Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection?
Abstract
1. Introduction
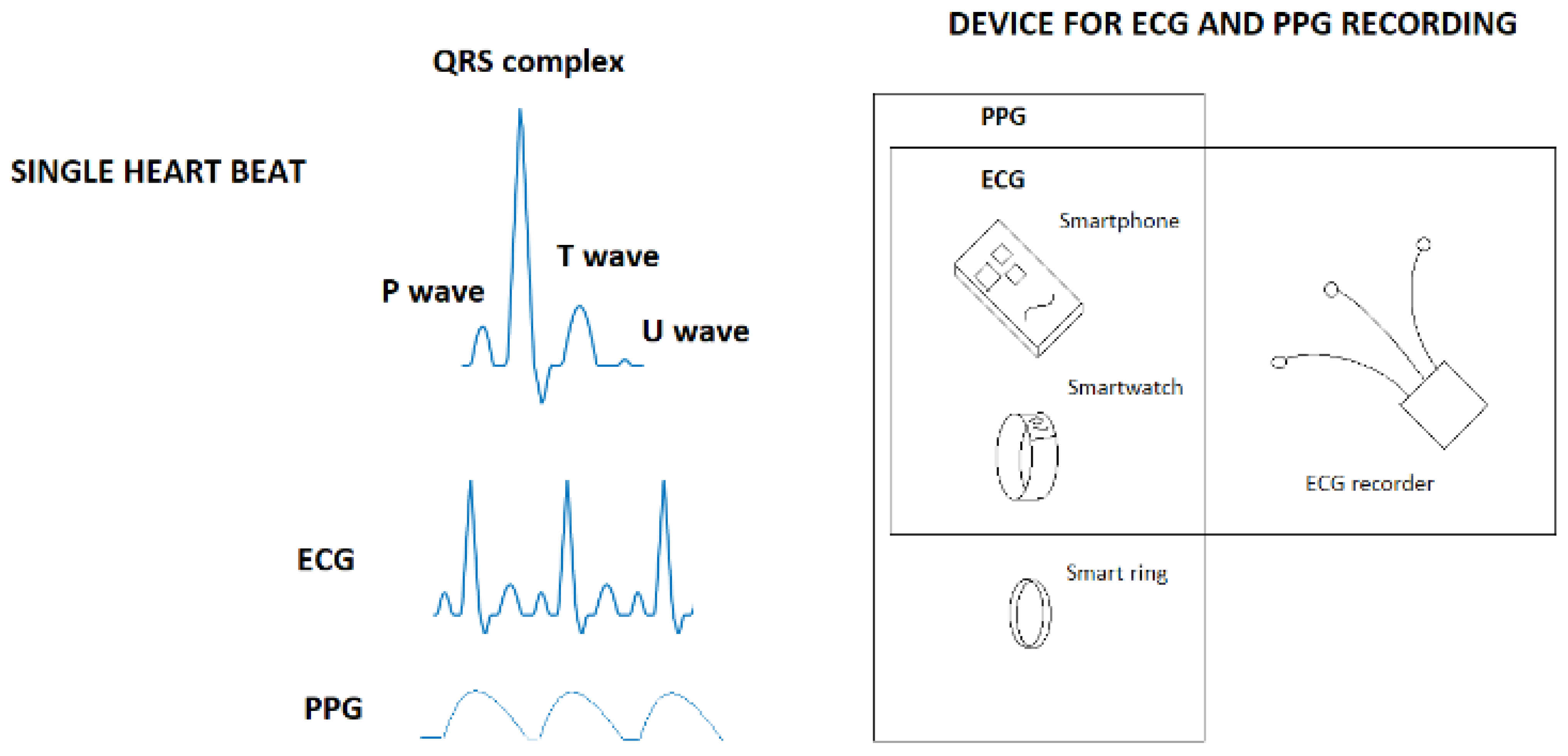
1.1. Wearable Devices
1.1.1. ECG and PPG
1.1.2. Smart Devices
1.1.3. ECG Recorders
1.2. Artificial Intelligence
2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, F.; Kwan, G.F.; Benjamin, E.J. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Carter, R.E.; Yao, X.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: A retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019, 394, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. A Review of Atrial Fibrillation Detection Methods as a Service. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörnmo, L.; Laguna, P. Bioelectrical Signal Processing in Cardiac and Neurological Application; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagido, R.B.; Lobo, J.; Leite, S.; Sousa, C.; Ferreira, L.; Silva-Cardoso, J. Using the smartphone camera to monitor heart rate and rhythm in heart failure patients. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Valencia, Spain, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 556–559. [Google Scholar]
- Shabaan, M.; Arshid, K.; Yaqub, M.; Jinchao, F.; Zia, M.S.; Bojja, G.R.; Iftikhar, M.; Ghani, U.; Ambati, L.S.; Munir, R. Survey: Smartphone-based assessment of cardiovascular diseases using ECG and PPG analysis. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isakadze, N.; Martin, S.S. How useful is the smartwatch ECG? Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 30, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, H.O.; Rantanen, A.; Kenttä, T.V.; Koskimäki, H. Feasible assessment of recovery and cardiovascular health: Accuracy of nocturnal HR and HRV assessed via ring PPG in comparison to medical grade ECG. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 04NT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardot, S.; Rey, B.; Audette, L.; Fan, K.; Huang, D.Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Irani, P. One Ring to Rule Them All: An Empirical Understanding of Day-to-Day Smartring Usage Through In-Situ Diary Study. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2022, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.H.; Beam, A.L.; Kohane, I.S. Artificial intelligence in healthcare. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.K.; Le, H.N.; Luu, K.; Nguyen, H.V.; Ayache, N. Deep reinforcement learning in medical imaging: A literature review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botvinick, M.; Ritter, S.; Wang, J.X.; Kurth-Nelson, Z.; Blundell, C.; Hassabis, D. Reinforcement Learning, Fast and Slow. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2019, 23, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albu, A. From Logical Inference to Decision Trees in Medical Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering, Sinaia, Romania, 22–24 June 2017; pp. 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, G.; Qi, X.; Zhou, X.; Chang, Q. A novel deep arrhythmia-diagnosis network for atrial fibrillation classification using electrocardiogram signals. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75577–75590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, D.; Hassabis, D.; Mcclelland, J.L. What Learning Systems do Intelligent Agents Need? Complementary Learning Systems Theory Updated. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2016, 20, 512–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.R.; Wang, X.J. Artificial neural networks for neuroscientists: A primer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.01001v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, O.; Kareem, M.; Ali, A.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. Automated Arrhythmia Detection Based on RR Intervals. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olier, I.; Ortega-Martorell, S.; Pieroni, M.; Lip, G.Y. How machine learning is impacting research in atrial fibrillation: Implications for risk prediction and future management. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 1700–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Chon, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, S.; Gil, Y.; et al. Compressed deep learning to classify arrhythmia in an embedded wearable device. Sensors 2022, 22, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muizniece, L.; Bertagnoli, A.; Qureshi, A.; Zeidan, A.; Roy, A.; Muffoletto, M.; Aslanidi, O. Reinforcement Learning to Improve Image-Guidance of Ablation Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 733139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Nava, A.M.; Atienza, F.; Bermejo, J.; Fernández-Avilés, F. Artificial intelligence for a personalized diagnosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H1337–H1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, A.Y.; Rajpurkar, P.; Haghpanahi, M.; Tison, G.H.; Bourn, C.; Turakhia, M.P.; Ng, A.Y. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.; Blanchard, D.G. Diagnosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation. Am. Fam. Physic. 