Abstract
Brassica napus is one of the most extensively cultivated oilseed crops in China, but its yield is significantly impacted by stem rot caused by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Receptor-like proteins (RLPs) and receptor-like kinases (RLKs) play essential roles in plant–pathogen interactions; however, their regulatory mechanisms remain largely unknown in B. napus. In this study, we investigated the function of the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein BnaRLP-G13-1 in Brassica napus immunity. Previous observations indicated that B. napus plants expressing BnaRLP-G13-1 exhibited enhanced resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. We hypothesized that BnaRLP-G13-1 mediates pathogen recognition and immune signaling. To test this, we employed mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity assays, transgenic overexpression analyses, and pathogen infection assays. Our results demonstrated that BnaRLP-G13-1 recognizes the conserved necrosis- and ethylene-inducing peptide Ssnlp24SsNEP2 derived from S. sclerotiorum, triggering MAPK cascades and subsequent immune responses. Furthermore, protein interaction studies revealed that BnaRLP-G13-1 physically interacts with the receptor-like kinase BnaSOBIR1, which is essential for full antifungal defense activation. These results elucidate the molecular basis of BnaRLP-G13-1-mediated immunity, providing insights into improving disease resistance in oilseed crops.
1. Introduction
Over the course of evolution, plants have developed a sophisticated surveillance system to monitor pathogen invasion and stimulate their own immunity [1]. Studies have demonstrated that higher plants contain numerous immune receptors, distributed on the cell surface and within cells, which detect various pathogenic molecules associated with infections [2,3]. Many pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on the surface of plant cells recognize signal molecules with unique conserved motifs, triggering the first layer of the innate immune response, which is called pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI). PRRs consist of two types of cell surface proteins: receptor-like proteins (RLPs) and receptor-like kinases (RLKs), both of which contain leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) [4].
To date, an increasing number of RLPs have been found to play roles in disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. For example, Atrlp1 did not recognize the enigmatic microbe-associated molecular pattern (MAMP) of Xanthomonas (eMAX) and stimulated the PTI immune response, indicating that AtRLP1 is the specific recognition receptor of eMAX and participates in the process of plant immunity [5,6]. AtRLP32 recognized bacterial translation initiation factor 1 (IF1), induced the plant immune response, and enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) strain DC3000 in A. thaliana [7]. Similarly, AtRLP23 has been reported to recognize conserved sequences in necrosis- and ethylene-inducing peptide 1 (Nep1)-like proteins (NLPs), which are widely present in pathogens, thereby activating immune responses. The overexpression of AtRLP23 in potato enhanced plant resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum [8]. Spraying small peptides synthesized from conserved sequences of NLPs in Botrytis cinerea improved the resistance of A. thaliana to Alternaria brassicicola [9]. However, not all nlp24 (a conserved 24-amino-acid fragment found in most NLPs) small peptides can be recognized by AtRLP23. For example, the conserved nlp24 small peptide in Pythium oligandrum stimulated plant resistance to pathogens, but not through the AtRLP23 pathway [10,11]. A conserved small peptide in S. sclerotiorum necrosis- and ethylene-inducible peptide 2 (SsNEP2) increased plant resistance to biotrophic oomycetes, but its mechanism remains unknown [12].
Due to the lack of a kinase domain, RLPs can only recognize pathogens, and their signal transduction requires the formation of complexes with specific LRR-RLKs [13,14]. Arabidopsis LRR-RLK SOBIR1 (suppressor of brassinosteroid-insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1 (BAK1)-interacting receptor-like kinase 1) and its homologs form complexes with different RLPs to transmit signals. For instance, AtSOBIR1 forms a complex with AtRLP23 and AtBAK1 to activate the NLP peptide immune response [8], and AtRLP30 forms a complex with AtBAK1 to activate the immune response to sclerotinia culture filtrate elicitor1 (SCFE1) in the fungal cell wall [15]. In addition, the signaling processes of AtRLP1, AtRLP32, and AtRLP42 require SOBIR1 [5,16]. The tomato receptors Verticillium effector 1 (Ve1), the Cladosporium fulvum resistance protein that is produced by secreting the effector avirulence protein 4 (Cf-4), and the Lycopersicon esculentum ethylene-inducing xylanase 1 (LeEix1) and LeEix2 also interact with the SOBIR1 homolog in tomato in response to fungal infection [17].
Brassica napus is an important oilseed crop planted globally for vegetable oilseed production, animal feed, and biofuel [18,19]. Sclerotinia stem rot (SSR), caused by S. sclerotiorum, is a devastating disease in oilseed rape that seriously affects yield and quality [20,21]. In China, yield losses in oilseed rape caused by SSR typically range from 10% to 20%, but can reach up to 80% during severe outbreak seasons [22]. Despite its devastating impact, the molecular mechanism behind the interaction between B. napus and S. sclerotiorum is still largely unknown. Oilseed rape is one of the main hosts, and the BnaRLP family may play a crucial role in resistance to S. sclerotiorum infection. Therefore, we conducted a series of studies to analyze the regulatory role of the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein BnaRLP-G13-1 in the interaction between B. napus and S. sclerotiorum. Our results indicate that BnaRLP-G13-1, in combination with BnaSOBIR1, enhances the resistance of B. napus to S. sclerotiorum by recognizing a conserved amino acid sequence derived from SsNEP2.
2. Results
2.1. BnaC04g56380D Overexpression Enhances Plant Resistance to S. sclerotiorum
In our previous study, we observed that BnaC04g56380D expression was upregulated in both resistant and susceptible oilseed rape cultivars following S. sclerotiorum infection [23]. Consistent with this, in the moderately resistant cultivar (Xiangyou 15, XY15), the expression of BnaC04g56380D was significantly increased after 48 and 96 h of S. sclerotiorum infection, indicating that BnaC04g56380D was induced after infection and might positively regulate resistance to S. sclerotiorum in B. napus (Figure 1A). To improve the disease resistance of XY15, we selected it as the target material for the cloning and resequencing of BnaC04g56380D, a candidate gene potentially involved in S. sclerotiorum resistance. Similarly to AtRLP23, BnaC04g56380D contained only one exon without an intron (Supplementary Figure S1). Although BnaC04g56380D had a small number of base variations, which caused individual amino acid changes compared with the database sequence, its secondary structure domain was not changed and still belonged to the RLP family (Supplementary Figure S2). Subcellular localization analysis indicates that BnaC04g56380D is localized to the plasma membrane (Figure 1B).
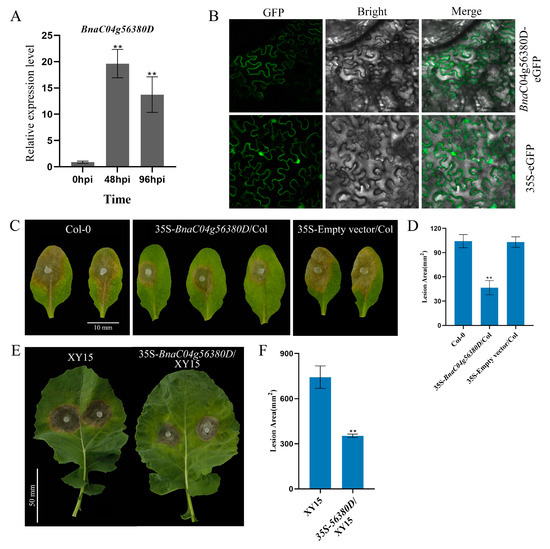
Figure 1.
