Circ_0000284 Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Blocking the Plasma Membrane Translocation of GLUT4 in Hepatocytes via IGF2BP2/PPAR-γ
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Model for Arsenite Exposure
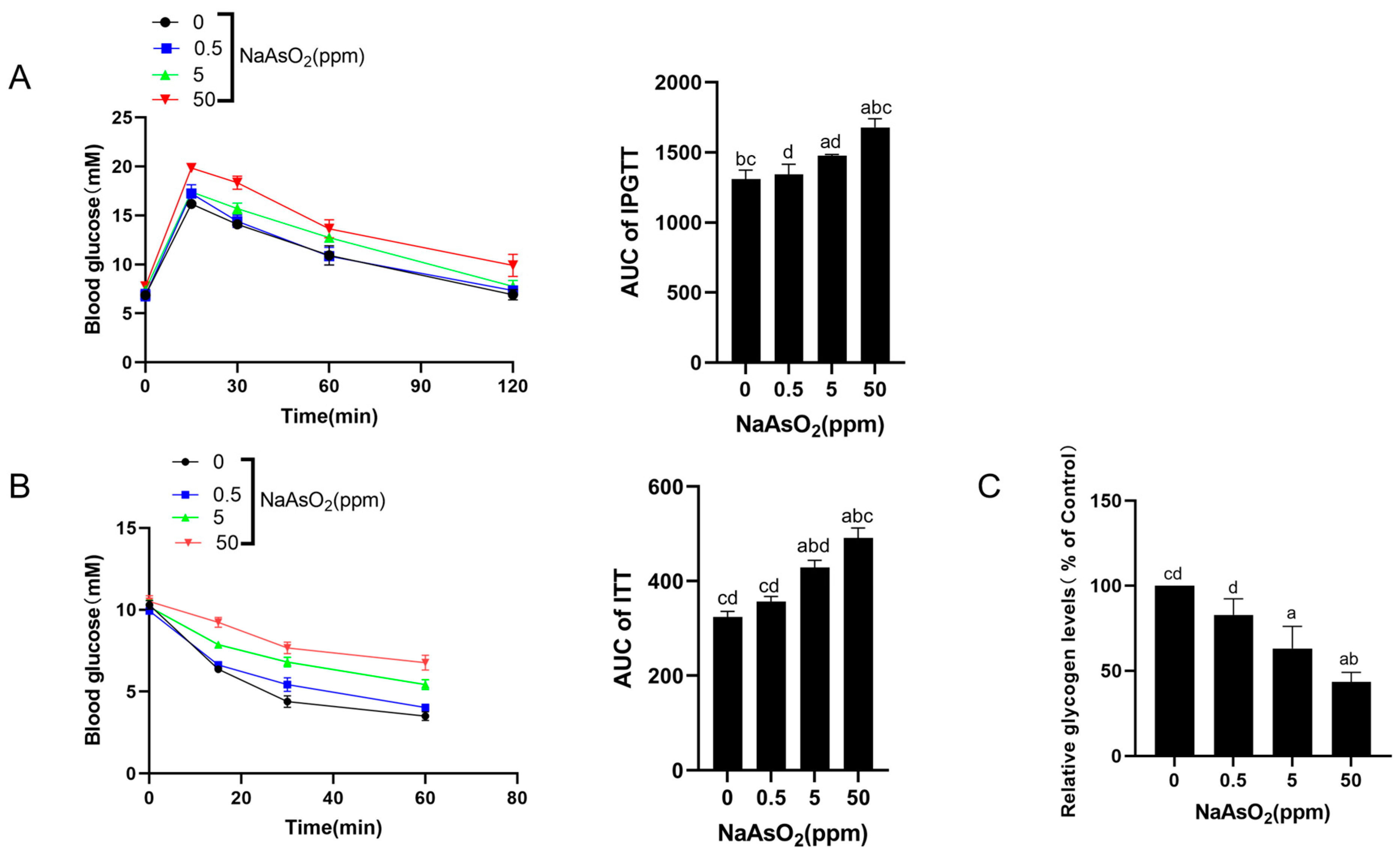
2.2. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Tests (IPGTTs) and Insulin Tolerance Tests (ITTs)
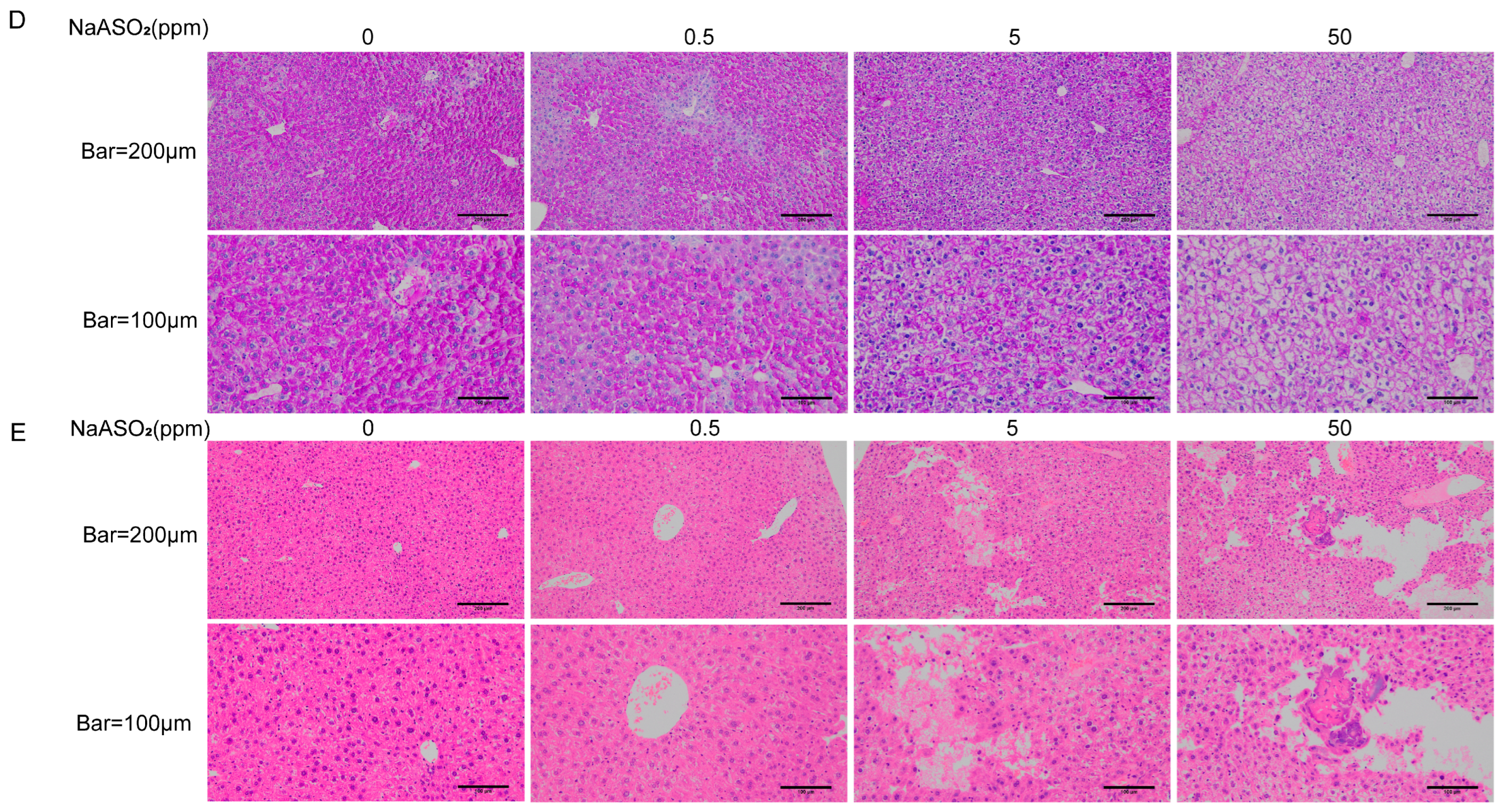
2.3. Liver Periodic Acid–Schiff (PAS) Staining
2.4. HE Staining
2.5. Cell Culture and Treatment
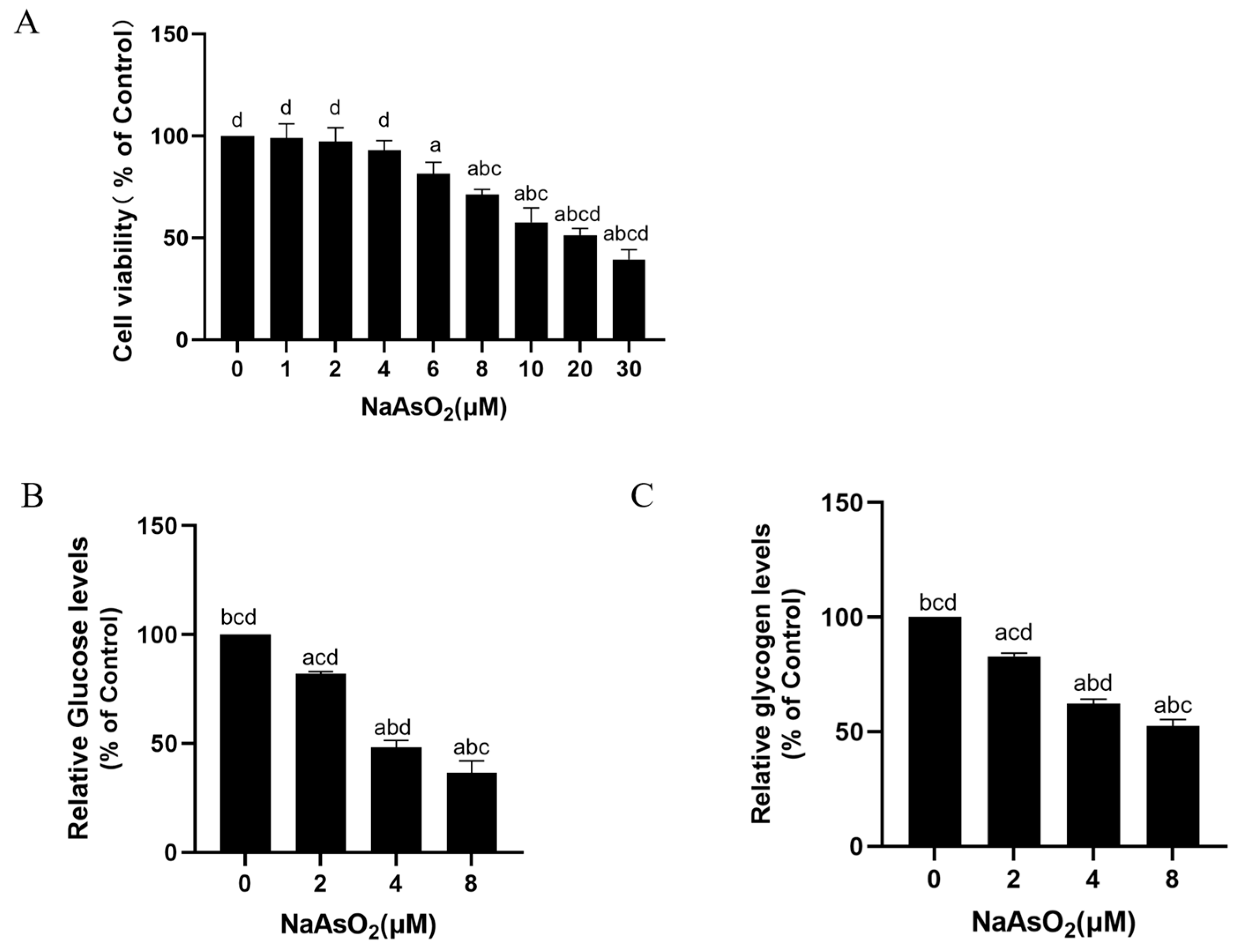
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Cell Transfection
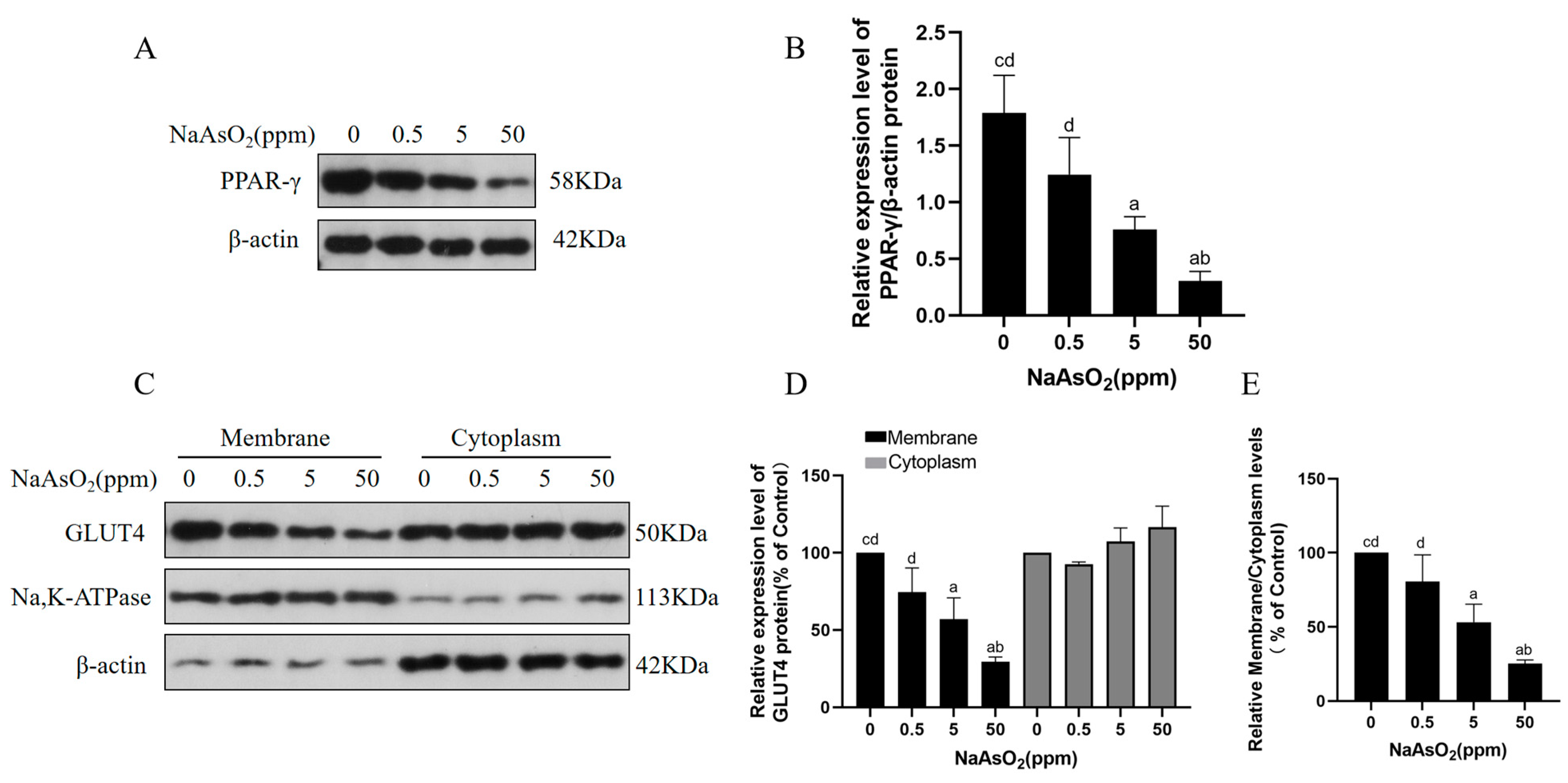
2.8. Membrane Protein Extraction and GLUT4 Analysis
2.9. Western Blots
2.10. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analyses
2.11. Glycogen and Glucose Consumption Levels
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chronic Sodium Arsenite Exposure Causes Liver Injury and Hepatic IR in Mice
3.2. Sodium Arsenite Increases Levels of Circ_0000284 Levels and Decreases IGF2BP2 Levels in Mouse Livers
3.3. Arsenic Exposure Decreases PPAR-γ and Membrane GLUT4 Levels in Mice
3.4. Sodium Arsenite Decreases Levels of Glucose Consumption and Glycogen in Insulin-Treated HepG2 Cells
3.5. Sodium Arsenite Increases Levels of Circ_0000284 and Decreases Levels of IGF2BP2, PPAR-γ, and Membrane GLUT4 in Insulin-Treated HepG2 Cells
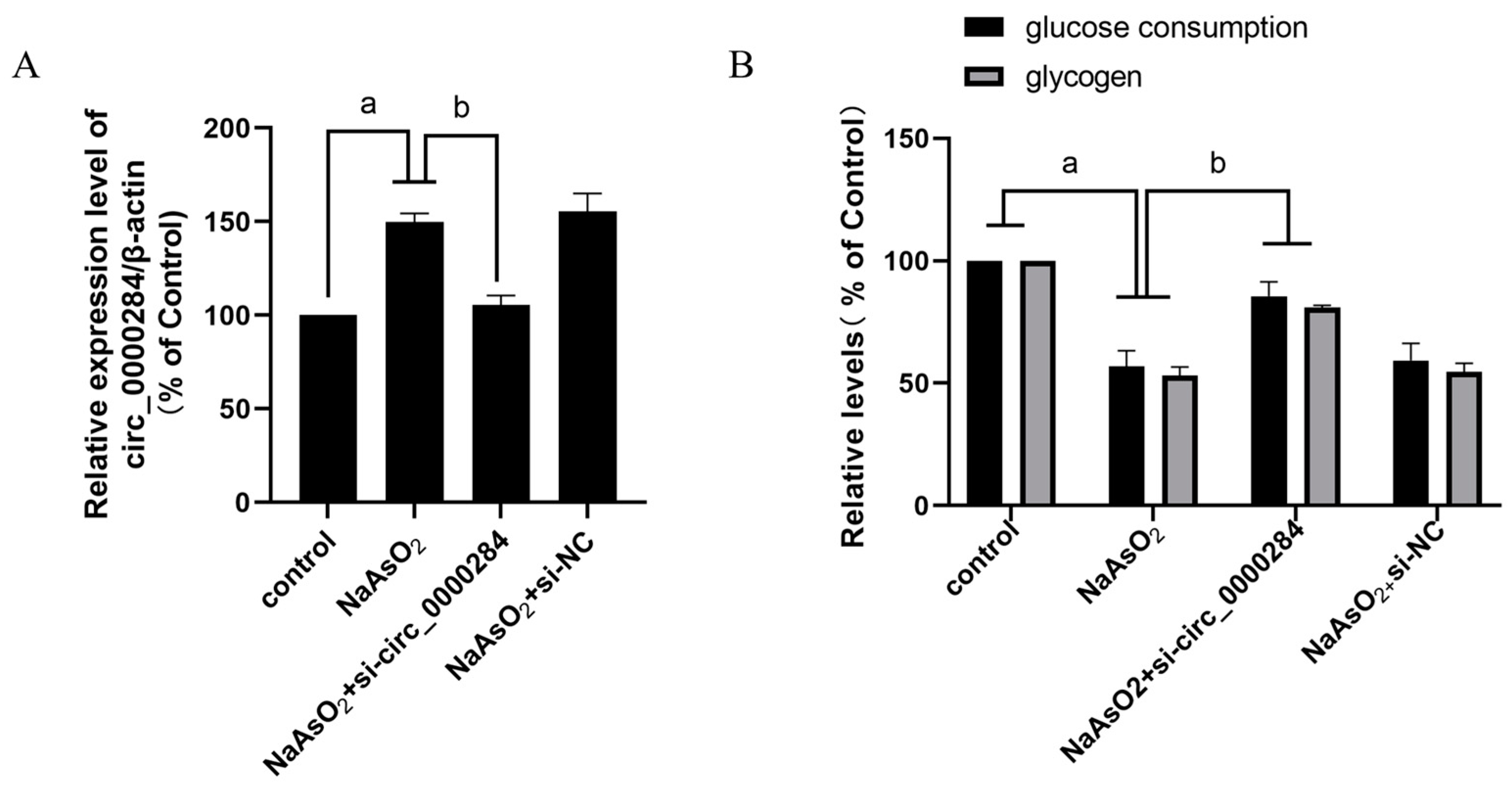
3.6. Inhibition of Circ_0000284 Blocks Sodium Arsenite-Induced Increases in Circ_0000284 Levels and Decreases in Glucose Consumption and Glycogen Levels in Insulin-Treated HepG2 Cells
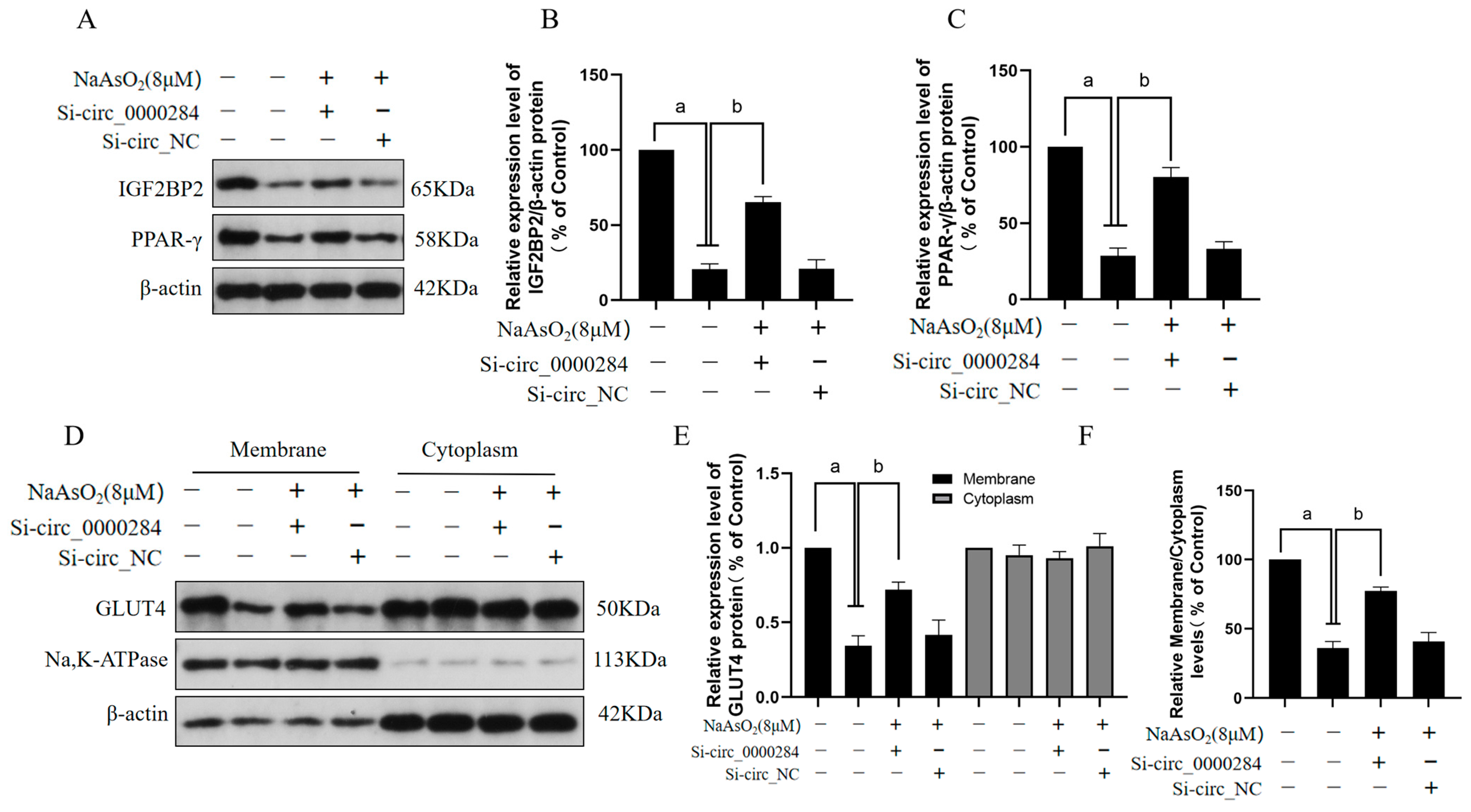
3.7. Inhibition of Circ_0000284 Blocks Sodium Arsenite-Induced Decreases in IGF2BP2, PPAR-γ, and Membrane GLUT4 Levels in Insulin-Treated HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, I.; Suhail, M.; Ahmad, A.; Alhosin, M.; Tabrez, S. Interlinking of diabetes mellitus and cancer: An overview. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Jin, T.; Weng, J. A thorough analysis of diabetes research in China from 1995 to 2015: Current scenario and future scope. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 46–62, Erratum in Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, M.C.; Vatner, D.F.; Shulman, G.I. Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garelick, H.; Jones, H.; Dybowska, A.; Valsami-Jones, E. Arsenic pollution sources. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 197, 17–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frisbie, S.H.; Mitchell, E.J. Arsenic in drinking water: An analysis of global drinking water regulations and recommendations for updates to protect public health. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Castillo, M.; García-Montalvo, E.A.; Arellano-Mendoza, M.G.; Sánchez-Peña, L.D.C.; Soria Jasso, L.E.; Izquierdo-Vega, J.A.; Valenzuela, O.L.; Hernández-Zavala, A. Arsenic exposure and non-carcinogenic health effects. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, S826–S850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Mise, N.; Sikder, M.T.; Ichihara, G.; Uddin, M.K.; Kurasaki, M.; Ichihara, S. Environmental arsenic exposure and its contribution to human diseases, toxicity mechanism and management. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Dodson, M.; Artiola, J.F.; Ramirez-Andreotta, M.; Root, R.A.; Ding, X.; Chorover, J.; Maier, R.M. Arsenic in Drinking Water and Diabetes. Water 2023, 15, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkley, A.G.; Carmean, C.M.; Ruiz, D.; Ye, H.; Regnier, S.M.; Poudel, A.; Hara, M.; Kamau, W.; Johnson, D.N.; Roberts, A.A.; et al. Arsenic exposure induces glucose intolerance and alters global energy metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, R294–R303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, L.; Sun, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xue, J.; Shi, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. MicroRNA-191 blocking the translocation of GLUT4 is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic insulin resistance through inhibiting the IRS1/AKT pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.S.; Hernández-Zavala, A.; Walton, F.S.; Adair, B.M.; Dědina, J.; Matoušek, T.; Stýblo, M. Examination of the effects of arsenic on glucose homeostasis in cell culture and animal studies: Development of a mouse model for arsenic-induced diabetes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghe, P.; Sarath, T.S.; Gupta, P.; Kutty, H.S.; Kandasamy, K.; Mishra, S.K.; Sarkar, S.N. Subchronic