The Effect of Digital Service Innovation on Strengthening Supply Chain Networks Against Disruptions: A Network Embedding Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Hypothesis
2.1. Network Embeddedness
2.2. The Relationship Between DSI and RRI
2.3. The Mediating Effect of RE
2.4. The Mediating Effect of Structural Embeddedness
2.5. The Moderating Effect of ITSC
3. Method
3.1. Measurement
3.1.1. Dependent Variable
3.1.2. Independent Variable
3.1.3. Mediating Variables
Relational Embedding
Structural Embedding
3.1.4. Moderating Variable
3.1.5. Control Variable
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis
3.3.1. CMV and Dimensional Consistency Test
3.3.2. Reliability and Validity
3.3.3. Variable Description and Correlation
4. Results
4.1. Main Effects and Mediation Effects Regression Analysis
4.2. Regression Analysis of Moderating Effects
4.3. Analysis of Moderated–Mediation Effects
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Management Implications
5.3. Limitations
5.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSI | Digital Service Innovation |
| NE | Network embeddedness |
| RE | Relational embedding |
| SE | Structural embedding |
| RRI | Resilience to Resist Interruption |
| ITSC | IT Support Capabilities |
References
- Sun, B.; Xi, Y. Supply chain concentration, digitalization and servitization of manufacturing firms. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2025, 36, 112–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opazo-Basáez, M.; Vendrell-Herrero, F.; Bustinza, O.F. Digital service innovation: A paradigm shift in technological innovation. J. Serv. Manag. 2022, 33, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, M.; Araujo, L. Beyond the service factory: Service innovation in manufacturing supply networks. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2013, 42, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freije, I.; de la Calle, A.; Ugarte, J.V. Role of supply chain integration in the product innovation capability of servitized manufacturing companies. Technovation 2022, 118, 102216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abourokbah, S.H.; Mashat, R.M.; Salam, M.A. Role of absorptive capacity, digital capability, agility, and resilience in supply chain innovation performance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, D.; Thongpapanl, N.; Voronov, M. Sustainability in the face of institutional adversity: Market turbulence, network embeddedness, and innovative orientation. J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 148, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. An Empirical Study on the Innovation Performance of Regional (Enterprise) by Dual Network Embedding in E-commerce Environment. Int. J. Front. Sociol. 2021, 3, 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Iqbal, S.; Anwar, F.; Akhtar, S.; Khan, M.A.S.; Wang, W. Network embeddedness and innovation performance: A mediation moderation analysis using PLS-SEM. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2021, 27, 1590–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis-Sramek, B.; Omar, A.; Germain, R. Leveraging supply chain orientation for global supplier responsiveness: The impact of institutional distance. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2019, 30, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesböck, F.; Hess, T. Digital innovations: Embedding in organizations. Electron. Mark. 2020, 30, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Huang, H.-L.; Sung, S.-F. Alignment Effect between Electronic Business Strategy and Information Technology Capabilities on Value Creation in Employing Industrial Internet of Things. Sens. Mater. 2021, 33, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M. Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. Am. J. Sociol. 1985, 91, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzi, B. Social structure and competition in interfirm networks: The paradox of embeddedness. In The Sociology of Economic Life; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 213–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Gu, F.F. Reconsidering network embeddedness: Effects on different forms of opportunism. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 131, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trada, S.; Goyal, V. Tripartite role of communications in channel relationships: Mitigating exchange hazards, reducing opportunism, and curtailing its ill effects on relationship performance. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 85, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, N.; Liao, H.; Wang, Q. Multiple network embedding, green knowledge integration and green supply chain performance—Investigation based on agglomeration scenario. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, Z.; Fernandes, K.; Xiong, Y. Dual networks: How does knowledge network embeddedness affect firms’ supply chain learning? Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2023, 43, 1277–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Zheng, M.; Shen, Y. The effect of relational embeddedness on transparency in supply chain networks: The moderating role of digitalization. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2024, 44, 1621–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Review of quantitative methods for supply chain resilience analysis. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 125, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarov, S.Y.; Holcomb, M.C. Understanding the concept of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2009, 20, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalahmadi, M.; Parast, M.M. A review of the literature on the principles of enterprise and supply chain resilience: Major findings and directions for future research. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 171, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A. Dancing the supply chain: Toward transformative supply chain management. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2021, 57, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Werder, K.; Maedche, A. Novice digital service designers’ decision-making with decision aids—A comparison of taxonomy and tags. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 137, 113367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, A.; Bergvall-Kåreborn, B.; Elragal, A. Digital service innovation enabled by big data analytics-A review and the way forward. 2017. Available online: http://www.hicss.hawaii.edu (accessed on 8 March 2017).
