Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Analytical Methods and Instrumentation
2.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.4. Statistic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PCDD/F and dl-PCB Concentrations and Their TEQs
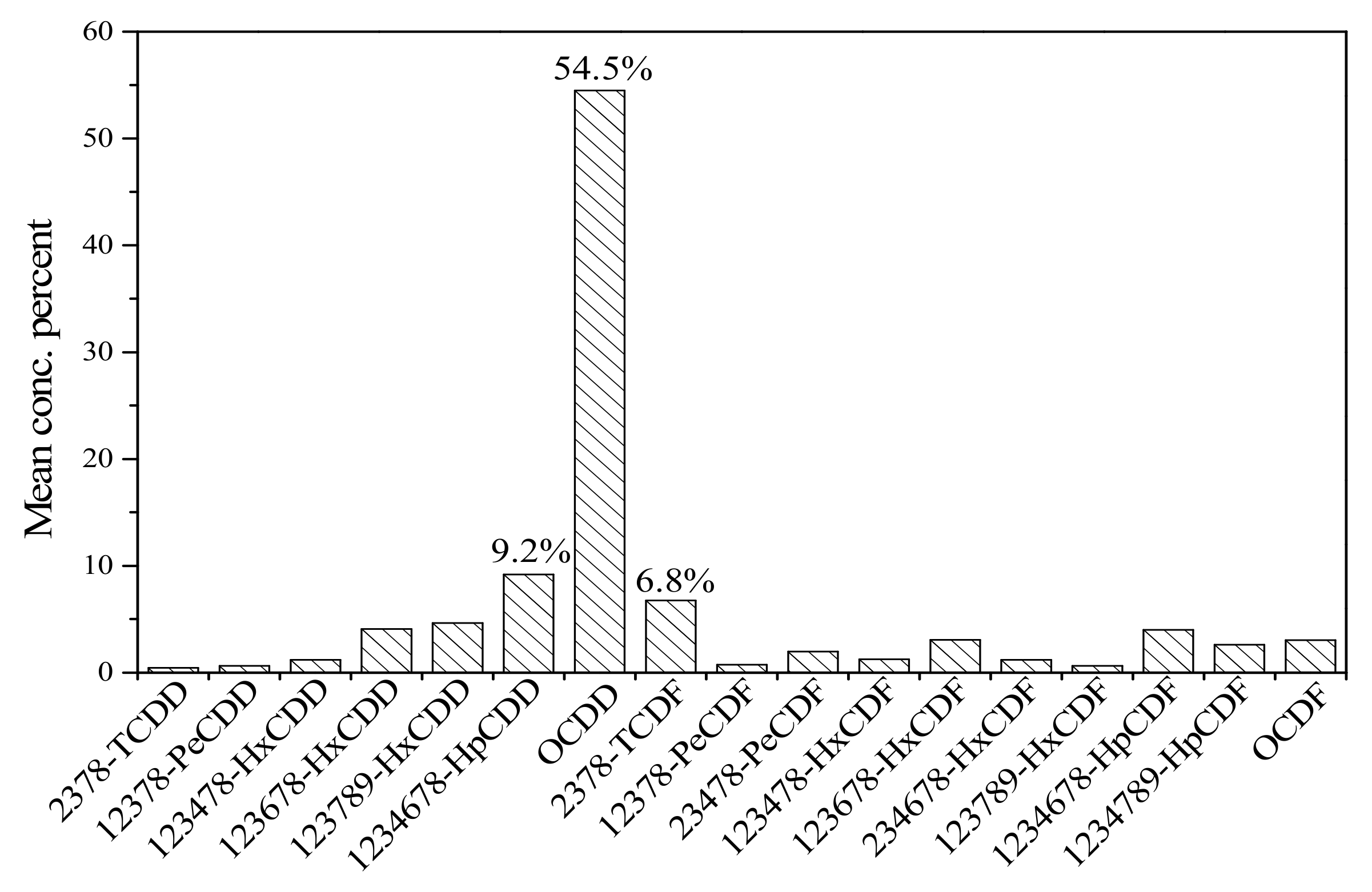
3.2. Congener Profiles of PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs
3.3. Comparison of TEQs of PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs with Those in Other Countries
3.4. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical approval code
References
- Brouwer, A.; Longnecker, M.P.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Cogliano, J.; Kostyniak, P.; Moore, J.; Schantz, S.; Winneke, G. Characterization of potential endocrine-related Health effects at low-dose levels of exposure to PCBs. Environ. Health Perspect. 1999, 107 (Suppl. 4), 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safe, S.H. Comparative toxicology and mechanism of action of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenxofurans. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1986, 26, 371–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogan, W.J.; Ragan, N.B. Evidence of effects of environmental chemicals on the endocrine system in children. Pediatrics 2003, 112 (Suppl. 1), 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Toft, G.; Hagmar, L.; Giwercman, A.; Bonde, J.P. Epidemiological evidence on reproductive effects of persistent organochlorines in humans. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schantz, S.L.; Widholm, J.J.; Rice, D.C. Effects of PCB exposure on neuropsychological function in children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, A.; Jorens, P.; Jacquemyn, Y.; Schepens, P. Distribution of PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in umbilical cord and maternal serum. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 298, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukata, H.; Omori, M.; Osada, H.; Todaka, E.; Mori, C. Necessity to measure PCBs and organochlorine pesticide concentrations in human umbilical cords for fetal exposure assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, G.; Nakano, M.; Nakano, S. Distribution of PCDDs/PCDFs and Co-PCBs in Human Maternal Blood, Cord Blood, Placenta, Milk, and Adipose Tissue: Dioxins Showing High Toxic Equivalency Factor Accumulate in the Placenta. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.; Ribas-Fitó, N.; Cardo, E.; de Muga, M.E.; Marco, E.; Mazón, C.; Verdú, A.; Grimalt, J.O.; Sunyer, J. Levels of hexachlorobenzene and other organochlorine compounds in cord blood: Exposure across placenta. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraczewska, K.; Lulek, J.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Kaluba-Skotarczak, A.; Drews, K.; Schepens, P. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls, organochlorine pesticides and poly-brominated diphenyl ethers in human umbilical cord serum, maternal serum and milk from Wielkopolska region, Poland. Sci Total Environ. 2006, 372, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schecter, A.; Kassis, I.; Papke, O. Partitioning of dioxins, dibenzofurans, and coplanar PCBS in blood, milk, adiposetissue, placenta and cord blood from five American women. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Lin, L.-Y.; Chou, W.-L.; Chang, L.W. Infant exposure to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and biphenyls (PCDD/Fs, PCBs)-correlation between prenatal and postnatal exposure. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 1459–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualini, J.R. Enzymes involved in the formation and transformation of steroid hormones in the fetal and placental compartments. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 97, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Päpke, O. PCDD/PCDF: Human background data for Germany, a 10-year experience. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. 2), 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.M.; Xu, F.L.; Dawson, R.; Cao, J.; Liu, W.X.; Li, B.G.; Shen, W.R.; Zhang, W.J.; Qin, B.P.; Sun, R. Residues of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers and their distribution characteristics in soils in the Tianjin area, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 46, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ba, Z.C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and biphenyls pollution in sediments from the Haihe River and Dagu Drainage River in Tianjin City, China. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappe, C.; Kjeller, L.O.; Kulp, S.E.; Wit, C.D.; Hasselsten, I.; Palm, O. Levels, profile and pattern of PCDDs and PCDFs in samples related to the production and use of chlorine. Chemosphere 1991, 23, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.C.; Wang, K.O.; Kang, J.X.; Zhao, L.W. Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in pentachlorophenol and sodium pentachlorophenate. Environ. Chem. 1995, 14, 317–321. [Google Scholar]
- Coenraads, P.J.; Olie, K.; Tang, N.J. Blood lipid concentrations of dioxins and dibenzofurans causing chloracne. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 141, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Yao, L.; Self, S.G.; Sun, X.; Tang, N. Levels of PCDDs, PCDFs and dl-PCBs in the blood of childbearing-aged women living in the vicinity of a chemical plant in Tianjin: A primary study. Chemosphere 2015, 118, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1613 Revision B: Tetra-Through Octachlorinated Dioxins and Furans by Isotope Dilution HRGC/HRMS, EPA 621-B-94-005; United States Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1668, Revision C: Chlorinated Biphenyl Congeners in Water, Soil, Sediment, Biosolids and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS, EPA820-R-10-005; Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Thomsen, C.; Bavel, B.V.; Neels, H. Evaluation of total lipids using enzymatic methods for the normalization of persistent organic pollutant levels in serum. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Hakansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittsiepe, J.; Schrey, P.; Ewers, U.; Wilhelm, M.; Selenka, F. Decrease of PCDD/F levels in human blood-trend analysis for the German population, 1991–1996. Environ. Res. 2000, 83, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.H.; Bao, Z.C.; Zhang, B.; Xu, X.B. Polychlorinated dibenzo-pdioxins and dibenzofurans in paper making from a pulp mill in China. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, W.; Lv, P.; Zhang, B.; Su, G.; Gao, L.; Xiao, K. A preliminary investigation of unintentional POP emissions from thermal wire reclamation at industrial scrap metal recycling parks in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.-D.; Tsai, C.-L.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-W.; Weng, Y.-M.; Chang, M.B. PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs concentrations in water samples of Taiwan. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.L.; Huang, J.; Hu, H.Y.; Yu, G.; Li, F.S. Occurrence of dissolved polychlorinated biphenyls and organicchlorinated pesticides in the surface water of Haihe River and Bohaiay, China. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2007, 28, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Yan, Z.G.; Bai, L.P.; Li, F.S. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in soils surrounding the Tanggu Chemical Industrial District of Tianjin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 3366–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljarrat, E.; De La Cal, A.; Larrazabal, D.; Fabrellas, B.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R.; Borrull, F.; Marce, R.M.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence of polybrominated diphenylethers, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans and biphenyls in coastal sediments from Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 136, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wan, Y.; Shao, B.; Jin, X.; An, W.; Jin, F.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Sugisaki, M. Occurrence of trace organic contaminants in Bohai Bay and its adjacent Nanpaiwu River, North China. Mar. Chem. 2005, 95, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments and aquatic organisms from the Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIP China. The People’s Republic of China National Implementation Plan for the Stockholm Convention of Persistent Organic Pollutants. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/sites/default/files/epd/english/international_conventions/pops/files/China_NIP_En.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Jin, J.; Li, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Polychlorinated biphenyl concentrations in pooled serum from people in different age groups from five Chinese cities. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coakley, J.; Bridgen, P.; Bates, M.N.; Douwes, J. Chlorinated persistent organic pollutants in serum of New Zealand adults, 2011–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Ito, S.; Yuasa, M.; Yoshioka, E.; Miyashita, C.; Araki, A.; Sasaki, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Kajiwara, J.; Hori, T.; et al. Association of prenatal exposure to PCDD/Fs and PCBs with maternal and infant thyroid hormones: The Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children’s Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, M.; Mari, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Monitoring dioxins and furans in plasma of individuals living near a hazardous waste incinerator: Temporal trend after 20 years. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Vanderpuije, P.; Megson, D.; Jobste, K.; Jones, G.R.; Reiner, E.; Sandau, C.D.; Clarke, E.; Adu-Kumi, S.; Gardella, J.A., Jr. Background levels of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (dlPCBs), polychlorinated, polybrominated and mixed halogenated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs, PBDD/Fs & PXDD/Fs) in sera of pregnant women in Accra, Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.-F.; Lee, C.-C.; Su, H.-J.; Chen, H.-L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Liao, P.-C. Evaluation of background persistent organic pollutant levels in human from Taiwan: Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dario, C.; Raffaella, S.; Pier Alberto, B. Blood levels of dioxins, furans, dioxin-like PCBs, and TEQs in general populations: A review, 1989–2010. Environ. Int. 2012, 44, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Boda, H.; Nghi, T.N.; Nishijo, M.; Thao, P.N.; Tai, P.T.; Van Luong, H.; Anh, T.H.; Morikawa, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Nishijo, H. Prenatal dioxin exposure estimated from dioxins in breast milk and sex hormone levels in umbilical cord blood in Vietnamese newborn infants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivik, K.; Sweetman, A.; Pacyna, J.M.; Jones, K.C. Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners—A mass balance approach 3. An update. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovancová, J.; Čonka, K.; Fabišiková, A.; Sejáková, Z.S.; Dömötörová, M.; Drobná, B.; Wimmerová, S. PCDD/PCDF, dl-PCB and PBDE serum levels of Slovak general population. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrio-Baldassarri, L.; Abate, V.; Battistelli, C.L.; Carasi, S.; Casella, M.; Iacovella, N.; Indelicato, A.; La Rocca, C.; Scarcella, C. Silvia Alivernini. PCDD/F and PCB in human serum of differently exposed population groups of an Italian city. Chemosphere 2008, 73, S228–S234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakind, J.S.; Hays, S.M.; Aylward, L.L.; Naiman, D.Q. Perspective on serum dioxin levels in the United States: An evaluation of the NHANES data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylward, L.L.; LaKind, J.S.; Hays, S.M. Derivation of biomonitoring equivalent (BE) values for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and related compounds: A screening tool for interpretation of biomonitoring data in a risk assessment context. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2008, 71, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Compounds | DL | DR (%) | Min. | Median | Max. | Mean | Mean TEQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∑PCDD/Fs | 100.0 | 43.0 | 227 | 1335 | 336 | 14.0 | |
| ∑PCDDs | 100.0 | 9.76 | 175 | 1234 | 252 | 7.34 | |
| 2,3,7,8-TCDD | 0.24 | 20.8 | ND | ND | 14.0 | 1.49 | 1.49 |
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD | 0.36 | 36.3 | ND | ND | 18.7 | 2.14 | 2.14 |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDD | 0.12 | 37.5 | ND | ND | 33.8 | 4.08 | 0.41 |
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDD | 0.12 | 62.5 | ND | 3.99 | 164 | 13.8 | 1.38 |
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD | 0.12 | 54.2 | ND | 2.95 | 150 | 15.6 | 1.56 |