arsenic exposure through drinking water alters vascular redox homeostasis and affects physical health in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 162, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lv, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Xiong, Y.; Qian, L. Decrypting the circular RNAs does a favor for us: Understanding, diagnosing and treating diabetes mellitus and its complications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Feng, M.; Zou, H.; Mao, Y.; Yu, W. Circ_0000284 facilitates the growth, metastasis and glycolysis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through miR-152-3p-mediated PDK1 expression. Histol. Histopathol. 2023, 38, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, X.; Lin, J.; Cai, Q.; Li, X. Circular RNA HIPK3 contributes to hyperglycemia and insulin homeostasis by sponging miR-192-5p and upregulating transcription factor forkhead box O1. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, J.; Kolte, A.M.; Hansen Tv Nielsen, F.C. IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 2: Biological function and putative role in type 2 diabetes. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 43, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, J. Hsa_circ_0001756 promotes ovarian cancer progression through regulating IGF2BP2-mediated RAB5A expression and the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N. The Diverse Functions of IMP2/IGF2BP2 in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regué, L.; Minichiello, L.; Avruch, J.; Dai, N. Liver-specific deletion of IGF2 mRNA binding protein-2/IMP2 reduces hepatic fatty acid oxidation and increases hepatic triglyceride accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11944–11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yan, W.; Ma, X.; Huang, H.; Yan, H. Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein 2—A Potential Link Between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 2807–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tan, H.; Wan, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, X. PPAR-γ signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 245, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Zhang, P.; Hong, T.; Tang, S.; Meng, R.; Bi, Y.; Zhu, D. Erythropoietin