BnaC04g56380D overexpression enhances plant immunity to S. sclerotiorum. (A) Relative expression levels of BnaC04g56380D in XY15 after S. sclerotiorum infection for 48 or 96 h. (B) Subcellular localization of BnaC04g56380D protein. BnaC04g56380D-eGFP transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves with 35S-eGFP construct as negative control. Merge: Merged via GFP and bright-field microscopy. (C,D) S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) inoculation on detached leaves of A. thaliana Col-0 and 35S-BnaC04g56380D/Col-0. Data recorded at 48 hpi. Bar = 10 mm. ImageJ v1.51 used to analyze lesion areas. Three leaves from Col-0 or 35S-BnaC04g56380D/Col-0 plants selected for each infection experiment. (E,F) S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) inoculation on detached leaves of B. napus XY15 and 35S-BnaC04g56380D/XY15. One leaf from XY15 or 35S-BnaC04g56380D/XY15 selected for each infection experiment, and two mycelial plugs were inoculated on each leaf. Data recorded at 48 hpi. Bar = 50 mm. ImageJ used to analyze lesion areas. Experiments conducted three times, with similar results. Error bars represent SD (** p < 0.01).
We then further overexpressed BnaC04g56380D in A. thaliana and B. napus to explore its function. While the overexpression of BnaC04g56380D did not affect the growth and development of A. thaliana (Supplementary Figure S3), the lesion area of the 35S- BnaC04g56380D/Col overexpression plants was much smaller than that of Col-0 after S. sclerotiorum infection (Figure 1C,D). Furthermore, when BnaC04g56380D was overexpressed in XY15, the growth phenotype of the identified T1 generation of the overexpression lines was not affected (Supplementary Figure S4). According to the RT-qPCR results, the lines with the highest overexpression of BnaC04g56380D were selected for S. sclerotiorum infection testing. As shown in Figure 1E, the lesion areas of the plants overexpressing BnaC04g56380D were significantly smaller, at only about 50% the size of those of the wild-type XY15 plants (Figure 1F). These results demonstrate that the overexpression of BnaC04g56380D can effectively improve plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum.
2.2. BnaC04g56380D Shares Functional Similarity with AtRLP23
A phylogenetic tree constructed using the maximum likelihood method revealed that BnaC04g56380D clustered closely with AtRLP23, suggesting a high degree of homology between the two proteins [23]. However, further validation was required to determine whether BnaC04g56380D shared the same function as AtRLP23. Mutants of AtRLP23 were generated using CRISPR gene-editing technology or obtained as T-DNA insertion mutants (Supplementary Figure S5). Infection assays revealed that the lesion areas in the rlp23-1 and rlp23-3 mutants were larger than those in Col-0, indicating an increased susceptibility to S. sclerotiorum (Figure 2A,B). When BnaC04g56380D was introduced into rlp23-1, the immunodeficiency caused by the AtRLP23 mutation was restored (Figure 2D,E). Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades serve as an important signaling pathway in plant immune responses and play a critical role in Brassica napus defense against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infection [24]. To determine whether MAPK cascades were activated in rlp23-1 and rlp23-3, Western blot analysis was performed. As shown in Figure 2C, the MAPK pathway was induced normally in the complemented plants containing BnaC04g56380D, demonstrating that BnaC04g56380D functions similarly to AtRLP23. Since BnaC04g56380D and AtRLP23 belong to the same group (Group 13) in the phylogenetic tree [23], we designated BnaC04g56380D as BnaRLP-G13-1 (BnaRLP-Group13-1).
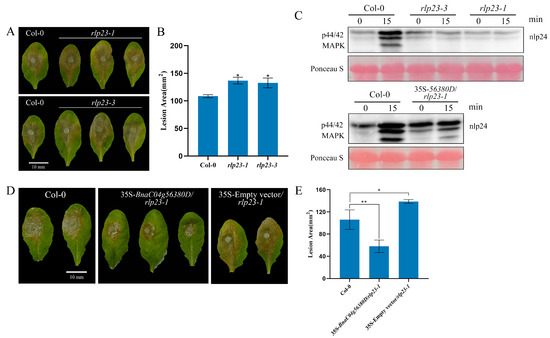
Figure 2.
BnaC04g56380D functionally complements loss of AtRLP23. (A,B) S. sclerotiorum (wild type) inoculation on detached leaves of A. thaliana Col-0, rlp23-1, rlp23-3. Data recorded at 48 hpi. Bar = 10 mm. ImageJ used to analyze lesion areas. (C) nlp24-induced MAPK activation in A. thaliana. Seedlings treated with 1 μM of nlp24. Western blot analysis with anti-pERK antibody used for evaluation of MAPK activation. Ponceau staining served as internal reference. Experiments conducted three times, with similar results. (D,E) Lesion areas of Col-0, 35S-BnaC04g56380D/rlp23-1 and 35S-Empty vector/rlp23-1 on leaves after S. sclerotiorum infection. Bar = 10 mm. ImageJ used to analyze lesion areas. Three leaves of Col-0, rlp23-1, rlp23-3, or 35S-BnaC04g56380D/rlp23-1 plants selected for each infection experiment. Experiments conducted three times with similar results. Error bars represent SD. Statistical significance between Col-0 and mutant analyzed using Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
2.3. BnaRLP-G13-1 Enhances Plant Immunity by Recognizing Ssnlp24SsNEP2
In a previous study, we found that the 24 conserved amino acids (Ssnlp24SsNEP2) from SsNEP2 could enhance plant resistance to Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis Noco2 in A. thaliana [12], but the specific mechanism for this remained unknown. To further explore whether the enhancement of plant immunity by Ssnlp24SsNEP2 was related to AtRLP23, the expression levels of AtRLP23 and related genes after small-peptide treatment were detected. After Ssnlp24SsNEP2 treatment for 4 h, the expression level of AtRLP23 was found to be increased, and it continued rising over time (Figure 3A). The transcript level of AtSOBIR1, which formed a complex with AtRLP23 to transmit signals, was significantly upregulated after small-peptide treatment (Figure 3A). Another essential component of the signaling pathway, AtBAK1, was also enhanced slightly (Figure 3A). These results illustrate that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 can increase the expression level of AtRLP23 and its related genes.
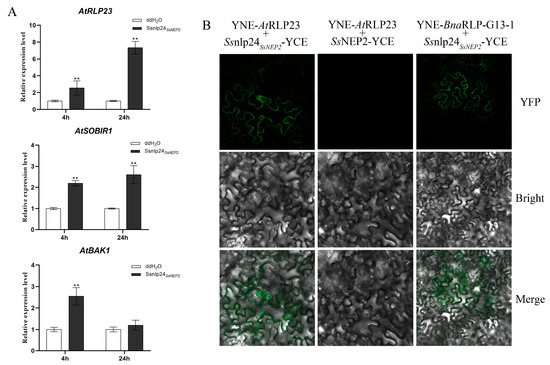
Figure 3.
