Gordon, G.I.; Secor, S.M.; Knight, R. Postprandial remodeling of the gut microbiome in Burmese pythons. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 4, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, H.; Kato, Y.; Chikaraishi, T.; Moritani, M.; Ban-Tokuda, T.; Wakita, M. Microbial diversity in ostrich ceca as revealed by 16s ribosomal RNA gene clone library and detection of novel Fibrobacter species. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, A.; Brulc, J.M.; Wilson, M.K.; Law, B.F.; Theoret, J.R.; Joens, L.A.; Konkel, M.E.; Angly, F.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.E.; Nelson, K.E.; White, B.A. Comparative metagenomics reveals host-specific metavirulomes and horizontal gene transfer elements in the chicken cecum microbiome. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, F.; Luginbühl, P.; Ivanova, N.; Ghassemian, M.; Richardson, T.H.; Stege, J.T.; Cayouette, M.; McHardy, A.C.; Djordjevic, G.; Aboushadi, N.; et al. Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiome of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 2007, 450, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suen, G.; Scot, J.J.; Aylward, F.O.; Adams, S.M.; Tringe, S.G.; Pinto-Tomàs, A.A.; Foster, C.E.; Pauly, M.; Weimer, P.J.; Barry, K.W.; et al. An insect herbivore microbiome with high plant biomass-degrading capacity. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Microbiome Jumpstart Reference Strains Consortium. A catalog of reference genomes from the human microbiome. Science 2010, 328, 994–999. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, J.I.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Curtis, T.P.; Ellis, R.J.; Firestone, M.K.; Freckleton, R.P.; Green, J.L.; Green, L.E.; Killham, K.; Lennon, J.J.; et al. The role of ecological theory in microbial ecology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenfeld, N.; Woose, C. Life is physics: Evolution as a collective phenomenon far from equilibrium. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2011, 2, 375–399. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, C.; Maciá, M.D.; Oliver, A.; Schachar, I.; Buckling, A. Coevolution with viruses drives the evolution of bacterial mutation rates. Nature 2007, 450, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medini, D.; Serruto, D.; Parkhill, J.; Relman, D.A.; Donati, C.; Moxon, R.; Falkow, S.; Rappuoli, R. Microbiology in the post-genomic era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Vallvé, S.; Romeu, A.; Palau, J. Horizontal gene transfer in bacterial and archaeal complete genomes. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, O.; Pupko, T. Inference and characterization of horizontally transferred gene families using stochastic mapping. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehemann, J.H.; Correc, G.; Barbeyron, T.; Helbert, W.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Transfer of carbohydrate-active enzymes from marine bacteria to Japanese gut microbiome. Nature 2010, 464, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Yildrim, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Durkin, A.S.; Torralba, M.; Sutton, G.; Buhay, C.J.; Ding, Y.; Dugan-Rocha, S.P.; Muzny, D.M.; et al. Comparative genomics of Gardnerella vaginalis strains reveals substantial differences in metabolic and virulence potential. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, N.; Goldenfeld, N. Statistical mechanics of horizontal gene transfer in evolutionary ecology. J. Stat. Phys. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Vetsigian, K.; Woese, C.; Goldenfeld, N. Collective evolution and the genetic code. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10696–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Deem, M.W. Spontaneous emergence of modularity in a model of evolving individuals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 228107:1–228107:4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Martin-Cuadrado, A.; Rodriguez-Brito, B.; Pasic, L.; Thingstad, T.F.; Rohwer, F.; Mira, A. Explaining microbial population genomics through phage predation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberg, R.; Lipatov, M.; Small, P.M.; Sheffer, H.; Niemann, S.; Homolka, S.; Roach, J.C.; Kremer, K.; Petrov, D.A.; Feldman, M.W.; Gagneux, S. High functional diversity in Mycobacterium tuberculosis driven by genetic drift and human demography. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauchop, T.; Elsden, S.R. The growth of microorganisms in relation to their energy supply. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1960, 23, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.B.; Baldwin, R.L. Comparison of maintenance energy expenditure and growth yields among several rumen bacteria grown on continuous culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.B.; Delfino, F.J.; Baldwin, R.L. Effects of combinations of substrates on maximum growth rates of several rumen bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 37, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Southamer, A.H. The search for correlation between theoretical and experimental growth yields. In International Review of Biochemistry and Molecular Biochemistry; Quayle, J.R., Ed.; University Park Press: Baltimore, USA, 1979; Volume 21, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, J.B. A re-assessment of bacterial growth efficiency: the heat production and membrane potential of Streptococcus bovis in batch and continuous culture. Arch. Microbiol. 