A GMMA-CPS-Based Vaccine for Non-Typhoidal Salmonella
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Media and Growth Conditions
2.2. Generation of S. Typhimurium Mutant Strains
2.3. Generation of Transposon Mutants
2.4. Generation of Plasmid Vectors
2.5. Purification and Neutral Monosaccharide Analysis of Capsular Polysaccharide
2.6. Endotoxin Removal from Purified EPS
2.7. Conjugation of EPS to Truncated Glycoprotein D (tgD) and CRM197
2.8. Outer Membrane Vesicles (GMMAs) Production and Purification
2.9. Vaccine Formulation
2.10. Murine Immunization Experiments
2.11. Murine Infection Experiments
2.12. ELISA
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The yih Operons Are Not Involved in S. Typhimurium Virulence
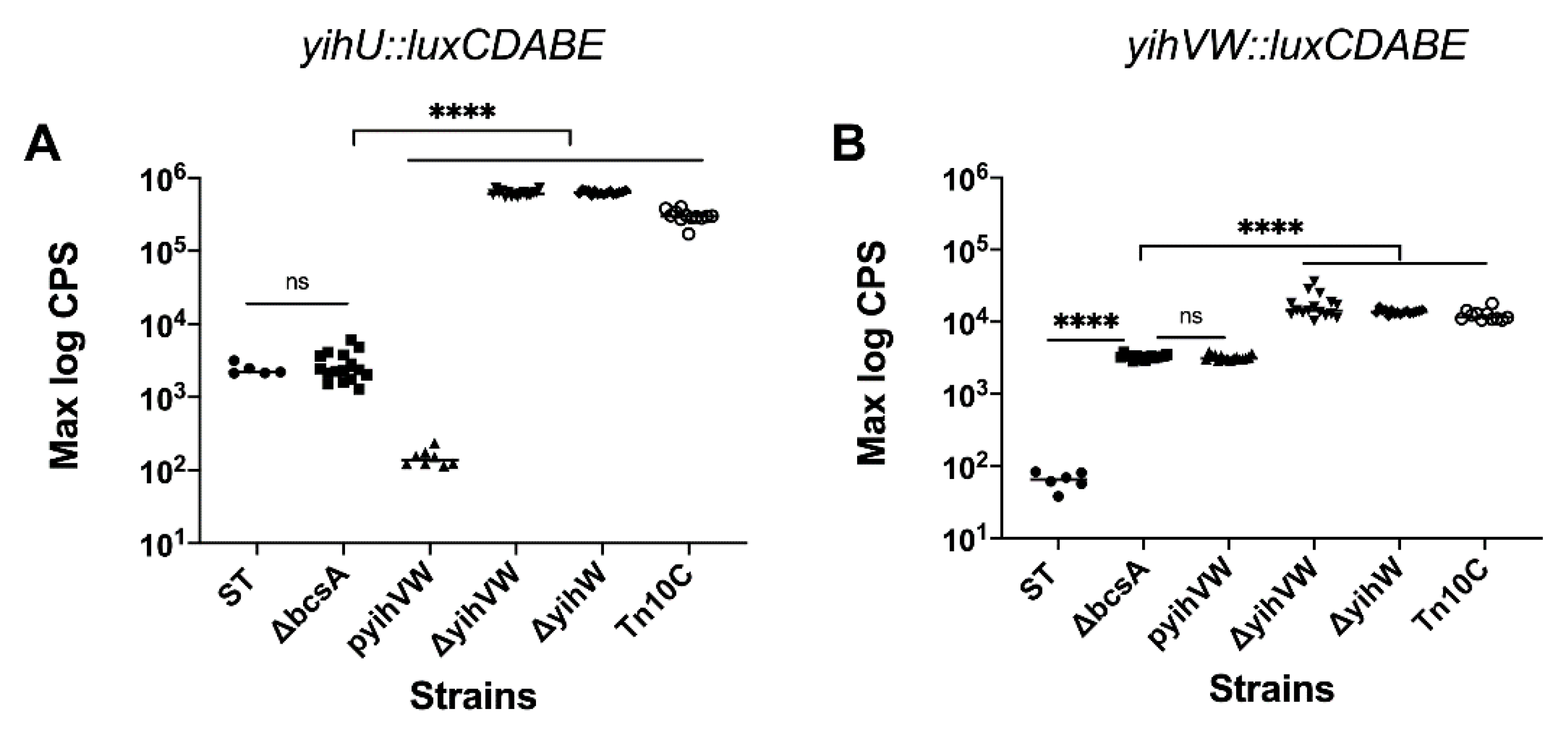
3.2. YihW Represses Expression of the Yih Operons
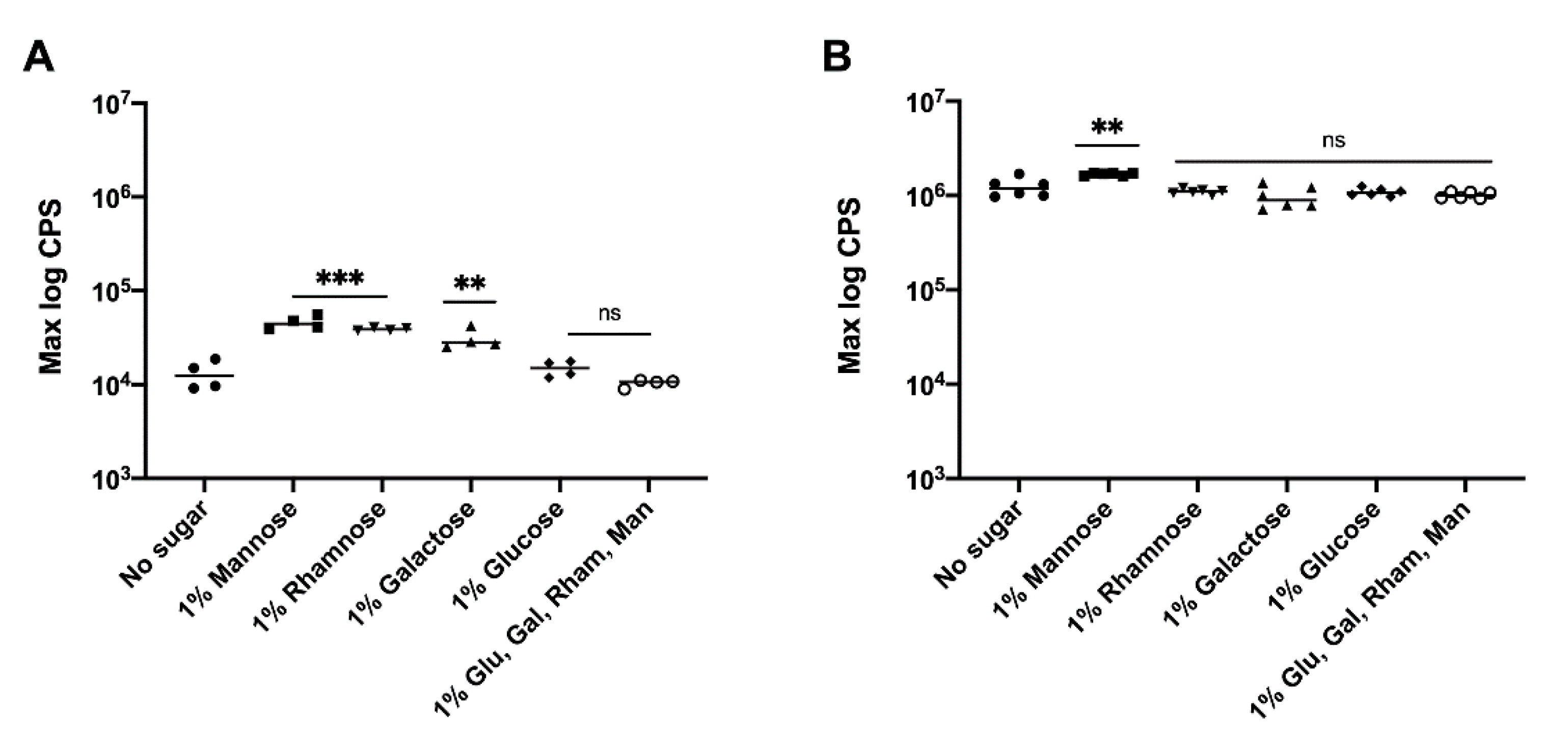
3.3. Effect of Precursor Sugars on yihUTSRQPO Promoter Activity
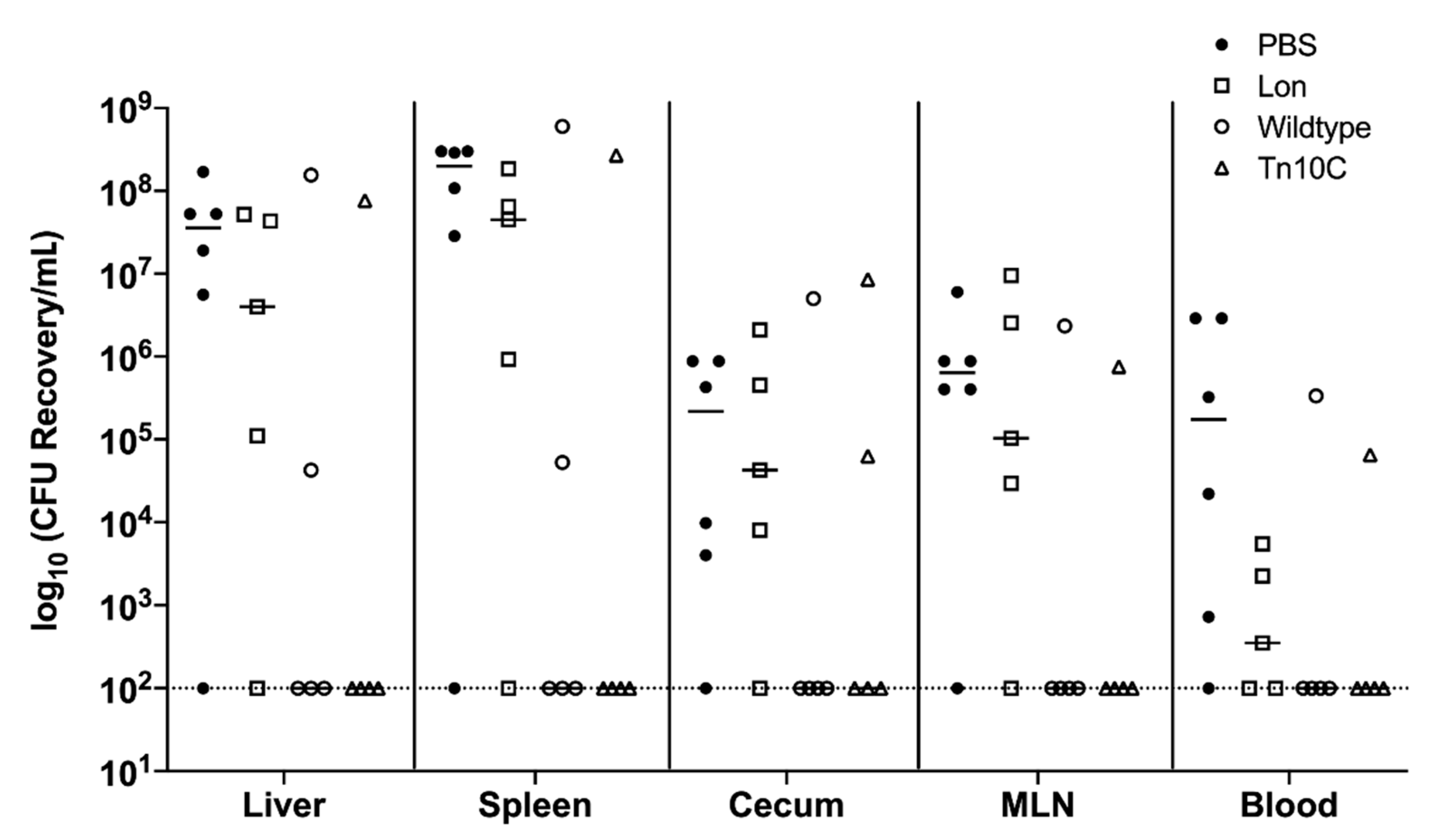
3.4. Overproduction of CPS in Transposon Mutants
3.5. Increased CPS Production by Salmonella Grown in Buffered Media
3.6. Overproduction of Colanic Acid in S. Typhimurium
3.7. Removal of Contaminating LPS from Purified CPS
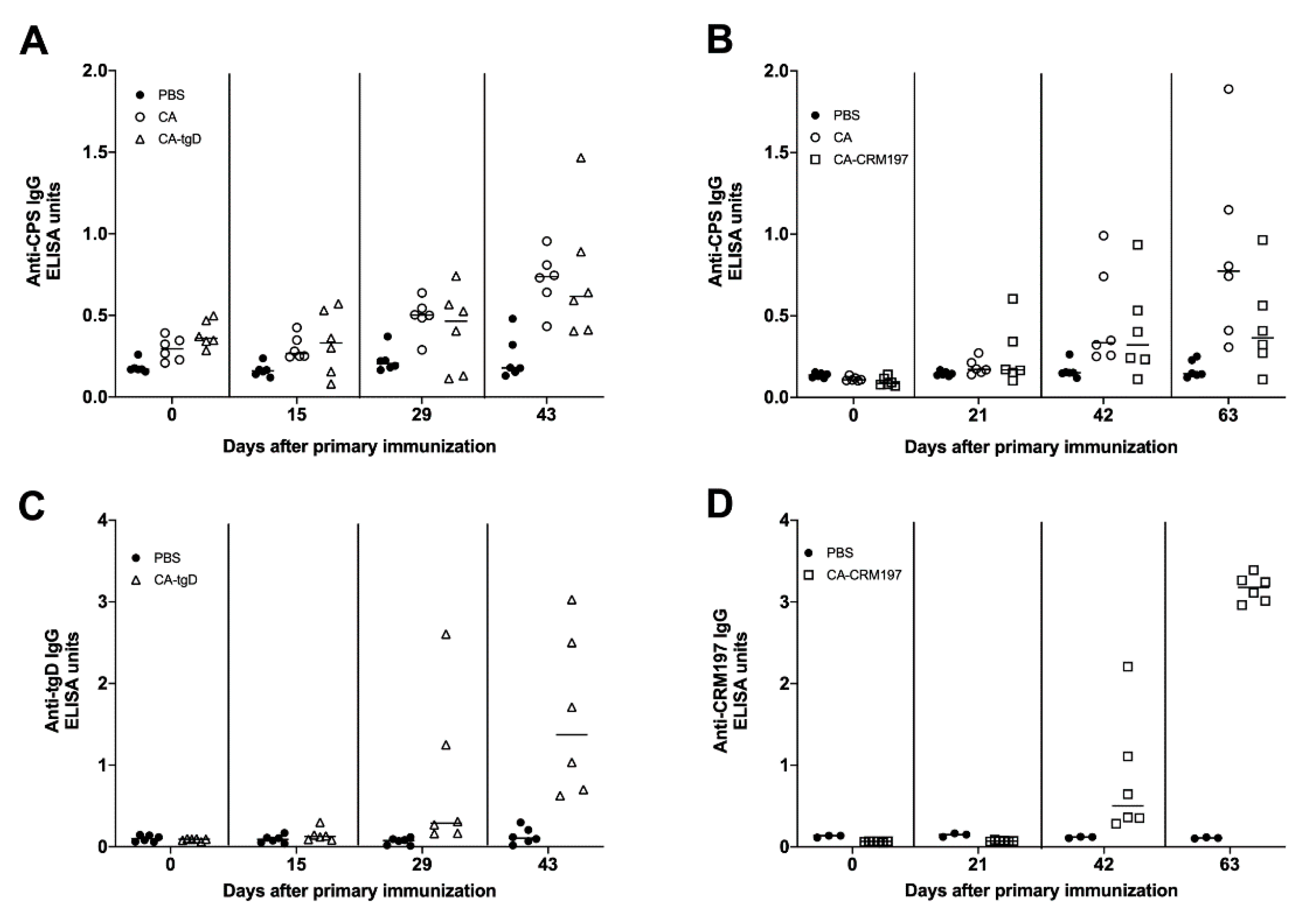
3.8. Immune Response Induced by Colanic Acid
3.9. Immunization with Colanic Acid Does Not Induce a Protective Immune Response
3.10. Immunogenicity of GMMAs
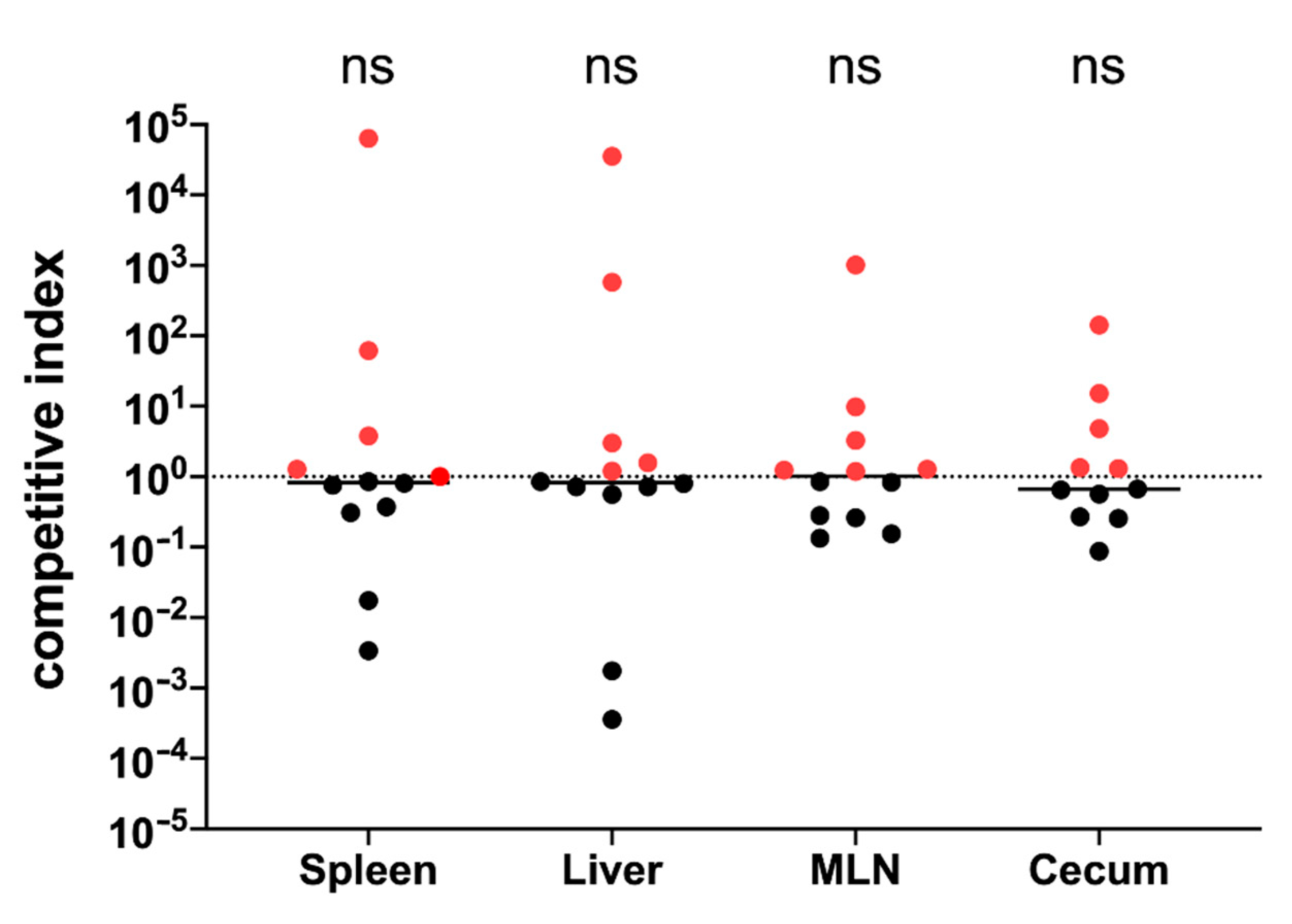
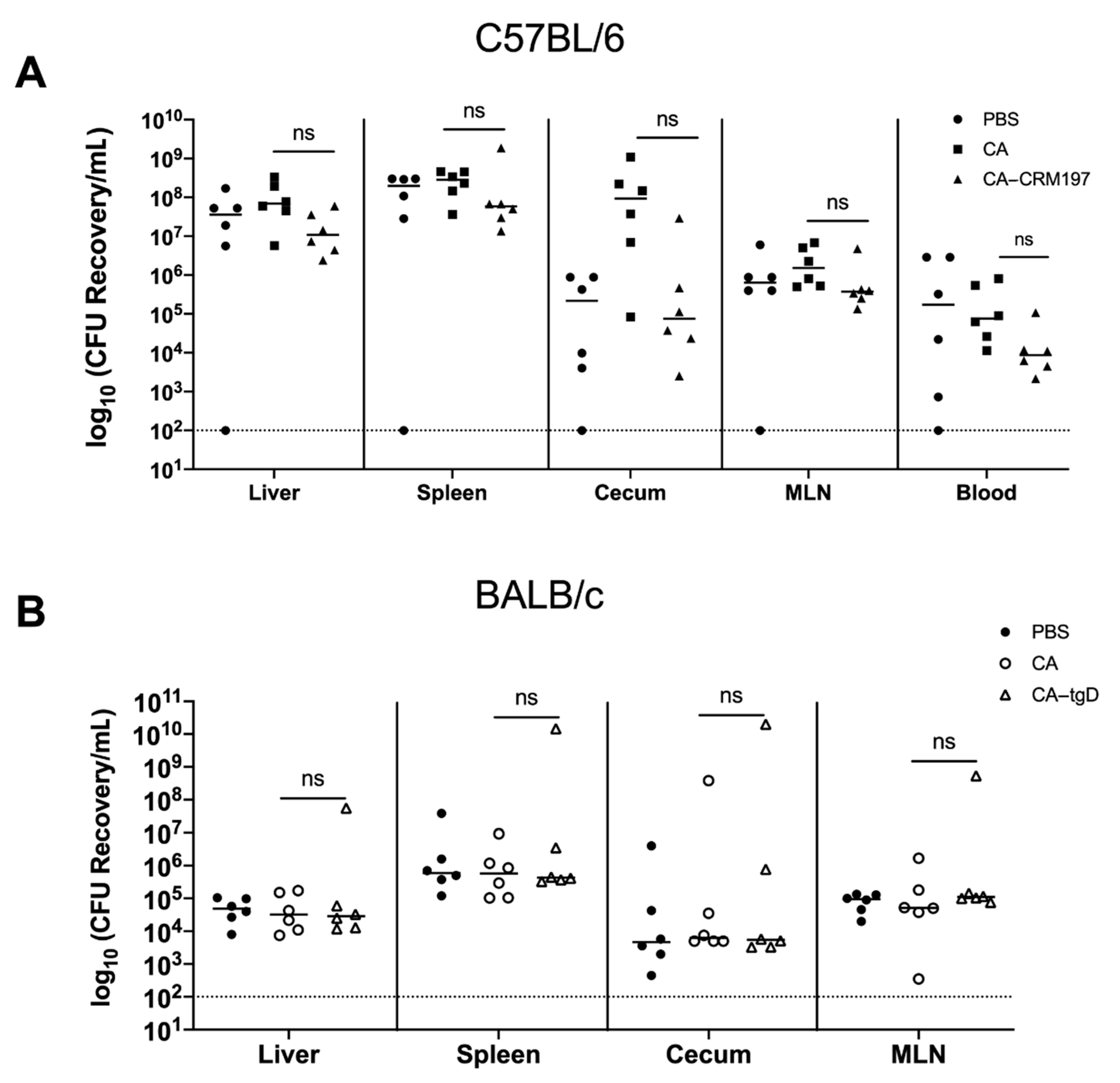
3.11. Immunization with GMMA Reduced Salmonella Colonization of Mice Organs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, M.D.; Pires, S.M.; Black, R.E.; Caipo, M.; Crump, J.A.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Döpfer, D.; Fazil, A.; Fischer-Walker, C.L.; Hald, T.; et al. World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 22 Foodborne Bacterial, Protozoal, and Viral Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Mor, O.; Boyle, E.C.; Grassl, G.A. Same Species, Different Diseases: How and Why Typhoidal and Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Enterica Serovars Differ. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; for the International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, S.-K.; Pusparajah, P.; Mutalib, N.-S.A.; Ser, H.-L.; Chan, K.-G.; Lee, L.-H. Salmonella: A Review on Pathogenesis, Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, E.A.; Shaw, A.V.; Crump, J.A. Community-Acquired Bloodstream Infections in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feasey, N.A.; Dougan, G.; Kingsley, R.A.; Heyderman, R.S.; Gordon, M.A. Invasive Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Disease: An Emerging and Neglected Tropical Disease in Africa. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2012, 379, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C. EPS—Then and Now. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Structural Studies on Colanic Acid, the Common Exopolysaccharide Found in the Enterobacteriaceae, by Partial Acid Hydrolysis. Oligosaccharides from Colanic Acid. Biochem. J. 1969, 115, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.L.; White, A.P.; Snyder, S.D.; Martin, S.; Heiss, C.; Azadi, P.; Surette, M.; Kay, W.W. Salmonella Produces an O-Antigen Capsule Regulated by AgfD and Important for Environmental Persistence. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7722–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, W.F. COLANIC ACID. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1963, 49, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenackers, H.; Hermans, K.; Vanderleyden, J.; Keersmaecker, S.C.J.D. Salmonella Biofilms: An Overview on Occurrence, Structure, Regulation and Eradication. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 502–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.M.; Gunn, J.S. The O-Antigen Capsule of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Facilitates Serum Resistance and Surface Expression of FliC. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3946–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondini, S.; Lanzilao, L.; Necchi, F.; O’Shaughnessy, C.M.; Micoli, F.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A. Invasive African Salmonella Typhimurium Induces Bactericidal Antibodies against O-Antigens. Microb. Pathog. 2013, 63, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Y.S.; Clare, S.; Micoli, F.; Saul, A.; Mastroeni, P.; MacLennan, C.A. Monoclonal Antibodies of a Diverse Isotype Induced by an O-Antigen Glycoconjugate Vaccine Mediate In Vitro and In Vivo Killing of African Invasive Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3722–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Lanzilao, L.; Gavini, M.; Alfini, R.; Brandt, C.; Clare, S.; Mastroeni, P.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A. Design of Glycoconjugate Vaccines against Invasive African Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.S.; Gibson, D.; Heiss, C.; Kay, W.; Azadi, P. Structure of a Capsular Polysaccharide Isolated from Salmonella enteritidis. Carbohyd. Res. 2006, 341, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phalipon, A.; Tanguy, M.; Grandjean, C.; Guerreiro, C.; Bélot, F.; Cohen, D.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Mulard, L.A. A Synthetic Carbohydrate-Protein Conjugate Vaccine Candidate against Shigella Flexneri 2a Infection. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2009, 182, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Steiner, S.; Fernandez, J.; Biltoft, C.; Wohl, M.E.; Sanchez, J.; Feris, J.; Balter, S.; Levine, O.S.; Carlone, G.M. Functional Antibody Activity Elicited by Fractional Doses Of Haemophilus Influenzae Type b Conjugate Vaccine (Polyribosylribitol Phosphate–Tetanus Toxoid Conjugate). Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immun. 2001, 8, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jan, A.T. Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) of Gram-Negative Bacteria: A Perspective Update. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-Membrane Vesicles from Gram-Negative Bacteria: Biogenesis and Functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernadac, A.; Gavioli, M.; Lazzaroni, J.C.; Raina, S.; Lloubès, R. Escherichia Coli Tol-Pal Mutants Form Outer Membrane Vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4872–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.; Pommier, S.; Journet, L.; Bernadac, A.; Gorvel, J.-P.; Lloubès, R. Improved Methods for Producing Outer Membrane Vesicles in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2004, 155, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, F.B.; Doro, F.; Rodríguez-Ortega, M.J.; Stella, M.; Liberatori, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Serino, L.; Moriel, D.G.; Nesta, B.; Fontana, M.R.; et al. Proteomics Characterization of Outer Membrane Vesicles from the Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli ΔtolR IHE3034 Mutant. Mol. Cell Proteom. Mcp. 2007, 7, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.J.; Osterrieder, N.; Metzger, S.M.; Buckles, E.; Doody, A.M.; DeLisa, M.P.; Putnam, D. Delivery of Foreign Antigens by Engineered Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3099–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Doody, A.M.; Chen, D.J.; Cremona, G.H.; Shuler, M.L.; Putnam, D.; DeLisa, M.P. Engineered Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles with Enhanced Functionality. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 380, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T.N.; Kuehn, M.J. Virulence and Immunomodulatory Roles of Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 2010, 74, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vipond, C.; Wheeler, J.X.; Jones, C.; Feavers, I.M.; Suker, J. Characterization of the Protein Content of a Meningococcal Outer Membrane Vesicle Vaccine by Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry. Hum. Vaccines 2005, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, F.; Rondini, S.; Alfini, R.; Lanzilao, L.; Necchi, F.; Negrea, A.; Rossi, O.; Brandt, C.; Clare, S.; Mastroeni, P.; et al. Comparative Immunogenicity and Efficacy of Equivalent Outer Membrane Vesicle and Glycoconjugate Vaccines against Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10428–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, T.; Roth, J.R. Characterization of Tn10d-Cam: A Transposition-Defective Tn10 Specifying Chloramphenicol Resistance. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1988, 213, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.P.; Gibson, D.L.; Kim, W.; Kay, W.W.; Surette, M.G. Thin Aggregative Fimbriae and Cellulose Enhance Long-Term Survival and Persistence of Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, J.C.; Davis, M.A.; Morisato, D.; Roberts, D.E.; Kleckner, N. New Tn10 Derivatives for Transposon Mutagenesis and for Construction of LacZ Operon Fusions by Transposition. Gene 1984, 32, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, J.; Southward, C.M.; Surette, M.G. Genomic Profiling of Iron-Responsive Genes in Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium by High-Throughput Screening of a Random Promoter Library. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 4973–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-Step Inactivation of Chromosomal Genes in Escherichia coli K-12 Using PCR Products. Proc. National Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloy, S.R.; Stewart, V.J.; Taylor, R.K. Genetic Analysis of Pathogenic Bacteria: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Plainview, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J.A.; Tan, H.; Collins, H.M.; Yap, K.; Khor, S.F.; Lim, W.L.; Xing, X.; Bulone, V.; Burton, R.A.; Fincher, G.B.; et al. Genetic and Environmental Factors Contribute to Variation in Cell Wall Composition in Mature Desi Chickpea (Cicer Arietinum L.) Cotyledons. Plant. Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettolino, F.A.; Walsh, C.; Fincher, G.B.; Bacic, A. Determining the Polysaccharide Composition of Plant Cell Walls. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1590–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, O.; Vercellone, A.; Paul, F.; Monsan, P.F.; Puzo, G. A Nondegradative Route for the Removal of Endotoxin from Exopolysaccharides. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordier, C. Phase Separation of Integral Membrane Proteins in Triton X-114 Solution. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 1604–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Ji, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, T. Conjugation of β-Glucan Markedly Increase the Immunogencity of Meningococcal Group Y Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Donkersgoed, J.V.; Kowalski, J.; van den Hurk, J.V.; Harland, R.; Babiuk, L.A.; Zamb, T.J. A Subunit GIV Vaccine, Produced by Transfected Mammalian Cells in Culture, Induces Mucosal Immunity against Bovine Herpesvirus-1 in Cattle. Vaccine 1994, 12, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivak, D.J.; MacKenzie, K.D.; Watson, N.L.; Pasternak, J.A.; Jones, B.D.; Wang, Y.; DeVinney, R.; Wilson, H.L.; Surette, M.G.; White, A.P. A Modular, Tn7-Based System for Making Bioluminescent or Fluorescent Salmonella and Escherichia Coli Strains. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2016, 82, 4931–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.P.; Gibson, D.L.; Grassl, G.A.; Kay, W.W.; Finlay, B.B.; Vallance, B.A.; Surette, M.G. Aggregation via the Red, Dry, and Rough Morphotype Is Not a Virulence Adaptation in Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.M.; Fisher, D.; Saunders, J.R.; Hart, C.A. The Role of Capsular Polysaccharide K2 1b of Klebsiella and of the Structurally Related Colanic-Acid Polysaccharide of Escherichia coli in Resistance to Phagocytosis and Serum Killing. J. Med. Microbiol. 1987, 24, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, G.; Lan, R.; Reeves, P.R. The Colanic Acid Gene Cluster of Salmonella Enterica Has a Complex History. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 191, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, S.; Warren, H.S.; Lowry, S.F.; Calvano, S.E.; Remick, D.; the Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury Investigators. Acute Inflammatory Response to Endotoxin in Mice and Humans. Clin. Diagnostic. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, P.O.; Lopes, A.M.; Mazzola, P.G.; Rangel-Yagui, C.; Penna, T.C.V.; Pessoa, A. Methods of Endotoxin Removal from Biological Preparations: A Review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. Publ. Can. Soc. Pharm. Sci. Société. Can. Des. Sci. Pharm. 2007, 10, 388–404. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, B.; Milsark, I.; Cerami, A. Passive Immunization against Cachectin/Tumor Necrosis Factor Protects Mice from Lethal Effect of Endotoxin. Science 1985, 229, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Babiuk, L.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Gerdts, V. A Novel Combination Adjuvant Platform for Human and Animal Vaccines. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4486–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesinski, G.; Westerink, M.A.J. Vaccines Against Polysaccharide Antigens. Curr. Drug Target.-Infect. Disord. 2001, 1, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappuoli, R. Glycoconjugate Vaccines: Principles and Mechanisms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, L.A.; Leite, F.P.L.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S. Bovine Herpesvirus Glycoprotein D: A Review of Its Structural Characteristics and Applications in Vaccinology. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoj, S.; Babiuk, L.A.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S. Immunization with a Dicistronic Plasmid Expressing a Truncated Form of Bovine Herpesvirus-1 Glycoprotein D and the Amino-Terminal Subunit of Glycoprotein B Results in Reduced GB-Specific Immune Responses. Virology 2003, 313, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malito, E.; Bursulaya, B.; Chen, C.; Surdo, P.L.; Picchianti, M.; Balducci, E.; Biancucci, M.; Brock, A.; Berti, F.; Bottomley, M.J.; et al. Structural Basis for Lack of Toxicity of the Diphtheria Toxin Mutant CRM197. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5229–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, E.; Colucci, A.M.; Micoli, F.; Sollai, L.; Gavini, M.; Saul, A.; Cioccio, V.D.; MacLennan, C.A. Simplified Low-Cost Production of O-Antigen from Salmonella Typhimurium Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA). J. Biotechnol. 