- Rabetino, R.; Kohtamäki, M.; Huikkola, T. Digital service innovation (DSI): A multidisciplinary (re) view of its origins and progress using bibliometric and text mining methods. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, J. Effect of intelligent logistics policy on shareholder value: Evidence from Chinese logistics companies. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 137, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Viability of intertwined supply networks: Extending the supply chain resilience angles towards survivability. A position paper motivated by COVID-19 outbreak. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 2904–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troilo, G.; De Luca, L.M.; Guenzi, P. Linking data-rich environments with service innovation in incumbent firms: A conceptual framework and research propositions. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2017, 34, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, H.; Savimäki, E.; Laukkanen, T. Fostering B2B sales with customer big data analytics. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 86, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, D.; Parida, V.; Kohtamäki, M.; Wincent, J. An agile co-creation process for digital servitization: A micro-service innovation approach. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 112, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohtamäki, M.; Parida, V.; Oghazi, P.; Gebauer, H.; Baines, T. Digital servitization business models in ecosystems: A theory of the firm. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönroos, C.; Voima, P. Critical service logic: Making sense of value creation and co-creation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2013, 41, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto Setzke, D.; Riasanow, T.; Böhm, M.; Krcmar, H. Pathways to digital service innovation: The role of digital transformation strategies in established organizations. Inf. Syst. Front. 2023, 25, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig-Thurau, T.; Aliman, D.N.; Herting, A.M.; Cziehso, G.P.; Linder, M.; Kübler, R.V. Social interactions in the metaverse: Framework, initial evidence, and research roadmap. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2023, 51, 889–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylén, D.; Holmström, J. Digital innovation strategy: A framework for diagnosing and improving digital product and service innovation. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A.; Durach, C.F. Two Perspectives on Supply Chain Resilience; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 42, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Liao, Z. Inter-firm dependence, inter-firm trust, and operational performance: The mediating effect of e-business integration. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaga, G.N.; Whipple, J.M. Relationship quality and performance outcomes: Achieving a sustainable competitive advantage. J. Bus. Logist. 