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDD | 0.24 | 70.8 | ND | 5.28 | 470 | 30.9 | 0.31 |
| OCDD | 0.20 | 91.7 | ND | 141 | 1200 | 183 | 0.06 |
| ∑PCDFs | 100.0 | 17.6 | 48.5 | 296 | 85.1 | 6.62 | |
| 2,3,7,8-TCDF | 0.20 | 95.8 | ND | 16.4 | 75.5 | 22.7 | 2.27 |
| 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDF | 0.39 | 33,3 | ND | ND | 35.8 | 2.45 | 0.07 |
| 2,3,4,7,8-PeCDF | 0.36 | 62.5 | ND | 2.18 | 46.8 | 6.60 | 1.98 |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8-HxCDF | 0.24 | 54.2 | ND | 2.20 | 13.9 | 4.23 | 0.42 |
| 1,2,3,6,7,8-HxCDF | 0.20 | 70.8 | ND | 4.05 | 111 | 10.4 | 1.04 |
| 2,3,4,6,7,8-HxCDF | 0.16 | 66.7 | ND | 1.03 | 27.8 | 3.98 | 0.40 |
| 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDF | 0.20 | 50.0 | ND | ND | 17.9 | 2.13 | 0.21 |
| 1,2,3,4,6,7,8-HpCDF | 0.20 | 29.2 | ND | 3.99 | 111 | 13.5 | 0.14 |
| 1,2,3,4,7,8,9-HpCDF | 0.24 | 75.0 | ND | ND | 171 | 8.84 | 0.09 |
| OCDF | 0.16 | 29.2 | ND | ND | 108 | 10.2 | 0.003 |
| ∑dl-PCBs | 100.0 | 330 | 1323 | 7908 | 2700 | 2.14 | |
| ∑non-ortho PCBs | 100.0 | 6.10 | 42.7 | 963 | 240 | 2.06 | |
| PCB 77 | 0.63 | 91.7 | ND | 33.2 | 880 | 207 | 0.02 |
| PCB 81 | 0.55 | 58.3 | ND | 5.34 | 35.5 | 11.1 | 0.003 |
| PCB 126 | 0.87 | 66.7 | ND | 16.1 | 75.0 | 19.6 | 1.96 |
| PCB 169 | 1.18 | 37.5 | ND | ND | 17.9 | 2.72 | 0.08 |
| ∑mono-ortho PCBs | 100.0 | 303 | 1226 | 6944 | 2460 | 0.07 | |
| PCB 105 | 0.95 | 95.8 | ND | 170 | 2045 | 568. | 0.02 |
| PCB 114 | 0.67 | 100.0 | 10.6 | 49.6 | 225 | 79.3 | 0.002 |
| PCB 118 | 0.75 | 100.0 | 138 | 585 | 3778 | 1311 | 0.04 |
| PCB 123 | 0.79 | 95.8 | ND | 18.7 | 94.8 | 28.8 | 0.0009 |
| PCB 156 | 1.18 | 100.0 | 31.0 | 201 | 604 | 265 | 0.08 |
| PCB 157 | 1.18 | 100.0 | 17.6 | 69.1 | 217 | 79.5 | 0.002 |
| PCB 167 | 1.07 | 100.0 | 13.0 | 66.9 | 217 | 91.3 | 0.003 |
| PCB 189 | 1.22 | 79.2 | ND | 19.4 | 113 | 37.8 | 0.001 |
| ∑(PCDD/Fs + dl-PCBs) | 100.0 | 476 | 1842 | 8307 | 3037 | 16.1 |
| OCDD | PCB 105 | PCB 114 | PCB 118 | PCB 123 | PCB 126 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCDD | 1 | |||||
| PCB 105 | 0.61 ** | 1 | ||||
| PCB 114 | 0.52 ** | 0.89 *** | 1 | |||
| PCB 118 | 0.56 ** | 0.98 *** | 0.90 *** | 1 | ||
| PCB 123 | 0.54 ** | 0.72 *** | 0.74 *** | 0.74 *** | 1 | |
| PCB 126 | 0.59 ** | 0.50 * | 0.48 * | 0.48 * | 0.41* | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Xiong, N.; Wen, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122178
Yu D, Liu X, Liu X, Cao W, Zhang X, Tian H, Wang J, Xiong N, Wen S, Wu Y, et al. Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Dezhong, Xiaofang Liu, Xiao Liu, Wencheng Cao, Xiaotian Zhang, Haoyuan Tian, Jin Wang, Nan Xiong, Sheng Wen, Yongning Wu, and et al. 2019. "Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122178
APA StyleYu, D., Liu, X., Liu, X., Cao, W., Zhang, X., Tian, H., Wang, J., Xiong, N., Wen, S., Wu, Y., Sun, X., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-Dioxins, Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans, and Dioxin-Like Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Umbilical Cord Serum from Pregnant Women Living Near a Chemical Plant in Tianjin, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122178