alleviates hepatic insulin resistance via PPARγ-dependent AKT activation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, L.; Qiu, T.; Wang, Z.; Pei, P.; Yang, G.; Liu, X.; Sun, X. Taurine improves low-level inorganic arsenic-induced insulin resistance by activating PPARγ-mTORC2 signalling and inhibiting hepatic autophagy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5143–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.K.; Dash, U.C.; Kanhar, S.; Sahoo, A.K. Network pharmacology-based elucidation of bioactive compounds and experimental exploration of antidiabetic mechanisms of Hydrolea zeylanica. Cell. Signal. 2024, 114, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odongo, K.; Abe, A.; Kawasaki, R.; Kawabata, K.; Ashida, H. Two Prenylated Chalcones, 4-Hydroxyderricin, and Xanthoangelol Prevent Postprandial Hyperglycemia by Promoting GLUT4 Translocation via the LKB1/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurabayashi, A.; Furihata, K.; Iwashita, W.; Tanaka, C.; Fukuhara, H.; Inoue, K.; Furihata, M.; Kakinuma, Y. Murine remote ischemic preconditioning upregulates preferentially hepatic glucose transporter-4 via its plasma membrane translocation, leading to accumulating glycogen in the liver. Life Sci. 2022, 290, 120261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheong, M.S.; Chen, X.; Farag, M.A.; Cheang, W.S.; Xiao, J. Baicalin ameliorates insulin resistance and regulates hepatic glucose metabolism via activating insulin signaling pathway in obese pre-diabetic mice. Phytomedicine 2024, 124, 155296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Engmann, M.; Medina, D.; Han, X.; Das, P.; Bartke, A.; Ellsworth, B.S.; Yuan, R. Metformin treatment of juvenile mice alters aging-related developmental and metabolic phenotypes in sex-dependent and sex-independent manners. Geroscience 2024, 46, 3197–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oyebode, O.A.; Erukainure, O.L.; Chuturgoon, A.A.; Ghazi, T.; Naidoo, P.; Chukwuma, C.I.; Islam, M.S. Bridelia ferruginea Benth. (Euphorbiaceae) mitigates oxidative imbalance and lipotoxicity, with concomitant modulation of insulin signaling pathways via GLUT4 upregulation in hepatic tissues of diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadt, A.; Al-Hasani, H. Glucose transporters in adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle in metabolic health and disease. Pflug. Arch. 2020, 472, 1273–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.B.; Krishnasamy, K.; Mayakrishnan, V.; Selvaraj, A. Moringa concanensis Nimmo extracts ameliorates hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and upregulates PPARγ and GLUT4 gene expression in liver and pancreas of streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, R. Circ_0000284 upregulates RHPN2 to facilitate pancreatic cancer proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis through sponging miR-1179. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, R.T.; Pessin, J.E. Intracellular organization of insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2001, 56, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irudayaraj, S.S.; Stalin, A.; Sunil, C.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Ignacimuthu, S. Antioxidant, antilipidemic and antidiabetic effects of ficusin with their effects on GLUT4 translocation and PPARγ expression in type 2 diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 256, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoman-Martínez, A.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J.; Zamilpa, A.; Huang, F.; Romero-Nava, R.; Román-Ramos, R.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C. α-Amyrin induces GLUT4 translocation mediated by AMPK and PPARδ/γ in C2C12 myoblasts. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yao, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Q.; Liu, A. Resveratrol protects against deoxynivalenol-induced ferroptosis in HepG2 cells. Toxicology 2023, 494, 153589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xiao, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. The lncRNA HOTAIR via miR-17-5p is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic fibrosis through regulation of Th17 cell differentiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443 Pt B, 130276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xiao, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. miRNA-21, which disrupts metabolic reprogramming to facilitate CD4+ T cell polarization