BnaRLP-G13-1 recognizes conserved sequences of NEP2 from S. sclerotiorum. (A) Relative expression levels of AtRLP23, AtSOBIR1, and AtBAK1 in Col-0 after treatment with 1 μM Ssnlp24SsNEP2 for 4 or 24 h. Experiments conducted three times, with similar results. Error bars represent SD (** p < 0.01). (B) Analysis of interactions between AtRLP23/BnaRLP-G13-1 and SsNEP2/Ssnlp24SsNEP2 by BiFC in N. benthamiana. AtRLP23 and BnaRLP-G13-1 fused to YNE, and Ssnlp24SsNEP2 or SsNEP2 fused to YCE. Merge: Merged via YFP and bright-field microscopy.
Then, the interaction between AtRLP23 and Ssnlp24SsNEP2 was detected by bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC). As shown in Figure 3B, a fluorescence signal appeared in the cells of the leaves co-transformed with Ssnlp24SsNEP2-YCE and YNE-AtRLP23, indicating that there was a direct interaction between Ssnlp24SsNEP2 and AtRLP23 and that the interaction occurred on the plasma membrane. Similarly, a direct interaction between Ssnlp24SsNEP2 and BnaRLP-G13-1 also occurred on the plasma membrane. However, no direct interaction was found between SsNEP2 and AtRLP23.
To further check whether AtRLP23 is the sole receptor of Ssnlp24SsNEP2 in A. thaliana, Ssnlp24SsNEP2 was evenly sprayed on the leaf surface of the AtRLP23 deletion mutants. The results showed that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 could cause a strong MAPK cascade reaction in Col-0 (Figure 4A). Nevertheless, Ssnlp24SsNEP2 still slightly activated MAPK cascades in the rlp23-1 and rlp23-3 mutants, although these activations were far less than that in Col-0. The above results indicate that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 may interact with other receptors in plants to activate MAPK cascades, in addition to AtRLP23. After treatment with Ssnlp24SsNEP2, the lesion area on the surface of Col-0 was reduced, suggesting that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 could enhance resistance in Arabidopsis to S. sclerotiorum (Figure 4B,C). However, the infection results showed no significant difference in lesion areas on the leaf surface of the rlp23-1 or rlp23-3 mutants compared to the control, regardless of Ssnlp24SsNEP2 treatment (Figure 4B,C). This evidence indicates that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 mainly interacts with AtRLP23 to induce plant immunity and that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 cannot enhance plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum after AtRLP23 deletion. Additionally, the results of the ROS burst assay indicate that, in the absence of RLP23, Ssnlp24SsNEP2 failed to induce a reactive oxygen burst in plants (Figure 4D).
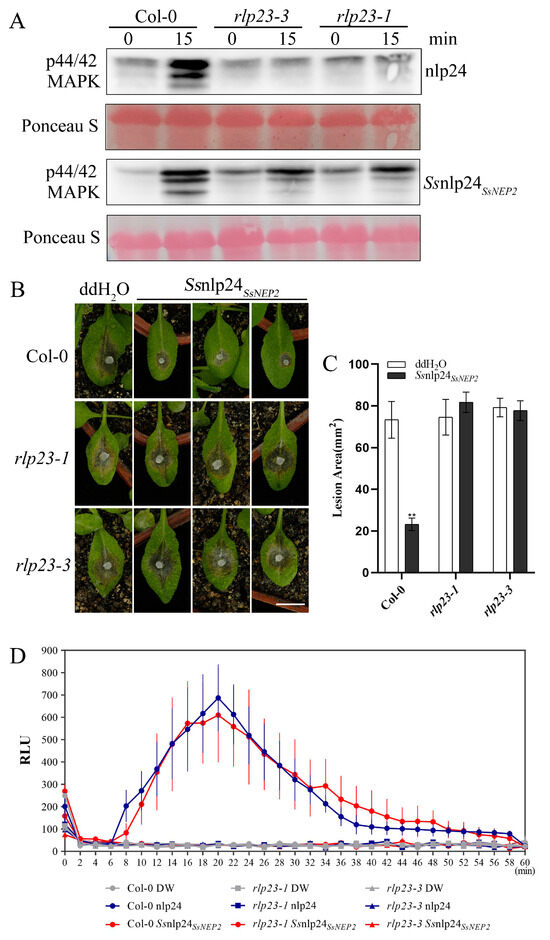
Figure 4.
Ssnlp24SsNEP2induces plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum, which requires AtRLP23. (A) The MAPK activation induced by Ssnlp24SsNEP2 in A. thaliana Col-0, rlp23-1, and rlp23-3. The seedlings were treated with 1 μM nlp24 or Ssnlp24SsNEP2. Western blot analysis with an anti-pERK antibody was used for the evaluation of MAPK activation. Ponceau staining served as the internal reference. The experiments were conducted three times. (B) Four-week-old soil-grown A. thaliana Col-0, rlp23-1, and rlp23-3 plants were pretreated with H2O and 1 μM Ssnlp24SsNEP2 and inoculated with S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) 24 h later. The data were recorded at 36 hpi. The scale bar = 10 mm. ImageJ was used to analyze the lesion areas. (C) The lesion areas of A. thaliana Col-0, rlp23-1, and rlp23-3 on the leaves after pretreatment with H2O and 1 μM Ssnlp24SsNEP2 and S. sclerotiorum infection. ImageJ was used to analyze the lesion areas. Three leaves of the Col-0, rlp23-1, rlp23-3 plants were selected for each infection experiment. The error bars represent SD (** p < 0.01). (D) Leaf disks from the true leaves of five-week-old Arabidopsis Col-0, rlp23-1, and rlp23-3 mutant plants were treated with 1 µM of nlp24, 1 µM of Ssnlp24SsNEP2, or H2O. The data are reported in relative light units (RLUs) and the error bars represent SD. The experiment was repeated three times, with similar results.
2.4. Identification of BnaRLP-G13-1 Downstream Protein BnaSOBIR1
AtSOBIR1, as the binding protein of AtRLP23, forms a complex with AtBAK1 to trigger the immune response. Since BnaRLP-G13-1 shares functional similarity with AtRLP23, we hypothesized that it might interact with SOBIR1 to mediate immune signaling. To test this, we used the AtSOBIR1 protein sequence as a query to perform BLASTP searches against the B. napus genome. Based on sequence similarity and domain composition, we identified six potential BnaSOBIR1 homologs, which are summarized in Table 1. The evolutionary relationship among these candidate genes was then analyzed, and their encoded proteins were found to have formed two branches during the evolution process. For better distinction, the branches including BnaA03g14760D and BnaC03g17800D were collectively referred to as class I and named “BnaSOBIR1 Group A”; the other branch was collectively referred to as class II and named “BnaSOBIR1 Group B” (Figure 5A). The results of the protein sequence alignment showed that the kinase domains of these six candidates were highly conserved, with differences observed only before the transmembrane domain (Supplementary Figure S6), indicating that these candidate genes may have a protein kinase activity similar to that of AtSOBIR1. Two genes were then randomly selected from the two branches for functional verification. BnaA03g14760D was selected to represent BnaSOBIR1 Group A, while BnaA04g18590D represented BnaSOBIR1 Group B. After the cloning and resequencing of BnaA03g14760D and BnaA04g18590D from XY15, we found that some base substitutions occurred in BnaA03g14760D and BnaA04g18590D, but these substitutions did not affect their secondary structure formation compared with the database sequences (Supplementary Figures S7–S9).

