Deciphering the Microbiota of Edible Insects Sold by Street Vendors in Thailand Using Metataxonomic Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Water Activity
2.3. Microbial Counts
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplificon-Based Sequencing, and Metataxonomic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Water Activity
3.2. Microbial Counts
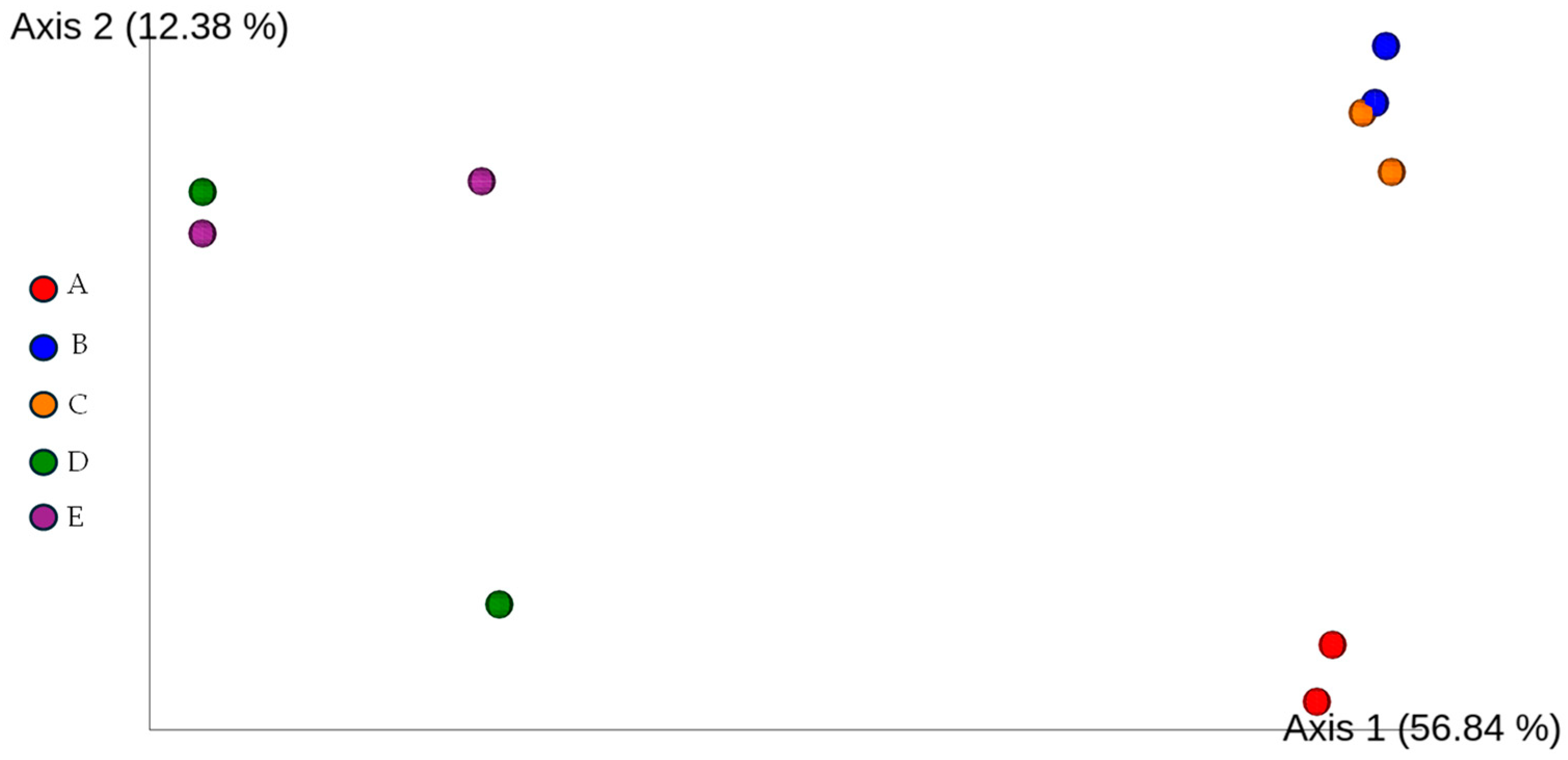
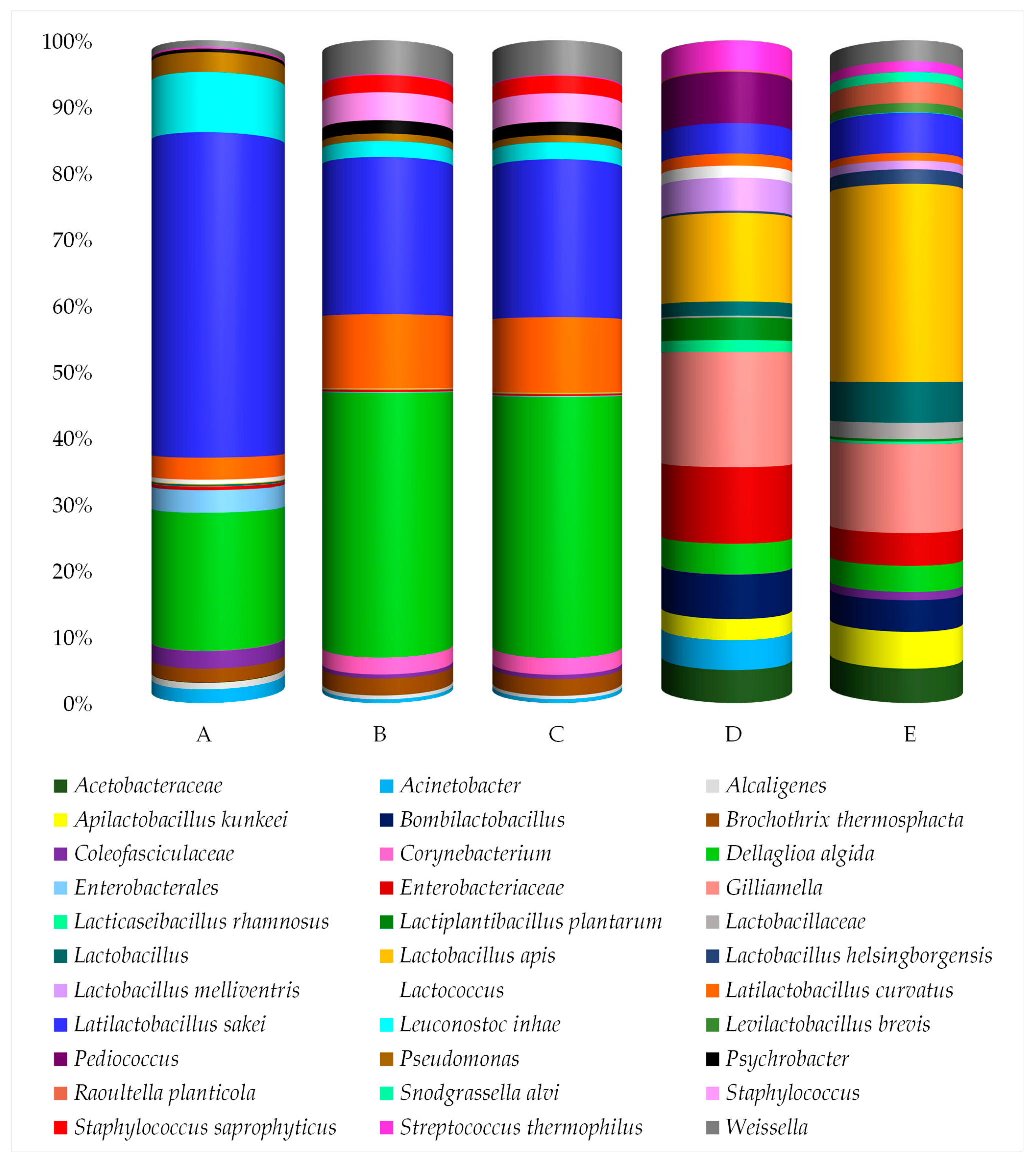
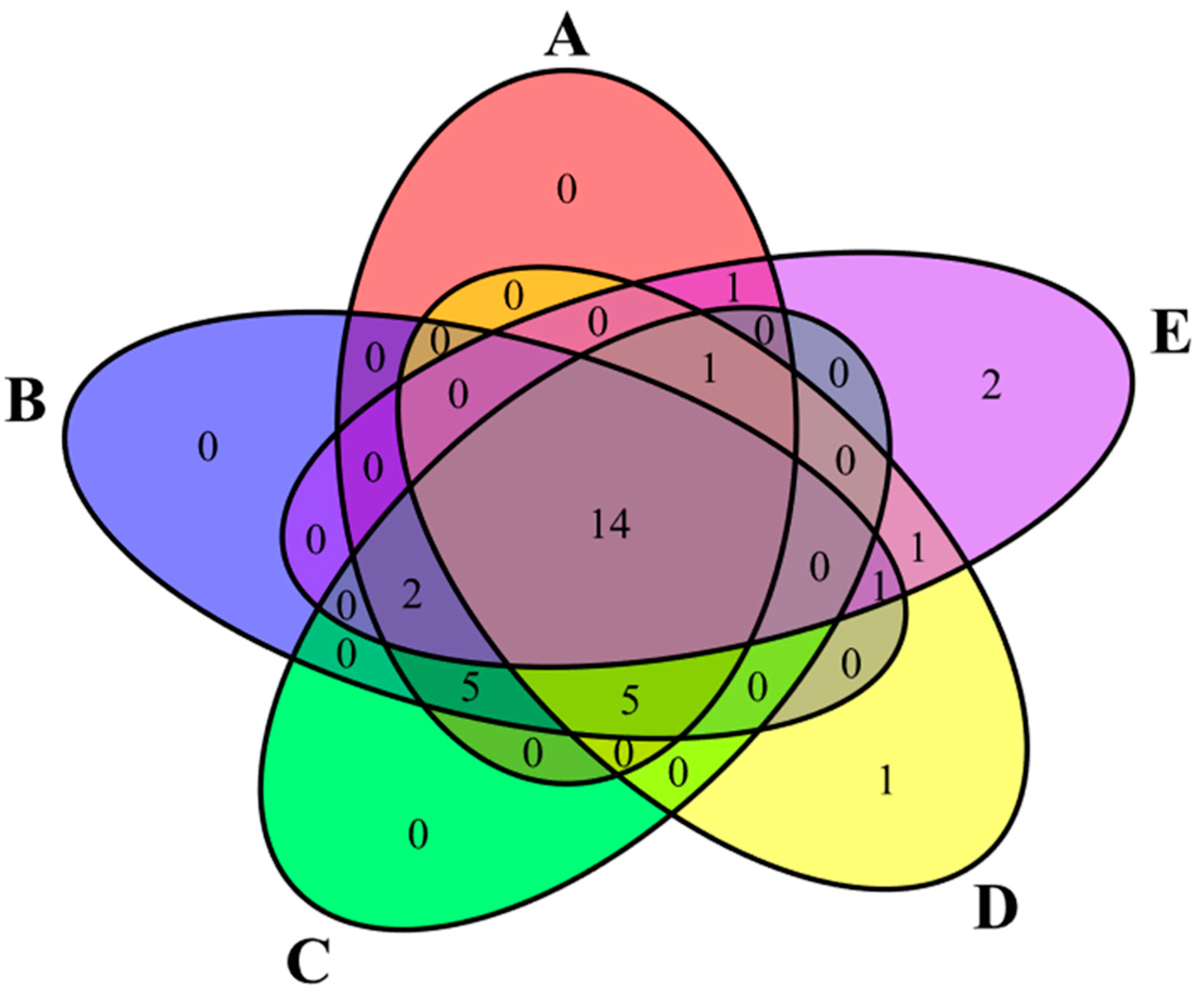
3.3. Taxonomic Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Köhler, R.; Kariuki, L.; Lambert, C.; Biesalski, H.K. Protein, Amino Acid and Mineral Composition of Some Edible Insects from Thailand. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirimungkararat, S.; Saksirirat, W.; Nopparat, T.; Natongkham, A. Edible Products from Eri and Mulberry Silkworms in Thailand. In Proceedings of the Forest Insects as Food: Humans Bite Back, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 19–21 February 2008; Durst, P.B., Johnson, D.V., Leslie, R.N., Shono, K., Eds.; FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific: Bangkok, Thailand, 2008; pp. 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Orkusz, A.; Orkusz, M. Edible Insects in Slavic Culture: Between Tradition and Disgust. Insects 2024, 15, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Clementi, F.; Osimani, A. Current Knowledge on the Microbiota of Edible Insects Intended for Human Consumption: A State-of-the-Art Review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Aquilanti, L. Spore-Forming Bacteria in Insect-Based Foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, C.; Erba, D.; Leonardi, M.G.; Lupi, D.; Savoldelli, S. Assessment of Vegetable and Fruit Substrates as Potential Rearing Media for Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, G.; Jucker, C.; Parma, P.; Lupi, D.; Crovetto, G.M.; Savoldelli, S.; Colombini, S. Impact of Agro-Industrial Byproducts on Bioconversion, Chemical Composition, in Vitro Digestibility, and Microbiota of the Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpanya, M.F.; Allotey, J.; Mpuchane, S.F. A Mycological Investigation of Phane, an Edible Caterpillar of an Emperor Moth, Imbrasia Belina. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpuchane, S.; Gashe, B.A.; Allotey, J.; Siame, B.; Teferra, G.; Ditlhogo, M. Quality Deterioration of Phane, the Edible Caterpillar of an Emperor Moth Imbrasia Belina. Food Control 2000, 11, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadi, E.N.; Ogbalu, O.K.; Barimalaa, I.S.; Pius, M. Microbiology and Nutritional Composition of an Edible Larva (Bunaea alcinoe Stoll) of the Niger Delta. J. Food Saf. 2005, 25, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbalu, O.K.; Renner, R.N. Microbiological Investigations on Gryllotalpa africana [Orthoptera: Gryllotalpidae], an Edible Cricket of the Niger Delta. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2015, 10, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachukwu, C.K.; Thomas, C.N.; Kigigha, L.T. Microorganisms Associated with Palm Weevil Larvae (Rhynchophorus phoenicis). Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2002, 21, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ekrakene, T.; Igeleke, C.L. Microbial Isolates from the Roasted Larva of the Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus phoenicis [F]) from Edo and Delta States of Nigeria. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2007, 1, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Braide, W.; Oranusi, S.; Udegbunam, L.I.; Oguoma, O.; Akobondu, C.; Nwaoguikpe, R.N. Microbiological Quality of an Edible Caterpillar of an Emperor Moth, Bunaea alcinoe. J. Ecol. Nat. Environ. 2011, 3, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Amadi, E.N.; Kiin-Kabari, D.B.; William-West, D.P.; Pepple, G.E. Microbiological Flora and Proximate Composition of the Yam Beetle, Heteroligus meles. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleggia, L.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Franciosa, I.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Cardinali, F.; Boscaino, F.; Cesaro, C.; Rampanti, G.; et al. Spotlight on Autochthonous Microbiota, Morpho-Textural Characteristics, and Volatilome of a Traditional Polish Cold-Smoked Raw Sausage. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoops, J.; Crauwels, S.; Waud, M.; Claes, J.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial Community Assessment of Mealworm Larvae (Tenebrio molitor) and Grasshoppers (Locusta migratoria migratorioides) Sold for Human Consumption. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Taccari, M.; Cardinali, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Clementi, F. The Microbiota of Marketed Processed Edible Insects as Revealed by High-Throughput Sequencing. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeweyer, D.; Crauwels, S.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Metagenetic Analysis of the Bacterial Communities of Edible Insects from Diverse Production Cycles at Industrial Rearing Companies. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 261, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Cardinali, F.; Roncolini, A.; Sabbatini, R.; De Filippis, F.; Ercolini, D.; Gabucci, C.; Petruzzelli, A.; et al. Revealing the Microbiota of Marketed Edible Insects through PCR-DGGE, Metagenomic Sequencing and Real-Time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 276, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; Clementi, F.; Pasquini, M.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Loreto, N.; et al. The Bacterial Biota of Laboratory-Reared Edible Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor L.): From Feed to Frass. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 272, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssepuuya, G.; Wynants, E.; Verreth, C.; Crauwels, S.; Lievens, B.; Claes, J.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial Characterisation of the Edible Grasshopper Ruspolia differens in Raw Condition after Wild-Harvesting in Uganda. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Mann, A.; den Bakker, H.C. Analysis of Microbial Composition of Edible Insect Products Available for Human Consumption within the United States Using Traditional Microbiological Methods and Whole Genome Sequencing. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, C.; Mannozzi, C.; Lepre, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Corsi, L.; Franciosa, I.; Belleggia, L.; Milanović, V.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; et al. Fate of Escherichia Coli Artificially Inoculated in Tenebrio molitor L. Larvae Rearing Chain for Human Consumption. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaro, C.; Mannozzi, C.; Lepre, A.; Ferrocino, I.; Belleggia, L.; Corsi, L.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Riolo, P.; Petruzzelli, A.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Artificially Inoculated in Mealworm Larvae Rearing Chain for Human Consumption: Long-Term Investigation into Survival and Toxin Production. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milanović, V.; Osimani, A.; Pasquini, M.; Aquilanti, L.; Garofalo, C.; Taccari, M.; Cardinali, F.; Riolo, P.; Clementi, F. Getting Insight into the Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Specimens of Marketed Edible Insects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 227, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belleggia, L.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Corvaglia, M.R.; Milanović, V.; Cesaro, C.; Boscaino, F.; Di Renzo, T.; Garofalo, C.; Cardinali, F.; et al. Unfolding Microbiota and Volatile Organic Compounds of Portuguese Painho de Porco Preto Fermented Sausages. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R.; Anderson, K.E. Housing System and Laying Hen Strain Impacts on Egg Microbiology. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzzelli, A.; Osimani, A.; Pasquini, M.; Clementi, F.; Vetrano, V.; Paolini, F.; Foglini, M.; Micci, E.; Paoloni, A.; Tonucci, F. Trends in the Microbial Contamination of Bovine, Ovine and Swine Carcasses in Three Small-Scale Abattoirs in Central Italy: A Four-Year Monitoring. Meat Sci. 2016, 111, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Gong, S.; Guo, Z.; Bai, L. Street Food Vendors’ Hygienic and Handling Practices in China: Checklist Development and Observational Assessment. Food Control 2024, 166, 110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.V. Quality Control: Water Activity Considerations for Beyond-Use Dates. Int. J. Pharm. Compd. 