An Enhanced Multicell-to-Multicell Battery Equalizer Based on Bipolar-Resonant LC Converter
Abstract
1. Introduction
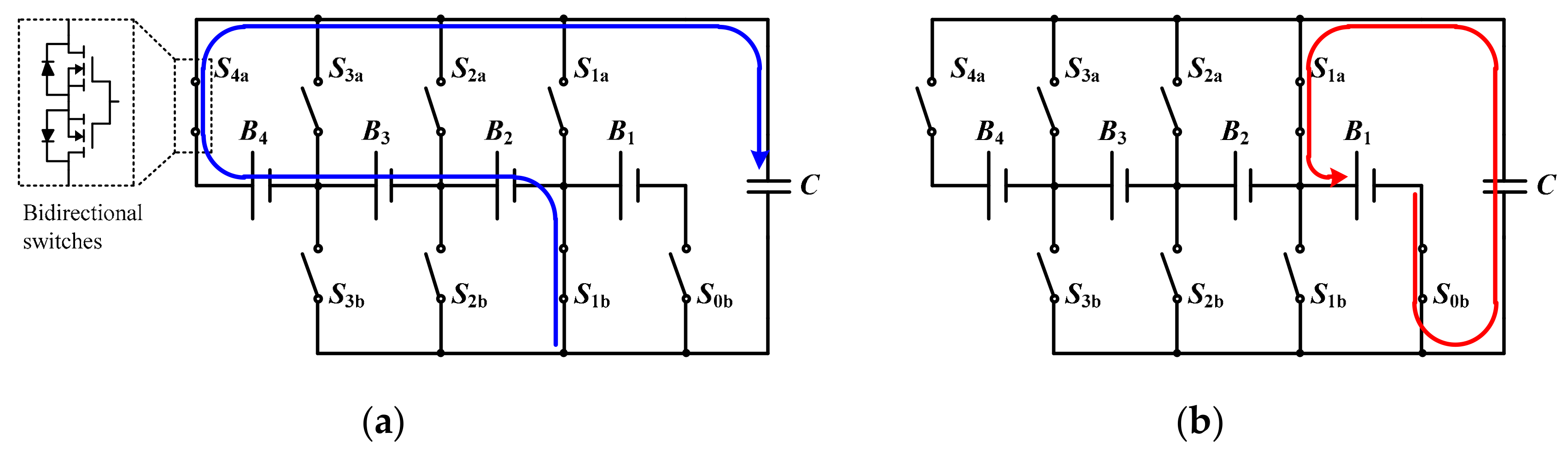
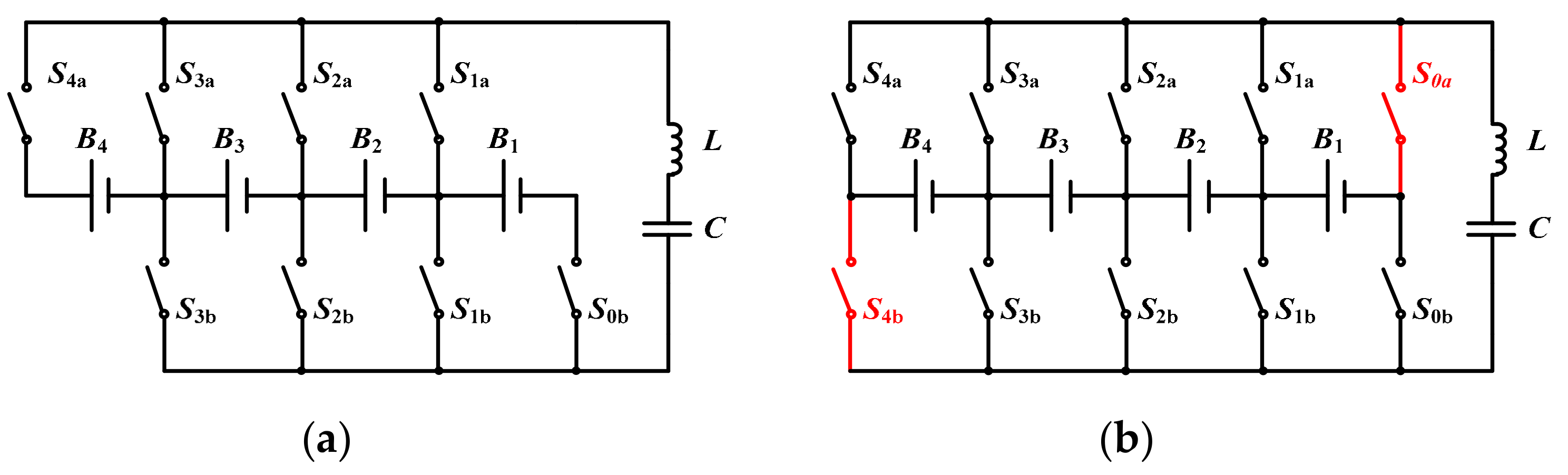
