Hydroxylated-Benz[a]anthracenes Induce Two Apoptosis-Related Gene Expressions in the Liver of the Nibbler Fish Girella punctata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Plasma and Bile Samples from Intraperitoneal Injection with BaA in Nibbler Fish
2.3. Measurement of Plasma Calcium (Ca) and Inorganic Phosphorus (iP) Levels in Nibbler Fish
2.4. Measurement of Plasma Total Bile Acids, Total Bilirubin, Free Bilirubin, ALP, AST, and Minerals in Nibbler Fish
2.5. Detection of 3-OHBaA in Nibbler Fish
2.6. Toxic Effect of 3-OHBaAs on Cultured Liver Tissue of Nibbler Fish
2.7. De Novo RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Analysis and Selection of Apoptosis-Related Genes
2.8. qPCR for Two Apoptosis-Related Genes in 3-OHBaA-Exposed Cultured Liver
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
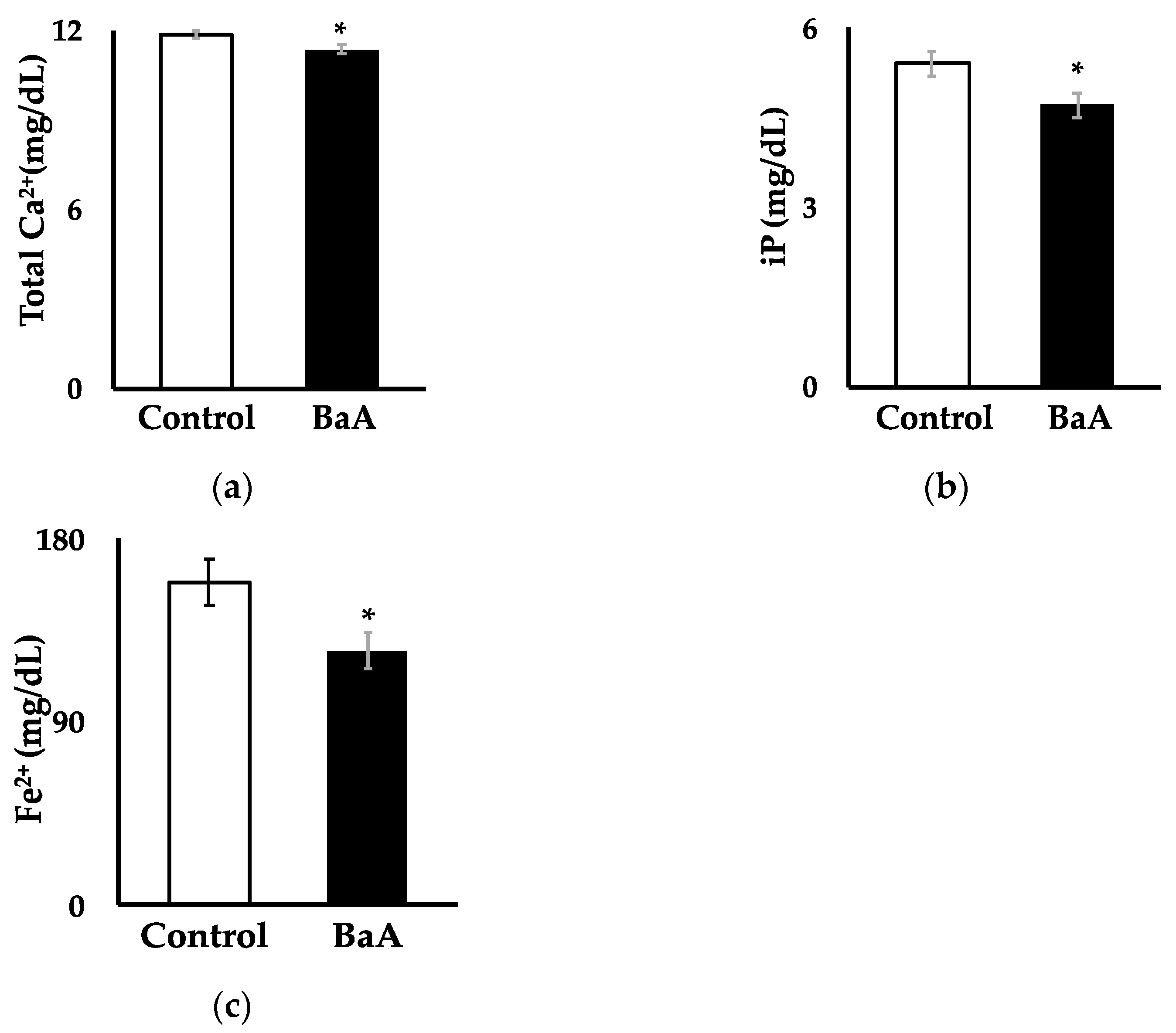
3.1. BaA Significantly Reduces Plasma Levels of Ca, iP, and Fe2+ in Nibbler Fish
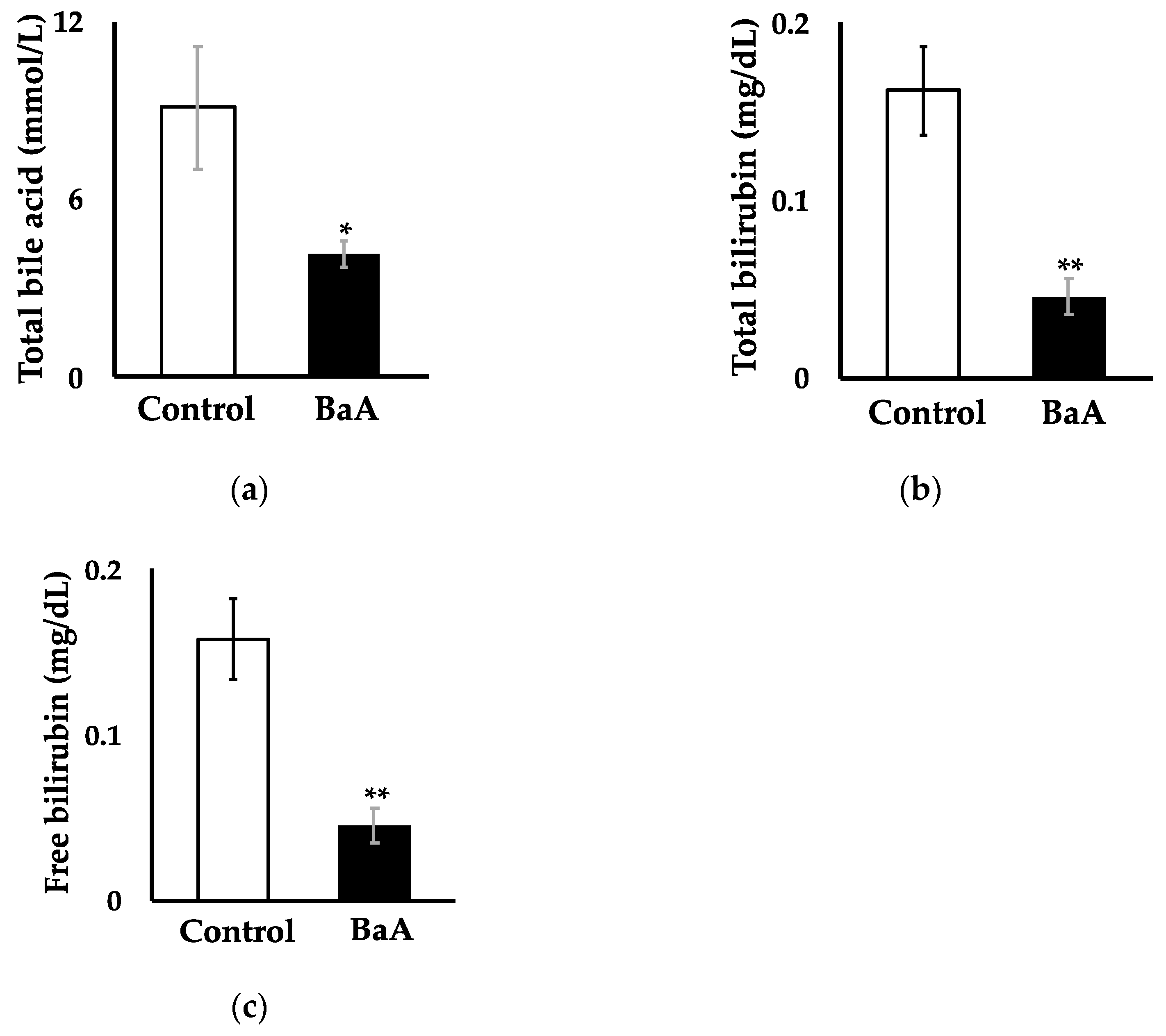
3.2. Intraperitoneal Injection of BaA in Nibbler Fish Significantly Reduces Plasma, Total Bile Acid, Total Bilirubin, and Free Bilirubin Levels
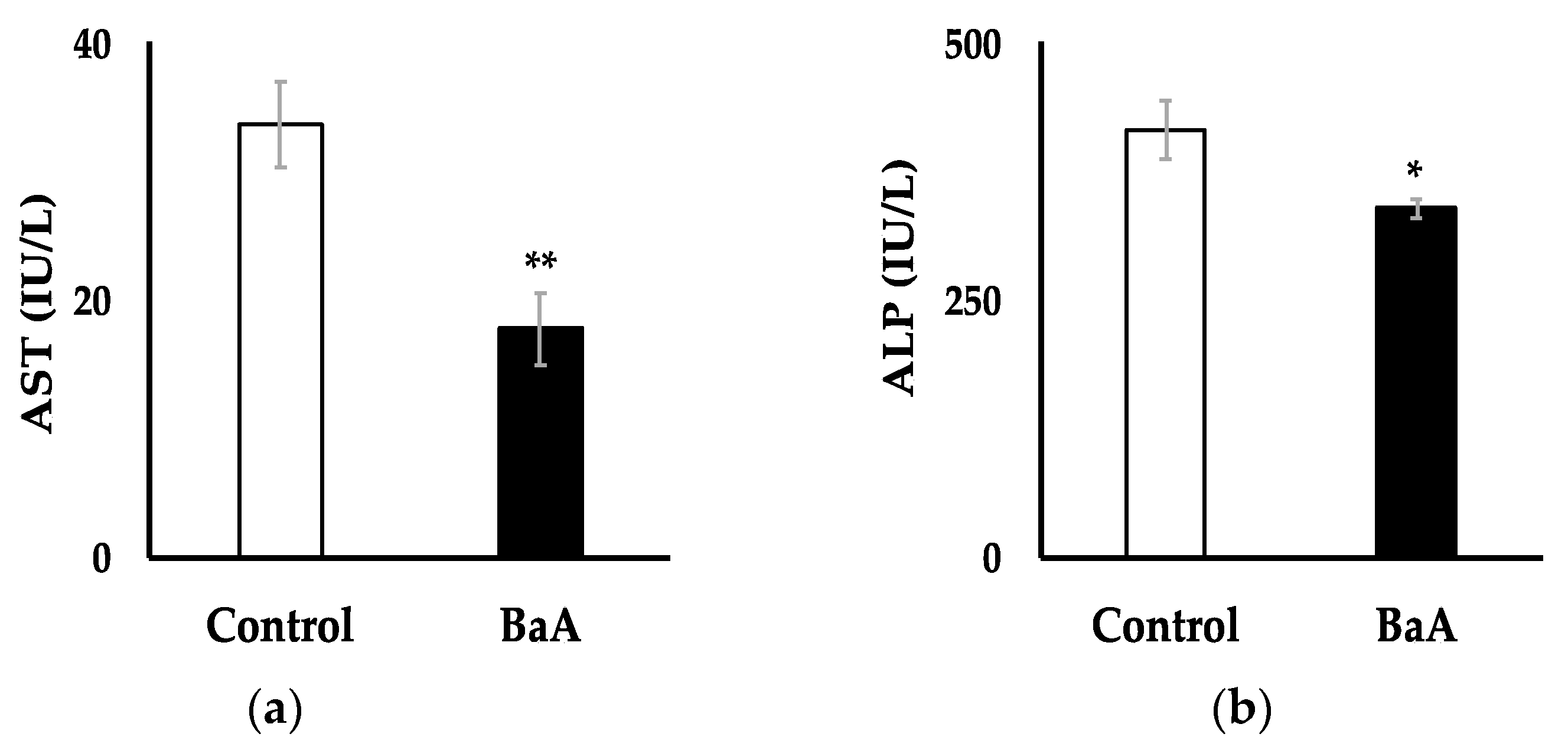
3.3. Intraperitoneal Injection of BaA in Nibbler Fish Significantly Reduces Plasma Levels of AST and ALP
3.4. Detection of 3-OHBaA in the Bile of BaA-Treated Nibbler Fish
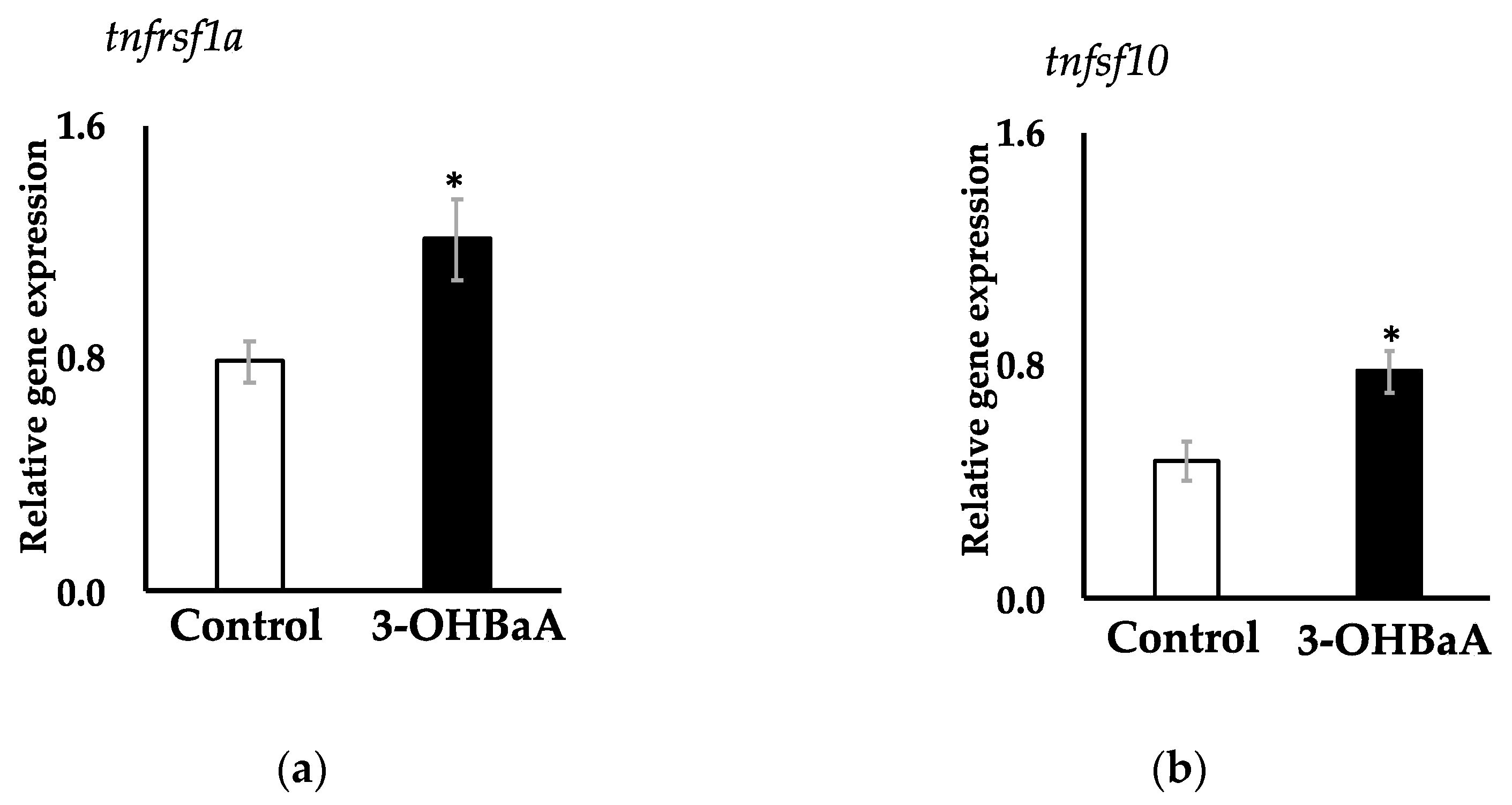
3.5. Expression of Two Apoptosis-Related Genes in 3-OHBaA-Exposed Cultured Liver
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lima, A.L.C.; Eglinton, T.I.; Reddy, C.M. High-resolution record of pyrogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon deposition during the 20th century. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, M.; Suzuki, N. Toxicities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for aquatic animals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bue, B.G.; Sharr, S.; Seeb, J.E. Evidence of damage to pink salmon populations inhabiting Prince William Sound, Alaska, two generations after