2015, 198, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, G.D.; Alfini, R.; Cescutti, P.; Caboni, M.; Lanzilao, L.; Necchi, F.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A.; Rondini, S.; Micoli, F. Characterization of O-Antigen Delivered by Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens (GMMA) Vaccine Candidates against Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Vaccine 2017, 35, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, D.; Waxman, L.; Goldberg, A.L.; Roth, J. Isolation and Characterization of Lon Mutants in Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 165, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C. Vaccines Based on the Cell Surface Carbohydrates of Pathogenic Bacteria. Anais Acad. Bras. Ciências 2005, 77, 293–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, A. Bacterial Polysaccharide–Protein Conjugate Vaccines. Brit. Med. Bull. 2004, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettu, R.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-Y. Synthetic Carbohydrate-Based Vaccines: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, C.A.; Borsutzky, S.; Griot-Wenk, M.; Metcalfe, I.C.; Pearman, J.; Collioud, A.; Favre, D.; Dietrich, G. Vaccines against Typhoid Fever. Vaccine 2006, 24, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeboer, N.A.; Jones, B.D. Exopolysaccharide Sugars Contribute to Biofilm Formation by Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium on HEp-2 Cells and Chicken Intestinal Epithelium. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3214–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Wang, W.; Xia, C.; Liu, F. Salmonella Virulence Factor SsrAB Regulated Factor Modulates Inflammatory Responses by Enhancing the Activation of NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, M.J.; Ching, K.H.L.; Heffron, F. Salmonella SsrB Activates a Global Regulon of Horizontally Acquired Genes. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondari, E.M.; Klemm, E.J.; Msefula, C.L.; Ghany, M.A.E.; Heath, J.N.; Pickard, D.J.; Barquist, L.; Dougan, G.; Kingsley, R.A.; MacLennan, C.A. Rapid Transcriptional Responses to Serum Exposure Are Associated with Sensitivity and Resistance to Antibody-Mediated Complement Killing in Invasive Salmonella Typhimurium ST313. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaniz, R.C.; Deatherage, B.L.; Lara, J.C.; Cookson, B.T. Membrane Vesicles Are Immunogenic Facsimiles of Salmonella Typhimurium That Potently Activate Dendritic Cells, Prime B and T Cell Responses, and Stimulate Protective Immunity In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7692–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yi, J.; Liang, K.; Liu, T.; Roland, K.L.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, Q. Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Salmonella Typhimurium Mutants with Truncated LPS Induce Cross-Protective Immune Responses against Infection of Salmonella enterica Serovars in the Mouse Model. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. Ijmm. 2016, 306, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yi, J.; Liang, K.; Hu, B.; Zhang, X.; Curtiss, R.; Kong, Q. Outer Membrane Vesicles from Flagellin-Deficient Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Induce Cross-Reactive Immunity and Provide Cross-Protection against Heterologous Salmonella Challenge. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Kim, S.I.; Ryu, S.; Yoon, H. Identification and Characterization of Outer Membrane Vesicle-Associated Proteins in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, O.; Caboni, M.; Negrea, A.; Necchi, F.; Alfini, R.; Micoli, F.; Saul, A.; MacLennan, C.A.; Rondini, S.; Gerke, C. Toll-Like Receptor Activation by Generalized Modules for Membrane Antigens from Lipid A Mutants of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhimurium and Enteritidis. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2016, 23, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malabirade, A.; Habier, J.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; May, P.; Godet, J.; Halder, R.; Etheridge, A.; Galas, D.; Wilmes, P.; Fritz, J.V. The RNA Complement of Outer Membrane Vesicles From Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Under Distinct Culture Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakano, M.; Watanabe, H.; Schleheck, D.; Ishihama, A. Regulatory Role of CsqR (YihW) in Transcription of the Genes for Catabolism of the Anionic Sugar Sulfoquinovose (SQ) in Escherichia coli K-12. Microbiology+ 2019, 165, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaznadzey, A.; Shelyakin, P.; Belousova, E.; Eremina, A.; Shvyreva, U.; Bykova, D.; Emelianenko, V.; Korosteleva, A.; Tutukina, M.; Gelfand, M.S. The Genes of the Sulphoquinovose Catabolism in Escherichia coli Are Also Associated with a Previously Unknown Pathway of Lactose Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looijesteijn, P.J.; Boels, I.C.; Kleerebezem, M.; Hugenholtz, J. Regulation of Exopolysaccharide Production By Lactococcus lactis Subsp. Cremoris by the Sugar Source. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Datta, S.; Biswas, D. Towards a Better Production of Bacterial Exopolysaccharides by Controlling Genetic as Well as Physico-Chemical Parameters. Appl. Microbiol. Bio. 2018, 102, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzi, F.; Rollan, G.; de Giori, G.S.; de Valdez, G.F. Effect of Galactose and Glucose on the Exopolysaccharide Production and the Activities of Biosynthetic Enzymes in Lactobacillus Casei CRL 87. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denger, K.; Weiss, M.; Felux, A.-K.; Schneider, A.; Mayer, C.; Spiteller, D.; Huhn, T.; Cook, A.M.; Schleheck, D. Sulphoglycolysis in Escherichia coli K-12 Closes a Gap in the Biogeochemical Sulphur Cycle. Nature 2014, 507, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speciale, G.; Jin, Y.; Davies, G.J.; Williams, S.J.; Goddard-Borger, E.D. YihQ Is a Sulfoquinovosidase That Cleaves Sulfoquinovosyl Diacylglyceride Sulfolipids. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacoman, J.L.; Badish, L.N.; Sharkey, T.D.; Hollingsworth, R.I. The Metabolic and Biochemical Impact of Glucose 6-Sulfonate (Sulfoquinovose), a Dietary Sugar, on Carbohydrate Metabolism. Carbohyd. Res. 2012, 362, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, J.D.; Jahn, C.E.; Gibson, D.L.; Charkowski, A.O. The Role of Cellulose and O-Antigen Capsule in the Colonization of Plants by Salmonella enterica. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvasi, M.; Cox, C.E.; Xu, Y.; Noel, J.T.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Teplitski, M. Differential Regulation of Salmonella Typhimurium Genes Involved in O-Antigen Capsule Production and Their Role in Persistence within Tomato Fruit. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2013, 26, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.W.; Gibson, D.L.; Kay, W.W.; Gunn, J.S. Identification of a Bile-Induced Exopolysaccharide Required for Salmonella Biofilm Formation on Gallstone Surfaces. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.A.; McGroarty, E.J. High-Molecular-Weight Components in Lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Minnesota, and Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 162, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, G.L.; Attridge, S.R.; Morona, R. Regulation of Salmonella Typhimurium Lipopolysaccharide O Antigen Chain Length Is Required for Virulence; Identification of FepE as a Second Wzz: LPS Chain Length Regulation in S. Typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strains or Plasmids | Genotype | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| S. Typhimurium LT2 | ||
| TT10423 | proAB47/F’ pro(+) lac(+) zzf-1831::Tn10(del) 16 (del) 17 | [30] |
| S. Typhimurium 14028 | Wild-type strain | ATCC |
| ΔbcsA | Deletion of bcsA ORF | [31] |
| ΔyihVW | Deletion of yihVW operon | This study |
| ΔyihW | Deletion of yihW ORF | This study |
| Δyih | Deletion of yihUTSRQPO and yihVW operons | This study |
| ΔbcsA ΔyihW | Deletion of bcsA and yihW ORF | This study |
| ΔwcaJ | Deletion of wcaJ ORF | This study |
| Tn10A | Tn10dtet insertion in Tnp IS200 | This study |
| Tn10B | Tn10dtet insertion in filD | This study |
| Tn10C | Tn10dtet insertion in srfA | This study |
| Tn10D | Tn10dtet insertion in stm14_2260 | This study |
| Tn10E | Tn10dtet insertion in fhlA | This study |
| Tn10F | Tn10dtet insertion in ompS | This study |
| Tn10G | Tn10dtet insertion in stm14_3662 | This study |
| Tn10C ΔtolR | Tn10dtet insertion in srfA and deletion of tolR ORF | This study |
| ΔtolR | Deletion of tolR ORF | This study |
| Δlon ΔtolR | Deletion of lon and tolR ORF | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| pNK972 | pBR322 derived plasmid with Tn10 transposase gene | [32] |
| pBR322/yihVW | yihVW from S. Typhimurium 14028 | This study |
| pCS26 | Bacterial luciferase | [33] |
| pCS26-yihUTSRQPO | yihU promoter | [9] |
| pCS26-yihVW | yihVW promoter | [9] |
| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| yih operon F | TTATTGGCCGGATAAAGCGCTGACGCGACC CTCCGGCGCAAGGGCGCTTGGTGTAGGCTG GAGCTGCTTC | To amplify cat gene from pKD3 to generate Δyih strain by lambda-red recombination |
| yih operon R | AATATAGGGAAGCCGCCATCCATCGGGATG GATAAAGCGGCAAGCGTCGTCCTCCTTAGT TCCTATTCCG | |
| yih operon PF | GGTTATAGGCCTCACGGTTT | To confirm deletion of yihUTSRQPO/yihVW operons |
| yih operon PR | TAATACGCGGTTAAAGTCGATGT | |
| yihVWkoFOR | TTCGTGAAATTAAAATGAGCACATCGAAAATGCTTGAGGAATGACCATGGGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC | To amplify cat gene product from pKD3 to generate ΔyihVW strain by lambda-red recombination |
| yihVWkoREV | TTGGCCGGATAAAGCGCTGACGCGACCCTCCGGCGCAAGGGCGCTTGTCACCTCCTTAGTTCCTATTCCG | |
| yihWkoFOR | TAATATGAGCAGTAGGAAGCTTTTAGAGGAATGCTCATGAGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC | Used with yihVWkoREV to generate ΔyihW strain |
| yihVWdetect1 | GCACATCGAAAATGCTTGAGGA | To confirm the deletion of yihVW and yihW from S. Typhimurium 14028 |
| yihVWdetect2 | ATATCGCCTGCATCACAGCG | |
| yihVWFOR | CGCGCTGCAGCTGTTTGTGATCGTATTTGTAATTTAT | Used to amplify yihVW from S. Typhimurium 14028 for cloning into pBR322. |
| yihVWREV | GATCGACGTCGCATCACAGCGCCGTTTTATTG | |
| yihVWseqF | GATCTTGCCGGGAAGCTAGAGTAAG | To confirm the cloning of yihVW into pBR322 |
| yihVWseqR | GATCTTCTTGAAGACGAAAGGGCCT | |
| TL | TCCATTGCTGTTGACAAAGGGAAT | Used for nested PCR (first reaction) to identify the site of Tn10dtet insertion |
| TR | ACCTTTGGTCACCAACGCTTTTCC | |
| ARB1 | GGCCACGCGTCGANNNNNNNNGATAT | |
| ARB6 | GGCCACGCGTCGANNNNNNNNACGCC | |
| Universal Tn | GACAAGATGTGTATCCACCTTAAC | Used for nested PCR (second reaction) |