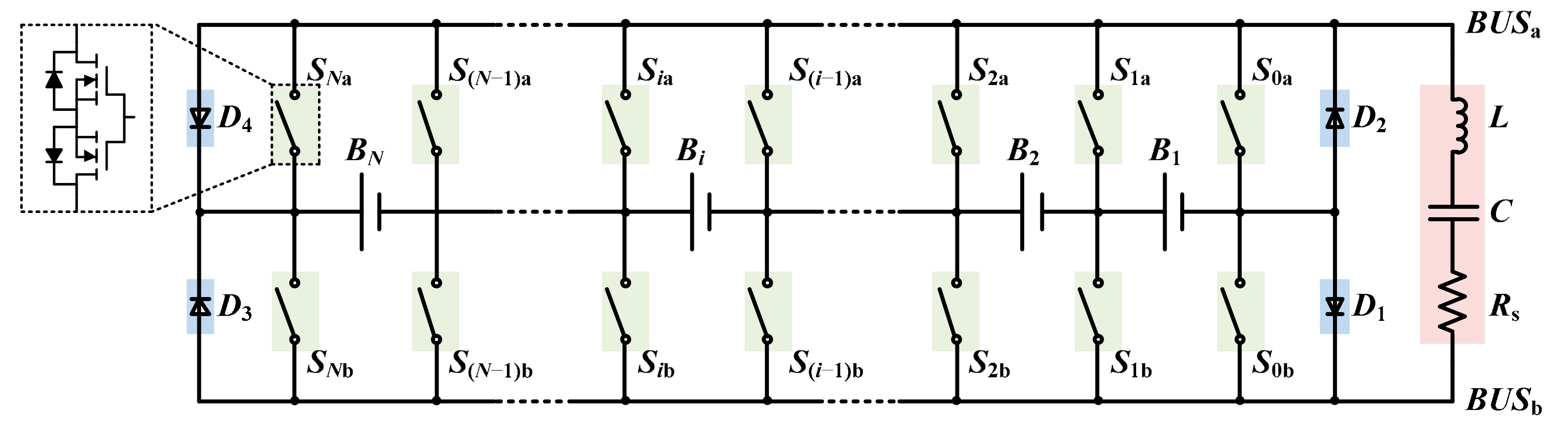
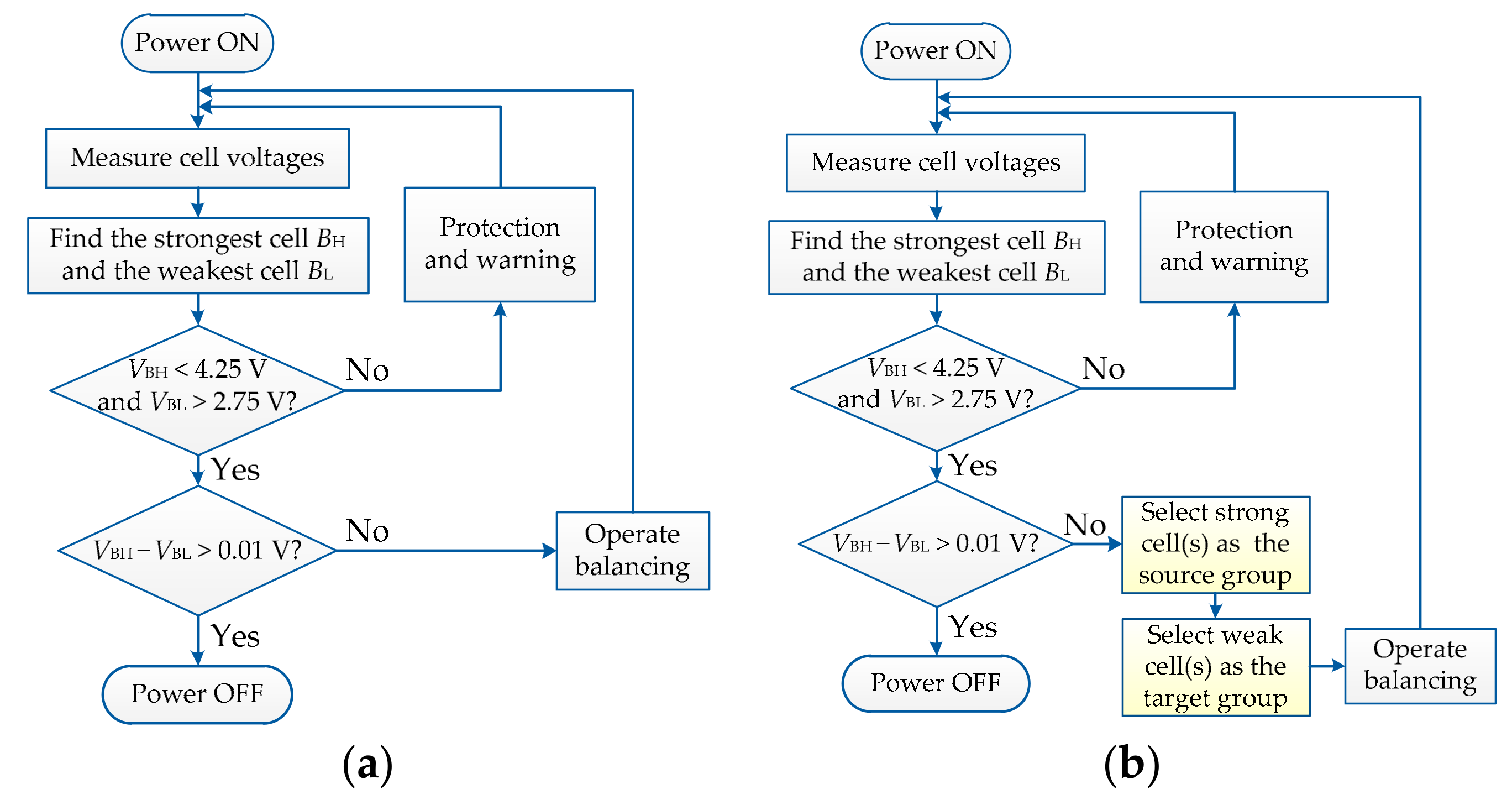
2. Proposed Equalizer
2.1. Circuit Structure
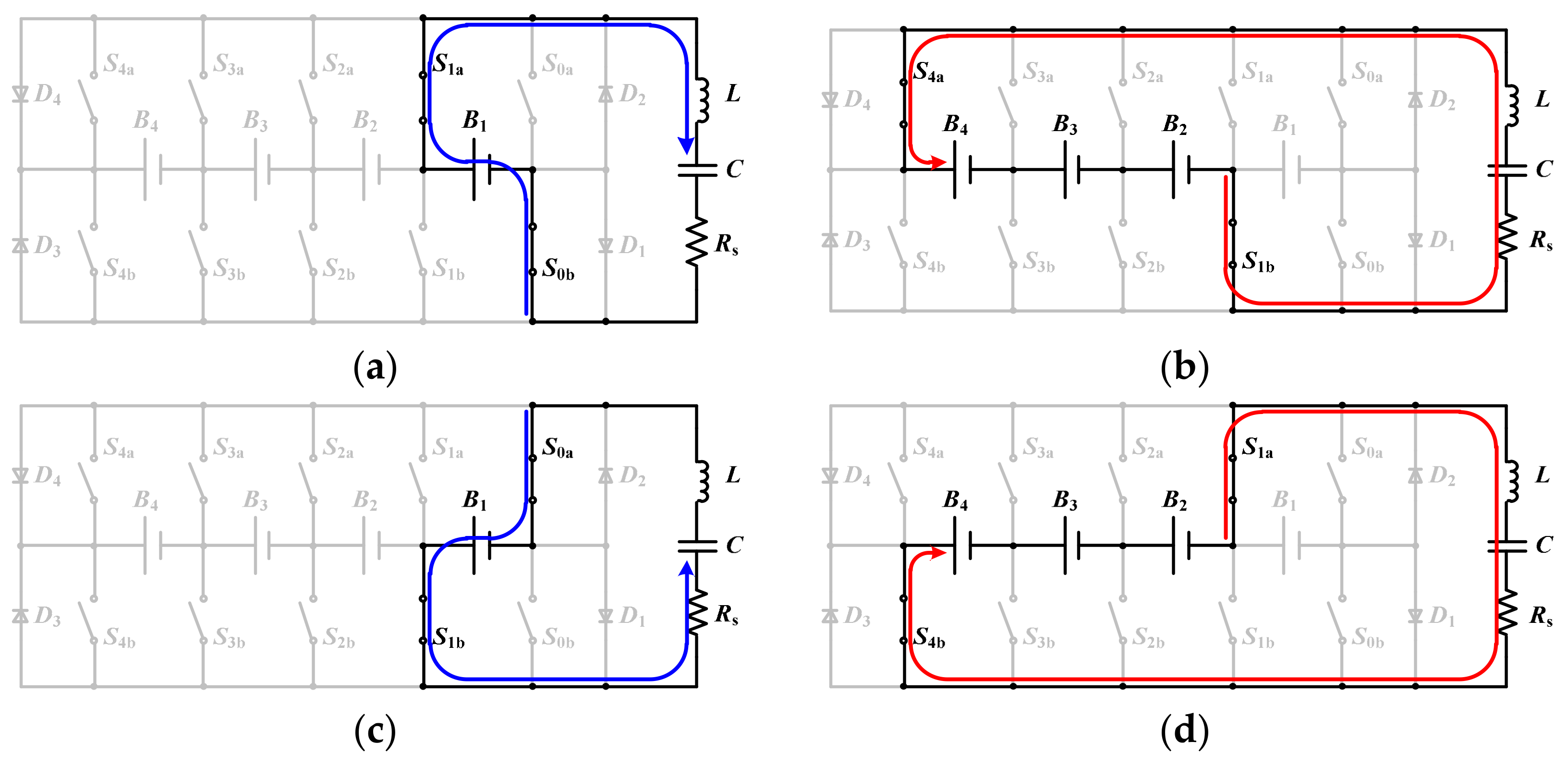
