Abstract
This article addresses the pervasive issue of fraud in financial transactions by introducing the Graph Attention Network (GAN) into graph neural networks. The article integrates Node Attention Networks and Semantic Attention Networks to construct a Dual-Head Attention Network module, enabling a comprehensive analysis of complex relationships in user transaction data. This approach adeptly handles non-linear features and intricate data interaction relationships. The article incorporates a Gradient-Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) to enhance fraud identification to create the GBDT–Dual-channel Graph Attention Network (GBDT-DGAN). In a bid to ensure user privacy, this article introduces blockchain technology, culminating in the development of a financial anti-fraud model that fuses blockchain with the GBDT-DGAN algorithm. Experimental verification demonstrates the model’s accuracy, reaching 93.82%, a notable improvement of at least 5.76% compared to baseline algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks. The recall and F1 values stand at 89.5% and 81.66%, respectively. Additionally, the model exhibits superior network data transmission security, maintaining a packet loss rate below 7%. Consequently, the proposed model significantly outperforms traditional approaches in financial fraud detection accuracy and ensures excellent network data transmission security, offering an efficient and secure solution for fraud detection in the financial domain.
1. Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of finance, thwarting fraudulent activities has emerged as a paramount concern for both financial institutions and regulatory bodies. Traditional fraud detection methods, relying heavily on personal information and historical records, face significant limitations in the face of technological advancements and the escalating complexity of financial transactions. These limitations are particularly pronounced when dealing with collaborative fraudulent activities involving multiple decisions and dynamically changing, high-dimensional data [1,2]. In today’s digital age, the rapid growth of financial transactions and the continuous evolution of financial fraud have led to an urgent need for more innovative and efficient anti-fraud solutions. With the development of financial technology, malicious actors have become increasingly cunning, using more complex means to engage in fraudulent activities, posing a serious threat to the stability of the financial system and the security of users’ assets.
So, in the face of increasingly complex financial transactions and technological advancements, how do we improve the generalization ability of financial anti-fraud models, ensure the effectiveness of the models, and protect customer privacy? The financial industry is thus confronted with an urgent need for more robust and intelligent fraud detection tools. In response to this challenge, deep learning, an artificial intelligence algorithm, has emerged as a promising solution. Through unsupervised learning on data information, deep learning can adeptly navigate complex financial network structures, comprehensively discerning data patterns and identifying potential abnormal behaviors or fraud patterns. This capability opens up new avenues for effectively addressing the intricate issue of financial fraud [3].
The prevalence of fraudulent activities in financial transactions has escalated into a pervasive global challenge. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), serving as deep learning models designed for graph-structured data, demonstrate proficiency in modeling intricate financial networks encompassing customer relationships, transaction processes, and fund flows. By leveraging their capacity to holistically capture patterns and regularities within data, GNNs excel in identifying potential abnormal behaviors and fraud patterns embedded in financial datasets. Their adeptness in handling unstructured data and discerning complex relationships between nodes provides them with a distinct advantage in uncovering potential risks and abnormal transactions [4].
Traditional anti-fraud methods have difficulty in effectively capturing these new types of fraudulent behaviors, so researchers are constantly striving to seek innovative solutions based on advanced technologies. A comprehensive survey by Ma et al. (2021) delved into deep learning methods in graph anomaly detection, underscoring the application advantages of GNN models in detecting anomalies within graph data [5]. Ashtiani and Raahemi (2021) compiled a comprehensive summary of applications and methodologies related to deep learning algorithms, including GNN-based works, in fraud detection. Their work offers an in-depth exploration and outlines research directions within the realm of financial fraud detection [6]. Additionally, Li et al. (2021) proposed a medical image fusion method based on deep learning, presenting more accurate and comprehensive image data prediction results for medical diagnosis and treatment [7].
Despite the considerable promise offered by GNNs in the realm of financial anti-fraud, practical implementations face several formidable challenges. Issues such as data quality and scale, model interpretability, and privacy protection emerge as significant hurdles. To address these challenges, blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized, tamper-resistant, and encryption security features, emerges as a powerful solution, particularly in enhancing the safeguarding of financial data privacy. By adopting a decentralized and distributed approach to storing transaction data, blockchain serves as a robust deterrent against data tampering and unauthorized access. This innovative application of technology empowers financial institutions to securely share and verify data, all while ensuring comprehensive protection of customer privacy [8,9].
