Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
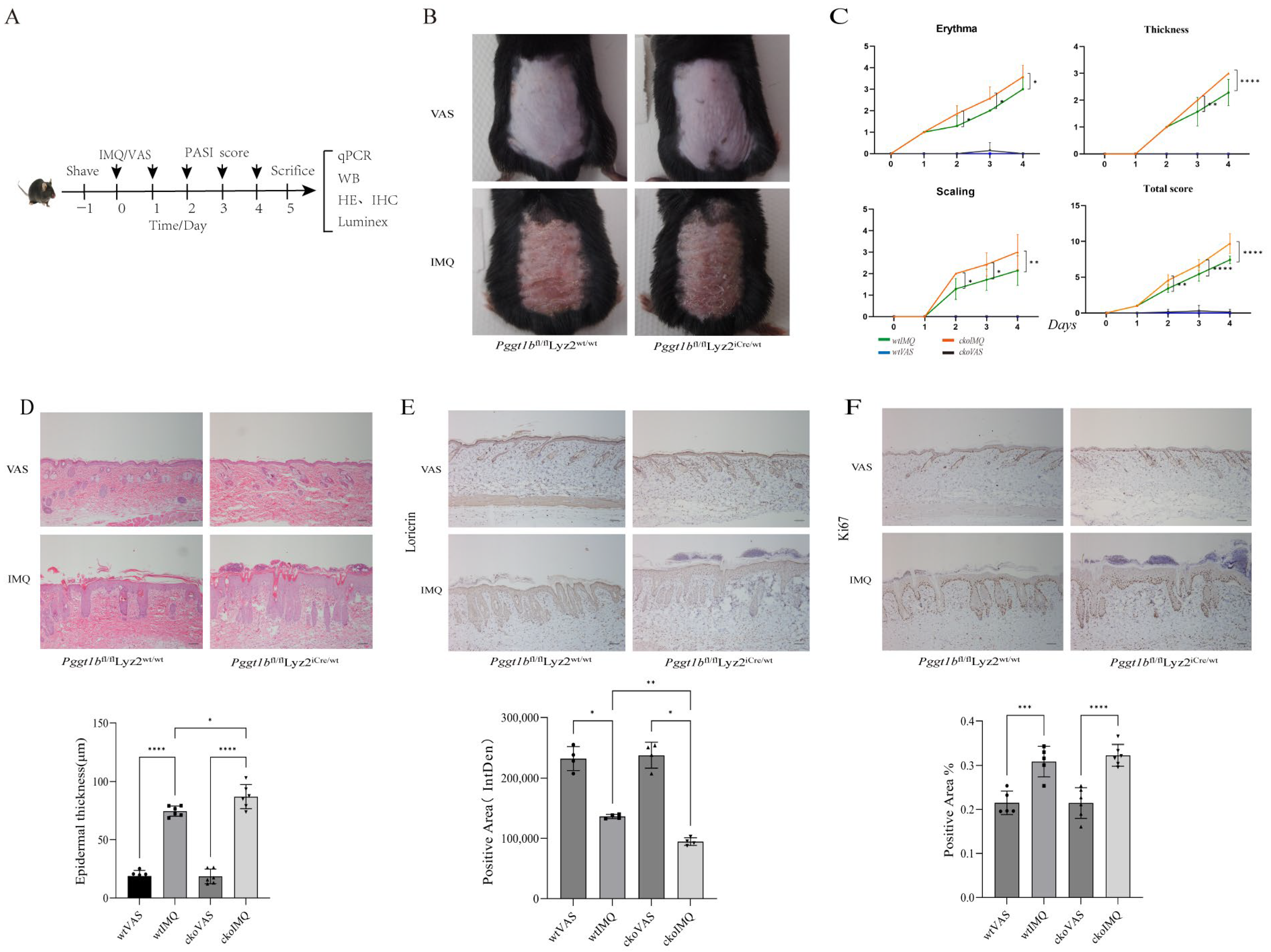
2.1. Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Exacerbates IMQ-Induced Psoriatic Rash in Mice
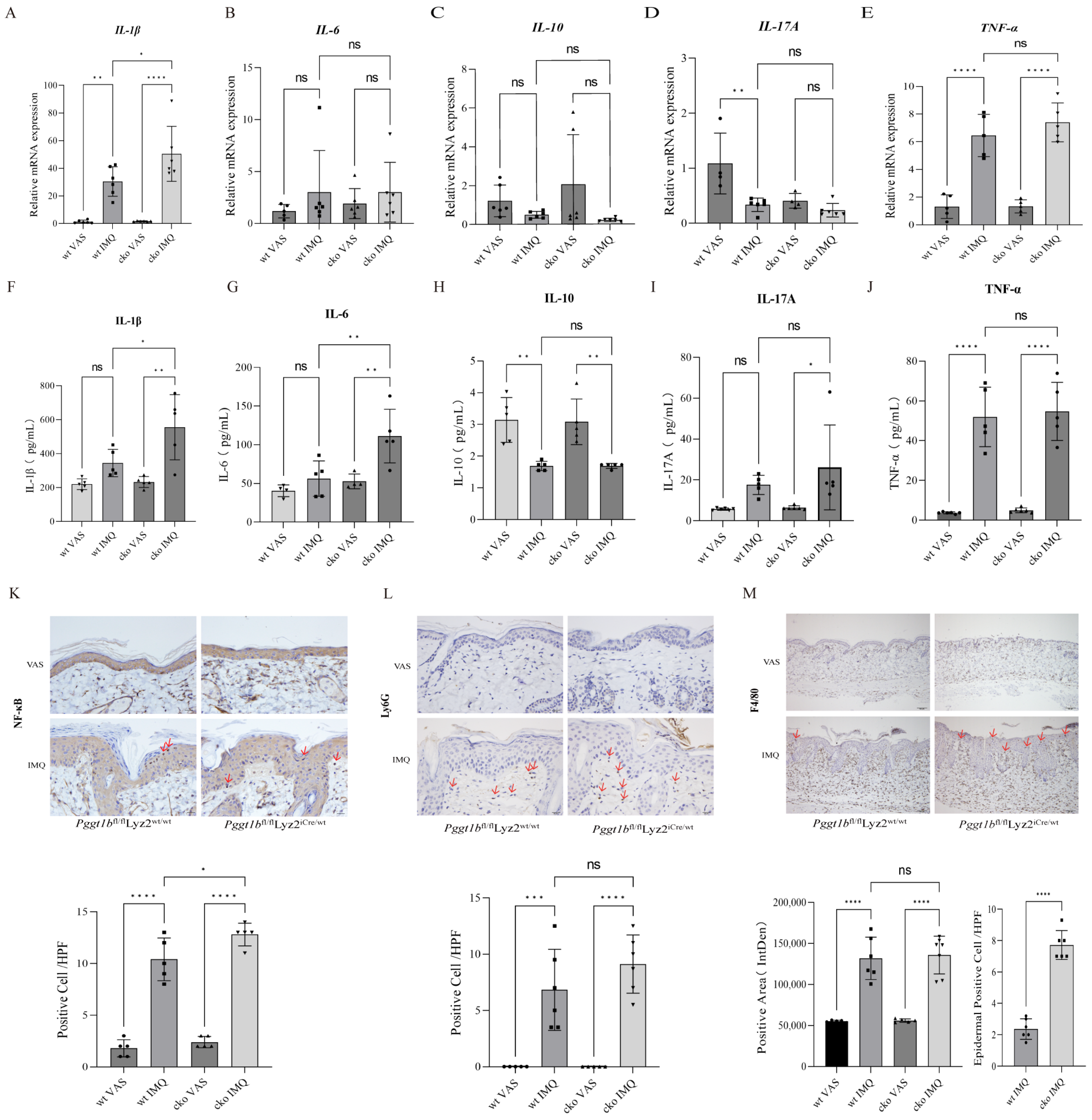
2.2. Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Aggravated Psoriasis-like Inflammation Induced by IMQ
2.3. PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes the Secretion of Proinflammatory Factors and Inhibits the Secretion of Anti-Inflammatory Factors in BMDMs
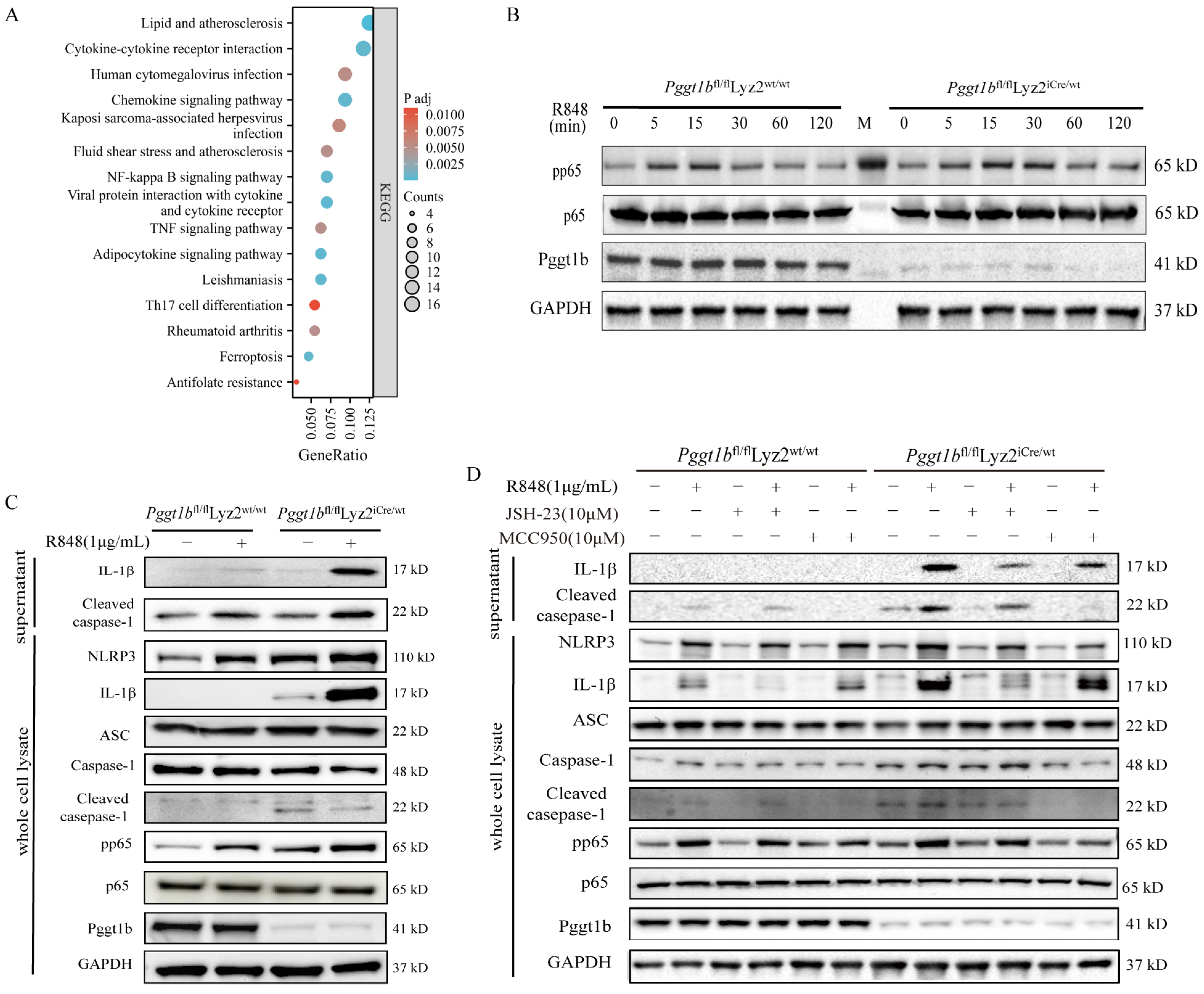
2.4. PGGT1B Defects Promoted NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and IL-1β Secretion Through NF-κB Signaling Pathway
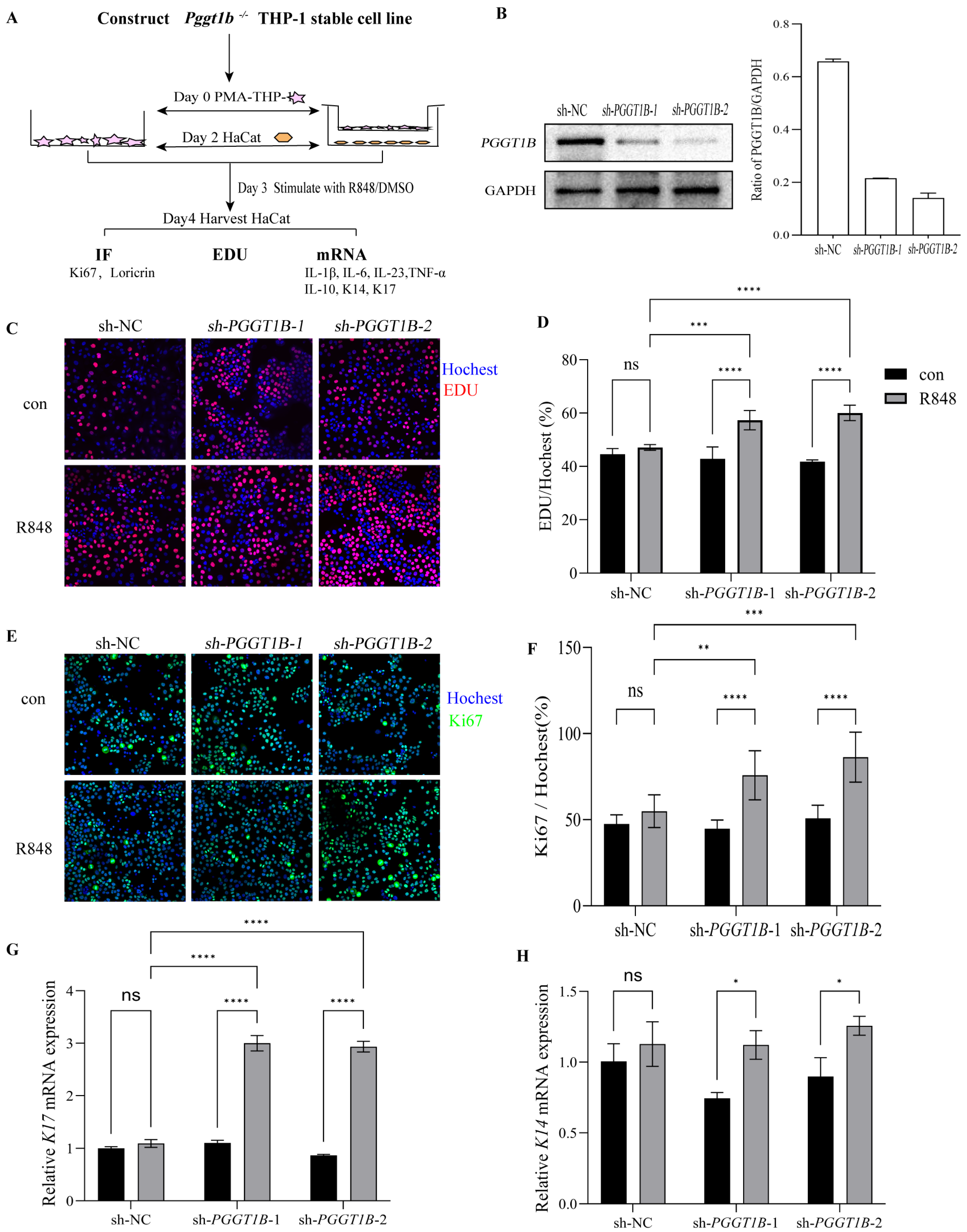
2.5. PGGT1B-Deficient Macrophages Promoted the Proliferation of HaCaT Cells in Contact Culture
2.6. Cdc42 Activation Mediated the Secretion of Proinflammatory Factors in PGGT1B-Deficient BMDMs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.1.1. Animal Origin
4.1.2. Construction of the Psoriasis Mouse Model
4.2. Cells
4.2.1. Cell Culture
4.2.2. Co-Culture of PMA-THP-1 with HaCaT
Direct Contact Co-Culture of PMA-THP-1 with HaCaT
Indirect Contact Co-Culture of PMA-THP-1 with HaCaT
4.2.3. BMDM Culture and Stimulation