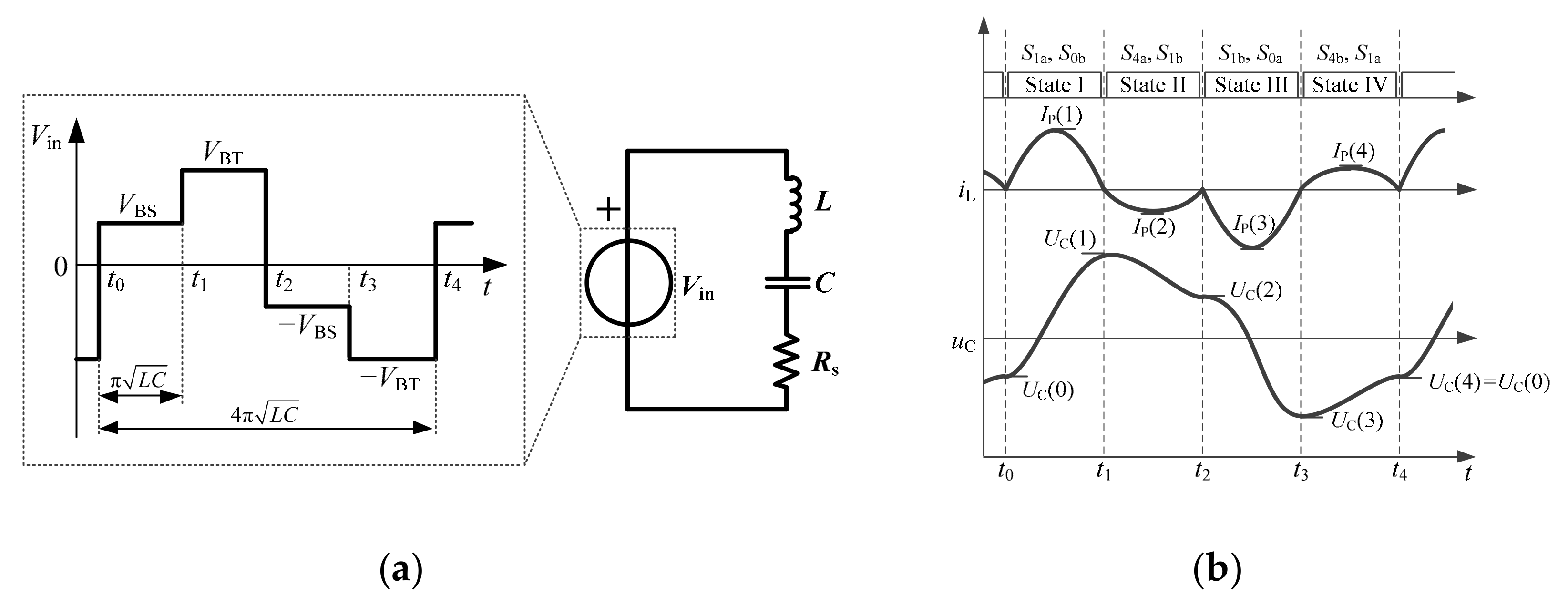
2.2. Operation Principle
2.3. Mathematical Model
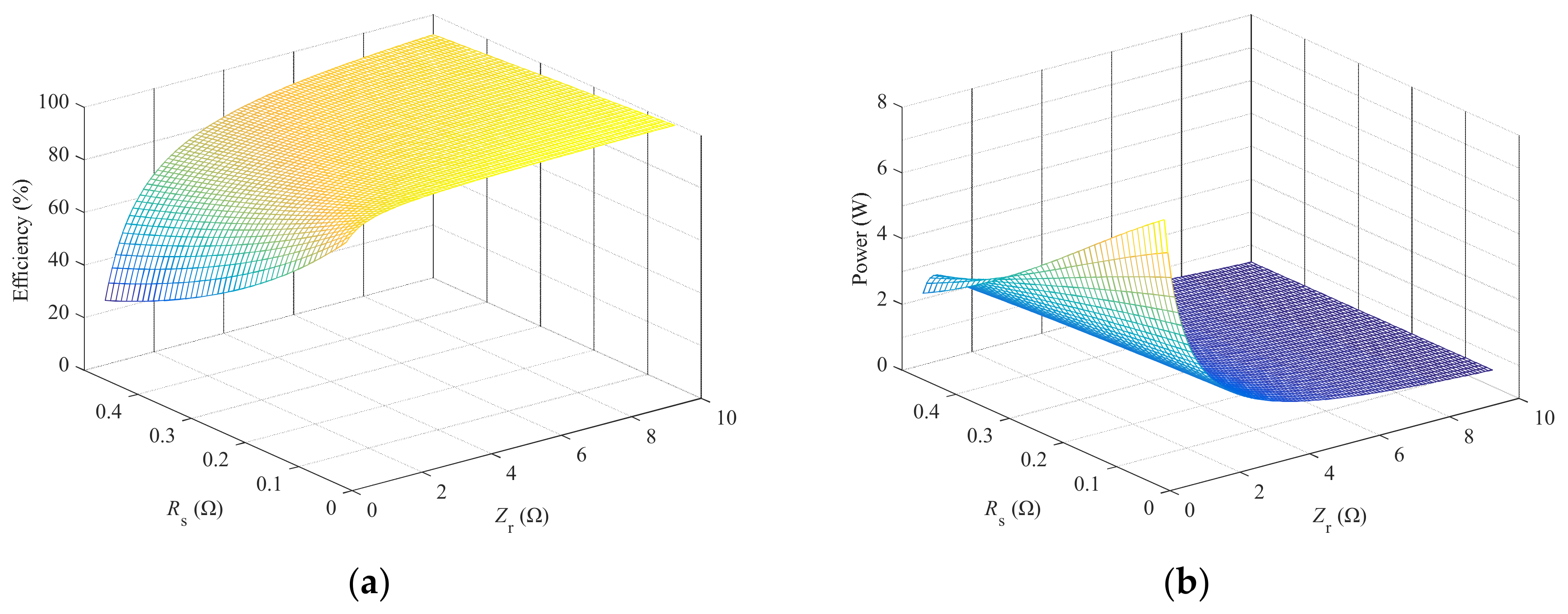
2.4. Comparative Analysis
