Change in Pull-Out Force during Resorption of Magnesium Compression Screws for Osteosynthesis of Mandibular Condylar Fractures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korzon, T. Nowa metoda chirurgicznego leczenia złamań wyrostków kłykciowych żuchwy. Pol. Tyg. Lek. 1970, 25, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Eckelt, U.; Rasse, M. Controle clinique, radiographique et axiographique apres osteosynthese par vis de traction des fractures de la region condylienne de la mandibule. Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac. 1995, 96, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, A.; Kolk, A.; Neff, F.; Horch, H.H. Surgical vs. conservative therapy of diacapitular and high condylar fractures with dislocation. A comparison between MRI and axiography. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 2002, 6, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Zink, S.; Chatelain, B.; Wilk, A. Clinical experience with osteosynthesis of subcondylar fractures of the mandible using TCP plates. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Galil, K.; Loukota, R. Fractures of the mandibular condyle: Evidence base and current concepts of management. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 48, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Chęciński, M.; Sielski, M.; Chlubek, D. The Use of 3D Titanium Miniplates in Surgical Treatment of Patients with Condylar Fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlychuk, T.; Chernogorskyi, D.; Chepurnyi, Y.; Neff, A.; Kopchak, A. Biomechanical evaluation of type p condylar head osteosynthesis using conventional small-fragment screws reinforced by a patient specific two-component plate. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlychuk, T.; Shydlovsky, M.; Kopchak, A. A comparative biomechanical evaluation of different osteosynthesis techniques used for intracapsular condylar head fractures. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 9, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, J.; Maciejczyk, M.; Antonowicz, B.; Sidun, J.; Świderska, M.; Zalewska, A. Free radical production, inflammation and apoptosis in patients treated with titanium mandibular fixations-an observational study. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, J.; Maciejczyk, M.; Antonowicz, B.; Kretowski, A.; Waszkiel, D.; Bortnik, P.; Czarniecka-Bargłowska, K.; Kocisz, M.; Szulimowska, J.; Czajkowski, M.; et al. Exposure to Ti4Al4V titanium alloy leads to redox abnormalities, oxidative stress, and oxidative damage in patients treated for mandible fractures. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, J.; Maciejczyk, M.; Antonowicz, B.; Kretowski, A.; Sidun, J.; Domel, E.; Dąbrowski, J.; Ładny, J.R.; Morawska, K.; Zalewska, A. Glutathione metabolism, mitochondria activity, and nitrosative stress in patients treated for mandible fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifici, L.; De Angelis, F.; Orefici, A.; Cielo, A. Metals used in maxillofacial surgery. Oral Implantol. 