In conclusion, the goal of this article is to improve the generalization ability of financial anti-fraud models while ensuring data privacy, in response to the challenges posed by increasingly complex fraudulent activities in the financial sector. This article first collects financial transaction data and performs preprocessing and feature engineering to provide input for the GNN model. Second, this article designs and trains a GNN model to identify patterns and anomalies in the data through unsupervised learning, thus identifying potential fraudulent patterns and abnormal behaviors. Next, this article integrates blockchain technology into the data storage and sharing process to ensure the privacy and security of transaction data. Finally, rigorous model performance evaluation and comparative experiments are conducted to propose improvements and solutions to real-world challenges. The contribution lies in providing financial institutions with more powerful fraud detection tools, promoting the development of financial technology, and promoting sustainable growth and secure operation of the financial industry. The synergistic application of GNN and blockchain heralds a new era in financial security, promising heightened efficiency and resilience against evolving threats in the dynamic landscape of financial transactions.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Review of Intelligent Recognition Research in Financial Anti-Fraud
In the dynamic landscape of financial fraud, traditional rules and statistical models encounter challenges in adapting to evolving methodologies, necessitating the exploration of more flexible and adaptive approaches. Many scholarly investigations have contributed significantly to the field of financial anti-fraud. Liu and Jiang (2023) [10] introduced an advanced persistent threat prediction analysis method, employing causal graph modeling to forecast advanced persistent threats—a pivotal stride in predictive analysis. Fang et al. (2021) [11] innovatively addressed internet loan fraud by integrating deep learning techniques, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in detecting fraudulent activities on online lending platforms. Alarfaj et al. (2022) [12] dedicated their efforts to employing advanced machine learning and deep learning algorithms in credit card fraud detection. Their model harnessed cutting-edge technologies, heightening the accuracy of credit card transaction fraud detection systems and fortifying the security of financial transactions. Cheng et al. (2020) [13] proposed a credit card fraud detection neural network integrating a spatiotemporal attention mechanism. This attention mechanism effectively captured spatiotemporal patterns in credit card transactions, augmenting the precision and reliability of fraud detection in financial transactions. Lei et al. (2022) [14] ventured into the development of an intelligent information system for financial analysis, leveraging supervised machine learning algorithms. This system facilitated comprehensive financial analysis, aiding decision-making by integrating supervised machine learning technology. In a consumer-centric approach, Xu et al. (2022) [15] constructed a consumer fraud victim model by incorporating individual-specific factors. This enhancement significantly improved the accuracy of the fraud victim prediction model, contributing to the construction of a more refined consumer fraud detection system. In pursuing enhanced privacy protection, Verykios et al. (2022) [16] delved into techniques for concealing sensitive data in the financial anti-fraud process. Their focus on safeguarding sensitive data during anti-fraud procedures maintained privacy while preserving an effective fraud detection mechanism. Exploring graph-based machine learning, Usman et al. (2023) [17] proposed an intelligent anti-money laundering fraud control model. Leveraging graph-based machine learning technology, their model elevated anti-money laundering measures, consequently enhancing fraud control and compliance in financial transactions. Collectively, these studies underscore the multifaceted and evolving nature of intelligent recognition in the realm of financial anti-fraud research.
2.2. Comprehensive Review of GNN Applications in the Financial Landscape
GNNs have emerged as powerful tools for handling unstructured financial data, offering a holistic approach to capturing intricate financial network structures. The versatility of GNNs in financial research is evident through various studies conducted by scholars in the field. Cheng et al. (2022) [18] proposed a multimodal Graph Attention Network (GAN) for financial time series prediction. Integrating diverse data modalities into a graph structure, the model significantly enhances the accuracy of financial time series analysis. By harnessing the power of GNNs, the model adeptly captures intricate relationships within financial data, thereby improving predictive performance. In a distinct domain, Zhang et al. (2023) [19] introduced a dynamic attribute-driven GAN for stock prediction in behavioral finance. By leveraging dynamic attributes to construct a GAN, this model effectively captures the evolving relationships among stock behaviors, considering dynamic features within the financial market to enhance the accuracy of stock prediction. Xu et al. (2022) [20] proposed a Hierarchical GAN tailored for classifying stocks with price limit changes. Embracing a hierarchical structure, the model adeptly captures multi-level relationships within financial data, thereby refining the accuracy of classifying stocks subject to price limit changes. Lazcano et al. (2023) [21] presented a combined model integrating recurrent neural networks and graph convolutional networks for financial time series prediction. This amalgamation effectively captures both time dependencies and graph-based features in financial data, resulting in improved accuracy for financial time series prediction. In conclusion, these studies underscore the versatility and efficacy of GNNs in various financial domains, showcasing their potential to enhance accuracy, capture intricate relationships, and refine predictive capabilities. Sun et al. (2024) [22] utilized GraphSAGE and deep reinforcement learning for optimizing financial investment portfolios. The results showed that this method performed well in handling complex financial relationships, but more empirical research was needed to verify its effectiveness in actual markets.
In summary, a meticulous examination of the reviewed literature underscores the substantial potential of emerging technologies, particularly machine learning and deep learning, in the realm of fraud detection. Pioneering studies by Fang et al. (2021), Xu et al. (2022), Verykios et al. (2022), and Usman et al. (2023) illustrate methodologies adept at discerning intricate patterns within vast, high-dimensional datasets. These innovative approaches identify anomalous behavior effectively and exhibit adaptability to evolving forms of fraud through continuous optimization. While the exploration of graph neural network applications in finance highlights their remarkable efficacy in fraud recognition and stock prediction, the existing body of research has overlooked concerns related to the leakage of user data information within the financial domain.
Although the aforementioned research extensively explores the applications of machine learning and deep learning technologies in the financial field, there is little mention of the potential of GNNs in financial anti-fraud. And the application of graph neural networks in the field of financial fraud has not been fully explored. This article aims to use GNNs to solve the problem of anti-fraud in the financial field and improve the accuracy and reliability of fraud detection. In particular, this article focuses on the complex correlations and unstructured data of financial transactions and explores these characteristics through GNN technology to fill the gap in existing research in this field and provide new research perspectives and solutions for the field of financial anti-fraud.
3. GNN Applications in Financial Anti-Fraud Research
3.1. Optimization Analysis of GNN Models Applied in Financial Anti-Fraud
In the realm of finance, intricate relationships among nodes in financial network data necessitate a nuanced approach for effective fraud detection. Recognizing the multifaceted nature of financial fraud requires a thorough understanding and capture of node information within financial network data. GNNs emerge as a powerful tool for this purpose, excelling in the capacity to capture associations between nodes and model complex relationships inherent in financial transactions [23,24]. It is noteworthy that GNN models encompass Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCNs) and GANs.
GCNs, rooted in convolutional operations, are tailored to handle graph data, specifically representing connections between nodes [25]. The fundamental concept of GCNs involves information propagation based on the underlying graph structure, facilitating each node in acquiring and integrating information from its neighboring nodes, as illustrated in Figure 1.
