Abstract
The prediction of bankruptcy risk poses a formidable challenge in the fields of economics and finance, particularly within the healthcare industry, where it carries significant economic implications. The burgeoning field of healthcare electronic commerce, continuously evolving through technological advancements and changing regulations, introduces additional layers of complexity. We collected financial data from 1265 U.S. healthcare industries to predict bankruptcy based on 40 financial ratios using multi-class classification machine learning models across various industry subsectors and market capitalizations. The exceptionally high post-tuning accuracy rates, exceeding 90%, along with high-performance metrics solidified the robustness and exceptional predictive capability of the gradient boosting model in bankruptcy prediction. The results also demonstrate the power and sensitivity of financial ratios in predicting bankruptcy based on financial ratios. The Altman models highlight the return on investment (ROI) as the most important parameter for predicting bankruptcy risk in healthcare industries. The Ohlson model identifies return on assets (ROA) as an important ratio specifically for predicting bankruptcy risk within industry subsectors. Furthermore, it underscores the significance of both ROA and the enterprise value to earnings before interest and taxes (EV/EBIT) ratios as important parameters for predicting bankruptcy based on market capitalization. Recognizing these ratios enables proactive decision making that enhances resilience. Our findings contribute to informed risk management strategies, allowing for better management of healthcare industries in crises like those experienced in 2022 and even on a global scale.
1. Introduction
Bankruptcy risk analysis, a critical domain in economic and financial research, presents significant challenges due to the varied benchmarks across industries and their complex interactions with diverse factors in finance, law, and economics [1,2]. Particularly within the healthcare sector, these challenges are magnified due to their substantial influence on public health and socio-economic stability. This sector not only plays a pivotal role in employment and serves as a key focus for investment but also substantially impacts the broader medical and financial ecosystems through the repercussions of hospital and health insurance provider bankruptcies [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Moreover, the correlation between healthcare sector financial distress and personal bankruptcies, notably driven by uninsured medical expenses, underscores this issue’s severity; nearly two-thirds of all U.S. personal bankruptcies are medically related [7,8]. Additionally, the interaction between instabilities in the healthcare industry bankruptcies has been recognized [11]. In this context, the burgeoning field of electronic commerce (e-commerce) emerges as a significant factor. The evolution and integration of e-commerce have revolutionized investment patterns and financial stability across many sectors, including healthcare. E-commerce platforms enhance the accessibility and distribution of healthcare services and products, thereby influencing the financial dynamics of healthcare institutions. These platforms also affect consumer behavior and spending on health services, potentially increasing the financial risk for healthcare providers that fail to adapt to digital marketplaces. Furthermore, e-commerce introduces new regulatory challenges and competitive pressures that can exacerbate financial instability in the healthcare sector. As e-commerce continues to expand, its impact on the stock market dynamics that underpin the financial health of medical entities cannot be overlooked. Therefore, the interplay between e-commerce and healthcare financial stability is critical for predicting potential bankruptcies in this sector. This study aims to address this nuanced landscape by focusing on the bankruptcy risk in U.S. medical and healthcare entities, influenced by stock market dynamics.
The year 2022 presents a unique context for analyzing bankruptcy risk in the U.S. healthcare industries, characterized by challenging economic conditions. This period saw a bear market, record-high inflation levels not seen in over four decades, and a marked increase in interest rates [Federal Reserve, 2023], all unfolding alongside the ongoing recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. Such conditions precipitated significant market volatility, acutely impacting growth-sensitive sectors, notably medical and healthcare. Our research is positioned to delve into bankruptcy risk within this particular timeframe, aiming to provide healthcare stakeholders with critical insights. By analyzing this period, we intend to alert them to potential financial instabilities and propose preemptive strategies to effectively navigate and mitigate bankruptcy risks during comparable periods of economic adversity.
2. Literature Review
Given the capability of financial ratios to reflect critical elements of a company’s financial status, several studies have investigated the use of these ratios in assessing bankruptcy risk, particularly in sectors outside of medical and healthcare. These studies typically employ traditional statistical methods, such as discriminant and regression analysis, to analyze bankruptcy risks. Supriyanto et al. conducted an investigation into financial distress in mining companies, with a specific focus on financial ratios [12]. Similarly, Amalia et al. examined financial ratios to predict company bankruptcy in the cigarette industry [13]. Lee et al. explored the financial ratios of savings banks in relation to bankruptcy through quantitative empirical analysis using statistical models [14]. Additionally, Tian et al. studied bankruptcy prediction across international markets with financial ratios by employing adaptive statistical techniques and a discrete hazard statistical model [15]. Traditional statistical methods can generally identify the significance and relationship of each individual parameter, such as financial ratios, with bankruptcy. Nevertheless, given the multi-factorial nature of bankruptcy, it is imperative to consider the impact of all financial ratios simultaneously for bankruptcy prediction. Moreover, the intricate interconnections between these ratios should also be taken into account during this predictive analysis. Therefore, these traditional statistical analyses may not be fully capable of discerning the intricate interplay between financial parameters and bankruptcy [16].
Artificial intelligence and machine learning methods have demonstrated a greater aptitude than traditional statistical analysis for addressing concerns in evaluating bankruptcy risk. Having emerged as pivotal technologies in the fourth industrial revolution [17,18], these methods enable the development of sophisticated models that consider both the multifaceted roles of financial ratios and the interrelationships between them. Recent studies have delved into the application of diverse machine learning algorithms to ascertain which models are most effective in predicting bankruptcy and financial distress [19,20,21,22]. These investigations aim to enhance the accuracy and reliability of bankruptcy predictions by leveraging the advanced analytical capabilities of machine learning. Additionally, some of these studies have applied these models to assess the dynamics of financial distress and bankruptcy in non-healthcare industries across various subsectors [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Carmona et al. implemented innovative machine learning algorithms to predict bankruptcy in French firms [36]. They assessed the prediction of business financial distress and bankruptcy in French firms using a novel machine learning model. In another study, they proposed an enhanced gradient boosting machine learning algorithm for bankruptcy prediction, and their experimental results substantiated its superiority in comparison to traditional feature selection methods [37]. Lombardo et al. contributed to the prediction of corporate bankruptcy by utilizing machine learning algorithms that estimate survival probabilities and predict defaults, employing time-series accounting data [38]. They also suggested an innovative method capable of detecting emerging risks within particular sectors and industries, thus aiding in the identification of market segments where firms remain undisturbed by disruptions [39]. Bragoli et al. also developed a predictive model that classified solvent and bankrupt firms, utilizing the enhanced gradient boosting machine learning algorithm [40].
Some studies have concentrated on predicting bankruptcy risk during specific critical time periods characterized by economic crises. This focus is crucial as economic downturns significantly alter the financial landscape, thereby impacting the accuracy and relevance of bankruptcy prediction models. Liu et al. focused on high-tech and startup businesses in Europe after the 2008 economic crisis, emphasizing the predictive capabilities of machine learning, which could potentially even contribute to preventing failures or acquisitions [41]. Papík et al. explored the prediction of financial distress and bankruptcy risk among small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) during the COVID-19 crisis using machine learning [42]. They advised against the use of qualitative indicators in SME prediction models and noted a shift in the relationship with historical financial data between 2019 and 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Liu et al. explored the influence of public health crises on the economic prospects of SMEs by utilizing machine learning analysis [43]. Their investigation into the predictive aspects of credit default risks for SMEs post COVID-19 underscores the effectiveness of machine learning methods in assessing and controlling credit risk, thereby elucidating its impact on SMEs.
3. Objective
Previous research has laid important groundwork in bankruptcy risk analysis; however, unresolved issues persist, and new challenges have emerged, particularly in the context of the economic climate of 2022 [1,38]. There is considerable uncertainty regarding the most effective financial metrics for predicting bankruptcy in the healthcare industry. Notably, the application of bankruptcy prediction within the healthcare industry, especially through machine learning techniques, remains underexplored. This study innovatively focuses on predicting bankruptcy across various subsectors and market capitalizations within the healthcare industry. We utilized a comprehensive set of financial ratios for prediction, acknowledging their widespread applicability and establishing a new precedent in financial analysis. Financial ratios offer a diverse set of financial metrics that provide a concise yet powerful snapshot of a company’s financial health and resilience [44]. This research aims to address these gaps by focusing on the bankruptcy risk analysis of healthcare industries in the United States, with particular emphasis on the economically tumultuous year of 2022. Our primary objective was to employ machine learning algorithms to analyze the intricate relationship between financial ratios and bankruptcy risk in the healthcare industry. Additionally, we aimed to identify the most effective financial ratios that are most crucial and sensitive for predicting bankruptcy in these sectors. Our approach seeks to provide strategic insights for stakeholders in the healthcare stock market, including investors, policymakers, shareholders, and healthcare professionals. Through this, we aspire to contribute to the financial stability and resilience of the medical and healthcare sectors by facilitating informed decision making.