2011, 32, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iden, J.; Eikebrokk, T.R.; Marrone, M. Process reference frameworks as institutional arrangements for digital service innovation. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 54, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, G.M.; Houston, M.B.; Jiang, B.; Lamberton, C.; Rindfleisch, A.; Zervas, G. Marketing in the sharing economy. J. Mark. 2019, 83, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mors, M.L. Innovation in a global consulting firm: When the problem is too much diversity. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 841–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebjamnia, N.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Sustainable tire closed-loop supply chain network design: Hybrid metaheuristic algorithms for large-scale networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X. The influence of platform service innovation on value co-creation activities and the network effect. J. Serv. Manag. 2017, 28, 348–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Govindan, K.; Kannan, D.; Mangla, S.K.; Garg, C.P. An integrated framework for sustainable supplier selection and evaluation in supply chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Fehrer, J.A.; Wieland, H.; Nariswari, A. The nature and fundamental elements of digital service innovation. J. Serv. Manag. 2024, 35, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nevo, S.; Benitez-Amado, J.; Kou, G. IT capabilities and product innovation performance: The roles of corporate entrepreneurship and competitive intensity. Inf. Manag. 2015, 52, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, L.; Uwizeyemungu, S.; Fabi, B.; St-Pierre, J. IT capabilities for product innovation in SMEs: A configurational approach. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 19, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yao, Q.; Boadu, F.; Xie, Y. Distributed innovation, digital entrepreneurial opportunity, IT-enabled capabilities, and enterprises’ digital innovation performance: A moderated mediating model. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2023, 26, 1106–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.M.; Herhausen, D.; Troilo, G.; Rossi, A. How and when do big data investments pay off? The role of marketing affordances and service innovation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 790–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroudi, P.; Gupta, S.; Nazarian, A.; Duda, M. Digital technology and marketing management capability: Achieving growth in SMEs. Qual. Mark. Res. Int. J. 2017, 20, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, W.; Wei, L.; Yang, S. How can digital collaboration capability boost service innovation? Evidence from the information technology industry. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 182, 121830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.F.; Laurindo, F.J.; Spínola, M.M.; Gonçalves, R.F.; Mattos, C.A. The strategic use of artificial intelligence in the digital era: Systematic literature review and future research directions. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 57, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hartley, J.L. Guanxi, IT systems, and innovation capability: The moderating role of proactiveness. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 90, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S. The distinctive domain of entrepreneurship research. In Seminal Ideas for the Next Twenty-Five Years of Advances; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2019; pp. 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Saldanha, T.J.; Mithas, S.; Krishnan, M.S. Leveraging customer involvement for fueling innovation. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadegan, A.; Dooley, K. A typology of supply network resilience strategies: Complex collaborations in a complex world. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2021, 57, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.-q.; Yuan, X.-j.; Deng, D.-s. Research on supply network resilience considering the ripple effect with collaboration. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 5553–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estay, D.A.S.; Sahay, R.; Barfod, M.B.; Jensen, C.D. A systematic review of cyber-resilience assessment frameworks. Comput. Secur. 2020, 97, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annarelli, A.; Palombi, G. Digitalization capabilities for sustainable cyber resilience: A conceptual framework. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Coreynen, W.; Matthyssens, P.; Shen, L. Platform-based servitization and business model adaptation by established manufacturers. Technovation 2022, 118, 102222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. An environmental supply chain network under uncertainty. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 542, 123478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Item | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | 0.023 | 0.890 | 0.203 | 0.124 | 0.120 |
| Q2 | −0.004 | 0.880 | 0.232 | 0.098 | 0.097 |
| Q3 | 0.000 | 0.910 | 0.218 | 0.106 | 0.088 |
| Q4 | −0.082 | 0.073 | 0.120 | 0.107 | 0.873 |
| Q5 | −0.083 | 0.110 | 0.107 | 0.103 | 0.885 |
| Q6 | −0.016 | 0.099 | 0.121 | 0.076 | 0.887 |
| Q7 | 0.028 | 0.154 | 0.132 | 0.885 | 0.106 |
| Q8 | 0.013 | 0.040 | 0.156 | 0.890 | 0.087 |
| Q9 | −0.036 | 0.121 | 0.179 | 0.867 | 0.099 |
| Q10 | 0.891 | 0.042 | 0.005 | 0.012 | −0.031 |
| Q11 | 0.846 | −0.009 | 0.058 | −0.031 | −0.049 |
| Q12 | 0.883 | 0.012 | 0.013 | −0.025 | −0.047 |
| Q13 | 0.869 | −0.027 | −0.039 | 0.049 | −0.057 |
| Q14 | −0.022 | 0.263 | 0.860 | 0.178 | 0.113 |
| Q15 | 0.018 | 0.240 | 0.869 | 0.201 | 0.118 |
| Q16 | 0.047 | 0.191 | 0.860 | 0.145 | 0.165 |
| Variables | Factor Loading | KMO | Cronbach’s α | CR | AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSI | DSI 1 | 0.929 | 0.754 | 0.924 | 0.952 | 0.868 |
| DSI 2 | 0.920 | |||||
| DSI 3 | 0.946 | |||||
| RE | RE 1 | 0.894 | 0.746 | 0.885 | 0.928 | 0.812 |
| RE 2 | 0.908 | |||||