toward the Th2 phenotype, accelerates arsenite-induced hepatic fibrosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.; Chen, L.; Zhong, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L. Long-term arsenic exposure decreases mice body weight and liver lipid droplets. Environ. Int. 2024, 192, 109025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaur, M.; Galvez-Fernandez, M.; Chen, Q.; Lombard, M.A.; Bostick, B.C.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Fretts, A.M.; Shea, S.J.; Navas-Acien, A.; Nigra, A.E. Association of Water Arsenic with Incident Diabetes in U.S. Adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and the Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndisang, J.F.; Vannacci, A.; Rastogi, S. Insulin Resistance, Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, and Related Complications 2017. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1478294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lou, Q.; Guo, N.; Su, M.; Gao, Y.; Qin, M.; Wu, L.; Huang, W.; et al. Research for type 2 diabetes mellitus in endemic arsenism areas in central China: Role of low level of arsenic exposure and KEAP1 rs11545829 polymorphism. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerich, J.E. Contributions of insulin-resistance and insulin-secretory defects to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sira, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Wabo, T.M.; Li, J.; Akiti, C.; Zhang, W.; Sun, D. Effects of Inorganic Arsenic on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus In Vivo: The Roles and Mechanisms of miRNAs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cai, Y.; Guo, J.; Gong, Y.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; et al. Circ_0000284: A risk factor and potential biomarker for prehypertension and hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Sun, B.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. circHIPK3 (hsa_circ_0000284) Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells via miR-326. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 3671–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Yu, T.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, R.; Zeng, Z. hsa-miR-607, lncRNA TUG1 and hsa_circ_0071106 can be combined as biomarkers in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, L.; Ren, L.; Hu, J.