the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1998, 127, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, R.A.; Rice, S.D.; Wertheimer, A.C.; Bradshaw, R.F.; Thrower, F.P.; Joyce, J.E.; Short, J.W. Delayed effects on growth and marine survival of pink salmon Oncorhynchus gorbuscha after exposure to crude oil during embryonic development. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 208, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Nomura, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Oguri, S.; Kawanishi, T.; Toriba, A.; Kizu, R.; Sakaguchi, T.; Tamiya, E. Damage to and recovery of coastlines polluted with C-heavy oil spilled from the Nakhodka. Water Res. 2006, 40, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Soysa, T.Y.; Ulrich, A.; Friedrich, T.; Pite, D.; Compton, S.L.; Ok, D.; Bernardos, R.L.; Downes, G.B.; Hsieh, S.; Stein, R.; et al. Macondo crude oil from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill disrupts specific developmental processes during zebrafish embryogenesis. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Esler, D.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.E.; Irons, D.B. Long-term ecosystem response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incardona, J.P.; Gardner, L.D.; Linbo, T.L.; Brown, T.L.; Esbaugh, A.J.; Mager, E.M.; Stieglitz, J.D.; French, B.L.; Labenia, J.S.; Laetz, C.A.; et al. Deepwater Horizon crude oil impacts the developing hearts of large predatory pelagic fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1510–E1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihanic, F.; Sommard, V.; Perrine, d.L.; Pichon, A.; Grasset, J.; Berrada, S.; Budzinski, H.; Cousin, X.; Morin, B.; Cachot, J. Environmental concentrations of benz[a]anthracene induce developmental defects and DNA damage and impair photomotor response in Japanese medaka larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrone, S.; Favaro, L.; Abete, M.C.; Vivaldi, B.; Prearo, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon levels in European catfish from the upper Po River basin. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 2313–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lin, Q.; Gu, Y.; Du, F.; Wang, X.; Shi, F.; Ke, C.; Xiang, M.; Yu, Y. Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in wild marine fish from the coastal waters of the northern South China Sea: Risk assessment for human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, N.; Zou, X.; Li, P.; Zou, S.; Luo, J.; Yang, Y. Pollution level and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine fish from two coastal regions, the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 168, 112376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbee, G.C.; Barich, J.; Duncan, B.; Bickham, J.W.; Matson, C.W.; Hintze, C.J.; Autenrieth, R.L.; Zhou, G.D.; McDonald, T.J.; Cizmas, L.; et al. In situ biomonitoring of PAH-contaminated sediments using juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanaty, M.I.; Sawada, N.; Kitani, Y.; Nassar, H.F.; Mahmoud, H.M.; Hayakawa, K.; Sekiguchi, T.; Ogiso, S.; Tabuchi, Y.; Urata, M.; et al. Influence of benz[a]anthracene on bone metabolism and on liver metabolism in nibbler fish, Girella punctate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N.; Tabata, M.J.; Takada, K.; Wada, S.; Omori, K.; Srivastav, A.K.; et al. Monohydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons inhibit both osteoclastic and osteoblastic activities in teleost scales. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Honda, M.; Sato, M.; Yoshitake, S.; Kawabe, K.; Tabuchi, Y.; Omote, T.; Sekiguchi, T.; Furusawa, Y.; Toriba, A.; et al. Hydroxylated benzo[c]phenanthrene metabolites cause osteoblast apoptosis and skeletal abnormalities in fish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Nakano, J.; Kawabe, K.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Sekiguchi, T.; Tabuchi, Y.; Ikegame, M.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Benz[a]anthracene decreases plasma calcium levels resulting from influence of scale osteoclastic and osteoblastic activities in goldfish. Int. J. Zool. Investig. 