Evaluation of NAPLES Prognostic Score to Predict Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
1. Introduction
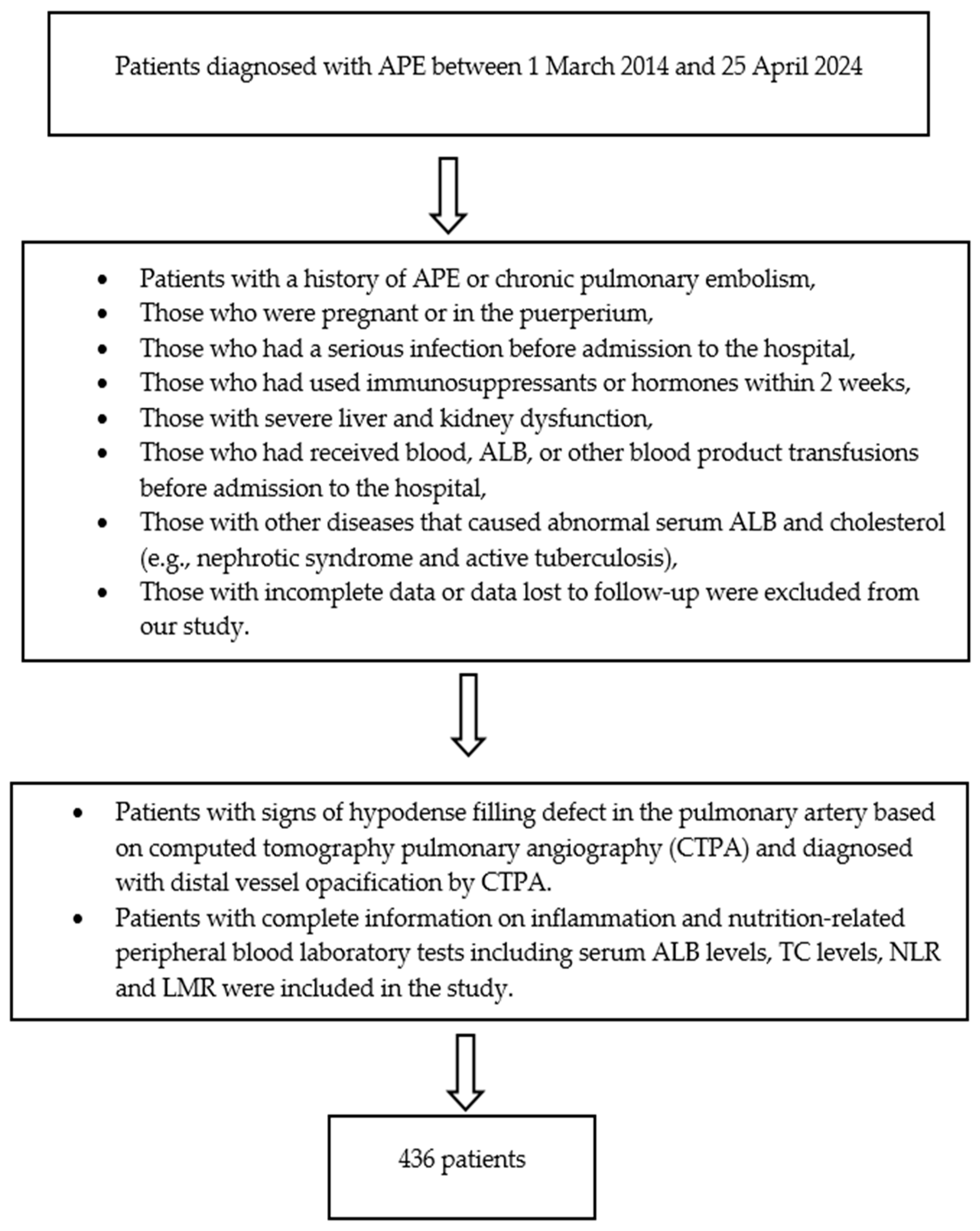
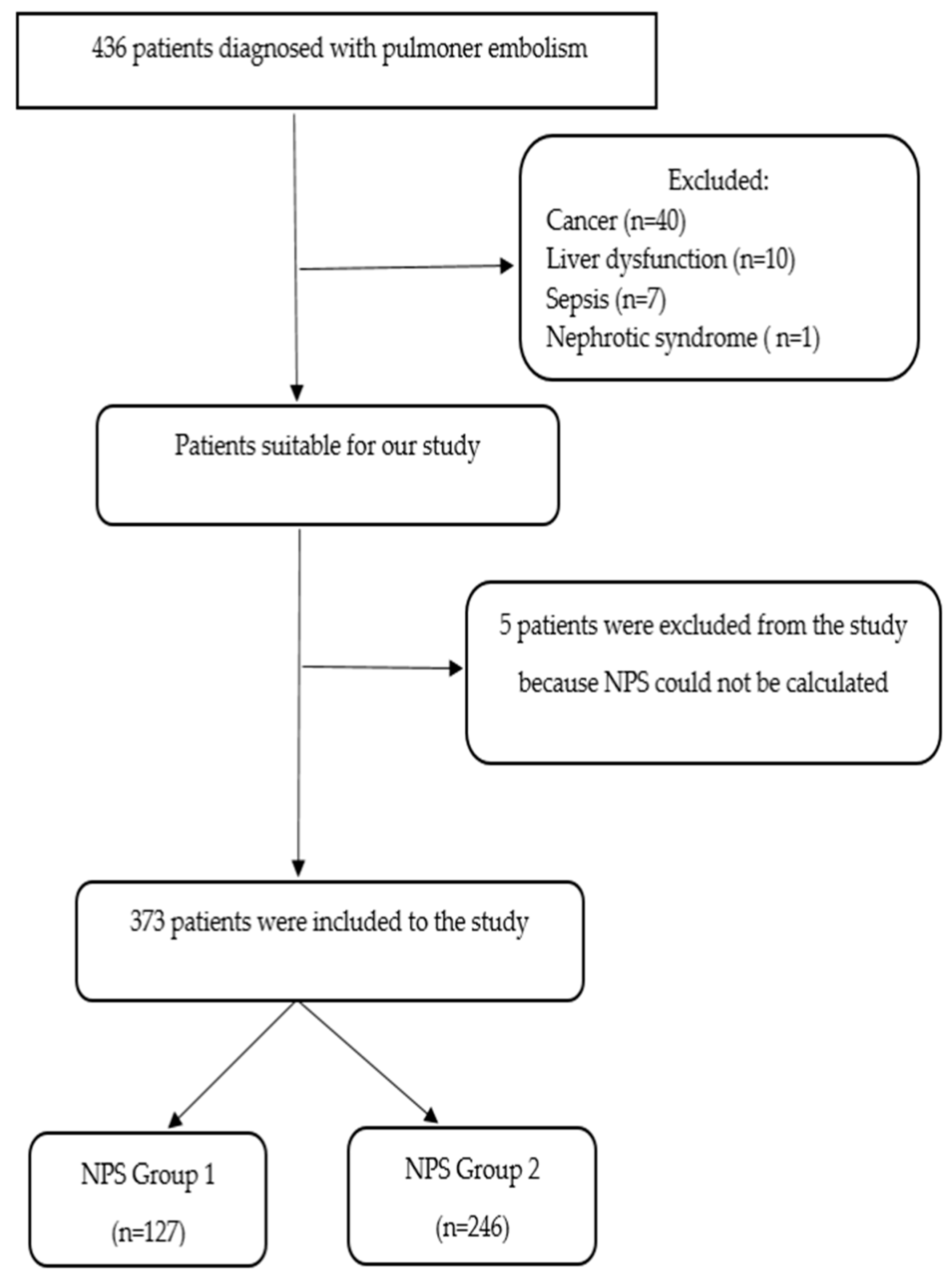
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagamalesh, U.M.; Prakash, V.S.; Naidu, K.C.K.; Sarthak, S.; Hegde, A.V.; Abhinay, T. Acute pulmonary thromboembolism: Epidemiology, predictors, and long-term outcome—A single center experience. Indian Heart J. 2017, 69, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, L. Acute pulmonary embolism. Clin. Med. J. R. Coll. Physicians Lond. 2019, 19, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Heit, J.A. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in the community. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2008, 28, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.; Brailovsky, Y.; Fareed, J.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Iqbal, O.; Darki, A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict all-cause mortality in acute pulmonary embolism. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost 2020, 26, 1076029619900549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Lin, S.; Cao, C. A novel prognostic prediction indicator in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: Naples prognostic score. Thromb. J. 2023, 21, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pay, L.; Çetin, T.; Keskin, K.; Dereli, Ş.; Tezen, O.; Yumurtaş, A.; Kolak, Z.; Eren, S.; Şaylık, F.; Çınar, T.; et al. Evaluation of Naples prognostic score to predict long-term mortality in patients with pulmonary embolism. Biomark. Med. 2024, 18, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galizia, G.; Lieto, E.; Auricchio, A.; Cardella, F.; Mabilia, A.; Podzemny, V.; Castellano, P.; Orditura, M.; Napolitano, V. Naples Prognostic Score, based on nutritional and inflammatory status, is an independent predictor of long-term outcome in patients undergoing surgery for colorectal cancer. Dis. Colon Rectum 2017, 60, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Yan, L.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, N.