4. Data, Methodology, and Variables
4.1. Data Collection
Due to the lack of precise financial information on the medical and healthcare stock market in available financial databases, we gathered financial data from the U.S. healthcare stock market via Sec.gov, covering 1265 companies. The data were sourced from official 2022 reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, all publicly available. For the purpose of this study, the time-dependent financial ratios were derived from data spanning a full calendar year, specifically from 1 January 2022 to 1 January 2023. This approach was deliberately chosen to align with standard financial reporting practices, which typically reflect the financial status of an entity at both the beginning and the end of each year. The calculated ratios in Table 1 encapsulate the financial dynamics within this period, offering a snapshot of each company’s financial health at these critical fiscal junctures. The detailed formulas and definitions for these 40 financial ratios are provided in Table 1 and Supplementary Material S1. These ratios encompass a multitude of nuanced sub-parameters across key financial dimensions, including but not limited to indebtedness, cash flow dynamics, profitability metrics, and sector-specific peculiarities, all of which are fundamentally extrapolated from an extensive array of financial data pertaining to stocks. For instance, the debt-to-equity ratio sheds light on a company’s leverage structure, whereas ratios such as the operating cash flow ratio, price-to-free cash flow ratio, and the cash ratio collectively provide a multifaceted understanding of its liquidity situation. In a similar vein, the current ratio and the debt ratio deliver a concise yet informative overview of the company’s debt landscape. On the front of profitability analysis, indicators such as the gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on equity are of paramount importance. Further, ratios like price-to-sales and price-to-book value are essential in gleaning insights on the peculiarities inherent to the specific industry in question. Collectively, these ratios are imperative in constructing a comprehensive and insightful portrayal of a firm’s financial vitality and its strategic standing within its respective sector.

Table 1.
The formulas for 40 financial ratios (features) used to evaluate the bankruptcy risk of healthcare industries in the U.S. The symbol # represents the number of financial ratios (FR number).
4.2. Study Design and Machine Learning Analysis
This study employed a machine learning classification approach to analyze bankruptcy risk. Forty financial ratios (detailed in Table 1) served as features within the machine learning methodology, with the bankruptcy value for each of the 1265 industries as the prediction target. To ensure rigorous computation of these targets (bankruptcies), we utilized three widely recognized empirical bankruptcy prediction models: the Altman Z-score model, the modified Altman model, and the Ohlson model—commonly referred to as the O-score. These models have been empirically validated in numerous studies for their effectiveness in predicting bankruptcy risk, providing a robust and reliable framework for the analysis [45,46,47,48,49]. The formulations for these three bankruptcy models are provided in Equations (1)–(3) [50,51,52,53].
Altman Z-score = 1.2P1 + 1.4P2 + 3.3P3 + 0.6P4 + 1.0P5
P1: Working capital/Total assets;
P2: Retained earnings/Total assets;
P3: Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)/Total assets;
P4: Market value of equity/Total liabilities;
P5: Sales/Total assets.
ModifiedAltman = 6.56K1 + 3.26K2 + 6.72K3 + 1.05K4
K1: Working capital/Total assets;
K2: Retained earnings/Total assets;
K3: EBIT/Total assets;
K4: Book value of equity/Total liabilities.
Ohlson = −1.32 − 0.407 X1 + 6.03X2 − 1.43X3 + 0.0757X4 − 2.37X5 − 1.83X6 + 0.285X7 − 1.72X8 − 0.521X9
X1: Log (total assets/(gross national product—level price index));
X2: Total liabilities/total assets;
X3: Working capital/total assets;
X4: Current liabilities/current assets;
X5: Net income/total assets;
X6: Cash flow from operations/total liabilities;
X7: 1 if net negative income; 0 if otherwise;
X8: 1 if the total liabilities > total assets; 0 if otherwise;
X9: (Net income T—Net income T-1)/(Net income T + Net income T-1); “T” refers to a specific time period.
The machine learning classification algorithms used to predict bankruptcy were logistic regression, decision tree, naive Bayes, K-nearest neighbors (KNN), and support vector machine (SVM), along with ensemble learning algorithms including adaptive boosting (AdaBoost), gradient boosting, and random forest algorithms. A comprehensive explanation of the machine learning algorithms employed in the current study, along with their corresponding equations, is provided in Supplementary Material S2.
Market capitalization serves as a powerful indicator of a company’s size, reflecting not only the equity value perceived by the market but also providing insight into the financial robustness of the firms. Previous studies have shown that the market capitalization of industries is of particular importance in the analysis of bankruptcy risks [54,55,56]. On the other hand, in examining bankruptcy risk in the healthcare industries, industry subsector classification plays a pivotal role, as each subsector contributes distinct elements to the overall risk profile. Given the significance of both market capitalization and industry subsectors in bankruptcy risk analysis, this study employs two approaches: Bankruptcy risks are analyzed based on the industry subsector and the market capitalization of industries. This dual perspective enables a nuanced assessment of how industry dynamics and company size characteristics interact to influence bankruptcy likelihood. To implement these approaches, we applied two distinct multi-class machine learning classifications. Firstly, the targets were classified into four different industry subsector classes. Secondly, the targets were classified into five different market capitalization classes. It is important to note that we had three targets (Altman Z-Score, modified Altman, and Ohlson bankruptcy models), and as a result, we repeated the entire machine learning multi-class classification procedure three times. Finally, the algorithm’s predictions were compared to the test outcomes using confusion matrices to evaluate accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 scores. The algorithm with the best performance metrics was selected as the final method for bankruptcy prediction. It is worth mentioning that all targets were not completely balanced. Hence, we employed stratified sampling in the train–test split to preserve the target variable bankruptcy distribution in both training and testing sets. Additionally, StratifiedKFold cross-validation was used, demonstrating the suitability of our chosen methodology for maintaining the proportion of classes across folds. These primary techniques effectively solved issues related to minor imbalances during the prediction process, making advanced methods such as over-sampling or under-sampling unnecessary. The machine learning code was implemented using Python software, version 3.11.
It should be noted that the four industry subsector classes, defined based on the healthcare sectors of the U.S. industries, include (1) biotechnology; (2) medical, which comprises medical devices, instruments and supplies, and medical distribution; (3) pharmacology, encompassing drug manufacturers—specialty and generic, as well as general—and pharmaceutical retailers; and (4) healthcare, which covers diagnostics and research, health information services, medical care facilities, and healthcare plans. The five market capitalization classes were defined as follows [57]: (1) large-cap, with a market value of USD 10 billion or more; (2) mid-cap, with a market value between USD 2 billion and USD 10 billion; (3) small-cap, with a market value between USD 300 million and USD 2 billion; (4) micro-cap, with a market value between USD 50 million and USD 300 million; and (5) nano-cap, with a market value of less than USD 50 million.
This study recognizes that dividing industries into various subsectors and market capitalizations has enabled a multi-class classification that includes some minority classes. Recent research suggests that for non-medical data, such as financial datasets, resampling methods can effectively address the prediction challenges associated with minority classes [58]. However, the research also advises that, in most cases, standard classifiers are preferable for non-medical datasets similar to those analyzed in this study. Based on these insights, this study employs standard classifiers and does not utilize resampling or cost-sensitive methods.
4.3. Statistical Analysis
For the assessment of baseline characteristics within our dataset, we employed statistical analysis methods and computed measures, including the mean and standard error (SE), for 40 distinct financial ratios. The Shapiro–Wilk test was applied to determine the normality of the distribution within our dataset. To ascertain the statistical significance of individual features, we utilized the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). A p-value threshold of 0.05 was set for determining statistical significance.
