Birds of a Feather Flock Together: Disadvantageous Decision Making in Augmented Restless Legs Syndrome Patients with and without Impulse Control Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Statistics
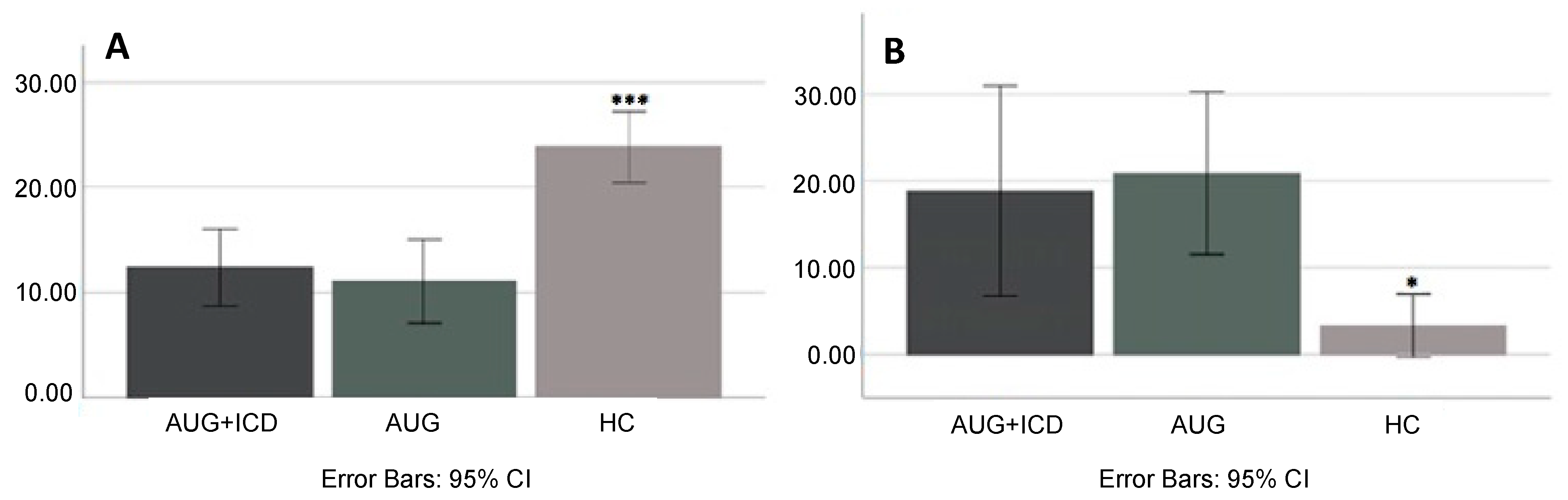
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Didriksen, M.; Rigas, A.S.; Allen, R.P.; Burchell, B.J.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Nielsen, M.H.; Jennum, P.; Werge, T.; Erikstrup, C.; Pedersen, O.B.; et al. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome and associated factors in an otherwise healthy population: Results from the Danish Blood Donor Study. Sleep Med. 2017, 36, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högl, B.; Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J.; Saletu, M.; Frauscher, B.; Seppi, K.; Müller, J.; Rungger, G.; Gasperi, A.; Wenning, G.; et al. Restless legs syndrome: A community-based study of prevalence, severity, and risk factors. Neurology 2005, 64, 1920–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijemanne, S.; Jankovic, J. Restless legs syndrome: Clinical presentation diagnosis and treatment. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haschka, D.; Volani, C.; Stefani, A.; Tymoszuk, P.; Mitterling, T.; Holzknecht, E.; Heidbreder, A.; Coassin, S.; Sumbalova, Z.; Seifert, M.; et al. Association of mitochondrial iron deficiency and dysfunction with idiopathic restless legs syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.P. Restless Leg Syndrome/Willis-Ekbom Disease Pathophysiology. Sleep Med. Clin. 2015, 10, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.P.; Ondo, W.G.; Ball, E.; Calloway, M.O.; Manjunath, R.; Higbie, R.L.; Lee, M.R.; Nisbet, P.A. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) augmentation associated with dopamine agonist and levodopa usage in a community sample. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voon, V.; Schoerling, A.; Wenzel, S.; Ekanayake, V.; Reiff, J.; Trenkwalder, C.; Sixel-Döring, F. Frequency of impulse control behaviours associated with dopaminergic therapy in restless legs syndrome. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, B.; Djamshidian, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Stefani, A.; Zamarian, L.; Pertl, M.T.; Brandauer, E.; Delazer, M.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W.; et al. Augmentation and impulsive behaviors in restless legs syndrome: Coexistence or association? Neurology 2016, 87, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, B.; Pertl, M.T.; Stefani, A.; Delazer, M.; Heidbreder, A.; Zamarian, L.; Brandauer, E.; Seppi, K.; Högl, B.; Poewe, W.; et al. Haste makes waste: Decision making in patients with restless legs syndrome with and without augmentation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Heim, B.; Pertl, M.T.; Stefani, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Zamarian, L.; Brandauer, E.; Averbeck, B.; Delazer, M.; Seppi, K.; Högl, B.; et al. Reflection impulsivity perceptual decision-making in patients with restless legs syndrome. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Hoops, S.; Shea, J.A.; Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R.; Driver-Dunckley, E.D.; Adler, C.H.; Potenza, M.N.; Miyasaki, J.; Siderowf, A.D.; et al. Validation of the questionnaire for impulsive-compulsive disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Borreguero, D.; Silber, M.H.; Winkelman, J.W.; Högl, B.; Bainbridge, J.; Buchfuhrer, M.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Inoue, Y.; Manconi, M.; Oertel, W.; et al. Guidelines for the first-line treatment of restless legs syndrome/Willis-Ekbom disease, prevention and treatment of dopaminergic augmentation: A combined task force of the IRLSSG, EURLSSG, and the RLS-foundation. Sleep Med. 2016, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huq, S.F.; Garety, P.A.; Hemsley, D.R. Probabilistic judgements in deluded and non-deluded subjects. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. A 1988, 40, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djamshidian, A.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Sanotsky, Y.; Sharman, S.; Matviyenko, Y.; Foltynie, T.; Michalczuk, R.; Aviles-Olmos, I.; Fedoryshyn, L.; Doherty, K.M.; et al. Decision making, impulsivity, and addictions: Do Parkinson’s disease patients jump to conclusions? Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, B.; Peball, M.; Saft, C.; von Hein, S.M.; Ellmerer, P.; Piater, J.M.; Seppi, K.; Djamshidian, A. Time will tell: Decision making in premanifest and manifest Huntington’s disease. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Robbins, T.W.; Ersche, K.D.; Sahakian, B.J. Reflection impulsivity in current and former substance users. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furl, N.; Averbeck, B.B. Parietal cortex and insula relate to evidence seeking relevant to reward-related decisions. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 17572–17582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Hammer, A.; Camara, E.; Munte, T.F. Pramipexole modulates the neural network of reward anticipation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Mamikonyan, E.; Detre, J.A.; Siderowf, A.D.; Stern, M.B.; Potenza, M.N.; Weintraub, D. Decreased ventral striatal activity with impulse control disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeves, T.D.; Miyasaki, J.; Zurowski, M.; Lang, A.E.; Pellecchia, G.; Van Eimeren, T.; Rusjan, P.; Houle, S.; Strafella, A.P. Increased striatal dopamine release in Parkinsonian patients with pathological gambling: A [11C] raclopride PET study. Brain 2009, 132 Pt 5, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamshidian, A.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Foltynie, T.; Aviles-Olmos, I.; Limousin, P.; Noyce, A.; Zrinzo, L.; Lees, A.J.; Averbeck, B.B. Dopamine agonists rather than deep brain stimulation cause reflection impulsivity in Parkinson’s disease. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2013, 3, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Mitterling, T.; Heidbreder, A.; Steiger, R.; Kremser, C.; Frauscher, B.; Gizewski, E.R.; Poewe, W.; Högl, B.; Scherfler, C. Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging reveals alterations of sensorimotor circuits in restless legs syndrome. Sleep 2019, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmerer, P.S.A.; Heim, B.; Bergmann, M.