2018, 22, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Leonard, W.; Fang, Z. Recent Advances in Edible Insect Processing Technologies. Food Res. Int. 2024, 182, 114137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, N.T.; Chhay, T.; Keo, S.; Lertpatarakomol, R.; Kajaysri, J.; Kang, K.; Miech, P.; Plötz, M.; Mitchaothai, J. Proximate Composition of Thai and Cambodian Ready-to-Eat Insects. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.F.; Pfister, J.; Fernandez, J.E.; Donà, V.; Rodriguez, V.; Retschnig, G.; Collaud, A.; Neumann, P.; Perreten, V. Whole-Genome Sequences of a Lactobacillus melliventris Strain and Its Myovirus Temperate Phage, PhIBH004, Isolated from the Digestive Tract of Apis Mellifera in Switzerland. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e00036-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klunder, H.C.; Wolkers-Rooijackers, J.; Korpela, J.M.; Nout, M.J.R. Microbiological Aspects of Processing and Storage of Edible Insects. Food Control 2012, 26, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleknavičius, D.; Lukša, J.; Strazdaitė-žielienė, Ž.; Servienė, E. The Bacterial Microbiota of Edible Insects Acheta Domesticus and Gryllus assimilis Revealed by High Content Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigerio, J.; Agostinetto, G.; Galimberti, A.; De Mattia, F.; Labra, M.; Bruno, A. Tasting the Differences: Microbiota Analysis of Different Insect-Based Novel Food. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säde, E.; Johansson, P.; Heinonen, T.; Hultman, J.; Björkroth, J. Growth and Metabolic Characteristics of Fastidious Meat-Derived Lactobacillus algidus Strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 313, 108379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.; Dominguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Franco, D. Main Groups of Microorganisms of Relevance for Food Safety and Stability. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Barba, F.J., Sant’Ana, A.S., Orlien, V., Koubaa, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 53–107. [Google Scholar]