1991, 155, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, J.H. A simple stochastic gene substitution model. Theor. Pop. Biol. 1983, 23, 202–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, J.H. Molecular evolution over the mutational landscape. Evolution 1984, 38, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Gerrish, P.; Lenski, R. The fate of competiting beneficial mutations in an asexual population. Genetica 1998, 103, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrish, P. The rhythm of microbial adaptation. Nature 2001, 413, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogle, C.A.; Nagle, J.L.; Desai, M.M. Clonal interference, multiple mutations and adaptation in large asexual populations. Genetics 2008, 180, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, C.O. The speed of adaptation in large asexual populations. Genetics 2004, 167, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Golding, G.B. Patterns of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria. In Microbial Population Genetics; Xu, J., Ed.; Caister Acadmeic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2010; pp. 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Haloin, J.R.; Strauss, S.Y. Interplay between ecological communities and evolution. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1133, 87–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, M.L.; Diamond, J.M. Ecology and Evolution of Communities; Belknap Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 342–444. [Google Scholar]
- Liebig, J. Die Organische Chemie in Ihrer Anwendung Auf Agriculture Und Physiologie; Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn: Braunschweig, Germany, 1840; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, M.A.; Gordon, D.M. The ecological role of bacteriocins in bacterial competition. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The roles of mutation, inbreeding, crossbreading, and selection in evolution. Proc. Sixth Int. Congress Gen. 1932, 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Gause, G.F. The Struggle for Existence; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, USA, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, R.A.; McGehee, R. Competitive exclusion. Am. Nat. 1980, 115, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography. In Monographs in Population biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 6, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of initial microbiome across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Fierer, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Bacterial composition variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.; Epstein, S.; D’Onofrio, A.; Ling, L.L. Uncultured microorganisms as a source of secondary metabolites. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2010, 63, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotta, M.A. Interaction of ruminal bacteria in the production and utilization of maltooligosaccharides from starch. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Treves, D.S.; Manning, S.; Adams, J. Repeated evolution of an acetate cross-feeding polymorphism in long-term populations of Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy, S.C.; Kelly, W.J.; Altermann, E.; Ronimus, R.S.; Yeoman, C.J.; Pacheco, D.M.; Li, D.; Kong, Z.; McTavish, S.; Sang, C.; Lambie, S.C.; Janssen, P.H.; Dey, D.; Attwood, G.T. The genome sequence of the rumen methanogen Methanobrevibacter ruminantium reveals new possibilities for controlling ruminant methane emissions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, A.; Crawford, J.M.; Stewart, E.J.; Witt, K.; Gavrish, E.; Epstein, S.; Clardy, J.; Lewis, K. Siderophores from neighboring organisms promote the growth of uncultured bacteria. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Bonhoeffer, S. Evolution of cross-feeding in microbial populations. Am. Nat. 2004, 163, E126–E135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klitford, N.; Segrè, D. The importance of compartmentalization in metabolic flux models: Yeast as an ecosystem of organelles. Genome Inform. 2010, 22, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Southamer, A.H. A theoretical study on the amount of ATP required for synthesis of microbial cell material. Anton. Leeuwenhoek 1973, 39, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.K.; Rainey, P.B.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Molin, S. Evolution of species interactions in a biofilm community. Nature 2007, 445, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadieux, P.A.; Burton, J.; Devillard, E.; Reid, G. Lactobacillus by-products inhibit the growth and virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60 (Suppl. 6), 13–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.D. Microbial fermentation in insect guts. In Gastrointestinal Microbiology; Mackie, R.I., White, B.A., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: New York, USA, 1997; pp. 269–317. [Google Scholar]