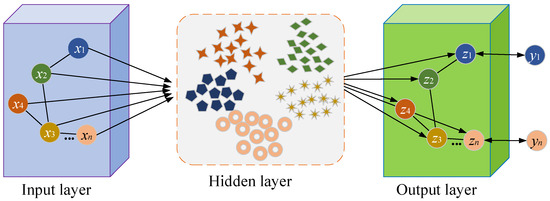
Figure 1.
GCN framework.
In GCNs, each node aggregates information about its neighboring nodes and adjusts weights to retain important information about node relationships. After aggregating neighbor information, nodes will propagate their feature information to neighboring nodes, forming a layer-by-layer information transmission process. At each layer, through graph convolution operations, nodes update their feature representations while considering the contributions of neighboring nodes. This graph-based information propagation enables GCNs to capture nonlinear relationships and interactions between nodes in complex networks, providing powerful modeling capabilities for the financial anti-fraud model.
Let the graph representing image information in the financial domain be denoted as , where the graph comprises vertices , with edge sets and edge weight . First, vertex features are extracted, where denotes the feature vector of the i-th vertex in the image. These features are then utilized as input for the GCN. In the context of the anti-fraud graph in the financial domain, can be defined as in Equation (1) below:
Equation (2) describes the GCN.
In Equation (2), denotes the l-th hidden layer; refers to the adjacency matrix of the subject interaction graph; signifies the identity matrix; refers to the degree matrix containing the entry and exit coefficients of each vertex of the interaction graph; represents the parameter matrix of network learning; and indicates the activation function, utilizing the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation.
The GAN accomplishes feature propagation and aggregation by adaptively learning attention weights between each node and its neighboring nodes [26,27].
In a standard GAN, the input and output of the graph attention layer are defined as in Equations (3) and (4), respectively:
Here, n stands for the number of vertices contained in the graph data, InD refers to the feature dimension of the input vertex, and OutD represents the feature dimension of the output vertex.
For the target node q, a forward propagation neural network is utilized to calculate the weight of its neighboring nodes , as defined in Equation (5):
In Equation (5), refers to the vector-splicing operation, denotes the learnable parameter matrix, and is the mapping function. and refer to the feature vectors. After obtaining the weights of neighboring nodes using GAN, the neighborhood weight is normalized using the softmax activation function, as defined in Equation (6):
Once GAN computes the weight distribution for all neighboring nodes of the node , it performs a weighted sum of the features of each neighboring node along with its weight. The feature vector of node is updated, as shown in Equation (7):
Furthermore, GAN employs independent attention heads to model relationships between nodes in different subspaces. The updated feature vector of node is represented as Equation (8):
The output of multi-head attention is formed by concatenating the features from all heads, providing a more comprehensive representation of node features in the graph. Additionally, the output of the last layer (prediction layer) in GAN is the average result across multiple attention heads, as denoted in Equation (9):
Based on the aforementioned computation process of GAN, the node feature-updating process is illustrated in Figure 2.
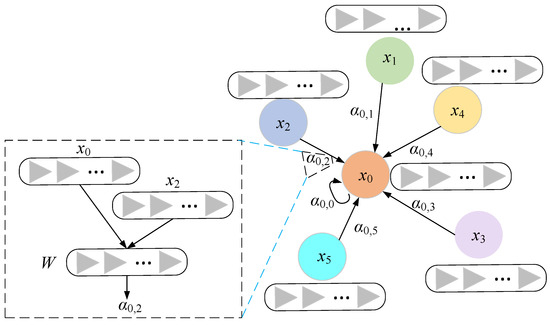
Figure 2.
Node-updating process of GAN.
In Figure 2, within the GAN, the node feature updating involves the following steps. Step 1: Employ a learnable function to compute the “similarity” weights between the features of neighboring nodes and the target node’s feature, followed by normalization using an activation function to form the weight distribution of neighboring nodes. Step 2: Weigh and sum the feature vectors of neighboring nodes to obtain a comprehensive feature vector of neighboring nodes. Step 3: Merge this integrated feature vector with the feature vector of the target node itself. Step 4: Update the target node’s feature through a non-linear transformation.
In this article, to mitigate redundancy and noise in fraud data within the financial domain network, a graph attention mechanism filters out noise and more accurately captures the semantic relationships between features and nodes. Simultaneously, the node channel attention and semantic channel attention in the GAN are combined to construct a Dual-channel Graph Attention Network (DGAN) module. This algorithm can filter out noise information, making the model more focused on extracting key features, thereby improving the sensitivity and accuracy of the model to data features. The design of the Dual-channel Attention Network module is illustrated in Figure 3.
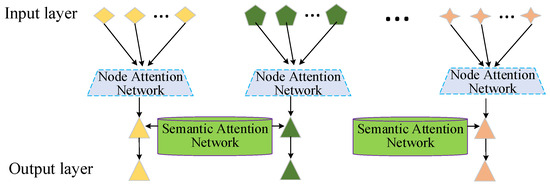
Figure 3.
DGAN module.
Moreover, to adeptly manage non-linear features and intricate interactive relationships within the data, Gradient-Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) [28] is incorporated. GBDT, as a powerful nonlinear model, has significant advantages in handling nonlinear features and complex data interactions. The DGAT network, which combines the graph attention mechanism, captures the relationship features between nodes more finely. GBDT is seamlessly integrated with the DGAN network, giving rise to the GBDT-DGAN network. The advantage of this combination lies in the fact that the GBDT-DGAT network can fully utilize the powerful nonlinear feature extraction ability of GBDT, while improving sensitivity to node relationships through the graph attention mechanism, thus considering the importance of features and relationships more comprehensively in the recognition of data information in the financial field. Subsequently, this amalgamated network is applied to identify data information within the financial domain.