- An, B.; Sam, C.; Dries, V.; Ruben, S.; Christel, V.; Mik, V.; Bart, L.; Leen, V. Comparison of Six Commercial Meat Starter Cultures for the Fermentation of Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) Paste. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sohaimy, A.A.; Masry, S.H.D.; Shehata, M.G.; Al-Kahtani, S.N.; Abdelwahab, T.E.; Abdelmotal, Y.A.T.; Nour, M.E. Isolation, Identification and Antimicrobial Activity of Unprecedented Lactic Acid Bacterial Isolates from Honeybees. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 23, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Niu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Ye, L.; Cao, H.; Shi, T.; Yu, L. Apilactobacillus kunkeei Alleviated Toxicity of Acetamiprid in Honeybee. Insects 2022, 13, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergalito, F.; Testa, B.; Cozzolino, A.; Letizia, F.; Succi, M.; Lombardi, S.J.; Tremonte, P.; Pannella, G.; Di Marco, R.; Sorrentino, E.; et al. Potential Application of Apilactobacillus kunkeei for Human Use: Evaluation of Probiotic and Functional Properties. Foods 2020, 9, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.-P.; Huo, Y.; Hoang, V.-A.; Yang, D.-U.; Yang, D.-C.; Kang, S.-C. Bombilactobacillus apium sp. nov., Isolated from the Gut of Honeybee (Apis cerana). Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daisley, B.A.; Pitek, A.P.; Torres, C.; Lowery, R.; Adair, B.A.; Al, K.F.; Niño, B.; Burton, J.P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Thompson, G.J.; et al. Delivery Mechanism Can Enhance Probiotic Activity against Honey Bee Pathogens. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killer, J.; Dubná, S.; Sedláček, I.; Švec, P. Lactobacillus apis sp. nov., from the Stomach of Honeybees (Apis mellifera), Having an in Vitro Inhibitory Effect on the Causative Agents of American and European Foulbrood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorjão, A.L.; de Oliveira, F.E.; Leão, M.V.P.; Jorge, A.O.C.; de Oliveira, L.D. Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus on the Response of Galleria mellonella against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli Infections. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Broderick, N.A. Inside Help from the Microbiome. eLife 2023, 12, e88873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storelli, G.; Defaye, A.; Erkosar, B.; Hols, P.; Royet, J.; Leulier, F. Lactobacillus plantarum Promotes Drosophila Systemic Growth by Modulating Hormonal Signals through TOR-Dependent Nutrient Sensing. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praet, J.; Cnockaert, M.; Meeus, I.; Smagghe, G.; Vandamme, P. Gilliamella intestini sp. nov., Gilliamella bombicola sp. nov., Gilliamella bombi sp. nov. and Gilliamella mensalis sp. nov.: Four Novel Gilliamella Species Isolated from the Bumblebee Gut. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Nishida, A.; Kwong, W.K.; Koch, H.; Engel, P.; Steele, M.I.; Moran, N.A. Metabolism of Toxic Sugars by Strains of the Bee Gut Symbiont Gilliamella apicola. mBio 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanol, E.; Gendrin, M. Insects and Microbes: Best Friends from the Nursery. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 66, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calumby, R.J.N.; de Almeida, L.M.; de Barros, Y.N.; Segura, W.D.; Barbosa, V.T.; da Silva, A.T.; Dornelas, C.B.; Alvino, V.; Grillo, L.A.M. Characterization of Cultivable Intestinal Microbiota in Rhynchophorus palmarum Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Determination of Its Cellulolytic Activity. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 110, e21881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandotra, S.; Kumar, A.; Naga, K.; Bhuyan, P.M.; Gogoi, D.K.; Sharma, K.; Subramanian, S. Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity in the Gut of the Muga Silkworm, Antheraea assamensis (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae), from India. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

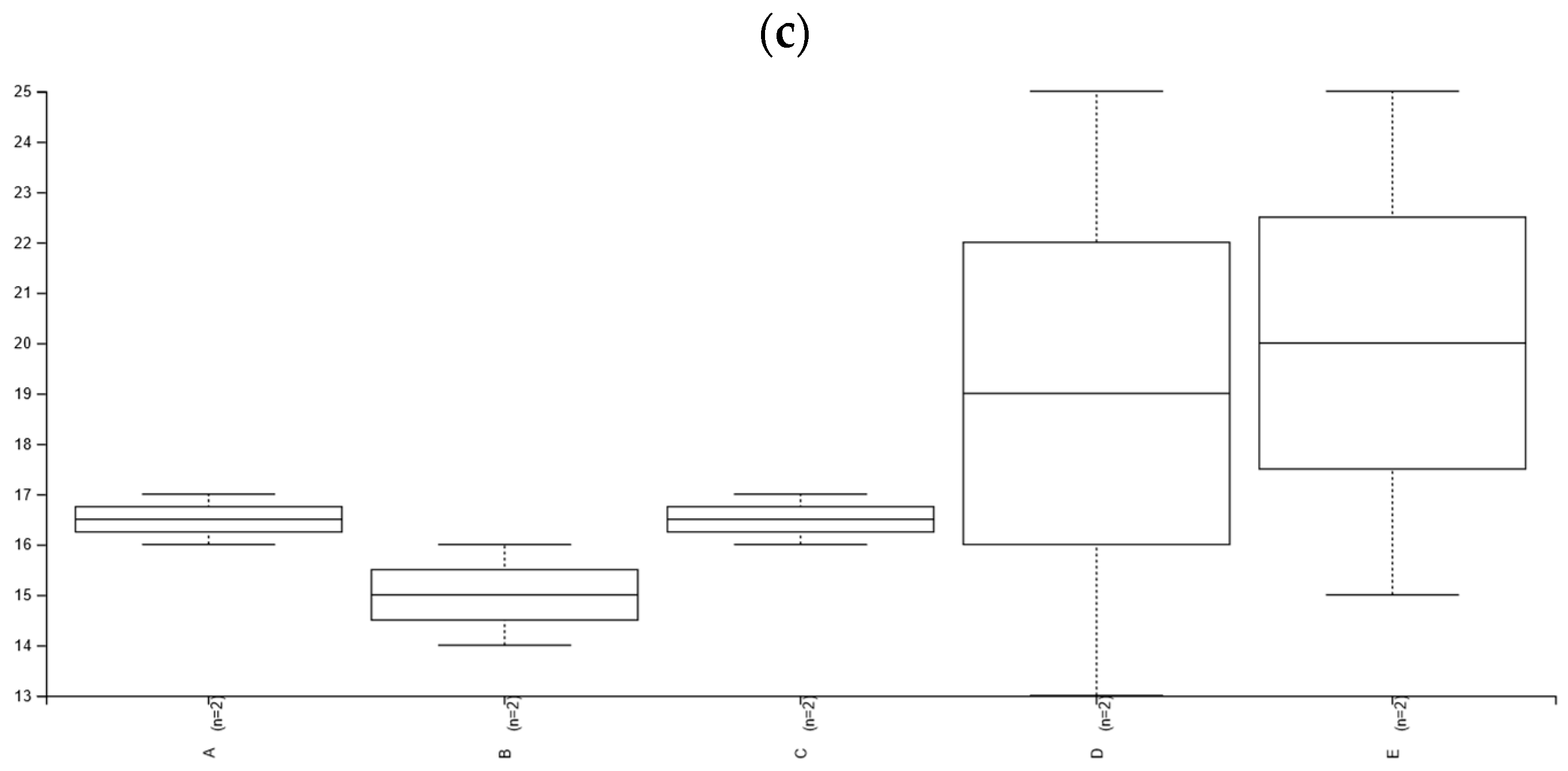