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. The Naples prognostic score serves as a predictor and prognostic indicator for cancer survivors in the community. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, A.; Fukuoka, T.; Shibutani, M.; Kasashima, H.; Kitayama, K.; Ohira, M.; Maeada, K. Prognostic significance of the Naples prognostic score in colorectal cancer patients undergoing curative resection: A propensity score matching analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Deng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, F.; Xue, Y.; Qin, L.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Modified Naples prognostic score for evaluating the prognosis of patients with obstructive colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Duan, G. Clinical significance of preoperative Naples prognostic score in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221129447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Lu, W.; Cheng, J.; Dai, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, D.D.; Fu, T.W.; Ye, T.W.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, C.W.; et al. Naples Prognostic Score is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients Undergoing Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xie, C.; Ren, K.; Xu, X. Prognostic Value of the Naples Prognostic Score in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancers: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2023, 75, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Huang, Q.; Yu, X.; Qiao, K.; Wu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y. Naples score: A novel prognostic biomarker for breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 16097–16110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Cong, R.; Wang, Y.; Kong, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, Q.; Ma, X. Naples prognostic score is an independent prognostic factor in patients with operable endometrial cancer: Results from a retrospective cohort study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 160, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N.; Yamada, S.; Sonohara, F.; Takami, H.; Hayashi, M.; Kanda, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Tanaka, C.; Nakayama, G.; Koike, M.; et al. Clinical Implications of Naples Prognostic Score in Patients with Resected Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulturk, I.; Yılmaz, M.; Tacar, S.Y.; Bakkaloglu, O.K.; Sonmezoz, G.B.; Erdal, G.S.; Ozmen, A.; Tural, D. Naples prognostic score may predict overall survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2024, 20, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, M.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Preoperative Naples prognostic score is a reliable prognostic indicator for newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Sec. Neuro-Oncol. Neurosurg. Oncol. 2022, 12, 775430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shen, W.; Xie, Z. The Osaka prognostic score and Naples prognostic score: Novel biomarkers for predicting short-term outcomes after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birdal, O.; Pay, L.; Aksakal, E.; Yumurtaş, A.Ç.; Çinier, G.; Yücel, E.; Tanboğa, İ.H.; Karagöz, A.; Oduncu, V. Naples prognostic score and prediction of left ventricular ejection fraction in STEMI patients. Angiology 2024, 75, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arugaslan, E. Naples Prognostic Score and Clinical Outcomes in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients. SiSli Etfal Hastan. Tip Bul./Med. Bull. Sisli Hosp. 2023, 57, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Lin, S.; Yu, H.; Liu, F.; Huang, W.; Cao, C. Naples prognostic score as a novel prognostic prediction indicator in adult asthma patients: A population-based study. World Allergy Organ. J. 2023, 16, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.W. Association of naples prognostic score and lung health: A population-based study. Respir. Med. 2024, 232, 107751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toosi, M.S.; Merlino, J.D.; Leeper, K.V. Prognostic Value of the Shock Index Along With Transthoracic Echocardiography in Risk Stratification of Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökçek, K.; Gökçek, A.; Demir, A.; Yıldırım, B.; Acar, E.; Alataş, Ö.D. In-hospital mortality of acute pulmonary embolism: Predictive value of shock index, modified shock index, and age shock index scores. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| NPS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cutoff Values | Partial Points | |