2016, 94, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linz, D.; Hermans, A.; Tieleman, R.G. Early atrial fibrillation detection and the transition to comprehensive management. EP Europace 2021, 23 (Suppl. 2), ii46–ii51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, A.; Zoha, A.; Mabrouk, I.B.; Sabbour, H.M.; Al-Sumaiti, A.S.; Alomainy, A.; Ali Imran, M.; Abbasi, Q.H. A review on the state of the art in atrial fibrillation detection enabled by machine learning. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashar, S.K.; Han, D.; Hajeb-Mohammadalipour, S.; Ding, E.; Whitcomb, C.; McManus, D.D.; Chon, K.H. Atrial fibrillation detection from wrist photoplethysmography signals using smartwatches. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Oster, J.; Reinertsen, E.; Li, Q.; Zhao, L.; Nemati, S.; Clifford, G.D. A comparison of entropy approaches for AF discrimination. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 074002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabanski, R.; Horoba, K.; Wrobel, J.; Matonia, A.; Martinek, R.; Kupka, T.; Jezewski, M.; Kahankova, R.; Jezewski, J.; Leski, J.M. Detection of atrial fibrillation episodes in long-term heart rhythm signals using a support vector machine. Sensors 2020, 20, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Bin, G.; Wu, S.; Bin, G.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z. Detection of atrial fibrillation from ECG recordings using decision tree ensemble with multi-level features. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 094008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerikäinen, L.M.; Bonomi, A.G.; Schipper, F.; Dekker, L.R.; de Morree, H.M.; Vullings, R.; Aarts, R.M. Detecting atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter in daily life using photoplethysmography data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 24, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, S.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Ding, E.; Walkey, A.J.; McManus, D.D.; Chon, K.H. Atrial fibrillation detection during sepsis: Study on MIMIC III ICU data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 3124–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahan, M.S.; Mansourvar, M.; Puthusserypady, S.; Wiil, U.K.; Peimankar, A. Short-term atrial fibrillation detection using electrocardiograms: A comparison of machine learning approaches. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2022, 163, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahul, J.; Sharma, L.D. Artificial intelligence-based approach for atrial fibrillation detection using normalised and short-duration time-frequency ECG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontis, K.C.; Yao, X.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Philippakis, A.A.; Noseworthy, P.A. How will machine learning inform the clinical care of atrial fibrillation? Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Acharya, U.R. HAN-ECG: An interpretable atrial fibrillation detection model using hierarchical attention networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.Y.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, J.M.; Kim, K.H.; Jeon, K.H.; Cho, S.; Park, J.; Oh, B.H. Explainable artificial intelligence to detect atrial fibrillation using electrocardiogram. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 328, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, O.; Kashou, A.H.; Noseworthy, P.A. Artificial intelligence and atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.C.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Joo, S. ECG data dependency for atrial fibrillation detection based on residual networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shen, B. Electrocardiogram generation with a bidirectional LSTM-CNN generative adversarial network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahawy, M.; Benkhelifa, E.; White, D. A Review on Plastic Artificial Neural Networks: Exploring the Intersection between Neural Architecture Search and Continual Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.05625. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mäkynen, M.; Ng, G.A.; Li, X.; Schlindwein, F.S. Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection? Sensors 2022, 22, 8588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228588
Mäkynen M, Ng GA, Li X, Schlindwein FS. Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection? Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228588
Chicago/Turabian StyleMäkynen, Marko, G. Andre Ng, Xin Li, and Fernando S. Schlindwein. 2022. "Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection?" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228588
APA StyleMäkynen, M., Ng, G. A., Li, X., & Schlindwein, F. S. (2022). Wearable Devices Combined with Artificial Intelligence—A Future Technology for Atrial Fibrillation Detection? Sensors, 22(22), 8588. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228588