2017, 9, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.C.; Valderrama, P.; Wilson, T.G.; Palmer, K.; Thomas, A.; Sridhar, S.; Adapalli, A.; Burbano, M.; Wadhwani, C. Titanium Corrosion Mechanisms in the Oral Environment: A Retrieval Study. Materials 2013, 6, 5258–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noumbissi, S.; Scarano, A.; Gupta, S. A Literature Review Study on Atomic Ions Dissolution of Titanium and Its Alloys in Implant Dentistry. Materials 2019, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolk, A.; Neff, A. Long-term results of ORIF of condylar head fractures of the mandible: A prospective 5-year follow-up study of small-fragment positional-screw osteosynthesis (SFPSO). J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skroch, L.; Fischer, I.; Meisgeier, A.; Kozolka, F.; Apitzsch, J.; Neff, A. Condylar remodeling after osteosynthesis of fractures of the condylar head or close to the temporomandibular joint. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareb, B.; Roossien, C.C.; van Bakelen, N.B.; Verkerke, G.J.; Vissink, A.; Bos, R.R.M.; van Minnen, B. Comparison of the mechanical properties of biodegradable and titanium osteosynthesis systems used in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.B.; Kindsfater, C.S. The use of biodegradable plates and screws to stabilize facial fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böker, K.O.; Richter, K.; Jäckle, K.; Taheri, S.; Grunwald, I.; Borcherding, K.; von Byern, J.; Hartwig, A.; Wildemann, B.; Schilling, A.F.; et al. Current State of Bone Adhesives—Necessities and Hurdles. Materials 2019, 12, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fu, X.; Pan, H.; Wan, P.; Wang, L.; Tan, L.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Chu, P.K. Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloys with enhanced osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and long-lasting antibacterial effects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrosielska, M.; Przekop, R.E.; Sztorch, B.; Brząkalski, D.; Zgłobicka, I.; Łępicka, M.; Dobosz, R.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Biogenic Composite Filaments Based on Polylactide and Diatomaceous Earth for 3D Printing. Materials 2020, 13, 4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, N.H.N.; Saeed, N.R. Treatment of fractures of the mandibular condylar head with ultrasound-activated resorbable pins: Early clinical experience. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 54, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, B.T.; Kim, W.H.; Park, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.-H. Biomechanical evaluation of unilateral subcondylar fracture of the mandible on the varying materials: A finite element analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallela, I.; Iizuka, T.; Salo, A.; Lindqvist, C. Lag-screw fixation of anterior mandibular fractures using biodegradable polylactide screws: A preliminary report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, A.S.; Koshy, J.C.; Weathers, W.M.; Wolfswinkel, E.M.; Kaufman, Y.; Sharabi, S.E.; Brown, R.H.; Hicks, M.J.; Hollier, L.H., Jr. Local foreign-body reaction to commercial biodegradable implants: An in vivo animal study. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2014, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, K.A.; Agrawal, C.M.; Barber, F.A.; Burkhart, S.S. Orthopaedic applications for PLA-PGA biodegradable polymers. Arthroscopy 1998, 14, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poircuitte, J.M.; Popkov, D.; Huber, H.; Polirsztok, E.; Lascombes, P.; Journeau, P. Resorbable osteosynthetic devices in pediatric traumatology: A prospective series of 24 cases. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2015, 25, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, L.; Perhomaa, M.; Kyrö, A.; Pokka, T.; Serlo, W.; Merikanto, J.; Sinikumpu, J.-J. Intramedullary nailing of forearm shaft fractures by biodegradable compared with titanium nails: Results of a prospective randomized trial in children with at least two years of follow-up. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedelin, H.; Larnert, P.; Hebelka, H.; Brisby, H.; Lagerstrand, K.; Laine, T. Innominate Salter osteotomy using resorbable screws: A retrospective case series and presentation of a new concept for fixation. J. Child. Orthop. 2019, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Pang, K.M.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 72, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, S.W.; Cho, S.W.; Byun, S.H.; Yang, B.E. Bioabsorbable Osteofixation Materials for Maxillofacial Bone Surgery: A Review on Polymers and Magnesium-Based Materials. Biomaterials 2020, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, P.; Lizio, G.; Marchetti, C.; Checchi, L.; Scarano, A. Magnesium-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Grafting Using the Vertical Inlay Technique. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2013, 33, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chapman, J.R.; Harrington, R.M.; Lee, K.M.; Anderson, P.A.; Tencer, A.F.; Kowalski, D. Factors affecting the pullout strength of cancellous bone screws. J. Biomech. Eng. 1996, 118, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assari, S.; Darvish, K.; Ilyas, A.M. Biomechanical analysis of second-generation headless compression screws. Injury 2012, 43, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, O.; Sagol, E.; Oflaz, H.; Sarikanat, M.; Havitcioglu, H. A biomechanical study on preloaded compression effect on headless screws. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2009, 129, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, R.; Evans, S.; Kosashvili, Y. Holding power of variable pitch screws in osteoporotic, osteopenic and normal bone: Are all screws created equal? Injury 2010, 41, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, G.W.; Zhai, Z.J.; Liu, L.N.; Li, H.W.