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W.; Hoegl, B.; Djamshidian, A. The Frontal Assessment Battery in RLS patients with and without augmentation. Sleep Med. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, G.; Vitale, C.; Trojano, L.; Verde, F.; Grossi, D.; Barone, P. Cognitive dysfunctions and pathological gambling in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayard, S.; Langenier, M.C.; Dauvilliers, Y. Decision-making, reward-seeking behaviors and dopamine agonist therapy in restless legs syndrome. Sleep 2013, 36, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AUG + ICD | AUG | HC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number (n) | 19 | 21 | 21 | |
| Mild augmentation (n = 26) | 9 | 17 | - | 0.026 * |
| Severe augmentation (n = 14) | 10 | 4 | ||
| ICD symptoms | 19 | - | - | - |
| Gender (male:female) | 9:9 | 8:14 | 7:14 | 0.73 |
| Age (years) | 61.6 ± 12.0 | 66.6 ± 7.6 | 59.5 ± 11.1 | 0.098 |
| Education (years) | 11.0 ± 3.1 | 10.1 ± 1.8 | 11.1 ± 1.6 | 0.46 |
| Disease duration (years) | 19.9 ± 16.0 | 16.3 ± 13.1 | - | 0.15 |
| IRLS (at time of assessment) | 25.3 ± 7.8 | 24.2 ± 7.5 | - | 1.0 |
| LEU (mg) | 153.1 ± 180.4 | 109.1 ± 133.1 | - | 0.81 |
| DA monotherapy (all) | 15 | 15 | - | - |
| Pramipexole | 11 | 12 | ||
| Rotigotine | 3 | 2 | ||
| Ropinirole | 1 | 1 | ||
| Levodopa monotherapy | 2 | 3 | - | - |
| Levodopa plus DA | 1 | 4 * | - | - |
| Pramipexole | - | 3 | ||
| Rotigotine | 1 | 2 | ||
| Ropinirole | - | 1 | ||
| Total draws (n) ± SD a | 12.4 ± 15.7 | 11.1 ± 18.1 | 22.9 ± 16.0 | <0.001 *** |
| Irrational choices (n) ± SD b | 2.0 ± 2.4 | 2.0 ± 2.1 | 0.3 ± 0.8 | 0.008 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heim, B.; Ellmerer, P.; Stefani, A.; Heidbreder, A.; Brandauer, E.; Högl, B.; Seppi, K.; Djamshidian, A. Birds of a Feather Flock Together: Disadvantageous Decision Making in Augmented Restless Legs Syndrome Patients with and without Impulse Control Disorders. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030383
Heim B, Ellmerer P, Stefani A, Heidbreder A, Brandauer E, Högl B, Seppi K, Djamshidian A. Birds of a Feather Flock Together: Disadvantageous Decision Making in Augmented Restless Legs Syndrome Patients with and without Impulse Control Disorders. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(3):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030383
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeim, Beatrice, Philipp Ellmerer, Ambra Stefani, Anna Heidbreder, Elisabeth Brandauer, Birgit Högl, Klaus Seppi, and Atbin Djamshidian. 2021. "Birds of a Feather Flock Together: Disadvantageous Decision Making in Augmented Restless Legs Syndrome Patients with and without Impulse Control Disorders" Brain Sciences 11, no. 3: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030383
APA StyleHeim, B., Ellmerer, P., Stefani, A., Heidbreder, A., Brandauer, E., Högl, B., Seppi, K., & Djamshidian, A. (2021). Birds of a Feather Flock Together: Disadvantageous Decision Making in Augmented Restless Legs Syndrome Patients with and without Impulse Control Disorders. Brain Sciences, 11(3), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030383







