Prolonged Hypoxia in Rat Living Myocardial Slices Affects Function, Expression, and Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
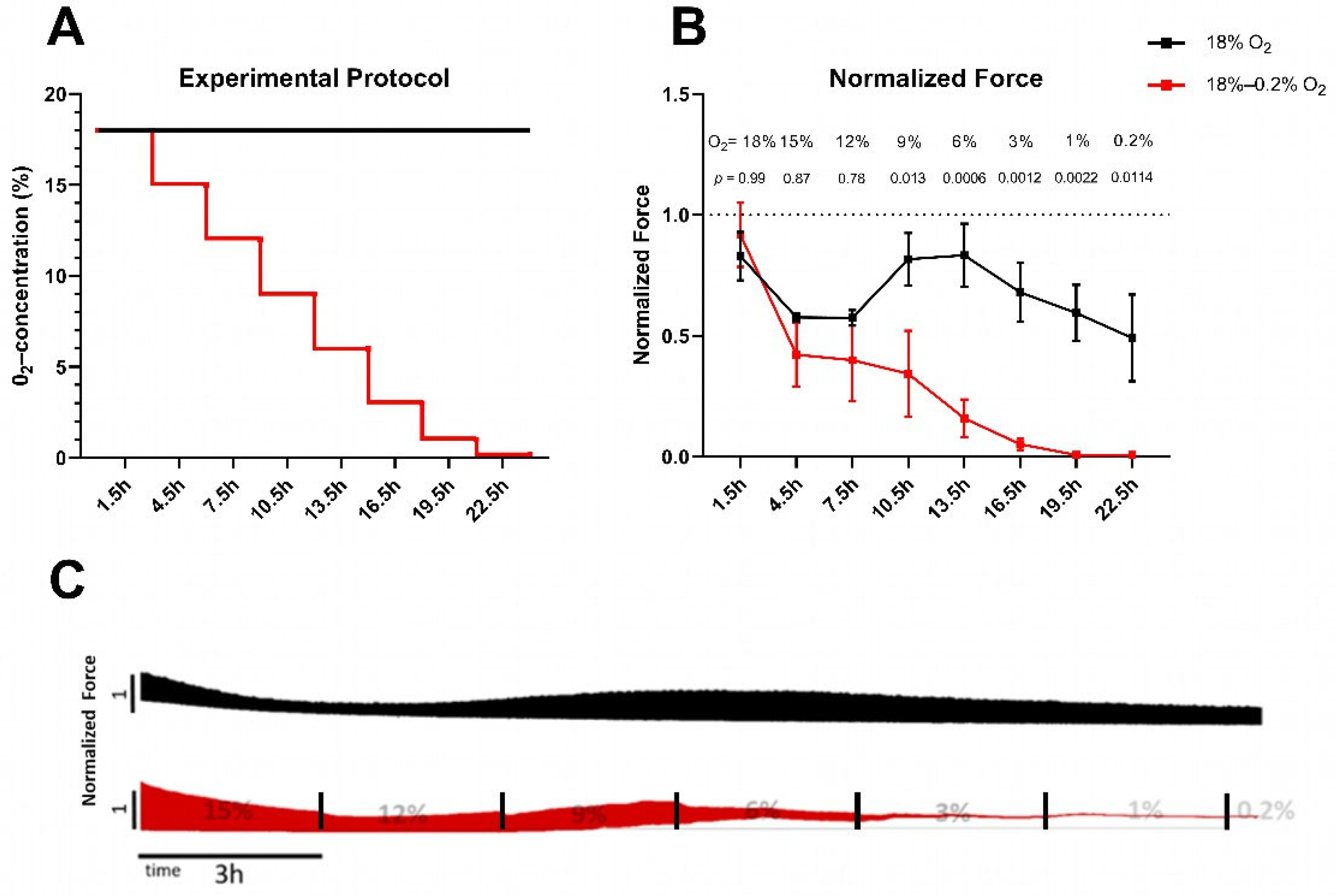
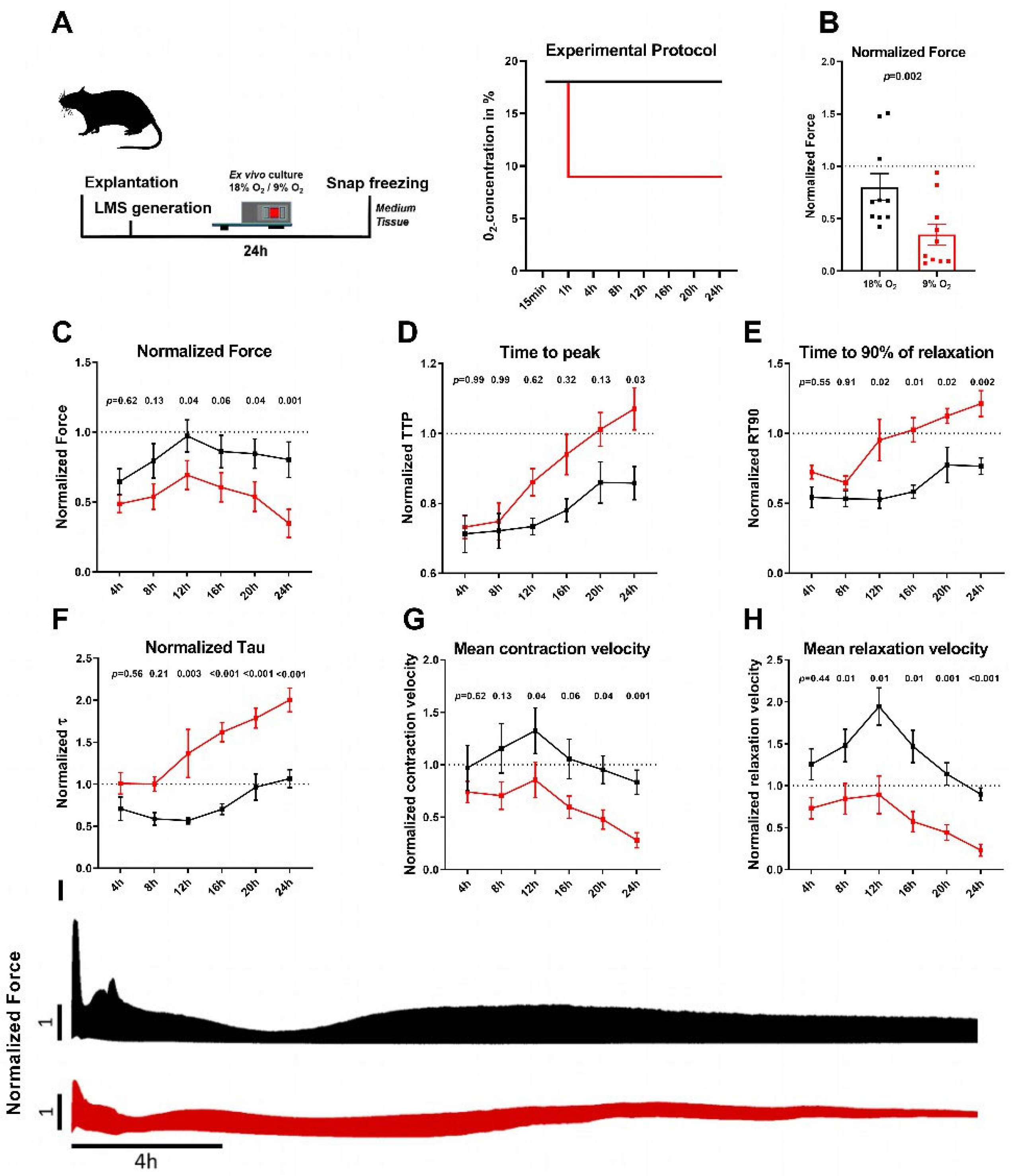
2.1. Permanent Hypoxia Reduces Force Generation and Prolongs Relaxation in Rat Myocardial Slices
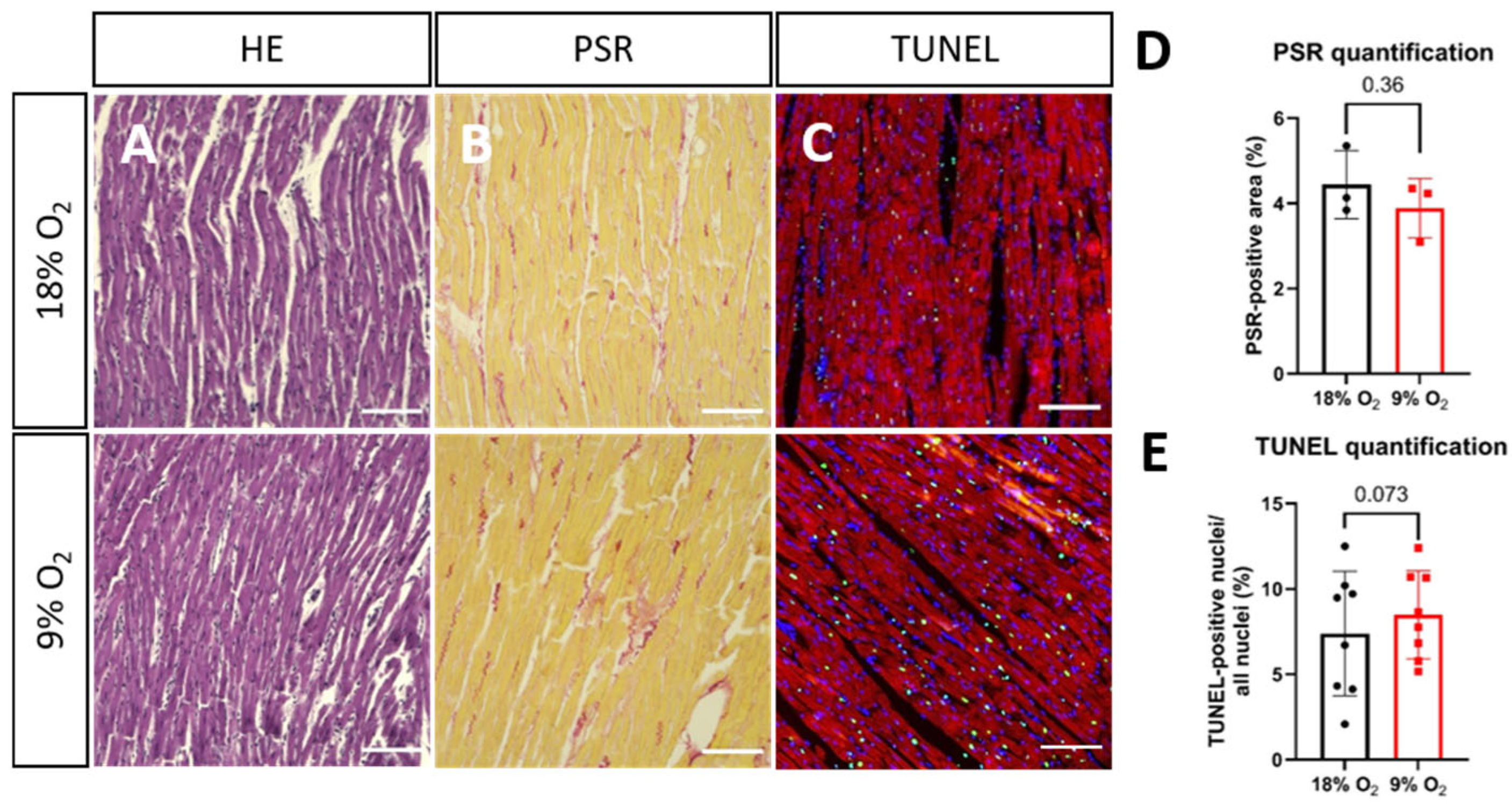
2.2. Hypoxia Induces Myofibrillar Disruption and Mitochondrial Changes in Rat LMS
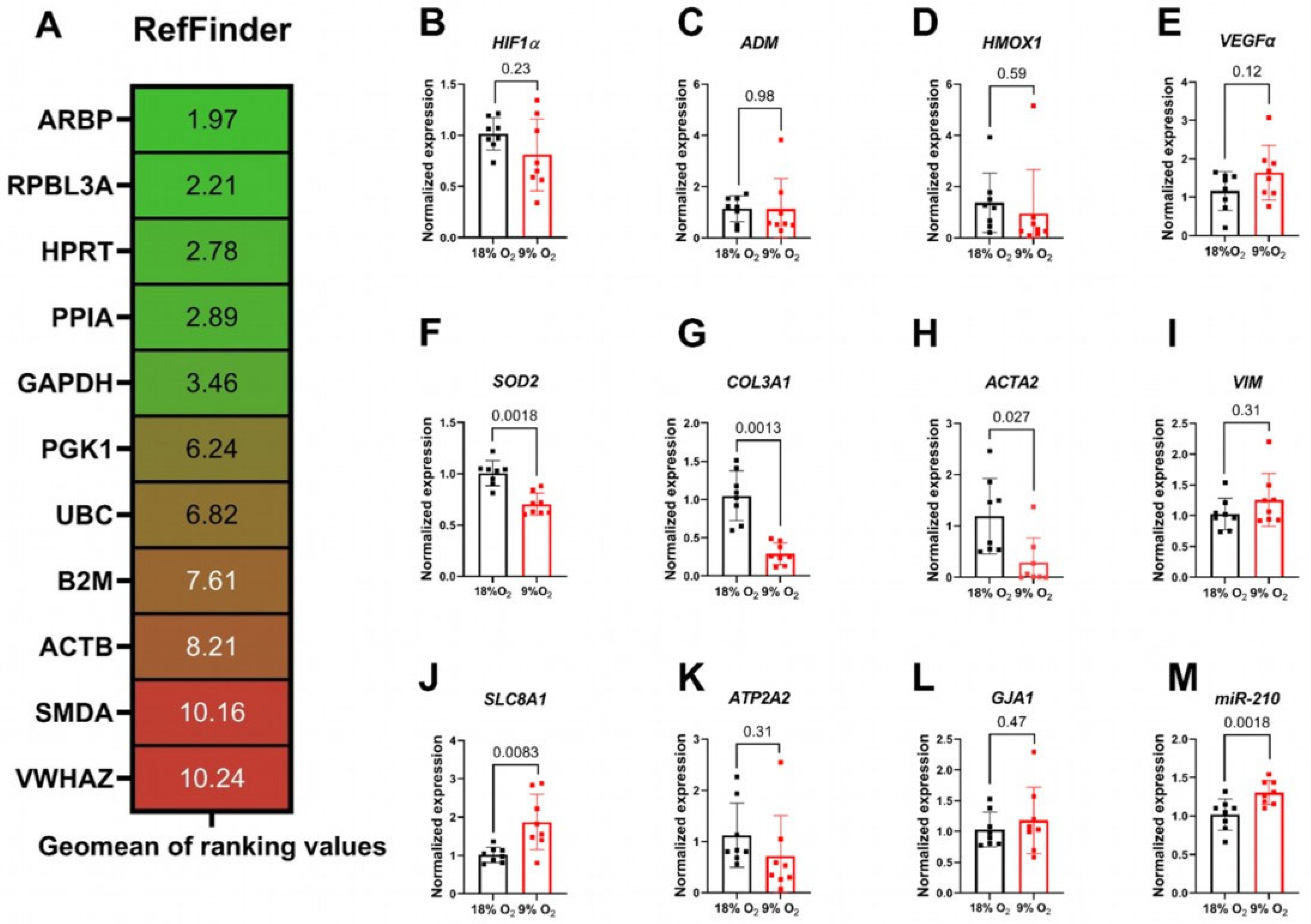
2.3. Expressional Alterations in Hypoxic Rat Myocardial Slices
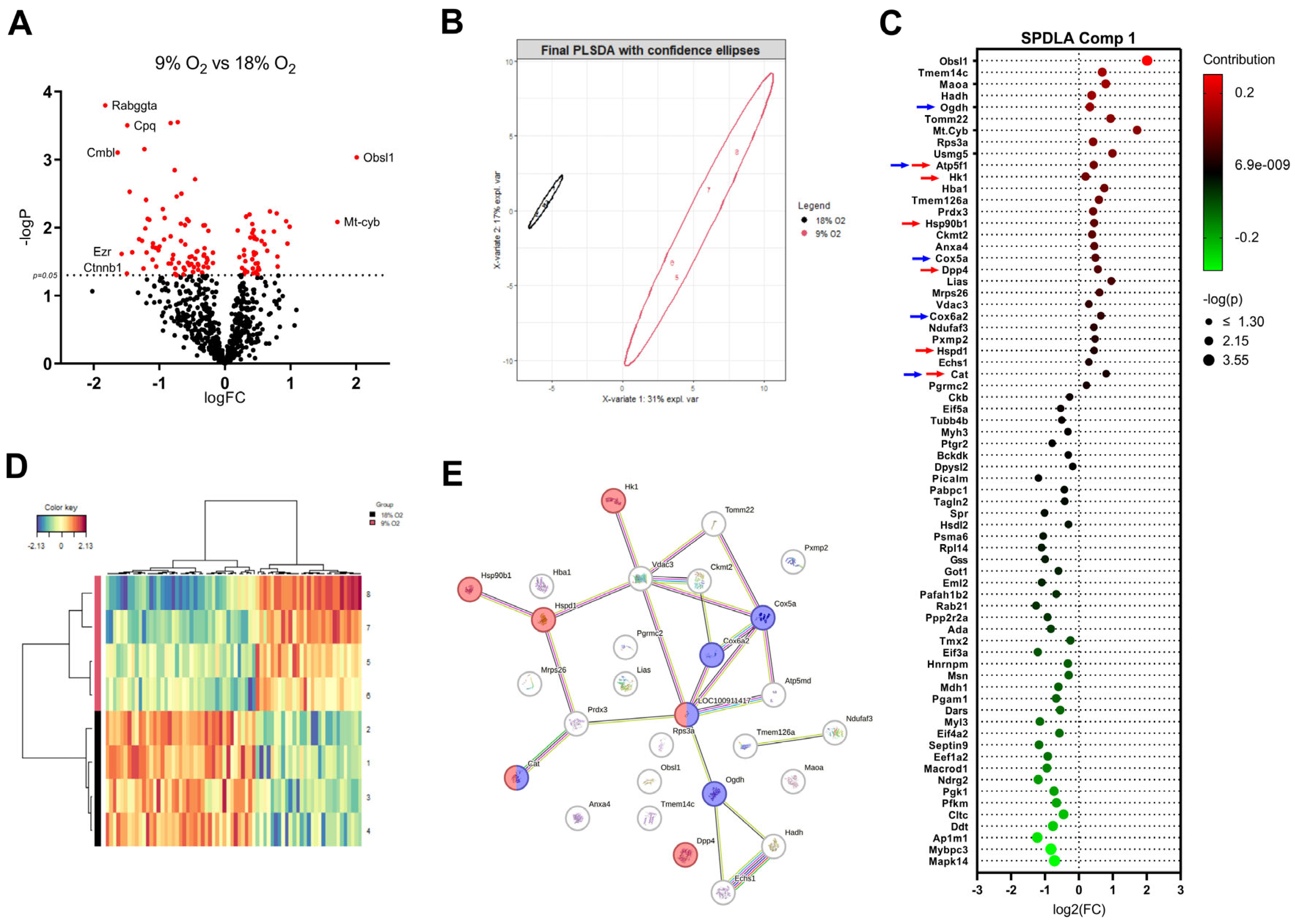
2.4. Proteome Changes in Hypoxic LMS Reveal Alterations in Metabolic Pathways, Oxidative Stress, and Activation of Heat Shock Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Living Myocardial Slice Preparation and Force Measurement
4.2. Ex Vivo Culture of Normoxic and Hypoxic LMS
4.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.4. Histology
4.5. TUNEL Staining
4.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.7. Protein Extraction and MS Analysis of Proteins
4.8. LC-MS Analysis
4.9. PLSDA and STRING Enrichment Analysis of the Proteome Data
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolwicz, S.C.; Purohit, S.; Tian, R. Cardiac Metabolism and Its Interactions With Contraction, Growth, and Survival of Cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Hashim, M.J.; Mustafa, H.; Baniyas, M.Y.; Al Suwaidi, S.K.B.M.; AlKatheeri, R.; Alblooshi, F.M.K.; Almatrooshi, M.E.A.H.; Alzaabi, M.E.H.; Al Darmaki, R.S.; et al. Global Epidemiology of Ischemic Heart Disease: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Adaptive Cardiac Metabolism Under Chronic Hypoxia: Mechanism and Clinical Implications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 625524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.V.; Downey, J.M. Signalling Pathways and Mechanisms of Protection in Pre- and Postconditioning: Historical Perspective and Lessons for the Future. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1913–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavadas, M.A.S.; Cheong, A.; Taylor, C.T. The Regulation of Transcriptional Repression in Hypoxia. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 356, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1: Regulatory Mechanisms and Drug Therapy in Myocardial Infarction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 963, 176277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boštjančič, E.; Zidar, N.; Glavač, D. MicroRNA Microarray Expression Profiling in Human Myocardial Infarction. Dis. Markers 2009, 27, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Huang, M.; Li, Z.; Jia, F.; Ghosh, Z.; Lijkwan, M.A.; Fasanaro, P.; Sun, N.; Wang, X.; Martelli, F.; et al. MicroRNA-210 as a Novel Therapy for Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease. Circulation 2010, 122, S124–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolk, M.V.V.; Meyberg, D.; Deuse, T.; Tang-Quan, K.R.; Robbins, R.C.; Reichenspurner, H.; Schrepfer, S. LAD-Ligation: A Murine Model of Myocardial Infarction. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 32, e1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppe, C.; Ramirez Flores, R.O.; Li, Z.; Hayat, S.; Levinson, R.T.; Liao, X.; Hannani, M.T.; Tanevski, J.; Wünnemann, F.; Nagai, J.S.; et al. Spatial Multi-Omic Map of Human Myocardial Infarction. Nature 2022, 608, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf-Klingebiel, M.; Reboll, M.R.; Klede, S.; Brod, T.; Pich, A.; Polten, F.; Napp, L.C.; Bauersachs, J.; Ganser, A.; Brinkmann, E.; et al. Myeloid-Derived Growth Factor (C19orf10) Mediates Cardiac Repair Following Myocardial Infarction. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.A.; Dendorfer, A.; Thum, T.; Perbellini, F. A Practical Guide for Investigating Cardiac Physiology Using Living Myocardial Slices. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 115, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yotnda, P. Induction and Testing of Hypoxia in Cell Culture. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 54, e2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.J.; Li, Y.; Kerr, C.M.; Yao, J.; Beeson, G.C.; Coyle, R.C.; Chen, X.; Jia, J.; Damon, B.; Wilson, R.; et al. Human Cardiac Organoids for the Modelling of Myocardial Infarction and Drug Cardiotoxicity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Matthys, O.B.; Joy, D.A.; Kauss, M.A.; Natarajan, V.; Lai, M.H.; Turaga, D.; Blair, A.P.; Alexanian, M.; Bruneau, B.G.; et al. Co-Emergence of Cardiac and Gut Tissues Promotes Cardiomyocyte Maturation within Human IPSC-Derived Organoids. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 2137–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racca, A.W.; Klaiman, J.M.; Pioner, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Beck, A.E.; Moussavi-Harami, F.; Bamshad, M.J.; Regnier, M. Contractile Properties of Developing Human Fetal Cardiac Muscle. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 437–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochais, F.; Sturny, R.; Chao, C.-M.; Mesbah, K.; Bennett, M.; Mohun, T.J.; Bellusci, S.; Kelly, R.G. FGF10 Promotes Regional Foetal Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Adult Cardiomyocyte Cell-Cycle Re-Entry. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 104, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.K.; Li, H.J.; Hsueh, Y.C.; Lee, D.S.; Chen, J.H.; Hwang, S.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Shih, E.; Hsieh, P.C.H. Fibroblast Growth Factor-10 Promotes Cardiomyocyte Differentiation from Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e0014414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, N.; Zhou, Z.-N. Effects of Intermittent Hypoxia on Action Potential and Contraction in Non-Ischemic and Ischemic Rat Papillary Muscle. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.A.; Scigliano, M.; Bardi, I.; Ascione, R.; Terracciano, C.M.; Perbellini, F. Preparation of Viable Adult Ventricular Myocardial Slices from Large and Small Mammals. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 2623–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, N.; Haas, J.A.; Xiao, K.; Fuchs, M.; Just, A.; Pich, A.; Perbellini, F.; Werlein, C.; Ius, F.; Ruhparwar, A.; et al. Inhibition of MiR-21: Cardioprotective Effects in Human Failing Myocardium Ex. Vivo. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waleczek, F.J.G.; Sansonetti, M.; Xiao, K.; Jung, M.; Mitzka, S.; Dendorfer, A.; Weber, N.; Perbellini, F.; Thum, T. Chemical and Mechanical Activation of Resident Cardiac Macrophages in the Living Myocardial Slice Ex Vivo Model. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 117, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, N.; Bentele, M.; Waleczek, F.J.G.; Fuchs, M.; Just, A.; Pfanne, A.; Pich, A.; Linke, S.; Neumüller, S.; Stucki-Koch, A.; et al. Ex Vivo Modelling of Cardiac Injury Identifies Ferroptosis-Related Pathways as a Potential Therapeutic Avenue for Translational Medicine. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2024, 196, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Milting, H.; Fein, E.; Reiser, E.; Lu, K.; Seidel, T.; Schinner, C.; Schwarzmayr, T.; Schramm, R.; Tomasi, R.; et al. Long-Term Functional and Structural Preservation of Precision-Cut Human Myocardium under Continuous Electromechanical Stimulation in Vitro. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. RefFinder: A Web-Based Tool for Comprehensively Analyzing and Identifying Reference Genes. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2023, 23, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Takeda, N. The Roles of HIF-1α Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korge, P.; Ping, P.; Weiss, J.N. Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Energized Cardiac Mitochondria During Hypoxia/Reoxygenation. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, C.; Greco, S.; Martelli, F.; Ivan, M. MiR-210: More than a Silent Player in Hypoxia. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccagnini, G.; Greco, S.; Longo, M.; Maimone, B.; Voellenkle, C.; Fuschi, P.; Carrara, M.; Creo, P.; Maselli, D.; Tirone, M.; et al. Correction: Hypoxia-Induced MiR-210 Modulates the Inflammatory Response and Fibrosis upon Acute Ischemia. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, C.H.; Kentish, J.C. Effects of Changes of PH on the Contractile Function of Cardiac Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. -Cell Physiol. 1990, 258, C967–C981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole-Wilson, P.A. Acidosis and Contractility of Heart Muscle. In Ciba Foundation Symposium; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; Volume 87, pp. 58–76. [Google Scholar]
- Solaro, R.J.; Lee, J.A.; Kentish, J.C.; Allen, D.G. Effects of Acidosis on Ventricular Muscle from Adult and Neonatal Rats. Circ. Res. 1988, 63, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, D.G.; Williams, D.A. Slow Amphibian Muscle Fibres Become Less Sensitive to Ca2+ with Increasing Sarcomere Length. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1983, 397, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moissac, D.d.; Gurevich, R.M.; Zheng, H.; Singal, P.K.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. Caspase Activation and Mitochondrial Cytochrome C Release during Hypoxia-Mediated Apoptosis of Adult Ventricular Myocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2000, 32, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benak, D.; Sotakova-Kasparova, D.; Neckar, J.; Kolar, F.; Hlavackova, M. Selection of Optimal Reference Genes for Gene Expression Studies in Chronically Hypoxic Rat Heart. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 461, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, A.; Vennemann, B.; Fracasso, T.; Lutz-Bonengel, S.; Vennemann, M. Apparent versus True Gene Expression Changes of Three Hypoxia-Related Genes in Autopsy Derived Tissue and the Importance of Normalisation. Int. J. Legal Med. 2013, 127, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julian, G.S.; Oliveira, R.W.d.; Tufik, S.; Chagas, J.R. Analysis of the Stability of Housekeeping Gene Expression in the Left Cardiac