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhong, F.; et al. The m6A reader IGF2BP2 regulates glycolytic metabolism and mediates histone lactylation to enhance hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Greenwald, W.W.; Chiou, J.; Yan, J.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, N.; Wang, A.; Nariai, N.; Aylward, A.; Han, J.Y.; Kadakia, N.; et al. Pancreatic islet chromatin accessibility and conformation reveals distal enhancer networks of type 2 diabetes risk. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, G.; Sundaram, R.; Muthu, K. Chebulagic acid attenuates HFD/streptozotocin induced impaired glucose metabolism and insulin resistance via up regulations of PPAR γ and GLUT 4 in type 2 diabetic rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2022, 32, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Guan, P.; Xu, L.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Han, L. Riligustilide alleviates hepatic insulin resistance and gluconeogenesis in T2DM mice through multitarget actions. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Y.; Feng, P.; Liu, R.; Li, G.; Zheng, J.; Xue, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ji, C.; Chen, D.; et al. The m6A Reader IGF2BP2 Regulates Macrophage Phenotypic Activation and Inflammatory Diseases by Stabilizing TSC1 and PPARγ. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Peng, J.; Song, J.; He, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.; Wu, H.; et al. Loss of Hilnc prevents diet-induced hepatic steatosis through binding of IGF2BP2. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Karuppiah, M.; Vasu, G.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Gothandam, K.; Thiruppathi, M. Effect of β-sitosterol on glucose homeostasis by sensitization of insulin resistance via enhanced protein expression of PPRγ and glucose transporter 4 in high fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cytotechnology 2020, 72, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, T.; Fang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Min, W. Peptides from walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim.) protect hepatic HepG2 