3.2. Analysis of Privacy Protection with Blockchain
In the realm of financial transactions, ensuring data privacy holds paramount significance. Blockchain technology, distinguished by its decentralized, highly secure, and tamper-resistant distributed ledger system, presents an innovative solution for safeguarding the privacy of financial transaction data [29]. Its structure comprises six layers: the application layer, smart contract layer, incentive layer, consensus layer, network layer, and data layer, as depicted in Figure 4.
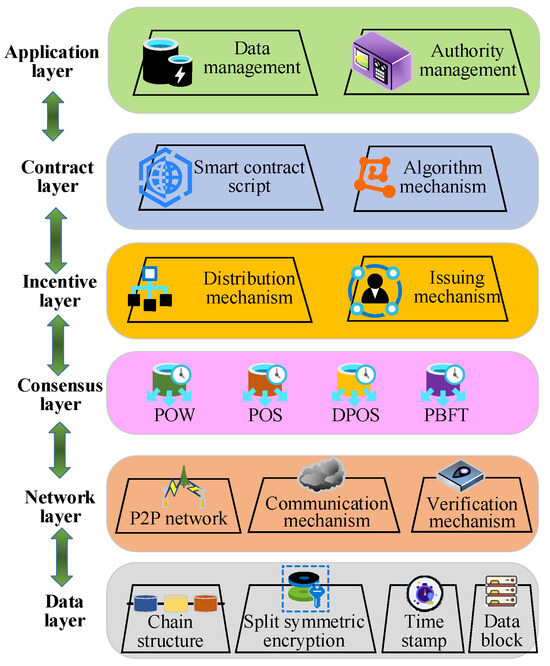
Figure 4.
Sketch map of the geographical location of the study area.
In the blockchain architecture diagram depicted in Figure 4, the application layer involves programmable currency and programmable finance applications provided by the Ethereum platform through smart contracts. The contract layer utilizes a scripting language unique to the Ethereum blockchain, facilitating interaction with the upper-level application and lower-level data layers. The incentive layer comprises mechanisms involving cryptographic currencies, incentivizing participants to operate and maintain the blockchain network. The consensus layer ensures a more efficient consensus on data within blocks in a fully distributed environment, employing various algorithms as indicated in Table 1. The network layer is primarily responsible for node connectivity, transaction broadcasting, and block broadcasting. The data layer predominantly employs distributed data structures to store and manage information within the blockchain [30,31].

Table 1.
Summary of consensus algorithms in blockchain.
As presented in Table 1, the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm is a prevalent method in the consensus layer of blockchain. It identifies the block owner through the calculation of the difficulty value, ensuring the security of user data in the financial domain and preventing malicious activities and data tampering [32]. In the event of information conflicts, PoW places trust in the chain branch with the highest number of blocks. Consequently, a malicious attacker must ensure that the length of the attack chain they send surpasses that of the main chain to acquire the authority to tamper with the entire blockchain [33]. The probability Pn can be expressed as Equation (10):
In Equation (10), represents the probability that the next block belongs to an honest node, represents the probability that the next block belongs to a malicious node, and represents the probability of a malicious attacker tampering with blocks. Expanding on this, assuming that an honest node can generate a block every average expected time, the potential progress of malicious nodes should follow a Poisson distribution, with an expected value . As shown in Equation (11):
Thus, when the number of blocks published by malicious nodes exceeds the number of blocks published by honest nodes, the malicious nodes have successfully conducted an attack. The probability of this situation occurring should be determined by multiplying the probability density of the Poisson distribution of the number of blocks already published by malicious nodes with the probability that malicious nodes can still complete the attack at that point. The specific calculation results are given by Equation (12):
Further simplify the occurrence probability , and the result is as shown in Equation (13):
Through computational analysis, when the computational power of malicious nodes is below 50%, the probability of a successful attack decreases with an increase in . In the context of specific applications for securing enterprise intelligent financial data, is often set to 6. This implies that information from a new block is considered safe and valid only after undergoing six block generations following its creation.
Therefore, when applying blockchain technology to the privacy protection of user data in the financial domain, this article selects the PoW consensus algorithm to offer a more comprehensive and reliable safeguard for the privacy and security of financial data.
3.3. Construction and Analysis of a Financial Anti-Fraud Model Integrating Blockchain with GNN
In the domain of fraud detection within the financial sector, this article introduces the GAN from GNNs to effectively identify fraudulent information in user transactions. The Node Attention Network (NAN) is combined with the Semantic Attention Network, designing a Dual-Head Attention Network module. Additionally, to better handle non-linear features and the complex interactive relationships within data, this study integrates the GBDT. This integration results in the GBDT-DGAN network, which is utilized to detect fraudulent activities in user transactions.
Furthermore, blockchain technology is introduced to ensure the effective protection of private information during user transactions. In the end, a financial anti-fraud model based on the integration of blockchain with the GBDT-DGAN algorithm is constructed, as depicted in Figure 5.
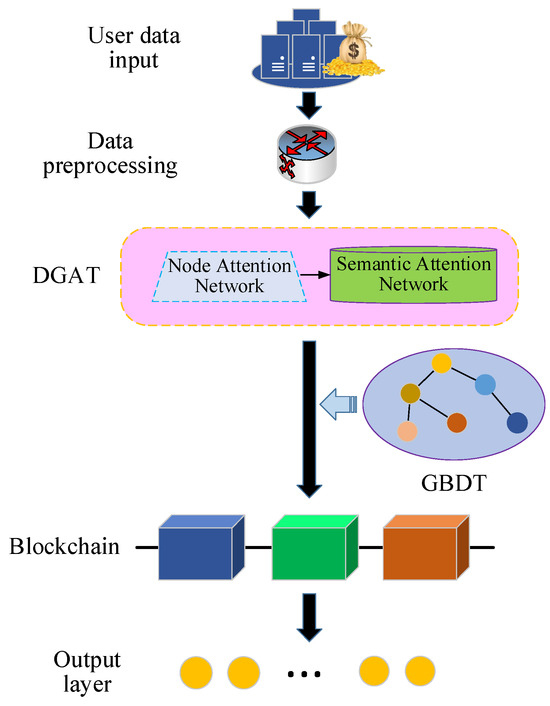
Figure 5.
