MiR-200c-3p Modulates Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer by ZEB1-Independent Mechanisms
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Transient Transfection
2.3. Generation of Stable miRNA Overexpression Cell Lines
2.4. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. Cisplatin Sensitivity Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
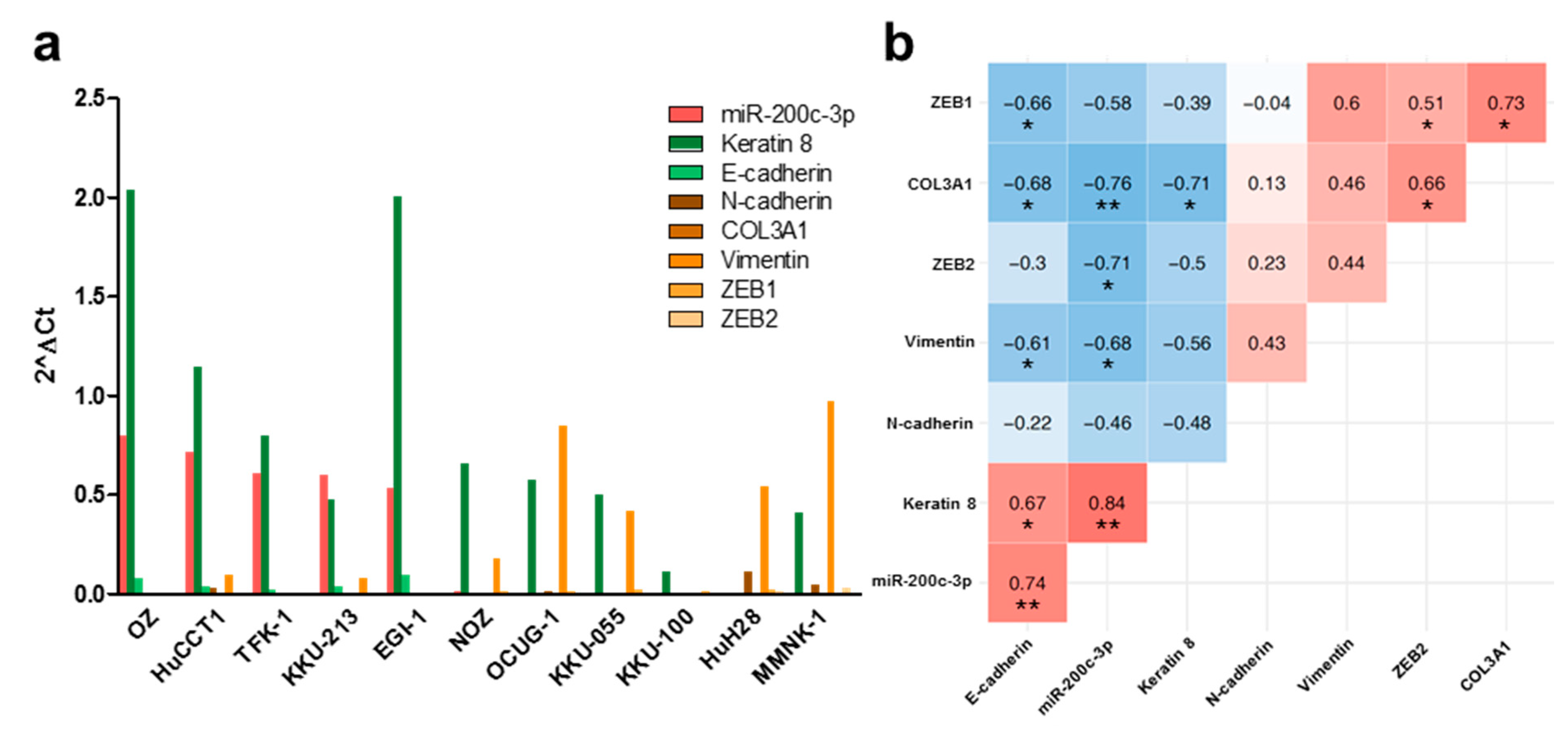
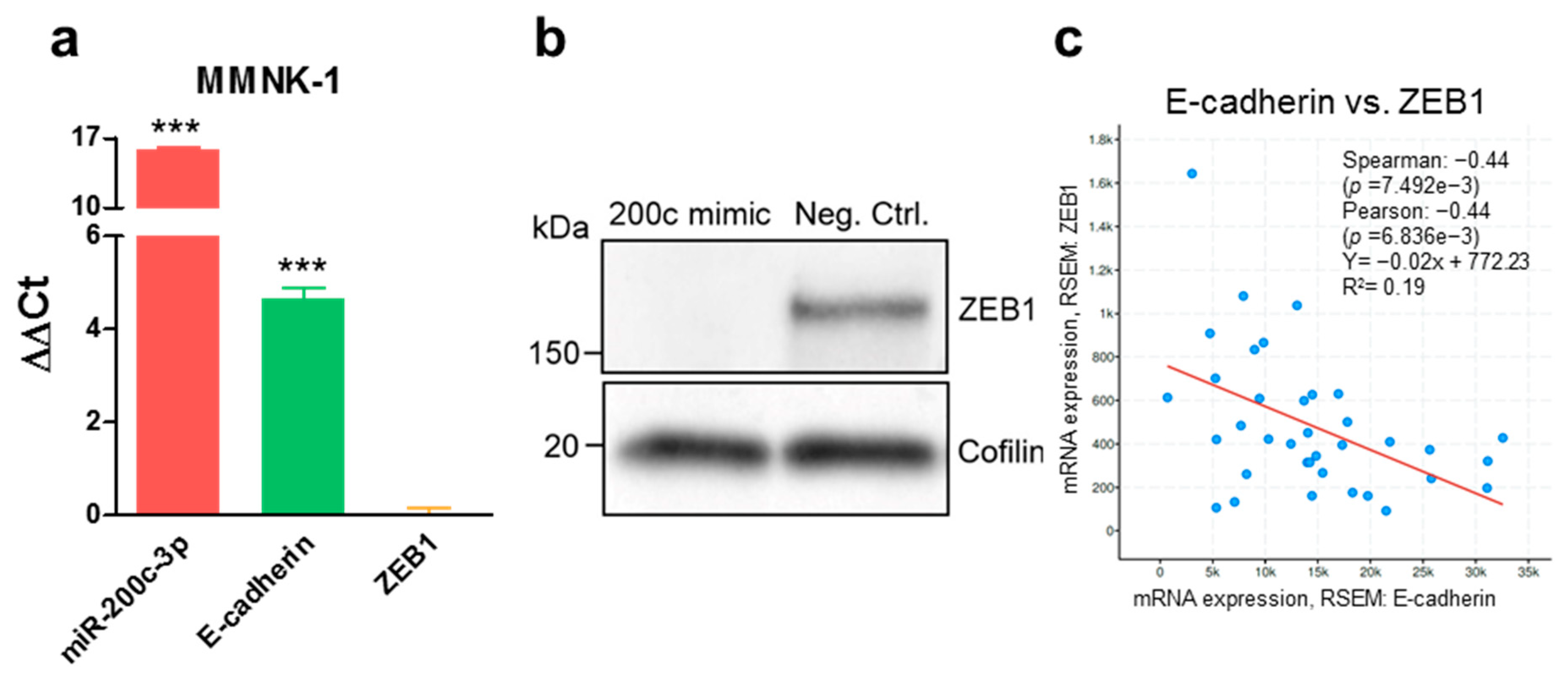
3.1. MiR-200c-3p and Its Influence on EMT Markers in Immortalized Cholangiocytes, Biliary Tract Cancer Cell Lines, and Human Tissue
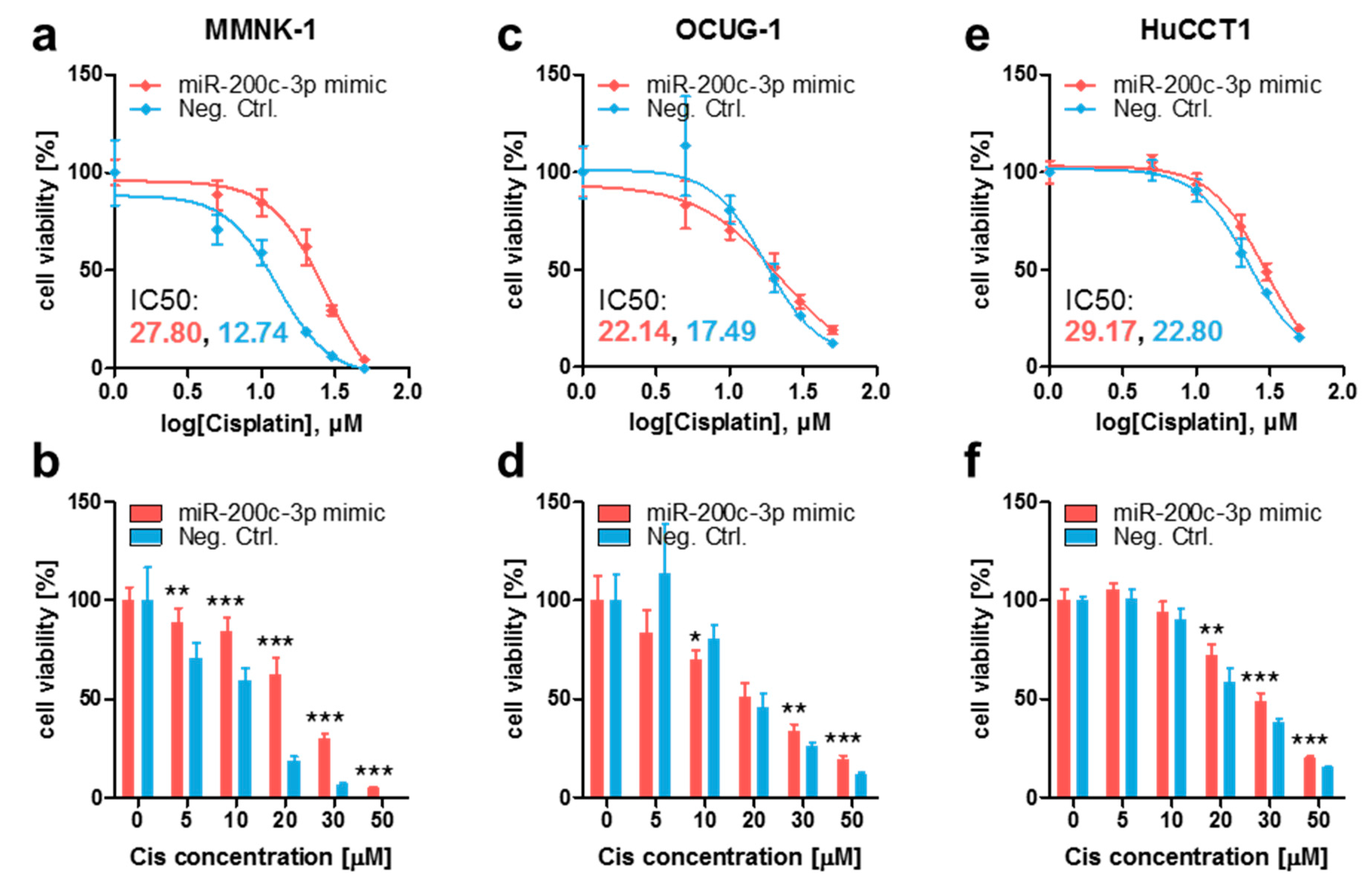
3.2. Ectopic MiR-200c-3p Overexpression Increases Cisplatin Resistance in Immortalized Cholangiocytes and Biliary Tract Cancer Cells
3.3. Stable Endogenous MiR-200c-3p Overexpression Increases Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer Cells
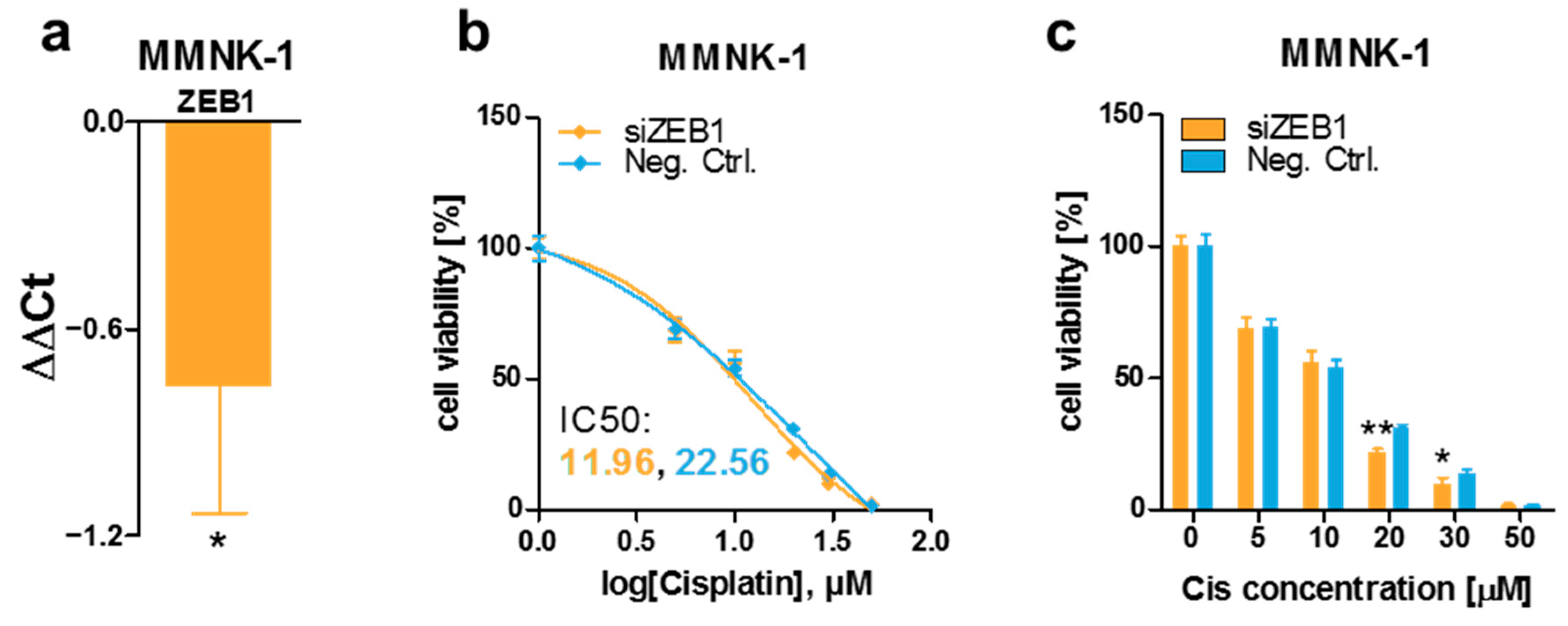
3.4. ZEB1 Knockdown Decreases Cisplatin Resistance of MMNK-1 Cells, Rescue Experiments and Cisplatin-Resistance Associated Gene Expression Pattern
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moeini, A.; Haber, P.K.; Sia, D. Cell of origin in biliary tract cancers and clinical implications. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2021, 3, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Baria, K. The world-wide incidence of biliary tract cancer (BTC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouri, Y.; Mian, I.; Blechacz, B. Cancer review: Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Carcinog. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Kelley, R.K.; Nervi, B.; Oh, D.Y.; Zhu, A.X. Biliary tract cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.; Wasan, H.; Palmer, D.H.; Cunningham, D.; Anthoney, A.; Maraveyas, A.; Madhusudan, S.; Iveson, T.; Hughes, S.; Pereira, S.P.; et al. Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine versus Gemcitabine for Biliary Tract Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morizane, C.; Ueno, M.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Ishii, H.; Furuse, J. New developments in systemic therapy for advanced biliary tract cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, S.; Esaki, M.; Ban, D.; Takamoto, T.; Shimada, K.; Ioka, T.; Okusaka, T.; Ishii, H.; Furuse, J. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy for biliary tract cancer: A review of clinical trials. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basourakos, S.P.; Li, L.; Aparicio, A.M.; Corn, P.G.; Kim, J.; Thompson, T.C. Combination Platinum-based and DNA Damage Response-targeting Cancer Therapy: Evolution and Future Directions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amable, L. Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 106, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, L. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Cisplatin Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.D.; Zhou, S.; Yang, S.J.; Shen, H.Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Zhao, J.-H.; Tang, J.-H. MiRNAs-mediated cisplatin resistance in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12905–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, P.; Hedayat, S.; Fassan, M.; Cardinale, V.; Lampis, A.; Guzzardo, V.; Vicentini, C.; Scarpa, A.; Cascione, L.; Costantini, D.; et al. Modulation of Biliary Cancer Chemo-Resistance Through MicroRNA-Mediated Rewiring of the Expansion of CD133+ Cells. Hepatology 2020, 72, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Wernicke, D.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA and cancer—A brief overview. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2015, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, M.; Raza, U.; Saatci, Ö.; Eyüpoğlu, E.; Yurdusev, E.; Şahin, Ö. miR-200c: A versatile watchdog in cancer progression, EMT, and drug resistance. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tian, W.; He, H.; Chen, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Downregulation of miR-200c-3p contributes to the resistance of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel by targeting SOX2. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3821–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Xiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Zhou, W.B. LncRNA XIST promotes chemoresistance of breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by sponging miR-200c-3p to upregulate ANLN. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Wu, S.G.; Hsu, C.L.; Chang, T.H.; Tsai, M.F.; Lin, Y.T.; Shih, J.Y. MiR-200c-3p suppression is associated with development of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer via a mediating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 28, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Niu, R.; Huang, W.; Da, L.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, C. Long Noncoding RNA PTPRG Antisense RNA 1 Reduces Radiosensitivity of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cells Via Regulating MiR-200c-3p/TCF4. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820942615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, E.; Kunkel, M.; Evans, D.; Silvers, T.; Delosh, R.; Laudeman, J.; Ogle, C.; Reinhart, R.; Selby, M.; Connelly, J.