- Laland, K.N.; Odling-Smee, F.J.; Feldman, M.W. Evolutionary consequences of niche construction and their implications for ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 97, 10242–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, H.R. Sources, Sinks and population regulation. Am. Nat. 1988, 132, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Krone, S.M.; Forney, L.J. Application of ecological network theory to the human microbiome. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2008, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elton, C. Animal Ecology; Sidgwick and Jackson: London, UK, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Yannarell, A.C.; Steppe, T.F.; Paerl, H.W. Disturbance and recovery of microbial community structure and function following hurricane Frances. Env. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microflora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaneveld, J.R.; Lozupone, C.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R. Ribosomal RNA diversity predicts genome diversity in gut bacteria and their relatives. Nucl. Acid. Res. 2010, 38, 3869–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; Plague, G.R. Genomic challenges following host restriction in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, N.; Goldenfeld, N. The dynamics of gene duplication and transposons in microbial genomes following a sudden environmental change. 2010; arXiv:1005.3349v2. [Google Scholar]
- Vallino, J.J. Ecosystem biogeochemistry considered as a distributed metabolic network ordered by maximum entropy production. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Han, Y.; Dodd, D.; Schroeder, C.M.; Mackie, R.I.; Cann, I.K. Thermostable enzymes as biocatalysts in the biofuel industry. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 70, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stingl, U.; Radek, R.; Yang, H.; Brune, A. “Endomicrobia”: Cytoplasmic symbionts of termite gut protozoa form a separate phylum of prokaryotes. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockhurst, M.A.; Fenton, A.; Roulston, B.; Rainey, P.B. The impact of phages on interspecific competition in experimental populations of bacteria. BMC Ecol. 2006, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomidova, A.; Kulikov, E.; Isaeva, A.; Manykin, A.; Letarov, A. The diversity of coliphages and coliforms in horse feces reveals a complex pattern of ecological interactions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5975–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Held, N.L.; Herrera, A.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Whitaker, R.J. CRISPR associated diversity within a population of Sulfolobus islandicus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Wolf, Y.I. Is evolution Darwinian or/and Lamarckian? Biol. Direct 2009, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, P.; Barrangou, R. CRISPR/Cas, the immune system of bacteria and archaea. Science 2010, 327, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T.; Simek, K.; Vrba, J.; Pernthaler, A.; Glöckner, F.O.; Nübel, U.; Psenner, R.; Amann, R. Predator-specific enrichment of Actinobacteria from a cosmopolitan freshwater clade in mixed continuous culture. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2145–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernthaler, J. Predation on prokaryotes in the water column and its ecological implications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Off the hook–how bacteria survive protozoan grazing. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simek, K.; Vrba, J.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T.; Hartman, P.; Nedoma, J.; Psenner, R. Morphological and compositional shifts in an experimental bacterial community influenced by protists with contrasting feeding modes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraune, S.; Bosch, T.C.G. Long-term maintenance of species-specific bacterial microbiome in the basal metazoan Hydra. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.L.; Nkrumah, J.D.; Basarab, J.A.; Moore, S.S. Linkage of microbial ecology to phenotype: correlation of rumen microbial ecology to cattle’s feed efficiency. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 288, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzal, M.D.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.P.J.; Sprenger, N.; Monotoliu, I.; Rezzi, S.; Kochhar, S.; Nicholson, J.K. Dietary modulation of gut functional ecology studied by fecal metabonomics. J. Prot. Res. 2010, 9, 5284–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.; Loo, R.L.; Stamler, J.; Bictash, M.; Yap, I.K.S.; Chan, Q.; Ebbels, T.; Iorio, M.D.; Brown, I.J.; Veselkov, K.A.; et al. Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet and blood pressure. Nature 2008, 453, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booijink, C.C.; El-Aidy, S.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Heilig, H.G.; Troost, F.J.; Smidt, H.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Zoetendal, E.G. High temporal and inter-individual variation detected in the human ileal microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 3213–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaura, E.; Keijser, B.J.; Huse, S.M.; Crielaard, W. Defining the healthy “core microbiome” of oral microbial communities. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochman, H.; Worobey, M.; Kuo, C.; Ndjango, J.N.; Peeters, M.; Hahn, B.H.; Hugenholtz, P. Evolutionary relationships of wild hominids recapitulated by gut microbial communities. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlovski, A.; Doré, J.; Levenez, F.; Monique, A.; Brugère, J. Molecular evaluation of the human gut methanogenic archaeal microbiome reveals an age-associated increase in diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierenfeld, E.S.; Hintz, H.F.; Robertson, J.B.; Van Soest, P.J.; Oftedal, O.T. Utilization of bamboo by the giant panda. J. Nutr. 1982, 112, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2008, 453, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.A.; McNulty, N.P.; Guruge, J.L.; Gordon, J.I. IgA response to symbiotic bacteria as a mediator of gut homeostasis. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, E.K.; Pascal, K.E.; Mordechai, E.; Adelson, M.E.; Trama, J.P. Atopobium vaginae triggers an innate immune response in an in-vitro model of bacterial vaginosis. Microbes. Infect. 2008, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Meek, B.; Doi, Y.; Muramatsu, M; Chiba, T.; Honjo, T.; Fagarasan, S. Aberrant expansion of segmented filamentous bacteria in IgA-deficient gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay-Kumar, M.; Aitken, J.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Cullender, T.C.; Mwangi, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiome in mice lacking toll-like receptor 5. Science 2010, 328, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genc, M.R.; Vardhana, S.; Delaney, M.L.; Onderdonk, A.; Tuomala, R.; Norwitz, E.; Witkin, S.S. Relationship between a toll-like receptor-4 gene polymorphism, bacterial vaginosis-related flora and vaginal cytokine responses in pregnant women. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 116, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genc, M.R.; Witkin, S.S.; Delaney, M.L.; Paraskevas, L.R.; Tuomala, R.E.; Norwitz, E.R.; Onderdonk, A.B. A disproportionate increase in IL-1 beta over IL-1ra in the cervicovaginal secretions of pregnant women with altered vaginal microflora correlates with preterm birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Hamady, M.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R. The influence of sex, handedness, and washing on the diversity of hand surface bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17994–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, J.L. Effects of gender, age, and body mass index on gastrointestinal transit times. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodmansey, E.J. Intestinal bacteria and ageing. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, P.; Sudo, N.; Dinan, T.; Taylor, V.H.; Bienenstock, J. Mood and gut feelings. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezzi, S.; Ramadan, Z.; Martin, F.P.; Fay, L.B.; van Bladeren, P.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Kochhar, S. Human metabolic phenotypes link directly to specific dietary preferences in healthy individuals. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 4469–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.C.; Wheeler, P. The expensive-tissue hypothesis. Curr. Anthropol. 1995, 36, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Wolfaardt, G.M.; Lawrence, J.R. Do bacterial communities transcend Darwinism? Adv. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 15, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, R.V.; Bascompte, J. Complexity in ecological systems. In Self-Organization in Complex Ecosystems; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 42, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Traulsen, A.; Nowak, M.A. Evolution of cooperation by multilevel selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10952–10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijma, P.; Muir, W.M.; Van Arendonk, J.A.M. Multilevel Selection 1: Quantitative genetics of inheritance and response to selection. Genetics 2007, 175, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijma, P.; Muir, W.M.; Ellen, E.D.; Wolf, J.B.; Van Arendonk, J.A.M. Multilevel selection 2: Estimating the genetic parameters determining inheritance and response to selection. Genetics 2007, 175, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard Smith, J. Group selection and Kin selection. Nature 