Framework of the financial anti-fraud model based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm.
As illustrated in Figure 5, upon inputting user transaction data, the initial step involves preprocessing financial transaction data. This encompasses data cleaning, feature extraction, and transformation, converting transaction data into a graph representation with nodes and edges. Subsequently, the Dual-Head Attention Network module, combining the NAN and the Semantic Attention Network, is employed to handle transaction relationships within the data. The data processed through DGAN is then fused with the GBDT, specifically utilizing the GBDT-DGAN network to identify data information features of user transactions in the network. Finally, the model output data is integrated with blockchain technology, recording it on the blockchain to protect privacy information and ensure data integrity. In the blockchain network, zero-knowledge proof technology is utilized to construct trusted zero-knowledge proofs [34]. This enables the network to publish keywords required by users, regulatory agencies, and financial institutions for querying. Smart contracts verify whether the user transaction data provided in the blockchain meets anti-fraud requirements. Ultimately, the transaction data receives a label indicating fraud or security after model prediction.
In this framework model, the constructed GBDT-DGAT algorithm combines DGAT and GBDT and trains a GNN on graph G with node feature through minimization of and gradient descent. It also optimizes the node feature and minimizes the loss function through a dual-attention mechanism, establishes a GBDT model for f decision trees, and updates the node feature to using the GBDT model .
In the second iteration of the model algorithm, the initial input node feature and the updated feature are used as inputs to the DGAT algorithm. The updated node feature is represented as , and the difference between the node feature (as shown in Equation (14)) and the new node feature optimized using the dual-channel attention mechanism is used as the label for constructing the next decision tree, as shown in Equation (15):
GBDT is used as the gradient descent update of node feature by DGAT. The aggregation result of predicted values is shown in Equation (16):
is the predictive performance of DGAT on this basis of .
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Environments and Evaluation
To validate the performance of the financial anti-fraud model based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm constructed in this article, the data source utilized was the YelpChi dataset “https://www.datafountain.cn/datasets (accessed on 25 March 2021)”. The data in this dataset were desensitized and preprocessed through normalization, data cleaning, and transformation, resulting in 13,481 data points, which were split into a training set and a testing set in a 7:3 ratio. In this experiment, assuming that certain users frequently post a large number of false comments within a specific time window, this behavior may be identified as abnormal behavior that does not conform to normal patterns. The model can capture these abnormal features, such as the frequency of comments and the similarity of content. For example, among merchants in the dataset, certain behaviors that frequently engage in high-value transactions during specific time periods are considered abnormal trading patterns by the model, deviating from normal trading behavior. This may indicate the existence of potential fraud risks.
For example, user A in the dataset posted 100 comments within 24 h, while the average number of comments for most users is 10. This has been identified as abnormal behavior and may involve false comments. User B posted 50 comments within an hour, which were clearly different from normal user behavior and marked as abnormal. There are also examples of abnormal transaction patterns, such as merchant conducting 10 high-value transactions in a short period of time at night, while other merchants have more stable transaction patterns. This abnormal behavior may imply potential fraudulent activities. Merchant frequently engages in micro-transactions during non-peak hours, which is inconsistent with the normal trading mode of the merchant and may be an indicator of abnormal behavior. By identifying these abnormal behaviors through models, financial institutions can further review and take appropriate measures to reduce potential fraud risks. Below are some cases of normal and abnormal modes, as shown in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4. These tables provide detailed information about comment frequency, content similarity, and trading behavior, including various indicators of users/user pairs and whether they are identified as abnormal.

Table 2.
Comment frequency distribution.

Table 3.
Content similarity distribution.

Table 4.
Analysis of trading behavior.
In the experiments, the Hyperledger Fabric consortium blockchain platform was employed. The CPU model running on the computer was CORE-i7-4720HQ-2.6GHz. Matrix operations were performed using the open-source tools Numpy and Pandas. Numpy is an open-source matrix-processing library, and Pandas provides excellent support for data cleaning and preprocessing in data analysis. The chaincode (smart contract) was implemented in the Go language. The Pandas library in Python was instrumental in data cleaning and preprocessing. Simultaneously, the TensorFlow platform was introduced to construct the GBDT-DGAN network, utilizing various modules provided by Python. Specific hyperparameter settings were as follows: The L2 regularization parameter was set to 0.0005, and the dropout for each layer was set at 0.6, with a total of 100 iterations. The optimizer used was Adam, which applied the stochastic gradient descent algorithm to optimize the loss function with an initial learning rate of 0.001.
To assess the performance of the model proposed in this article, the model algorithm was compared with GCN, BiLSTM [35], CNN [36], and the model algorithm proposed by Usman et al. [17]. (2023) from related literature. An evaluation was conducted based on convergence, precision, recall, F1 score, and data transfer security metrics.
4.2. Analysis of Recognition Accuracy Results for Different Algorithms
The recognition performance of the model proposed in this article is compared with GCN, BiLSTM, CNN, and the model algorithm proposed by Usman et al. (2023) [17] from related literature. The convergence situations are illustrated in Figure 6. Further comparisons are made for precision, recall, and F1 score, and the results are presented in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9.
