Nonlinear Impact of Digital Service Innovation on Value Creation in Manufacturing Firms: Based on TOE Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
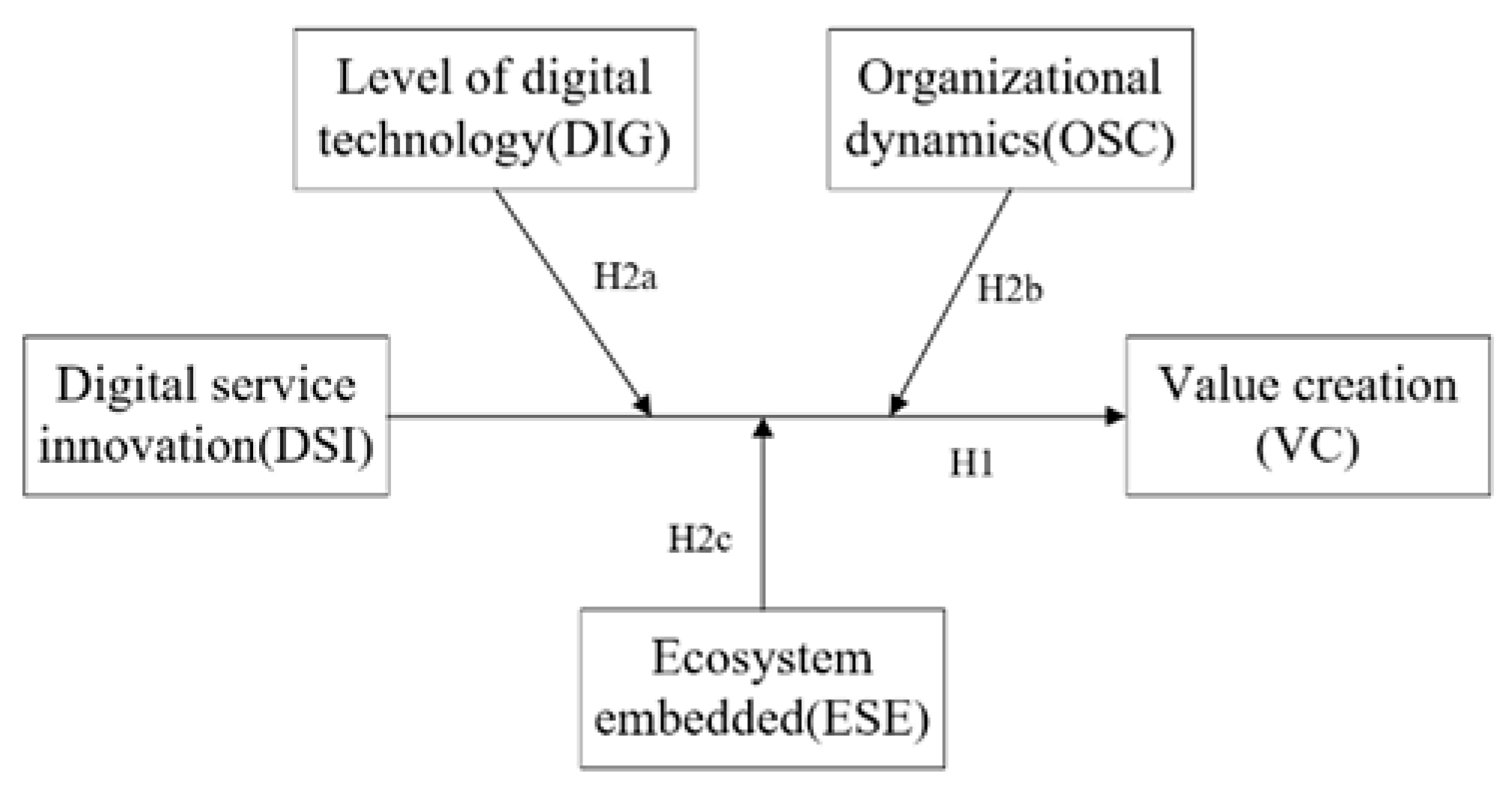
2. Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses
2.1. The Relationship Between Digital Service Innovation and Value Creation
2.2. Value Creation in Digital Service Innovation from a TOE Perspective
- (1)
- Technological dimension
- (2)
- Organizational Dimension
- (3)
- Environmental Dimension
3. Method
3.1. Model Building
3.1.1. Baseline Regression Model
3.1.2. Panel Threshold Effects Model
3.2. Variable Definition
3.2.1. Dependent Variable: Value Creation (VC)
3.2.2. Independent Variable: Digital Service Innovation (DSI)
3.2.3. Threshold Variables
- (1)
- Digital Technology Level (DIG)
- (2)
- Organizational Dynamic Capability (ODC)
- (3)
- Ecosystem Embeddedness (ESE)
3.2.4. Control Variable
3.3. Sample Selection and Data Sources
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Multicollinearity Diagnostics
4.2. Benchmark Regression and Robustness Tests
4.2.1. Baseline Regression Analysis
4.2.2. Robustness Tests
4.3. Threshold Effect Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Theoretical Contributions
5.3. Practical Implications
6. Conclusions
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opazo Basáez, M.; Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Bustinza, O.F.; Raddats, C. Guest Editorial: Digital Service Innovation: Ontology, Context and Theory. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, A.; Saba, M.; Baldovino, J.A. A Critical Review of NIO’s Business Model. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichfeldt, H.; Faullant, R. Performance Effects of Digital Technology Adoption and Product & Service Innovation—A Process-Industry Perspective. Technovation 2021, 105, 102275. [Google Scholar]
- Raddats, C.; Naik, P.; Ziaee Bigdeli, A. Creating Value in Servitization through Digital Service Innovations. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 104, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalkowski, C.; Wirtz, J.; Ehret, M. Digital Service Innovation in B2B Markets. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 280–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usai, A.; Fiano, F.; Messeni Petruzzelli, A.; Paoloni, P.; Farina Briamonte, M.; Orlando, B. Unveiling the Impact of the Adoption of Digital Technologies on Firms’ Innovation Performance. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Chen, J. The Non-Linear Impact of Digitalization on the Performance of SMEs: A Hypothesis Test Based on the Digitalization Paradox. Systems 2024, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrodegari, F.; Saccani, N. Business Models for the Service Transformation of Industrial Firms. Serv. Ind. J. 2017, 37, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Fehrer, J.A.; Wieland, H.; Nariswari, A. The Nature and Fundamental Elements of Digital Service Innovation. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklyar, A.; Kowalkowski, C.; Tronvoll, B.; Sörhammar, D. Organizing for Digital Servitization: A Service Ecosystem Perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Bustinza, O.F.; Parry, G.; Georgantzis, N. Servitization, Digitization and Supply Chain Interdependency. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 60, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohtamäki, M.; Parida, V.; Oghazi, P.; Gebauer, H.; Baines, T. Digital Servitization Business Models in Ecosystems: A Theory of the Firm. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.; Story, V.M.; Zolkiewski, J.; Nisha, N. Digital Service Innovation Challenges Faced during Servitization: A Multi-Level Perspective. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 202–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciasullo, M.V.; Polese, F.; Montera, R.; Carrubbo, L. A Digital Servitization Framework for Viable Manufacturing Companies. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2021, 36, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, R. The Role of Innovation Capabilities Upgradation and Digitalization in Value Co-Creation and PSS Innovation Performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2024, 123, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, L.; Matthyssens, P.; Kowalkowski, C. The Co-Evolution of Actor Engagement and Value Co-Creation on Digital Platforms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2025, 279, 109467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skålén, P.; Gummerus, J.; Von Koskull, C.; Magnusson, P.R. Exploring Value Propositions and Service Innovation: A Service-Dominant Logic Study. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhult, E.; Chirumalla, K.; Oghazi, P.; Parida, V. Value Logics for Service Innovation: Practice-Driven Implications for Service-Dominant Logic. Serv. Bus. 2018, 12, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilden, R.; Akaka, M.A.; Karpen, I.O.; Hohberger, J. The Evolution and Prospects of Service-Dominant Logic: An Investigation of Past, Present, and Future Research. J. Serv. Res. 2017, 20, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Gao, T.; Zhou, W. The Coordination Mechanism of Value Co-Creation between Developers and Users in Digital Innovation Ecosystems. Electron. Mark. 2024, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häikiö, J.; Koivumäki, T. Exploring Digital Service Innovation Process through Value Creation. J. Innov. Manag. 2016, 4, 96–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iden, J.; Eikebrokk, T.R.; Marrone, M. Process Reference Frameworks as Institutional Arrangements for Digital Service Innovation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 54, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo-Basáez, M.; Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Bustinza, O.F. Digital Service Innovation: A Paradigm Shift in Technological Innovation. J. Serv. Manag. 2022, 33, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, X.; Gu, H. How Technological, Organizational, and Environmental Factors Drive Enterprise Digital Innovation: Analysis Based on the Dynamic fsQCA Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, R.; Fei, J.; Khanal, R. Enhancing Digital Innovation Ecosystem Resilience through the Interplay of Organizational, Technological, and Environmental Factors: A Study of 31 Provinces in China Using NCA and fsQCA. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Gong, J.; Fan, W. Cost comparison between digital management and traditional management of cotton fields—Evidence from cotton fields in Xinjiang, China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmerar, T.Z.; Theodoropoulos, T.; Fevereiro, D.; Rosa, L.; Rodrigues, J.; Taleb, T.; Barone, P.; Giuliani, G.; Tserpes, K.; Cordeiro, L. Towards Establishing Intelligent Multi-Domain Edge Orchestration for Highly Distributed Immersive Services: A Virtual Touring Use Case. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 4223–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, T.L. Predictive Maintenance Using Artificial Intelligence in Critical Infrastructure: A Decision-Making Framework. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2024, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Dillon, T.; Rahayu, W. Edge Computing-Assisted IoT Framework with an Autoencoder for Fault Detection in Manufacturing Predictive Maintenance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek, T.; Öner, M.A.; Kunday, Ö.; Olcay, G.A. A Journey towards a Digital Platform Business Model: A Case Study in a Global Tech-Company. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 175, 121372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hassanain, E.; Alhamid, M.F.; Guizani, M. Blockchain and IoT-Based Cognitive Edge Framework for Sharing Economy Services in a Smart City. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18611–18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, D.; Kumar Singh, R.; Paul, J.; Hao, A.; Xu, S. Digital Platforms for Business-to-Business Markets: A Systematic Review and Future Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 137, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathupadi, K.; Achar, S.; Bhaskaran, S.V.; Faruqui, N.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Uddin, J. Edge-Cloud Synergy for AI-Enhanced Sensor Network Data: A Real-Time Predictive Maintenance Framework. Sensors 2024, 24, 7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijji, M.; Iqbal, R.; Kumar Pandey, A.; Doctor, F.; Karyotis, C.; Rajeh, W.; Alshehri, A.; Aradah, F. 6G Connected Vehicle Framework to Support Intelligent Road Maintenance Using Deep Learning Data Fusion. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 7726–7735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larian, H.; Safi-Esfahani, F. InTec: Integrated Things-Edge Computing: A Framework for Distributing Machine Learning Pipelines in Edge AI Systems. Computing 2025, 107, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, B.; Haja, D.; Németh, B.; Szalay, M.; Czentye, J.; Szabó, R.; Ullah, R.; Kim, B.-S.; Toka, L. Scalable Edge Cloud Platforms for IoT Services. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 170, 102785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmaged, M.G. Predicting E-Readiness at Firm-Level: An Analysis of Technological, Organizational and Environmental (TOE) Effects on e-Maintenance Readiness in Manufacturing Firms. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2014, 34, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.A.; Shorna, S.A.; Joy, Z.H.; Rahman, M.M. Data-Driven Transformation: Optimizing Enterprise Financial Management and Decision-Making with Big Data. Acad. J. Bus. Adm. Innov. Sustain. 