Towards an Accurate Real-Time Digital Elevation Model Using Various GNSS Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Kinematic PPP Mathematical Model
3. GNSS Kinematic Trajectory Survey
4. Results and Analysis
5. Discussion
- The three-dimensional kinematic positioning accuracy is within one decimeter level for the RTK scenario, whereas it is about five and six decimeters for the RT-PPP and PPP scenarios, respectively;
- For DEM validation, the RTK-derived DEM has superiority in comparison to both the RT-PPP and PPP counterparts;
- The created DEM from the RT-PPP solution outperforms the PPP DEM for both the elevation’s accuracy and earthworks volume validations;
- It can be said that with one receiver, an accurate, real-time, cost-effective digital elevation model can be produced; thus, this produced DEM can be used in many civil engineering applications;
- The RTK solution produces a highly accurate DEM; however, its limitation is the need for two receivers. On the other hand, RT-PPP is an affordable solution because only one receiver is used.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akturk, E.; Altunel, A.O. Accuracy assessment of a low-cost UAV derived digital elevation model (DEM) in a highly broken and vegetated terrain. Measurement 2019, 136, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapiewski, S. Assessment of the Applicability of UAV for the Creation of Digital Surface Model of a Small Peatland. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 834923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Alves, D.C.; Weschenfelder, J.; Albuquerque, M.d.G.; Espinoza, J.M.d.A.; Ferreira-Cravo, M.; Almeida, L.P.M.d. Digital elevation model generation using UAV-SfM photogrammetry techniques to map sea-level rise scenarios at Cassino Beach, Brazil. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szypuła, B. Accuracy of UAV-based DEMs without ground control points. GeoInformatica 2023, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees, M.T.; Abu Bakar, A.F.B.; Khan, M.M.A.; Syakir, M.I.; Abdullah, K.; Nordin, M.N.M.; Abdelrahman, K.; Eldosouky, A.M.; Andráš, P.; Nasehir, N.K.; et al. An alternative approach to estimate river cross-sections using LIDAR-based digital elevation model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, E.; Campbell, J.D.; Melebari, A.; Bringer, A.; Johnson, J.T.; Moghaddam, M. Using Lidar Digital Elevation Models for Reflectometry Land Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3256303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W. Comparing LiDAR and SfM digital surface models for three land cover types. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, O.G.; Abdikan, S.; Gullu, M.; Lindenbergh, R.; Balik Sanli, F.; Yilmaz, I. Improving global digital elevation models using space-borne GEDI and ICESat-2 LiDAR altimetry data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2316113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, M.; Yurtseven, H.; Gulci, S.; Akay, A.E. Evaluation of UAV- and GNSS-Based DEMs for Earthwork Volume. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudra, P.; Demarchi, L.; Wierzbicki, G.; Chormański, J. A Comparative Assessment of Multi-Source Generation of Digital Elevation Models for Fluvial Landscapes Characterization and Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Lin, J.T.; Chu, H.K.; Chen, C.W.; Lu, C.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Chi, C.C. High-resolution LiDAR digital elevation model referenced landslide slide observation with differential interferometric radar, GNSS, and underground measurements. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Space Borne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER). Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM). Available online: https://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/gdem.asp (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS). World 3D-30m (AW3D30). Available online: https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/dataset/aw3d30/aw3d30_e.htm (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). Available online: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/sensors/srtm (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- TanDEM-X. Available online: https://tandemx-science.dlr.de/ (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Abdel-Maguid, R.H. Evaluation of vertical accuracy of different digital elevation models sources for Buraydah city. Appl. Geomat. 2021, 13, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.O.; Thaker, T.; Chaurasia, A.; Patel, P.; Singh, A.K. Vertical accuracy evaluation of SRTM-GL1, GDEM-V2, AW3D30 and CartoDEM-V3.1 of 30-m resolution with dual frequency GNSS for lower Tapi Basin India. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yin, X.; Tang, B.H.; Yang, M. Accuracy Assessment of High-Resolution Globally Available Open-Source DEMs Using ICESat/GLAS over Mountainous Areas, A Case Study in Yunnan Province, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, R.; Jayadevan Sarunjith, K.; Rajakumari, S.; Muruganandam, R.; Ramesh, R. Quality assessment of open sourced digital elevation models in southeast coast of India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, A.; Ampatzidis, D. European digital elevation model validation against extensive global navigation satellite systems data and comparison with SRTM DEM and ASTER GDEM in Central Macedonia (Greece). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakoksung, K.; Takagi, M. Assessment and comparison of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) products in varying topographic, land cover regions and its attribute: A case study in Shikoku Island Japan. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchabhadel, R.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K.; Yamanoi, K.; Thapa, B.R. Assessment of vertical accuracy of open source 30m resolution space-borne digital elevation models. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.M.A.; Saber, A.; Hamama, M.A.; Rabah, M.; Zaki, A. Evaluation of vertical accuracy of TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Model in Egypt. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, A.; Saifeldin, A.; Abomariam, A.; Ali, R. Efficiency of Using GNSS-PPP for Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Production. Artif. Satell. 2020, 55, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Assaad, H.; Boucher, C.; Daher, A.; Shahin, A.; Noyer, J.C. Statistical modelling of digital elevation models for GNSS-based navigation. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2023, 14, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, Z.M.; Nagai, M. An approach for the precise DEM generation in urban environments using multi-GNSS. Measurement 2021, 177, 109311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briole, P.; Bufferal, S.; Dimitrov, D.; Elias, P.; Journeau, C.; Avallone, A.; Kamberos, K.; Capderou, M.; Nercessian, A. Using Kinematic GNSS Data to Assess the Accuracy and Precision of the TanDEM-X DEM Resampled at 1-m Resolution over the Western Corinth Gulf, Greece. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3016–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, S.J.; Musa, T.A.; Ameen, T.H.; Din, A.H.M.; Aris, W.A.W.; Ebrahim, J.M. Optimizing the Global Digital Elevation Models (GDEMs) and accuracy of derived DEMs from GPS points for Iraq’s mountainous areas. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 11, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ran, M.; Xia, H.; Deng, M. Evaluating Vertical Accuracies of Open-Source Digital Elevation Models over Multiple Sites in China Using GPS Control Points. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, B.; Huber, M.; Wohlfart, C.; Marschalk, U.; Kosmann, D.; Roth, A. Accuracy assessment of the global TanDEM-X Digital Elevation Model with GPS data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 139, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; You, L.; Deng, M.; Kou, Y.; Yang, Y. Accuracy Assessment of Google Earth and Open-source Digital Elevation Models in China Using GPS on Field Control Points. Sens. Mater. 2023, 35, 3325–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Montenbruck, O. Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, X.; Chen, Q. The update of BDS-2 TGD and its impact on positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 2645–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNES. Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales. Available online: http://www.ppp-wizard.net/products/REAL_TIME/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- IGS. International GNSS Service. Available online: https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/products/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- BRDM. IGS Broad Cast Ephemeris. Available online: https://cddis.nasa.gov/archive/gnss/data/daily/2024/brdc/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, B04406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS Software. Available online: https://qgis.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).