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.L.; Wan, P.; Liu, X.Q.; Ouyang, Z.X.; et al. Antibacterial properties of magnesium in vitro and in an in vivo model of implant-associated methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 7586–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Lin, X.; Tan, L.L.; Yang, K. Effect of surface coating on antibacterial behawior of magnesium based metals. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3509–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Griffith, R.W.; Shechtman, D.; Evans, R.B.; Conzemius, M.G. In vitro antibacterial properties of magnesium metal against escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococcus aureus. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, H.M. Review Tetracycline-based histological analysis of bone remodeling. Calcif. Tissue Res. 1969, 3, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakiewicz, M. Are Magnesium Screws Proper for Mandibular Condyle Head Osteosynthesis? Materials 2020, 13, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.A.; Kuiper, J.H.; Kelly, C.P. Biomechanical evaluation of a new composite bioresorbable screw. J. Hand Surg. 2006, 31, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicciù, M.; Fiorillo, L.; Herford, A.; Crimi, S.; Bianchi, A.; D’Amico, C.; Laino, L.; Cervino, G. Bioactive titanium surfaces: Interactions of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells of nano devices applied to dental practice. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.J.; Qu, X.H.; Li, H.W.; Yang, K.; Wan, P.; Tan, L.L.; Ouyang, Z.X.; Liu, X.Q.; Tian, B.; Xiao, F.; et al. The effect of metallic magnesium degradation products on osteoclast-induced osteolysis and attenuation of NF-kappa B and NFATc1 signaling. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6299–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, A.; Maier, J.; Rock, E.; Gueux, E.; Nowacki, W.; Rayssiguier, Y. Magnesium and the inflammatory response: Potential physiopathological implications. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Han, Z.; Wang, E.; Xu, Z.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y. Degradable magnesium-based implant materials with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 101, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokkanen, P.U.; Böstman, O.; Hirvensalo, E.; Mäkelä, E.; Partio, E.K.; Pätiälä, H.; Vainionpää, S.; Vihtonen, K.; Törmälä, P. Bioabsorbable fixation in orthopaedic surgery and traumatology. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2607–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yu, X.; Wan, P.; Yang, K. Biodegradable materials for bone repairs: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rai, S.; Gao, Y.; Ze, R.; Tang, X.; Liu, R.; Hong, P. Biodegradable pins for lateral condylar fracture of the humerus with an early delayed presentation in children: A retrospective study of biodegradable pin vs. Kirschner wire. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, M.; Pietak, A.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Feyerabend, F.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Qin, L. Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based orthopaedic implants: A review from clinical translational perspective. Biomaterials 2017, 112, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakiewicz, M.; Świniarski, J. Treatment of high fracture of the neck of the mandibular condylar process by rigid fixation performed by lag screws: Finite element analysis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2017, 54, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, H.; Franke, A.; McLeod, N.; Lauer, G.; Nowak, A. Fixation of fractures of the condylar head of the mandible with a new magnesium-alloy biodegradable cannulated headless bone screw. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 55, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, M. Comparison of compression screws used for mandible head fracture treatment—Experimental study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 4059–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.-C.J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Tung, Y.-Y.; Chiang, Y.-Y.; Lai, E.H.-H.; Chen, W.-P.; Lin, C.-P. Effects of thread depth, taper shape, and taper length on the mechanical properties of mini-implants. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2012, 141, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, H.; Ashammakhi, N.; Kontio, R.; Waris, T.; Salo, A.; Lindqvist, C.; Gratz, K.; Suuronen, R. The use of bioabsorbable osteofixation devices in craniomaxillofacial surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 94, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsma, E.J.; Rozema, F.R.; Bos, R.R.; De Bruijn, W.C. Foreign body reactions to resorbable poly(l-lactide) bone plates and screws used for the fixation of unstable zygomatic fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 51, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Galil, K.; Loukota, R. Fixation of comminuted diacapitular fractures of the mandibular condyle with ultrasound-activated resorbable pins. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 46, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Xiong, M.; Guan, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Yuan, G. The in vivo degradation and bone-implant interface of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy screws: 18 months post-operation results. Corros. Sci. 2016, 113, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokat, H.; Seitz, J.-M.; Açil, Y.; Damm, T.; Möller, I.; Gülses, A.; Wiltfang, J. Osteosynthesis of a cranio-osteoplasty with a biodegradable magnesium plate system in miniature pigs. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakiewicz, M. Small-diameter compression screws completely embedded in bone for rigid internal fixation of the condylar head of the mandible. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukotjo, C.; Lima-Neto, T.J.; Santiago Júnior, J.F.; Faverani, L.P.; Miloro, M. Is There a Role for Absorbable Metals in Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mg/Mg Alloy Based Implants. Materials 2020, 18, 3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, R.; Kozakiewicz, M.; Świniarski, J. Comparison of Titanium and Bioresorbable Plates in “A” Shape Plate Properties—Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Yang, S.