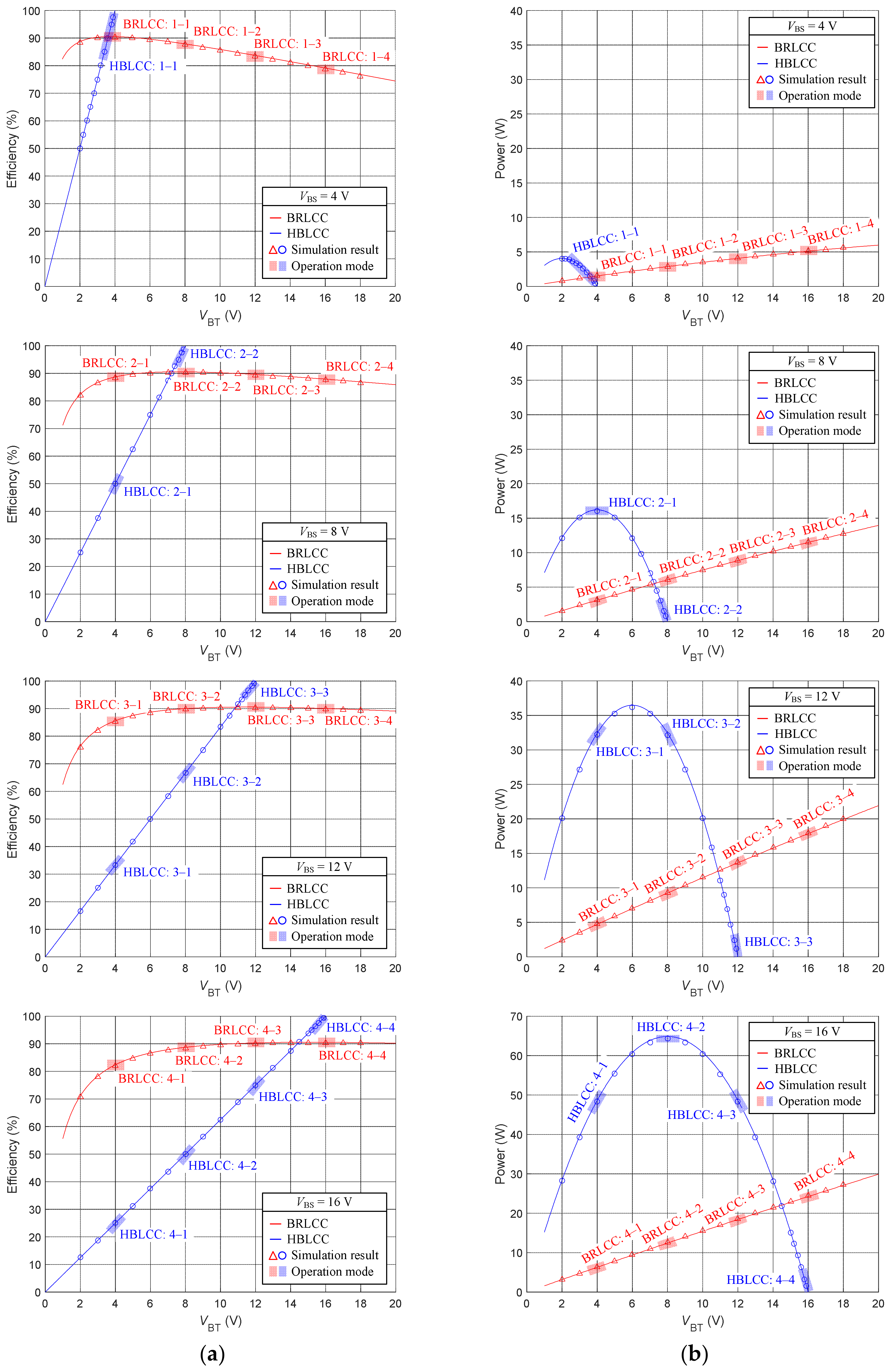
3. Simulation Comparison with Conventional Equalizers
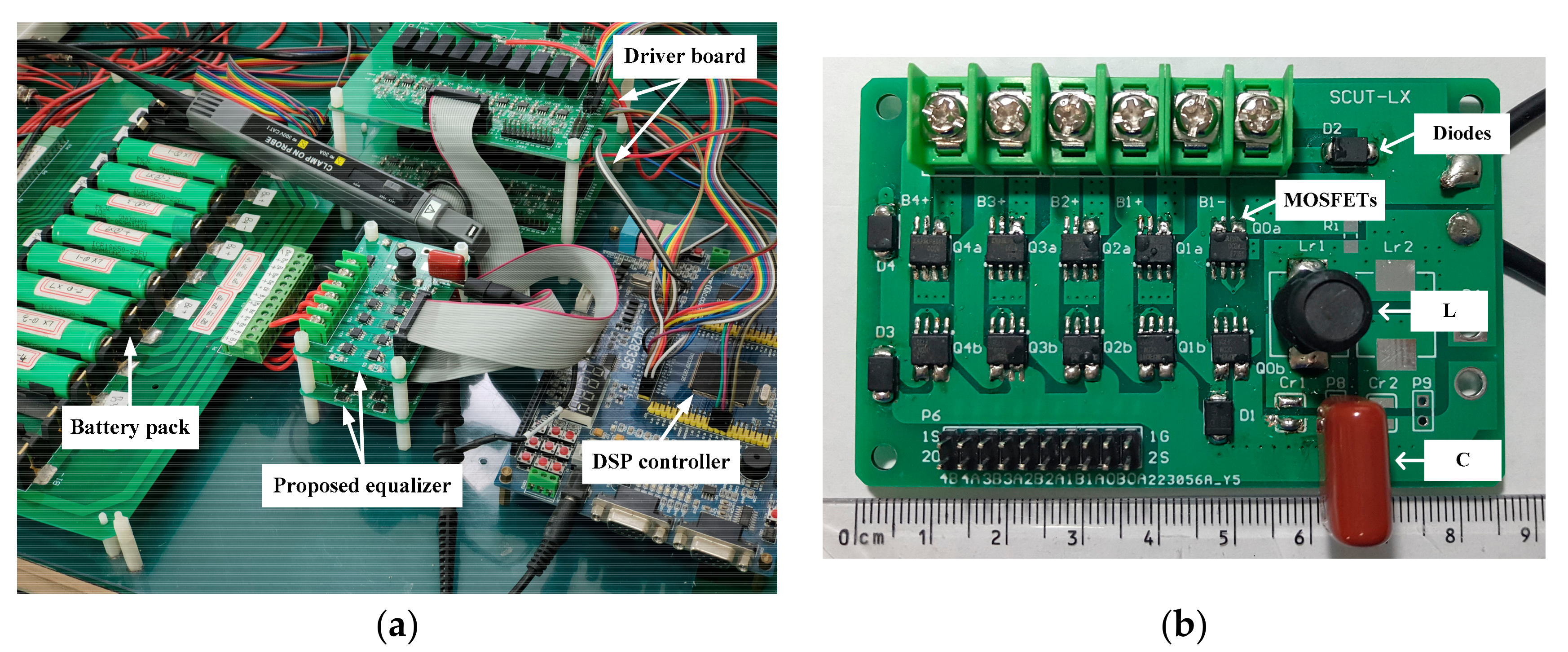
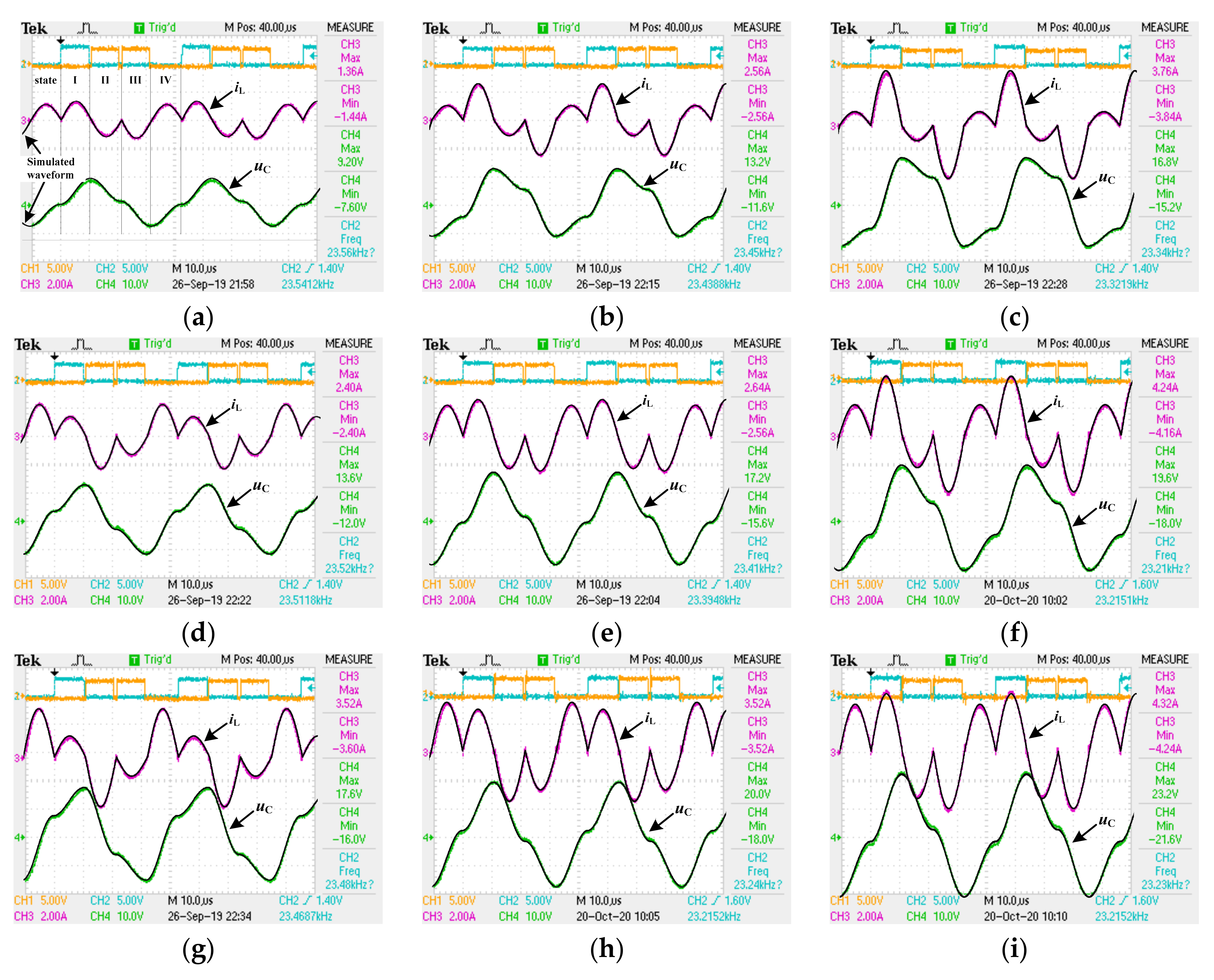