| RE 3 | 0.901 | |||||
| SE | SE 1 | 0.914 | 0.748 | 0.891 | 0.932 | 0.821 |
| SE 2 | 0.904 | |||||
| SE 3 | 0.900 | |||||
| ITSC | ITSC 1 | 0.892 | 0.835 | 0.897 | 0.928 | 0.764 |
| ITSC 2 | 0.849 | |||||
| ITSC 3 | 0.885 | |||||
| ITSC 4 | 0.870 | |||||
| RRI | RRI 1 | 0.924 | 0.751 | 0.910 | 0.943 | 0.847 |
| RRI 2 | 0.932 | |||||
| RRI 3 | 0.905 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Size | 1 | ||||||||||
| 2. Ownership | 0.211 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 3. Age | 0.258 ** | 0.187 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 4. FS | 0.219 ** | 0.252 ** | 0.278 ** | 1 | |||||||
| 5. RD | 0.062 | −0.154 ** | 0.030 | 0.016 | 1 | ||||||
| 6. NP | −0.068 | −0.047 | −0.064 | −0.023 | 0.089 | 1 | |||||
| 7. DSI | 0.144 ** | −0.109 * | −0.024 | −0.206 ** | 0.191 ** | 0.113 * | 1 | ||||
| 8. RE | 0.316 ** | 0.101 | 0.163 ** | 0.097 | 0.241 ** | −0.032 | 0.249 ** | 1 | |||
| 9. SE | 0.290 ** | 0.089 | 0.154 ** | −0.004 | 0.182 ** | 0.068 | 0.278 ** | 0.242 ** | 1 | ||
| 10. ITSC | −0.015 | −0.064 | −0.117 * | −0.075 | −0.095 | −0.036 | 0.009 | −0.115 * | 0.000 | 1 | |
| 11. RRI | 0.112 * | −0.219 ** | −0.080 | −0.249 ** | 0.471 ** | 0.055 | 0.498 ** | 0.306 ** | 0.390 ** | 0.019 | 1 |
| 12. Mean | 3.16 | 0.61 | 2.73 | 2.68 | 2.90 | 3.02 | 3.94 | 3.87 | 3.94 | 4.16 | 3.79 |
| 13. SD | 1.47 | 0.49 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.49 | 1.42 | 1.91 | 1.81 | 1.85 | 1.66 | 1.71 |
| DV: RRI M1–M4 | DV: RE M5–M6 | DV: SE M7–M8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | |
| Size | 0.177 (0.056) | 0.102 (0.052) * | 0.068 (0.053) | 0.046 (0.051) | 0.267 (0.066) *** | 0.225 (0.066) *** | 0.268 (0.069) *** | 0.224 (0.068) *** |
| Ownership | −0.115 (0.170) * | −0.091 (0.155) * | −0.103 (0.153) * | −0.112 (0.148) ** | 0.067 (0.2) | 0.079 (0.196) | 0.071 (0.207) | 0.084 (0.203) |
| Age | −0.047 (0.057) | −0.047 (0.052) | −0.058 (0.051) | −0.073 (0.05) | 0.074 (0.067) | 0.074 (0.066) | 0.103 (0.07) | 0.102 (0.068) |
| FS | −0.253 (0.056) *** | −0.166 (0.052) *** | −0.173 (0.052) *** | −0.151 (0.05) *** | −0.003 (0.066) | 0.045 (0.066) | −0.11 (0.068) * | −0.059 (0.068) |
| RD | 0.446 (0.053) *** | 0.387 (0.049) *** | 0.356 (0.05) *** | 0.353 (0.048) *** | 0.235 (0.063) *** | 0.202 (0.063) *** | 0.168 (0.065) ** | 0.133 (0.065) * |
| NP | 0.013 (0.055) | −0.025 (0.051) | −0.018 (0.05) | −0.039 (0.048) | −0.027 (0.065) | −0.048 (0.064) | 0.078 (0.067) | 0.056 (0.066) |
| DSI | 0.367 (0.04) *** | 0.336 (0.04) *** | 0.314 (0.039) *** | 0.204 (0.050) *** | 0.213 (0.052) *** | |||
| RE | 0.151 (0.043) *** | |||||||
| SE | 0.249 (0.04) *** | |||||||
| R2 | 0.310 | 0.428 | 0.445 | 0.479 | 0.145 | 0.179 | 0.120 | 0.158 |
| F | 26.103 *** | 36.818 *** | 34.598 *** | 39.424 *** | 10.469 *** | 11.456 *** | 8.631 *** | 9.987 *** |
| Types | Effect | Standard Error | p | LLCI | ULCI | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediator | Main Effects | 0.329 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.251 | 0.407 | 100% |
| RE | Direct effect | 0.301 | 0.040 | <0.001 | 0.223 | 0.380 | 91.49% |