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, D.; Meng, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. A fully biodegradable and self-electrified device for neuroregenerative medicine. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Nune, K.C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, N.; Misra, R.D.K.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.; Yan, J. The effect of different coatings on bone response and degradation behavior of porous magnesium-strontium devices in segmental defect regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1765–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Yue, J.; Mi, J.; Zheng, L.; Dai, B.; Huang, W.; et al. Combination of magnesium ions and vitamin C alleviates synovitis and osteophyte formation in osteoarthritis of mice. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Li, T.; Jia, G.; Chang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Pei, J.; Yu, D.; Zhai, Z. Exposure to high levels of magnesium disrupts bone mineralization in vitro and in vivo. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Cao, C.; Wang, X.; Tao, J.; Li, C.; Xin, H.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Ai, F. Magnesium-alloy rods reinforced bioglass bone cement composite scaffolds with cortical bone-matching mechanical properties and excellent osteoconductivity for load-bearing bone in vivo regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
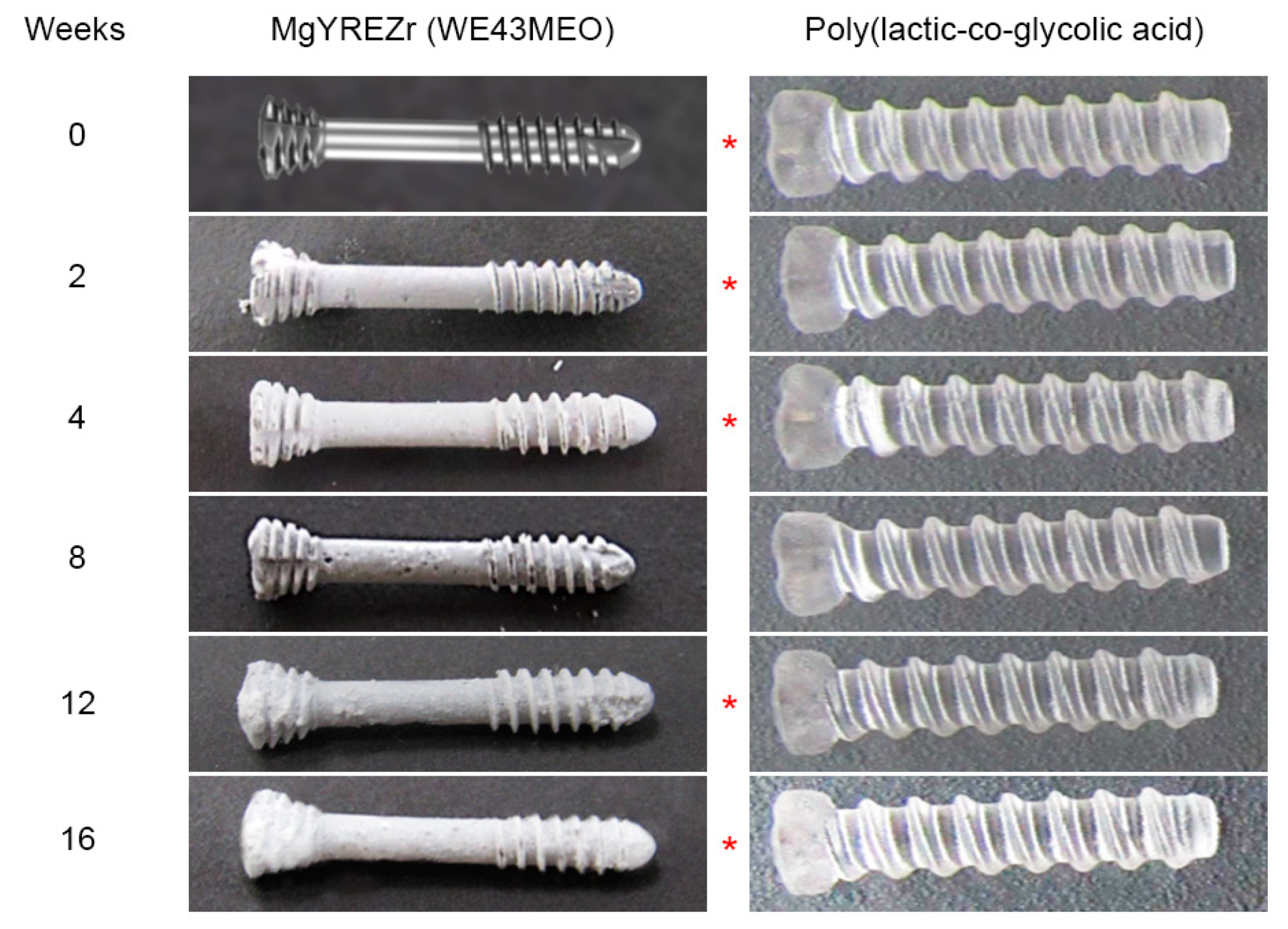
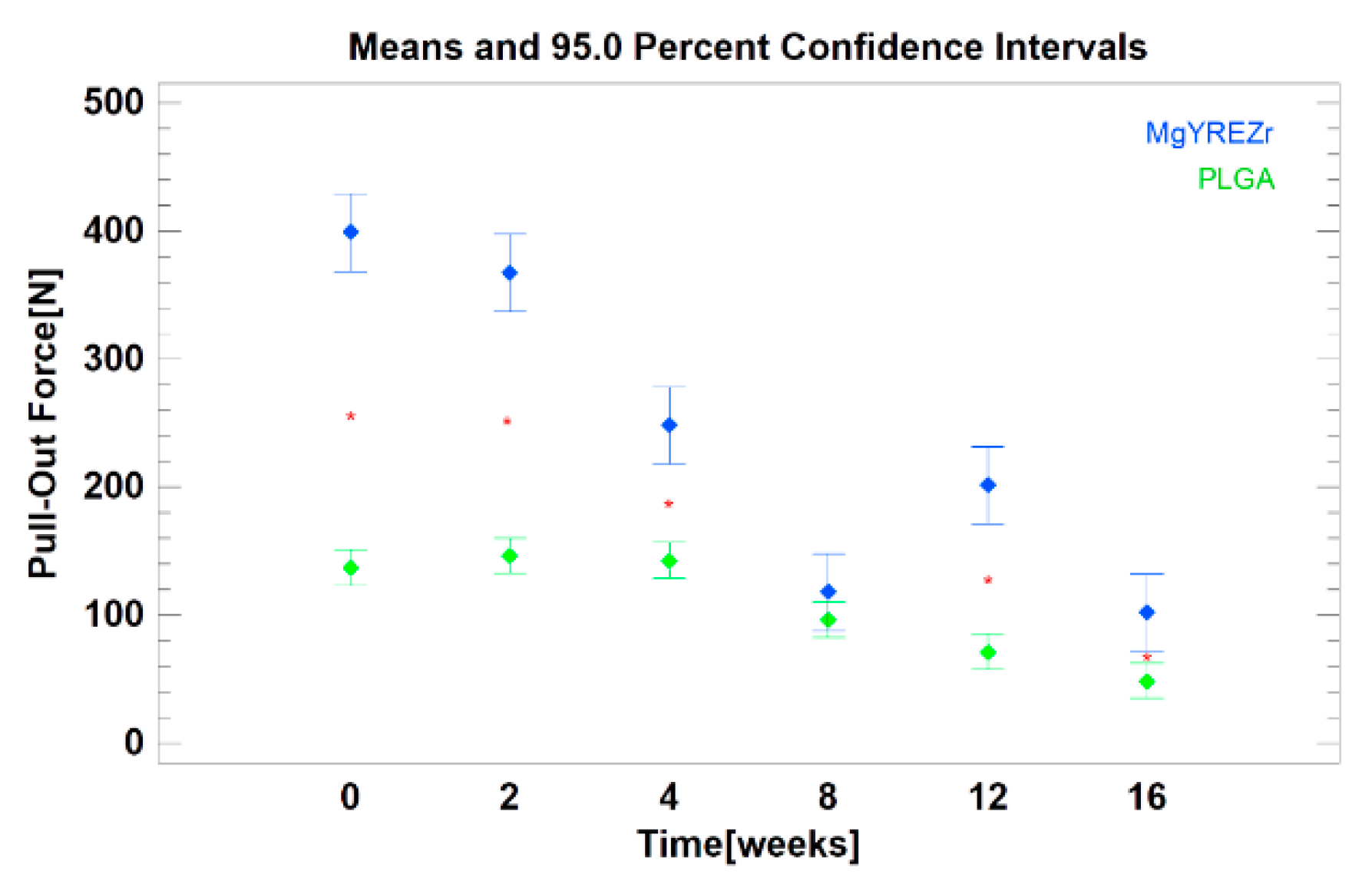
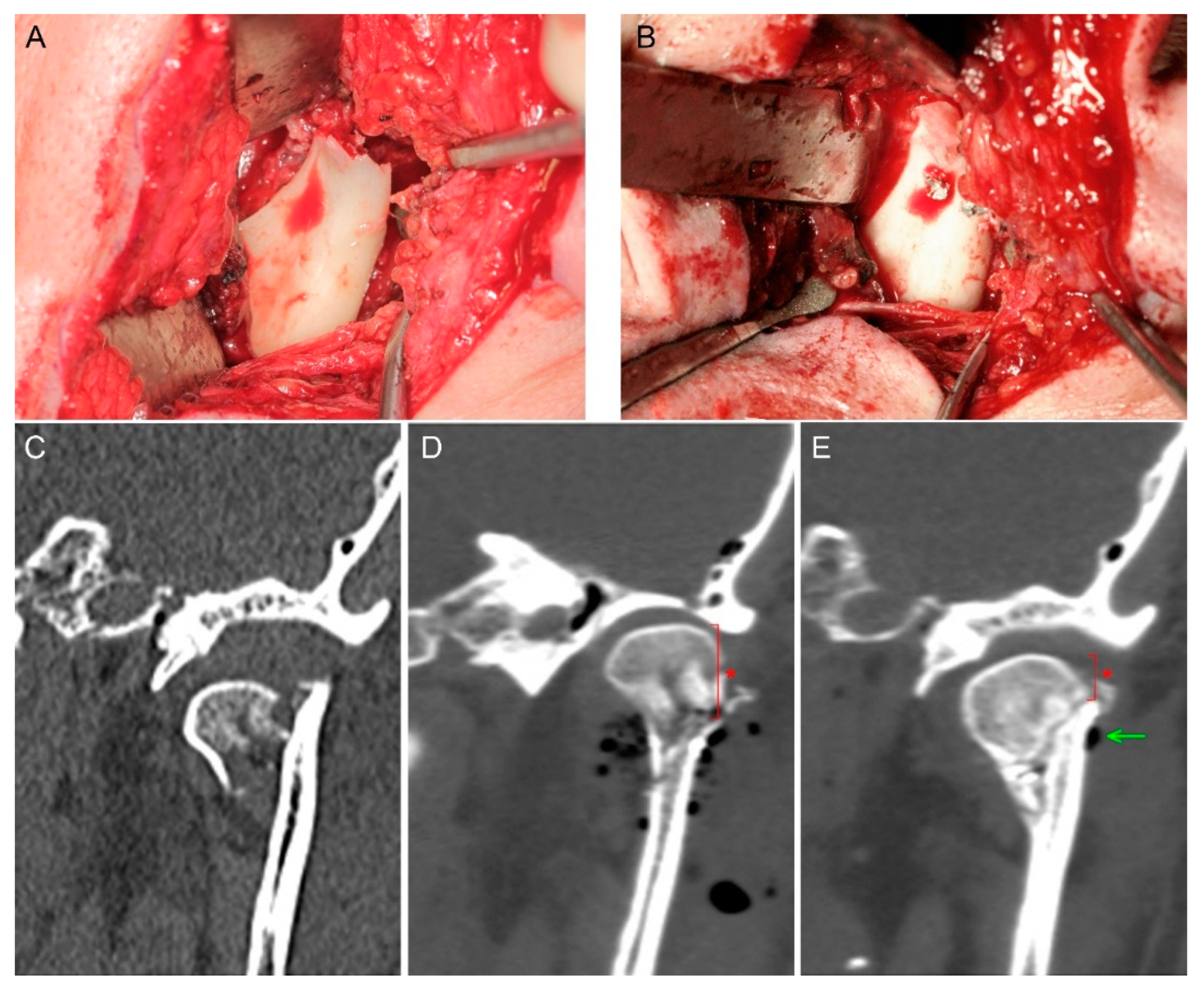
| Time [Weeks] | MgYREZr [N] | PLGA [N] | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 399 ± 7.5 | 138 ± 26.5 | p < 0.01 |
| 2 | 367 ± 28.6 | 147 ± 4.3 | p < 0.01 |
| 4 | 249 ± 34.2 | 143 ± 11.0 | p < 0.01 |
| 8 | 118 ± 71.1 | 97 ± 17.3 | NS |
| 12 | 201 ± 27.1 | 72 ± 27.2 | p < 0.01 |
| 16 | 102 ± 36.4 | 49 ± 7.0 | p < 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozakiewicz, M. Change in Pull-Out Force during Resorption of Magnesium Compression Screws for Osteosynthesis of Mandibular Condylar Fractures. Materials 2021, 14, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020237
Kozakiewicz M. Change in Pull-Out Force during Resorption of Magnesium Compression Screws for Osteosynthesis of Mandibular Condylar Fractures. Materials. 2021; 14(2):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020237
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozakiewicz, Marcin. 2021. "Change in Pull-Out Force during Resorption of Magnesium Compression Screws for Osteosynthesis of Mandibular Condylar Fractures" Materials 14, no. 2: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020237
APA StyleKozakiewicz, M. (2021). Change in Pull-Out Force during Resorption of Magnesium Compression Screws for Osteosynthesis of Mandibular Condylar Fractures. Materials, 14(2), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020237





