Challenges of E-Waste Dismantling in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
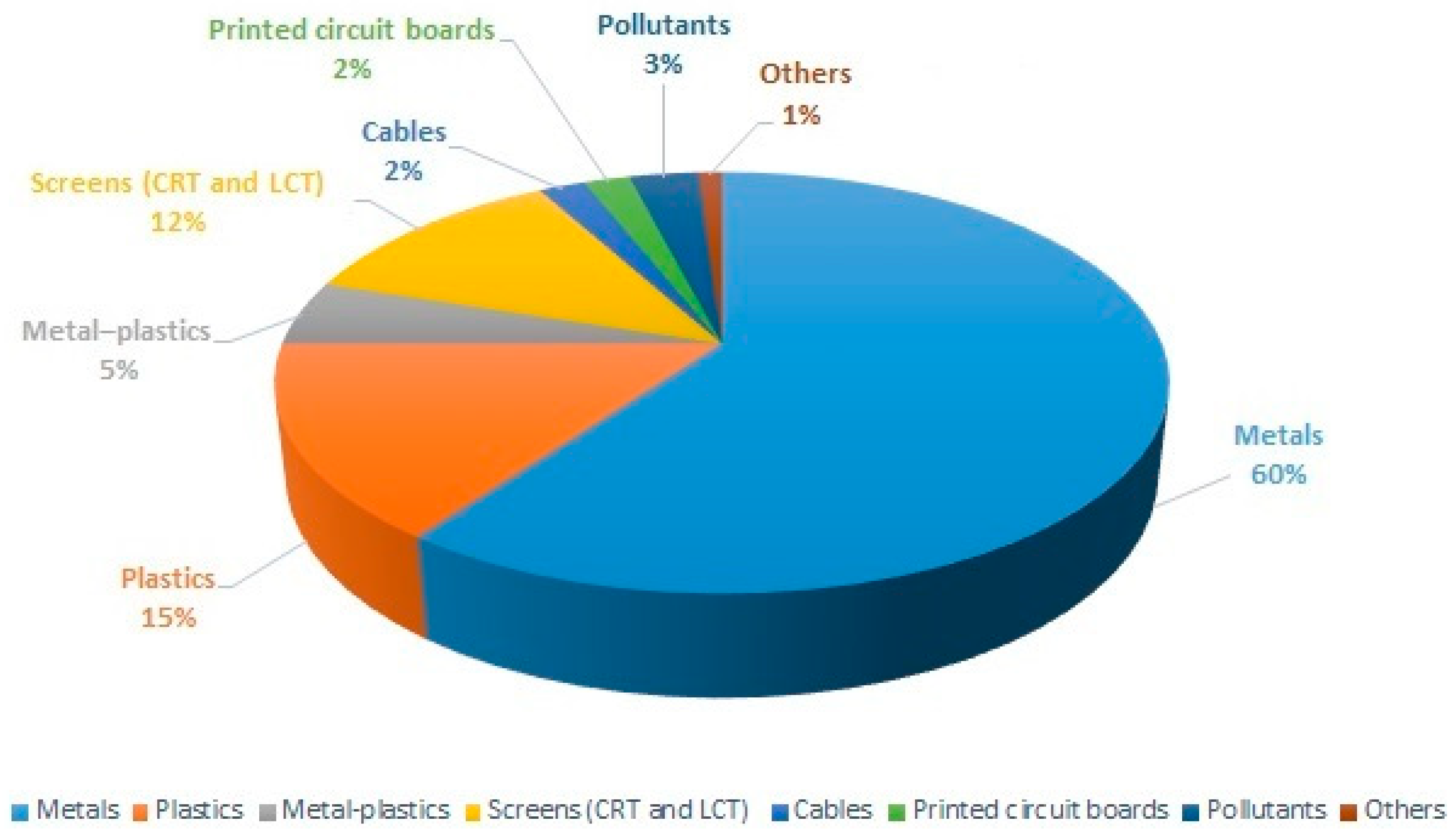
2. Compositions of E-Waste
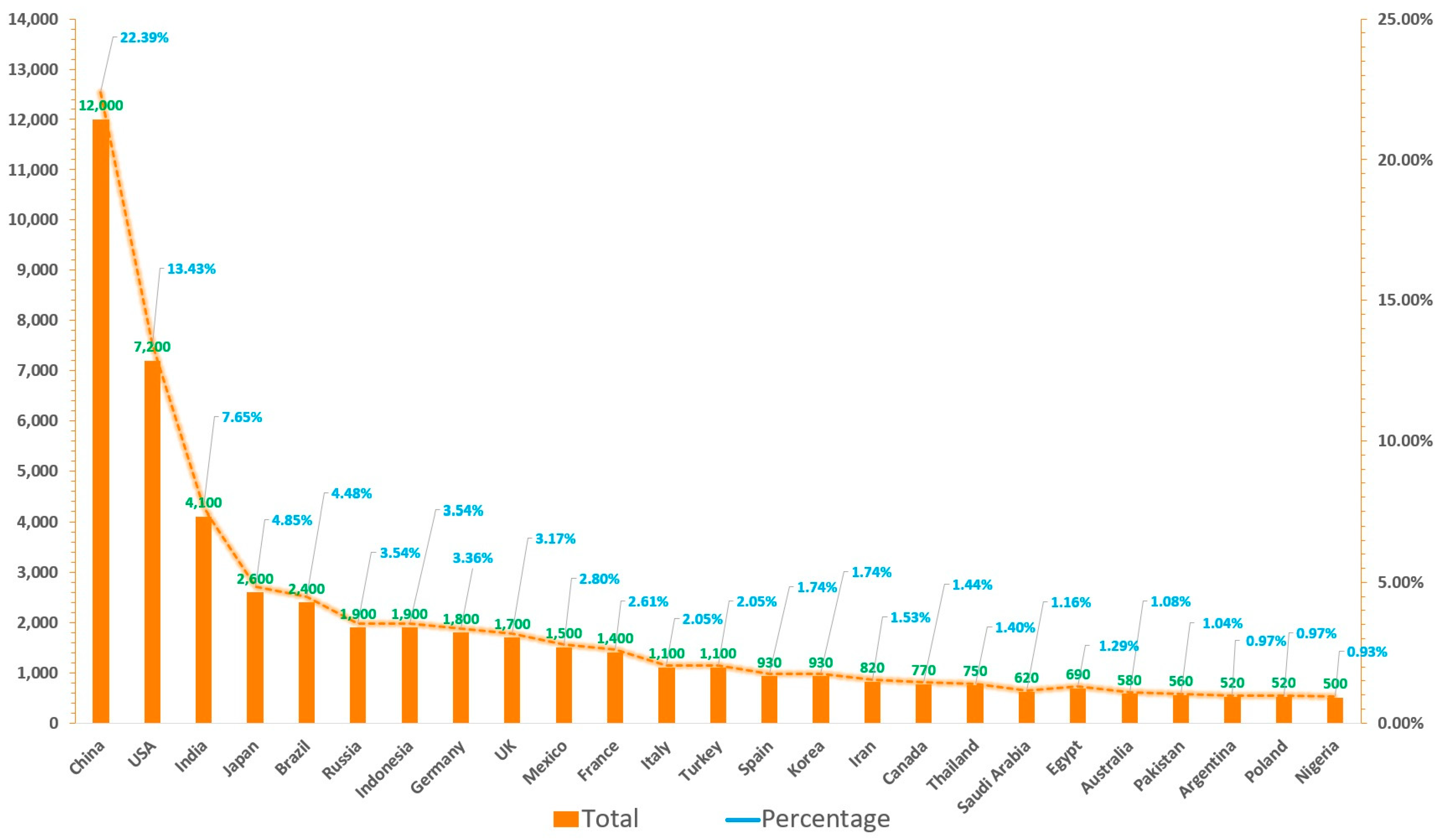
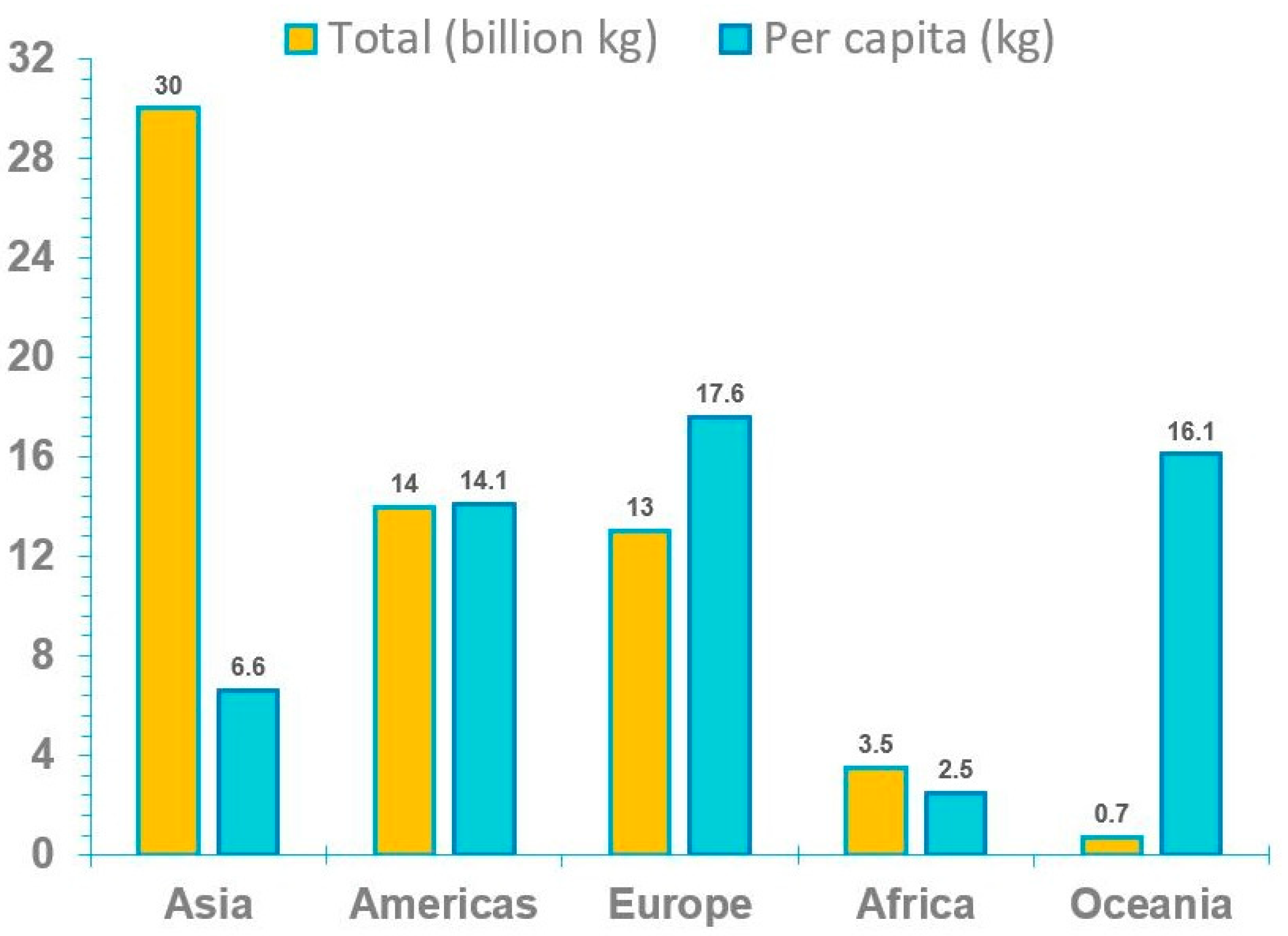
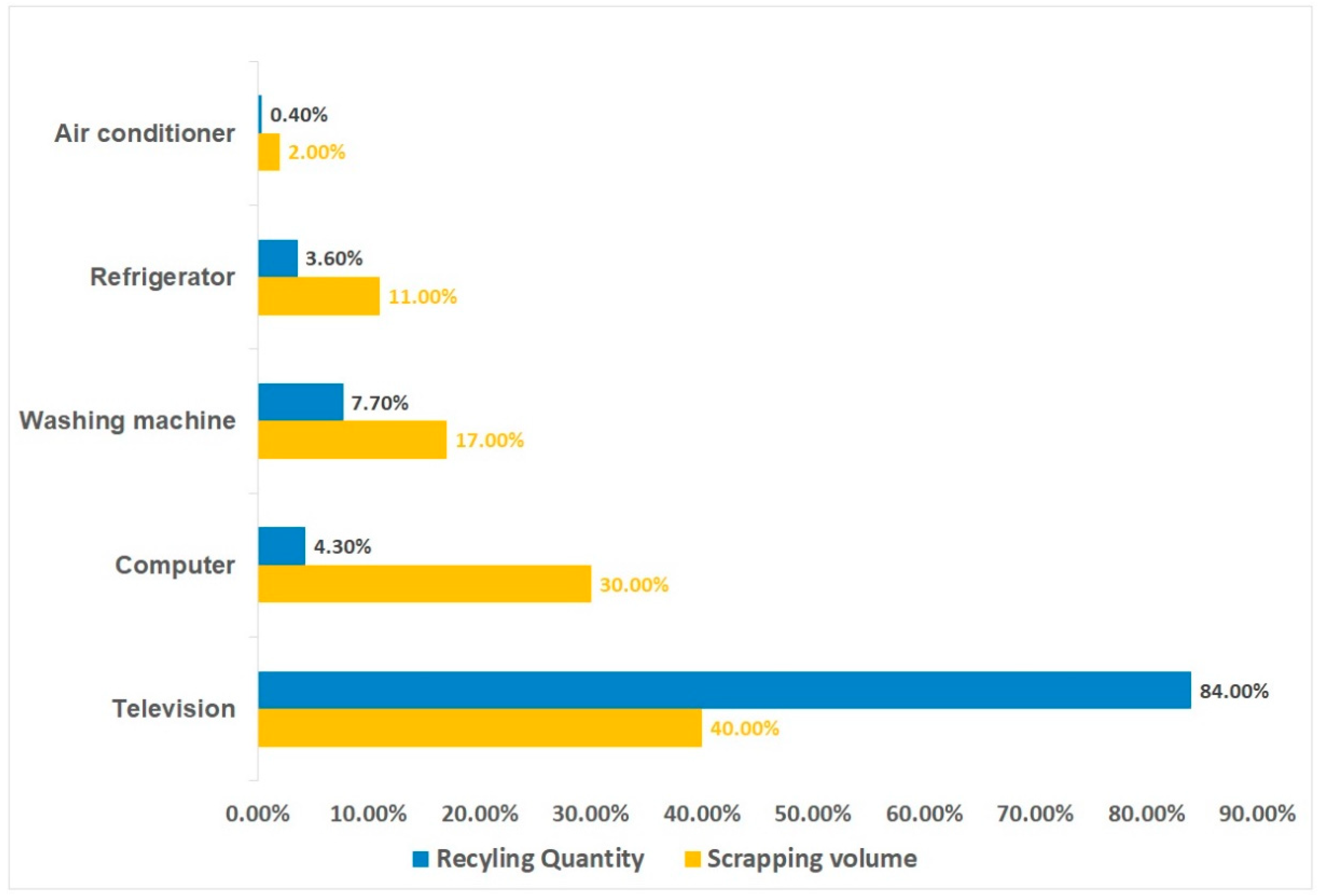
3. Generation and Cost of E-Waste
4. Flow of E-Waste
5. Environmental Impact of E-Waste in China
5.1. Soil
5.2. Air
5.3. Water
6. Health Effect of E-Waste
7. E-Waste Management Policies and Regulations in China
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutta, D.; Rautela, R.; Gujjala, L.K.S.; Kundu, D.; Sharma, P.; Tembhare, M.; Kumar, S. A review on recovery processes of metals from E-waste: A green perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provisions on the Administration of Environmental Protection Relating to Solid Waste in the Category of Import Restriction Usable as Raw Material. Available online: https://leap.unep.org/en/countries/cn/national-legislation/provisions-administration-environmental-protection-relating-solid (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Yamamoto, T.; McDonald, R.; D’Angelo, E.; Althaf, S.; Bel, G.; Deubzer, O.; Fernandez-Cubillo, E.; Forti, V.; et al. Global E-Waste Monitor 2024; International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR). 2024. Available online: https://api.globalewaste.org/publications/file/297/Global-E-waste-Monitor-2024.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Q.; Ye, K.; Wu, W.; Huo, X. Heavy metal exposure has adverse effects on the growth and development of preschool children. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmer, R.; Oswald-Krapf, H.; Sinha-Khetriwal, D.; Schnellmann, M.; Boni, H. Global perspectives on e-waste. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2005, 25, 436–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Sekyere, K.; Batteiger, A.; Afoblikame, R.; Hafner, G.; Kranert, M. Assessing data in the informal e-waste sector: The Agbogbloshie Scrapyard. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, W.; Huo, X. PM2.5 exposure and pediatric health in e-waste dismantling areas. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Goel, S. Understanding the gap between formal and informal e-waste recycling facilities in India. Waste Manag. 2021, 125, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Achal, V. Environmental and health impacts due to e-waste disposal in China—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Huo, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, W. E-waste lead exposure and children’s health in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qian, J.; Liu, L. Understanding Environmental Pollutions of Informal E-Waste Clustering in Global South via Multi-Scalar Regulatory Frameworks: A Case Study of Guiyu Town, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Streicher-Porte, M.; Wang, M.Y.; Reuter, M.A. Informal electronic waste recycling: A sector review with special focus on China. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannath, A.; Shetty, V.K.; Saidutta, M.B. Bioleaching of copper from electronic waste using Acinetobacter sp. Cr B2 in a pulsed plate column operated in batch and sequential batch mode. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Comparative assessment of metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste with special emphasis on bioleaching. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6989–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, P.; Kumar, S. Metallurgical processes unveil the unexplored “sleeping mines” e-waste: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 32359–32370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilankoon, I.; Ghorbani, Y.; Chong, M.N.; Herath, G.; Moyo, T.; Petersen, J. E-waste in the international context—A review of trade flows, regulations, hazards, waste management strategies and technologies for value recovery. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Huang, J.; Ogunseitan, O.A.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Y.M. Comparative study on copper leaching from waste printed circuit boards by typical ionic liquid acids. Waste Manag. 2015, 41, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.X.; Chen, H.Y. Lead during the leaching process of copper from waste printed circuit boards by five typical ionic liquid acids. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, R.; Sivasankari, C.; Thirunavukkarasu, A. Electronic waste generation, regulation and metal recovery: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1347–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, W.; Tobias, M.; Mu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Geng, Y.; Xue, B. An overview of e-waste management in China. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.Y.; Schoenung, J.M. Economic analysis of electronic waste recycling: Modeling the cost and revenue of a materials recovery facility in California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, A.; Schluep, M.; Renaud, F.G.; Streicher, M.; Kuehr, R.; Hagelüken, C.; Gerecke, A.C. A review of the environmental fate and effects of hazardous substances released from electrical and electronic equipments during recycling: Examples from China and India. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, A.; Mursheda, A.; Rafiq, I. E-Waste Trading Impact on Public Health and Ecosystem Services in Developing Countries. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanage, S.V.; Habib, K. Life Cycle Assessment and Material Flow Analysis: Two Under-Utilized Tools for Informing E-Waste Management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbaghi, M.; Cade, W.; Olson, W.; Behdad, S. The Global Flow of Hard Disk Drives: Quantifying the Concept of Value Leakage in E-waste Recovery Systems. J. Ind. Ecol. 2019, 23, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautela, R.; Arya, S.; Vishwakarma, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, S. E-waste management and its effects on the environment and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petridis, N.E.; Petridis, K.; Stiakakis, E. Global e-waste trade network analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Duan, H.; Wang, F.; Li, J. Examining environmental management of e-waste: China’s experience and lessons. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, B.; Lu, S.; Gao, C.; Huang, L.; Bai, X.; Xie, L.; Gui, M.; Qiu, R.L. Heavy metals in human urine, foods and drinking water from an e-waste dismantling area: Identification of exposure sources and metal-induced health risk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, M.L.; Houseman, E.A.; Breton, C.V.; Smith, T.; Quamruzzaman, Q.; Rahman, M.; Mahiuddin, G.; Christiani, D.C. Dietary arsenic exposure in bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Li, B.; Shao, J.J.; Wang, T.; He, B.; Shi, J.B.; Ye, Z.H.; Jiang, G.B. Accumulation of total mercury and methylmercury in rice plants collected from different mining areas in China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Du, Y.; Kong, D.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, T. Trace metals in e-waste lead to serious health risk through consumption of rice growing near an abandoned e-waste recycling site: Comparisons with PBDEs and AHFRs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Leung, J.Y.; Geng, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y. Heavy metal contamination of soil and water in the vicinity of an abandoned e-waste recycling site: Implications for dissemination of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y. Effects of soil properties, heavy metals, and PBDEs on microbial community of e-waste contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Xiang, L.; Luan, H.; Wei, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, P. The health concern of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in a notorious e-waste recycling site. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Xu, X.; Eskenazi, B.; Asante, K.A.; Chen, A.; Fobil, J.; Bergman, Å.; Brennan, L.; Sly, P.D.; Nnorom, I.C.; et al. Severe dioxin-like compound (DLC) contamination in e-waste recycling areas: An under-recognized threat to local health. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gu, J.; Leung, J.Y.S.; Mai, B.; Xiao, T.; Liu, W.; Fu, J. Vertical profile of soil/sediment pollution and microbial community change by e-waste recycling operation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.H.; Rao, K.; Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Zha, J.; Huang, S.; Xu, Y.; Ma, M. PBBs, PBDEs, and PCBs levels in hair of residents around e-waste disassembly sites in Zhejiang Province, China, and their potential sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 397, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.F.