4.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.4. Immunohistochemistry, HE Staining Experiment Procedure, Luminex Detection Technology, Bioinformatics Analysis, and Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMDM | Bone marrow-derived macrophage |
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cellular component |
| CDC42 | Cell division cycle 42 |
| cko | Conditional knockout |
| DEPs | Differentially expressed proteins |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| IMQ | Imiquimod |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| PGGT1B | Protein geranylgeranyl transferase type I β subunit |
| PASI | Psoriasis area and severity index |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| UVB | Ultraviolet B (UVB) |
| VAS | Vaseline |
| wt | Wild type |
References
- Parisi, R.; Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global Psoriasis A: National, regional, and worldwide epidemiologyof psoriasis: Systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendon, A.; Schakel, K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, N.J. Management of psoriasis as a systemic disease: What is the evidence? Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Dai, C.; Zeng, F. Cellular Mechanisms of Psoriasis Pathogenesis: A Systemic Review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 2503–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raharja, A.; Mahil, S.K.; Barker, J.N. Psoriasis: A brief overview. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Lian, N.; Gu, H.; Chen, M. The diagnostic significance of PGGT1B in psoriasis. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, O.M.; Akula, M.K.; Skalen, K.; Karlsson, C.; Stahlman, M.; Young, S.G.; Boren, J.; Bergo, M.O. Targeting GGTase-I activates RHOA, increases macrophage reverse cholesterol transport, and reduces atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation 2013, 127, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Sanchez, L.D.C.; Ngo, P.A.; Pradhan, R.; Becker, L.S.; Boehringer, D.; Soteriou, D.; Kubankova, M.; Schweitzer, C.; Koch, T.; Thonn, V.; et al. Epithelial RAC1-dependent cytoskeleton dynamics controls cell mechanics, cell shedding and barrier integrity in intestinal inflammation. Gut 2023, 72, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Posadas, R.; Fastancz, P.; Martinez-Sanchez, L.D.C.; Panteleev-Ivlev, J.; Thonn, V.; Kisseleva, T.; Becker, L.S.; Schulz-Kuhnt, A.; Zundler, S.; Wirtz, S.; et al. Inhibiting PGGT1B Disrupts Function of RHOA, Resulting in T-cell Expression of Integrin alpha4beta7 and Development of Colitis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.P.; Yang, J.; Qian, G.F.; Xu, W.W.; Zhang, X.Q. Geranylgeranyl Transferase-I Knockout Inhibits Oxidative Injury of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Attenuates Diabetes-Accelerated Atherosclerosis. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7574245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akula, M.K.; Ibrahim, M.X.; Ivarsson, E.G.; Khan, O.M.; Kumar, I.T.; Erlandsson, M.; Karlsson, C.; Xu, X.; Brisslert, M.; Brakebusch, C.; et al. Protein prenylation restrains innate immunity by inhibiting Rac1 effector interactions. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Fang, H.; Mi, J.; Qi, Q.; Yang, M. Daphnetin inhibits proliferation and inflammatory response in human HaCaT keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesion in mice. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Senra, L.; Boehncke, W.H. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Psoriasis: IL-17A and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondeljak, N.; Lugovic-Mihic, L.; Tomic, L.; Parac, E.; Pedic, L.; Lazic-Mosler, E. Key Factors in the Complex and Coordinated Network of Skin Keratinization. Their Significance and Involvement in Common Skin Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Li, X.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.; Chaparala, V.; Murphy, W.; Zhou, W.; Cao, J.; Lowes, M.A.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics suggest distinct upstream drivers of IL-17A/F in hidradenitis versus psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.W.; Moon, S.J. Inflammatory Cytokines in Psoriatic Arthritis: Understanding Pathogenesis and Implications for Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Kadono, T.; Furue, M. Psoriasis and the TNF/IL23/IL17 axis. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 154, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Jiang, W.; Li, G.; Lu, L.; Shan, J.; Feng, L.; Jin, L. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound at ST36 improves the gastric motility by TNF-alpha/IKKbeta/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in diabetic rats. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Shao, Y.; Chen, Y. LncRNA Snhg5 Attenuates Status Epilepticus Induced Inflammation through Regulating NF-kappaBeta Signaling Pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, H.; Hsu, V.W. Cdc42 and Cellular Polarity: Emerging Roles at the Golgi. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Fan, L.; Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y. Longitudinal change in CDC42 in psoriasis: Correlation with disease activity and treatment response. Biomark. Med. 2023, 17, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ward, N.L. Mouse Models of Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
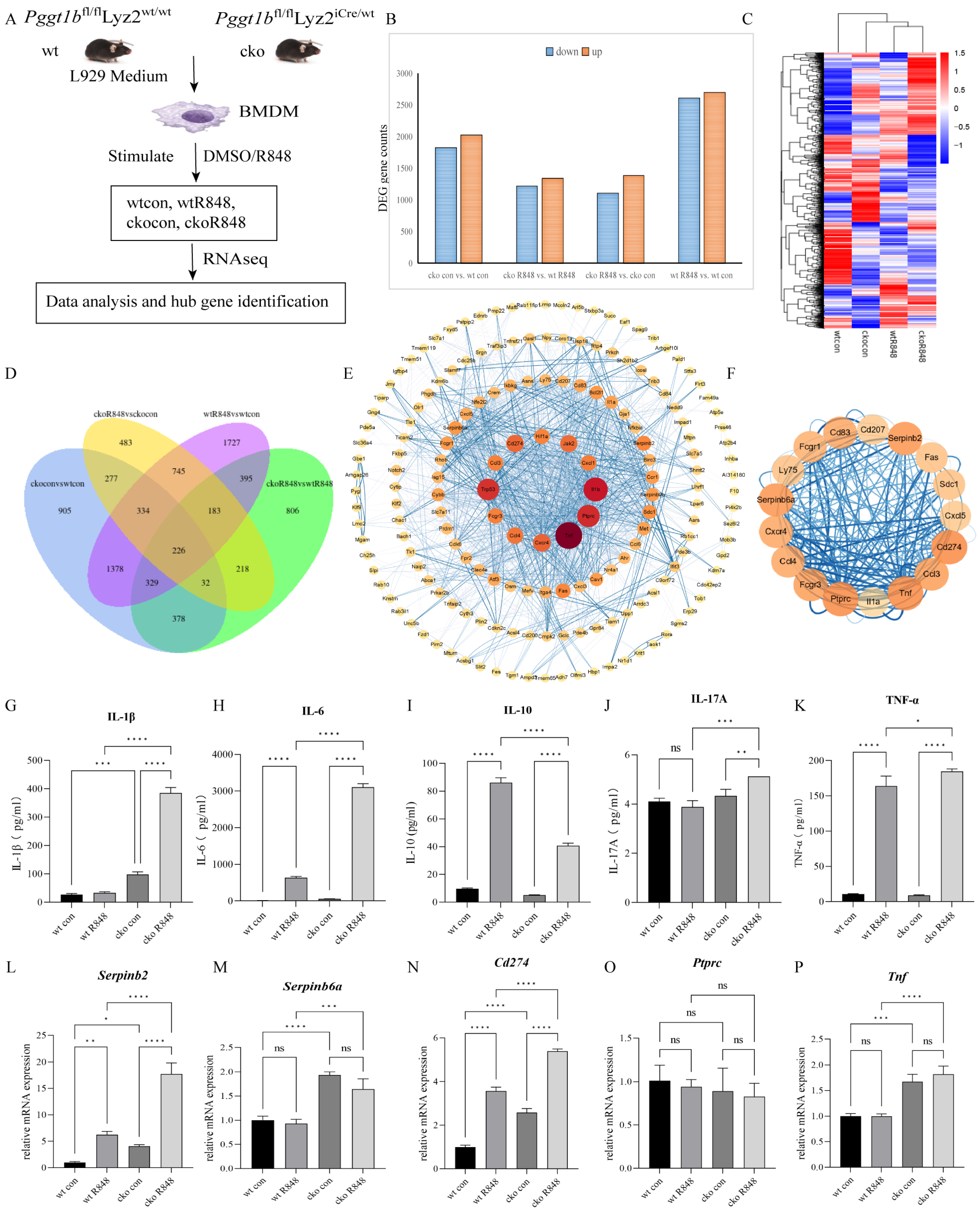