1964, 201, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttenberg, N.; Goldenfeld, N. Cascade of complexity in evolving predator-prey dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R. On the evolution of cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8742–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adami, C.; Ofria, C.; Collier, T.C. Evolution of biological complexity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4463–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, H.A. Adaptation and the cost of complexity. Evolution 2003, 54, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Knops, J.; Wedin, D.; Reich, P.; Ritchie, M.; Siemann, E. The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science 1997, 5330, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, J.S. Functional redundancy in ecology and conservation. Oikos 2002, 98, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.E.; Frank, K.A.; Mason, D.M.; Ulanowicz, R.E.; Taylor, W.W. Compartments revealed in food-web structure. Nature 2003, 426, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, P.B.; Cooper, T.F. Evolution of bacterial diversity and the origins of modularity. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patthy, L. Modular assembly of genes and the evolution of new functions. Genetica 2003, 118, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Mering, C.; Zdobnov, E.M.; Tsoka, S.; Ciccarelli, F.D.; Pereira-Leal, J.B.; Ouzounis, C.A.; Bork, P. Genome evolution reveals biochemical networks and functional modules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15428–15433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimer, A.; Borenstein, E.; Gophna, U.; Ruppin, E. The evolution of modularity in bacterial metabolic networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6976–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parter, M.; Kashtan, N.; Alon, U. Environmental variability and modularity of bacterial metabolic networks. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, D.J.; Homer, K.A.; Marsh, P.D.; Beighton, D. Metabolic cooperation in oral microbial communities during growth on mucin. Microbiology 1994, 140, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.H.; Molla, M.N.; Cantor, C.R.; Collins, J.J. Bacterial charity work leads to population-wide resistance. Nature 2010, 467, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, W.D. The genetical evolution of social behavior (parts I and II). J. Theor. Biol. 1964, 7, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivers, R.L. The evolution of reciprocal altruism. Quart. Rev. Biol. 1971, 46, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebeli, M.; Hauert, C.; Killingback, T. The evolutionary origin of cooperators and defectors. Science 2004, 306, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travisano, M.; Velicer, G.J. Strategies of microbial cheater control. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 12, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dethlefsen, L.; McFall-Ngai, M.; Relman, D.A. An ecological and evolutionary perspective on human-microbe mutualism and disease. Nature 2007, 449, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiome revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.K.; Kelly, S.A.; Legge, R.; Ma, F.; Low, S.J.; Kim, J.; Zhang, M.; Oh, P.L.; Nehrenberg, D.; Hua, K.; et al. Individuality in gut microbiome composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18933–18938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ridaura, V.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zella, G.C.; Hait, E.J.; Glavan, T.; Gevers, D.; Ward, D.V.; Kitts, C.L.; Korzenik, J.R. Distinct microbiome in pouchitis compared to healthy pouches in ulcerative colitis and familial adenomatous polyposis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeoman, C.J.; Chia, N.; Yildirim, S.; Miller, M.E.B.; Kent, A.; Stumpf, R.; Leigh, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; White, B.A.; Wilson, B.A. Towards an Evolutionary Model of Animal-Associated Microbiomes. Entropy 2011, 13, 570-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e13030570
Yeoman CJ, Chia N, Yildirim S, Miller MEB, Kent A, Stumpf R, Leigh SR, Nelson KE, White BA, Wilson BA. Towards an Evolutionary Model of Animal-Associated Microbiomes. Entropy. 2011; 13(3):570-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e13030570
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeoman, Carl J., Nicholas Chia, Suleyman Yildirim, Margret E. Berg Miller, Angela Kent, Rebecca Stumpf, Steven R. Leigh, Karen E. Nelson, Bryan A. White, and Brenda A. Wilson. 2011. "Towards an Evolutionary Model of Animal-Associated Microbiomes" Entropy 13, no. 3: 570-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e13030570
APA StyleYeoman, C. J., Chia, N., Yildirim, S., Miller, M. E. B., Kent, A., Stumpf, R., Leigh, S. R., Nelson, K. E., White, B. A., & Wilson, B. A. (2011). Towards an Evolutionary Model of Animal-Associated Microbiomes. Entropy, 13(3), 570-594. https://doi.org/10.3390/e13030570