Effects of Laser Irradiation in High-Speed Gas Flow for Surface Treatments of Copper
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
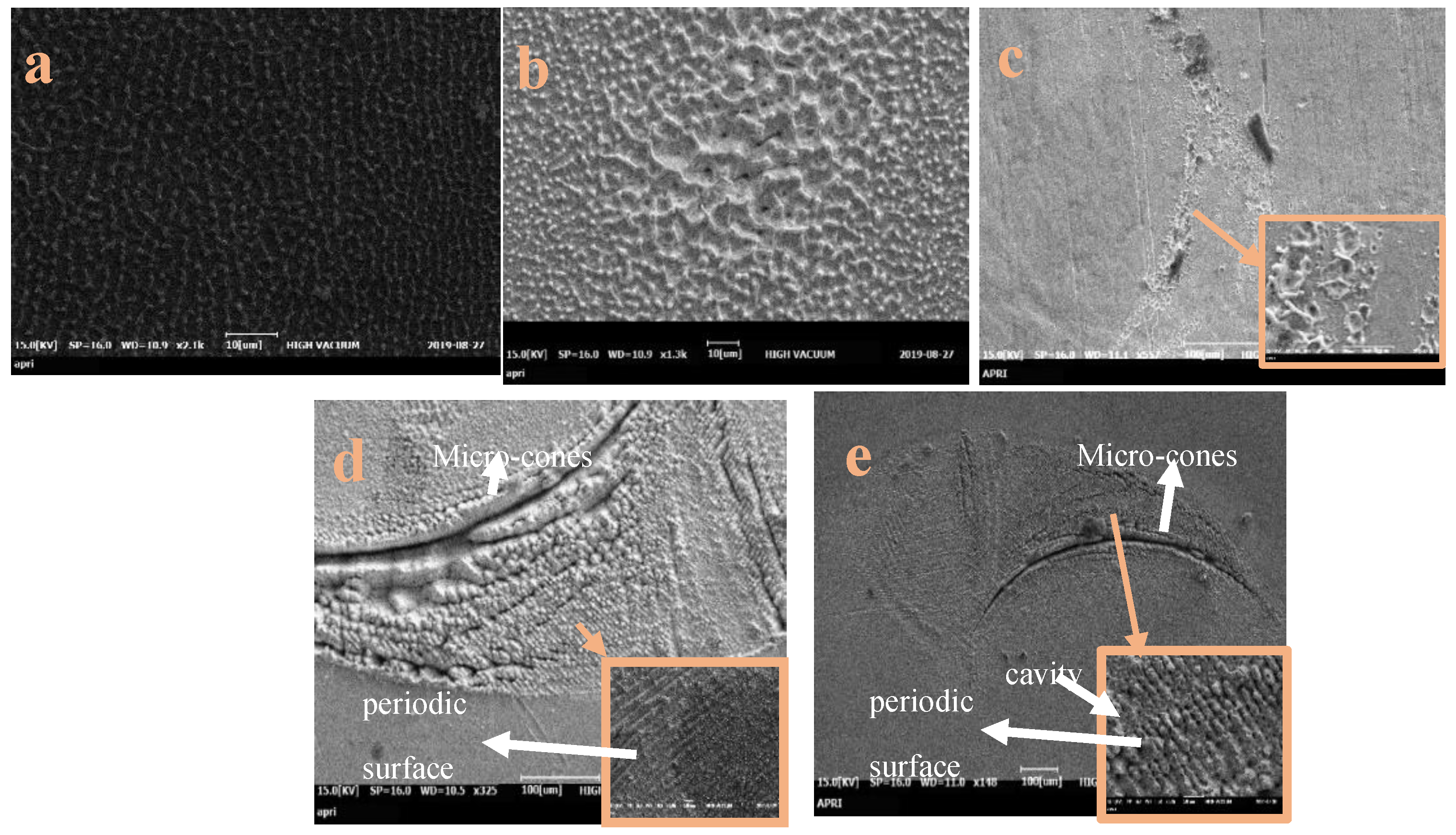
3.1. Surface Morphology
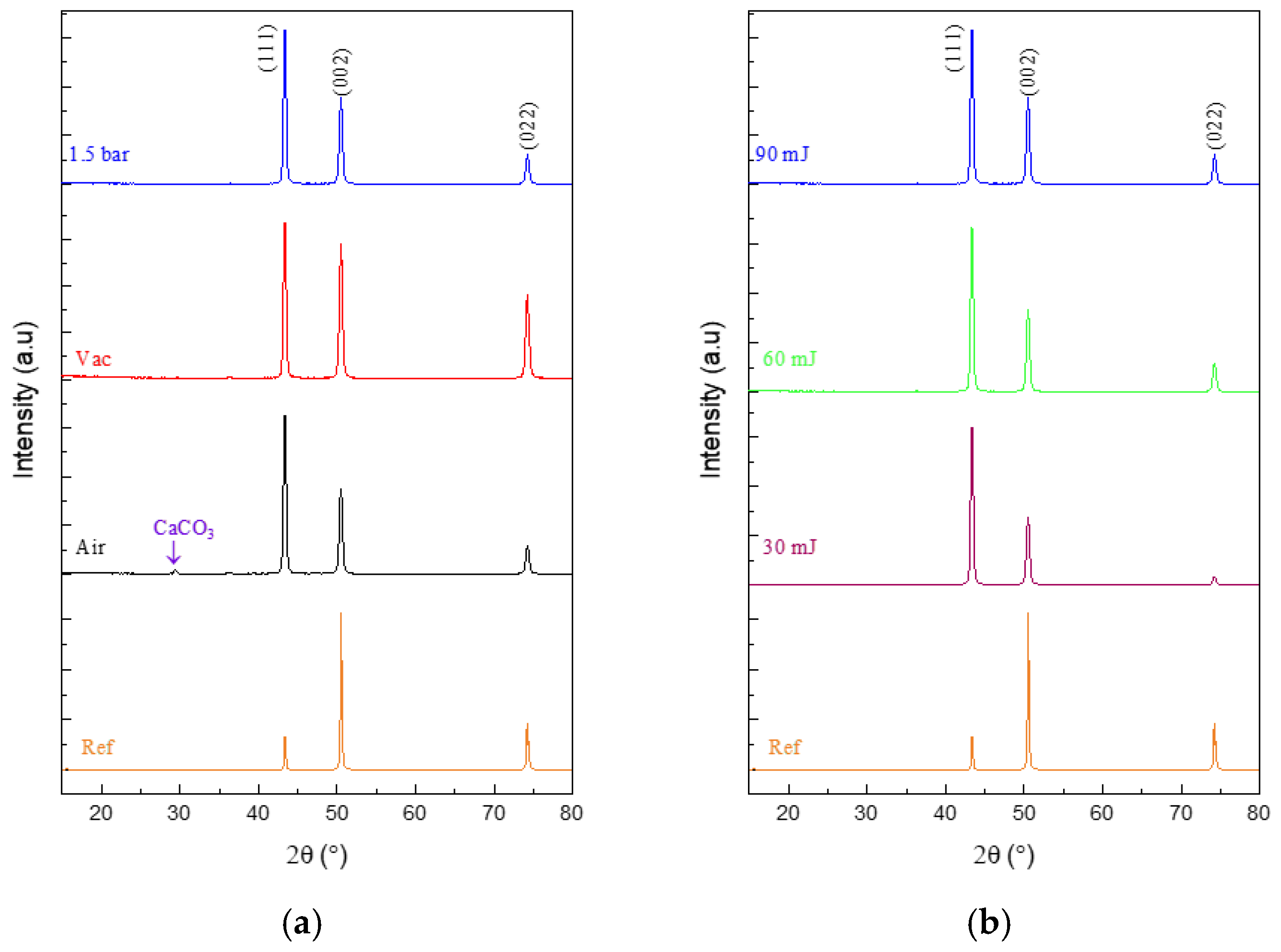
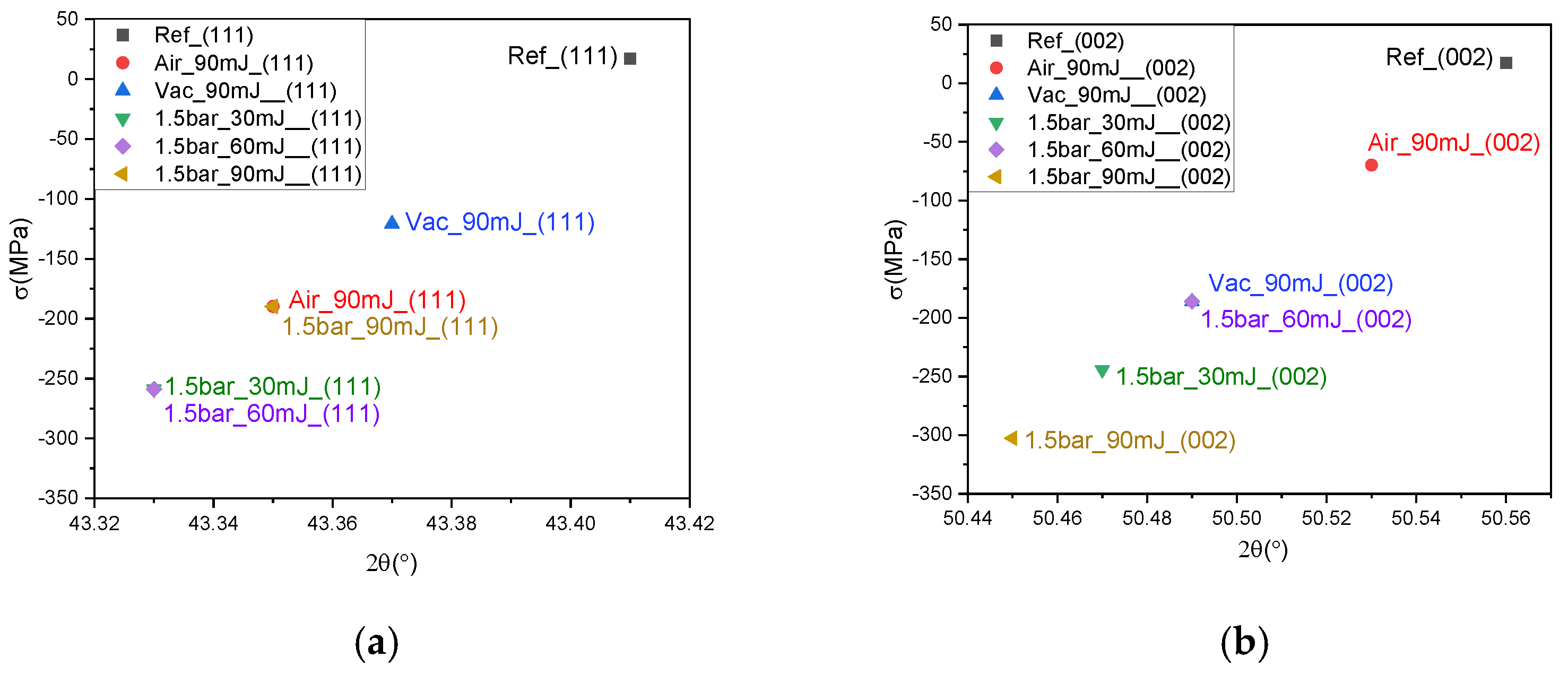
3.2. XRD Analysis
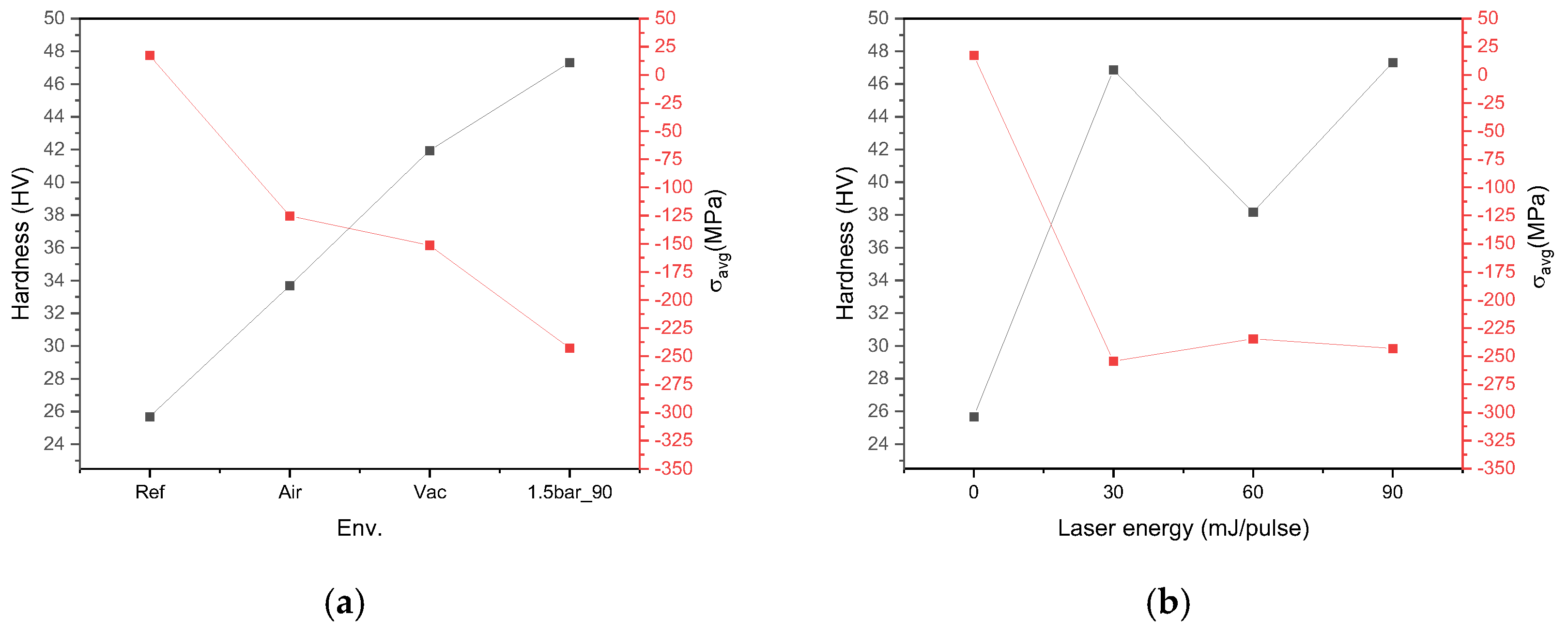
3.3. Hardness Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gärtner, F.; Stoltenhoff, T.; Voyer, J.; Kreye, H.; Riekehr, S.; Kocak, M. Mechanical properties of cold-sprayed and thermally sprayed copper coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 6770–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tao, N.R.; Lu, K. Fabrication of a gradient nano-micro-structured surface layer on bulk copper by means of a surface mechanical grinding treatment. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiskumar, R.; Murugan, N.; Dinaharan, I.; Vijay, S. Prediction of mechanical and wear properties of copper surface composites fabricated using friction stir processing. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Islam, A.; Pathak, M.; Khan, M.K.; Keshri, A.K. Plasma sprayed copper coatings for improved surface and mechanical properties. Vacuum 2019, 168, 108834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Lin, J. Effects of ultrasonic shot peening process parameters on nanocrystalline and mechanical properties of pure copper surface. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C. Recent developments and novel applications of laser shock peening: A review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Li, L.; Xia, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Tan, C. Enhancing the wettability for 4043 aluminum alloy on 301L stainless steel via chemical-etched surface texturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 305, 117577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, H.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Su, X.; Peng, J.; Ma, Y.; Tan, C.; Song, X.; Wu, T. Enhancing the reliability of laser welded-brazed aluminum/stainless steel joints via laser-chemical hybrid surface texturing. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 199, 111780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, H.; Sendova, M. Laser-induced sub-half-micrometer periodic structure on polymer surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M.; El-Waily, M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Ismail, Y. Treatment of aluminum alloys surface by nanosecond laser. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2018, 25, 1850079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poate, J.M.; Foti, G.; Jacobson, D. Surface Modification and Alloying: By Laser, Ion, and Electron Beams; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bäuerle, D. Laser Processing and Chemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Henari, F.; Blau, W. Excimer-laser surface treatment of metals for improved adhesion. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montross, C.S.; Wei, T.; Ye, L.; Clark, G.; Mai, Y.-W. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannava, S.; McDaniel, A.E.; Cowie, W.D. Laser Shock Peened Rotor Components for Turbomachinery. U.S. Patent 5,492,447, 20 February 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mannava, S.; McDaniel, A.E.; Cowie, W.D.; Halila, H.; Rhoda, J.E.; Gutknecht, J.E. Laser Shock Peened Gas Turbine Engine Fan Blade Edges. U.S. Patent 5,591,009, 7 January 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno, S.J.; McAllister, K.G.; Mannava, S. Laser Shock Peened Gas Turbine Engine Seal Teeth. U.S. Patent 6,200,689, 13 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Casarcia, D.A.; Cowie, W.D.; Mannava, S. Laser Shock Peened Bearings. U.S. Patent 5,584,586, 17 December 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cazzaniga, A.; Ettlinger, R.B.; Canulescu, S.; Schou, J.; Pryds, N. Nanosecond laser ablation and deposition of silver, copper, zinc and tin. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.-Q.; Yao, C.-Z.; Liu, H.; Wan, Y.; Ding, R.-J.; Yuan, X.-D.; Xu, S.-Z. Femtosecond laser ablation of Al-Mg alloy in vacuum and air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 447, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Rafique, M.S.; Nathala, C.S.; Ajami, A.A.; Husinsky, W.; Whitmore, K. Pulse duration and environmental effects on the surface nanostructuring and mechanical properties of zinc during femtosecond laser irradiation. JOSA B 2020, 37, 2878–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasemi, N.; Pacher, U.; Zhigilei, L.; Bomatí-Miguel, O.; Lahoz, R.; Kautek, W. Pulsed laser ablation and incubation of nickel, iron and tungsten in liquids and air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Zhan, Z.; Singh, S.C.; Chen, F.; Guo, C. Femtosecond laser-structured underwater “superpolymphobic” surfaces. Langmuir 2019, 35, 9318–9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, A.; Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, M.; Rafique, M.; Bhatti, K. Surface morphologic and structural analysis of IR irradiated silver. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.; Poate, J. Laser surface alloying. Int. Met. Rev. 1985, 30, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Kwok, C.; Man, H.C.; Guo, D. Laser fabrication of W-reinforced Cu layers: I. Corrosion behavior in 3.5% NaCl solution and synthetic acid rain. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 181, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Kwok, C.; Man, H.C.; Guo, D. Laser fabrication of W-reinforced Cu layers: II. Electrical wear behavior in air and synthetic acid rain. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 177, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, A.; Kobayashi, K.F. Surface alloying of copper with chromium by CO2 laser. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 174, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Issa, A.; Fouquet, F. Possibilities and limitations of laser surface alloying by melting of predeposited layers. Le J. De Phys. IV 1991, 1, C7-87–C7-90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.; Wong, P.; Man, H.C. Laser surface alloying of copper with titanium: Part I. Electrical wear resistance in dry condition. Part II. Electrical wear resistance in wet and corrosive condition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 297, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.; Kwok, C.; Man, H.C.; Cheng, F. Corrosion behavior of laser-alloyed copper with titanium fabricated by high power diode laser. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.T.; Wong, P.K.; Man, H.C. Enhancement in corrosion and electrical wear resistance of copper via laser surface alloying with NiTi. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cristino, V.; Tam, L.; Lo, K.; Kwok, C. Laser surface alloying of copper with Cr/Ti/CNT for enhancing surface properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Dawood, A.; Hayat, A.; Askar, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, M.A. Laser-assisted plasma formation and ablation of Cu in a controlled environment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M.; Aniculaesei, C.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.K.; Nam, C.H. Gas flow effect on the surface modification of aluminum and silver targets irradiated by a nanosecond laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 163, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabalin, L.; Laserna, J. Experimental determination of laser induced breakdown thresholds of metals under nanosecond Q-switched laser operation. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1998, 53, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.H.; Bashir, S.; Rafique, M.S.; Dawood, A.; Akram, M.; Mahmood, K.; Hayat, A.; Ahmad, R.; Hussain, T.; Mahmood, A. Pulsed laser ablation of Germanium under vacuum and hydrogen environments at various fluences. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 344, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.; Lau, Y.; Gilgenbach, R.M.; Spindler, H.; Lash, J.; Kovaleski, S. Surface instability of multipulse laser ablation on a metallic target. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 4466–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Ali, D.; Aftab, M.; Tanveer, M.U. Surface topography and structure of laser-treated high-purity zinc. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2015, 3, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Ali, D.; Tanveer, M.U.; Naseem, S. Surface roughness and electrical resistivity of high-purity zinc irradiated with nanosecond visible laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Javed, A.; Khaliq, M.W.; Ali, D.; Bashir, F. Impact of 1064 nm–10 ns pulsed laser on the surface morphology, structure, and hardness of Pd 80 Ni 20 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 1857–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.Z.; Khaliq, M.W.; Majeed, A.M.; Ali, D. Impact of 532 nm 6 ns laser pulses on (104) oriented zinc single crystal: Surface morphology, phase transformation, and structure hardness relationship. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 096503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciun, V.; Bassim, N.; Singh, R.; Craciun, D.; Hermann, J.; Boulmer-Leborgne, C. Laser-induced explosive boiling during nanosecond laser ablation of silicon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 186, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.; Bashir, S.; Akram, M.; Hayat, A.; Ahmed, S.; Iqbal, M.H.; Kazmi, A.H. Effect of nature and pressure of ambient environments on the surface morphology, plasma parameters, hardness, and corrosion resistance of laser-irradiated Mg-alloy. Laser Part. Beams 2015, 33, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E. The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1951, 64, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenröder, R. A model for the generation of small particles in laser ablation ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2006, 21, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, P.; Magee, J.; Coyne, E.; O’connor, G.; Glynn, T. The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 233, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popok, V.; Prasalovich, S.; Samuelsson, M.; Campbell, E.E. Design and capabilities of a cluster implantation and deposition apparatus: First results on hillock formation under energetic cluster ion bombardment. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2002, 73, 4283–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.C.; Haglund, R.F. (Eds.) Laser Ablation and Desorption. Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences; Elsevier Science & Technology: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.; Singh, A.K. Self-assembled microcones generated on solid surface through pulsed laser irradiation. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2013, 4, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaddadene, C.; Djemaa, A.; Belaroussi, Y.; Kerdja, T.; Gabouze, N.; Keffous, A.; Guerbous, L. Optical properties of silicon microcolumn grown by nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 3308–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’ev, S.; Ivanov, A.Y.; Liopo, V. Changes in the crystal structure of metals under laser radiation. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2007, 80, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badekas, H.; Koutsomichalis, A.; Panagopoulos, C. The influence of excimer laser treatment on an aluminium alloy surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1988, 34, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, C.; Michaelides, A. Laser surface treatment of copper. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Ali, N.; Akram, M.; Mahmood, K.; Ahmad, R. Effect of ambient environment on excimer laser induced micro and nano-structuring of stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Bleiner, D.; Bogaerts, A. Effect of ambient pressure on laser ablation and plume expansion dynamics: A numerical simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 063304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, M.; Rafique, M.; Bhatti, K.; Imran, M. Irradiation effects on copper. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2009, 164, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidin, N.; Qindeel, R.; Daud, M.; Bhatti, K. Plasma splashing from Al and Cu materials induced by an Nd:YAG pulsed laser. Laser Phys. 2007, 17, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.F. Principles of Materials Science and Engineering; U.S. Department of Energy: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1986.