| Gene ID | Gene Name | Gene Description | MCODE Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENSMUSG00000000982 | Ccl3 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 3 | 9.34 |
| ENSMUSG00000018930 | Ccl4 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4 | 9.34 |
| ENSMUSG00000045382 | Cxcr4 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 | 9.01 |
| ENSMUSG00000016496 | Cd274 | CD274 antigen | 8.76 |
| ENSMUSG00000059498 | Fcgr3 | Fc receptor, IgG, low affinity III | 8.76 |
| ENSMUSG00000029371 | Cxcl5 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 | 8.51 |
| ENSMUSG00000015947 | Fcgr1 | Fc receptor, IgG, high affinity I | 8.19 |
| ENSMUSG00000015396 | Cd83 | CD83 antigen | 8.01 |
| ENSMUSG00000034783 | Cd207 | CD207 antigen | 8.0 |
| ENSMUSG00000060147 | Serpinb6a | serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor, clade B, member 6a | 7.91 |
| ENSMUSG00000062345 | Serpinb2 | serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor, clade B, member 2 | 7.91 |
| ENSMUSG00000024401 | Tnf | tumor necrosis factor | 7.78 |
| ENSMUSG00000026395 | Ptprc | protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, C | 7.78 |
| ENSMUSG00000027399 | Il1a | interleukin 1 alpha | 7.64 |
| ENSMUSG00000024778 | Fas | Fas (TNF receptor superfamily member 6) | 7.56 |
| ENSMUSG00000026980 | Ly75 | lymphocyte antigen 75 | 7.56 |
| ENSMUSG00000020592 | Sdc1 | syndecan 1 | 7.56 |
