Implementation of Electronic Consent at a Biobank: An Opportunity for Precision Medicine Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Traditional Approaches to Informed Consent
2. Materials and Methods
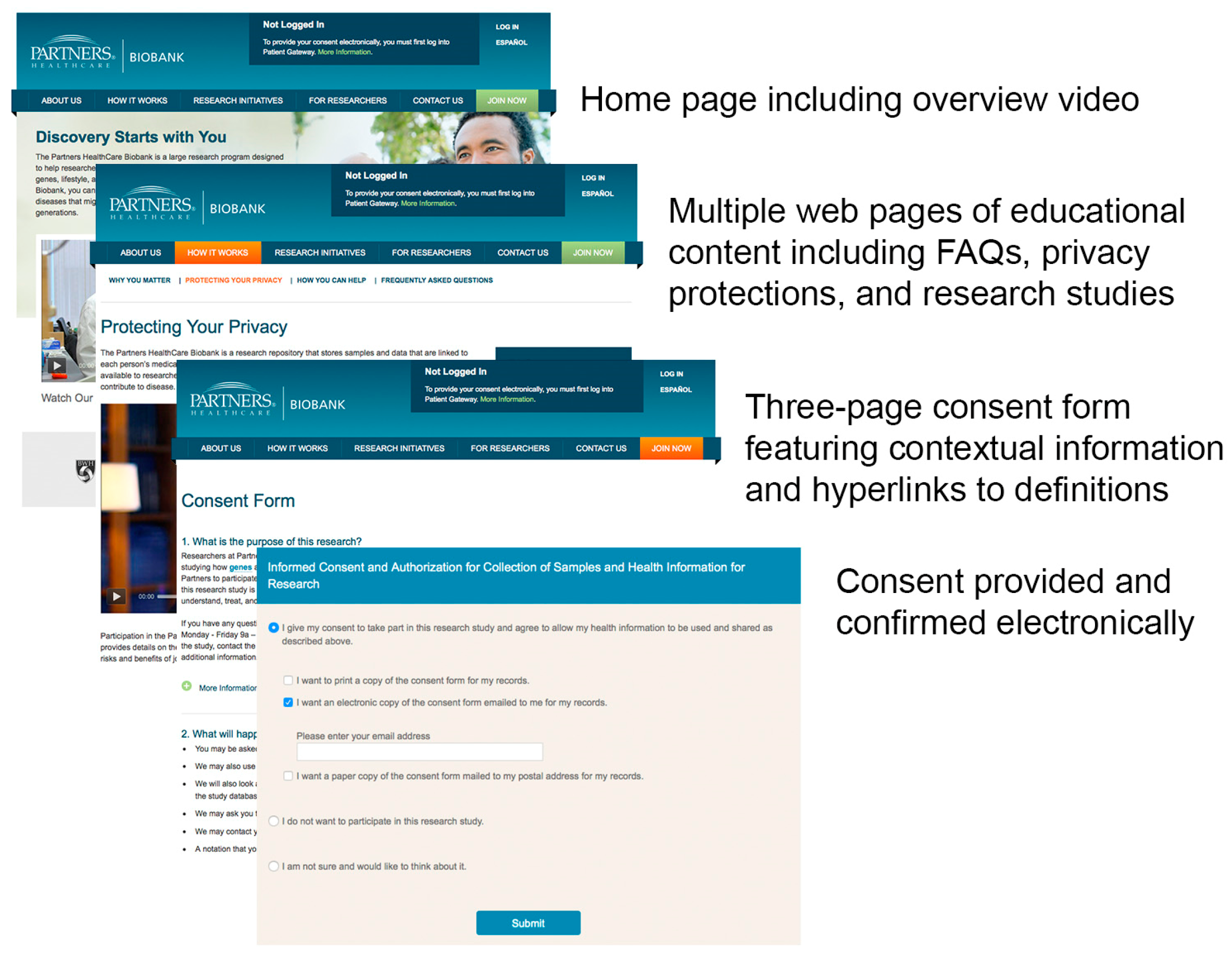
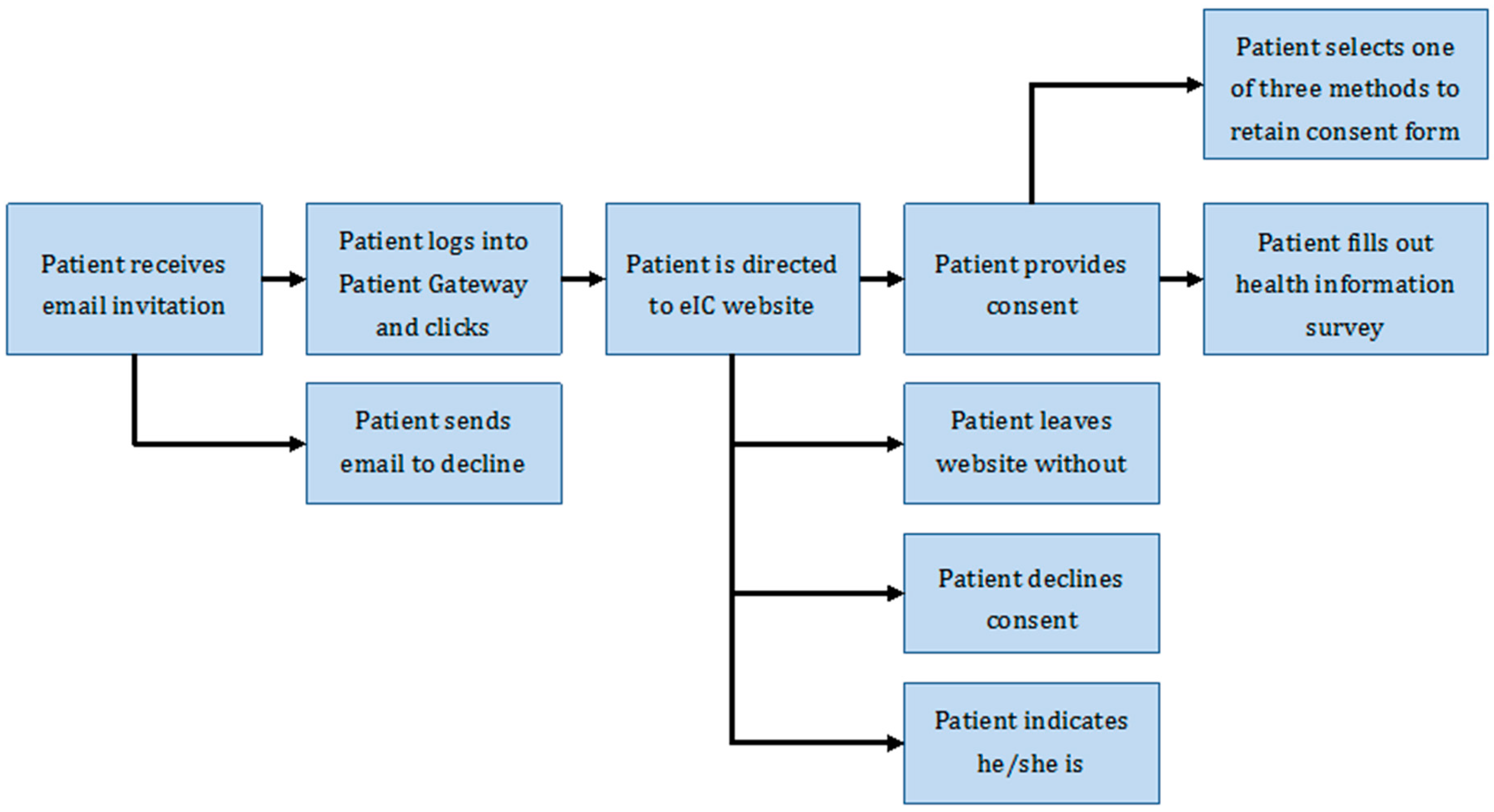
Electronic Approach to Informed Consent
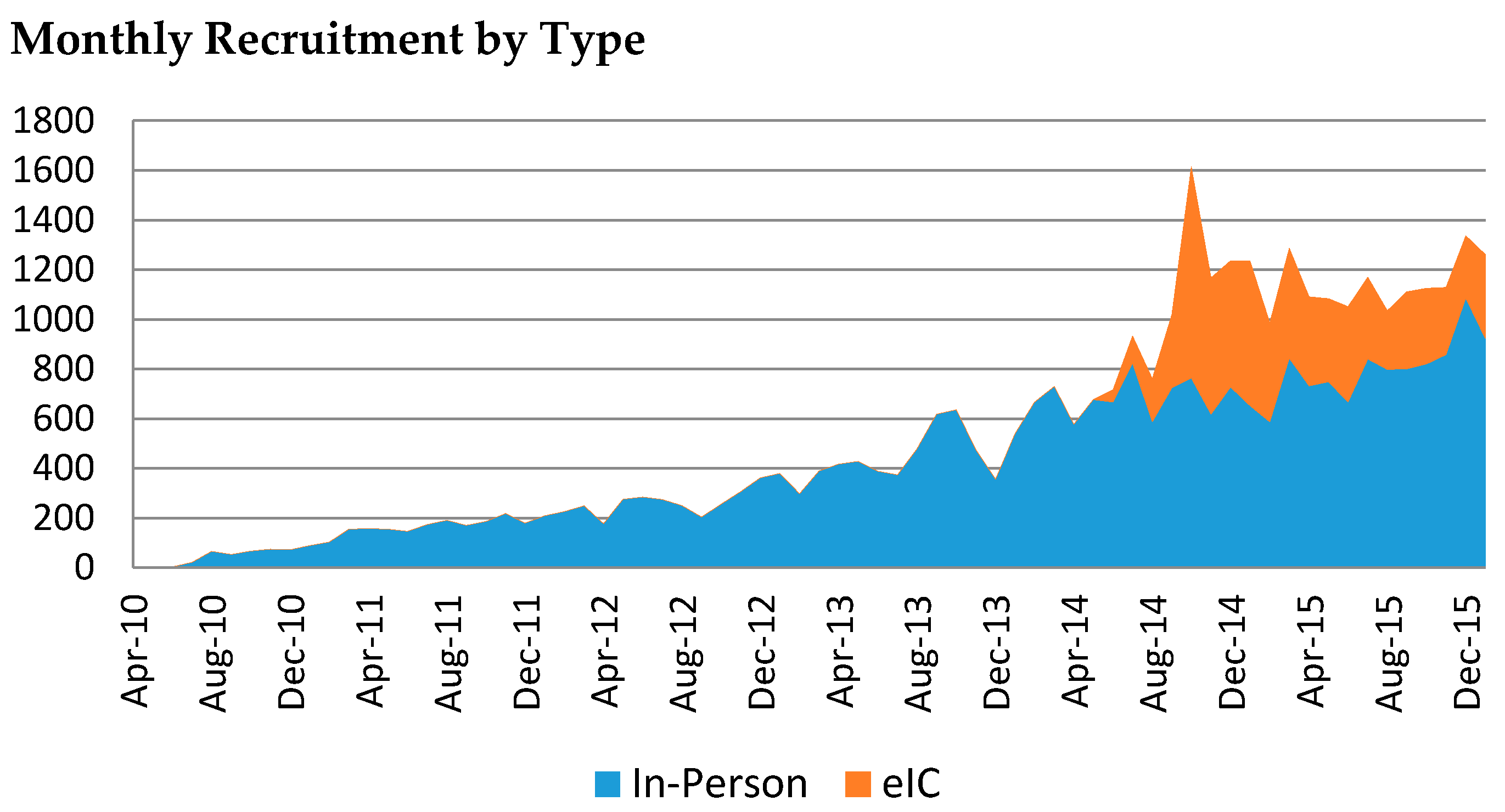
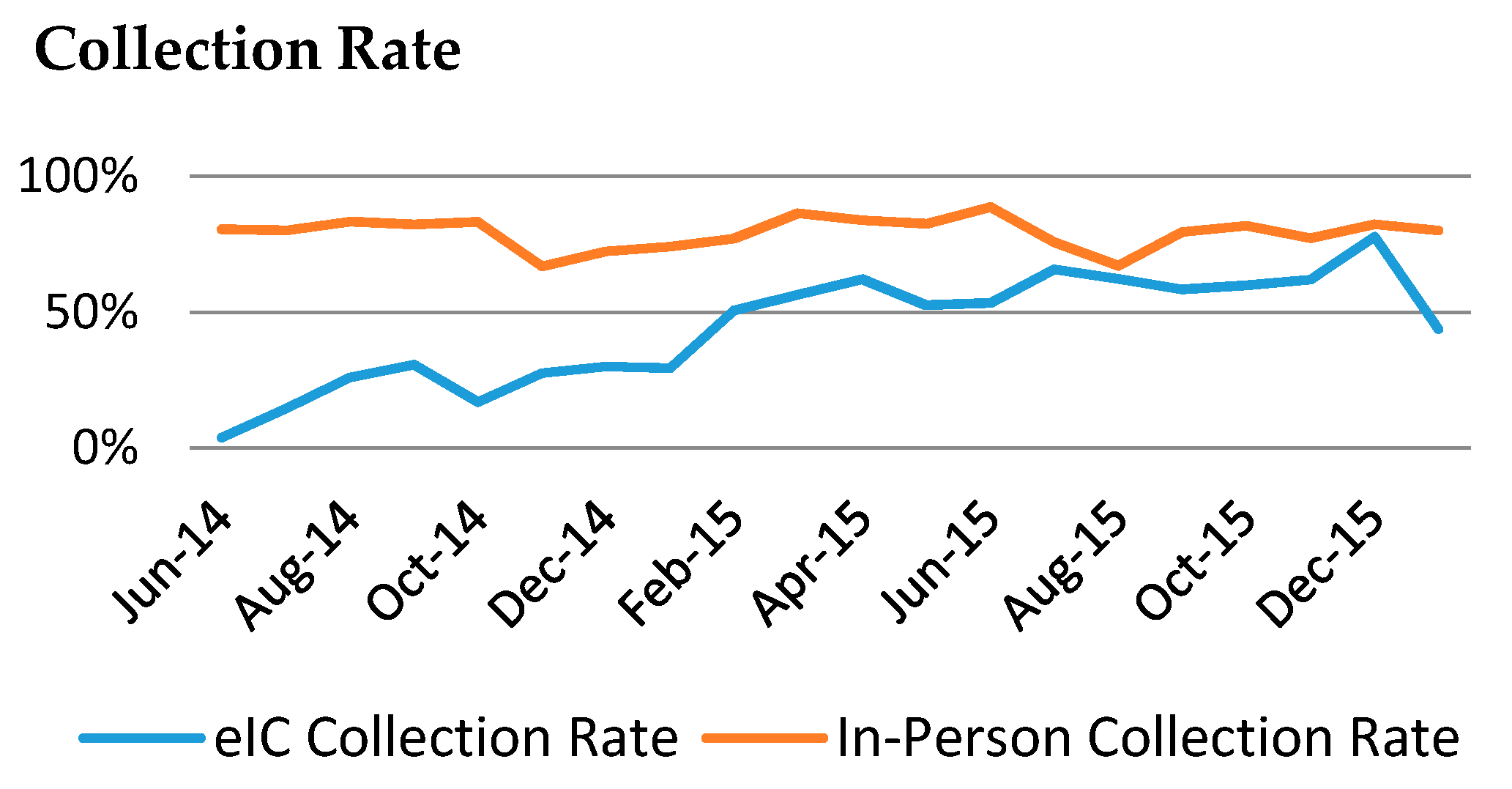
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Requirements and Prerequisites
4.2. Benefits
4.3. Challenges and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaught, J.; Kelly, A.; Hewitt, R. A review of international biobanks and networks: Success factors and key benchmarks. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2010, 7, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, R.; Hainaut, P. Biobanking in a fast moving world: An international perspective. J. Nat. Cancer Inst. Monoraphs 2011, 42, 50–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, J.C.; Bastarache, L.; Ritchie, M.D.; Carroll, R.J.; Zink, R.; Mosley, J.D.; Field, J.R.; Pulley, J.M.; Ramirez, A.H.; Bowton, E.; et al. Systematic comparison of phenome-wide association study of electronic medical record data and genome-wide association study data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Precision Medicine Initiative Cohort Program—Building a Research Foundation for 21st Century Medicine; Precision Medicine Initiative (PMI) Working Group Report to the Advisory Committee to the Director; National Institutes of Health: New York City, NY, USA, 2015.
- Olson, J.E.; Ryu, E.; Johnson, K.J.; Koenig, B.A.; Maschke, K.J.; Morrisette, J.A.; Liebow, M.; Takahashi, P.Y.; Fredericksen, Z.S.; Sharma, R.G.; et al. The mayo clinic biobank: A building block for individualized medecine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, D.; Bollinger, J.; Dvoskin, R.; Scott, J. Preferences for opt-in and opt-out enrollment and consent models in biobank research: A national survey of veterans administration patients. Genet. Med. 2012, 14, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langanke, M.; Brothers, K.B.; Erdmann, P.; Weinert, J.; Krafczyk-Korth, J.; Hoffmann, W.; Kroemer, H.K.; Assel, H. Comparing different scientific approaches to personalized medicine: Research ethics and privacy protection. Personal. Med. 2011, 8, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Liao, K.P.; Shaw, S.; Gainer, V.S.; Churchill, S.E.; Szolovits, P.; Murphy, S.N.; Kohane, I.S.; Cai, T. Toward high-throughput phenotyping: Unbiased automated feature extraction and selection from knowledge sources. AMIA 2015, 22, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, D.M.; Pulley, J.M.; Basford, M.A.; Bernard, G.R.; Clayton, E.W.; Balser, J.R.; Masys, D.R. Development of a large-scale de-identified DNA biobank to enable personalized medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 84, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health Genomic Data Sharing Policy. Available online: http://gds.nih.gov/pdf/nih_gds_policy.pdf. (accessed on 28 February 2016).