Ventricle of Rats Submitted to Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2016, 42, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.C.; Carr, C.A.; Yeoh, K.K.; Schofield, C.J.; Davies, K.E.; Clarke, K. Identification of Valid Housekeeping Genes for Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis of Cardiosphere-Derived Cells Preconditioned under Hypoxia or with Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase Inhibitors. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 4857–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Borne, S.W.M.; Diez, J.; Blankesteijn, W.M.; Verjans, J.; Hofstra, L.; Narula, J. Myocardial Remodeling after Infarction: The Role of Myofibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terracciano, C.M.; MacLeod, K.T. Effects of Acidosis on Na+/Ca2+ Exchange and Consequences for Relaxation in Guinea Pig Cardiac Myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 1994, 267, H477–H487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecova, S.; Kubovcakova, L.; Kvetnansky, R.; Kopacek, J.; Pastorekova, S.; Novakova, M.; Knezl, V.; Tarabova, B.; Lacinova, L.; Sulova, Z.; et al. Modulation of Expression of Na + /Ca 2+ Exchanger in Heart of Rat and Mouse under Stress. Acta Physiol. 2007, 190, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, T.G.; Wang, J.-F.; DeAngelis, J.; Amende, I.; Philipson, K.D.; Morgan, J.P. Enhanced Gene Expression of Na + /Ca 2+ Exchanger Attenuates Ischemic and Hypoxic Contractile Dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. -Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H2846–H2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddine, M.; Gehmlich, K. Structural and Signaling Proteins in the Z-Disk and Their Role in Cardiomyopathies. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1143858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Anzai, A.; Katsumata, Y.; Matsuhashi, T.; Ito, K.; Endo, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Takeshima, A.; Shinmura, K.; Shen, W.; et al. Temporal Dynamics of Cardiac Immune Cell Accumulation Following Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Lee, H.; Ryu, H.G.; Singha, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Reo, Y.J.; Jun, Y.W.