| Sample | aw | Enterobacteriaceae | Escherichia coli | Staphylococcus aureus | Total Mesophilic Aerobes | Sulfite- Reducing Clostridia Viable Cells | Sulfite- Reducing Clostridia Spores | Bacillus cereus | Listeria monocytogenes | Salmonella spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.97 ± 0.00 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | 8.13 ± 0.05 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | Absent in 25 g | Absent in 25 g |
| B | 0.94 ± 0.01 b | <1 | <1 | <1 | 8.18 ± 0.02 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | Absent in 25 g | Absent in 25 g |
| C | 0.93 ± 0.00 b | <1 | <1 | <1 | 8.05 ± 0.02 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | Absent in 25 g | Absent in 25 g |
| D | 0.92 ± 0.01 b | <1 | <1 | <1 | 8.24 ± 0.01 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | Absent in 25 g | Absent in 25 g |
| E | 0.91 ± 0.01 b | 4.05 ± 0.02 a | <1 | <1 | 8.02 ± 0.02 a | <1 | <1 | <1 | Absent in 25 g | Absent in 25 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rampanti, G.; Cardinali, F.; Ferrocino, I.; Milanović, V.; Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Aquilanti, L. Deciphering the Microbiota of Edible Insects Sold by Street Vendors in Thailand Using Metataxonomic Analysis. Insects 2025, 16, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020122
Rampanti G, Cardinali F, Ferrocino I, Milanović V, Garofalo C, Osimani A, Aquilanti L. Deciphering the Microbiota of Edible Insects Sold by Street Vendors in Thailand Using Metataxonomic Analysis. Insects. 2025; 16(2):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020122
Chicago/Turabian StyleRampanti, Giorgia, Federica Cardinali, Ilario Ferrocino, Vesna Milanović, Cristiana Garofalo, Andrea Osimani, and Lucia Aquilanti. 2025. "Deciphering the Microbiota of Edible Insects Sold by Street Vendors in Thailand Using Metataxonomic Analysis" Insects 16, no. 2: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020122
APA StyleRampanti, G., Cardinali, F., Ferrocino, I., Milanović, V., Garofalo, C., Osimani, A., & Aquilanti, L. (2025). Deciphering the Microbiota of Edible Insects Sold by Street Vendors in Thailand Using Metataxonomic Analysis. Insects, 16(2), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16020122