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Screen of Oncology Drugs, Investigational Agents, and Gene and microRNA Expression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, M.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, J.; Liu, P.; Gu, K. MicroRNA-200c reverses drug resistance of human gastric cancer cells by targeting regulation of the NER-ERCC3/4 pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamano, R.; Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kurokawa, Y.; Hara, J.; Moon, J.H.; Nakajima, K.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mori, M.; et al. Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. mir-200b and mir-200c co-contribute to the cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting DNA methyltransferases. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, G.; Ling, Y.; Tan, W.; Tan, L.; Andrews, R.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, X.; Song, E.; et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_001783 regulates breast cancer progression via sponging miR-200c-3p. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Song, N.; Gu, M. MicroRNA-200c-3p/ZEB2 loop plays a crucial role in the tumor progression of prostate carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.-H.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Shao, C.-C.; Guo, C.-P.; Wei, X.-L.; Li, Y.-C.; Huang, W.-H.; Zhang, G.-J. Long noncoding RNA ATB promotes the epithelial−mesenchymal transition by upregulating the miR-200c/Twist1 axe and predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, M.; Yuan, C.; Han, T.; Cui, J.; Jiao, F.; Wang, L. A novel feedback loop between high MALAT-1 and low miR-200c-3p promotes cell migration and invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is predictive of poor prognosis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bure, I.V.; Nemtsova, M.V.; Zaletaev, D.V. Roles of e-cadherin and noncoding rnas in the epithelial–mesenchymal transition and progression in gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-López, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Cano, A. Role of microRNA in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis and clinical perspectives. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kong, G. Roles and epigenetic regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and its transcription factors in cancer initiation and progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4643–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, T.; Pichler, M.; Neureiter, D. Epigenetic control of epithelial-mesenchymal-transition in human cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherdin, G.; Garbrecht, K.M. In vitro interaction of α-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) and human recombinant interferon-a (rIFN-a) on human cancer cell lines. Immunobiology 1987, 175, 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Saijyo, S.; Kudo, T.; Suzuki, M.; Katayose, Y.; Shinoda, M.; Muto, T.; Fukuhara, K.