cells from high glucose-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8112–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armoni, M.; Harel, C.; Karnieli, E. Transcriptional regulation of the GLUT4 gene: From PPAR-gamma and FOXO1 to FFA and inflammation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes | F (5′→3′) | R (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-circ_0000284 | CGGCAGCCTTACAGGGTTAA | GACCAAGACTTGTGAGGCCA |
| mmu-circ_0000284 | TGTTGGIGGATCCTGTTCGC | GACCAAGACTTGTGAGGCCA |
| IGF2BP2 | GTCCTACTCAAGTCCGGCTAC | CATATTCAGCCAACAGCCCAT |
| hsa-β-actin | CAGATGIGGATCAGCAAGCAGGAG | GTCAAGAAAGGGTGTAACGCAACTAAG |
| mmu-β-actin | GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG | CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT |
| Si-circ_0000284 | GUACUACAGGUAUGGCCUGdTdT | GAGGCCAUACCLGUAGUACdTdT |
| Si-circ_NC | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Circ_0000284 Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Blocking the Plasma Membrane Translocation of GLUT4 in Hepatocytes via IGF2BP2/PPAR-γ. Toxics 2024, 12, 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120883
Xu S, Hu Z, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Ma T, Wang S, Wang X, Wang L. Circ_0000284 Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Blocking the Plasma Membrane Translocation of GLUT4 in Hepatocytes via IGF2BP2/PPAR-γ. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):883. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120883
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shiqing, Zhida Hu, Yujie Wang, Qiyao Zhang, Zhi Wang, Teng Ma, Suhua Wang, Xiaohui Wang, and Li Wang. 2024. "Circ_0000284 Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Blocking the Plasma Membrane Translocation of GLUT4 in Hepatocytes via IGF2BP2/PPAR-γ" Toxics 12, no. 12: 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120883
APA StyleXu, S., Hu, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Ma, T., Wang, S., Wang, X., & Wang, L. (2024). Circ_0000284 Is Involved in Arsenite-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Blocking the Plasma Membrane Translocation of GLUT4 in Hepatocytes via IGF2BP2/PPAR-γ. Toxics, 12(12), 883. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120883