| Serum ALB (g/L) | ALB ≥ 40 g/L ALB < 40 g/L | 0 point 1 point |
| TC (mg/dL) | TC > 180 mg/dL TC ≤ 180 mg/dL | 0 point 1 point |
| NLR | NLR ≤ 2.96 NLR > 2.96 | 0 point 1 point |
| LMR | LMR ≥ 4.44 LMR < 4.44 | 0 point 1 point |
| Shock Index (SI) Name Variation | Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| SI | HR/SBP | |
| Modified SI (MSI) | HR/MAP |
|
| Age SI | Age × (HR/SBP) |
|
| Group 1 NPS 0–2 | Group 2 NPS 3–4 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 58.58 ± 14.95 | 64.34 ± 16.07 | <0.001 |
| Clinical hospital stay | 7.32 ± 5.17 | 7.92 ± 6.36 | 0.608 |
| Pulse | 94.14 ± 17.57 | 100.79 ± 20.70 | 0.002 |
| SBP level | 122.06 ± 16.57 | 119.19 ± 19.95 | 0.116 |
| Average blood pressure level | 85.31 ± 11.98 | 85.47 ± 14.51 | 0.911 |
| SI | 0.79 ± 0.23 | 0.92 ± 0.66 | 0.044 |
| Modified SI | 1.14 ± 0.33 | 1.24 ± 0.46 | 0.026 |
| Age-related SI | 47.08 ± 21.74 | 58.70 ± 42.93 | 0.004 |
| AST | 33.86 ± 82.78 | 60.63 ± 141.76 | <0.001 |
| CRP | 29.19 ± 57.67 | 41.29 ± 62.60 | 0.011 |
| Thrombocyte | 241.35 ± 109.93 | 241.80 ± 108.02 | 0.935 |
| Hematocrit | 40.50 ± 6.22 | 37.76 ± 6.86 | <0.001 |
| D-dimer | 965.23 ± 2021.16 | 932.28 ± 2961.40 | 0.170 |
| Lactate | 1.66 ± 1.88 | 1.95 ± 1.75 | 0.003 |
| Pro-BNP | 6681.71 ± 12,700.86 | 5626.69 ± 8311.57 | 0.795 |
| Right ventricular diameter | 3.59 ± 0.53 | 3.82 ± 0.61 | <0.001 |
| Right ventricle/left ventricle ratio | 0.79 ± 0.17 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.027 |
| Pulmonary artery diameter | 2.06 ± 0.41 | 2.21 ± 0.54 | 0.008 |
| PAPS | 34.42 ± 17.03 | 37.59 ± 17.03 | 0.018 |
| Group 1 NPS 0–2 | Group 2 NPS 3–4 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-month mortality | |||
| No | 123 (96.8) | 217 (88.2) | 0.005 |
| Yes | 4 (3.1) | 29 (11.7) | |
| Mortality in hospital | |||
| No | 123 (96.8) | 223 (90.6) | 0.029 |