- Simon, C.M.; Klein, D.W.; Schartz, H.A. Interactive mulitmedia consent for biobanking: A randomized trial. Genet. Med. 2015, 18, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, J.; Whitley, E.A.; Lund, D.; Morrison, M.; Teare, H.; Melham, K. Dynamic consent: A patient interface for twenty-first century research networks. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 23, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgeway, J.L.; Han, L.C.; Olson, J.E.; Lackore, K.A.; Koenig, B.A.; Beebe, T.J.; Ziegenfuss, J.Y. Potential bias in the bank: What distinguishes refusers, non-responders and participants in a clinic-based biobank. Public Health Genom. 2013, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Churchill, S.; Bry, L.; Chueh, H.; Weiss, S.; Lazarus, R.; Zeng, Q.; Dubey, A.; Gainer, V.; Mendis, M.; Glaser, J.; Kohane, I. Instrumenting the health care enterprise for discovery research in the genomic era. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecora, N.D.; Li, N.; Allard, M.; Li, C.; Albano, E.; Delaney, M.; Dubois, A.; Onderdonk, A.B.; Bry, L. Genomically informed surveillance for carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae in a health care system. mBio 2015, 6, e1030–e1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Rate of Consent by Emailed Patient | Patients | Consent Rate |
|---|---|---|
| First email | 184,387 | 1.5% |
| Second email | 163,238 | 1.4% |
| Third email | 114,327 | 1.1% |
| Fourth email | 12,881 | 1.0% |
| Any email | 184,387 | 3.5% |
| Rate of Consent by Website Visitors | Visitor | Consent Rate |
| Logged-in visitors (excluding those who consented in person) | 23,562 | 30% |
| Title | In-Person | eIC | Total | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 28,930 | 7067 | 35,997 | |
| Age | 0.302 1 | |||
| Average age | 56.5 | 56.7 | 56.5 | |
| Gender (%) | <0.0001 2 | |||
| Female | 57 | 60 | 58 | |
| Male | 43 | 40 | 42 | |
| Race (%) | <0.0001 2 | |||
| Asian | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Black | 7 | 1 | 6 | |
| Hispanic | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| White | 81 | 92 | 83 | |
| Other | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Unknown | 4 | 3 | 4 | |
| Education (%) | <0.0001 2 | |||
| 8th grade or less | 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| Some high-school | 3 | 0 | 2 | |
| High school/GED | 18 | 6 | 16 | |
| Some college | 6 | 4 | 6 | |
| College | 51 | 72 | 55 | |
| Graduate school | 2 | 4 | 3 | |
| Unknown | 18 | 14 | 17 |
| Format | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| In-Person Consent |
|
|
| Electronic Informed Consent |
|
|
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boutin, N.T.; Mathieu, K.; Hoffnagle, A.G.; Allen, N.L.; Castro, V.M.; Morash, M.; O’Rourke, P.P.; Hohmann, E.L.; Herring, N.; Bry, L.; et al. Implementation of Electronic Consent at a Biobank: An Opportunity for Precision Medicine Research. J. Pers. Med. 2016, 6, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm6020017
Boutin NT, Mathieu K, Hoffnagle AG, Allen NL, Castro VM, Morash M, O’Rourke PP, Hohmann EL, Herring N, Bry L, et al. Implementation of Electronic Consent at a Biobank: An Opportunity for Precision Medicine Research. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2016; 6(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm6020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoutin, Natalie T., Kathleen Mathieu, Alison G. Hoffnagle, Nicole L. Allen, Victor M. Castro, Megan Morash, P. Pearl O’Rourke, Elizabeth L. Hohmann, Neil Herring, Lynn Bry, and et al. 2016. "Implementation of Electronic Consent at a Biobank: An Opportunity for Precision Medicine Research" Journal of Personalized Medicine 6, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm6020017
APA StyleBoutin, N. T., Mathieu, K., Hoffnagle, A. G., Allen, N. L., Castro, V. M., Morash, M., O’Rourke, P. P., Hohmann, E. L., Herring, N., Bry, L., Slaugenhaupt, S. A., Karlson, E. W., Weiss, S. T., & Smoller, J. W. (2016). Implementation of Electronic Consent at a Biobank: An Opportunity for Precision Medicine Research. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 6(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm6020017