2017, 3, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N.; Nakamura, H. Seasonal variability and risk assessment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and hydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Kanazawa, Japan. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, K.; Yoshida, M.A.; Hirayama, J.; Kitani, Y.; Hattori, A.; Ogiso, S.; Watabe, Y.; Sekiguchi, T.; Tabuchi, Y.; Urata, M.; et al. Deep ocean water alters the cholesterol and mineral metabolism of squid Todarodes pacificus and suppresses its weight loss. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Leung, H.C.M.; Luo, R.; Wong, C.K.; Ting, H.F.; Lam, T.W. AC-DIAMOND v1: Accelerating large-scale DNA-protein alignment. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3744–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naudé, P.J.W.; den Boer, J.A.; Luiten, P.G.M.; Eisel, U.L.M. Tumor necrosis factor receptor cross-talk. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, P.; Myles, I.A. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors: Pleiotropic Signaling Complexes and Their Differential Effects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, S.R.; Schooley, K.; Smolak, P.J.; Din, W.S.; Huang, C.P.; Nicholl, J.K.; Sutherland, G.R.; Smith, T.D.; Rauch, C.; Smith, C.A. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995, 3, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Ruppert, S.; Donahue, C.J.; Moore, A.; Ashkenazi, A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12687–12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrache, A.; Micheau, O. TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand: Non-Apoptotic Signalling. Cells 2024, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Quan, X.-B.; Zeng, W.-J.; Yang, X.-O.; Wang, M.