| Yes | 4 (3.1) | 23 (9.3) | |
| Location of involvement on CTPA | |||
| Main pulmonary artery | 37 (29.1) | 83 (33.7) | 0.660 |
| Segmental involvement | 80 (62.9) | 144 (58.5) | |
| Subsegmental involvement | 10 (7.8) | 19 (7.7) | |
| Heart failure | |||
| Yes | 8 (6.3) | 36 (14.6) | 0.018 |
| No | 119 (93.7) | 210 (85.3) | |
| Group 1 NPS 0–2 | Group 2 NPS 3–4 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DVT existence | |||
| Yes | 45 (35.4) | 102 (41.4) | 0.259 |
| No | 82 (64.5) | 144 (58.5) | |
| Doppler not checked | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Low-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 76 (59.8) | 87 (35.3) | <0.001 |
| No | 51 (40.1) | 159 (64.6) | |
| High-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 3 (2.3) | 11 (4.4) | 0.310 |
| No | 124 (97.6) | 235 (95.5) | |
| Intermediate-low-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 29 (22.8) | 88 (35.7) | 0.011 |
| No | 98 (77.1) | 158 (64.2) | |
| Intermediate-high-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 20 (15.7) | 60 (24.3) | 0.054 |
| No | 107 (84.2) | 186 (75.6) | |
| Thrombolytic administration | |||
| Yes | 6 (4.7) | 24 (9.7) | 0.090 |
| No | 121 (95.2) | 222 (90.2) | |
| Additional diseases | |||
| Absent | 56 (44.0) | 100 (40.6) | 0.003 |
| COPD | 4 (3.1) | 19 (7.7) | |
| CAD/HF | 11 (8.6) | 34 (13.8) | |
| Immobilization | 18 (14.1) | 48 (19.5) | |
| Fracture | 7 (5.5) | 12 (4.8) | |
| Obesity | 8 (6.3) | 1 (0.4) | |
| OC use | 3 (2.3) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Others | 20 (15.7) | 31 (12.6) | |
| (a) | |||
| Total n/Censored % | Mean | p Value | |
| NPS | |||
| NPS 0–2 | 127 (96.9) | 4669.4 | 0.006 |
| NPS 3–4 | 246 (88.2) | 4359.4 | |
| CRF | |||
| Yes | 32 (75.0) | 3208.8 | <0.001 |
| No | 341 (92.7) | 4578.5 | |
| ALB (g/L) | |||
| ≥40 g/L | 84 (98.8) | 4766.6 | 0.006 |
| <40 g/L | 289 (88.9) | 4394.5 | |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | |||
| ≥180 mg/dL | 176 (96.0) | 4482.0 | 0.002 |
| <180 mg/dL | 197 (86.8) | 4290.1 | |
| AST (U/L) | |||
| ≤50 U/L | 309 (93.2) | 4560.3 | 0.001 |
| >50 U/L | 64 (81.3) | 4015.3 | |
| CRP (mg/L) | |||