Table 1.
Candidate genes of BnaSOBIR1.
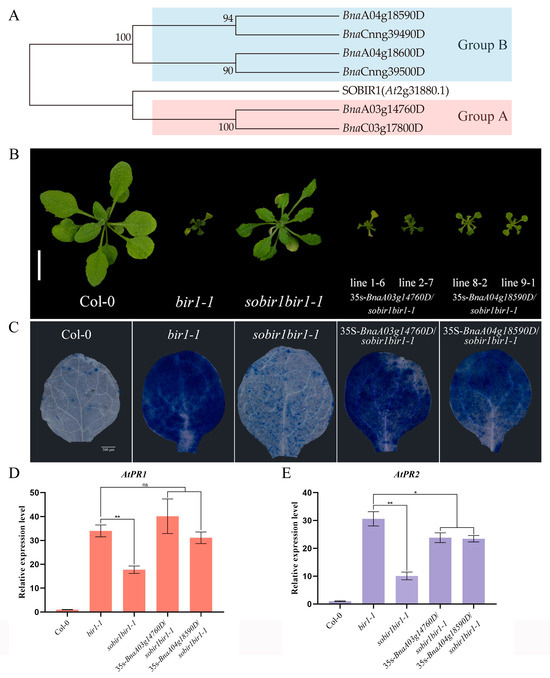
Figure 5.
The identification of SOBIR1-encoding genes in B. napus. (A) The phylogenetic tree of SOBIR1 was constructed based on amino acid sequences from A. thaliana and B. napus. The data were downloaded from Ensembl plants (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html, accessed on 1 January 2022). (B) The morphological phenotypes of the A. thaliana Col-0, bir1-1, sobir1bir1-1, and 35s-BnaSOBIR1/sobir1bir1-1 seedlings. All the plants were grown in soil at 22 °C in parallel and photographed when they were 4 weeks old. The scale bar = 10 mm. (C) The DAB staining of true leaves of A. thaliana Col-0, bir1-1, sobir1bir1-1, and 35s-BnaSOBIR1/sobir1bir1-1. All the plants were grown on 1/2 MS medium plates at 22 °C in an incubator and stained when they were 2 weeks old. The scale bar = 500 μm. (D,E) The relative expression levels of AtPR1 and AtPR2 in A. thaliana Col-0, bir1-1, sobir1bir1-1, and 35s-BnaSOBIR1/sobir1bir1-1. The experiments were conducted three times, with similar results. The error bars represent SD (ns: non-significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
AtSOBIR1 was originally discovered during the screening of AtBIR1 inhibitors. As AtBIR1 negatively regulates plant immunity, and its deletion mutants have obvious disease-resistant phenotypes, the sobir1bir1-1 double mutant suppresses the disease resistance phenotype caused by AtBIR1 deletion to a certain extent [25]. Based on this, the sobir1bir1-1 double mutant was transformed with the BnaSOBIR1 gene. As shown in Figure 5B, either BnaA03g14760D or BnaA04g18590D could restore the double mutant phenotype to a bir1-1 single mutant. The transformants became dwarf again, with curled and senescent leaves. The Trypan blue staining results showed, in the 35s-BnaSOBIR1/sobir1bir1-1 plants, the reappearance of a high level of cell death (Figure 5C). Furthermore, the PR genes of 35s-BnaA03g14760D/sobir1bir1-1 and 35s-BnaA04g18590D/sobir1bir1-1 were significantly upregulated, to the same level as the bir1-1 single mutant (Figure 5D,E). Together, these results prove that BnaA03g14760D and BnaA04g18590D also play similar roles to the homologous gene of AtSOBIR1. According to the results of the phylogenetic tree (Figure 5A), BnaA03g14760D and BnaA04g18590D were subsequently named as BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2, respectively.
2.5. BnaSOBIR1 Improves Plant Resistance to S. sclerotiorum
The expression level of BnaSOBIR1 Group A did not change significantly after 48 h of S. sclerotiorum infection. However, 96 h after inoculation, its expression was significantly upregulated, reaching approximately three times the pre-inoculation level. On the contrary, the overall expression of BnaSOBIR1 Group B was downregulated after S. sclerotiorum inoculation (Figure 6A). To explore whether BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 were both involved in the plant immune response, they were overexpressed in Arabidopsis. As expected, the overexpression of BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 did not affect the growth of the transformants (Supplementary Figure S10). Moreover, it was found that the overexpression of either BnaSOBIR1-1 or BnaSOBIR1-2 resulted in reduced lesion areas in the plants, which were approximately 25% of those observed in the Col-0 plants (Figure 6B,C). This indicates that both BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 can enhance plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum.
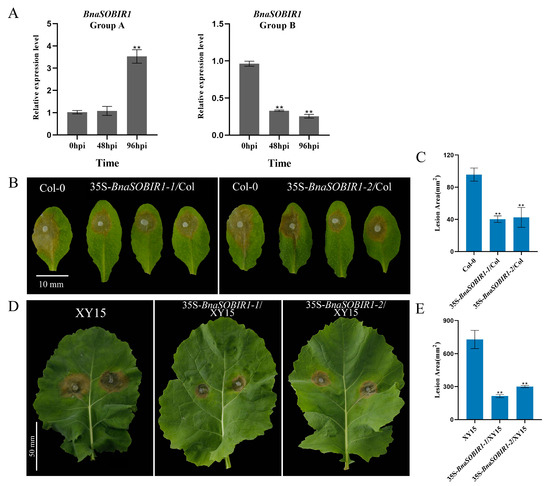
Figure 6.
BnaSOBIR1 enhances plant immunity to S. sclerotiorum. (A) Relative expression levels of BnaSOBIR1 Group A and BnaSOBIR1 Group B in XY15 after S. sclerotiorum infection for 48 or 96 h. (B,C) Inoculated S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) on detached leaves of A. thaliana Col-0 and 35S-BnaSOBIR1/Col-0. Data recorded at 48 hpi. Bar = 10 mm. ImageJ used to analyze lesioned areas. Three leaves of Col-0 or 35S-BnaSOBIR1/Col-0 plants selected for each infection experiment. (D,E) Inoculated S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) on detached B. napus XY15 and 35S-BnaSOBIR1/XY15 leaves. Data recorded at 48 hpi. One leaf from XY15 or 35S-BnaSOBIR1/XY15 plant selected for each infection experiment, and two mycelial plugs inoculated on each leaf. Bar = 50 mm. ImageJ used to analyze lesion areas. Experiments conducted three times, with similar results. Error bars represent SD (** p < 0.01).