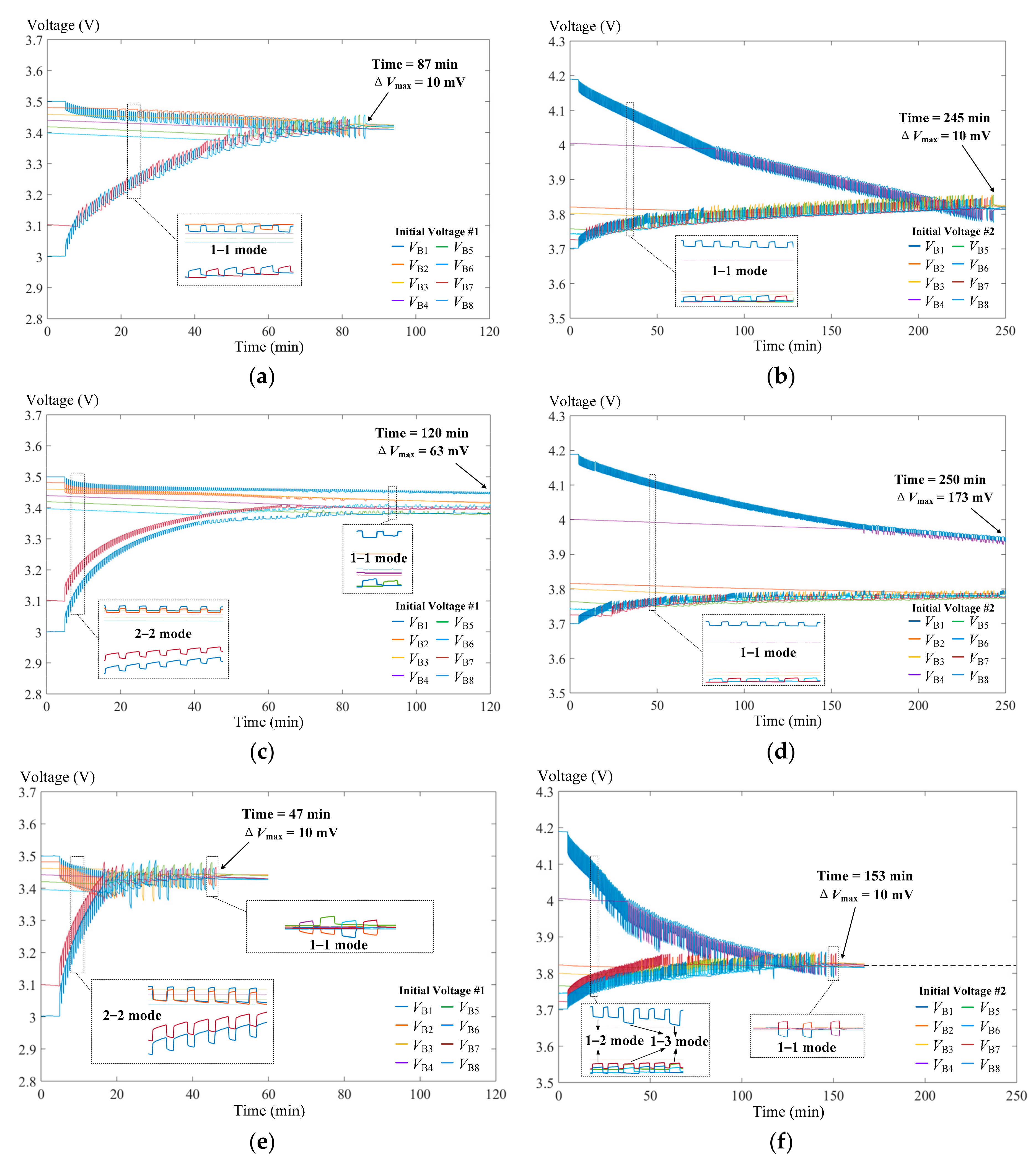
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
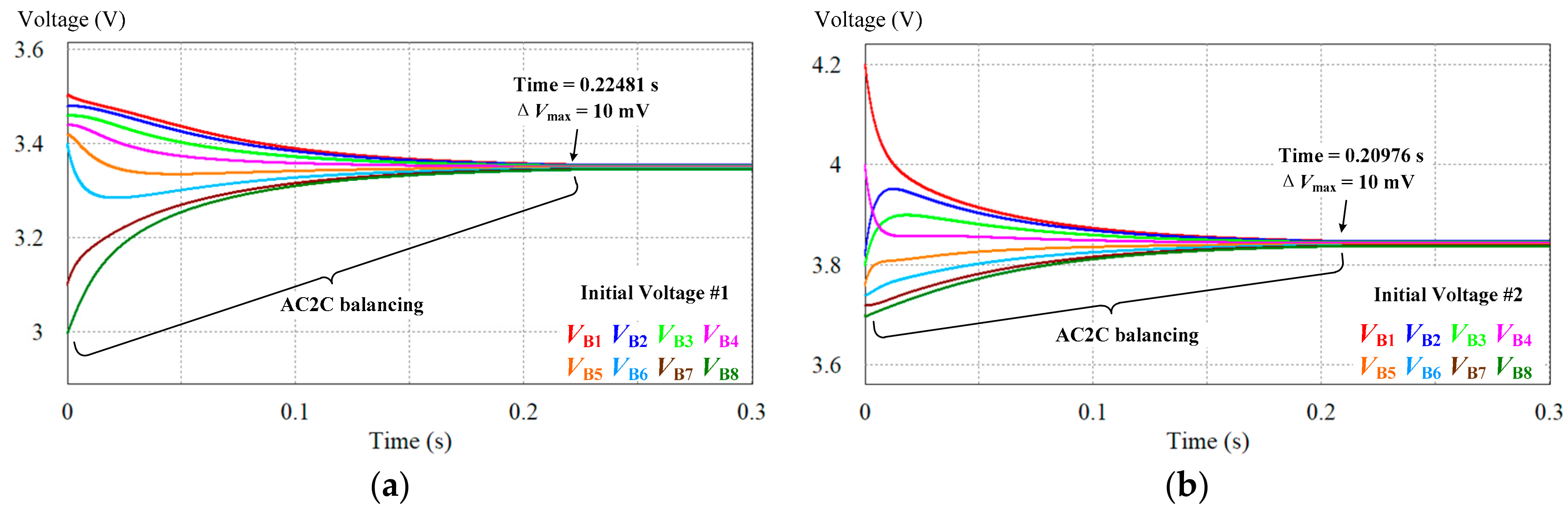
5.1. AC2C Equalizer
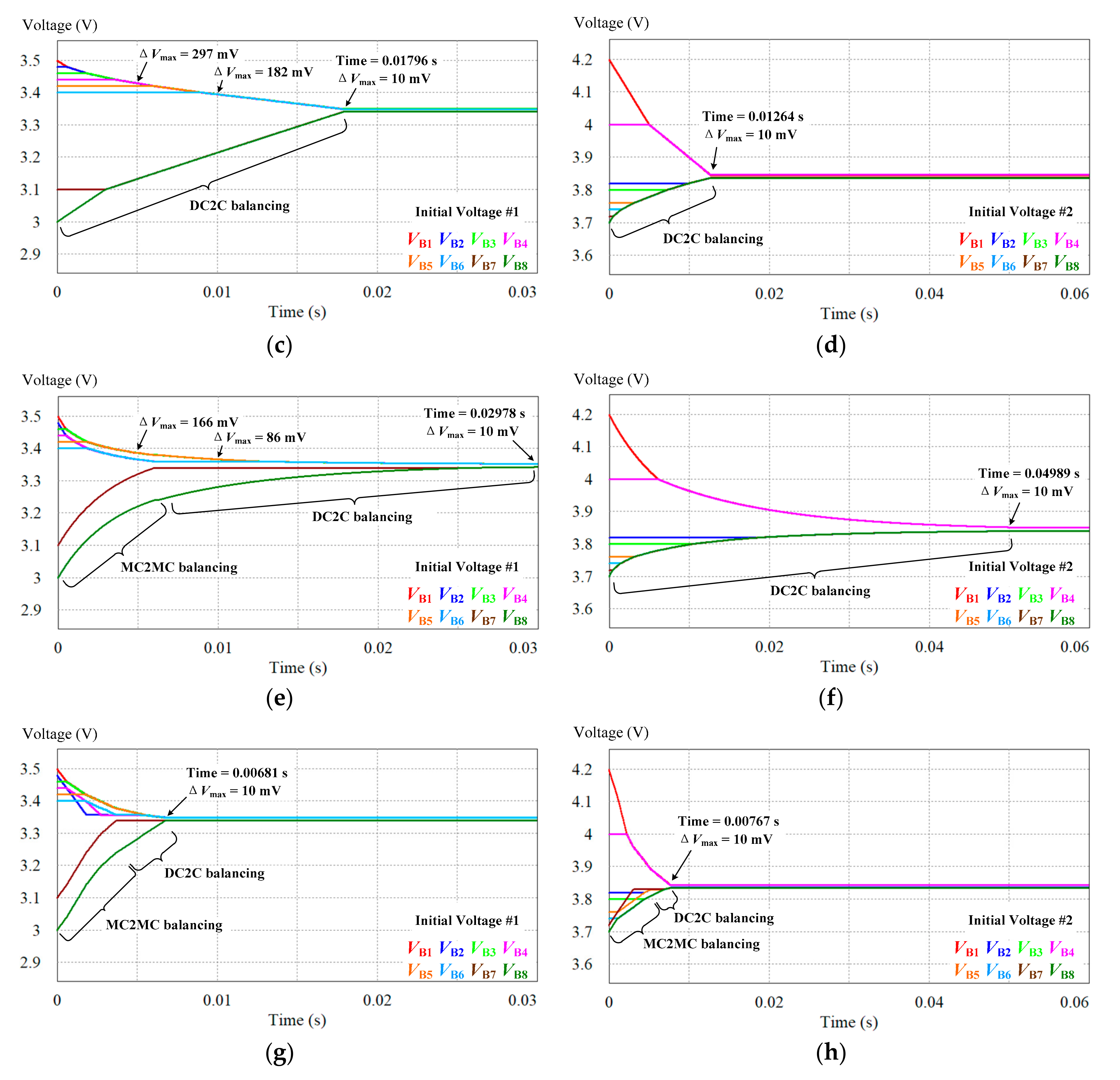
5.2. DC2C Equalizer
5.3. MC2MC Equalizer
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Step-up MC2MC operation modes like 1–2, 1–3, 2–3 modes are realized with good efficiency.