2024, 4, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq Ali Khan, M.; Jamshed, H.; Bano, S.; Anwar, M.N. Big Data Management in Connected World of Internet of Things. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dutta, J.; Puthal, D. Advancing eHealth in Society 5.0: A Fuzzy Logic and Blockchain-Enhanced Framework for Integrating IoMT, Edge, and Cloud with AI. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 195710–195730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, G.; Capaldo, G.; Secundo, G.; Corvello, V. Revisiting the Idea of Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities for Digital Transformation. J. Knowl. Manag. 2024, 28, 532–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, G.; Luu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tang, T.T.T.; Pham, N.T. Entrepreneurial Leadership Fostering Service Innovation in the Hospitality Firms: The Roles of Knowledge Acquisition, Market-Sensing Capability and Competitive Intensity. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 36, 1143–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Singh, A.; Bryde, D.; Graham, G. Leveraging Digital Technology Capability for Circular Economy Innovation in the Food Products Supply Chain: A Mixed-Method Study. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2024, 71, 13997–14010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosalvas Vaca, C.A.; Manosalvas Vaca, L.; Guerrero Bejarano, M.A.; Silva Siu, D.R. Absorptive Capacity in Inbound and Outbound Open Innovation in Emerging Economy Context. Rev. Venez. Gerenc. 2023, 28, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccin, K.; Balestrin, A.; Volkmer Martins, B.; Bitencourt, C.C. Knowledge-Based Dynamic Capabilities: A Joint R&D Project in the French Semiconductor Industry. J. Knowl. Manag. 2019, 23, 439–465. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wen, S. The Relationship between Dynamic Capabilities and Global Value Chain Upgrading: The Mediating Role of Innovation Capability. J. Strategy Manag. 2024, 17, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idries, A.; Krogstie, J.; Rajasekharan, J. Dynamic Capabilities in Electrical Energy Digitalization: A Case from the Norwegian Ecosystem. Energies 2022, 15, 8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, P.M.D.; De-Pablos-Heredero, C.; Montes, J.L.; García, A. Impact of Dynamic Capabilities on Customer Satisfaction through Digital Transformation in the Automotive Sector. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, L.; Laghouag, A.A.; Ali Sahli, A.; Belaid, F. Impact of Entrepreneurial Orientation on Innovation Capability: The Mediating Role of Absorptive Capability and Organizational Learning Capabilities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazon, G.; Soares, T.C.; Birch, R.S.; Schneider, J.; Andrade Guerra, J.B.S.O.D.A. Green Absorptive Capacity, Green Dynamic Capabilities and Green Service Innovation: A Study in Brazilian Universities. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2023, 24, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Du, D.; Shi, W.; Hou, C.; Gui, Q. Dynamic Absorptive Capability and Innovation Performance: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, A.; Kamboj, S.; Sharma, N.; Pereira, V.; Salwan, P.; Chavan, M.; Pathak, A.A. Linking Dynamic Absorptive Capacity and Service Innovation for Born Global Service Firms: An Organization Innovation Lens Perspective. J. Int. Manag. 2023, 29, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.F.R.; Galina, S.V.R. Measuring Dynamic Absorptive Capacity in National Innovation Surveys. Manag. Decis. 2020, 59, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Horng, J.-S.; Chou, S.-F.; Yu, T.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lapuz, M.C.B. Discovery of the Mutual Relationships among Dynamic Capabilities and Intellectual Capital: The Moderating Roles of Service Innovation. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2023, 28, 1147–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medase, K.; Barasa, L. Absorptive Capacity, Marketing Capabilities, and Innovation Commercialisation in Nigeria. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 22, 790–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sellero, P.; Rosell-Martínez, J.; García-Vázquez, J.M. Absorptive Capacity from Foreign Direct Investment in Spanish Manufacturing Firms. Int. Bus. Rev. 2014, 23, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli Cevallos, G.; Guevara Sánchez, D. Dynamic Capabilities and Performance of Family Businesses in Emerging Economies. Bus. Theory Pract. 2024, 25, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, Y. Specialized Complementary Assets and Disruptive Innovation: Digital Capability and Ecosystem Embeddedness. Manag. Decis. 2024, 62, 3704–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Ruiz, J.C.; Ferreira, J.; Jardim-Goncalves, R.; Ortiz, Á. Relational Network of Innovation Ecosystems Generated by Digital Innovation Hubs: A Conceptual Framework for the Interaction Processes of DIHs from the Perspective of Collaboration within and between Their Relationship Levels. J. Intell. Manuf. 2025, 36, 1505–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Qin, S. Integrating Crowd-/Service-Sourcing into Digital Twin for Advanced Manufacturing Service Innovation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, B.W.; Müller, W.M. An Integrative Collaborative Ecosystem for Smart Cities—A Framework for Organizational Governance. Int. J. Public Adm. 2023, 46, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, C. How Can Small and Medium-Sized Manufacturing Enterprises Improve Green Innovation Performance through Innovation Ecosystems? Sustainability 2024, 16, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, X. Network Characteristics of Innovation Ecosystem: Knowledge Collaboration and Enterprise Innovation. Sci. Technol. Soc. 2023, 28, 488–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Li, M. Research on Collaborative Innovation Behavior of Enterprise Innovation Ecosystem under Evolutionary Game. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 206, 123508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubler, S.; Robert, J.; Hefnawy, A.; Framling, K.; Cherifi, C.; Bouras, A. Open IoT Ecosystem for Sporting Event Management. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 7064–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervás, R.; Francisco, V.; Concepción, E.; Sevilla, A.F.G.; Méndez, G. Creating an API Ecosystem for Assistive Technologies Oriented to Cognitive Disabilities. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 163224–163240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, C.Y.; Bogers, M.L.A.M.; Kapoor, R.; West, J. Focusing the Ecosystem Lens on Innovation Studies. Res. Policy 2024, 53, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnicka-Sycz, E.; Kaczyński, M.; Sycz, P. Innovative Ecosystems behind Regional Smart Specializations: The Role of Social, Cognitive and Geographical Proximity. J. Entrep. Manag. Innov. 2020, 16, 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asni, N.; Agustia, D. The Mediating Role of Financial Performance in the Relationship between Green Innovation and Firm Value: Evidence from ASEAN Countries. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2022, 25, 1328–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suseno, Y.; Laurell, C.; Sick, N. Assessing Value Creation in Digital Innovation Ecosystems: A Social Media Analytics Approach. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2018, 27, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawaststjerna, T.; Olander, H. Managing Digital Transformation in Digital Business Ecosystems. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 2021, 25, 2140003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyana, M.; Nurhayati, T.; Putri, E.R.P. Improvement of Marketing Performance: Role of Market Sensing, Digital Marketing, and Value Creation Ambidexterity. Contad. Adm. 2023, 69, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Selen, W. Dynamic Capability Building in Service Value Networks for Achieving Service Innovation. Decis. Sci. 2009, 40, 431–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Meng, Z.; Ma, N.; Wu, C.-H. Enterprise Digital Transformation, Dynamic Capabilities, and ESG Performance: Based on Data from Listed Chinese Companies. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2024, 32, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xue, X.; Zhu, H.; Huang, Q. Exploring the digitalization paradox: The impact of digital technology convergence on manufacturing firm performance. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2025, 36, 277–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean | SD | VC | DSI | Size | ATO | Cashflow | INV | FIXED | TobinQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VC | 0.032 | 0.099 | 1 | |||||||
| DSI | 0.035 | 0.026 | 0.096 *** | 1 | ||||||
| Size | 22.44 | 1.21 | 0.115 *** | 0.036 ** | 1 | |||||
| ATO | 0.66 | 0.44 | 0.169 *** | 0.0160 | 0.188 *** | 1 | ||||
| Cashflow | 0.053 | 0.067 | 0.415 *** | 0.103 *** | 0.038 ** | 0.166 *** | 1 | |||
| INV | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.004 | 0.054 *** | 0.139 *** | 0.113 *** | 0.161 *** | 1 | ||
| FIXED | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.011 | 0.198 *** | 0.00700 | 0.057 *** | 0.169 *** | 0.210 *** | 1 | |
| TobinQ | 1.96 | 1.27 | 0.151 *** | 0.030 * | 0.345 *** | 0.0140 | 0.206 *** | 0.086 *** | 0.066 *** | 1 |
| Variable | VC |
|---|---|