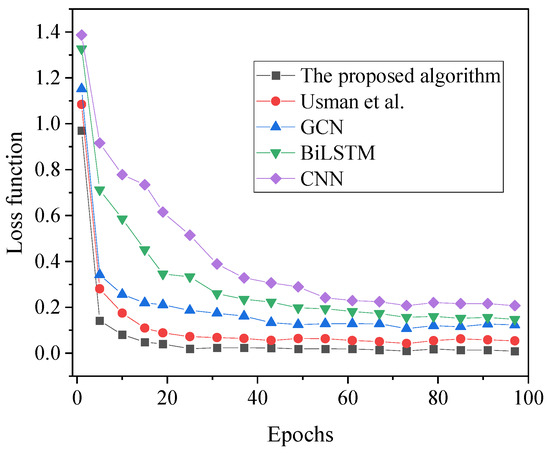
Figure 6.
Convergence performance results [17].
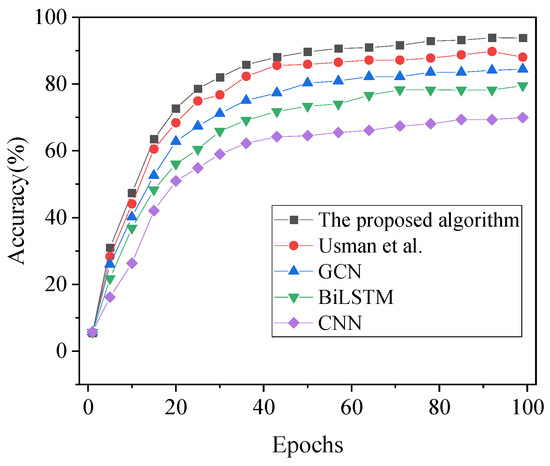
Figure 7.
Accuracy results of financial fraud detection under different algorithms with varying iteration cycles [17].
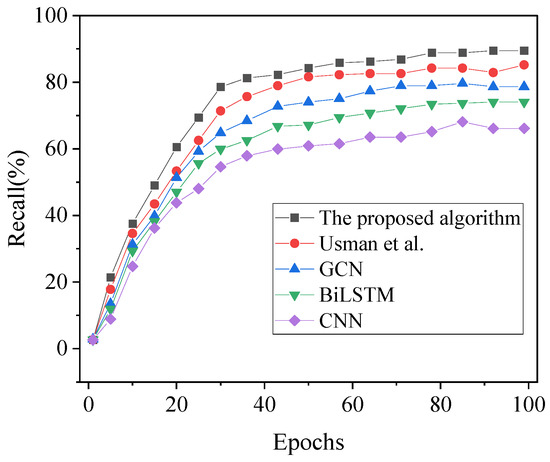
Figure 8.
Recall results of financial fraud detection under different algorithms with varying iteration cycles [17].
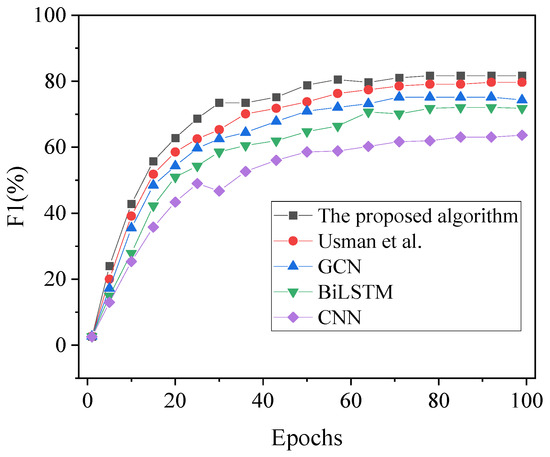
Figure 9.
F1 score results of financial fraud detection under different algorithms with varying iteration cycles [17].
As depicted in Figure 6, the analysis of loss values for each algorithm reveals that the proposed model algorithm in this article attains the minimum loss value, stabilizing around 0.013 by the 25th iteration. In contrast, the final loss functions of other algorithms all exceed 0.054. Hence, the financial anti-fraud model based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm proposed in this article demonstrates superior convergence, characterized by lower loss values.
As illustrated in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, it is evident that the accuracy, recall, and F1 scores of each algorithm exhibit an initial increase followed by stabilization with the variation in iteration cycles. In the comparative analysis involving model algorithms proposed by GCN, BiLSTM, CNN, and the algorithm presented by Usman et al. (2023) [17], the accuracy of the model algorithm developed in this article reaches 93.82%. The classification recognition performance of each algorithm, ranked from highest to lowest, is as follows: model algorithm in this article > Usman et al. (2023) [17] algorithm > GCN > BiLSTM > CNN. Notably, in comparison to other algorithms, the model algorithm in this article achieves a minimum of a 5.76% increase in accuracy. Furthermore, consistent trends in recall and F1 values are observed across the algorithms, with the recall and F1 values of the model algorithm in this article reaching 89.5% and 81.66%, respectively. Consequently, the financial anti-fraud model based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm, developed in this article, demonstrates superior predictive accuracy for identifying fraudulent data in user transactions.
Overall, the financial anti-fraud model proposed here based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm has achieved significant advantages in multiple indicators such as loss value, accuracy, recall rate, and F1 score. This model not only performs excellently in convergence but also surpasses other comparative algorithms in accuracy and overall performance. This proves that the proposed algorithm has excellent predictive performance in accurately identifying fraudulent data in user transactions.
4.3. Security Performance Analysis of the Model under Different Algorithms
In this section, a comprehensive analysis of the security performance of the proposed model algorithm is conducted, comparing it with GCN, BiLSTM, CNN, and the algorithm presented by Usman et al. (2023) [17]. The evaluation focuses on data transmission security, as illustrated in Figure 10.