- (2)
- Step-down modes like 2–1, 3–1, 3–2 modes can have higher efficiency.
- (3)
- Stable balancing power is guaranteed at small voltage gap.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, M.; Qu, J.; Lan, H.; Wu, Q.; Lin, H.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, W. An Active and Passive Hybrid Battery Equalization Strategy Used in Group and between Groups. Electronics 2020, 9, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Kang, B. Active Charge Equalizer of Li-Ion Battery Cells Using Double Energy Carriers. Energies 2019, 12, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Kang, L.; Luo, X.; Linghu, J.; Lin, H. A Novel Lithium Battery Equalization Circuit with Any Number of Inductors. Energies 2019, 12, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. A Novel Layered Bidirectional Equalizer Based on a Buck-Boost Converter for Series-Connected Battery Strings. Energies 2017, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Lozano, J.; Romero-Cadaval, E.; Milanes-Montero, M.I.; Guerrero-Martinez, M.A. Battery equalization active methods. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzan Moghaddam, A.; Van den Bossche, A. An Efficient Equalizing Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Coupled Inductor Balancing. Electronics 2019, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Tanaka, K. Double-Switch Single-Transformer Cell Voltage Equalizer Using a Half-Bridge Inverter and a Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Supercapacitors. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 3920–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, Y. A Module-Integrated Distributed Battery Energy Storage and Management System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8260–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Ma, E.W.M.; Tsui, K.L.; Pecht, M. Battery Management Systems in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. Energies 2011, 4, 1840–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Ueno, T.; Yoshino, K. Cell Voltage Equalizer Using a Selective Voltage Multiplier with a Reduced Selection Switch Count for Series-Connected Energy Storage Cells. Electronics 2019, 8, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.K.; Shrivastava, P.; Tey, K.S.; Bin Idris, M.Y.I.; Mekhilef, S.; Jamei, E.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A. Advancement of lithium-ion battery cells voltage equalization techniques: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Chen, Z. A method for the estimation of the battery pack state of charge based on in-pack cells uniformity analysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Kang, L.; Huang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, H. Research on a Novel Power Inductor-Based Bidirectional Lossless Equalization Circuit for Series-Connected Battery Packs. Energies 2015, 8, 5555–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.; Duong, V.; Choi, W. A Low Cost and Fast Cell-to-Cell Balancing Circuit for Lithium-Ion Battery Strings. Electronics 2020, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelie, M.; Braun, T.; Knips, M.; Nordmann, H.; Ringbeck, F.; Zappen, H.; Sauer, D. Battery Management System Hardware Concepts: An Overview. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linghu, J.; Kang, L.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Feng, Y.; Lu, C. Estimation for state-of-charge of lithium-ion battery based on an adaptive high-degree cubature Kalman filter. Energy 2019, 189, 116204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E. Analysis and Design of Zero-Current Switching Switched-Capacitor Cell Balancing Circuit for Series-Connected Battery/Supercapacitor. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cui, N.; Guerrero, J.M. A Cell-to-Cell Battery Equalizer with Zero-Current Switching and Zero-Voltage Gap Based on Quasi-Resonant LC Converter and Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 3731–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, H.; Huang, P.; Zhou, L. A Novel Composite Equalizer Based on an Additional Cell for Series-Connected Lithium-Ion Cells. Electronics 2018, 7, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Q. Recognition of battery aging variations for LiFePO4 batteries in 2nd use applications combining incremental capacity analysis and statistical approaches. J. Power Sources 2017, 360, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, J.; Kim, J. Incremental Capacity Curve Peak Points-Based Regression Analysis for the State-of-Health Prediction of a Retired LiNiCoAlO2 Series/Parallel Configured Battery Pack. Electronics 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Qiao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, M.; Han, X.; Zhou, L. A rapid screening and regrouping approach based on neural networks for large-scale retired lithium-ion cells in second-use applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 776–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, N.; Duan, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, C. Multicell-to-Multicell Equalizers Based on Matrix and Half-Bridge LC Converters for Series-Connected Battery Strings. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Cheng, K.W.E.; Yeung, Y.P.B. Zero-Current Switching Switched-Capacitor Zero-Voltage-Gap Automatic Equalization System for Series Battery String. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, N.; Zhang, C. A Cell-to-Cell Equalizer Based on Three-Resonant-State Switched-Capacitor Converters for Series-Connected Battery Strings. Energies 2017, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.H.; Collet, A.; Crebier, J. An Optimized Topology for Next-to-Next Balancing of Series-Connected Lithium-ion Cells. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4603–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.; Hartley, T.T.; Husain, I. A Battery Management System Using an Active Charge Equalization Technique Based on a DC/DC Converter Topology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chung, Y.; Sung, C.; Kang, B. Active Cell Balancing of Li-Ion Batteries Using LC Series Resonant Circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5491–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Choi, Y.; Kang, B. Modularized Design of Active Charge Equalizer for Li-Ion Battery Pack. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8697–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Zou, J.; Yang, S. A Multi-winding Transformer Cell-to-Cell Active Equalization Method for Lithium-Ion Batteries with Reduced Number of Driving Circuits. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 4916–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, F.