| <5 mg/L | 117 (95.7) | 4650.2 | 0.036 |
| ≥5 mg/L | 255 (89.0) | 4399.0 | |
| Neutrophil (103/uL) | |||
| <6.96 103/uL | 174 (94.3) | 4578.9 | 0.050 |
| ≥6.96 103/uL | 199 (88.4) | 4370.6 | |
| Thrombocyte (103/µL) | |||
| 0–149 103/µL | 53 (86.8) | 4288.2 | 0.056 |
| 150–365 103/µL | 286 (93.0) | 4550.5 | |
| ≥366 103/µL | 34 (82.4) | 3119.6 | |
| Troponin | |||
| Normal | 211 (97.2) | 4799.7 | <0.001 |
| High | 162 (83.3) | 3685.2 | |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | |||
| <1.6 mmol/L | 213 (97.2) | 4800.7 | <0.001 |
| ≥1.6 mmol/L | 160 (83.1) | 3246.7 | |
| sPESI score | |||
| 0 | 155 (98.7) | 4828.2 | <0.001 |
| 1 | 218 (85.8) | 4239.6 | |
| Pulse | |||
| <100 per min | 207 (94.7) | 4632.5 | 0.006 |
| ≥100 per min | 166 (86.7) | 4286.7 | |
| SBP (mmHg) | |||
| <90 mmHg | 22 (68.2) | 2198.2 | <0.001 |
| ≥90 mmHg | 351 (92.6) | 4574.8 | |
| DBP (mmHg) | |||
| <60 mmHg | 84 (84.5) | 3788.0 | 0.012 |
| ≥60 mmHg | 289 (93.1) | 4598.9 | |
| (b) | |||
| Total n/Censored % | Mean | p Value | |
| SI | |||
| ≤0.7 | 141 (97.2) | 4752.9 | 0.002 |
| >0.7 | 232 (87.5) | 4324.1 | |
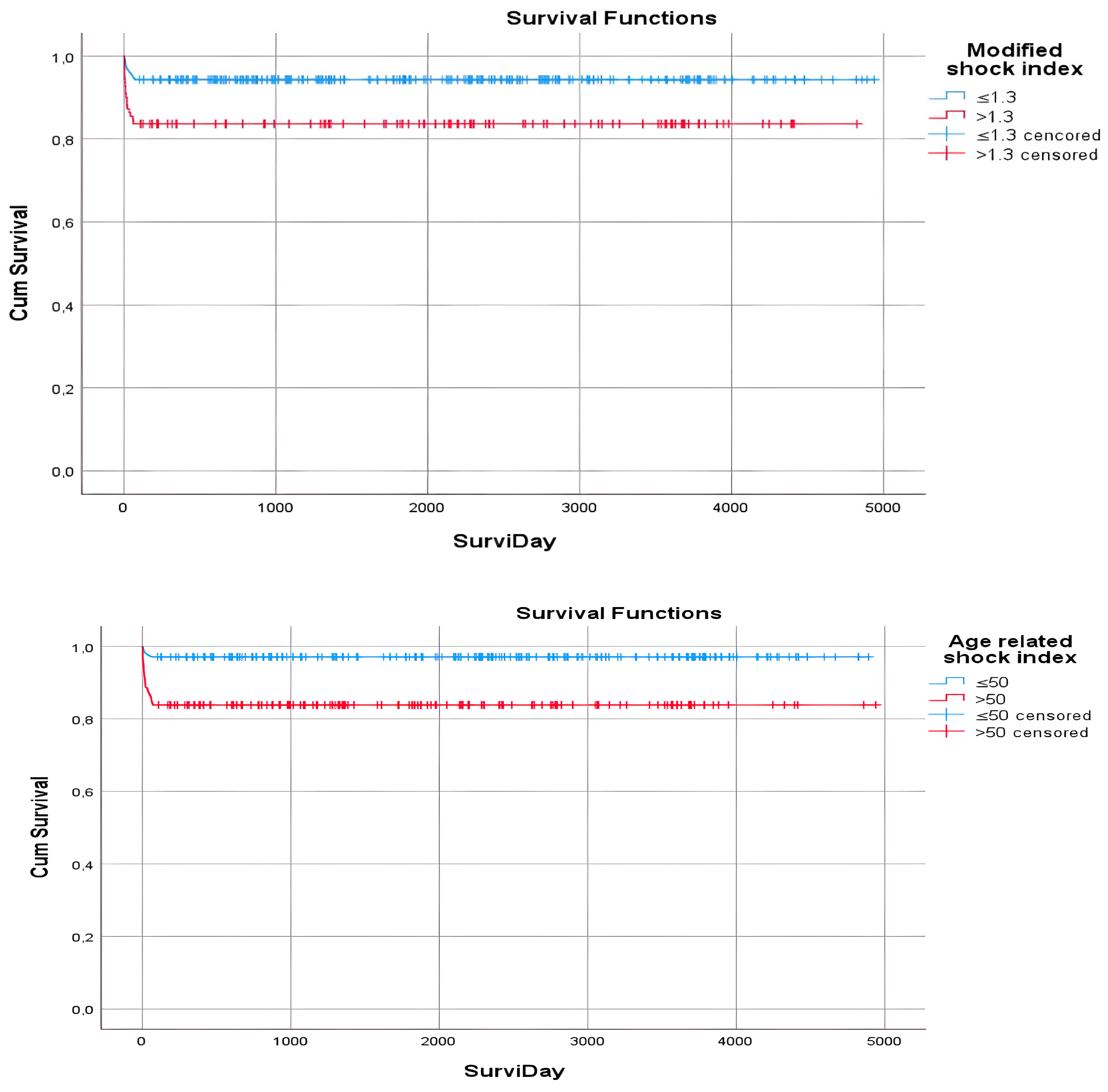
| Modified SI | |||
| ≤1.3 | 263 (94.3) | 4658.7 | 0.001 |
| >1.3 | 110 (83.6) | 4037.4 | |
| Age-related SI | |||
| ≤50 | 206 (97.1) | 4749.1 | <0.001 |
| >50 | 167 (83.8) | 4143.9 | |
| Right ventricular value | |||
| ≤4 cm | 269 (94.4) | 4665.1 | <0.001 |
| >4 cm | 104 (82.7) | 3651.7 | |
| Right ventricle/left ventricle ratio | |||
| <0.9 cm | 247 (94.3) | 4660.6 | 0.002 |
| ≥0.9 cm | 126 (84.9) | 3749.8 | |
| Aortic diameter value | |||
| ≤3.7 cm | 288 (93.8) | 4631.8 | 0.001 |
| >3.7 cm | 85 (82.4) | 3637.2 | |
| Pulmonary artery diameter value | |||
| ≤2.1 cm | 264 (95.1) | 4697.2 | <0.001 |
| >2.1 cm | 108 (81.5) | 3002.2 | |
| Low-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 163 (98.2) | 4849.1 | <0.001 |
| No | 210 (85.7) | 3790.2 | |
| High-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 14 (71.4) | 1995.0 | 0.005 |
| No | 359 (91.9) | 4541.7 | |
| Intermediate-high-risk APE | |||
| Yes | 80 (80.0) | 2947.6 | <0.001 |
| No | 293 (94.2) | 4654.0 | |
| Thrombolytic administration status | |||