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, K.Y.; Zeng, Z.J.; Dai, C.X.; Huo, X. Risk assessment and partitioning behavior of PFASs in environmental matrices from an e-waste recycling area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Adebayo, A.; Jia, J.; Xing, Y.; Deng, S.; Guo, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D. Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, D.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Yin, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. The influence of e-waste recycling on the molecular ecological network of soil microbial communities in Pakistan and China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma; Kumar, A. E-wastes and their impact on environment and public health. Int. J. Appl. Res. 2020, 6, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.J.; Louie, P.K.K.; Liu, W.K.; Bi, X.H.; Fu, J.M.; Wong, M.H. Atmospheric levels and cytotoxicity of PAHs and heavy metals in TSP and PM2.5 at an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6945–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, L.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Peng, P. Severe PCDD/F and PBDD/F pollution in air around an electronic waste dismantling area in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5641–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Feng, J.; Han, W.; Wu, M.; Fu, J.; Sheng, G. Characteristics of organic matter in PM2.5 from an e-waste dismantling area in Taizhou, China. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Reponen, T.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Heavy metals in PM2.5 and in blood, and children’s respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.A.; Adeoluwa, Y.M.; Huo, X.; Xu, X.; Bakare, A.A. Environmental contamination and public health effects of electronic waste: An overview. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 1209–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Guo, X.K. Impact of electronic wastes recycling on environmental quality. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2006, 19, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, K.-H.; Yan, X.; Chen, S.-J.; Hu, G.-C.; Peng, X.-W.; Yuan, J.-G.; Mai, B.-X.; Yang, Z.-Y. Heavy metals in food, house dust, and water from an e-waste recycling area in South China and the potential risk to human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Wu, S.C.; Deng, W.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Luo, Q.; Leung, A.O.; Wong, C.S.; Luksemburg, W.J.; Wong, A.S. Export of toxic chemicals—A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.Y.; Lu, C.