Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Expression of TLRs in the Gut
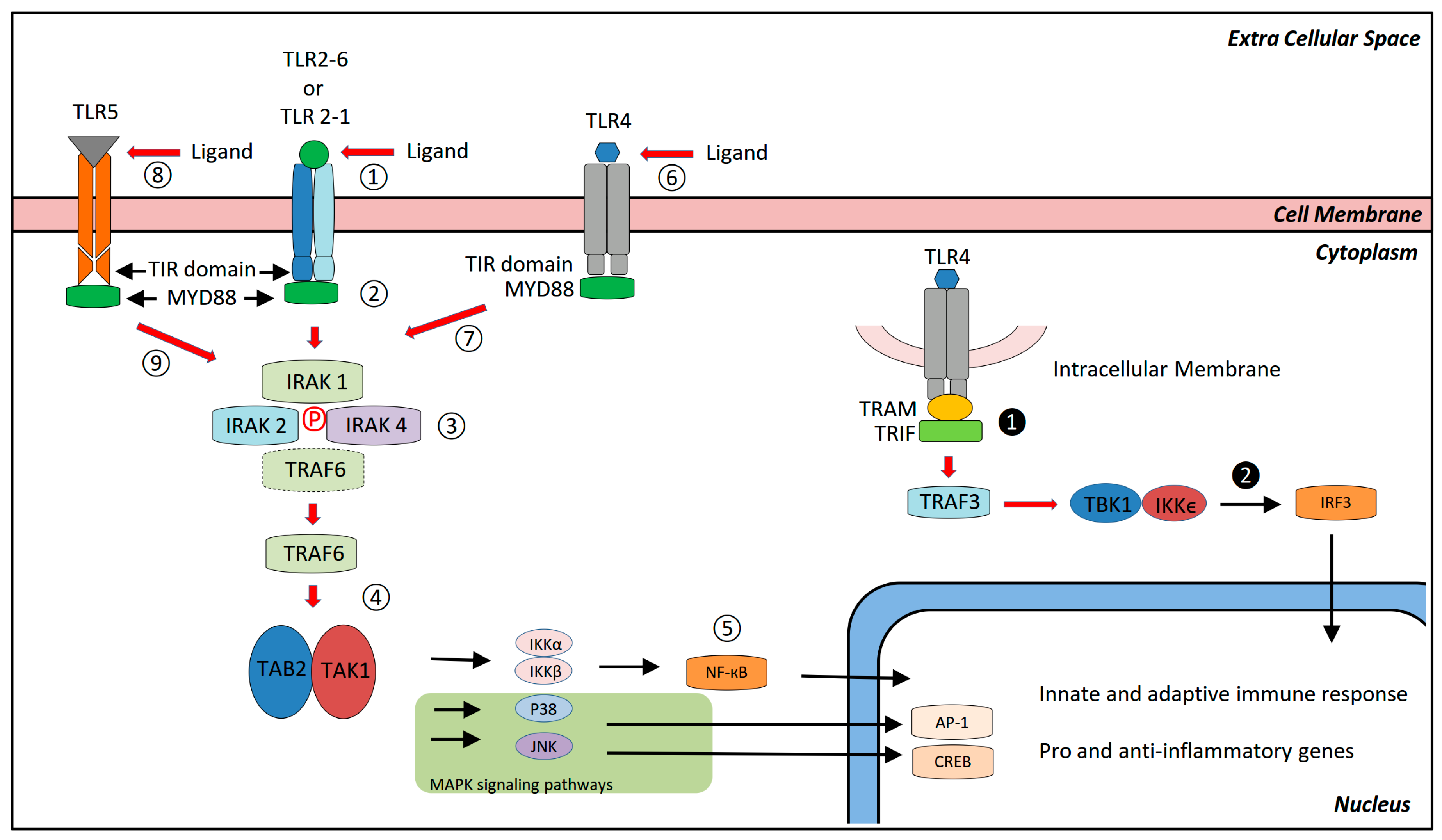
3. Signaling Pathways
3.1. TLR2
3.2. TLR4
3.3. TLR5
3.4. Soluble TLRs
3.5. Non-Bacterial Ligands Interacting with TLRs
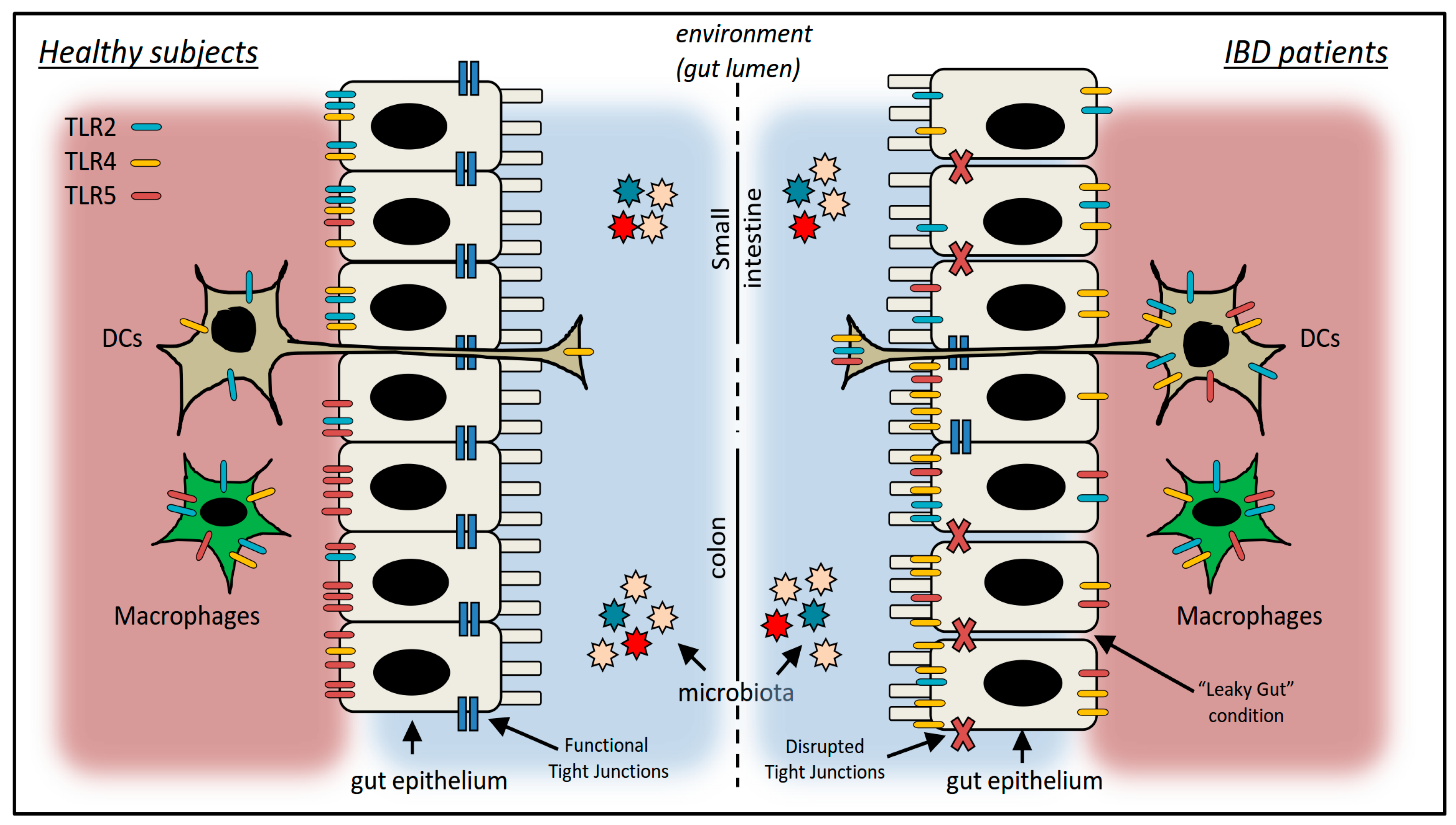
3.6. TLR—Microbiota Interaction in IBD
4. Outlook
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frosali, S.; Pagliari, D.; Gambassi, G.; Landolfi, R.; Pandolfi, F.; Cianci, R. How the intricate interaction among toll-like receptors, microbiota, and intestinal immunity can influence gastrointestinal pathology. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 489821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature 2007, 449, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiu, J.H.; Dorweiler, B.; Woo, C.W. Interaction between gut microbiota and toll-like receptor: From immunity to metabolism. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 95, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieling, P.A.; Modlin, R.L. Toll-like receptors: Mammalian “taste receptors” for a smorgasbord of microbial invaders. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, K.I.; Matsuguchi, T.; Masuda, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Musikacharoen, T.; Yoshikai, Y. Cutting edge: Naturally occurring soluble form of mouse toll-like receptor 4 inhibits lipopolysaccharide signaling. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6682–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Xu, D.; Brint, E.K.; O’Neill, L.A. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Coyne, C.B.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. Pamps and damps: Signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruysschaert, J.M.; Lonez, C. Role of lipid microdomains in TLR-mediated signalling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidya, M.K.; Kumar, V.G.; Sejian, V.; Bagath, M.; Krishnan, G.; Bhatta, R. Toll-like receptors: Significance, ligands, signaling pathways, and functions in mammals. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuven, E.M.; Fink, A.; Shai, Y. Regulation of innate immune responses by transmembrane interactions: Lessons from the TLR family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Varga, J. Endogenous ligands of TLR4 promote unresolving tissue fibrosis: Implications for systemic sclerosis and its targeted therapy. Immunol. Lett. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Martinez, I.; Shaker, M.E.; Mehal, W.Z. Therapeutic opportunities in damage-associated molecular pattern-driven metabolic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, K. Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger signals by cell surface toll-like receptors. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, Y.; Watari, M.; Jerud, E.S.; Young, D.W.; Ishizaka, S.T.; Rose, J.; Chow, J.C.; Strauss, J.F., III. The extra domain a of fibronectin activates toll-like receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10229–10233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.B.; Brunn, G.J.; Kodaira, Y.; Platt, J.L. Receptor-mediated monitoring of tissue well-being via detection of soluble heparan sulfate by toll-like receptor 4. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5233–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, L.; Babelova, A.; Kiss, E.; Hausser, H.J.; Baliova, M.; Krzyzankova, M.; Marsche, G.; Young, M.F.; Mihalik, D.; Gotte, M.; et al. The matrix component biglycan is proinflammatory and signals through toll-like receptors 4 and 2 in macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiley, S.T.; King, J.A.; Hancock, W.W. Fibrinogen stimulates macrophage chemokine secretion through toll-like receptor 4. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Termeer, C.; Benedix, F.; Sleeman, J.; Fieber, C.; Voith, U.; Ahrens, T.; Miyake, K.; Freudenberg, M.; Galanos, C.; Simon, J.C. Oligosaccharides of hyaluronan activate dendritic cells via toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.R.; Yamasaki, K.; Radek, K.A.; Di Nardo, A.; Goodarzi, H.; Golenbock, D.; Beutler, B.; Gallo, R.L. Recognition of hyaluronan released in sterile injury involves a unique receptor complex dependent on toll-like receptor 4, CD44, and MD-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18265–18275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Endogenous toll-like receptor ligands and their biological significance. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2592–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science 2010, 327, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosenbrug, T.; van de Graaff, M.J.; Ressing, M.E.; van Kasteren, S.I. Chemical tools for studying TLR signaling dynamics. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarember, K.A.; Godowski, P.J. Tissue expression of human toll-like receptors and differential regulation of toll-like receptor mrnas in leukocytes in response to microbes, their products, and cytokines. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Gao, N. Compartmentalizing intestinal epithelial cell toll-like receptors for immune surveillance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, L.A.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; O’Neill, L.; Netea, M.G. Toll-like receptors and chronic inflammation in rheumatic diseases: New developments. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, E.; Taboubi, S.; Torres, D.; Delbauve, S.; Hachani, A.; Whitehead, M.A.; Pearce, W.P.; Berenjeno, I.M.; Nock, G.; Filloux, A.; et al. The p110delta isoform of the kinase PI(3)K controls the subcellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornef, M.W.; Normark, B.H.; Vandewalle, A.; Normark, S. Intracellular recognition of lipopolysaccharide by toll-like receptor 4 in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.T. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: How bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cario, E.; Podolsky, D.K. Differential alteration in intestinal epithelial cell expression of toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4 in inflammatory bowel disease. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 7010–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamonic, G.; Pasternak, J.A.; Wilson, H.L. Recognizing conserved non-canonical localization patterns of toll-like receptors in tissues and across species. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santaolalla, R.; Fukata, M.; Abreu, M.T. Innate immunity in the small intestine. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 27, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.L.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Rigby, R.J.; Bell, S.J.; Emmanuel, A.V.; Knight, S.C.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J. Characteristics of intestinal dendritic cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamadevan, A.S.; Fukata, M.; Arnold, E.T.; Thomas, L.S.; Hsu, D.; Abreu, M.T. Regulation of Toll-like receptor 4-associated MD-2 in intestinal epithelial cells: A comprehensive analysis. Innate Immun. 2010, 16, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausmann, M.; Kiessling, S.; Mestermann, S.; Webb, G.; Spottl, T.; Andus, T.; Scholmerich, J.; Herfarth, H.; Ray, K.; Falk, W.; et al. Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 are up-regulated during intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front. Immunol 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Lind, J.; Tegtmeyer, N.; El-Omar, E.M.; Backert, S. Interplay of the gastric pathogen helicobacter pylori with toll-like receptors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 192420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; O’Neill, L.A. Signal transduction by the lipopolysaccharide receptor, Toll-like receptor-4. Immunology 2004, 113, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The role of TLR2 in infection and immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, A.; Balschun, T.; Karlsen, T.H.; Sventoraityte, J.; Nikolaus, S.; Mayr, G.; Domingues, F.S.; Albrecht, M.; Nothnagel, M.; Ellinghaus, D.; et al. Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, A.T.; Navas, T.A.; Lyons, S.; Godowski, P.J.; Madara, J.L. Cutting edge: Bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1882–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.H.; Im, E.; Riegler, M.; Kokkotou, E.; O’Brien, M.; Pothoulakis, C. Pathophysiological role of toll-like receptor 5 engagement by bacterial flagellin in colonic inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13610–13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodes, M.J.; Cong, Y.; Elson, C.O.; Mohamath, R.; Landers, C.J.; Targan, S.R.; Fort, M.; Hershberg, R.M. Bacterial flagellin is a dominant antigen in crohn disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, K.A.; Yang, H.; Ippoliti, A.; Mei, L.; Elson, C.O.; Hershberg, R.M.; Vasiliauskas, E.A.; Fleshner, P.R.; Abreu, M.T.; Taylor, K.; et al. Anti-flagellin (CBir1) phenotypic and genetic Crohn’s disease associations. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawn, T.R.; Verbon, A.; Lettinga, K.D.; Zhao, L.P.; Li, S.S.; Laws, R.J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Beutler, B.; Schroeder, L.; Nachman, A.; et al. A common dominant TLR5 stop codon polymorphism abolishes flagellin signaling and is associated with susceptibility to legionnaires’ disease. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, A.T.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Brant, S.R.; Duerr, R.H.; Nicolae, D.L.; Cho, J.H. Dominant-negative TLR5 polymorphism reduces adaptive immune response to flagellin and negatively associates with crohn’s disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G1157–G1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Burisch, J.; Pedersen, N.; Roug, S.; Galsgaard, J.; Ydegaard Turino, S.; Brodersen, J.B.; Rashid, S.; Kaiser Rasmussen, B.; et al. Polymorphisms in the toll-like receptor and the IL-23/IL-17 pathways were associated with susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in a Danish cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, N.K.; Ahuja, V.; Meena, K.; Paul, J. Association of TLR5 gene polymorphisms in ulcerative colitis patients of north India and their role in cytokine homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, B.; Rietschel, E.T. Innate immune sensing and its roots: The story of endotoxin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, B.; Jiang, Z.; Georgel, P.; Crozat, K.; Croker, B.; Rutschmann, S.; Du, X.; Hoebe, K. Genetic analysis of host resistance: Toll-like receptor signaling and immunity at large. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 353–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Horiuchi, T.; Hoshino, K.; Takeda, K.; Dong, Z.; Modlin, R.L.; Akira, S. Cutting edge: Role of toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune response to microbial lipoproteins. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, T.D. Cholera toxin, LT-I, LT-IIa and LT-IIb: The critical role of ganglioside binding in immunomodulation by Type I and Type II heat-labile enterotoxins. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2007, 6, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Wang, M.; Tapping, R.I.; Stepensky, V.; Nawar, H.F.; Triantafilou, M.; Triantafilou, K.; Connell, T.D.; Hajishengallis, G. Ganglioside GD1a is an essential coreceptor for toll-like receptor 2 signaling in response to the B subunit of type iib enterotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7532–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, H.L.; Alderwick, L.J.; Appelmelk, B.J.; Maaskant, J.; Bhatt, A.; Singh, A.; Nigou, J.; Eggeling, L.; Geurtsen, J.; Besra, G.S. A truncated lipoglycan from mycobacteria with altered immunological properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2634–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Banerjee, P.; Biswas, T. Porin of Shigella dysenteriae directly promotes toll-like receptor 2-mediated CD4+ T cell survival and effector function. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 3076–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, P.; Visintin, A.; Gunawardana, J.; Halmen, K.A.; King, C.A.; Golenbock, D.T.; Wetzler, L.M. Meningococcal porin porb binds to TLR2 and requires TLR1 for signaling. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Muhlradt, P.F.; Morr, M.; Radolf, J.D.; Zychlinsky, A.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by toll-like receptor 6. Int. Immunol. 2001, 13, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, Y.; Akashi, S.; Nagafuku, M.; Ogata, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Akira, S.; Kitamura, T.; Kosugi, A.; Kimoto, M.; Miyake, K. Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, F.; Smith, K.D.; Ozinsky, A.; Hawn, T.R.; Yi, E.C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Eng, J.K.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M.; Aderem, A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001, 410, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horng, T.; Barton, G.M.; Flavell, R.A.; Medzhitov, R. The adaptor molecule tirap provides signalling specificity for toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 420, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, M.; Piermattei, A.; Di Sante, G.; Migliara, G.; Delogu, G.; Ria, F. Immunomodulation by gut microbiota: Role of toll-like receptor expressed by T cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 586939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melmed, G.; Thomas, L.S.; Lee, N.; Tesfay, S.Y.; Lukasek, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B.; Arditi, M.; Abreu, M.T. Human intestinal epithelial cells are broadly unresponsive to toll-like receptor 2-dependent bacterial ligands: Implications for host-microbial interactions in the gut. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, D.J.; Kuhn, R.; Rajewsky, K.; Muller, W.; Menon, S.; Davidson, N.; Grunig, G.; Rennick, D. Interleukin-10 is a central regulator of the response to LPS in murine models of endotoxic shock and the shwartzman reaction but not endotoxin tolerance. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cario, E. Toll-like receptors in inflammatory bowel diseases: A decade later. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, D.; Cheung, J.; Scheerens, H.; Poulet, F.; McClanahan, T.; McKenzie, B.; Kleinschek, M.A.; Owyang, A.; Mattson, J.; Blumenschein, W.; et al. IL-23 is essential for T cell-mediated colitis and promotes inflammation via IL-17 and IL-6. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Chang, C.H. Negative regulation of MYD88-dependent signaling by IL-10 in dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18327–18332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Round, J.L.; Kasper, D.L. A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature 2008, 453, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glocker, E.O.; Kotlarz, D.; Boztug, K.; Gertz, E.M.; Schaffer, A.A.; Noyan, F.; Perro, M.; Diestelhorst, J.; Allroth, A.; Murugan, D.; et al. Inflammatory bowel disease and mutations affecting the interleukin-10 receptor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Shibolet, O. Toll-like receptors in inflammatory bowel disease-stepping into uncharted territory. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5149–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canto, E.; Ricart, E.; Monfort, D.; Gonzalez-Juan, D.; Balanzo, J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, J.L.; Vidal, S. TNF alpha production to TLR2 ligands in active IBD patients. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.S.; Kim, S.E.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, M.E.; Kim, H.M.; Paik, S.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. Crystal structure of the TLR1–TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 2007, 130, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Ranoa, D.R.; Jiang, S.; Mutha, S.K.; Li, X.; Baudry, J.; Tapping, R.I. Human TLRs 10 and 1 share common mechanisms of innate immune sensing but not signaling. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5094–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazli, A.; Kafka, J.K.; Ferreira, V.H.; Anipindi, V.; Mueller, K.; Osborne, B.J.; Dizzell, S.; Chauvin, S.; Mian, M.F.; Ouellet, M.; et al. HIV-1 GP120 induces TLR2- and TLR4-mediated innate immune activation in human female genital epithelium. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4246–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Popova, L.; Kwinn, L.; Haynes, L.M.; Jones, L.P.; Tripp, R.A.; Walsh, E.E.; Freeman, M.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Anderson, L.J.; et al. Pattern recognition receptors TLR4 and CD14 mediate response to respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Akashi, S.; Shimazu, R.; Yoshida, T.; Miyake, K.; Nishijima, M. Mouse toll-like receptor 4·MD-2 complex mediates lipopolysaccharide-mimetic signal transduction by taxol. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2251–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Yeh, W.C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szebeni, B.; Veres, G.; Dezsofi, A.; Rusai, K.; Vannay, A.; Mraz, M.; Majorova, E.; Arato, A. Increased expression of toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 in the colonic mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Buning, C.; Geerdts, L.; Schmidt, H.H.; Genschel, J.; Fiedler, T.; Gentz, E.; Molnar, T.; Nagy, F.; Lonovics, J.; et al. The c.1-260C>T promoter variant of CD14 but not the c.896A>G (p.D299g) variant of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) genes is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 2007, 76, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchimont, D.; Vermeire, S.; El Housni, H.; Pierik, M.; Van Steen, K.; Gustot, T.; Quertinmont, E.; Abramowicz, M.; Van Gossum, A.; Deviere, J.; et al. Deficient host-bacteria interactions in inflammatory bowel disease? The toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 Asp299gly polymorphism is associated with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut 2004, 53, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, B.L.; Huebner, C.; Petermann, I.; Gearry, R.B.; Barclay, M.L.; Shelling, A.N.; Ferguson, L.R. Has toll-like receptor 4 been prematurely dismissed as an inflammatory bowel disease gene? Association study combined with meta-analysis shows strong evidence for association. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torok, H.P.; Glas, J.; Tonenchi, L.; Mussack, T.; Folwaczny, C. Polymorphisms of the lipopolysaccharide-signaling complex in inflammatory bowel disease: Association of a mutation in the toll-like receptor 4 gene with ulcerative colitis. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 112, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.E.; Noyce, R.S.; Mossman, K.L. Innate cellular response to virus particle entry requires IRF3 but not virus replication. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, O.V.; Kostyukova, A.S. Domain structure of flagellin. FEBS Lett. 1984, 171, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Bajwa, P.; Deb, R.; Chellappa, M.M.; Dey, S. Flagellin a toll-like receptor 5 agonist as an adjuvant in chicken vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrick, B.M.; Yao, X.D.; Taha, A.Y.; German, J.B.; Rosenthal, K.L. Insights into soluble toll-like receptor 2 as a downregulator of virally induced inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBouder, E.; Rey-Nores, J.E.; Rushmere, N.K.; Grigorov, M.; Lawn, S.D.; Affolter, M.; Griffin, G.E.; Ferrara, P.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Morgan, B.P.; et al. Soluble forms of toll-like receptor (TLR)2 capable of modulating TLR2 signaling are present in human plasma and breast milk. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6680–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, G.; Sandelin, J.; Salem, A.; Nordstrom, D.C.; Waris, E. Toll-like receptors and their soluble forms differ in the knee and thumb basal osteoarthritic joints. Acta Orthop. 