| Yes | 30 (80.0) | 2960.6 | 0.018 |
| No | 343 (92.1) | 4551.9 | |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | HR (%95 CI) | p Value | HR (%95 CI) | p Value | HR (%95 CI) | p Value | HR (%95 CI) | p Value |
| NPS | 1.030 (0.243–4.364) | 0.968 | 1.030 (0.244–4.360) | 0.968 | - | - | - | |
| CRF | 2.505 (0.751–8.352) | 0.135 | 2.505 (0.752–8.350) | 0.135 | 2.505 (0.752–8.347) | 0.135 | 2.499 (0.751–8.314) | 0.135 |
| ALB | 0.194 (0.020–1.926) | 0.161 | 0.194 (0.020–1.904) | 0.159 | 0.195 (0.019–1.857) | 0.155 | 0.192 (0.020–1.805) | 0.149 |
| TC | 0.659 (0.213–2.037) | 0.469 | 0.659 (0.216–2.008) | 0.463 | 0.664 (0.235–1.883) | 0.442 | 0.669 (0.237–1.885) | 0.447 |
| sPESI | 0.372 (0.071–1.951) | 0.242 | 0.372 (0.071–1.947) | 0.242 | 0.373 (0.072–1.943) | 0.242 | 0.378 (0.073–1.947) | 0.245 |
| Pulse | 1.443 (0.359–5.793) | 0.605 | 1.443 (0.360–5.789) | 0.605 | 1.447 (0.363–5.766) | 0.600 | 1.468 (0.375–5.741) | 0.581 |
| SBP | 0.780 (0.136–4.483) | 0.781 | 0.780 (0.138–4.410) | 0.779 | 0.783 (0.139–4.394) | 0.781 | 0.769 (0.140–4.205) | 0.761 |
| DBP | 1.093 (0.297–4.025) | 0.894 | 1.093 (0.297–4.014) | 0.894 | 1.093 (0.297–4.014) | 0.894 | 1.082 (0.297–3.940) | 0.904 |
| SI | 0.735 (0.150–3.604) | 0.705 | 0.735 (0.150–3.597) | 0.704 | 0.735 (0.150–3.597) | 0.704 | 0.738 (0.151–3.608) | 0.708 |
| Modified SI | 0.688 (0.162–2.910) | 0.611 | 0.687 (0.165–2.868) | 0.607 | 0.686 (0.165–2.852) | 0.604 | 0.678 (0.165–2.786) | 0.590 |
| Age-related SI | 0.321 (0.084–1.229) | 0.097 | 0.321 (0.084–1.228) | 0.097 | 0.321 (0.084–1.228) | 0.097 | 0.315 (0.085–1.167) | 0.084 |
| AST | 0.559 (0.207–1.513) | 0.253 | 0.559 (0.209–1.497) | 0.247 | 0.560 (0.211–1.492) | 0.246 | 0.559 (0.210–1.486) | 0.244 |
| CRP | 0.542 (0.165–1.779) | 0.312 | 0.542 (0.165–1.777) | 0.312 | 0.542 (0.165–1.777) | 0.312 | 0.537 (0.165–1.746) | 0.302 |
| Neutrophil | 0.550 (0.202–1.499) | 0.243 | 0.550 (0.202–1.497) | 0.242 | 0.552 (0.206–1.482) | 0.238 | 0.551 (0.206–1.477) | 0.236 |
| Thrombocyte | 0.482 (0.099–2.352) | 0.367 | 0.482 (0.099–2.351) | 0.367 | 0.482 (0.099–2.350) | 0.367 | 0.478 (0.099–2.319) | 0.360 |