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuno, S. Establishment of a New Extrahepatic Bile Duct Carcinoma Cell Line, TFK-1. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1995, 177, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagiwa, M.; Ichida, T.; Tokiwa, T.; Sato, J.; Sasaki, H. A new human cholangiocellular carcinoma cell line (HuCC-T1) producing carbohydrate antigen 19/9 in serum-free medium. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 1989, 25, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusaka, Y.; Tokiwa, T.; Sato, J. Establishment and characterization of a cell line from a human cholangiocellular carcinoma. Res. Exp. Med. 1988, 188, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sripa, B.; Leungwattanawanit, S.; Nitta, T.; Wongkham, C.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Puapairoj, A.; Sripa, C.; Miwa, M. Establishment and characterization of an opisthorchiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma cell line (KKU-100). World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripa, B.; Seubwai, W.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Silsirivanit, A.; Kaewkong, W.; Muisuk, K.; Dana, P.; Phoomak, C.; Lert-itthiporn, W.; et al. Functional and genetic characterization of three cell lines derived from a single tumor of an Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma patient. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, S.; Hasumura, S.; Nagamori, S.; Kameda, H. Establishment and characterization of a human gall bladder carcinoma cell line NOZ. Hum. Cell Off. J. Hum. Cell Res. Soc. 1988, 1, 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, N.; Chung, Y.S.; Ohtani, H.; Ikeda, T.; Onoda, N.; Sawada, T.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Hasuma, T.; Sowa, M. Establishment and characterization of a new human gallbladder carcinoma cell line (OCUG-1) producing TA-4. Int. J. Oncol. 1997, 10, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Nagamori, S.; Fujise, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Hasumura, S.; Sujino, H.; Matsuura, T.; Shimizu, K.; Kameda, H.; Takaki, K. Human bile duct carcinoma cell line producing abundant mucin in vitro. Gastroenterol. Jpn. 1987, 22, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Westerman, K.A.; Sakaguchi, M.; Allain, J.E.; Totsugawa, T.; Okitsu, T.; Fukazawa, T.; Weber, A.; Stolz, D.B.; et al. Establishment of a highly differentiated immortalized human cholangiocyte cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation 2004, 77, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motulsky, H.J.; Brown, R.E. Detecting outliers when fitting data with nonlinear regression—A new method based on robust nonlinear regression and the false discovery rate. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, W.; Shen, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, J. miR-145 sensitizes gallbladder cancer to cisplatin by regulating multidrug resistance associated protein 1. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 10553–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Ma, J.; Tao, L.; Mo, L.; Chen, W. MiR-199a-3p enhances cisplatin sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma cells by inhibiting mTOR signaling pathway and expression of MDR1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33621–33630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, M.; Liu, Y.; Gong, W. MiR-31 regulates the cisplatin resistance by targeting Src in gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83060–83070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Zhan, M.; Chen, T.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yan, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J. MIR-125b-5p enhances chemotherapy sensitivity to cisplatin by down-regulating Bcl2 in gallbladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danarto, R.; Astuti, I.; Umbas, R.; Haryana, S.M. Urine miR-21-5p and miR-200c-3p as potential non-invasive biomarkers in patients with prostate cancer. Turk. J. Urol. 2020, 46, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Han, Q.; Chi, C.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, J.; Dong, B.; Huang, Y.; Xia, W.; Xue, W.; Sha, J. Transcriptional regulation of PRKAR2B by miR-200b-3p/200c-3p and XBP1 in human prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Gu, Q. MIR-200c-3p suppresses the proliferative, migratory, and invasive capacities of nephroblastoma cells via targeting FRS2. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2019, 17, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gu, K.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Huang, X. MicroRNA-200c as a prognostic and sensitivity marker for platinum chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51190–51199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Suna, J. MicroRNA-200c promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration by directly targeting dachshund family transcription factor 1 by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer. Drugs 2019, 30, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo-Yasukochi, T.; Morioka, M.; Hazekawa, M.; Yasukochi, A.; Nishinakagawa, T.; Ono, K.; Kawano, S.; Nakamura, S.; Nakashima, M. miR-200c-3p spreads invasive capacity in human oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila, H.J.; Sanabria-Salas, M.C.; Meneses, X.; Rios, R.; Huertas-Salgado, A.; Serrano, M.L. Circulating miR-141-3p, miR-143-3p and miR-200c-3p are differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and advanced adenomas. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, L.-r.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, P.; Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, W. Five serum microRNAs for detection and predicting of ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. X 2019, 3, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Moxley, K.; Ruskin, R.; Dhanasekaran, D.N.; Zhao, Y.D.; Ramesh, R. A Non-invasive Liquid Biopsy Screening of Urine-Derived Exosomes for miRNAs as Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer Patients. AAPS J. 2018, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.J.; Wang, L.J.; Yu, B.; Li, Y.H.; Jin, Y.; Bai, X.Z. LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and invasionmetastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11652–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.; Mitsui, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Gill, A.; Wong, D.K.; Yamamura, S.; Shahryari, V.; Laura Tabatabai, Z.; Dahiya, R.; Shin, D.M.; et al. Loss of miR-200c up-regulates CYP1B1 and confers docetaxel resistance in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7774–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K. The role of microRNAs in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Song, Q.; Tang, P. Identification of microRNAs associated with the survival of patients with gallbladder carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, Q.; Shao, S.; Fang, H. Exosomal miR-200 family as serum biomarkers for early detection and prognostic prediction of cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3870–3876. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Guan, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Su, Z.; Kang, P.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y. Yin Yang 1-induced LINC00667 up-regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 to promote proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells by sponging miR-200c-3p. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbas, R.; Mayr, C.; Klieser, E.; Fuereder, J.; Bach, D.; Stättner, S.; Primavesi, F.; Jaeger, T.; Stanzer, S.; Ress, A.L.; et al. Relevance of microRNA200 family and microRNA205 for epithelial to mesenchymal transition and clinical outcome in biliary tract cancer patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Kalantari, M.