2017, 88, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.G.; Hsu, F.C.; Carter, D.; Orr, M.T. The science of vaccine adjuvants: Advances in TLR4 ligand adjuvants. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 41, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zunt, S.L.; Burton, L.V.; Goldblatt, L.I.; Dobbins, E.E.; Srinivasan, M. Soluble forms of toll-like receptor 4 are present in human saliva and modulate tumour necrosis factor-alpha secretion by macrophage-like cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 156, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, F.; Zhao, N.; Yang, F.; Ren, X. Expression of TLR4 in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with PD-L1 and poor prognosis in patients receiving pulmonectomy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, W.; Yang, L.; Ren, X. Soluble toll-like receptor 4 is a potential serum biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40106–40114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Toll-like receptor 4-related immunostimulatory polysaccharides: Primary structure, activity relationships, and possible interaction models. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ina, K.; Kataoka, T.; Ando, T. The use of lentinan for treating gastric cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Ende, W. Multifunctional fructans and raffinose family oligosaccharides. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, L.; Ramasamy, U.; Meyer, D.; Pullens, G.; Venema, K.; Faas, M.M.; Schols, H.A.; de Vos, P. Immune modulation by different types of beta2-->1-fructans is toll-like receptor dependent. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, L.M.; Meyer, D.; Pullens, G.; Faas, M.M.; Venema, K.; Ramasamy, U.; Schols, H.A.; de Vos, P. Toll-like receptor 2 activation by beta2-->1-fructans protects barrier function of T84 human intestinal epithelial cells in a chain length-dependent manner. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, L.M.; Sahasrabudhe, N.M.; Ramasamy, U.; Meyer, D.; Pullens, G.; Faas, M.M.; Venema, K.; Schols, H.A.; Vos, P.D. The impact of lemon pectin characteristics on TLR activation and T84 intestinal epithelial cell barrier function. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dou, W.; Zhang, E.; Sun, A.; Ding, L.; Wei, X.; Chou, G.; Mani, S.; Wang, Z. Paeoniflorin abrogates dss-induced colitis via a TLR4-dependent pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G27–G36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Sohn, K.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Hwang, D. Saturated fatty acids, but not unsaturated fatty acids, induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mediated through toll-like receptor 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16683–16689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Long chain fatty acids and gene expression in inflammation and immunity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ye, J.; Gao, Z.; Youn, H.S.; Lee, W.H.; Zhao, L.; Sizemore, N.; Hwang, D.H. Reciprocal modulation of toll-like receptor-4 signaling pathways involving MyD88 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT by saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37041–37051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, D.M.; Caldas, A.P.; Oliveira, L.L.; Bressan, J.; Hermsdorff, H.H. Saturated fatty acids trigger TLR4-mediated inflammatory response. Atherosclerosis 2016, 244, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.W.; Kwon, M.J.; Choi, A.M.; Kim, H.P.; Nakahira, K.; Hwang, D.H. Fatty acids modulate toll-like receptor 4 activation through regulation of receptor dimerization and recruitment into lipid rafts in a reactive oxygen species-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27384–27392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, K.; Manabe, I.; Oishi-Tanaka, Y.; Ohsugi, M.; Kono, N.; Ogata, F.; Yagi, N.; Ohto, U.; Kimoto, M.; Miyake, K.; et al. Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link beta cell dysfunction and islet inflammation. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Shin, J.; Park, K.S.; Cho, Y.M. Genome-wide identification of palmitate-regulated immediate early genes and target genes in pancreatic beta-cells reveals a central role of NF-kappaB. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Haghiac, M.; Glazebrook, P.; Minium, J.; Catalano, P.M.; Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. Saturated fatty acids enhance TLR4 immune pathways in human trophoblasts. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erridge, C.; Samani, N.J. Saturated fatty acids do not directly stimulate toll-like receptor signaling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessler, M.B.; Rudel, L.L.; Brown, J.M. Toll-like receptor signaling links dietary fatty acids to the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009, 20, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignacio, A.; Morales, C.I.; Camara, N.O.; Almeida, R.R. Innate sensing of the gut microbiota: Modulation of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Paglino, J.; Eslami-Varzaneh, F.; Edberg, S.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 2004, 118, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Wilmanski, J.; Forsman, H.; Hrncir, T.; Hao, L.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H.; Kobayashi, K.S. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling plays an essential role in homeostasis of the intestine. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, C.T.; Sharma, V.; Elmen, L.; Peterson, S.N. Immune homeostasis, dysbiosis and therapeutic modulation of the gut microbiota. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Fata, G.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Probiotics and the gut immune system: Indirect regulation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 10, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, E.R.; Zisman, T.L.; Suskind, D.L. The microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease: Current and therapeutic insights. J. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; Robertson, C.E.; Hamm, C.M.; Kpadeh, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Zhu, W.; Sartor, R.B.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; et al. Disease phenotype and genotype are associated with shifts in intestinal-associated microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.L.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; LeLeiko, N.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehri, S.; Kotlowski, R.; Bernstein, C.N.; Krause, D.O. Microbial diversity of inflamed and noninflamed gut biopsy tissues in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulard, O.; Asquith, M.J.; Powrie, F.; Maloy, K.J. TLR2-independent induction and regulation of chronic intestinal inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Villablanca, E.J.; De Calisto, J.; Gomes, D.C.; Nguyen, D.D.; Mizoguchi, E.; Kagan, J.C.; Reinecker, H.C.; Hacohen, N.; Nagler, C.; et al. MYD88-dependent TLR1/2 signals educate dendritic cells with gut-specific imprinting properties. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Lee, S.M.; Li, J.; Tran, G.; Jabri, B.; Chatila, T.A.; Mazmanian, S.K. The toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011, 332, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Srinivasan, S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, C.P.; Neal, M.D.; Siggers, R.; Sho, S.; Ma, C.; Branca, M.F.; Prindle, T., Jr.; Russo, A.M.; Afrazi, A.; Good, M.; et al. Intestinal epithelial toll-like receptor 4 regulates goblet cell development and is required for necrotizing enterocolitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Jang, M.H.; Yang, B.G.; Jung, Y.J.; Nishiyama, M.; Sato, S.; Tsujimura, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Yokota, Y.; et al. Regulation of humoral and cellular gut immunity by lamina propria dendritic cells expressing toll-like receptor 5. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hold, G.L.; Smith, M.; Grange, C.; Watt, E.R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Mukhopadhya, I. Role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: What have we learnt in the past 10 years? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1192–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, L.; O’Reilly, S.C. Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: Recent and emerging translational developments. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2016, 5, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sepehri, Z.; Kiani, Z.; Nasiri, A.A.; Kohan, F. Toll-like receptor 2 and type 2 diabetes. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2016, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S.; Massillon, L.; Follett, P.; Jensen, F.E.; Ratan, R.; Rosenberg, P.A.; Volpe, J.J.; Vartanian, T. Activation of innate immunity in the CNS triggers neurodegeneration through a toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8514–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.C.; Lathia, J.D.; Selvaraj, P.K.; Jo, D.G.; Mughal, M.R.; Cheng, A.; Siler, D.A.; Markesbery, W.R.; Arumugam, T.V.; Mattson, M.P. Toll-like receptor-4 mediates neuronal apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide and the membrane lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 213, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kigerl, K.A.; Lai, W.; Rivest, S.; Hart, R.P.; Satoskar, A.R.; Popovich, P.G. Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4 regulate inflammation, gliosis, and myelin sparing after spinal cord injury. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jou, I.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Joe, E.H.; Park, E.J. Gangliosides trigger inflammatory responses via TLR4 in brain glia. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagyoszi, P.; Wilhelm, I.; Farkas, A.E.; Fazakas, C.; Dung, N.T.; Hasko, J.; Krizbai, I.A. Expression and regulation of toll-like receptors in cerebral endothelial cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, K.; Kim, H.D.; Jin, J.J.; Maxwell, J.A.; Li, L.; Fukuchi, K. Role of toll-like receptor signalling in abeta uptake and clearance. Brain 2006, 129, 3006–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, T.; Porro, C.; Calvello, R.; Panaro, M.A. Biological role of toll-like receptor-4 in the brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 268, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbhandari, L.; Tegenge, M.A.; Shrestha, S.; Ganesh Kumar, N.; Malik, A.; Mithal, A.; Hosmane, S.; Venkatesan, A. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency impairs microglial phagocytosis of degenerating axons. Glia 2014, 62, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga, A.; Pradillo, J.M.; Cuartero, M.I.; Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Oses, M.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I. Toll-like receptor 4 modulates cell migration and cortical neurogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4710–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TLRs Dimers–Ligand | References |
|---|---|
| TLR2/1–Triacyl lipopeptides | [40,41,42] |
| TLR2/1–Heat-labile enterotoxins | [40,43,44] |
| TLR2/1–Lipomannan/Lipoarabinomannan | [40,45] |
| TLR2/1–Porins | [40,46,47] |
| TLR2/6–Diacyl lipopeptides (MALP-2) | [40,41,48] |
| TLR2/6–Lipoteichoic acid | [40,41] |
| TLR4/4–LPS (CD14-dependent) | [41] |
| TLR4/4–LPS (MD-2 dependent) | [41,49] |
| TLR5/5–Flagellin | [50] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020203
Hug H, Mohajeri MH, La Fata G. Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients. 2018; 10(2):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020203
Chicago/Turabian StyleHug, Hubert, M. Hasan Mohajeri, and Giorgio La Fata. 2018. "Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut" Nutrients 10, no. 2: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020203
APA StyleHug, H., Mohajeri, M. H., & La Fata, G. (2018). Toll-Like Receptors: Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients, 10(2), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020203