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.F.; Zhou, B.S. Characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in water and sediment surrounding two e-waste dismantling regions in Taizhou, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottes, M.; Mainardis, M.; Simeoni, P. Assessing the Techno-Economic Feasibility of Waste Electric and Electronic Equipment Treatment Plant: A Multi-Decisional Modeling Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.; Douglas, P.; Dowling, M.; Liversage, G.; Davies, M. Towards Increased Recovery of Critical Raw Materials from WEEE–evaluation of CRMs at a component level and pre-processing methods for interface optimisation with recovery processes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Wang, M.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Environmental pollution and human body burden from improper recycling of e-waste in China: A short-review. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zeng, X.; Boezen, H.M.; Huo, X. E-waste environmental contamination and harm to public health in China. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahir, F.; Rizwi, S.J.; Haq, S.K.; Khan, R.H. Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Ye, K.; Wang, C.; Huo, X. Air pollution and body burden of persistent organic pollutants at an electronic waste recycling area of China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.O.; Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Heavy metals concentrations of surface dust from e-waste recycling and its human health implications in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Peng, L.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, B.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, B.; Han, D.; Piao, Z. Elevated blood lead levels of children in Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling town in China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huo, X.; Yekeen, T.A.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M.; Xu, X. Effects of lead and cadmium exposure from electronic waste on child physical growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4441–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zeng, X.; Qin, Q.; Xu, X. Maternal urinary metabolites of PAHs and its association with adverse birth outcomes in an intensive e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Li, J. A review on human health consequences of metals exposure to e-waste in China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K.; Li, J. E-waste management in India: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Schnoor, J.L.; Zeng, E.Y. E-waste recycling: Where does it go from here? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10861–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Li, J. “Internet+resource recycling” mode promotes the resource recycling revolution in China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2016, 38, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, T.; Tang, Z. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management. Molecules 2021, 26, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, G.; Yin, W.; Xie, B.; Ren, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Z. Airborne PCDD/Fs in two e-waste recycling regions after stricter environmental regulations. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 62, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Xia, W. New technology for recovering residual metals from nonmetallic fractions of waste printed circuit boards. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Wen, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Weng, Z. Factors Influencing Residents’ Behavior in Internet Recycling: From the Perspective of the Adoption of New Technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, H.; Liu, T.; Tian, X.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, T. “Internet plus “ recyclable resources: A new recycling mode in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 134, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Schnoor, J.L.; Zeng, E.Y. Decadal Journey of E-Waste Recycling: What Has It Achieved? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12785–12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.W.; Chen, B.Y.; Shang, Y.P.; Song, M.L. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Sarkis, J.; Ulgiati, S.; Zhang, P. Environment and development. Measuring China’s circular economy. Science 2013, 339, 1526–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Environmental Media | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|
| Soil | Heavy metals can be absorbed by plants through their roots and then transferred to the stem and leaf. |
| Soils from e-waste dismantling are known to release PCBs, PAHs, and PCDD/Fs into the environment. | |
| Air | Severe PM and POPs pollution in China’s e-waste recycling zones since the 2010s. |
| Water | Pb concentration in the water from Guiyu reached 0.4 mg/L, which exceeded 8 times the limit. |
| The concentrations of metals in the groundwater were significantly higher in the e-waste areas compared to non-e-waste areas in south China. | |
| In the Lianjiang river, running through Guiyu, PFAS were detected, which was found to be significantly more contaminated in the water in the Guiyu e-waste recycling area than in Haojiang. | |
| PBDEs, PBB, and PBT were detected in all the water and sediment samples in Taizhou, indicating ubiquitous contamination in the aquatic environment in Taizhou. | |
| Positive aspect | Recycling e-waste reuses resources, which can reduce carbon dioxide emissions and mitigate climate warming. |
| More jobs were created. |
| Year | Name of Regulation | Significance of Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | Basel Convention | Control of transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and their disposals |
