microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
Abstract
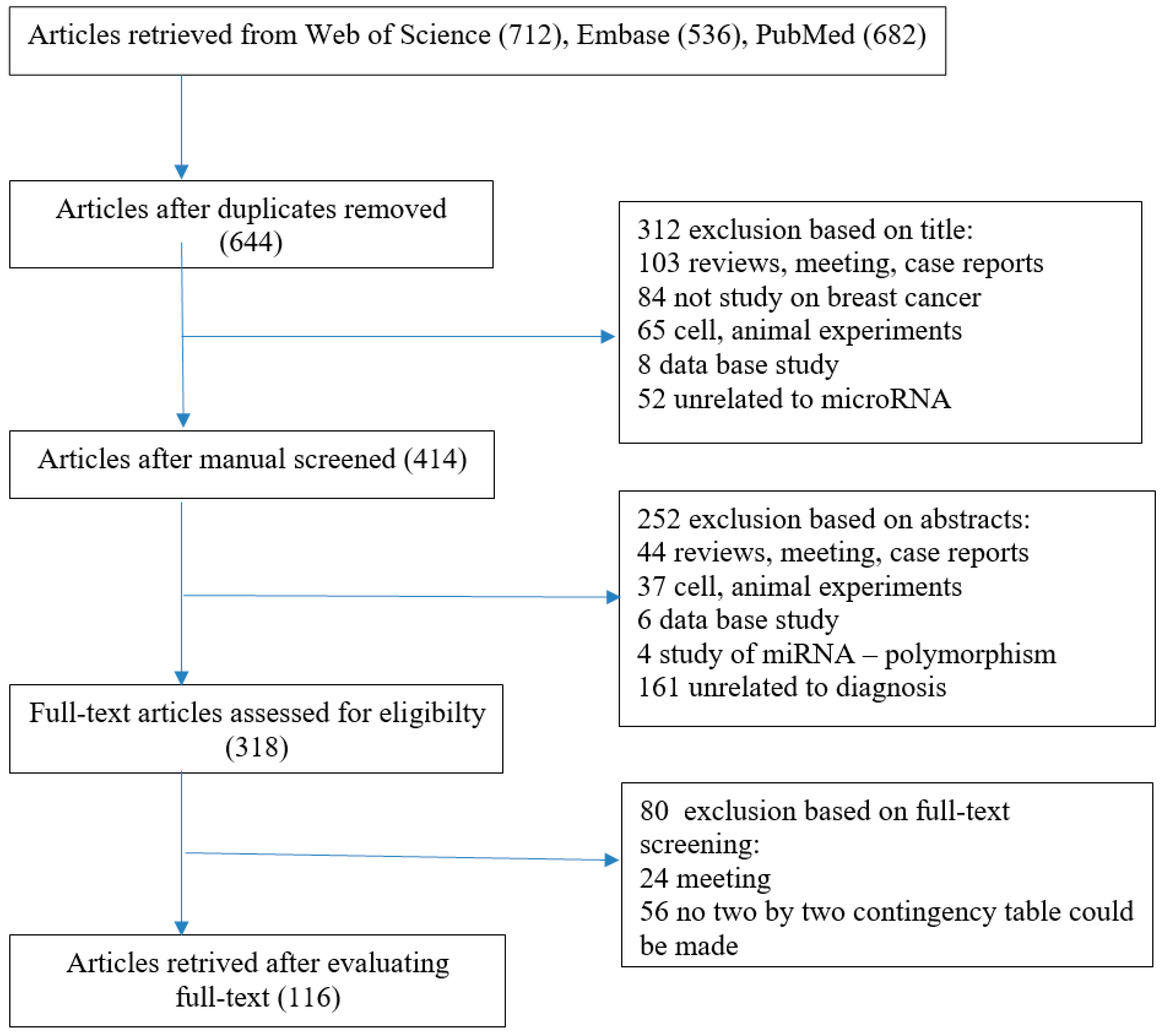
1. Introduction
2. Function of microRNAs
3. The Role of microRNAs in Carcinogenesis
4. microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
5. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombonati, A.; Sgroi, D.C. The molecular pathology of breast cancer progression. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Chu, P.-Y. Current and developing liquid biopsy techniques for breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisel, J.; Raghu, M.; Hooley, R. The role of ultrasound in breast cancer screening: The case for and against ultrasound. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2018, 39, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.X.; Lim, Z.L.; Ho, P.J.; Li, J. Breast cancer in Asia: Incidence, mortality, early detection, mammography programs and risk-based screening initiatives. Cancers 2022, 14, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilam, A.; Shai, A.; Ashkenazi, I.; Sarid, A.L.; Drobot, A.; Bickel, A.; Shomron, N. MicroRNA regulation of progesterone receptor in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25963–25976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babei, G.; Raei, N.; Toofani, M.; Gholizadeh-Ghaleh, A.S.; Pourjabbar, N.; Geravand, F. The emerging role of miR-200 family in metastasis: Focus on EMT, CSCs, angiogenesis, and anoikis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 6935–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.; Mitra, T.; Rajiv, R.; Rajan, E.J.E.; Pierret, C.; Enninga, E.A.L.; Janardhanan, R. Exosomal microRNAs in breast cancer: Towards theranostic applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1330144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.L.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Calin, G.A. MiR-200 family and cancer: From a meta-analysis view. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Luo, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, J.; Gu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, P.; Zhao, G.H.; et al. A panel of serum noncoding RNAs for the diagnosis and monitoring of response to therapy in patients with breast cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2476–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Kaushik, A.C.; Zhang, J. The emerging role of major regulatory RNAs in cancer control. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Fischer, U.; Backes, C.; Galata, V.; Minet, M.; Hart, M.; Abu-Halima, M.; Grasser, F.A.; Lenhof, H.P.; et al. An estimate of the total number of true human miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, A.L.; Enguita, F.J. A structural view of miRNA biogenesis and function. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Yu, T.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, H.; Yan, W. MicroRNAs control mRNA fate by compartmentalization based on 3′UTR length in male germ cells. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasculli, B.; Barbano, R.; Parrella, P. Epigenetics of breast cancer: Biology and clinical implication in the era of precision medicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 51, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.K.; Kumar, A.; Banik, K.; Verma, E.; Khatoon, E.; Harsha, C.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.C.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Long noncoding RNAs in triple-negative breast cancer: A new frontier in the regulation of tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 7938–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveto, S.; Mancino, M.; Manfrini, N.; Biffo, S. Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YerukalaSathipati, S.; Ho, S.-Y. Identifying a miRNA signature for predictingthe stage of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16138. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Han, X.; Yu, K.; Sun, S.; Zhen, L.; Li, Z. microRNA-200c downregulates XIAP expression to suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madu, C.O.; Wang, S.; Madu, C.O.; Lu, Y. Angiogenesis in breast cancerprogression, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4474–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschetto, L.M. miRNA activation is an endogenous gene expression pathway. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmatzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Asghari, F.; Yousefi, M. The role of oncomirs in the pathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 78, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ayub, H.; Khan, T.; Wahid, F. MicroRNA biogenesis, gene silencing mechanisms and role in breast, ovarian and prostate cancer. Biochimie 2019, 167, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Cui, Q.; Yin, Y. Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: From functions to targets. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Bao, P.P.; Su, Y.; Cai, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, F.; Guo, X.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Tumor tissue microRNA expression in association with triple-negative breast cancer outcomes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 152, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovicova, D.; Smolkova, B.; Magyerkova, M.; Sestakova, Z.; Kajabova, V.H.; Kulcsar, L.; Zmetakova, I.; Kalinkova, L.; Krivulcik, T.; Karaba, M. Down-regulation of traditional oncomiRs in plasma of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77369–77384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanek-Trzeciak, M.O.; Galka-Marciniak, P.; Nawrocka, P.M.; Kowal, E.; Szwec, S.; Giefing, M.; Kozlowski, P. Pan-cancer analysis of somatic mutations in miRNA genes. EBioMedicine 2020, 61, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto, A.S.; Parchem, R.J. KRAS Hijacks the miRNA regulatory pathway in cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canatan, D.; Yılmaz, O.; Sönmez, Y.; Çim, A.; Coşkun, H.S.; Göksu, S.S.; Ucar, S.; Aktekin, M.R. Circulating microRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarkers for breast cancer detection. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021028. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Sun, T.; Li, D.; Xu, X.; Rui, Y.; Li, C.; Chong, M.; Ibrahim, T.; Mercatali, L. miR-126and miR-126* repress recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells and inflammatory monocytes to inhibit breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahmood, S.; Sapiezynski, J.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T. Metastatic and triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and treatment options. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1483–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Dai, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, X. miR-494 suppresses the progression ofbreast cancer in vitro by targeting CXCR4 through the Wnt/_-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graveel, C.R.; Calderone, H.M.; Westerhuis, J.J.; Winn, M.E.; Sempere, L.F. Critical analysis of the potential for microRNA biomarkers in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer 2015, 23, 59–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shen, J.; Medico, L.; Wang, D.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Liu, S. A pilot study of circulating miRNAs as potential biomarkers of early stage breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlmann, T.; Ludwig, N.; Backes, C.; Meese, E.; Keller, A. Distribution of microRNA biomarker candidates in solid tissues and body fluids. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzaman, K.; Karami, J.; Zarei, Z.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Kazemi, M.H.; Moradi-Kalbolandi, S.; Safari, E.; Farahmand, L. Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.; Harbeck, N.; Nap, M.; Molina, R.; Nicolini, A.; Senkus, E.; Cardoso, F. Clinical use of biomarkers in breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, F.; Hanif, M.; Ahmed, A.; Jamal, Q.; Khan, A. Clinicopathological features associated to MiRNA-195 expression in patients with breast cancer: Evidence of a potential biomarker. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Lee, W.; Coffey, C.; Lean, A.; Wu, X.; Tan, X.; Mam, Y.-G.; Brem, R.F. miRNAs as potential biomarkers in early breast cancer detection following mammography. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridrichova, I.; Zmetakova, I. MicroRNAs contribute to breast cancer invasiveness. Cell 2019, 8, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; Garcia-Venzor, A.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Maldonado, V. New emerging roles of microRNAs in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Cui, Q. The relationship of human tissue microRNAs with those from body fluids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, A.M.; Ianculescu, L.M.; Suciu, N. MiRNAs as potential biomarkers in early breast cancer detection: A systemic review. J. Med. Life 2024, 17, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-W.; Yang, X.; Wen, D.-Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Ye, Z.-H.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.Y.; He, Y.; Pang, Y.Y.; et al. Utility of miR-133a-3p as a diagnostic indicator for hepatocellular carcinoma: An investigation combined with GEO, TCGA, meta-analysis and bioinformatics. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Papukashvili, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, Z.; Rcheulishvili, N.; et al. Potential utility of miRNAs for liquid biopsy in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 940314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swellam, M.; Zahran, R.F.K.; Abo El-Sadat Taha, H.; El-Khazragy, N.; Abdel-Malak, C. Role of some circulating MiRNAs on breast cancer diagnosis. Arch. PhysiolBiochem 2019, 125, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamam, R.; Hamam, D.; Alsaleh, K.A.; Kassem, M.; Zaher, W.; Alfayez, M.; Aldahmash, A.; Alajez, N.M. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalighfard, S.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Irani, S.; Omranipour, R. Plasma miR-21, miR-155, miR-10b, and Let-7a as the potential biomarkers for the monitoring of breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gautam, M.; Chaudhary, A.; Chaurasia, B. Impact of three miRNA signature as potential diagnostic marker for triple negative breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.K.; Beevi, S.S.; Nair, R.A.; Kumar, A.; Kiran, R.; Alexander, L.E.; Dinesh Kumar, L. MicroRNA signatures differentiate types, grades, and stages of breast invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): miRNA-target interacting signaling pathways. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochor, M.; Basova, P.; Pesta, M.; Dusilkova, N.; Bartos, J.; Burda, P. Oncogenic microRNAs: miR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Eades, G.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Characterization of a stem-like subpopulation in basal-like ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) lesions. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.J.; Yang, H.B.; Jing, J.F.; Jia, M.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Guo, F.; Gao, J.N. Identification of serum exosomal miR-148a as a novel prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 7303–7309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, X. MicroRNA-21 in breast cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic potential. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2014, 16, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.G.; Jiang, Y.D.; Zhang, C.H. A novel panel of serum miR-21/miR-155/miR-365 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2017, 92, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, N. miR-21 might be involved in breast cancer promotion and invasion rather than in initial events of breast cancer development. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, T.; Wadhwa, R.; Gupta, R.; Paudel, K.R.; Collet, T.; Chellappan, D.K.; Gupta, G.; Perumalsamy, H.; Mehta, M.; Satija, S.; et al. MicroRNAs as Biomarker for Breast Cancer. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.-Drug Targets 2020, 20, 1597–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, D.; Zucknick, M.; Wallwiener, M.; Cuk, K.; Modugno, C.; Scharpff, M.; Schott, S.; Heil, J.; Turchinovich, A.; Yang, R.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012, 18, 5972–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, J.; Shahid, S.; Shahzadi, S.; Ahktar, M.W.; Sadaf, S. Identification of circulating miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers of triple negative breast cancer in the population of Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2019, 51, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, X. Effect of miR-200c on the proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells and relevantmechanisms. J. Buon 2019, 24, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhong, Q. MicroRNA-200c inhibits the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by targeting ZEB2, an epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 50, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Papadaki, C.; Stratigos, M.; Markakis, G.; Spiliotaki, M.; Mastrostamatis, G.; Nikolaou, C.; Mavroudis, D.; Agelaki, S. Circulating microRNAs in the early