- Koehler, J. Attempt to design a strong solid. Phys. Rev. B 1970, 2, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | O | Ca | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.23 | 2.31 | 3.66 | 1.77 | 83.03 |
| Material | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 8.96 | 4796 | 385 | 401 | 1.16 | 3.27 |
| Environment | Diffraction Plane | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref (as-received) | (111) | 43.405 | 43.41 | +0.005 | 17.22 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.56 | +0.006 | 17.42 | |
| Air, 90 mJ/pulse | (111) | 43.405 | 43.35 | –0.055 | –189.75 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.53 | –0.024 | –69.73 | |
| Vacuum, 90 mJ/pulse | (111) | 43.405 | 43.37 | –0.035 | –120.69 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.49 | –0.064 | –186.10 | |
| 1.5 bar, 30 mJ/pulse | (111) | 43.405 | 43.33 | –0.075 | –258.87 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.47 | –0.084 | –244.36 | |
| 1.5 bar, 60 mJ/pulse | (111) | 43.405 | 43.33 | –0.075 | –258.87 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.49 | –0.064 | –186.10 | |
| 1.5 bar, 90 mJ/pulse | (111) | 43.405 | 43.35 | –0.055 | –189.75 |
| (002) | 50.554 | 50.45 | –0.104 | –302.67 |
| Laser Energy (mJ/Pulse) | Hardness (HV) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Vacuum | 0.5 Bar | 1 Bar | 1.5 Bar | |
| Ref | 25.68 | 25.68 | 25.68 | 25.68 | 25.68 |
| 30 | 28.78 | 30.10 | 31.82 | 39.77 | 46.86 |
| 60 | 30.86 | 35.73 | 53.56 | 41.62 | 38.16 |
| 90 | 33.68 | 41.94 | 32.72 | 71.22 | 47.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezzat, M.; Aniculaesei, C.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.K. Effects of Laser Irradiation in High-Speed Gas Flow for Surface Treatments of Copper. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111296
Ezzat M, Aniculaesei C, Lee JW, Lee SK. Effects of Laser Irradiation in High-Speed Gas Flow for Surface Treatments of Copper. Micromachines. 2024; 15(11):1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111296
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzzat, Mohamed, Constantin Aniculaesei, Joong Wook Lee, and Seong Ku Lee. 2024. "Effects of Laser Irradiation in High-Speed Gas Flow for Surface Treatments of Copper" Micromachines 15, no. 11: 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111296
APA StyleEzzat, M., Aniculaesei, C., Lee, J. W., & Lee, S. K. (2024). Effects of Laser Irradiation in High-Speed Gas Flow for Surface Treatments of Copper. Micromachines, 15(11), 1296. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15111296