| ARB2 | GGCCACGCGTCGACTAGTAC | |
| lonF | CTATACTATCTGATTACCTGGCGGACACTAAACTAAGAGAGAGCTCTATGATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACC | To amplify kan gene product from pKD13 to generate Δlon strain by lambda-red recombination |
| lonR | TTATTAGCGCTATTTGCGCGAGGTCACTATTTTGCGGTTACAACCTGCATTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG | |
| lonPF | AACACGCCGTTGAATGTGTG | To confirm the deletion of lon from S. Typhimurium 14028 |
| lonPR | TTATATCAGGCCTGCCACGC | |
| wcaJ-ko-F | ATCTCCCCTTACCGCCTGCGGGTAAGGGGCC AATCACAGGAACAACGATGATTCCGGGGATC CGTCGACC | To amplify kan gene product from pKD13 to generate ΔwcaJ strain by lambda-red recombination |
| wcaJ-ko-R | GTAAAATAGCCTTGTGGGTCAGGTTCTTAATA CGCCGCTTTATTAACAAATGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCG | |
| wcaJ-verF | CCAGAACCTGTTCACAAGGC | To confirm the deletion of wcaJ from S. Typhimurium 14028 |
| wcaJ-verR | GCCTGAATGTGGAATCACGC | |
| TolR-ko_For | TTCTGCACCGCCAGGCGTTTACCGTAAGCGA AAGCAACAAGGGGTAAGCCGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC | To amplify cat gene product from pDK3 to generate ΔtolR strain by lambda-red recombination |
| TolR-ko_Rev | AAACTGTTCGCCTGTTACTCGCCGTCTTTCAAGCCAACGGGACGCAGACTCCTCCTTAGTTCCTATTCCG | |
| TolR-F | CTGCTCGACGTACTGTTG | To confirm the deletion of tolR from S. Typhimurium 14028 |
| TolR-R | ATCACCTGTTCAGACGGCAG |
| S. Typhimurium Strains A | Identified Site of Tn10 Insertion | Crude Polysaccharide B (mg) | Polysaccharide after Chromatography (mg) | Endotoxin Removal with Triton X-114 (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔbcsA | - | 59.5 | 12.5 | <0.5 |
| ΔbcsA ΔyihW | 130 | 18 | <0.5 | |
| Tn10A | Tnp IS200 | 132 | 41.1 | <0.5 |
| Tn10B | fliD | 44 | - | - |
| Tn10C | srfA | 500 | 157.2 | 10 |
| Tn10D | stm14_2260 | 209 | 37 | <2 |
| Tn10E | fhlA | 332 | 49.8 | <0.5 |
| Tn10F | ompS | 67 | - | - |
| Tn10G | stm14_3662 | 344 | 61 | <0.5 |
| Tn10C (MOPS) C | - | 2000 | 500 | 100 |
| Monosaccharides | Crude CPS | Polysaccharide Isolated from Crude CPS | Colanic Acid | O-Ag Capsule |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhamnose | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | NA | 22 |
| Fucose | 32.3 ± 0.9 | 31.9 ± 0.3 | 27 | NA |
| Mannose | 5.7 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | NA | 24 |
| Galactose | 35.2 ± 0.4 | 34.6 ± 0.4 | 28.8 | 28 |
| Abequose | NT | NT | NA | 18 |
| Glucose | 22.4 ± 0.5 | 22.4 ± 0.3 | 17.9 | 9.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokaribo, A.S.; Perera, S.R.; Sereggela, Z.; Krochak, R.; Balezantis, L.R.; Xing, X.; Lam, S.; Deck, W.; Attah-Poku, S.; Abbott, D.W.; et al. A GMMA-CPS-Based Vaccine for Non-Typhoidal Salmonella. Vaccines 2021, 9, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020165
Sokaribo AS, Perera SR, Sereggela Z, Krochak R, Balezantis LR, Xing X, Lam S, Deck W, Attah-Poku S, Abbott DW, et al. A GMMA-CPS-Based Vaccine for Non-Typhoidal Salmonella. Vaccines. 2021; 9(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokaribo, Akosiererem S., Sumudu R. Perera, Zoe Sereggela, Ryan Krochak, Lindsay R. Balezantis, Xiaohui Xing, Shirley Lam, William Deck, Sam Attah-Poku, Dennis Wade Abbott, and et al. 2021. "A GMMA-CPS-Based Vaccine for Non-Typhoidal Salmonella" Vaccines 9, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020165
APA StyleSokaribo, A. S., Perera, S. R., Sereggela, Z., Krochak, R., Balezantis, L. R., Xing, X., Lam, S., Deck, W., Attah-Poku, S., Abbott, D. W., Tamuly, S., & White, A. P. (2021). A GMMA-CPS-Based Vaccine for Non-Typhoidal Salmonella. Vaccines, 9(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020165