Similarly, when BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 were overexpressed in XY15, it was observed that their overexpression did not impact the normal growth and development of B. napus (Supplementary Figure S11). Subsequently, the lines with the highest levels of BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 overexpression in XY15 were selected for a pathogen infection assay. As shown in Figure 6D,E, the lesions on the leaf surfaces of 35S-BnaSOBIR1-1/XY15 and 35S-BnaSOBIR1-2/XY15 were significantly smaller than those on XY15, indicating that the overexpression of BnaSOBIR1-1 or BnaSOBIR1-2 in oilseed rape could improve plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum. Thus, it can be concluded that both BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 play a role in the interaction between plants and S. sclerotiorum, significantly enhancing plant resistance to this pathogen.
2.6. BnaRLP-G13-1 Interacts with BnaSOBIR1 on Plasma Membrane
To determine whether BnaRLP-G13-1 physically interacts with BnaSOBIR1, as previously reported for AtRLP23 and AtSOBIR1 in A. thaliana [8], BiFC assays were conducted. As expected, fluorescence was observed in the leaf cells at the transformation site following the co-transformation of YNE-BnaRLP-G13-1 and YCE-BnaSOBIR1 in tobacco (Figure 7A). This confirms that BnaRLP-G13-1 can interact with both BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2, with the interaction occurring at the plasma membrane.
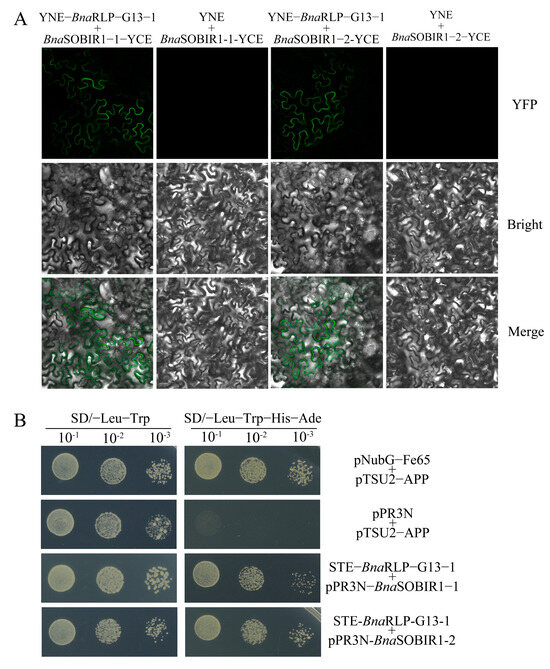
Figure 7.
The analysis of the interactions between BnaRLP-G13-1 and BnaSOBIR1. (A) BnaRLP-G13-1 was fused to YNE, and BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 were fused to YCE. YNE + BnaSOBIR1-1-YCE and YNE + BnaSOBIR1-2-YCE were the negative controls. Merge: Merged via YFP and bright-field microscopy. (B) BnaRLP-G13-1 were fused to pBT3-STE, and BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 were fused to pPR3N. pNubG-Fe65 + pTSU2-APP served as the positive control, and pPR3N + pTSU2-APP served as the negative control. The data were recorded after 5 days.
To further verify protein interactions occurring on the plasma membrane of the cell, a yeast two-hybrid membrane system (Y2H) was selected and Y2H experiments were conducted. As shown in Figure 7B, yeast co-transformed with pPR3N-BnaSOBIR1-1 and the target vector could grow normally on the SD/-Leu-Trp-His-Ade media, and yeast co-transformed with the bait vector containing the target gene and pPR3N-BnaSOBIR1-2 could also grow normally (Figure 7B). Together, these results illustrate that BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 can interact with BnaRLP-G13-1.
3. Discussion
Our previous findings indicated that BnaC04g56380D, a member of the BnaRLP family, was upregulated upon S. sclerotiorum infection in B. napus [23]. This observation has drawn our attention to its potential role in plant defense. To optimize germplasm resources and enhance disease resistance in rapeseed, we selected XY15 (a high-quality, moderately resistant cultivar) as a sample for the further investigation of BnaC04g56380D. Following S. sclerotiorum infection, the expression level of BnaC04g56380D was significantly upregulated in XY15, suggesting its positive regulatory role in the interaction between B. napus and S. sclerotiorum. Resequencing results revealed that BnaC04g56380D was transcribed as an intronless gene, a feature it shares with AtRLP23, which is also composed of a single exon. Secondary structure predictions confirmed that BnaC04g56380D in XY15 retained the essential structural domains of the RLP family and was localized to the plasma membrane. The heterologous overexpression of AtRLP23 in potato can increase the resistance of S. sclerotiorum [8]. Similarly, overexpression of BnaC04g56380D in both A. thaliana and B. napus enhanced plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum.
Given that BnaC04g56380D and AtRLP23 belonged to the same phylogenetic group, we hypothesized that they might share similar functions. To verify this, we performed a genetic complementation assay using the rlp23-1 mutant. Theoretically, the lesion size in the complemented lines should have been similar to that of Col-0; however, the transgenic 35S-BnaC04g56380D/rlp23-1 plants exhibited significantly smaller lesion areas than the wild type (WT), which might be attributed to the overexpression of BnaC04g56380D in the rlp23-1 background. RLP23 can specifically recognize nlp24 to activate MAPK cascades [8]. Western blot analysis revealed that BnaC04g56380D was able to activate the MAPK signaling cascade and restored the recognition of the nlp24 peptide, a function that was lost in the rlp23-1 mutant. Notably, the transgenic lines exhibited excessive MAPK activation, which we speculated to be due to the overexpression of BnaC04g56380D. It is important to note that MAPK activation was evaluated relative to the transgenic plants themselves rather than Col-0.
Although other AtRLP members were also present within the same phylogenetic group, here, we focused solely on the role of BnaC04g56380D in disease resistance and named BnaC04g56380D as BnaRLP-G13-1. Whether BnaC04g56380D exhibits functional similarity with other AtRLP members remains to be investigated.
As reported in our previous study [12], SsNEP1 is not secreted under normal conditions and does not participate in the infection process of S. sclerotiorum, whereas SsNEP2 is secreted and causes visible damage to plant leaves. Therefore, we selected its conserved sequence for further investigation. Albert et al. found that both the full nlp24 sequence and a shorter 20-amino-acid fragment could trigger plant immune responses [8]. However, as the 24-amino-acid sequence is a conserved motif in NLPs and is widely used in research, this study employed nlp24 and Ssnlp24SsNEP2 peptides to explore their functions. Consistently, Ssnlp24SsNEP2 could induce the expression of AtRLP23, AtSOBIR1, and AtBAK1, although the expression levels varied over time. AtRLP23 may function as a receptor for the recognition of Ssnlp24SsNEP2, thereby eliciting a sustained upregulation in its expression. AtSOBIR1 acted as a co-receptor binding to AtRLP23, and its expression level was affected by AtRLP23. In addition, AtSOBIR1 played an important regulatory role in plant immunity as a suppressor of AtBIR1 and a co-receptor of multiple RLPs [5,16]. Therefore, its expression is strictly regulated, and a sustained high expression level might cause cell death [16]. Compared with AtSOBIR1, brassinosteroid-insensitive 1-associated receptor kinase 1 (BAK1) had more binding proteins and was also involved in the regulation of brassinosteroid [26]. The prolonged high expression of BAK1 may lead to increased cell death. Despite differences in their expression levels, AtRLP23, AtSOBIR1, and AtBAK1 were all upregulated at the onset of Ssnlp24SsNEP2 induction. This suggests that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 might activate plant immunity through the RLP23-SOBIR1-BAK1 signaling pathway.