5. Results
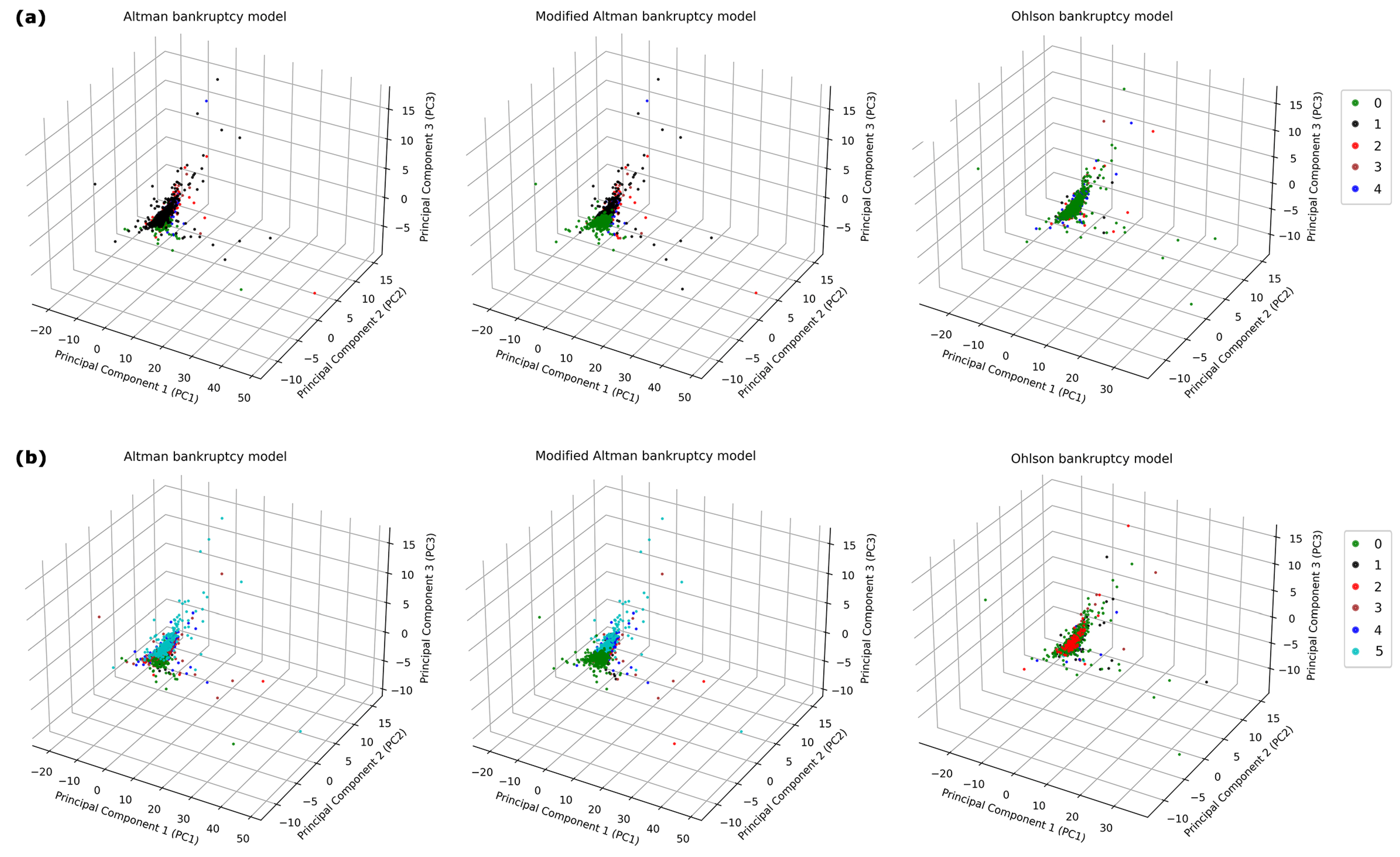
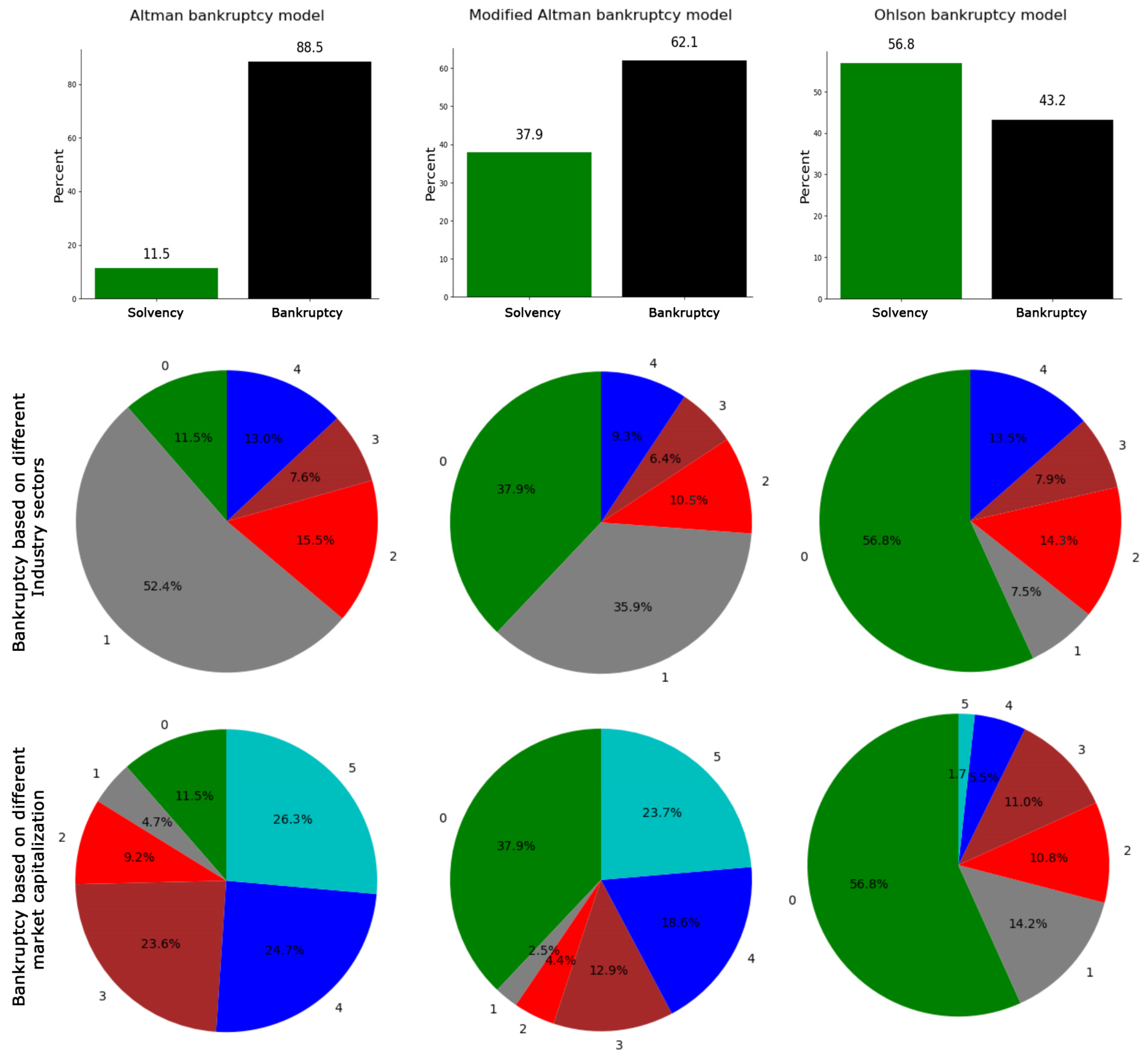
Table 2 presents a summary of the financial ratios, including the mean, SE, and p-values, which underscore the observed differences in the financial ratios. A three-dimensional principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on the dataset, comprising industries and their corresponding financial ratios (Figure 1). The resulting graphical panels highlight variations in the distribution of industries, categorized by industry subsectors and market capitalization tiers. This method of dimensionality reduction effectively preserves the inherent variance within the dataset, facilitating a more nuanced examination of the complex attributes of the industries [59]. Within the derived three-dimensional space, individual industries are represented as points, with their positions reflecting the synthesized financial ratios. The results, as depicted in Figure 2, reveal a significant bankruptcy risk for healthcare industries in the U.S. during 2022. The bankruptcy risk, calculated based on the Altman Z-Score, modified Altman, and Ohlson models, is depicted at 88.5%, 62.1%, and 43.2%, respectively, as shown in the non-green segments of Figure 2. The observed disparities in bankruptcy risk evaluations are attributable to the distinct methodological underpinnings of the Altman models and Ohlson model. The Altman models, originally calibrated for manufacturing firms, predominantly rely on financial ratios reflective of this sector’s characteristics. In contrast, the Ohlson model boasts a design intended for broad applicability across diverse corporate environments, such as service-centric industries, and integrates an extensive array of financial ratios.

Table 2.
Statistical summary of financial ratios (features) including mean, SE, and p-value. FR, financial ratio; SE, standard error.