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, W.J.; Ahn, K.H. A Study on Hypoxia Susceptibility of Organ Tissues by Fluorescence Imaging with a Ratiometric Nitroreductase Probe. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, L.; Zambrano-González, E.; Flores, M.E.; Contreras, M.; Crispín, J.C.; Alemán, G.; Bravo, C.; Armenta-Espinosa, A.; Valdés, V.J.; Tovar, A.; et al. Ethical Considerations in Animal Research: The Principle of 3R’s. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2021, 73, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perbellini, F.; Thum, T. Living Myocardial Slices: A Novel Multicellular Model for Cardiac Translational Research. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2406–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusch, G. Myocardial Ischaemia–Reperfusion Injury and Cardioprotection in Perspective. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, S.; Li, T.; Hegermann, J.; Bounader, K.; Hanke, J.; Meyer, T.; Jannsen-Peters, H.; Haverich, A.; Schmitto, J.D.; Dogan, G. Biocompatibility of an Apical Ring Plug for Left Ventricular Assist Device Explantation: Results of a Feasibility Pre-clinical Study. Artif. Organs 2022, 46, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochim, N.; Gerhard, R.; Just, I.; Pich, A. Impact of Clostridial Glucosylating Toxins on the Proteome of Colonic Cells Determined by Isotope-Coded Protein Labeling and LC-MALDI. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant Enables High Peptide Identification Rates, Individualized p.p.b.-Range Mass Accuracies and Proteome-Wide Protein Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus Computational Platform for Comprehensive Analysis of (Prote)Omics Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing v. 3.6.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 28 December 2024).