The BiFC results showed that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 could interact with AtRLP23 in Arabidopsis; however, SsNEP2 could not be directly recognized by AtRLP23. A previous study showed that PyaNLPs could bind GIPC to exert its cytolytic activity [27], and SsNEP2, as a member of the NLP family, might exert its toxic effect to promote S. sclerotiorum infection in a similar way. In this scenario, it is plausible to speculate that NLPs secreted by pathogens might be cleaved by enzymes evolved from host plants during the interaction processes between plants and S. sclerotiorum, exposing the conserved 24-amino-acid sites and triggering plant immunity after being recognized by RLP23, thereby enhancing resistance to S. sclerotiorum.
As MAPK cascades could still be activated by Ssnlp24SsNEP2 spraying on rlp23-1 or rlp23-3, we suggest that there may be another receptor that can recognize Ssnlp24SsNEP2 in Arabidopsis. In plants, MAPK cascades not only participate in the immune process but also play an important role in responding to abiotic stress [28]. However, the lesion areas on the leaf surfaces of the mutants treated with Ssnlp24SsNEP2 were not significantly different from those on the WT, indicating that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 could not enhance plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum without AtRLP23. The ROS burst results also indicate that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 cannot induce a reactive oxygen burst in plants without AtRLP23. Based on these results, we suggest that Ssnlp24SsNEP2 mainly interacts with AtRLP23 to trigger plant immunity. Although Ssnlp24SsNEP2 might be recognized by other receptors to activate MAPK cascades, it still cannot effectively activate the plant immune response.
AtRLP23 needs to combine with AtSOBIR1 to form a complex so as to transmit the recognition signal of a pathogen downstream and activate the plant immune response [8]. The orthologs of AtSOBIR1 in B. napus naturally formed two branches during evolution, which might be due to sequence differences before the transmembrane domain, and the protein kinase domain after the transmembrane domain showed high degrees of similarity and identity, indicative of protein kinase activity conservation in both branches. As a suppressor of BIR1, SOBIR1 can inhibit the function of BIR1 in plants [25]. BIR1 is a negative regulator of plant immunity, and its mutant bir1-1 exhibits obvious disease-resistance-related phenotypes [25]. Compared to bir1-1, the growth phenotype of the double mutant sobir1bir1-1 more closely resembles that of the wild type with reduced disease resistance [25]. After transforming BnaSOBIR1-1/BnaSOBIR1-2 into sobir1bir1-1 double mutants, it was found that the phenotypes of bir1-1 reappeared for the complementation lines, indicating that both were homolog genes of AtSOBIR1 in B. napus. Although only two genes were selected as representatives of the two branches of BnaSOBIR1 Group A and BnaSOBIR1 Group B for testing, it is reasonable to speculate that the remaining BnaSOBIR1 genes may have the same important function because of their high sequence similarity and identity.
The overexpression of BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 in A. thaliana and B. napus improved resistance to S. sclerotiorum, and their effects were more significant than those in the BnaRLP23 overexpression plants. This may be because SOBIR1 is a binding protein of various RLPs, so its overexpression can improve not only the RLP23-mediated pathway, but also other RLP pathways involved in the regulation of plant immunity, and the synergistic nature of multiple pathways produces cumulative effects. Similarly, oilseed rape LepR3 can recognize AvrLm1 (Leptosphaeria maculans effector 1) in the blackleg pathogen and interact with SOBIR1 to trigger the plant immune response [29]. Both Y2H and BiFC assays verified that BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 could interact with BnaRLP-G13-1. Together, these experimental results prove that in B. napus, BnaSOBIR1 also acts as a co-receptor to bind to BnaRLP-G13-1, thereby activating the downstream immune response and enhancing the plant’s resistance to pathogens.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Sequence Analysis of BnaRLP-G13-1 and BnaSOBIR1
AtRLP23 (AT2G32680)/AtSOBIR1 (AT2G31880) genomic sequence and annotation data were downloaded from TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org, accessed on 1 January 2022). BnaRLP-G13-1/BnaSOBIR1 genomic sequence and annotation data were downloaded from Ensembl plants (http://http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html, accessed on 1 January 2022). The multiple sequence alignment of BnaSOBIR1 was performed using Clustal x1.83 software and opened with MEGA7.0 software; then, the maximum likelihood (ML) method was used to construct an evolutionary tree. Bootstrap was set to 1000. The domains contained in the sequence were analyzed by PredictProtein (https://predictprotein.org/, accessed on 1 June 2022).
4.2. Fungal Strains and Plant Materials
The wild-type strain 1980 was subcultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) in an incubator at 20 °C for daily storage and 4 °C for long-term storage. Because the AtRLP23 T-DNA insertion mutant (salk_034225) ordered from (Arashare) was named as rlp23-1 [30], the AtRLP23 CRISPR mutant generated in this study was named as rlp23-3. Knockout mutants, overexpression plants, and complementation plants were transformed with the vector into Col-0 (or rlp23-1) through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation [31]. The overexpression lines of B. napus were generated via tissue culture using Agrobacterium-mediated hypocotyl transformation [32]. The obtained plants were subjected to antibiotic screening and PCR identification. The A. thaliana and B. napus (XY15 or its transformant, Xiangyou 15, a high-quality variety of Brassica napus planted widely in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China, referred to as XY15 in this article) used for the S. sclerotiorum virulence assays were cultured in a growth room at 22 °C with 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness; 4-week-old (A. thaliana) or 150-day-old (B. napus) plants were used for the assays.
4.3. Pathogen Infection Assay
Mycelial plugs (2 or 5 mm in diameter) from S. sclerotiorum (wild-type) were harvested from the edges of colonies maintained in PDA cultures for 48 h and then inoculated on leaves, with 2 mm plugs for A. thaliana and 5 mm plugs for B. napus. Lesion areas were measured 48 h later and counted with ImageJ. Two leaves were used per experiment, and each experiment was repeated three times. The data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics v.24.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t-test, with p-values < 0.05 considered significant.
To analyze Ssnlp24SsNEP2-induced pattern-triggered immunity, leaves from 4-week-old Arabidopsis were sprayed with 1 μM Ssnlp24SsNEP2 (the small peptide was synthetically produced and used after being diluted with ddH2O). After 24 h, seedlings were inoculated with S. sclerotiorum (wild-type). Lesion areas were measured 36 h later and counted with ImageJ.
4.4. MAPK Activity Assay
Two-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings grown on 1/2 MS medium plates were sprayed with 1 µM Ssnlp24SsNEP2, and samples were collected 0 and 15 min after each treatment. Then, protein extract buffer was added to extract the total protein. The phosphorylation of MAPK was detected via Western blot analysis with anti-pERK (no. 4370S, 1:2500 dilution; Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA). Ponceau staining served as the internal reference. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times.