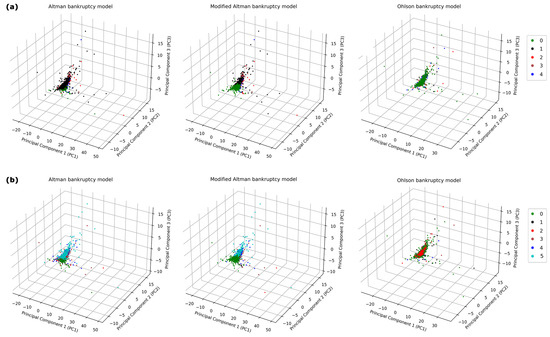
Figure 1.
Three-dimensional principal component analysis (PCA) of U.S. healthcare industries features: This figure illustrates the PCA plots of 1265 U.S. healthcare industries, visualized in three-dimensional space through the first three principal components. This analytical approach is used to identify patterns regarding (a) bankruptcy across different medical industry subsectors and (b) bankruptcy relative to market capitalization categories. Each data point represents a unique stock, with its spatial positioning derived from an aggregation of features within the dimensions defined by principal components 1, 2, and 3. In panels (a), industry subsector classes are labeled as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 4 for bankruptcy in biotechnology, medical devices, pharmacology, and healthcare services, respectively. In panels (b), market capitalization classes are defined as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 5 for bankruptcy in large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, micro-cap, and nano-cap categories, respectively.
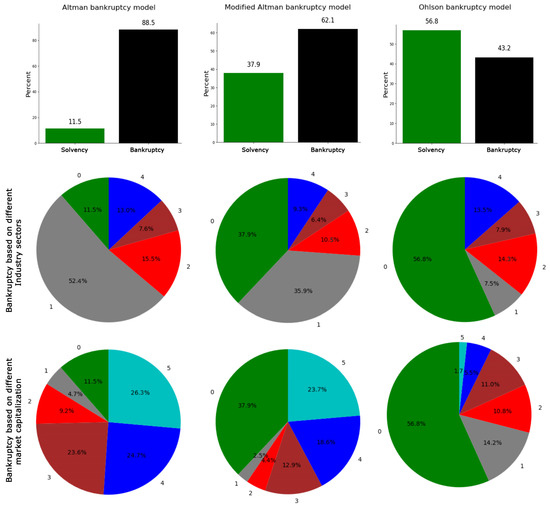
Figure 2.
Percentage difference insolvency/bankruptcy prediction across various bankruptcy prediction models. Pie charts display the differences in bankruptcy and solvency percentages based on various industry subsectors and market capitalization classifications using three bankruptcy models. Industry subsector classes are labeled as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 4 for bankruptcy in biotechnology, medical devices, pharmacology, and healthcare services, respectively. Market capitalization classes are defined as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 5 for bankruptcy in large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, micro-cap, and nano-cap categories, respectively.
In our investigation, StratifiedKFold cross-validation was systematically applied to each classifier, ensuring that the folds preserved a proportional distribution of classes. This procedure, in conjunction with detailed hyperparameter optimization—as documented in Supplementary Material S3—was critical in reducing the likelihood of data leakage. The application of these meticulous stratification and tuning strategies led to enhancements in models’ predictive accuracy, with increases ranging from 7.1% to 10.3%. In addition, all models exhibited acceptable accuracy post tuning, with the sole exception of the naive Bayes classifier (Supplementary Material S3). It should be noted that the naive Bayes model, despite its probabilistic foundation and advantages in simplicity and computational speed, did not achieve as high an accuracy as the other models in predicting bankruptcy within the U.S. healthcare industries. The relatively lower performance of this model may be explained by the model’s assumption of independence among predictors, a condition presumably not met by the complex interactions inherent in our dataset. The consistency of performance improvements post tuning across the remaining models substantiates the robustness of our analytical framework and corroborates the nonexistence of overfitting within our results. Our final tuned models exhibited acceptable accuracy rates for predicting bankruptcy using financial ratios inspired by the Altman Z-score model, with performance by classifier as follows: SVM (87.3%), KNN (82.3%), naive Bayes (68.0%), logistic regression (86.3%), decision tree (86.4%), AdaBoost (87.3%), random forest (90.6%), and gradient boosting (90.8%), as detailed in Supplementary Material S3 for industry subsectors. The accuracies for the modified Altman bankruptcy model were 88.1%, 83.3%, 66.7%, 87.3%, 87.4%, 84.1%, 90.3%, and 90.6%, respectively, while the Ohlson model showed comparable performance with accuracies of 87.9%, 80.0%, 69.1%, 87.8%, 88.2%, 74.5%, 89.3%, and 90.0%. Classifications based on market capitalization also yielded acceptable accuracy rates, broadly aligning with those based on industry subsectors (Supplementary Material S3). The results depicted indicate that, in addition to accuracy, the precision, recall, and F1 scores for the models fall within a satisfactory range. Finally, the results of our analysis demonstrated that both the random forest and gradient boosting algorithms exhibited exceptional accuracy and robustness in predicting bankruptcy based on all three bankruptcy models utilized. Upon closer examination of the results, the gradient boosting model was found to have a marginally higher accuracy compared to the random forest algorithm. Therefore, we chose to focus our analysis on this particular algorithm.
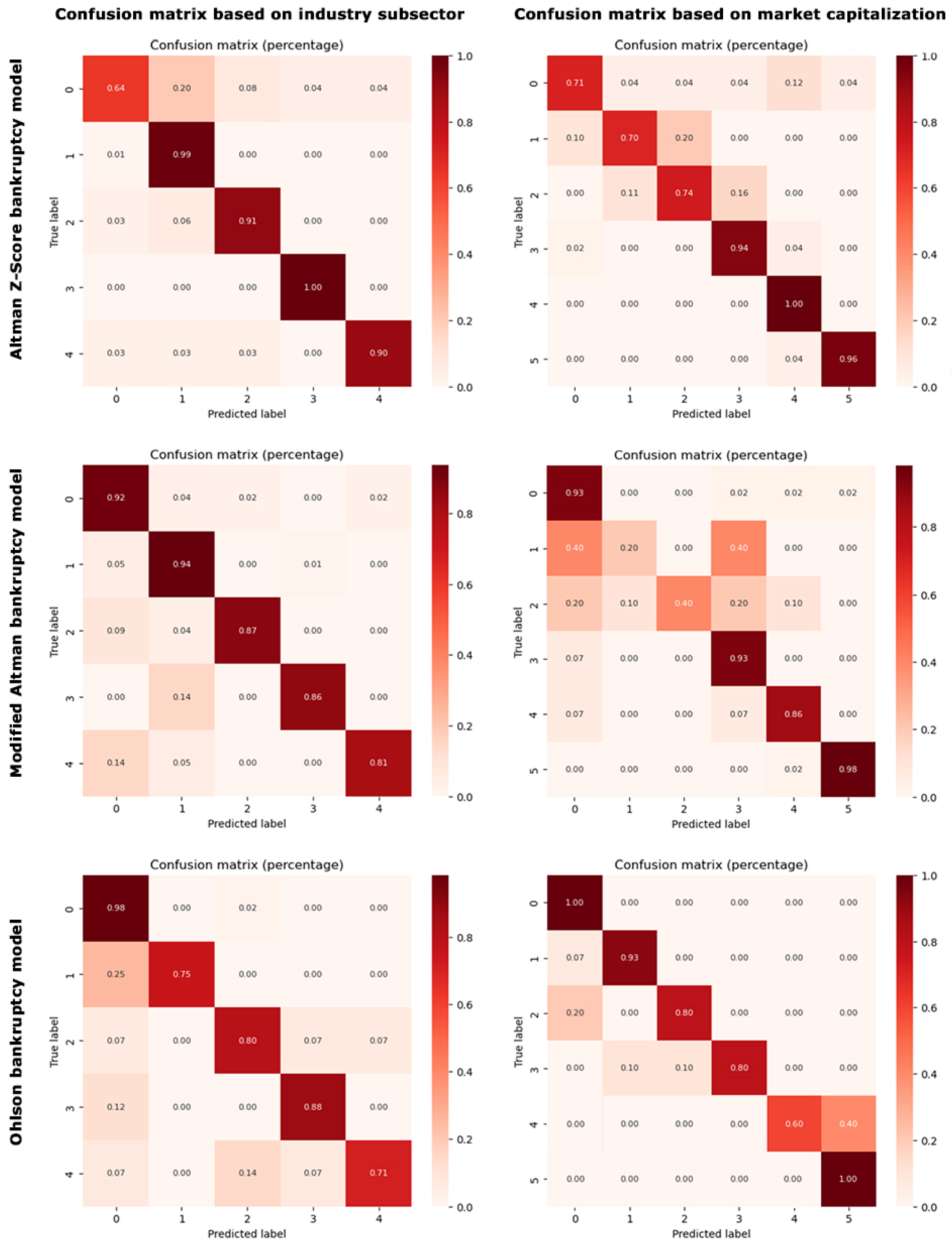
Figure 3 presents a heatmap of the confusion matrix for our final tuned gradient boosting model, offering a visual representation of the model’s performance across different classes. The gradation of colors reflects the proportion of true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives, thereby providing an intuitive overview of classification accuracy and misclassification patterns. The heatmap of the confusion matrix, as depicted in Figure 3, further corroborates the high accuracy and robust performance of the gradient boosting model in predicting bankruptcy based on financial ratios. The predominance of high values along the matrix’s main diagonal and lower values in off-diagonal cells indicates a substantial rate of correct predictions relative to the misclassifications. This visualization underscores the gradient boosting model’s effectiveness in distinguishing between the various classes.