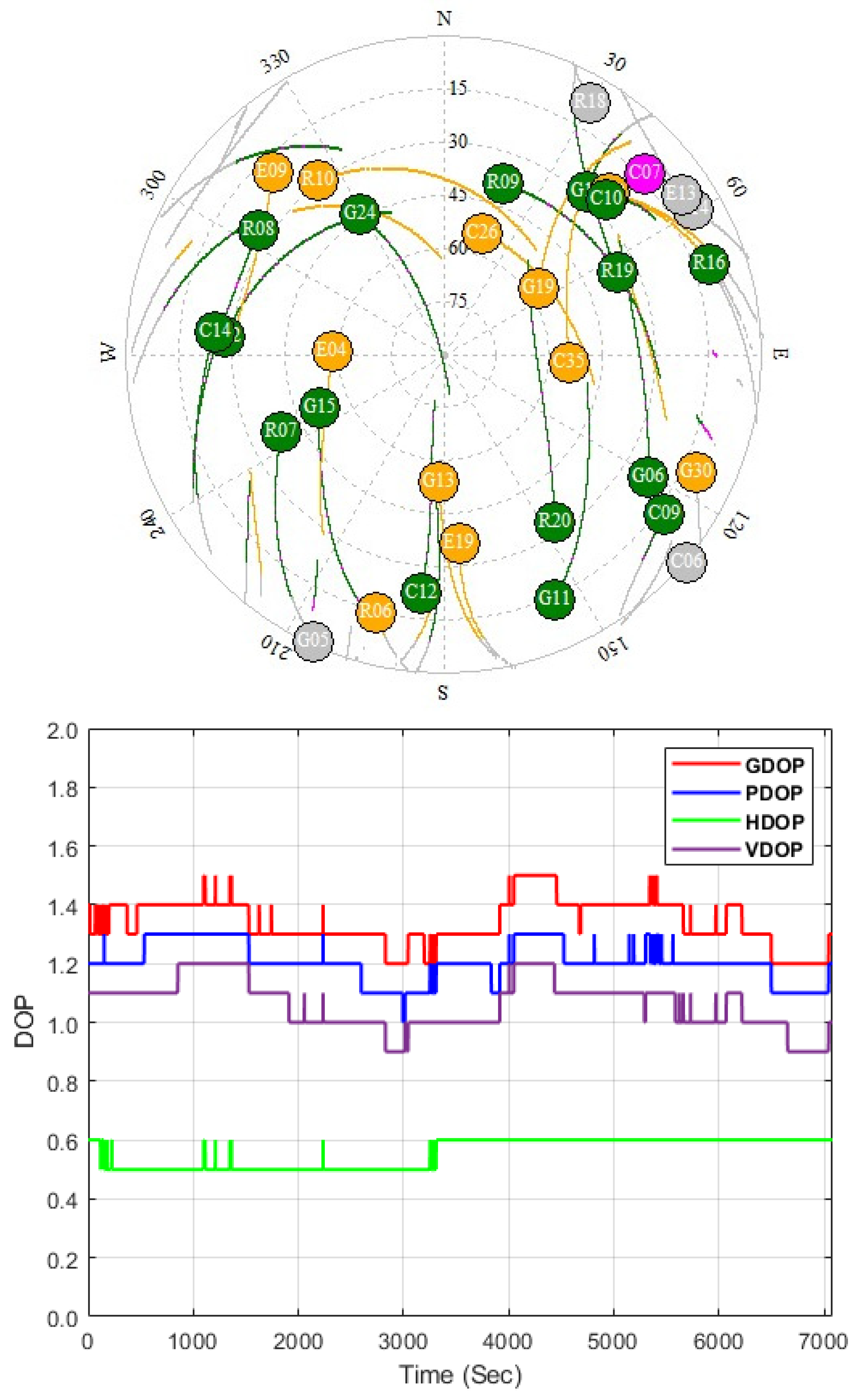
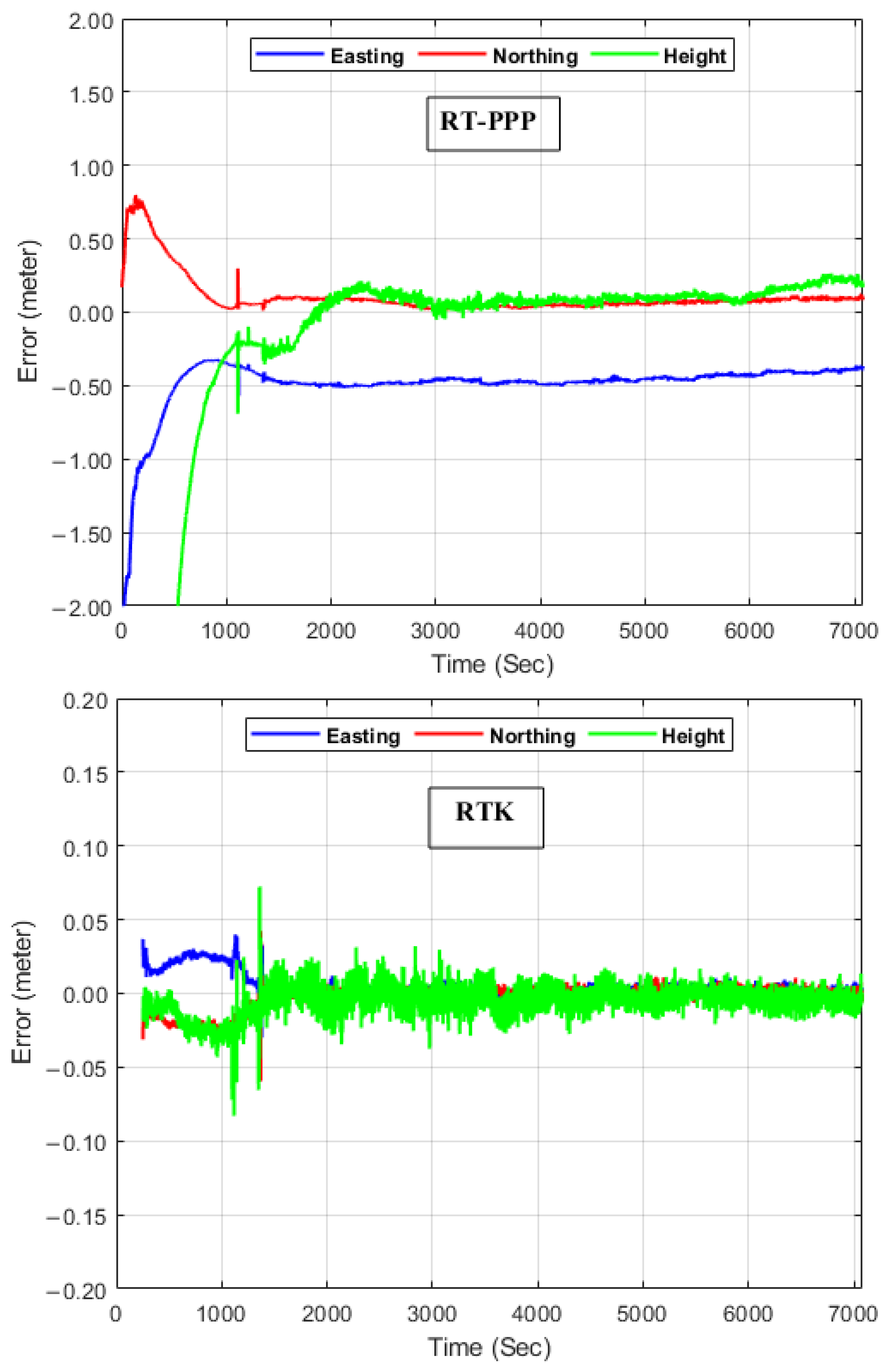









| Parameter | Solution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-PPP | RTK | PPP | Differential | |
| System | GNSS | GNSS | GNSS | GNSS |
| Mathematical model | Undifferenced | Differenced | Undifferenced | Differenced |
| Tropospheric model | Saastamoinen model + Global mapping function | |||
| Sampling rate | 1 Hz | |||
| Mask angle | 10° | |||
| Orbits and clocks | CNES | BRDM | IGS-final | IGS-final |
| Parameter estimation | Kalman filter | |||
| Parameter | RT-PPP | RTK | PPP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2D | H | 3D | 2D | H | 3D | 2D | H | 3D | |
| Mean | 0.454 | 0.016 | 0.454 | 0.015 | −0.083 | 0.084 | 0.548 | 0.048 | 0.550 |
| RMSE | 0.456 | 0.151 | 0.480 | 0.071 | 0.072 | 0.101 | 0.588 | 0.220 | 0.628 |
| DEM Model | Statistical Parameters (m) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBE | RMSE | STD | STD50% | STD90% | STD95% | STD99% | |
| RT-PPP | −0.035 | 0.249 | 0.247 | 0.167 | 0.406 | 0.484 | 0.741 |
| RTK | −0.004 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.009 |
| PPP | −0.060 | 0.264 | 0.257 | 0.174 | 0.423 | 0.504 | 0.772 |
| Graded Elevation (m) | Differential (m3) | RT-PPP (m3) | RTK (m3) | PPP (m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 143.00 | 411,201 | 414,022 | 411,482 | 415,974 |
| 143.50 | 371,303 | 374,095 | 371,585 | 376,075 |
| 144.00 | 331,504 | 334,271 | 331,786 | 336,285 |
| 144.50 | 291,926 | 294,638 | 292,210 | 296,722 |
| 145.00 | 252,858 | 255,472 | 253,144 | 257,637 |
| 145.50 | 214,436 | 217,011 | 214,721 | 219,200 |
| 146.00 | 177,088 | 179,580 | 177,371 | 181,781 |
| 146.50 | 141,095 | 143,471 | 141,375 | 145,658 |
| 147.00 | 106,795 | 109,066 | 107,065 | 111,206 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelazeem, M.; Abazeed, A.; Kamal, H.A.; Mohamed, M.O.A. Towards an Accurate Real-Time Digital Elevation Model Using Various GNSS Techniques. Sensors 2024, 24, 8147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248147
Abdelazeem M, Abazeed A, Kamal HA, Mohamed MOA. Towards an Accurate Real-Time Digital Elevation Model Using Various GNSS Techniques. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):8147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248147
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelazeem, Mohamed, Amgad Abazeed, Hussain A. Kamal, and Mudathir O. A. Mohamed. 2024. "Towards an Accurate Real-Time Digital Elevation Model Using Various GNSS Techniques" Sensors 24, no. 24: 8147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248147
APA StyleAbdelazeem, M., Abazeed, A., Kamal, H. A., & Mohamed, M. O. A. (2024). Towards an Accurate Real-Time Digital Elevation Model Using Various GNSS Techniques. Sensors, 24(24), 8147. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24248147