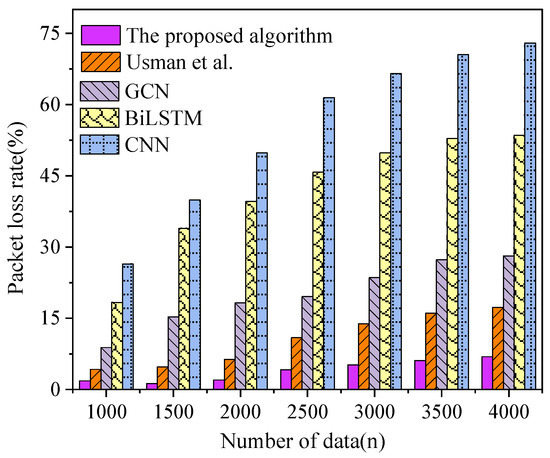
Figure 10.
Security results of each algorithm under different data amounts [17].
The examination of network data security transmission performance under varying data volumes reveals compelling insights. As depicted in Figure 10, the packet loss rate of the model proposed in this article demonstrates consistent performance, maintaining below 7% even as the volume of transmitted data increases. In contrast to alternative algorithms, the proposed model exhibits a lower packet loss rate, while other algorithms experience rates exceeding 17.3%. In summary, considering different data volumes, the financial anti-fraud model based on the blockchain-integrated GBDT-DGAN algorithm, as constructed in this article, showcases a significantly reduced packet loss rate, establishing its excellence in network data security transmission performance. This performance advantage is crucial for the secure transmission of financial transaction data. While maintaining a low packet loss rate, this model can effectively ensure the integrity and confidentiality of user transaction information. This is essential for financial institutions, especially when dealing with large amounts of transaction data; ensuring the reliability of network transmission is crucial for preventing fraudulent behavior and protecting user privacy. Therefore, the proposed financial anti-fraud model not only has a breakthrough in fraud detection performance but also performs excellently in network data security transmission performance. This makes the model more widely feasible and practical in practical financial applications, providing a comprehensive, efficient, and secure anti-fraud solution for the financial field.
5. Discussion
The target audience is mainly stakeholders in the financial sector, including financial institutions and regulatory agencies, as well as individuals and enterprises related to financial transactions. For financial institutions, it is a significant advancement that helps improve the security and reliability of financial transactions and reduces potential fraud risks. But data quality and quantity may be a potential challenge, as models rely heavily on high-quality and sufficient data. In addition, real-time and latency issues in the financial environment may affect the application of models, especially for trading environments that require rapid responses. The interpretability of the model may also become a key issue, and financial institutions may need to have a clear understanding of the basis for model judgments to meet regulatory requirements or customer needs. For individuals and businesses involved in financial transactions, this model will also provide them with a safer trading environment to enhance their confidence in financial transactions and reduce losses caused by fraudulent behavior.
Therefore, although the financial anti-fraud model has achieved encouraging results in experiments, some limitations still need to be addressed. Firstly, the model may have potential biases and errors, which can arise from biases in the data collection process, incomplete feature selection, or excessive reliance on certain types of fraudulent behavior. To address these issues, this article proposes a more diverse dataset collection and feature engineering optimization as a response. Secondly, data quality issues may affect the performance and robustness of the model. To address this issue, this article suggests conducting more thorough data cleaning and preprocessing, while improving the accuracy and consistency of data annotation. Finally, the model may perform well in specific financial environments, but its generalization ability is limited in other environments. Hence, it is recommended to adjust and optimize the model parameters to improve the adaptability of the model in different environments and conduct cross-environment validation to evaluate its universality.
6. Conclusions
This article introduces an advanced financial anti-fraud model, namely the GBDT–Dual-channel Graph Attention Network (GBDT-DGAN), which utilizes blockchain technology to enhance privacy protection. The structure of the GAN constructs a Dual-Head Attention Network module by integrating a Node Attention Network and a Semantic Attention Network. This module enables the comprehensive analysis of the complex relationships in user transaction data and skillfully deals with nonlinear characteristics and complex data interaction relationships. After verification, the model achieves a significant accuracy of 93.82%, which is at least 5.76% higher than baseline algorithms such as CNN. The recall rate and F1 score further demonstrate the effectiveness of the model, reaching 89.5% and 81.66%, respectively. In addition, the model performs excellently in ensuring network data transmission security, maintaining a packet loss rate of less than 7%. The experimental evaluation consolidates the superiority of the proposed model in terms of accuracy, emphasizing its potential as a powerful solution for financial transaction fraud detection. The introduction of the GBDT-DGAN algorithm, combined with blockchain technology, not only improves accuracy but also significantly enhances user privacy.