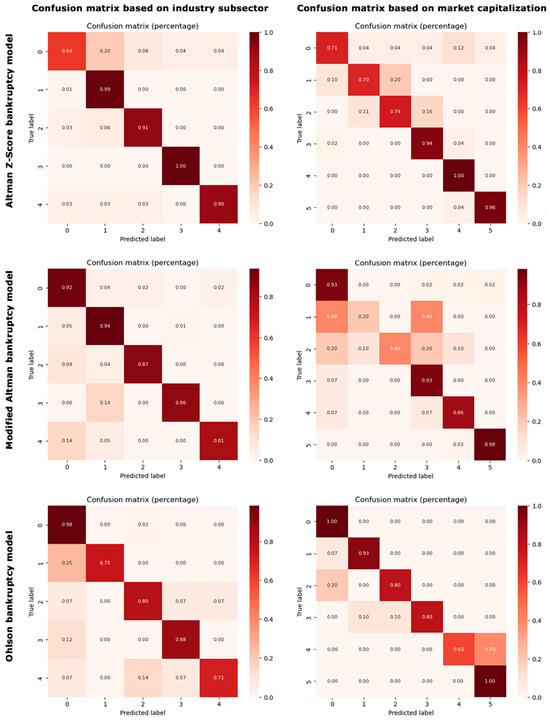
Figure 3.
Heatmaps of the confusion matrices showcasing the classification models performance in differentiating between solvency and bankruptcy across industry subsectors and market capitalization classes. Industry subsector classes are labeled as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 4 for bankruptcy in biotechnology, medical devices, pharmacology, and healthcare services, respectively. Market capitalization classes are defined as 0 for solvency and from 1 to 5 for bankruptcy in large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, micro-cap, and nano-cap categories, respectively.
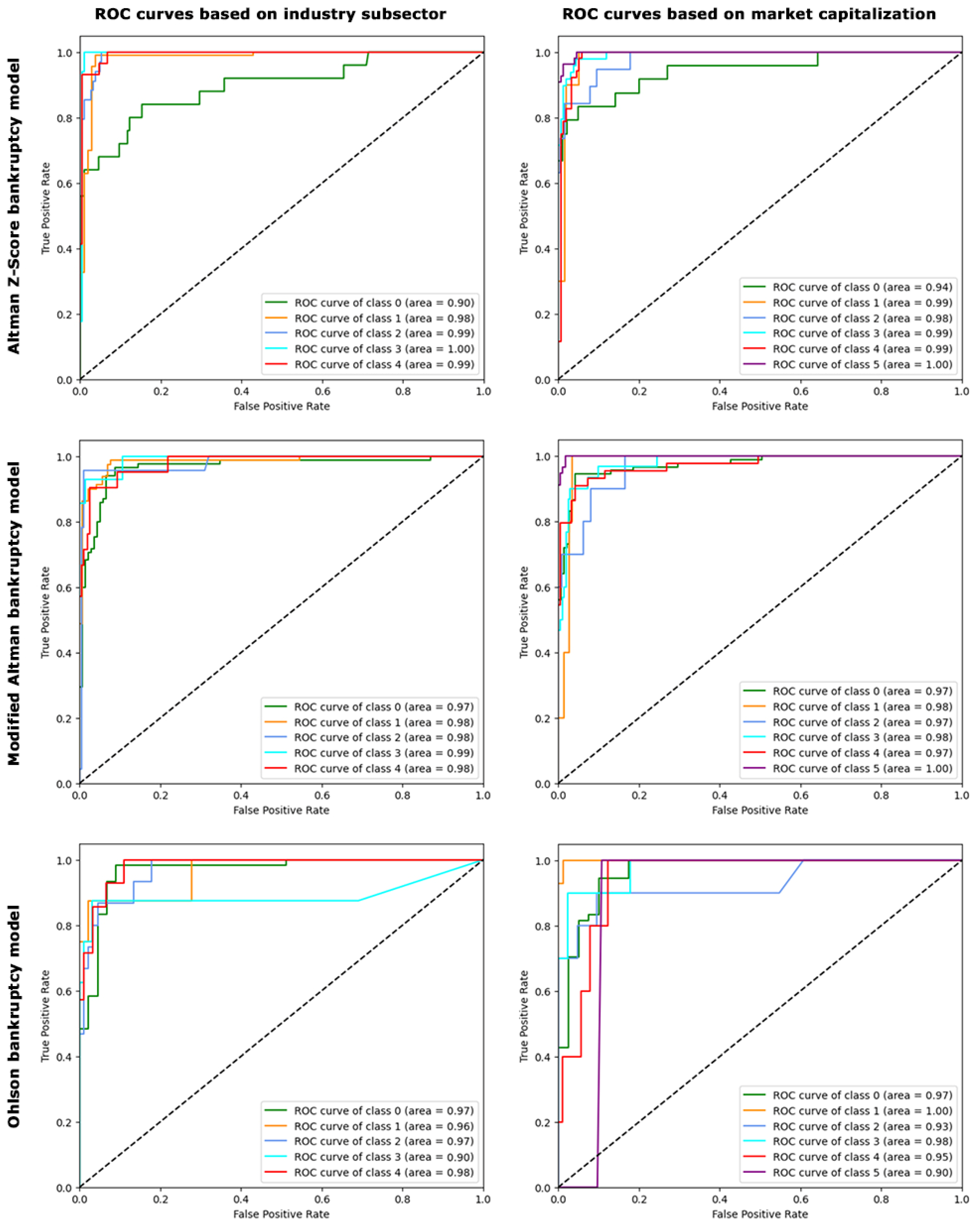
Given the critical importance of minimizing false negatives in bankruptcy prediction, where failing to identify an impending bankruptcy could have drastic financial repercussions, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve’s ability to illustrate the trade-off between sensitivity (true-positive rate) and specificity (false-positive rate) across different thresholds makes it a fitting choice. It facilitates the identification of an optimal balance, ensuring that the model minimally overlooks actual cases of bankruptcy, which is of paramount concern in financial analytics. Therefore, we compared ROC curves in Figure 4 based on different bankruptcy models and classifications for the gradient boosting model. The areas under the ROC curves for the Altman Z-score, modified Altman, and Ohlson bankruptcy prediction models were notably high (greater than 90%) for classifications based on industry subsectors and market capitalization. The high ROC curve areas show the exceptional capability of our gradient boosting algorithm in differentiating bankrupt from solvent healthcare industries. This suggests not only the accuracy of our predictions but also confirms their consistency and robustness across diverse industry contexts and varying scales of market capitalization. The superior performance of the gradient boosting model and the suitable size of our dataset reinforce the notion that this efficient and transparent model is advantageous, particularly in scenarios where complexity is unnecessary, and high-dimensional deep learning approaches do not confer additional benefits.
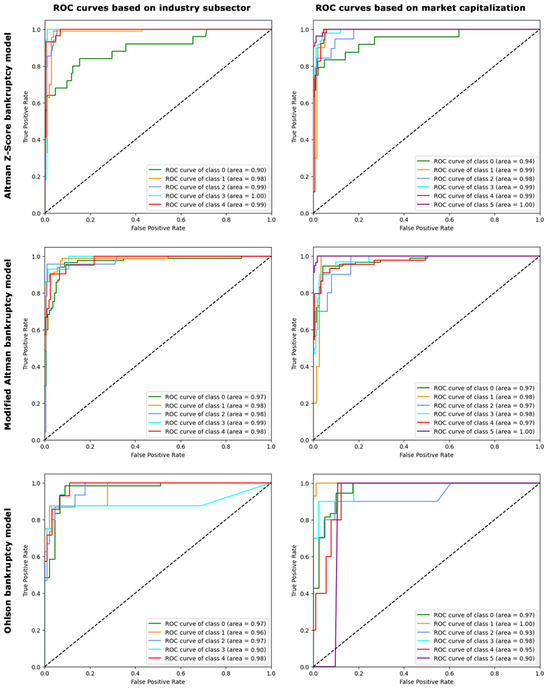
Figure 4.