4.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
The gene expression levels of BnaC04g56380D, BnaSOBIR1 Group A, and BnaSOBIR1 Group B were analyzed at 48 and 96 h after inoculation with S. sclerotiorum (wild-type). Leaf samples (B. napus, XY15) were collected from a 5 mm area surrounding the inoculation site, including necrotic tissue. In contrast, the expression levels of AtRLP23, AtSOBIR1, and AtBAK1 were examined at 4 and 24 h following Ssnlp24SsNEP2 treatment, with samples collected from the entire leaf (A. thaliana, Col-0). The RNA of the test samples was extracted using an EastepTM Super Total RNA Extraction Kit, and the GoScript™ Reverse Transcription System Kit was used for cDNA synthesis (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Quantitative expression assays were performed using the SYBR® Green Premix Pro Taq HS qPCR Kit II (AG11702, Accurate Biotechnology (Hunan) Co., Ltd., Changsha, China) with the StepOneTM Real-time PCR Instrument Thermal Cycling Block. The primers were designed by the Primer Premier 5.0 program and amplicon-sized between 100 and 400 bp (Supplementary Table S1). The internal references were Actin1 for A. thaliana and UBC9 for B. napus [33].
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species Burst Assay
The ROS burst assay was conducted following the previously described procedure, with slight modifications [34]. Leaf disks from true leaves from five-week-old plants (A. thaliana, Col-0) grown in soil were kept in the dark overnight with 200 µL of sterile distilled water in a 96-well plate. A reaction solution (170 μL) including 100 µM of luminol, 20 µg/mL of horseradish peroxidase, and 1 µM of synthetic peptides (nlp24 and Ssnlp24SsNEP2) was added into each well just before measurement. Luminescence was recorded at 2-minute intervals using Spark®(Tecan, Männedorf, Swiss Confederation) over a duration of approximately 60 minutes. Each treatment involved the measurement of six biological replicates, and the experiments were independently repeated three times.
4.7. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC)
For the BiFC assays, the full-length cDNA of BnaRLP-G13-1 was amplified via PCR using specific primer pairs (Supplementary Table S1), inserted into the plasmid pSPYNE digested with KpnI and BamHI, and BnaSOBIR1 was cloned into a pSPYCE plasmid digested with KpnI and BamHI. pSPYNE and pSPYCE represent two segments of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), with YNE containing the N-terminus of the YFP and YCE containing the C-terminus of the YFP. The constructs for bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BIFC) were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 via electroporation. A. tumefaciens cultures carrying recombinant plasmids were diluted with infiltration buffer (10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM MES, 150 μM AS, pH = 5.6) to obtain OD600 = 1. Then, equal amounts of each culture were mixed and used for infiltration. Leaves (N. benthamiana) were imaged for BiFC after 36–72 h infiltration (Axio Imager 2, ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany). YFP was excited at 470–490 nm and acquired at 500–540 nm.
4.8. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) Assays
For the yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assays, the full-length cDNAs of BnaRLP-G13-1 were amplified via PCR using specific primer pairs (Supplementary Table S1) and then inserted into the plasmid pBT3-STE digested with SfiI to generate bait constructs. BnaSOBIR1 was cloned into a pPR3-N plasmid digested with SfiI to create the prey construct. All the prey and bait constructs were co-transformed into competent cells of the NMY51 yeast strain. Yeast transformants expressing each pair of proteins were assayed for growth on SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade. pNubG-Fe65 + pTSU2-APP was used as the positive control, and pGADT7-T and pGBKT7-Lam served as the negative controls.
4.9. Trypan Blue Staining
Two-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings grown on 1/2 MS medium plates were soaked in 1% Trypan blue solution for 1 h and then decolorized with bleaching solution and photographed (Stemi 508, ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany).
4.10. Subcellular Localization Assay
To assess the subcellular localization of BnaC04g56380D in N. benthamiana, a BnaC04g56380D-eGFP fusion gene driven by the 35S promoter was employed. The construct was introduced via Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101-mediated transformation, and the bacterial suspension was infiltrated into the abaxial epidermal cells of four-week-old leaves [35]. Fluorescence microscopy was performed 48–72 h post-infiltration using an Axio Imager 2 fluorescence microscope (ZEISS). GFP was excited at 470–490 nm and acquired at 500–540 nm.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that the overexpression of BnaC04g56380D (BnaRLP-G13-1) enhanced plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum and further investigated its underlying mechanism. BnaRLP-G13-1 contributed to plant immunity by recognizing a conserved amino acid sequence in SsNEP2. Additionally, we screened for downstream proteins that interacted with BnaRLP-G13-1 in B. napus and analyzed their roles during infection. The overexpression of BnaSOBIR1-1 and BnaSOBIR1-2 in both A. thaliana and B. napus improved resistance to S. sclerotiorum, and these proteins were found to interact with BnaRLP-G13-1. Based on these findings, we propose that BnaRLP-G13-1, as a membrane surface receptor, recognizes Ssnlp24SsNEP2 and forms a complex with BnaSOBIR1 and BnaBAK1, transmitting signals to activate downstream immune responses (Figure 8). As a key immune signal transducer, BnaRLP-G13-1 plays a crucial regulatory role in the interaction between rapeseed and S. sclerotiorum.
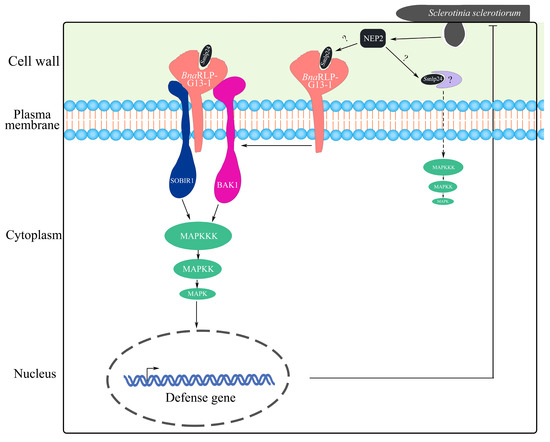
Figure 8.
A model of BnaRLP-G13-1 enhancing plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum. S. sclerotiorum promotes infection by secreting a toxic protein (SsNEP2). To resist the infection, plants cleave SsNEP2 to generate a small peptide (Ssnlp24SsNEP2) through an as yet unknown mechanism. After recognizing Ssnlp24SsNEP2, BnaRLP-G13-1 forms a complex with SOBIR1 and BAK1 to activate the MAPK cascade reaction and promote immunity-related gene expression, enhancing plant resistance to S. sclerotiorum.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26104569/s1.