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. Performance comparison of active balancing techniques for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 267, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, M.; Guertlschmid, W.; Blochberger, T.; Kumpusch, R.; Permann, R.; Conte, F.V.; Kral, C.; Fleig, J. A Current Equalization Method for Serially Connected Battery Cells Using a Single Power Converter for Each Cell. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 4227–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, A.M.; Khan, F.H. “Time Shared Flyback Converter” Based Regenerative Cell Balancing Technique for Series Connected Li-Ion Battery Strings. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5960–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, M.; Moon, G. A Modularized Charge Equalizer Using a Battery Monitoring IC for Series-Connected Li-Ion Battery Strings in Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Lee, K.; Ku, N.; Hyun, D.; Kim, R. A Modularized Equalization Method Based on Magnetizing Energy for a Series-Connected Lithium-Ion Battery String. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.; Liang, T.; Chen, S.O.; Horng, W.; Chung, Y. A Novel High-Efficiency Compact-Size Low-Cost Balancing Method for Series-Connected Battery Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5927–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, M.; Kukita, A. Double-Switch Equalizer Using Parallel- or Series-Parallel-Resonant Inverter and Voltage Multiplier for Series-Connected Supercapacitors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 812–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Sebastian, J.; Hernando, M.M.; Viscarret, U.; Gil, I. Practical Application of the Wave-Trap Concept in Battery-Cell Equalizers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 5616–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Eric Cheng, K.W.; Liu, J.; Xu, C. A Family of Dual-Phase-Combined Zero-Current Switching Switched-Capacitor Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4209–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, A.; Peretz, M.M.; Ben-Yaakov, S. A Generic and Unified Global-Gyrator Model of Switched-Resonator Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8945–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, O. Electromagnetic Susceptibility of Battery Management Systems’ ICs for Electric Vehicles: Experimental Study. Electronics 2020, 9, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Equalizer | Initial Voltage #1 | Initial Voltage #2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Efficiency | Time | Efficiency | |
| AC2C based on QRSCC [24] | 0.22481 s | 93.36% | 0.20976 s | 94.39% |
| DC2C based on LCSRC [28] | 0.01796 s | 88.32% | 0.01264 s | 88.36% |
| MC2MC based on HBLCC [23] | 0.02978 s | 93.46% | 0.04989 s | 94.66% |
| Proposed MC2MC based on BRLCC | 0.00681 s | 89.15% | 0.00767 s | 86.86% |
| Components | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Resonant tank | Inductor | L = 9.53 μH, ESRL = 72.92 mΩ |
| Capacitor | C = 1.04 μF, ESRC = 13.77 mΩ | |
| Switch matrix | nMOSFET | IRF7351TRPBF (Infineon, Ltd., Munich, Germany), RDS(on) < 17.8 mΩ |
| Driver board | MOSFET driver | 1EDI20N12AFXUMA1 (Infineon, Ltd., Munich, Germany) |
| Protection network | Diode | MBRS3200T3G (ON Semiconductor, Ltd., Phoenix, AZ, USA) |
| Battery pack | Lithium-ion battery | ICR18650-22F (Samsung SDI Co., Ltd., Yongin, Korea), R0 ≈ 50 mΩ |
| Operation Mode | VBS (V) | VBT (V) | IP(1) (A) | IP(1) (A) | PS (W) | PT (W) | η (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Model | Exp. | Model | Error | ||||||
| 1–1 | 3.818 | 3.929 | 1.28 | 1.14 | 1.556 | 1.426 | 1.429 | 91.65 | 90.52 | 1.13 |
| 1–2 | 3.830 | 7.863 | 2.48 | 1.06 | 3.023 | 2.653 | 2.714 | 87.75 | 87.68 | 0.06 |
| 1–3 | 3.857 | 11.806 | 3.68 | 1.02 | 4.518 | 3.833 | 3.875 | 84.84 | 83.45 | 1.39 |
| 2–1 | 7.689 | 4.001 | 1.32 | 2.28 | 3.231 | 2.904 | 3.008 | 89.88 | 88.93 | 0.95 |
| 2–2 | 7.780 | 7.897 | 2.48 | 2.24 | 6.142 | 5.631 | 5.855 | 91.68 | 90.53 | 1.15 |
| 2–3 | 7.380 | 12.019 | 4.08 | 2.16 | 9.584 | 8.264 | 8.182 | 86.22 | 89.19 | −2.97 |
| 3–1 | 11.576 | 4.064 | 1.36 | 3.44 | 5.011 | 4.450 | 4.639 | 88.80 | 86.08 | 2.72 |
| 3–2 | 11.090 | 8.099 | 2.86 | 3.42 | 10.096 | 8.817 | 8.687 | 87.33 | 90.24 | −2.91 |
| 3–3 | 11.014 | 12.103 | 4.06 | 3.26 | 14.234 | 12.559 | 12.648 | 88.23 | 90.46 | −2.22 |
| Equalizer | Type | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | DR | L | C | D | ||
| QRSCC [24] | AC2C | 2n | 2n | n − 1 | n − 1 | 0 |
| TRSCC [25] | AC2C | 4(n − 1) | 4(n − 1) | n − 1 | n − 1 | 0 |
| CI [26] | AC2C | 4(n − 1) | 4(n − 1) | 2(n − 1) | 0 | 0 |
| LCSRC [28] | DC2C | 2n + 10 | n + 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| HBLCC [23] | MC2MC | 4n | 2n | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Proposed | MC2MC | 4(n + 1) | 2(n + 1) | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Equalizer | Type | Component | Cost ($) | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | DR | L | C | D | ||||||||
| QRSCC [24] | AC2C | 216 | 216 | 95 | 95 | 0 | 292.0 | + | +++ | ZCS | ++++ | ++++ |
| TRSCC [25] | AC2C | 380 | 380 | 95 | 95 | 0 | 456.0 | ++ | ++ | ZCS | ++ | +++ |
| CI [26] | AC2C | 380 | 380 | 190 | 0 | 0 | 494.0 | +++ | ++ | - | +++ | ++ |
| LCSRC [28] | DC2C | 346 | 173 | 13 | 13 | 52 | 225.8 | +++ | +++ | ZCS | ++ | +++ |
| HBLCC [23] | MC2MC | 432 | 216 | 13 | 13 | 52 | 277.4 | +++ | +++ | ZCS | ++ | +++ |
| Proposed | MC2MC | 484 | 242 | 13 | 13 | 52 | 308.6 | ++++ | +++ | ZCS | ++ | +++ |
| Average | - | 373 | 268 | 70 | 38 | 26 | 342.3 | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Kang, L.; Lu, C.; Linghu, J.; Lin, H.; Hu, B. An Enhanced Multicell-to-Multicell Battery Equalizer Based on Bipolar-Resonant LC Converter. Electronics 2021, 10, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030293
Luo X, Kang L, Lu C, Linghu J, Lin H, Hu B. An Enhanced Multicell-to-Multicell Battery Equalizer Based on Bipolar-Resonant LC Converter. Electronics. 2021; 10(3):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xuan, Longyun Kang, Chusheng Lu, Jinqing Linghu, Hongye Lin, and Bihua Hu. 2021. "An Enhanced Multicell-to-Multicell Battery Equalizer Based on Bipolar-Resonant LC Converter" Electronics 10, no. 3: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030293
APA StyleLuo, X., Kang, L., Lu, C., Linghu, J., Lin, H., & Hu, B. (2021). An Enhanced Multicell-to-Multicell Battery Equalizer Based on Bipolar-Resonant LC Converter. Electronics, 10(3), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030293