The ROC curves illustrating the true-positive rate against the false-positive rate at various threshold settings for the classification models applied to industry subsectors and market capitalization classes. ROC, receiver operating characteristic.
6. Discussion
Predicting the probability of bankruptcy remains among the most formidable challenges in contemporary economic and financial research [1,2]. Specifically, the evaluation of bankruptcy risk in the industries and, more precisely, within the medical and healthcare sectors holds immense significance due to its profound financial implications. Consequently, the present study was designed to achieve a precise prediction of bankruptcy risk for U.S. healthcare industries based on comprehensive financial ratios that encapsulate a wide array of financial metrics. This allows for the early detection of financial fragilities, the protection of economic interests, and the provision of timely insights for stakeholders. Effective prediction aids in the enhancement of management strategies, the attainment of well-informed advancement and risk control measures, and ensures the provision of high-quality healthcare services to not only the American population but potentially the global community as well. Our results indicated high bankruptcy risks as predicted by Altman, modified Altman, and Ohlson bankruptcy models, which can be attributed to the distinctive economic landscape of 2022. This can be related to significant industry volatility driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, escalating inflationary pressures, and a series of aggressive interest rate hikes in 2022. These factors led to increased borrowing costs that impacted market liquidity and valuations, particularly within growth-oriented sectors such as healthcare, which are traditionally more sensitive to interest rate changes.
6.1. The High Robustness and Predictive Power of Gradient Boosting Machine Learning Algorithm
Logical and meaningful improvements in cross-validation accuracies following hyperparameter tuning (by 7.1–10.3%), combined with the remarkably high levels of post-tuning accuracy (exceeding 90%) for the gradient boosting model, as well as elevated precision, recall, and F1 scores—as evidenced by the confusion matrices—and areas under the ROC curve surpassing 0.9 jointly affirm the robustness and exceptional predictive capability of this model. Therefore, the gradient boosting model can efficiently predict the bankruptcy risk of healthcare industries based on financial ratios with high accuracy and robustness. The study by Carmona et al. on predicting financial distress in French firms corroborated and further supported our findings regarding the effectiveness of gradient boosting algorithms in financial distress prediction [36,37]. The results also revealed that even the accuracies of our other machine learning algorithms were higher than those reported in some corresponding studies related to the prediction of bankruptcy risk based on other financial parameters, even with a larger database [60]. This underscores the power and sensitivity of financial ratios in predicting bankruptcy within the healthcare industries, providing creditors, investors, and other stakeholders with the opportunity to take proactive measures to mitigate financial challenges.
6.2. Important Financial Ratios Sensitive to Bankruptcy Prediction
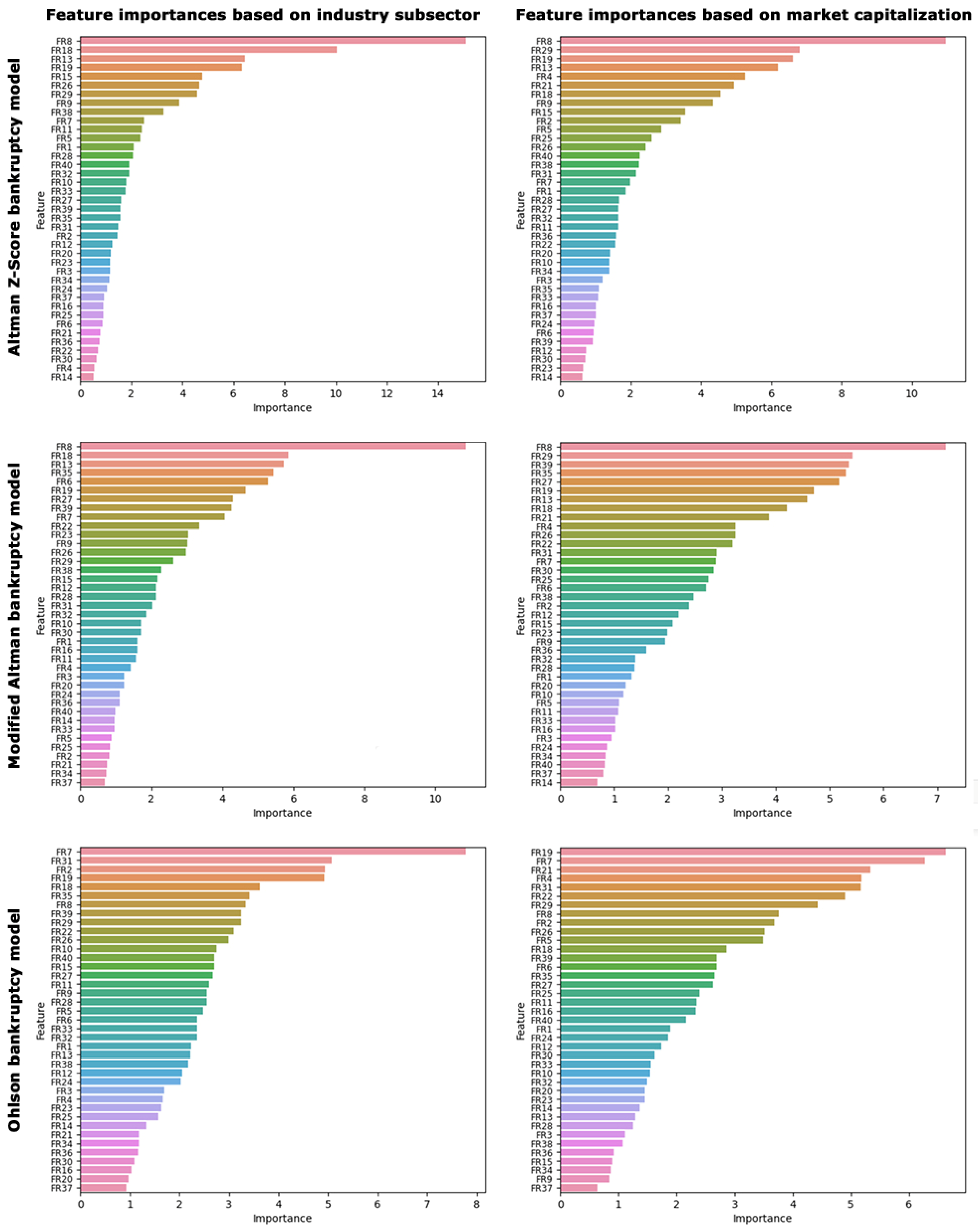
The feature importance analysis presented in Figure 5 indicated that, according to both Altman models, the most important and sensitive ratio for predicting bankruptcy risk across various industry subsectors and market capitalizations is the return on investment (ROI). ROI is a measure comparing net income to investment. A high ROI indicates that the investment’s gains are favorable compared to its cost. Conversely, the Ohlson model identified the return on assets (ROA) as the important ratio in predicting bankruptcy risk specific to industry subsectors, with a feature importance of 7.8%. ROA is a financial metric showing a company’s profitability relative to its total assets. It helps determine if a company efficiently uses its assets to generate profit. For the predictions based on market capitalization, the Ohlson model highlighted not only the ROA ratio with an importance of 6.3% but also the enterprise value to earnings before interest and taxes (EV/EBIT) ratio, which has an importance of 6.6%. The comprehensive details regarding the relative importance of all parameters under investigation are illustrated in Figure 5. Notwithstanding the absence of prior scholarly work specific to bankruptcy risk prediction within the healthcare industries, the extant literature on bankruptcy assessment in disparate industries also reinforces the significance of several ratios analogous to those we identified as pivotal [12,13,14,15,61].