prediction of disease recurrence in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Turchinovich, A.; Feisst, M.; Riedel, F.; Haßdenteufel, K.; Scharli, P.; Hartkopf, A.D.; Brucker, S.Y.; Michel, L.; Burwinkel, B.; et al. Circulating miR-200 Family and CTCs in metastatic breast cancer before, during, and after a wew line of systemic treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, I.; Ciccarese, F.; Sharova, E.; Urso, L.; Raimondi, V.; Silic-Benussi, M.; D’Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. The miR-200 Family of microRNAs: Fine tuners of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and circulating cancer biomarkers. Cancers 2021, 13, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran-Gale, J.; Purvis, J.E.; Sethupathy, P. An integrative transcriptomics approach identifies miR-503 as a candidate master regulator of the estrogen response in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. RNA 2016, 22, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, S.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; van Diest, P.J.; van der Groep, P. miRNA expression patterns in normal breast tissue and invasive breast cancers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 germ-line mutation carriers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32115–32137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, V.; Davey, M.G.; Annuk, H.; Miller, N.; Dwyer, R.M.; Lowery, A.; Kerim, M.J. MicroRNAs in Molecular Classification and Pathogenesis of Breast Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Abdallah, Z.F.; Nassar, H.R.; Hilal, A.; El Desouki, H.; Said, M.; Elsalam, I.A. Deregulated expression of candidate MicroRNAs and BRCA mutations frequency in breast cancer patients. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 23–35. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovic, N.; Davidovic, R.; Bajic, V.; Obradovic, M.; Isenovic, R.E. MicroRNA in breast cancer: The association with BRCA1/2. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 19, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, M.M.; Nassar, F.J.; Tfayli, A.H.; Talhouk, R.S.; Chamandi, G.K.; Itani, A.R.S.; Makoukji, J.; Boustany, R.-M.N.; Hou, L.; Zgheib, N.K.; et al. A Signature of Four Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosing early-stage breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yelihamu, D.; Guo, C. Diagnostic value of 5 miRNAs combined detection for breast cancer. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1482927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, A.D.; Catalan, O.M.; Vázquez-Romo, R.; Porras Reyes, F.I.; Alvarado-Miranda, A.; Lara Medina, F.; Bargallo-Rocha, J.E.; Orozco Moreno, L.T.; Cantú De León, D.; Herrera, L.A.; et al. miRNA profile obtained by next-generation sequencing in metastatic breast cancer patients is able to predict the response to systemic treatments. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, A.; Ghovahi, A.; Abbasvandi, F.; Amani, D. Experimental validation of miR-4443, miR-572, and miR-150-5p in serum and tissue of breast cancer patients as a potential diagnostic biomarker: A study based on bioinformatics prediction. Biochem. Genet. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Xiu, C. Clinical utility of quantitative ultrasonography parameters combined with serum cancer antigen 15-3, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and soluble E-cadherin in diagnosing mass-type breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2025, 29, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, W.M.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Fan, Y.C.; Yang, P.E.; Kang, S.T.; Liao, C.T. A novel multi-gene detection platform for the analysis of miRNA expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, I.W.; Bzorek, M.; Olsen, J.; Grum-Schwensen, B.; Troelsen, J.T.; Pedersen, O.B. A novel approach for microRNA in situ hybridization using locked nucleic acid probes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagrass, H.A.; Sharaf, S.; Pasha, H.F.; Tantawy, E.A.; Mohamed, R.H.; Kassem, R. Circulating microRNAs—A new horizon in molecular diagnosis of breast cancer. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhelbawy, N.G.; Zaid, I.F.; Khalifa, A.A.; Gohar, S.F.; Fouda, E.A. miRNA-148a and miRNA-30c expressions as potential biomarkers in breast cancer patients. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 27, 101060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Ramasubramanian, B.; Kanji, S.; Chakraborty, A.R.; Haque, S.J.; Chakravarti, A. Circulating microRNAs in cancer: Hope or hype? Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W. Circulating microRNA biomarker studies: Pitfalls and potential solutions. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Peng, H.; McGowan, E.M.; Hutvagner, G.; Li, J. An isomer expression panel based novel breast cancer classification approach using improved mutual information. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, A.; Komuro, H.; Aminova, S.; Harada, M. A Comprehensive review of cancer microRNA therapeutic delivery strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søkilde, R.; Persson, H.; Ehinger, A.; Pirona, A.C.; Fernö, M.; Hegardt, C.; Larsson, C.; Loman, N.; Malmberg, M.; Rydén, L.; et al. Refinement of breast cancer molecular classification by miRNA expression profiles. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K.; Sinha, R. Functions of differentially regulated miRNAs in breast cancer progression: Potential markers for early detection and candidates for therapy. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaal, A.M.; Sohal, I.S.; Iyer, S.; Sudarshan, K.; Kothandaraman, H.; Lanman, N.A.; Low, P.S.; Kasinski, A.L. A first-in-class fully modified version of miR-34a with outstanding stability, activity, and anti-tumor efficacy. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Turowski, S.G.; Spernyak, J.A.; Tracz, A.; Abdelaal, A.M.; Sudarshan, K.; et al. Developing Folate-Conjugated miR-34a therapeutic for prostate cancer: Challenges and promises. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Symbol | Expression | Materials | Function | Biomarker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| microRNA-23a | Up | Plasma | Modify tumor micro-environment, metastasis | Prediction of survival |
| microRNA-200a | Down | Biopsy, Blood, Urine | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-200b | Down | Biopsy, Blood, Urine | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-200c | Down | Biopsy, Blood, Urine | Proliferation, invasion metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-21 | Up | Plasma | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Early detection, monitoring recurrences |
| microRNA-141 | Down | Biopsy, Blood, Urine | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-429 | Down | Biopsy, Blood, Urine | Proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-181b | Up | Blood | Proliferation, migration, invasion | Prediction of survival |
| microRNA-182 | Down | Blood | Apoptosis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-125b | Up | Plasma, Serum | Proliferation, migration, invasion | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-130a | Down | Plasma, Serum | Migration, invasion | Prediction of treatment response |
| microRNA-193a-3p | Down | Plasma | Proliferation, migration, invasion | Prediction of treatment response |
| microRNA-451 | Up | Biopsy, Plasma | Proliferation, migration | Diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of treatment response |
| microRNA-331 | Up | Blood | Proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis | Diagnosis, prognosis, prediction of survival |
| microRNA-100 | Up | Plasma | Proliferation, | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-145 | Down | Plasma | Cancer cell motility inhibition | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-195 | Up | Serum | Proliferation, migration | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-155 | Up | Plasma, Serum | Proliferation, metastasis | Prediction of survival, monitoring recurrences |
| microRNA-342-3p | Up | Plasma, serum | Apoptosis | Response to treatment |
| microRNA-187-3p | Up | Plasma, serum | Apoptosis | Response to treatment |
| microRNA-365 | Down | Serum | Migration, apoptosis | Diagnosis, prognosis |
| microRNA-425-5p | Up | Plasma, Serum | Proliferation, migration, invasion | Prediction of survival |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jelski, W.; Okrasinska, S.; Mroczko, B. microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094395
Jelski W, Okrasinska S, Mroczko B. microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094395
Chicago/Turabian StyleJelski, Wojciech, Sylwia Okrasinska, and Barbara Mroczko. 2025. "microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094395
APA StyleJelski, W., Okrasinska, S., & Mroczko, B. (2025). microRNAs as Biomarkers of Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094395