| 1995 | Law on the Prevention of Environmental Pollution by Solid Wastes | Recycling and disposal of toxic and hazardous solid wastes, including e-waste, are regulated |
| 2000 | Notification on Issues Associated with the Import of the Seventh Category of Waste | Most e-waste is banned from entering China |
| 2003 | Measures for the Administration of Pollution Prevention and Control of Electronic Information Products | Restrictions on toxic and hazardous substances contained in electronic products |
| 2005–2007 | Regulations on the Administration of the Recycling and Disposal of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment | Promote the recycling of renewable resources and regulate the development of recycling industry |
| 2007 | Management Measures for Environmental Pollution Prevention and Control of Electronic Waste | Regulate the dismantling and disposal of e-waste |
| 2008 | Regulations on the Management of Recycling and Disposal of Waste Electrical and Electronic Products | Regulate the recycling and treatment activities of electrical and electronic waste products, promote comprehensive utilization of resources and the development of circular economy, protect the environment and human health |
| 2009 | Circular Economy Promotion Law of People’s Republic of China | EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) was issued |
| 2009–2011 | Home Appliance Old for New Rebate Program | Old appliances go straight to formal e-waste collectors |
| 2011 | E-waste Recycling and Disposal Directive | Formal recycling activities are more strongly regulated |
| 2013 | Comprehensive Remediation Scheme of E-waste Pollution in Guiyu Town of Shantou City | Improved illegal e-waste economy in Guiyu |
| 2017 | Implementation Plan for Prohibiting the Entry of Foreign Garbage and Promoting the Reform of the Solid Waste Import Management System | Completely cut off overseas e-wastes into China |
| 2020 | Peak carbon emission by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060 | Advocate low-carbon life to cope with climate change |
| 2022 | Implementation Plan for Promoting Green Consumption | Proposed active implementation of “Internet + recycling” concept |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Ding, X.; Zeng, X. Challenges of E-Waste Dismantling in China. Toxics 2024, 12, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120867
Li B, Liu D, Zhang L, Wu Y, Ding X, Zeng X. Challenges of E-Waste Dismantling in China. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120867
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bitong, Dongling Liu, Lina Zhang, Yue Wu, Xianlin Ding, and Xiang Zeng. 2024. "Challenges of E-Waste Dismantling in China" Toxics 12, no. 12: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120867
APA StyleLi, B., Liu, D., Zhang, L., Wu, Y., Ding, X., & Zeng, X. (2024). Challenges of E-Waste Dismantling in China. Toxics, 12(12), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120867