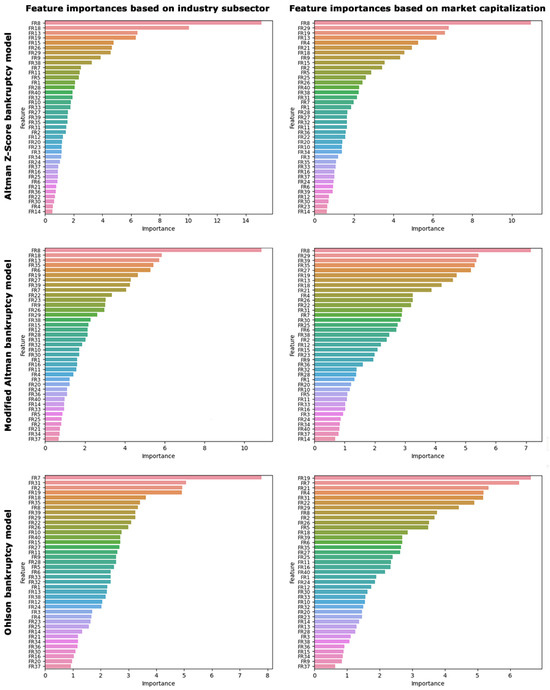
Figure 5.
Feature importance analysis highlighting the relative importance of each financial ratio in determining bankruptcy risk based on different industry subsectors and market capitalizations.
The importance and sensitivity of the ROI as illuminated by the Altman models suggest that investors and analysts in medical and healthcare sectors place considerable emphasis on the immediate efficiency of capital usage. This ratio’s predictive potency could potentially stem from its ability to encapsulate the sector’s unique capital structures and reinvestment patterns critical to sustaining operations in the complex healthcare market. On the other hand, the Ohlson model’s emphasis on ROA accentuates the critical role of effective asset utilization in the financial viability of healthcare firms, hinting at a market environment where operational efficiency is a harbinger of fiscal health. Additionally, the Ohlson model’s accentuation of the EV/EBIT ratio underscores the market’s valuation of profitability relative to a company’s total valuation. The nuanced divergence observed between the models regarding the most influential ratios offers compelling insights into the multifaceted nature of bankruptcy risk assessment in this sector, underscoring the need for a multidimensional analytic approach in financial prognostication efforts within the healthcare industries. Consequently, for an augmented and holistic forecast of bankruptcy risk, it is incumbent upon both researchers and practitioners to amalgamate the varied lenses provided by the Altman and Ohlson models.
It should be noted that our investigation, as described, revealed widespread financial distress among U.S. healthcare industries in 2022. This trend might partly be attributed to these key financial ratios identified by these models, which likely reflect the broader fiscal challenges faced by these entities. These bankruptcy models were originally conceptualized to be effective over a two-year period; hence, the important and sensitive parameters suggested by these models theoretically remain relevant and effective until 2024. Financial analysts should continue to monitor these ratios closely to maintain the solvency of the medical and healthcare sectors. Therefore, recognizing these ratios not only offers a retrospective analysis of past financial difficulties but also provides strategic foresight. By vigilantly tracking these financial indicators, stakeholders can better prepare to address fiscal vulnerabilities proactively, thereby reducing the risk of similar financial challenges in the future. In addition to managing the aforementioned financial ratios based on our findings, recent advancements in medical technology also help address some challenges in the financial aspects of healthcare industries [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71]. Therefore, technological advancements can be beneficial beyond just controlling our recognized financial ratios.
6.3. Limitations and Future Directions
It should be noted that, although 40 financial ratios covering key financial domains were utilized to predict bankruptcy, future research could enhance our findings by incorporating additional predictive parameters. Alzayed et al. recently highlighted the importance of corporate governance alongside financial ratios in the context of bank failure predictions [72]. Hence, incorporating factors like corporate governance, competitive dynamics, and regulatory considerations may also prove significant in enhancing the prediction of bankruptcy for the healthcare industries, an area ripe for future academic exploration. Future studies could benefit from repeating our analysis using data from a more typical financial year as a control group. This comparison would allow researchers to discern whether the financial metrics identified as crucial during the crisis conditions of 2022 hold similar significance in more stable times. Such a study would also help in evaluating the robustness of these metrics across varying economic conditions, providing a deeper understanding of their utility in continuous risk management and strategic financial planning in the healthcare sector. Advancements in natural language processing in future studies could provide mechanisms to evaluate market sentiment and management discourse, while machine learning models like the gradient boosting algorithm demonstrated in this study could be further refined by integrating sector-specific data for a more tailored risk assessment. Exploring the impact of emergent global health issues and economic disruptions beyond COVID-19 may also be essential in shaping more resilient financial prediction frameworks for the sector.
7. Conclusions
This study predicted the risk of bankruptcy in the U.S. healthcare industries based on financial ratios across different industry sub-sectors and varying market capitalizations, using machine learning analysis. The results suggest that financial ratios serve as robust predictors of bankruptcy, and the gradient boosting algorithm can significantly enhance the predictive power of conventional models. This study has elucidated important financial ratios that served as potential harbingers of financial distress and heightened bankruptcy risk within U.S. healthcare industries during 2022. The identification of these ratios is instrumental not only for signaling potential red flags but also for equipping stakeholders with the insights necessary to devise strategies aimed at risk mitigation and ensuring the sustainability of the healthcare industries. The comprehensive perspective offered through this research enriches the academic discourse on bankruptcy prediction and offers strategic foresight for stakeholders within healthcare industries. Ultimately, the findings lay a robust foundation for future research and offer a framework for informed decision making that serves investors, policymakers, shareholders, and healthcare professionals, thereby contributing significantly to the financial stability and resilience of the medical and healthcare sectors.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jtaer19020066/s1, Supplementary Material S1: The definitions of the 40 financial ratios (features) used to assess the bankruptcy risk of medical and healthcare stocks in the U.S.; FR, financial ratio; FR, financial ratio. Supplementary Material S2: Overview of multi-class classification techniques that are used in the present study. Supplementary Material S3: Performance metrics and hyperparameters of bankruptcy prediction models for different machine and ensemble learning classifiers.
Author Contributions
H.G. contributed to conceptualization, study design, data collection, data pre-processing, investigation, methodology, machine learning analysis, software development, validation, and manuscript writing; M.A. contributed to data collection, investigation, project administration, data pre-processing, and initial draft preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the College of Business of Northern Michigan University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data can bot be shared from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Clement, C. Machine Learning in Bankruptcy Prediction—A Review. J. Public Adm. Financ. Law 2020, 17, 178–196. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, R.; Bose, I.; Chen, X. Prediction of financial distress: An empirical study of listed Chinese companies using data mining. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 241, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, M. Predicting Financial Distress at Dutch General Hospitals: A Machine Learning Approach. Master’s Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Beauvais, B.; Ramamonjiarivelo, Z.; Betancourt, J.; Cruz, J.; Fulton, L. The Predictive Factors of Hospital Bankruptcy—An Exploratory Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendergast, P.M.; Sousa, M.D.; Wadsworth, T. Health Insurance and Bankruptcy Risk: Examining the Impact of the Affordable Care Act. Brook. L. Rev. 2020, 86, 975. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.D. The Government’s Perspective on Health Care Bankruptcies. Am. Bankruptcy Inst. J. 2018, 37, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, B.J. The Medical Bankruptcy Myth; Fraser Institute: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shrime, M.G.; Weinstein, M.C.; Hammitt, J.K.; Cohen, J.L.; Salomon, J.A. Trading bankruptcy for health: A discrete-choice experiment. Value Health 2018, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelstein, D.U.; Thorne, D.; Warren, E.; Woolhandler, S. Medical bankruptcy in the United States, 2007: Results of a national study. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.; Notowidigdo, M.J. Health insurance and the consumer bankruptcy decision: Evidence from expansions of Medicaid. J. Public Econ. 2011, 95, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizel, S.; Bernardino, C.; Caine, M.; Garfinkle, J. Corporate Bankruptcy Panel: The Healthcare Industry Post-Affordable Care Act: A Bankruptcy Perspective. Emory Bankr. Dev. J. 2014, 31, 249. [Google Scholar]
- Supriyanto, J.; Darmawan, A. The effect of financial ratio on financial distress in predicting bankruptcy. J. Appl. Manag. Account. 2018, 2, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, S.; Fadjriah, N.E.; Nugraha, N.M. The influence of the financial ratio to the prevention of bankruptcy in cigarette manufacturing companies sub sector. Solid State Technol. 2020, 63, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.-H. A study on financial ratio and prediction of financial distress in financial markets. J. Distrib. Sci. 2018, 16, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Yu, Y. Financial ratios and bankruptcy predictions: An international evidence. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2017, 51, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.; Alfonse, M.; Salem, A.-B.M. Bankruptcy prediction using artificial intelligence techniques: A survey. In Digital Transformation Technology: Proceedings of ITAF 2020, Online, 26–27 January 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 335–360. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, T.V.N.; Gaddam, A.; Kurni, M.; Saritha, K. Reliance on artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in the era of industry 4.0. In Smart Healthcare System Design: Security and Privacy Aspects; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 281–299. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Yen, M.-F. A new perspective of performance comparison among machine learning algorithms for financial distress prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 83, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumani, Y.F.; Nwankpa, J.K.; Tanniru, M. Predicting firm failure in the software industry. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 4161–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Alvarez, F. Predicting firm-level bankruptcy in the Spanish economy using extreme gradient boosting. Comput. Econ. 2022, 59, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenkov, Y.; Fedorova, E.; Chekrizov, D. Two-step classification method based on genetic algorithm for bankruptcy forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeld, J.; Kuděj, M.; Smrčka, L. Financial health of enterprises introducing safeguard procedure based on bankruptcy models. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2018, 19, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-F.; Hsu, Y.-F.; Yen, D.C. A comparative study of classifier ensembles for bankruptcy prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 24, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, E.; García, N.; Gámez, M.; Elizondo, D. Bankruptcy forecasting: An empirical comparison of AdaBoost and neural networks. Decis. Support Syst. 2008, 45, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, F.; Tian, S.; Lee, C.; Ma, L. Deep learning models for bankruptcy prediction using textual disclosures. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antulov-Fantulin, N.; Lagravinese, R.; Resce, G. Predicting bankruptcy of local government: A machine learning approach. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2021, 183, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.; Musa, M.; Brédart, X. Bankruptcy Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S.; Bekiros, S. Can machine learning approaches predict corporate bankruptcy? Evidence from a qualitative experimental design. Quant. Financ. 2019, 19, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, H.; Ryu, D. Corporate bankruptcy prediction using machine learning methodologies with a focus on sequential data. Comput. Econ. 2022, 59, 1231–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liashenko, O.; Kravets, T.; Kostovetskyi, Y. Machine Learning and Data Balancing Methods for Bankruptcy Prediction. Ekonomika 2023, 102, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, C.-L. Financial information asymmetry: Using deep learning algorithms to predict financial distress. Symmetry 2021, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoričák, M.; Gnip, P.; Drotár, P.; Gazda, V. Bankruptcy prediction for small-and medium-sized companies using severely imbalanced datasets. Econ. Model. 2020, 84, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adosoglou, G.; Lombardo, G.; Pardalos, P.M. Neural network embeddings on corporate annual filings for portfolio selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzana, F.; Bee, M.; Hussin Adam Khatir, A.A. Machine learning techniques for default prediction: An application to small Italian companies. Risk Manag. 2024, 26, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, P.; Dwekat, A.; Mardawi, Z. No more black boxes! Explaining the predictions of a machine learning XGBoost classifier algorithm in business failure. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2022, 61, 101649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Jabeur, S.; Stef, N.; Carmona, P. Bankruptcy prediction using the XGBoost algorithm and variable importance feature engineering. Comput. Econ. 2023, 61, 715–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Pellegrino, M.; Adosoglou, G.; Cagnoni, S.; Pardalos, P.M.; Poggi, A. Machine Learning for Bankruptcy Prediction in the American Stock Market: Dataset and Benchmarks. Future Internet 2022, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adosoglou, G.; Park, S.; Lombardo, G.; Cagnoni, S.; Pardalos, P.M. Lazy network: A word embedding-based temporal financial network to avoid economic shocks in asset pricing models. Complexity 2022, 2022, 9430919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragoli, D.; Ferretti, C.; Ganugi, P.; Marseguerra, G.; Mezzogori, D.; Zammori, F. Machine-learning models for bankruptcy prediction: Do industrial variables matter? Spat. Econ. Anal. 2022, 17, 156–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Li, B.; Ma, L.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Anticipating financial distress of high-tech startups in the European Union: A machine learning approach for imbalanced samples. J. Forecast. 2022, 41, 1131–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papík, M.; Papíková, L. Impacts of crisis on SME bankruptcy prediction models’ performance. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214, 119072. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, C.; Tse, Y.; Zhang, L. The impact of public health emergencies on small and medium-sized enterprises: Evidence from China. Glob. Financ. J. 2023, 58, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudose, M.B.; Avasilcai, S. A review of the research on financial performance and its determinants. In Innovation in Sustainable Management and Entrepreneurship: Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium in Management (SIM2019), Timisoara, Romania, 25–26 October 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Najib, A.S.; Cahyaningdyah, D. Analysis of the bankruptcy of companies with Altman model and Ohlson model. Manag. Anal. J. 2020, 9, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bodla, B.S. Review and comparison of Altman and Ohlson model to predict bankruptcy of companies. ANVESAK 2022, 52, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, E.I.; Iwanicz-Drozdowska, M.; Laitinen, E.K.; Suvas, A. Distressed firm and bankruptcy prediction in an international context: A review and empirical analysis of Altman’s Z-score model. SSRN Electron. J. 2014, 2536340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elviani, S.; Simbolon, R.; Riana, Z.; Khairani, F.; Dewi, S.P.; Fauzi, F. The Accuracy of the Altman, Ohlson, Springate and Zmejewski Models in Bankruptcy Predicting Trade Sector Companies in Indonesia. Bp. Int. Res. Crit. Inst. (BIRCI-J.) 2020, 3, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.Y. Validity of Altmans Z-Score model in predicting Bankruptcy in recent years. Acad. Account. Financ. Stud. J. 2015, 19, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlson, J.A. Financial ratios and the probabilistic prediction of bankruptcy. J. Account. Res. 1980, 18, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E.I. Financial ratios, discriminant analysis and the prediction of corporate bankruptcy. J. Financ. 1968, 23, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, E.I.; Iwanicz-Drozdowska, M.; Laitinen, E.K.; Suvas, A. Financial distress prediction in an international context: A review and empirical analysis of Altman’s Z-score model. J. Int. Financ. Manag. Account. 2017, 28, 131–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matenda, F.R.; Sibanda, M.; Chikodza, E.; Gumbo, V. Bankruptcy prediction for private firms in developing economies: A scoping review and guidance for future research. Manag. Rev. Q. 2022, 72, 927–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeanu, D.-S.; Cioaca, S.-I. An assessment of the bankruptcy risk on the Romanian capital market. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 182, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frino, A.; Jones, S.; Wong, J.B. Market behaviour around bankruptcy announcements: Evidence from the Australian Stock Exchange. Account. Financ. 2007, 47, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, R.; Wahyudi, I. The effect of firm and stock characteristics on stock returns: Stock market crash analysis. J. Financ. Data Sci. 2016, 2, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.L. The Effect of Trading Activity and Holdings Market Capitalization on Portfolio Performance. Int. J. Econ. Financ. 2018, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S. Impact of Nature of Medical Data on Machine and Deep Learning for Imbalanced Datasets: Clinical Validity of SMOTE Is Questionable. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterstraat, M.G.; Dehghan, A.; Gholampour, S. Optimization of number and range of shunt valve performance levels in infant hydrocephalus: A machine learning analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1352490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, F.; Kimura, H.; Altman, E. Machine learning models and bankruptcy prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 83, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.G. The early indicators of financial failure: A study of bankrupt and solvent health systems. J. Healthc. Manag. 2008, 53, 333. [Google Scholar]
- Gholampour, S. Computerized biomechanical simulation of cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics: Challenges and opportunities. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S.; Deh, H.H.H. The effect of spatial distances between holes and time delays between bone drillings based on examination of heat accumulation and risk of bone thermal necrosis. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Droessler, J.; Frim, D. The role of operating variables in improving the performance of skull base grinding. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Hassanalideh, H.H.; Gholampour, M.; Frim, D. Thermal and physical damage in skull base drilling using gas cooling modes: FEM simulation and experimental evaluation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 212, 106463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Yamini, B.; Ichkitidze, L.; Asadi, M.; Fernandez, J.; Gholampour, S. Enhanced ionic polymer–metal composites with nanocomposite electrodes for restoring eyelid movement of patients with ptosis. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanalideh, H.H.; Gholampour, S. Finding the optimal drill bit material and proper drilling condition for utilization in the programming of robot-assisted drilling of bone. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Hajirayat, K. Minimizing thermal damage to vascular nerves while drilling of calcified plaque. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S. Feasibility of assessing non-invasive intracranial compliance using FSI simulation-based and MR elastography-based brain stiffness. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S. Can magnetic resonance elastography serve as a diagnostic tool for gradual-onset brain disorders? Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 47, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S. Modeling and simulation of cerebrospinal fluid disorders. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1331170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzayed, N.; Eskandari, R.; Yazdifar, H. Bank failure prediction: Corporate governance and financial indicators. Rev. Quant. Financ. Account. 2023, 61, 601–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).