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; Lê Cao, K.-A. MixOmics: An R Package for ‘omics Feature Selection and Multiple Data Integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mering, C.V. STRING: A Database of Predicted Functional Associations between Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward 5′-3′ Primer Sequence | Reverse 5′-3′ Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ACTB | CTGAGGAGCACCCTGTGCTG | CCAGAGGCATACAGGGACAA |
| ACTA2 | CATCACCAACTGGGACGACA | TCCGTTAGCAAGGTCGGATG |
| ADM | AATGAAGCTGGTTTCCATCG | TTAGCGCCCACTTATTCCAC |
| ARBP | AAAGGGTCCTGGCTTTGTCT | GCAAATGCAGATGGATCG |
| ATP2A2 | AAGCCACAGAGACTGCTCTCAC | CGCAGAATCTTCCAGGTGCATC |
| B2M | TGTCTCAGTTCCACCCACCT | ATTACATGTCTCGGTCCCAGG |
| COL3A1 | GAAACCCCAGCAAAACAAAA | TATTGGTGGGTGAAACAGCA |
| GAPDH | GAAGGGCTCATGACCACAGT | GGATGCAGGGATGATGTTCT |
| GJA1 | CGCCGGCTTCACTTTCATTA | ATGAAGAGCACTGACAGCCA |
| HIF1A | GCCTCTGAAACTCCAAAGCC | ACGTTCCAATTCCTGCTGCT |
| HMOX1 | CACGCATATACCCGCTACCT | AAGGCGGTCTTAGCCTCTTC |
| HPRT | CAGTCAACGGGGGACATAA | GCTGTACTGCTTGACCAAGG |
| PGK1 | CCAGTCTAGAGCTCCTGGAAGGTAA | ATCCCGATGCAGTAAAGACGAG |
| PPIA | TATCTGCACTGCCAAGACTGAGTG | CTTCTTGCTGGTCTTGCCATTCC |
| RPBL3A | GCGGAGGGGCAGGTTCTA | CGAGACGGGTTGGTGTTCAT |
| SDHA | TACTGTTGCAGCACAGGGAG | CAGTCAGAGCCTTTCACGGT |
| SLC8A1 | AGGTCCATGCTAGAGATCATCC | CCTCTCCTCCTCCTCTTTGC |
| SOD2 | AAAGGAGAGTTGCTGGAGGC | CCTGAACCTTGGACTCCCAC |
| UBC | TCGTACCTTTCTCACCACAGTATCTAG | GAAAACTAAGACACCTCCCCATCA |
| VEGFa | ACGGGCCTCTGAAACCATGA | GCAGCCTGGGACCACTTG |
| VIM | GGGAGGAGAGCAGGATTTCT | TCATCGTGGTGCTGAGAAGT |
| VWHAZ | GATGAAGCCATTGCTGAACTTG | GTCTCCTTGGGTATCCGATGTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waleczek, F.J.G.; Cipriano, G.; Haas, J.A.; Garg, A.; Pfanne, A.; Just, A.; Neumüller, S.; Hegermann, J.; Pich, A.; Radocaj, A.; et al. Prolonged Hypoxia in Rat Living Myocardial Slices Affects Function, Expression, and Structure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010218
Waleczek FJG, Cipriano G, Haas JA, Garg A, Pfanne A, Just A, Neumüller S, Hegermann J, Pich A, Radocaj A, et al. Prolonged Hypoxia in Rat Living Myocardial Slices Affects Function, Expression, and Structure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010218
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaleczek, Florian J. G., Giuseppe Cipriano, Jonas A. Haas, Ankita Garg, Angelika Pfanne, Annette Just, Susanne Neumüller, Jan Hegermann, Andreas Pich, Ante Radocaj, and et al. 2025. "Prolonged Hypoxia in Rat Living Myocardial Slices Affects Function, Expression, and Structure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010218
APA StyleWaleczek, F. J. G., Cipriano, G., Haas, J. A., Garg, A., Pfanne, A., Just, A., Neumüller, S., Hegermann, J., Pich, A., Radocaj, A., Xiao, K., Weber, N., & Thum, T. (2025). Prolonged Hypoxia in Rat Living Myocardial Slices Affects Function, Expression, and Structure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010218