| Troponin | 0.675 (0.148–3.079) | 0.612 | 0.676 (0.151–3.019) | 0.608 | 0.679 (0.155–2.981) | 0.608 | 0.673 (0.154–2.930) | 0.598 |
| Lactate | 0.242 (0.083–0.705) | 0.009 | 0.242 (0.083–0.705) | 0.009 | 0.243 (0.084–0.705) | 0.009 | 0.241 (0.083–0.699) | 0.009 |
| Right vent | 0.758 (0.163–3.532) | 0.724 | 0.758 (0.164–3.507) | 0.723 | 0.758 (0.164–3.506) | 0.723 | 0.758 (0.164–3.498) | 0.722 |
| Right/left vent | 1.376 (0.288–6.576) | 0.689 | 1.377 (0.288–6.575) | 0.689 | 1.380 (0.290–6.564) | 0.686 | 1.364 (0.290–6.405) | 0.694 |
| Aortic diameter | 0.563 (0.171–1.849) | 0.344 | 0.563 (0.173–1.878) | 0.339 | 0.562 (0.173–1.825) | 0.338 | 0.563 (0.174–1.825) | 0.338 |
| Pulmonary artery diameter | 0.997 (0.069–14.302) | 0.998 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Low-risk APE | 0.643 (0.098–4.235) | 0.646 | 0.643 (0.098–4.199) | 0.645 | 0.642 (0.098–4.194) | 0.644 | 0.649 (0.100–4.202) | 0.650 |
| High-risk APE | 1.794 (0.081–39.909) | 0.712 | 1.798 (0.171–18.875) | 0.625 | 1.808 (0.175–18.663) | 0.619 | 1.670 (0.233–11.975) | 0.610 |
| Intermediate-high risk | 1.577 (0.080–31.126) | 0.764 | 1.582 (0.411–6.091) | 0.505 | 1.593 (0.431–5.888) | 0.485 | 1.561 (0.439–5.544) | 0.491 |
| Thrombolytic use | 0.903 (0.171–4.782) | 0.905 | 0.904 (0.177–4.602) | 0.903 | 0.902 (0.178–4.576) | 0.901 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaya, S.; Tekin, V. Evaluation of NAPLES Prognostic Score to Predict Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030315
Kaya S, Tekin V. Evaluation of NAPLES Prognostic Score to Predict Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(3):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030315
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaya, Süheyla, and Veysi Tekin. 2025. "Evaluation of NAPLES Prognostic Score to Predict Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism" Diagnostics 15, no. 3: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030315
APA StyleKaya, S., & Tekin, V. (2025). Evaluation of NAPLES Prognostic Score to Predict Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism. Diagnostics, 15(3), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030315