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Javaheri, T.; Sethi, G. Association of the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) with Cisplatin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieszporek, A.; Skrzypek, K.; Adamek, G.; Majka, M. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2019, 66, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, A.; Han, X. The roles of ZEB1 in tumorigenic progression and epigenetic modifications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drápela, S.; Bouchal, J.; Jolly, M.K.; Culig, Z.; Souček, K. ZEB1: A Critical Regulator of Cell Plasticity, DNA Damage Response, and Therapy Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, H.B.; Wong, Z.L.; Wu, B.; Kong, L.R.; Png, C.W.; Cho, Y.-L.; Li, C.-W.; Xiao, F.; Xin, X.; Yang, H.; et al. DUSP16 promotes cancer chemoresistance through regulation of mitochondria-mediated cell death. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KK, L.; KT, C.; MY, C.; HK, W.; EY, F.; HY, L.; W, T.; LN, T.; DK, T.; RW, S.; et al. 14-3-3σ confers cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating DNA repair molecules. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Posch, F.; Prinz, F.; Balihodzic, A.; Mayr, C.; Kiesslich, T.; Klec, C.; Jonas, K.; Barth, D.A.; Riedl, J.M.; Gerger, A.; et al. MiR-200c-3p Modulates Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer by ZEB1-Independent Mechanisms. Cancers 2021, 13, 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163996
Posch F, Prinz F, Balihodzic A, Mayr C, Kiesslich T, Klec C, Jonas K, Barth DA, Riedl JM, Gerger A, et al. MiR-200c-3p Modulates Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer by ZEB1-Independent Mechanisms. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163996
Chicago/Turabian StylePosch, Florian, Felix Prinz, Amar Balihodzic, Christian Mayr, Tobias Kiesslich, Christiane Klec, Katharina Jonas, Dominik A. Barth, Jakob M. Riedl, Armin Gerger, and et al. 2021. "MiR-200c-3p Modulates Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer by ZEB1-Independent Mechanisms" Cancers 13, no. 16: 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163996
APA StylePosch, F., Prinz, F., Balihodzic, A., Mayr, C., Kiesslich, T., Klec, C., Jonas, K., Barth, D. A., Riedl, J. M., Gerger, A., & Pichler, M. (2021). MiR-200c-3p Modulates Cisplatin Resistance in Biliary Tract Cancer by ZEB1-Independent Mechanisms. Cancers, 13(16), 3996. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163996