Author Contributions
C.Y.: formal analysis, writing the original draft, performing most of the experiments described. W.Z.: data curation. W.L.: performing the screening. Y.X.: Trypan blue staining. L.Q. and X.T.: BiFC experiments. S.X.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, and supervision. All authors contributed to the manuscript and approved the submitted version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 31971836), Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (325QN336), and Scientific Research Foundation of Hainan Tropical Ocean University (No. RHDRC202321).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We cordially thank Xin Li (University of British Columbia) for the critical suggestions regarding the experiments, and Jeffrey Rollins (University of Florida) for sharing the WT S. sclerotiorum strain 1980. We thank all members of our laboratories for their helpful assistance with this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourelis, J.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L. Defended to the Nines: 25 Years of Resistance Gene Cloning Identifies Nine Mechanisms for R Protein Function. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Weyer, A.L.; Monteiro, F.; Furzer, O.J.; Nishimura, M.T.; Cevik, V.; Witek, K.; Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Weigel, D.; Bemm, F. A Species-Wide Inventory of NLR Genes and Alleles in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 2019, 178, 1260–1272.e1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Ding, P.; Jones, J.D.G. Thirty years of resistance: Zig-zag through the plant immune system. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1447–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, A.K.; Furst, U.; Lipschis, M.; Albert, M.; Felix, G. Perception of the novel MAMP eMax from different Xanthomonas species requires the Arabidopsis receptor-like protein ReMAX and the receptor kinase SOBIR. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e27408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, A.K.; Lipschis, M.; Albert, M.; Fallahzadeh-Mamaghani, V.; Furst, U.; Mueller, K.; Felix, G. The receptor-like protein ReMAX of Arabidopsis detects the microbe-associated molecular pattern eMax from Xanthomonas. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Frohlich, K.; Melzer, E.; Pruitt, R.N.; Albert, I.; Zhang, L.; Joe, A.; Hua, C.; Song, Y.; Albert, M.; et al. Genotyping-by-sequencing-based identification of Arabidopsis pattern recognition receptor RLP32 recognizing proteobacterial translation initiation factor IF1. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, I.; Bohm, H.; Albert, M.; Feiler, C.E.; Imkampe, J.; Wallmeroth, N.; Brancato, C.; Raaymakers, T.M.; Oome, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. An RLP23-SOBIR1-BAK1 complex mediates NLP-triggered immunity. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, E.; Mise, K.; Takano, Y. RLP23 is required for Arabidopsis immunity against the grey mould pathogen Botrytis cinerea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Y.; Ai, G.; Song, Q.; et al. Nep1-Like Proteins From the Biocontrol Agent Pythium oligandrum Enhance Plant Disease Resistance Independent of Cell Death and Reactive Oxygen Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 830636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Dong, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Jing, M.; Dou, D. Type 2 Nep1-Like Proteins from the biocontrol oomycete Pythium oligandrum Suppress Phytophthora capsici infection in Solanaceous plants. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Tang, X.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Peng, Z.; Xia, S. SsNEP2 contributes to the virulence of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pathogens 2022, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebrand, T.W.H.; van den Burg, H.A.; Joosten, M.H.A.J. Two for all: Receptor-associated kinases SOBIR1 and BAK1. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, A.A.; Felix, G. Receptor like proteins associate with SOBIR1-type of adaptors to form bimolecular receptor kinases. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Fraiture, M.; Kolb, D.; Loffelhardt, B.; Desaki, Y.; Boutrot, F.F.; Tor, M.; Zipfel, C.; Gust, A.A.; Brunner, F. Arabidopsis receptor-like protein30 and receptor-like kinase suppressor of BIR1-1/EVERSHED mediate innate immunity to necrotrophic fungi. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4227–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.S.; Kars, I.; Essenstam, B.; Liebrand, T.W.H.; Wagemakers, L.; Elberse, J.; Tagkalaki, P.; Tjoitang, D.; van den Ackerveken, G.; van Kan, J.A.L. Fungal Endopolygalacturonases Are Recognized as Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns by the Arabidopsis Receptor-Like Protein RESPONSIVENESS TO BOTRYTIS POLYGALACTURONASES1. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebrand, T.W.; van den Berg, G.C.; Zhang, Z.; Smit, P.; Cordewener, J.H.; America, A.H.; Sklenar, J.; Jones, A.M.; Tameling, W.I.; Robatzek, S.; et al. Receptor-like kinase SOBIR1/EVR interacts with receptor-like proteins in plant immunity against fungal infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10010–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.D.; Koch, M.A.; Mayer, M.; Mummenhoff, K.; O’Kane, S.L., Jr.; Warwick, S.I.; Windham, M.D.; Al-Shehbaz, I.A. Toward a global phylogeny of the Brassicaceae. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 2142–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.A.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B.; et al. Plant genetics. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.N.; Li, T.; Guo, X.J.; Li, M.; Liu, X.Y.; Cao, J.; Tan, X.L. Sclerotinia Stem Rot Resistance in Rapeseed: Recent Progress and Future Prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2965–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Gupta, N.; Ashraf, S.; Bouqellah, N.A.; Hamed, K.E.; Nayana R U, K. Understanding resistance mechanisms and genetic advancements for managing Sclerotinia stem rot disease in oilseed Brassica. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 136, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Qian, L.; Disi, J.O.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Frauen, M.; Cai, D.; Qian, W. Identification of resistant sources against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Brassica species with emphasis on B. oleracea. Euphytica 2011, 177, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.; Xia, S. Identification of receptor-like proteins induced by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 944763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.Y.; Tang, M.Q.; Chen, T.; Bao, L.L.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.L.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhu, K.M.; Liu, S.; et al. BnaMPK6 is a determinant of quantitative disease resistance against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in oilseed rape. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, F.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Z.; Bi, D.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; et al. Regulation of cell death and innate immunity by two receptor-like kinases in Arabidopsis. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 6, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; van der Does, D.; Ladwig, F.; Sticht, C.; Kolbeck, A.; Schurholz, A.K.; Augustin, S.; Keinath, N.; Rausch, T.; Greiner, S.; et al. A receptor-like protein mediates the response to pectin modification by activating brassinosteroid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15261–15266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenarcic, T.; Albert, I.; Bohm, H.; Hodnik, V.; Pirc, K.; Zavec, A.B.; Podobnik, M.; Pahovnik, D.; Zagar, E.; Pruitt, R.; et al. Eudicot plant-specific sphingolipids determine host selectivity of microbial NLP cytolysins. Science 2017, 358, 1431–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Yang, L.; Gai, Y. MAPKKKs in Plants: Multidimensional Regulators of Plant Growth and Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.S.; Borhan, M.H. The receptor-like kinase SOBIR1 interacts with Brassica napus LepR3 and is required for Leptosphaeria maculans AvrLm1-triggered immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ellendorff, U.; Kemp, B.; Mansfield, J.W.; Forsyth, A.; Mitchell, K.; Bastas, K.; Liu, C.M.; Woods-Tor, A.; Zipfel, C.; et al. A genome-wide functional investigation into the roles of receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoza, V.; Stewart, C.N. Increased Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and rooting efficiencies in canola (Brassica napus L.) from hypocotyl segment explants. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 21, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Truksa, M.; Shah, S.; Weselake, R.J. A survey of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction internal reference genes for expression studies in Brassica napus. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 405, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantean, L.; Okada, K.; Kawakatsu, Y.; Kurotani, K.I.; Notaguchi, M. Measurement of reactive oxygen species production by luminol-based assay in Nicotiana benthamiana, Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica rapa ssp. rapa. Plant Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tang, L.; Qin, L.; Zhong, W.; Tang, X.; Gong, X.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Xia, S. mRNA Turnover Protein 4 Is Vital for Fungal Pathogenicity and Response to Oxidative Stress in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Pathogens 2023, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).