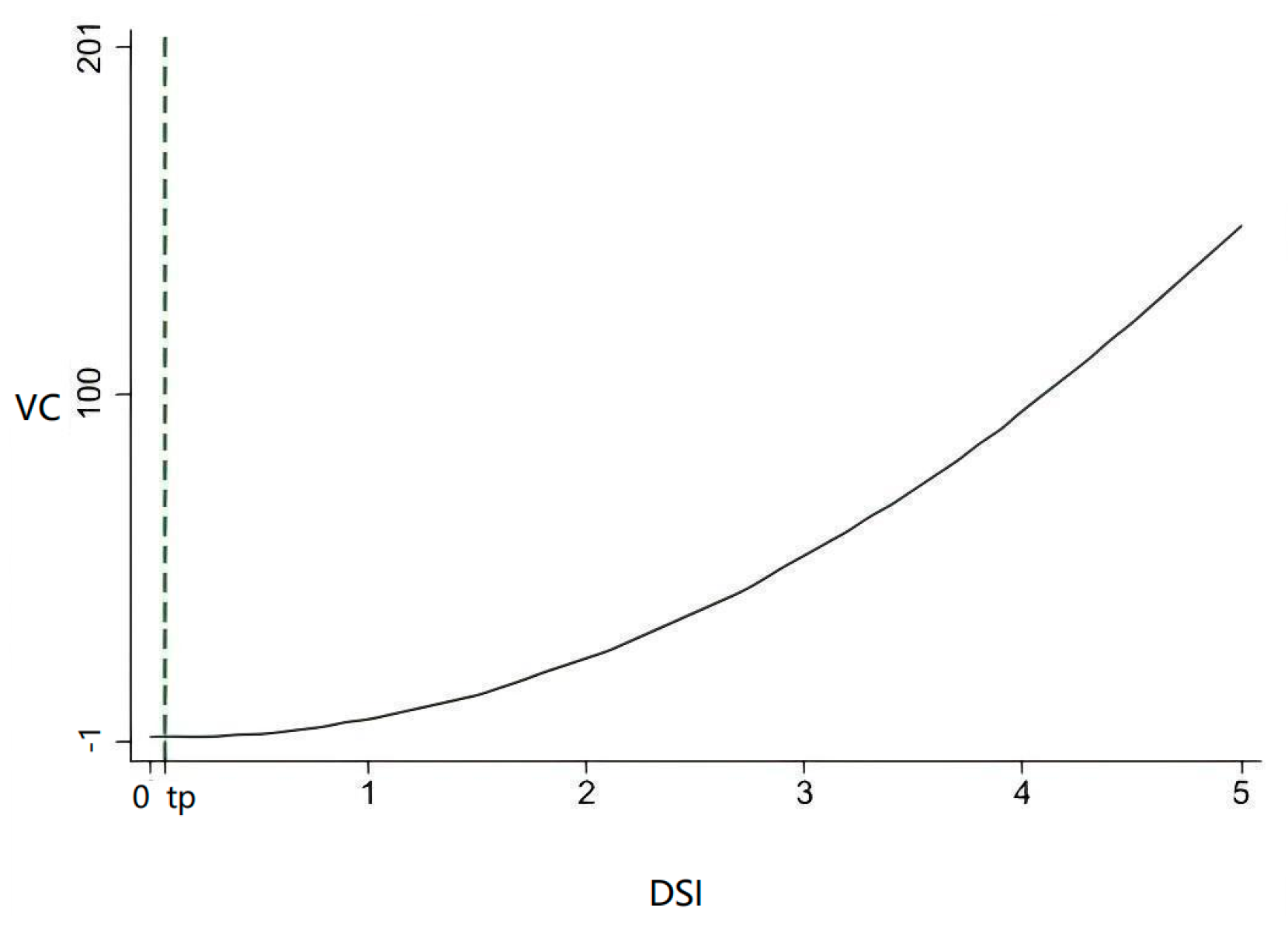
| DSI | −0.8801 ** |
| (−2.5538) | |
| DSI2 | 6.1482 ** |
| (2.4251) | |
| Size | 0.0362 *** |
| (7.2394) | |
| ATO | 0.0787 *** |
| (10.0107) | |
| Cashflow | 0.2435 *** |
| (9.7678) | |
| INV | 0.0468 |
| (1.4212) | |
| Fixed | −0.1643 *** |
| (−5.9812) | |
| TobinQ | 0.0065 *** |
| (3.6484) | |
| Individual effects | YES |
| Time effects | YES |
| cons | −0.9445 *** |
| (−7.5989) | |
| N | 3414 |
| r2_a | 0.4400 |
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |
|---|---|---|
| Interval | 0.0103 | 0.1443 |
| Slope | −0.7533 | 0.8943 |
| t-Value | −2.5509 | 2.1428 |
| p > |t| | 0.0054 | 0.01611 |
| Variable | Substitution of Explanatory Variables | Removing Extreme Values |
|---|---|---|
| ROE | VC | |
| DSI | 11.5007 ** | 6.1965 ** |
| (2.1952) | (2.0569) | |
| DSI2 | −1.5946 ** | −0.7612 ** |
| (−2.2391) | (−2.3281) | |
| Controls | YES | YES |
| Individual effects | YES | YES |
| Time effects | YES | YES |
| Cons | −2.4363 *** | −0.7078 *** |
| (−9.4857) | (−7.6405) | |
| N | 3414 | 3414 |
| r2_a | 0.4027 | 0.5191 |
| Variables | Nature of the Threshold | F | p | Threshold Value | Threshold Value | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 5% | 1% | ||||||
| ESE | Single threshold | 14.86 *** | 0.007 | 8.132 | 9.908 | 13.798 | 5.0000 | (3.0000, 9.0000) |
| Double threshold | 15.95 *** | 0.007 | 7.525 | 9.485 | 13.201 | 7.0000 | (6.0000, 8.0000) | |
| Triple threshold | 4.85 | 0.597 | 17.118 | 22.467 | 30.750 | 21.0000 | (·, ·) | |
| DIG | Single threshold | 3.59 | 0.720 | 11.550 | 13.348 | 16.480 | 27.0000 | (26.0000, 28.0000) |
| OSC | Single threshold | 14.34 ** | 0.020 | 9.445 | 11.923 | 14.947 | 0.6138 | (0.6106, 0.6177) |
| Double threshold | 2.36 | 0.853 | 9.164 | 11.083 | 15.129 | 0.3887 | (0.3865, 0.3913) | |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| ESE | OSG | |
| ESE ≤ 5 | −0.0017 | |
| (−0.0116) | ||
| 5 < ESE ≤ 7 | −0.8208 *** | |
| (−3.1746) | ||
| ESE > 7 | 0.4092 * | |
| (1.8912) | ||
| OSC ≤ 0.3887 | 0.0395 | |
| (0.3649) | ||
| OSC > 0.3887 | −0.4215 *** | |
| (−2.6074) | ||
| Controls | YES | YES |
| Cons | YES | YES |
| N | 3414 | 3414 |
| r2_a | 0.0195 | 0.0686 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Li, Z. Nonlinear Impact of Digital Service Innovation on Value Creation in Manufacturing Firms: Based on TOE Framework. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040263
Peng Y, Li Z. Nonlinear Impact of Digital Service Innovation on Value Creation in Manufacturing Firms: Based on TOE Framework. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research. 2025; 20(4):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040263
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yongtao, and Zheng Li. 2025. "Nonlinear Impact of Digital Service Innovation on Value Creation in Manufacturing Firms: Based on TOE Framework" Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 20, no. 4: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040263
APA StylePeng, Y., & Li, Z. (2025). Nonlinear Impact of Digital Service Innovation on Value Creation in Manufacturing Firms: Based on TOE Framework. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 20(4), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040263