| Gene | Sequences | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | F: TGCCACCTTTTGACAGTGATG R: TGATGTGCTGCTGCGAGATT | 138 |
| IL-6 | F:GACAAAGCCAGAGTCCTTCAGA R:TGTGACTCCAGCTTATCTCTTGG | 76 |
| IL-10 | F:CCAAGGTGTCTACAAGGCCA R;GCTCTGTCTAGGTCCTGGAGT | 136 |
| IL-17A | F:TCTTTAACTCCCTTGGCGCA R:TCAGGGTCTTCATTGCGGTG | 100 |
| TNF-α | F:GATCGGTCCCCAAAGGGATG R:CCACTTGGTGGTTTGTGAGTG | 92 |
| K17 | F:CACCATCCGCCAGTTTACCT R:AGGTCCGAGATGAACCTCCA | 74 |
| K14 | F:GAACCACGAGGAGGTGGC R:TTCATGCTGAGCTGGGACTG | 120 |
| Kras | F:AGCAGTCAACAAAACAAGTCAGA R:AACTCTTCTCTTTTCCCCCAAT | 73 |
| RhoA | F:GTCGGGAGTTGGACTAGGCA R:AACCCTCACTGTCTTCACCC | 107 |
| Cdc42 | F:GGCGGAGAAGCTGAGGAC R:ACCAACAGCACCATCACCAA | 110 |
| GAPDH | F:TGCAACCGGGAAGGAAATGA R:GCATCACCCGGAGGAGAAAT | 148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Long, F.; Wei, X.; Gu, H.; Hao, Z. Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104901
Yu S, Long F, Wei X, Gu H, Hao Z. Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104901
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shanshan, Fangyuan Long, Xuecui Wei, Heng Gu, and Zhimin Hao. 2025. "Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104901
APA StyleYu, S., Long, F., Wei, X., Gu, H., & Hao, Z. (2025). Myeloid PGGT1B Deficiency Promotes Psoriasiform Dermatitis by Promoting the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104901