-J. Mechanism of Hepatocyte Apoptosis. J. Cell Death 2016, 9, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New Capabilities and Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, A.; Ohira, T.; Shigematsu, A.; Okumura, T.; Mekuchi, M.; Toyota, K.; Mishima, H.; Kawamura, R.; Hatano, K.; Kawago, U.; et al. Functional analysis of a matrix peptide involved in calcification of the exoskeleton of the kuruma prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruchotikamol, A.; Jarukamjorn, K.; Sirisangtrakul, W.; Sakuma, T.; Kawasaki, Y.; Nemoto, N. Strong Synergistic Induction of CYP1A1 Expression by Andrographolide Plus Typical CYP1A Inducers in Mouse Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 224, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Restrepo, B.; Kannan, K.; Addink, R.; Adams, D.H. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Halogenated Analogues in Fish from Florida Coastal Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.-B.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kannan, K. Occurrence and Accumulation Patterns of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Synthetic Musk Compounds in Adipose Tissues of Korean Females. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.; Porte, C.; Solé, M.; Sturve, J. Biliary PAH and Alkylphenol Metabolites, Biomarker Enzyme Activities, and Gene Expression Levels in the Deep-Sea Fish Alepocephalus rostratus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Senthilkumar, K.; Alomirah, H.; Moon, H.B.; Minh, T.B.; Mohd, M.A.; Nakata, H.; Kannan, K. Concentrations and Profiles of Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolites (OH-PAHs) in Several Asian Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Stryker, Z.; Loganathan, B.G.; Kannan, K. Phthalate Metabolites, Hydroxy-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Bisphenol Analogues in Bovine Urine Collected from China, India, and the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11524–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Martinez-Moral, M.P.; Kannan, K. Variability in Urinary Biomarkers of Human Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Its Association with Oxidative Stress. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Negi, R.; Jacob, M.; Gayathri, A.; Rokade, A.; Sarma, H.; Kalita, J.; Tasfia, S.T.; Bharti, R.; Wakid, A.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Aquatic Ecosystem Exposed to the 2020 Baghjan Oil Spill in Upper Assam, India: Short-Term Toxicity and Ecological Risk Assessment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0293601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lu, Y.; Mao, W.; Hao, L. New insight into PAH4 induced hepatotoxicity and the dose-response assessment in rats model. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luderer, U.; Christensen, F.; Johnson, W.O.; She, J.; Ip, H.S.; Zhou, J.; Alvaran, J.; Krieg, E.F., Jr.; Kesner, J.S. Associations between urinary biomarkers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and reproductive function during menstrual cycles in women. Environ. Int. 2017, 100, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasehinde, T.A.; Olaniran, A.O. Neurotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A systematic mapping and review of neuropathological mechanisms. Toxics 2022, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, C.J.; King, D.E.; Player, M.S.; Matheson, E.M.; Post, R.E.; Mainous, A.G., 3rd. Association of urinary polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and serum C-reactive protein. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Comprehensive Review of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water Sources, Their Effects and Treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.L.; Oris, J.T. Altered gene expression: A mechanism for reproductive toxicity in zebrafish exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, S.; Deschaux, P. The effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the immune system of fish: A review. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 77, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, M.G.; Carls, M.G.; Heintz, R.; Rice, S.D. Evaluation of fish early life-stage toxicity models of chronic embryonic exposures to complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 78, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiard, S.M.; Timme-Laragy, A.R.; Wassenberg, D.M.; Cockman, C.; Di Giulio, R.T. The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway in mediating synergistic developmental toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafiuddin, M.A.; Matsubara, H.; Hatano, K.; Honda, M.; Toyota, K.; Kuroda, K.; Tsunoda, K.; Furusawa, Y.; Tabuchi, Y.; Hirano, T.; et al. Hydroxylated-Benz[a]anthracenes Induce Two Apoptosis-Related Gene Expressions in the Liver of the Nibbler Fish Girella punctata. Toxics 2024, 12, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120915
Rafiuddin MA, Matsubara H, Hatano K, Honda M, Toyota K, Kuroda K, Tsunoda K, Furusawa Y, Tabuchi Y, Hirano T, et al. Hydroxylated-Benz[a]anthracenes Induce Two Apoptosis-Related Gene Expressions in the Liver of the Nibbler Fish Girella punctata. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120915
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafiuddin, Muhammad Ahya, Hajime Matsubara, Kaito Hatano, Masato Honda, Kenji Toyota, Kouhei Kuroda, Keito Tsunoda, Yukihiro Furusawa, Yoshiaki Tabuchi, Tetsushi Hirano, and et al. 2024. "Hydroxylated-Benz[a]anthracenes Induce Two Apoptosis-Related Gene Expressions in the Liver of the Nibbler Fish Girella punctata" Toxics 12, no. 12: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120915
APA StyleRafiuddin, M. A., Matsubara, H., Hatano, K., Honda, M., Toyota, K., Kuroda, K., Tsunoda, K., Furusawa, Y., Tabuchi, Y., Hirano, T., Sakatoku, A., Hong, C.-S., Srivastav, A. K., Amornsakun, T., Shimizu, N., Zanaty, M. I., Harumi, T., Yamauchi, K., Müller, T., ... Suzuki, N. (2024). Hydroxylated-Benz[a]anthracenes Induce Two Apoptosis-Related Gene Expressions in the Liver of the Nibbler Fish Girella punctata. Toxics, 12(12), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120915