Although this article has achieved significant results, there are still some limitations. For example, this article uses the YelpChi dataset for experimentation. However, this dataset still has its limitations and may not fully cover all complex transaction patterns in the financial field. Future research can consider more extensive financial transaction data to improve the generalization of the model. Although feature engineering and data preprocessing are conducted in the article, there are still limitations that may not cover all potential patterns. Future research can further explore more refined feature engineering methods to improve the model’s ability to identify different fraudulent behaviors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; Data curation, S.W.; Formal analysis, S.W.; Funding acquisition, S.L.; Investigation, S.W.; Methodology, S.W.; Project administration, S.W. and S.L.; Resources, S.W.; Software, S.W.; Supervision, S.L.; Validation, S.W.; Visualization, S.W.; Writing—original draft, S.W.; Writing—review and editing, S.W. and S.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by “Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS)” through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (2021RIS-001 (1345370811)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| GBDT | Gradient-Boosting Decision Trees |
| GBDT-DGAN | Gradient-Boosting Decision Trees–Dual-channel Graph Attention Network |
| NAN | Node Attention Network |
| BiLSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| GCN | Graph Convolutional Network |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GAT | Graph Attention Network |
| PoW | Proof of Work |
| POS | Proof of Stake |
| DPOS | Delegated Proof of Stake |
| PBFT | Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance |
References
- Ali, A.; Razak, S.A.; Othman, S.H.; Eisa, T.A.E.; Al-Dhaqm, A.; Nasser, M.; Elhassan, T.; Elshafie, H.; Saif, A. Financial Fraud Detection Based on Machine Learning: A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragazou, K.; Passas, I.; Garefalakis, A. It Is Time for Anti-Bribery: Financial Institutions Set the New Strategic “Roadmap” to Mitigate Illicit Practices and Corruption in the Market. Adm. Sci. 2022, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendri, N.; Sari, S.U. Sistematic Literature Review: The Strategy for Preventing Government Financial Report Fraud. JAK (J. Akunt.) Kaji. Ilm. Akunt. 2023, 10, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, D. Research on Financial Fraud Detection Models Integrating Multiple Relational Graphs. Systems 2023, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wu, J.; Xue, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, C.; Sheng, Q.Z.; Xiong, H.; Akoglu, L. A comprehensive survey on graph anomaly detection with deep learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 12012–12038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, M.N.; Raahemi, B. Intelligent fraud detection in financial statements using machine learning and data mining: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access 2021, 10, 72504–72525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, J. Medical image fusion method by deep learning. Int. J. Cogn. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X. Tracking down financial statement fraud by analyzing the supplier-customer relationship network. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 178, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, J. An Accelerated Method for Protecting Data Privacy in Financial Scenarios Based on Linear Operation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, R. A Causal Graph-Based Approach for APT Predictive Analytics. Electronics 2023, 12, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, P.; Yan, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, T. Deep learning anti-fraud model for internet loan: Where we are going. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 9777–9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarfaj, F.K.; Malik, I.; Khan, H.U.; Almusallam, N.; Ramzan, M.; Ahmed, M. Credit card fraud detection using state-of-the-art machine learning and deep learning algorithms. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 39700–39715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Xiang, S.; Shang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, L. Spatio-temporal attention-based neural network for credit card fraud detection. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Mohamad, U.H.; Sarlan, A.; Shutaywi, M.; Daradkeh, Y.I.; Mohammed, H.O. Development of an intelligent information system for financial analysis depend on supervised machine learning algorithms. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Xu, L. Integrating Individual Factors to Construct Recognition Models of Consumer Fraud Victimization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verykios, V.S.; Stavropoulos, E.C.; Zorkadis, V.; Katsikatsos, G.; Sakkopoulos, E. Sensitive data hiding in financial anti-fraud process. Int. J. Electron. Gov. 2022, 14, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.; Naveed, N.; Munawar, S. Intelligent Anti-Money Laundering Fraud Control Using Graph-Based Machine Learning Model for the Financial Domain. J. Cases Inf. Technol. 2023, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Yang, F.; Xiang, S.; Liu, J. Financial time series forecasting with multi-modality graph neural network. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 121, 108218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P. A Dynamic Attributes-driven Graph Attention Network Modeling on Behavioral Finance for Stock Prediction. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2023, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, H.; Ying, X.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J. HGNN: Hierarchical graph neural network for predicting the classification of price-limit-hitting stocks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 607, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, A.; Herrera, P.J.; Monge, M. A Combined Model Based on Recurrent Neural Networks and Graph Convolutional Networks for Financial Time Series Forecasting. Mathematics 2023, 11, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wei, X.; Yang, X. GraphSAGE with deep reinforcement learning for financial portfolio optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamis, I.; Michail, D.; Glykou, F.; Tsantilas, P. A survey on the use of graph convolutional networks for combating fake news. Future Internet 2022, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, D.; Kanakaris, N.; Varlamis, I. Detection of fake news campaigns using graph convolutional networks. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2022, 2, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, A.; Beigy, H. SGCSumm: An extractive multi-document summarization method based on pre-trained language model, submodularity, and graph convolutional neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Tian, X. Detecting Phishing Accounts on Ethereum Based on Transaction Records and EGAT. Electronics 2023, 12, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. Mining Mobile Network Fraudsters with Augmented Graph Neural Networks. Entropy 2023, 25, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, M.; Hu, Z.; Niu, H. Textual Emotional Tone and Financial Crisis Identification in Chinese Companies: A Multi-Source Data Analysis Based on Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Bala, P.K.; Chakraborty, S. An Empirical Study of User Adoption of Cryptocurrency Using Blockchain Technology: Analysing Role of Success Factors like Technology Awareness and Financial Literacy. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2023, 18, 1580–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucari, N.; Lagasio, V.; Lia, G.; Torriero, C. The impact of blockchain in banking processes: The Interbank Spunta case study. Technol. Anal. Strateg. 2022, 34, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metawa, N.; Alghamdi, M.I.; El-Hasnony, I.M.; Elhoseny, M. Return Rate Prediction in Blockchain Financial Products Using Deep Learning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. A smart energy IoT model based on the Itsuku PoW technology. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Pianese, F.; Leach, T.; Oliveras, E. A great disturbance in the crypto: Understanding cryptocurrency returns under attacks. Blockchain Res. Appl. 2021, 2, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Cao, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, X. Privacy-preserving and efficient data sharing for blockchain-based intelligent transportation systems. Inf. Sci. 2023, 635, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Z.; Wen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, K. Ethereum Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection Model Based on Triplet Loss and BiLSTM. Electronics 2023, 12, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, P.C.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lee, B.G. Enhancing Financial Fraud Detection through Addressing Class Imbalance Using Hybrid SMOTE-GAN Techniques. Int. J. Financ. Stud. 2023, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).