| Indirect effect | 0.028 | 0.011 | <0.001 | 0.011 | 0.054 | 8.51% | |
| SE | Direct effect | 0.281 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.205 | 0.358 | 85.41% |
| Indirect effect | 0.048 | 0.015 | <0.001 | 0.024 | 0.083 | 14.59% |
| Variables | DV: RE M9–M10 | DV: SE M11–M12 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M9 | M10 | M11 | M12 | |
| Size | 0.228 (0.066) *** | 0.225 (0.064) *** | 0.223 (0.069) *** | 0.221 (0.067) *** |
| Ownership | 0.075 (0.196) | 0.056 (0.192) | 0.086 (0.203) | 0.07 (0.2) |
| Age | 0.065 (0.066) | 0.071 (0.064) | 0.105 (0.069) | 0.11 (0.067) * |
| FS | 0.042 (0.066) | 0.068 (0.065) | −0.058 (0.069) | −0.036 (0.068) |
| RD | 0.193 (0.063) *** | 0.142 (0.063) ** | 0.136 (0.065) ** | 0.092 (0.066) |
| NP | −0.051 (0.064) | −0.047 (0.062) | 0.057 (0.066) | 0.061 (0.065) |
| DSI | 0.204 (0.05) *** | 0.204 (0.049) *** | 0.213 (0.052) *** | 0.213 (0.051) *** |
| ITSC | −0.082 (0.055) | −0.103 (0.054) * | 0.03 (0.057) | 0.012 (0.056) |
| DSI × ITSC | 0.214 (0.028) *** | 0.184 (0.029) *** | ||
| R2 | 0.183 | 0.225 | 0.156 | 0.186 |
| F | 10.406 *** | 11.782 *** | 8.765 *** | 9.504 *** |
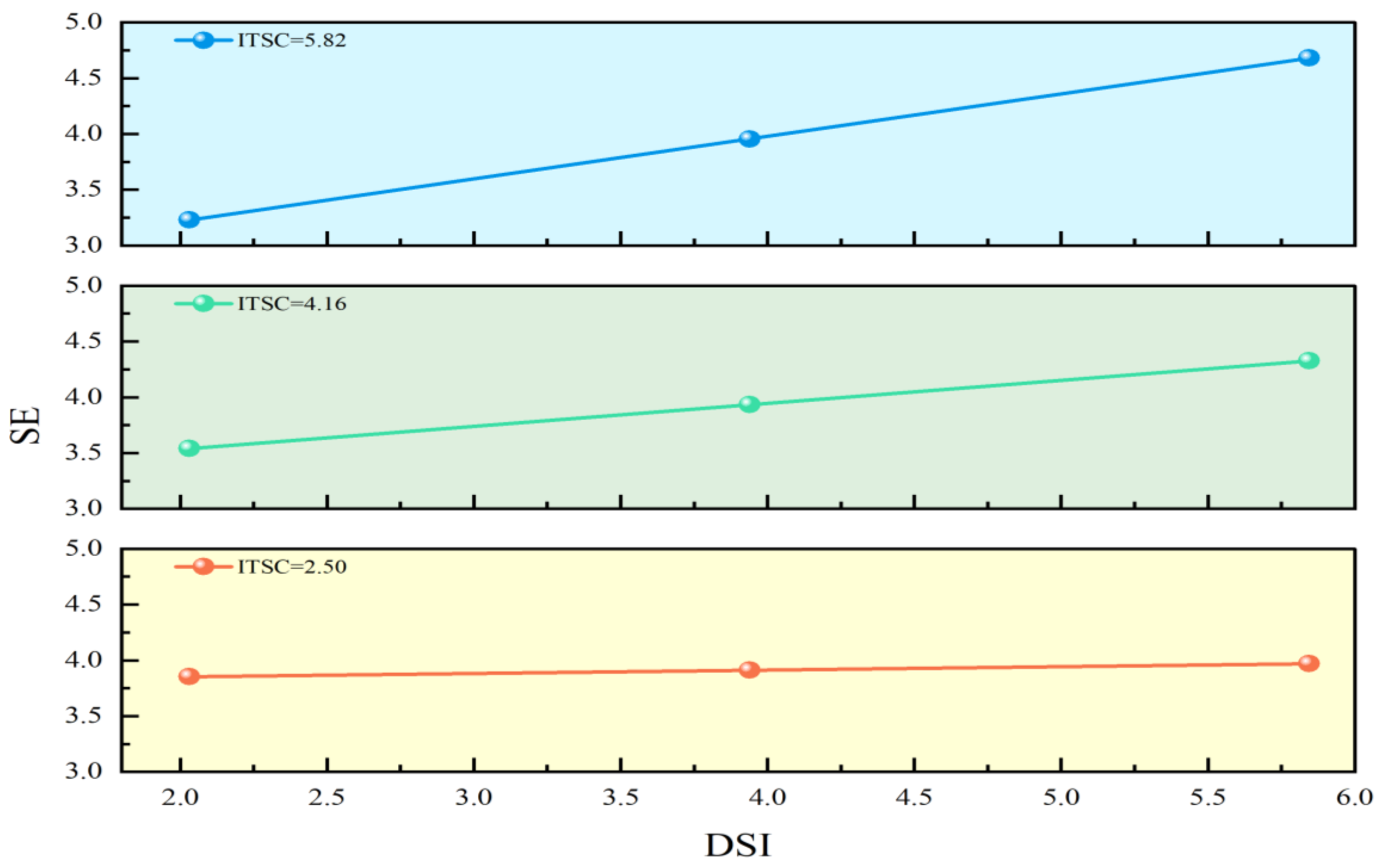
| Mediator | ITSC | Effect | SE | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE | 2.503 | −0.001 | 0.011 | −0.027 | 0.020 |
| 4.159 | 0.028 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.054 | |
| 5.816 | 0.056 | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.104 | |
| Moderated mediation | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.037 | |
| SE | 2.502 | 0.007 | 0.018 | −0.025 | 0.046 |
| 4.159 | 0.047 | 0.015 | 0.024 | 0.083 | |
| 5.816 | 0.088 | 0.024 | 0.048 | 0.145 | |
| Moderated mediation | 0.024 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.044 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, Y.; Xu, M.; Abruquah, L.A.; Li, X. The Effect of Digital Service Innovation on Strengthening Supply Chain Networks Against Disruptions: A Network Embedding Approach. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20030164
Gou Y, Xu M, Abruquah LA, Li X. The Effect of Digital Service Innovation on Strengthening Supply Chain Networks Against Disruptions: A Network Embedding Approach. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research. 2025; 20(3):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20030164
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Yanjie, Maozeng Xu, Lucille Aba Abruquah, and Xudong Li. 2025. "The Effect of Digital Service Innovation on Strengthening Supply Chain Networks Against Disruptions: A Network Embedding Approach" Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 20, no. 3: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20030164
APA StyleGou, Y., Xu, M., Abruquah, L. A., & Li, X. (2025). The Effect of Digital Service Innovation on Strengthening Supply Chain Networks Against Disruptions: A Network Embedding Approach. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 20(3), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20030164







